- How long can gas be stored in cylinders?
- Permissible operation period
- Unsuitable for further use
- Gas cylinder valve repair
- Gas cylinders - operating rules
- Gas cylinders: coloring, inscriptions, marking
- Cylinder rejection
- Scheme of the device and operation of the gas cylinder reducer
- Inspection of cylinders - technical nuances
- When is the qualification of gas tanks performed?
- Cylinder certification: sequence of operations
- SAFETY REQUIREMENTS DURING WORK
- HEALTH REQUIREMENTS BEFORE STARTING WORK
- When not suitable for use?
- About hydraulic testing
How long can gas be stored in cylinders?

The duration of storage is largely influenced by the gas with which the container is filled.
- Propane-butane is stored indefinitely, provided that the operating pressure is maintained.
You can find out about the expiration dates and methods for disposing of an expired gas mask here.
Oxygen from the moment of filling is good for 18 months.
Acetylene is a potentially explosive gas, but it is stored for a long time, subject to all standards by the manufacturer.
Hydrogen can be used for three years.
Pure argon and nitrogen can be used for 18 months.
Permissible operation period
In accordance with the FNP ORPD, the service life is set by the manufacturer. According to paragraph 485 of the rules, if the manufacturer's technical documentation does not contain data on the service life of the cylinder, then the service life is set to 20 years.
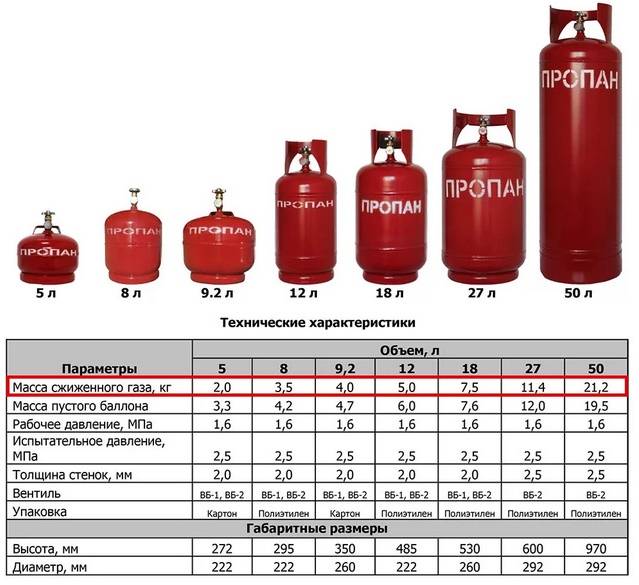
The greatest demand is for containers manufactured in accordance with GOST 949-73 “Steel cylinders of small and medium volume for gases at P (p) <= 19.6 MPa (200 kgf / sq. cm). Specifications (with Amendments No. 1-5)". According to clause 6.2. warranty period of use - 24 months from the date of commissioning.
Devices manufactured in accordance with GOST 15860-84 “Welded steel cylinders for liquefied hydrocarbon gases for pressure up to 1.6 MPa. Specifications (with Amendments No. 1, 2) ”according to clause 9.2, have a warranty period of use - 2 years and 5 months from the date of sale through the distribution network, and for non-market devices - from the date of receipt by the user.
In accordance with the methods of technical diagnostics MTO 14-3R-004-2005 and MTO 14-3R-001-2002 developed for devices manufactured in accordance with GOST 15860-84 and GOST 949-73, respectively, the service life should not exceed 40 years, subject to conditions for the examination once every 5 years, after which the devices are rejected.
It is forbidden to use cylinders manufactured according to the above GOST before 02/01/2014, the service life of which is over 40 years.
According to paragraph 22 of the Technical Regulations of the Customs Union "On the safety of equipment operating under excessive pressure", cylinders manufactured after 02/01/2014 are operated according to the estimated service life specified by the manufacturer in the device passport.
Learn more about the service life and conditions gas cylinder storage read in this article.
We solve legal problems of any complexity. #Stay home and leave your question to our lawyer in the chat. It's safer that way.
Ask a Question
Unsuitable for further use
Why cylinders that have worked out the standard service life, but have passed the technical examination, should not be accepted for refueling?
