- Features of choosing the type of gas pipeline
- Security zones of other networks
- Nuances of protected zones
- Organization of a high-pressure gas pipeline security zone
- Laying technology and assembly rules
- Detailed description of the main stages of work: tie-in to the water supply
- Materials: cast iron and others
- Do-it-yourself installation in 7 steps: clamp, saddle, sewerage scheme, coupling
- Rules for the placement of sewerage wells
- Violation of the gas pipeline security zone. Legal and environmental implications
- Bandwidth calculation rules
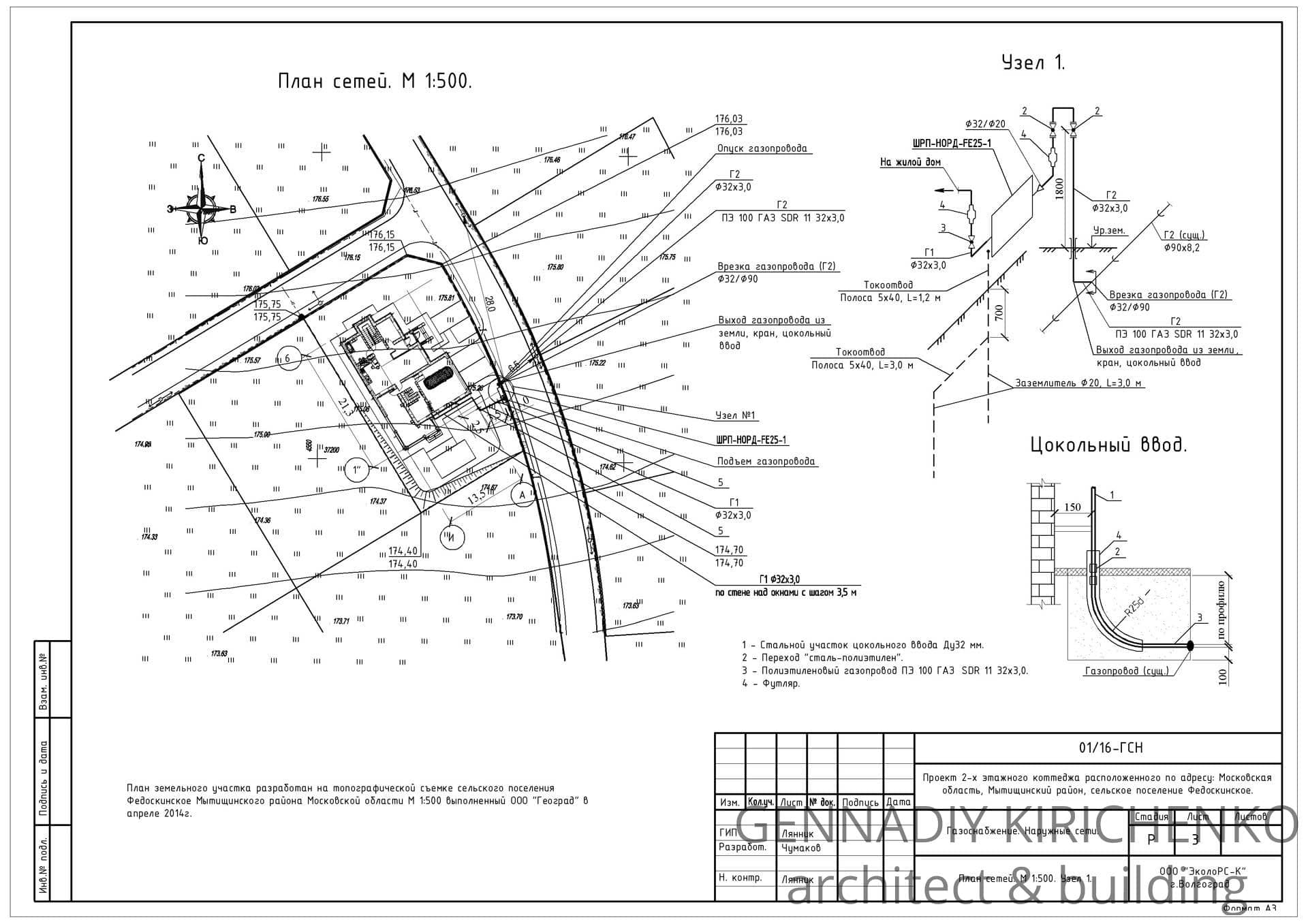
- Gas base inlets
- High-pressure gas pipeline security zone: how many meters according to SNiP (SP)
- The purpose of monitoring the condition of an underground gas pipeline
- Varieties of gas pipelines
- What determines the choice of communications
- Which pipe to choose: types
Features of choosing the type of gas pipeline
Before the construction of the highway, you should decide on the best option that is suitable for specific conditions, and familiarize yourself with the rules for laying it. Since all this affects financial costs, efficiency and labor costs.