According to paragraph 485 of the Rules ..., even gas vessels that have successfully passed the technical test and have served the regulatory period are unsuitable for further use.
The same paragraph states that if cases of successful re-examination after November 2014 of a tank whose service life has expired are found, these results should be canceled, since according to the new Rules. examination of cylinders beyond their service life is prohibited.

A material that has used up its strength resource is capable of collapsing at any time.
All these measures and more stringent regulations are aimed at enhancing the safety of the operation of gas containers in which the contents are under pressure.
This is due to the increased use of end-of-life cylinders and, as a result, the occurrence of accidents.
To resist the requirements of these Rules ... means to endanger not only your health and life, but also the lives of other people, which is not only unreasonable, but also criminal.
What requirements must gas cylinders meet, how to use them correctly, what is an examination and what procedure do cylinders go through at a gas filling station? About it in the video:
Didn't find an answer to your question? Find out how to solve your particular problem - call right now:
For storage and transportation of compressed and liquefied gases, containers made of metal or composite materials are used. These vessels are designed for the fact that the gas will be stored in them under a certain pressure. So, GOST 15860-84 determines that the operating pressure in a propane tank should not exceed 1.6 MPa. There are also containers designed for a higher pressure of 5 MPa. All containers used for gas storage must be tested and periodically surveyed.
Checking the gas cylinder
Examination of a gas cylinder is an event that is necessary first of all for its owner. The certification can ensure that the cylinder is safe to operate and can be used for its intended purpose, otherwise they are not allowed to be used. There is a single survey procedure, during which the surfaces of the cylinders are inspected to detect damage to the surface.
They perform a quality check of marking and coloring for compliance with the requirements of GOST, the condition of the crane. In addition, in the process of certification, hydraulic tests of gas storage tanks are carried out. The results of the inspection and tests carried out are recorded in the passport that accompanies the product throughout its operation.
Without carrying out such measures, refueling and operation of containers for storage and transportation of gas are unacceptable. Inspection of cylinders and issuance of a conclusion on them can only be carried out by an organization that has all the necessary permits and powers from the relevant state supervisory authorities.
Vessels for the storage of gases must be certified once every few years.The duration depends on several parameters - on the material, for example, if the cylinders are made of alloyed or carbon steel, then it is enough for them to go through this procedure once every five years. Cylinders installed on cars as part of LPG must be certified in three or five years.
Cylinders, which operate in stationary conditions and are intended for the storage of inert gases, undergo the necessary examinations once every ten years.
The designated inspection periods must be strictly adhered to. It's all about safety. If the containers are intended for the storage and transportation of propane, acetylene or other explosive gas, any defect on the outer surface of the cylinder can lead to irreparable consequences.
As soon as doubts arise about the performance of a gas storage tank, it is necessary to withdraw it from circulation and purchase or rent a new one.
Gas cylinder valve repair
The main malfunctions of gas valves
In fact, the design of the gas valve is not difficult and there is nothing special to break in it. But nevertheless, for a number of reasons, it can either start to pass gas or completely fail. One of the reasons for its breakdowns is the careless attitude of the staff. For example, applying excessive force when opening or closing. This can either strip the thread or break the stem.
In addition, foreign particles entering the regulator may prevent them from fully closing the valve, and this will inevitably lead to gas leakage.In any case, at the slightest suspicion of defects in the body or mechanism of the gas valve, the cylinder must be removed from the workplace or amenity premises and sent for repair.
Yes, no doubt, the gas valve can be removed from the cylinder and inspected by yourself and, if necessary, purged or repaired, but we must not forget that any work with a gas cylinder carries a potential hazard. That is why there is a strict ban on dismantling gas valves independently in artisanal conditions. If there is even a small opportunity to transfer the repair of a gas valve to a workshop, then it is better to do so.