Since, first of all, the gas pipeline must be reliable, when choosing an option, it is necessary to take into account such points as:
- corrosive activity of soils;
- building density;
- the presence of stray currents;
- terrain features;
- type of road surface, if the gas pipeline will cross it;
- entrance width;
- the presence of water barriers and many others.
In addition, it is necessary to determine the type of gas that will be supplied. And also its quantity - volumes should be enough to meet the needs of all consumers.
 To avoid associated risks, as well as unnecessary financial expenses, the laying of any gas pipeline should begin with special calculations, the result of which will be the creation of a project
To avoid associated risks, as well as unnecessary financial expenses, the laying of any gas pipeline should begin with special calculations, the result of which will be the creation of a project
Consideration should also be given to the security of supply. In view of this, it should be remembered that a ring gas pipeline is preferable to a dead-end or mixed one. For example, if gas is supplied to the so-called non-switchable consumer, then the specified option should be chosen.
All of the above points cannot be ignored - each of them is indicated in the documents regulating issues related to the laying of gas pipelines. Among which are SP 62.13330.2011 and others.
Also, we must not forget that the construction and modernization of any gas pipelines must be carried out in accordance with gas supply schemes. Which are developed at various levels - from federal to regional.
Therefore, before starting the design, the owner of the building, the premises must:
- obtain a permit for gasification in the city, district architectural and design department;
- apply in writing to the local gorgaz (raygaz) in order to obtain the so-called technical assignment, which is a set of information necessary for the creation of a gas pipeline.
And only after that it is allowed to start designing. Which ends with the agreement in Gorgaz (Reigaz).
Only after that it will be possible to start laying the gas pipeline.Which, by readiness, should provide consumers with fuel in the required quantity and be safe.
The subtleties of the gasket gas pipeline to a private house we described in the next post.
 The place of laying the gas pipeline must be fenced off and marked with special signs. Moreover, this rule is relevant for all cases. This is done to ensure safety.
The place of laying the gas pipeline must be fenced off and marked with special signs. Moreover, this rule is relevant for all cases. This is done to ensure safety.
Security zones of other networks
It should be borne in mind that water supply, sewerage and other communications also have their own sanitary protection zones. They are also called security guards. Yes, the protected area of the gas pipeline already takes this into account.
 Underground heating network
Underground heating network
However, before carrying out any work, it is important to take into account such parameters for each network so that nothing is left without attention. And so that in the end it does not turn out that some network does not fit in any way relative to others
It is important to take into account that the sanitary zone for certain communications must be installed on each side of the axis. Each such system with a security zone has its own SNiP (SP) table with distance standards to certain objects
You should always be guided precisely by building codes and rules about how many meters in each direction should be retreated.
Nuances of protected zones
It is also important to consider that the main gas pipeline is a completely different story than a gas distribution station or hub. And the security zone in high-pressure highways reaches 50 meters
 The size of the protection zone of the main pipe
The size of the protection zone of the main pipe
As a rule, these are pipes of large diameter. With such a width, in case of an accident, the leak will be much larger and more intense. This is due to the volume of the substance inside and the speed of its transportation.
The rules for the location of security zones are valid everywhere, both in Moscow and in the Nizhny Novgorod region. After all, according to the definition of experts, this pipeline has the status of a HIF (dangerous production facility).
Aboveground main gas pipeline
And it's not just about serious legal consequences for those who violate the protective zone. Judging by the practice of decades, with the illiterate laying of gas communications, it is possible to face such risks that will pose a threat to the lives of others.
Organization of a high-pressure gas pipeline security zone
The security zone of the high-pressure gas pipeline is organized by the organization operating it on the basis of a project that refines the survey carried out after the completion of construction and the issued permits. To maintain it, the following activities are carried out.

- Every six months, an organization operating high-pressure gas pipelines is obliged to remind individuals and organizations that operate land in protected areas about the features of land use in these areas.
- Every year, the route must be updated and, if necessary, all documentation issued on it must be corrected. The security zone of the high-pressure gas pipeline is specified accordingly.
- The security zone of the high-pressure gas pipeline is marked on its linear sections with the help of columns located at a distance of no more than 1000 m (Ukraine) and no more than 500 m (Russia), all angles of rotation of the pipe should also be indicated with a column.
- The places of intersection of the gas pipeline with transport highways and other communications are necessarily marked with special signs notifying that there is a high-pressure gas pipeline exclusion zone.Stopping vehicles within the designated security zone is prohibited.
- Each column is supplied with two posters with information about the depth of the route, as well as its direction. The first plate is installed vertically, and the other with mileage marks - at an angle of 30 degrees for the possibility of visual control from the air.
Laying technology and assembly rules
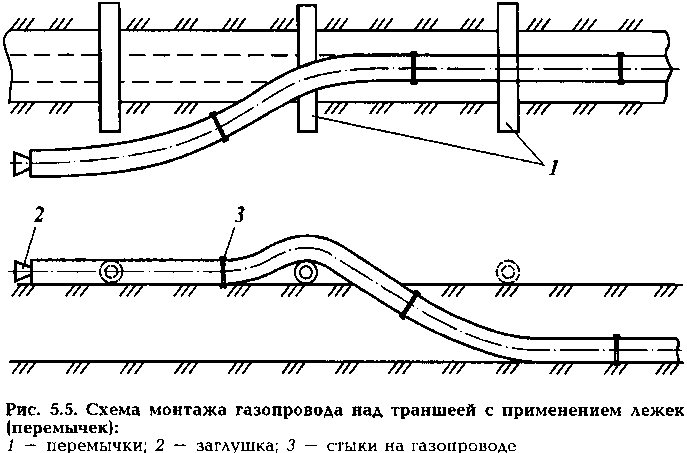

Installation of a pipeline from individual pipes of a specific length or sections on deck chairs above the trench
The laying of gas pipeline communications is a difficult and time-consuming process, which is carried out in stages and includes several stages. A preparatory stage is required, including the development of a gas pipeline project.
The project should be developed only by qualified specialists; on its basis, installation will be carried out in the future. The project must necessarily take into account the features of the landscape and soil of the site where the installation work will be carried out, as well as the climatic conditions of the area.
The second stage includes the direct work on the installation of gas pipelines. Next, start-up work is carried out.
The final stage is the control of the installed gas pipeline. It is necessary to test it for strength and perform a sealing check of all structural elements. All hydraulic checks can only be carried out after all accessories have been installed.
The gas pipeline is an explosive structure, therefore no construction can be carried out in the immediate vicinity. For this, special columns are used that mark the security zone. The size of the buffer zone depends on the type of gas pipeline. Appropriate warning signs are installed where required.
Main conclusions:
Only specially trained people should carry out the installation process.
The gas pipeline is a structure that creates a danger.
Installation requires strict adherence to safety regulations, the violation of which can lead to dangerous consequences.
Prepare the necessary technical documentation for the permit and installation of gas equipment.
Only specially trained people should carry out the design and installation process.
It is important to comply with all requirements for materials and components of the gas pipeline.
Detailed description of the main stages of work: tie-in to the water supply
When deciding how to make a tie-in to the water supply without turning off the pressure in the central system, you must carefully familiarize yourself with each stage of the work. In the beginning, it is necessary to calculate the route of the pipes. A depth of 1.2 m is considered optimal for them. Pipes should go straight from the central highway to the house.