Gas cylinders - operating rules
Gas cylinders: coloring, inscriptions, marking
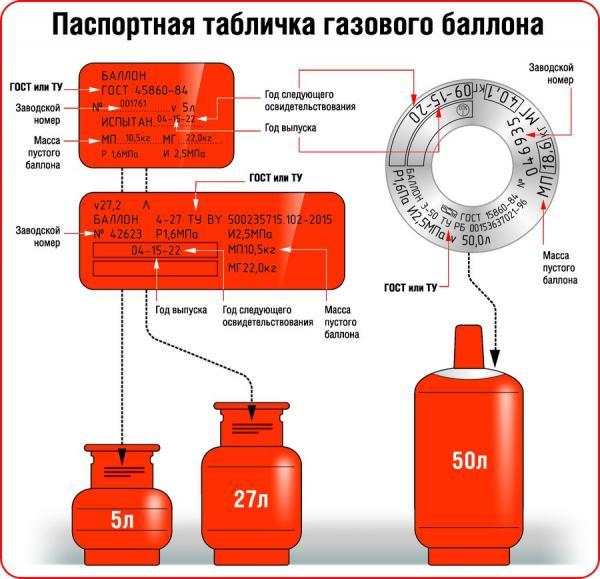
On the upper spherical part of the cylinder, data about the cylinder must be clearly stamped:
1. Cylinder number
2. Stamp of the test point (diameter 12 mm)
3. Trademark of the manufacturer
4. Working pressure (kgf/cm2)
5. Actual weight of an empty cylinder, kg
6. Stamp of the quality control department of the manufacturer (diameter 10 mm)
7. Capacity, l
8. Trial hydraulic pressure, (kgf/cm2)
9. Month and year of manufacture (IV-1999) and year of the next (2004) survey
10. Month and year of the conducted (IV-2004) and the year of the subsequent (2009) survey
On cylinders for acetylene, in addition, must be indicated:
M III-99 - date (month and year) of filling the balloon with a porous mass
III-01 - month and year of the porous mass check
- stamp of the filling station
- a stamp with a diameter of 12 mm, certifying the verification of the porous mass
It is only allowed to release gas from a cylinder through a reducer designed for this gas and painted in the appropriate color!
- protective cap
- Valve
- Neck thread
- Passport data
- porous mass
- backing rings
- support shoe
1. Protective cap
2. Valve
4. Passport data
6. Washer rings
Cylinder rejection
External damage to the cylinder, due to which it should be rejected: 1. Valve failure 2. Neck thread wear 3. Not all data have been stamped or the certification period has expired4. Severe external corrosion5. Cracks6. Coloring and inscription do not correspond to the norm7. Dents8. Bulges 9. Shells and risks with a depth of more than 10% of the nominal wall thickness10. Slanted or damaged shoe
Also, gas cylinders are not allowed to be used if:
| REDUCER: | MANOMETER: | VALVE: |
| - when the adjusting screw is completely turned out, the gas passes into the working chamber - the thread of the union nut is damaged - one or both pressure gauges are faulty - the pressure in the working chamber increased after the gas supply was stopped - the safety valve is faulty | - there is no seal or stamp with a check mark - the check period has expired - the arrow does not return to zero when the pressure gauge is turned off by more than half of the permissible error - the glass is broken or there are other damages that may affect the correctness of the readings | - there is no plug fitting - the presence of traces of oil, grease, dust - the handwheel does not turn - there is a gas leak |
It is forbidden to consume gas from the cylinder completely! Residual pressure must be at least 0.05 MPa (0.5 kgf/cm2)
The residual pressure in acetylene cylinders must not be lower than the following values:
| Ambient temperature | FROM | below 0 | 0-15 | 16-25 | 26-35 |
| Minimum residual pressure | MPa | 0,05 | 0,1 | 0,2 | 0,3 |
| kgf/cm2 | 0,5 | 1,0 | 2,0 | 3,0 |
Scheme of the device and operation of the gas cylinder reducer
Non-working and working position of the gearbox
In the left figure, the gearbox is in a non-working position. The gas (the gas filling area is colored blue) does not pass in this case. In the right figure, the reducer is in working position, the gas flows through the reducer.
Reducer structure:
1. Union nut for connecting the reducer to the valve fitting
2. High pressure gauge
3. Reverse spring
4. Low pressure gauge (working)
5. Safety valve
6. Hose connection nipple
7. Membrane for rubberized fabric
8. Pressure spring
9. Adjusting screw
10. Working (low pressure) chamber
11. Pressure reducing valve
12. High pressure chamber
Inspection of cylinders - technical nuances
Working with industrial gases requires strict adherence to the rules for operating gas-using equipment and gas tanks, which must be periodically certified
It is important to understand that the scheduled inspection of cylinders is not a whim of the regulatory authorities, but a necessary measure for the timely detection of design defects and the prevention of hazardous situations in production.