Materials: cast iron and others
They can be made from the following materials:
- polyethylene;
- cast iron;
- Cink Steel.
Artificial material is preferable, since the tie-in to the water supply does not require welding in this case.
To simplify work on the tie-in place, a well (caisson) is built. For this, the pit is deepened by 500-700 mm. A gravel cushion is filled up at 200 mm. Roofing material is rolled out on it, and concrete 100 mm thick with a reinforcing grid of 4 mm is poured.
A cast plate with a hole for a hatch is installed on the neck. Vertical walls are coated with a waterproofing substance. The pit at this stage is covered with previously selected soil.
The channel breaks through manually or with the help of an excavator.The main thing is that the depth meets the requirements of the project. It is below the border of soil freezing in this climatic zone. But the minimum depth is 1 m.
For tie-in, it is better to use artificial material
Do-it-yourself installation in 7 steps: clamp, saddle, sewerage scheme, coupling
The installation process takes place according to the following technology.
- The device for tapping under pressure is located in a special collar pad. This element is installed on a pipe previously cleaned from thermal insulation. The metal is rubbed with sandpaper. This will remove rust. The cross-sectional diameter of the outgoing pipe will be narrower than that of the central one.
- A clamp with a flange and a branch pipe is installed on the cleaned surface. On the other side, a gate valve with a sleeve is mounted. A device is attached here in which the cutter is located. With her participation, an insertion into the general system is carried out.
- A drill is inserted into the pipe through an open valve and a gland of a blind flange. It must match the size of the hole. Drilling in progress.
- After that, the sleeve and cutter are removed, and the water valve closes in parallel.
- The inlet pipe at this stage must be connected to the flange of the pipeline valve. The protective coating of the surface and insulating materials are restored.
- Along the route from the foundation to the main canal, it is necessary to provide a slope of 2% from the tie-in to the inlet outlet pipe.
- Then a water meter is installed. A shut-off coupling valve is mounted on both sides. The meter may be in the well or in the house. To calibrate it, the shut-off flange valve is closed and the meter is removed.
This is a common tapping technique.The puncture is carried out in accordance with the type of material and design of the reinforcement. For cast iron, grinding is performed before work, which allows you to remove the compacted outer layer. A flanged cast-iron gate valve with a rubberized wedge is installed at the tie-in point. The body of the pipe is drilled with a carbide crown. It matters what material the cutting element is made of. A cast iron flanged valve requires only strong crowns, which will have to be changed about 4 times during the tapping process. Tapping under pressure into a water pipe is carried out only by competent specialists.
For steel pipes, it is not necessary to use a clamp. The pipe must be welded to it. And already a valve and a milling device are attached to it. The quality of the weld is assessed. If necessary, it is additionally strengthened.
The polymer pipe is not ground before a pressure tapping tool is put on the puncture site. The crown for such material can be both strong and soft. This is another reason why polymer pipes are considered beneficial.
The next step involves testing. Stop valves (flanged valve, gate valve) and joints are checked for leaks. When pressure is applied through the valve, air is bled. When water begins to flow, the system is inspected with the channel not yet buried.
If the test is successful, they bury the trench and the pit above the tie-in. Works are carried out in compliance with safety regulations and in accordance with the instructions.
This is a reliable, productive method that does not disturb the comfort of other consumers. Work can be done in any weather
Therefore, the presented method is so popular today.Connecting to the water supply is a very important technical event.
Rules for the placement of sewerage wells
Wells of drainage systems are an important part of the network, providing the possibility of maintenance, cleaning, technology for moving the flow. They are installed at a given distance from each other.
The density of the containers placement depends on the diameter of the channel. For example, for a line of 150 mm between the inspection tanks there should be 35 m. For pipes of 200 and up to 450 mm, the distance between the wells increases to 50 m. These standards are due to the specifics of the work and the parameters of the equipment that cleans the channels. It is impossible to break them, because because of this, the possibility of restoring the network will disappear.
What should be the distance from the gas pipeline to the sewer, the norms do not directly indicate. The main requirements relate to gaps between foundations, site boundaries, drinking wells or wells, reservoirs, etc. It is believed that there is no threat to the gas pipeline from the sewerage. However, both for the sewerage network and for gas communications, sanitary and protective standards apply. They do not meet technical requirements, which often becomes a source of disputes and disagreements.