There are many private companies supplying technical gases, which, neglecting the certification procedure, provide customers with expired cylinders. Getting a cheaper product at their disposal, the buyer is often unaware of the possible consequences. What threatens the operation of non-certified tanks, read the article: gray producers of technical gases.
At the same time, responsible organizations take care of the safety of their customers by fulfilling the requirements of the FNP, which relate to the arrangement of test points for the examination of cylinders. To obtain approval from the regulatory authorities to conduct tests, the company must have:
- a suitable area;
- technical means;
- certified specialists;
- brand with the code of the organization;
- production instructions.
When is the qualification of gas tanks performed?
The frequency of technical certification for pressure vessels is 5 years. That is, from the date of manufacture, every 5 years, the cylinder must be subjected to tests, during which the integrity of the body and valve, the mass of the structure, the internal capacity and the ability to withstand increased pressure are determined.
However, in some situations, the survey is carried out ahead of schedule, when:
- broken valve;
- a leak was detected at the junction of the cylinder-valve;
- the ring on the neck is faulty or missing;
- damaged shoe;
- the outer surface is of poor quality.
The decision to repair or reject such vessels is made only on the basis of the results of visual inspection and technical studies.
Cylinder certification: sequence of operations
The status check is carried out in the following sequence:
1) Preparation.
At the preparation stage, the rest of the gas is removed from the vessel, the valve is dismantled, after which air is blown and the surface is thoroughly cleaned using water and, if necessary, a solvent.The dismantled valve is subjected to a separate check, and in case of a malfunction, it is sent for repair or rejected with subsequent replacement.
Preparing the balloon before testing
2) Visual inspection. The purpose of a visual inspection is to identify any structural defects: cracks, dents, captivity, shells, deep scratches (more than 10% of the wall thickness), thread wear, etc. For internal inspection, it is allowed to use a lighting device with a supply voltage of up to 12 V. If a loosening of the ring on the neck or an incorrect shoe fitting is detected, the test is suspended until these faults are eliminated.
Inspection for defects
3) Checking the weight and capacity. To determine how much corrosion and other physical and chemical transformations of the metal have reduced the wall thickness, they measure the mass and internal volume of the product, as well as compare the obtained indicators with the initial data from the passport. Weighing is carried out on a scale with an accuracy of 200 g. To determine the capacity, an empty vessel is first weighed, and then filled with water, after which the mass of water is found by the difference in indicators with a further calculation of its volume.
Weight and capacity check by weighing
4) Hydraulic test. To determine the strength of the container, it is filled with water under high pressure. The value of the test pressure is set by the manufacturer, it must be at least 1.5 times higher than the working indicator. The duration of the check is at least 1 minute. Hydrotesting is considered successful if during its execution the pressure gauge showed a stable value, and cracks, leaks, tears and visible deformations were not found on the body.
SAFETY REQUIREMENTS DURING WORK
3.1.Do not allow different types of oils to come into contact with oxygen cylinders and touch them with oil-contaminated hands. 3.2. Show maximum attention when doing work, not being distracted by other things and extraneous conversations. 3.3. Keep the workplace clean and tidy, preventing it from being cluttered with foreign objects. 3.4. Oxygen cylinders should be located at a distance of at least 5 m from heat sources. 3.5. Do not remove the protective cap from the oxygen cylinder by hitting with a hammer, chisel or other tool that can cause a spark. 3.6. In the event of a violation of the technological process or an incident, in the event of an accident, detection of equipment malfunctions, immediately inform your immediate supervisor about this. 3.7. Do not allow sudden opening and closing of the valve, which can lead to self-ignition of oxygen and burnout of parts of the valve and reducer. 3.8. Do not repair the valve, tighten the threaded connections in the presence of oxygen in the cylinder. 3.9. Avoid dropping the oxygen cylinder, carrying them on your arms and shoulders. 3.10. Do not store and move oxygen cylinders without protective caps screwed onto their necks and plugs on the side fittings of the valves. 3.11. During transportation, the following requirements must be observed: — workers in clean, oil- and grease-free overalls are allowed to transport oxygen cylinders.Hands should not be oily; – transportation of oxygen cylinders by road is carried out in accordance with the “Rules for the transport of inert gases and oxygen by road: compressed and liquid”; – transportation of oxygen cylinders is allowed on spring vehicles, as well as on special hand carts and stretchers. 3.12. When loading oxygen cylinders on a trolley and removing it from it, it is necessary to take measures to prevent its spontaneous movement. 3.13. During containerless transportation of oxygen cylinders, the following requirements must be met: - safety caps must be screwed on the cylinders; - cylinders should be placed in wooden blocks with carved nests, upholstered with felt or other soft material; - when loading more than one row of cylinders, spacers should be used for each row to protect them from contact with each other.It is allowed to use as a gasket a hemp rope with a diameter of at least 25 mm and rubber rings with a thickness of at least 25 mm; - cylinders should be laid only across the car body with valves in one direction - right in the direction of the car; - stowage of cylinders is allowed within the height of the sides; - during loading and unloading, it is not allowed to drop cylinders and hit them against each other, as well as unloading with valves down; - it is forbidden to load cylinders on cars and other vehicles if there is dirt, debris and traces of oils in the body; - it is allowed to transport cylinders in special containers, as well as without containers in a vertical position, always with gaskets between them and a fence that prevents possible falls; - joint transportation of oxygen and acetylene cylinders on all modes of transport is prohibited; - in the summer, the transported cylinders must be protected from sunlight with a tarpaulin or other covering; — the person responsible for the transportation of oxygen cylinders is the driver of the vehicle; - the permissible speed of the vehicle carrying oxygen cylinders is 60 km / h; - in conditions of poor visibility (fog, rain, snowfall, etc.) up to 300 m, the transportation of oxygen cylinders is prohibited; - it is forbidden to transport people in the same body with filled oxygen cylinders. 3.14
Moving oxygen cylinders over short distances within one workplace is allowed to be carried out by carefully tilting it in a vertical position with a slight inclination.Moving a cylinder from one room to another, even adjacent, must be carried out on specially adapted trolleys or stretchers that ensure the safe transportation of cylinders
HEALTH REQUIREMENTS BEFORE STARTING WORK
2.1. Make sure that the oxygen cylinder has clearly visible data stamped at the manufacturer: - trademark of the manufacturer; - cylinder number; - the actual mass of an empty cylinder with an accuracy of 0.2 kg; — date (month, year) of manufacture and the next survey; — working pressure (kgf/cm2); — test hydraulic pressure (kgf/cm2); - capacity of the cylinder with an accuracy of 0.3 l; - stamp of the quality control department of the manufacturer of a round shape with a diameter of 10 mm. 2.2. Place the oxygen cylinder out of direct sunlight. 2.3. Make sure that the oxygen cylinder is complete and in good condition, that it has the appropriate inscription “Oxygen” on it. 2.4. Clean the cylinder valve from scale, dust, sand, oil stains. 2.5. Make sure that there is no depressurization of nodes, connecting parts. 2.6. Transportation of oxygen cylinders should be carried out only on spring vehicles, as well as on special hand trucks and stretchers. 2.7. Obtain safety instructions from your direct supervisor. 2.8. Remove from the workplace unnecessary items that interfere with the performance of work. 2.9. Put on overalls, safety shoes, determined by the industry-specific Norms for issuing overalls, safety shoes for this category of workers. 2.10. Check the serviceability of the equipment and devices used in the performance of work. 2.11. Report all observed malfunctions of equipment and devices to the immediate supervisor.2.12. Before connecting the reducer to the oxygen cylinder, check the serviceability of the inlet fitting and union nut of the reducer, make sure that there are no oils and fats on their surface, as well as the presence and serviceability of the sealing fiber gasket and the filter on the inlet fitting of the reducer. 2.13. When storing oxygen cylinders, the following requirements must be met: - oxygen cylinders can be stored both in special rooms and in the open air, in the latter case they must be protected from precipitation and sunlight; - storage in the same room of cylinders with oxygen and combustible gases is prohibited; - oxygen cylinders installed indoors must be at least 1 m from radiators, other heating appliances, stoves and at least 5 m from heat sources with open fire; - Filled cylinders should only be stored in an upright position. To protect against falling, cylinders must be installed in specially equipped nests, cages or protected by a barrier; - Warehouses for storing cylinders should be one-story with light-type coatings, not have attic spaces. Walls, partitions, coverings of warehouses must be made of non-combustible materials of at least III degree of fire resistance. Windows and doors should open outwards. Window and door glass must be frosted or painted over with white paint. The height of storage facilities must be at least 3.25 m from the floor to the lower protruding parts of the roofing.Warehouse floors must be flat with a non-slip surface; - instructions, rules and posters for handling cylinders should be posted in warehouses; - the enterprise must appoint a person responsible for storing oxygen cylinders in the warehouse, issuing cylinders from the warehouse and returning them to the warehouse; - in the warehouse where oxygen cylinders are stored, there should be a log for the issuance and return of oxygen cylinders; - the issuance and receipt of oxygen cylinders in the warehouse should be carried out by the person responsible for storing oxygen cylinders in the warehouse.