Yes, for gas pipelines buffer zone is 2 m around the pipe. For sewer security zone is 5 m around the pipeline or well. Therefore, according to SanPiN standards, the distance from the gas pipeline to the sewerage system must be at least 7 m. This can be ensured when erecting large buildings, but such a requirement cannot be met in private construction. The size of the plots, the proximity of other objects and other factors will make it difficult to meet the standards.
It should be taken into account that the security zone of communications increases significantly if there are reservoirs, drinking wells and other water bodies nearby. Therefore, the location of pipelines is the subject of constant controversy. They are allowed, guided by the conditions of the location of the building, the size of the site and other factors. At the same time, the formal right to complain about violations in the laying of networks in the SES services remains, although they do not try too hard to use it.
Violation of the gas pipeline security zone. Legal and environmental implications
Violation of the protected zone of the gas pipeline can cause a serious man-made accident, fire or explosion. They can be caused by unauthorized earthworks in protected areas without agreement with the gas pipeline service organization, falling trees, and damage by cars.
At best, there will be a violation of the insulation, at worst, cracks and other defects will appear on the pipe, which over time will cause gas leakage. Such defects may not appear immediately and only eventually cause an emergency condition.
Damage to gas pipelines due to violation of security zones is punishable by a large administrative fine, which depends on the degree of damage. Demolition of buildings and structures built on the territory of protected zones is carried out by decision of the administrative court.
Carrying out unauthorized earthworks, unauthorized planting of trees and shrubs, organizing sports competitions, placing sources of fire, constructing buildings, developing sand pits, as well as fishing, deepening or cleaning the bottom, and arranging a watering hole in the places where the underwater section of the gas pipeline passes, is punishable by fines from 5 thousand rubles.
Bandwidth calculation rules
The main factor responsible for the continuous supply of blue fuel to consumers is the value of the throughput of the gas pipeline. The calculation of this parameter is carried out according to a special algorithm. Moreover, it is made regardless of the type of pipes used.
The maximum throughput of a gas pipe can be calculated using the following formula:
Q max. \u003d 196.386 × D² × P / Z × T,
where:
- P is the working pressure maintained in the gas pipeline, plus 0.1 MPa or the absolute pressure of the gas;
- D is the inner diameter of the pipe;
- T is the temperature of the pumped blue fuel, measured on the Kelvin scale;
- Z is the compressibility factor.
This formula establishes the following pattern: the higher the value of the T indicator, the greater the network bandwidth should be.
Otherwise, depressurization of the gas transmission line will occur, which will inevitably lead to an explosion of this dangerous substance.
Having made the choice of the type of pipes for the gas pipeline, it is important to correctly determine the method of tie-in
There is a more complicated formula. However, the algorithm given above is quite sufficient to perform the necessary calculations prior to tie-in into the gas pipeline.