When not suitable for use?
If gross violations are found during the repair, the cylinder will be sent for disposal:
- significant external damage: dents, corrosion, cracks;
- absence or illegibility of the passport, marking;
- cracks in the weld in a third of the length.
After the expiration of the standard operating life, the containers are disposed of. It is forbidden to accept them for refueling, despite the external integrity. Such strict measures are aimed at protecting the user: the material that has served the allotted time will begin to break down at any moment, over-limit operation is dangerous. In addition, with the above gross faults, it is also impossible to continue using the vessel.
In order for the use of the gas cylinder to take place in accordance with all accepted safety rules, and the possibility of an unforeseen situation was excluded, it is necessary to undergo certification and re-examination for serviceability periodically within a clearly defined period. In case of detection of the slightest defect, the cylinder is subject to repair or removal for disposal, depending on the degree of damage.
Each cylinder has its own service life, but cannot exceed 20 years. The manufacturer independently determines this period, which notifies the consumer in the product passport.
To resolve your issue, contact a lawyer for help. We will select a specialist for you. Call 8 (800) 350-14-90
Badly
Healthy!
About hydraulic testing
Hydraulic testing of gas cylinders is carried out using a pressure of 25 kgf / cm2. Duration - 1 minute.
Then the parameters are brought to working. A thorough inspection of the container is carried out. All its welds are tapped with a hammer weighing 500 grams.
Products have passed this test if they do not have:
- breaks.
- Significant deformations.
- Leaks.
Then a pneumatic test is arranged. It is applied by pressure of 16 kgfs/sq.cm. Duration - 2 minutes.
The container is placed in a tank of water. A water column 2-4 cm high is formed above it.
If leakage and air leakage are detected, the cylinder must be repaired. After that, these operations are repeated. The maximum number of capacity patches allowed is 2.
The hydraulic test takes place behind a solid solid fence with a minimum height of 2 m. It should allow inspecting the tank when the pressure in it is reduced to normalized values.
For such testing, a professional stand is usually used. In work the manual pump GN-200 is used.
Models designed for liquefied gas are placed on stands where compressed air is used in the process.
The parameters of the stand used for the indicated testing has parameters of 50-55 l.
Its view is carousel with two positions. It has a special element - a head with a telescopic tube.It is necessary for this test and the elimination of water from the tank after the procedures.
Also, this stand is used for pneumatic operations and studying the density of contact between the valve and the gas container.
Often, the UGIB5-04 device is used for these operations.
Its composition:
- Welded table frame.
- Clamping pneumatic cylinder. It is located in the center of the upper side of item 1
- Collector. It is arranged in paragraph 2. It supplies compressed air or water to the tank.
- Fixture for placement of a cylinder. It is under item 2.
- Water tank. The location is the lower left side of this device.
- Pneumatic hydraulic booster. Located on the right side of the machine. It creates the necessary pressure for testing. Pneumatic and hydraulic cylinders are sequentially arranged in it.
After all operations, drains are formed. They are eliminated into the sewer network through a special sump. Thanks to this measure, the gas does not penetrate into the sewer.