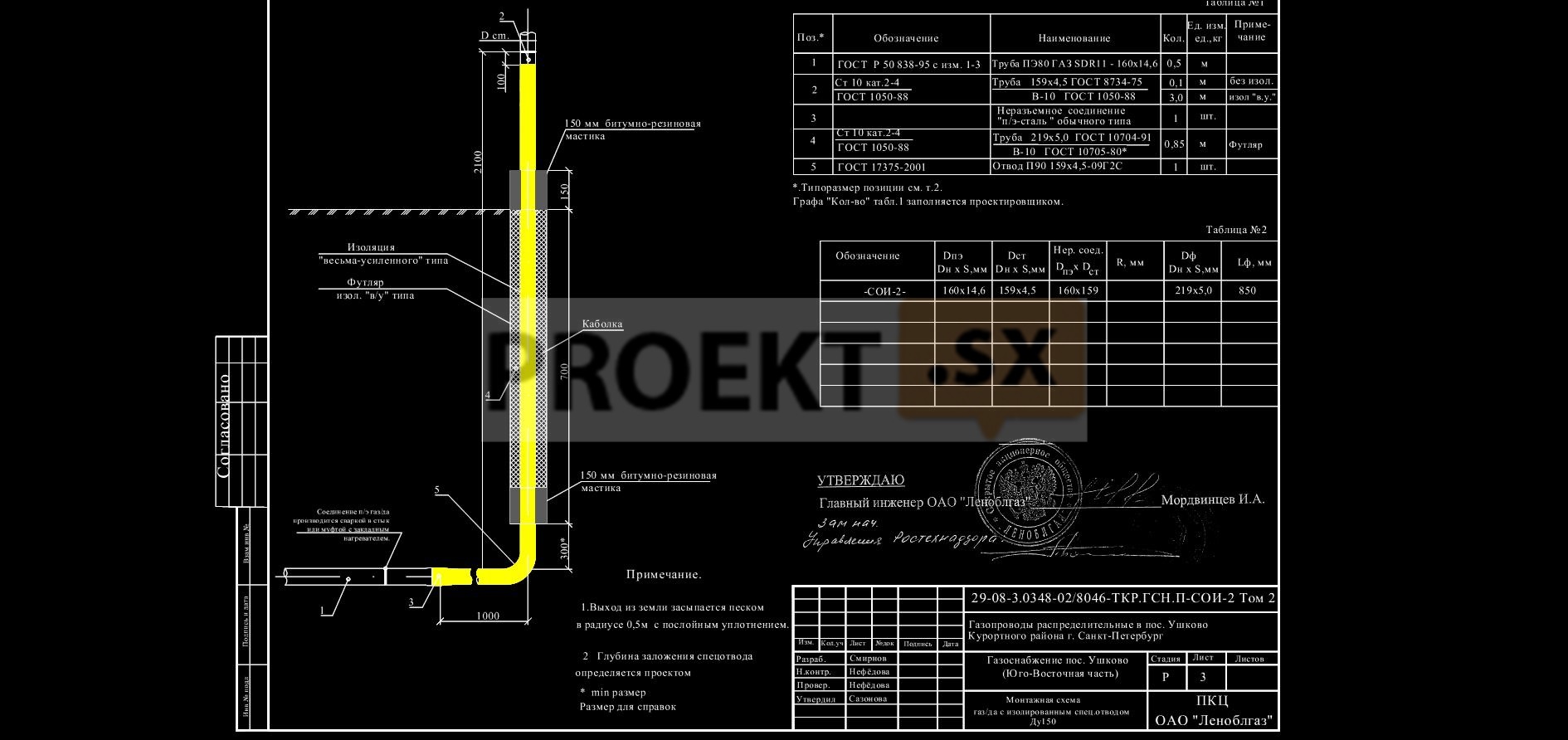
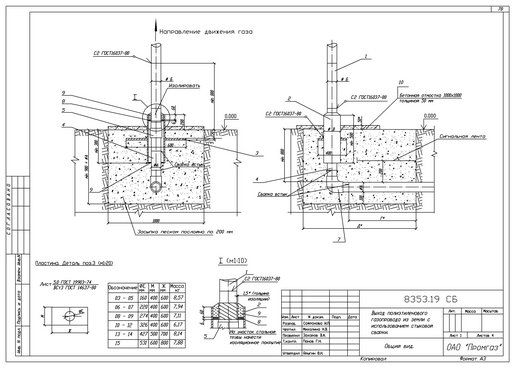
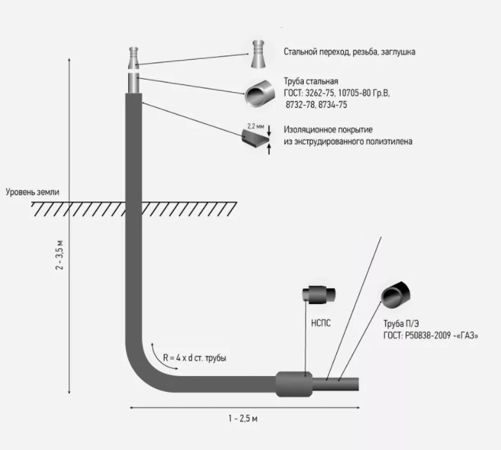
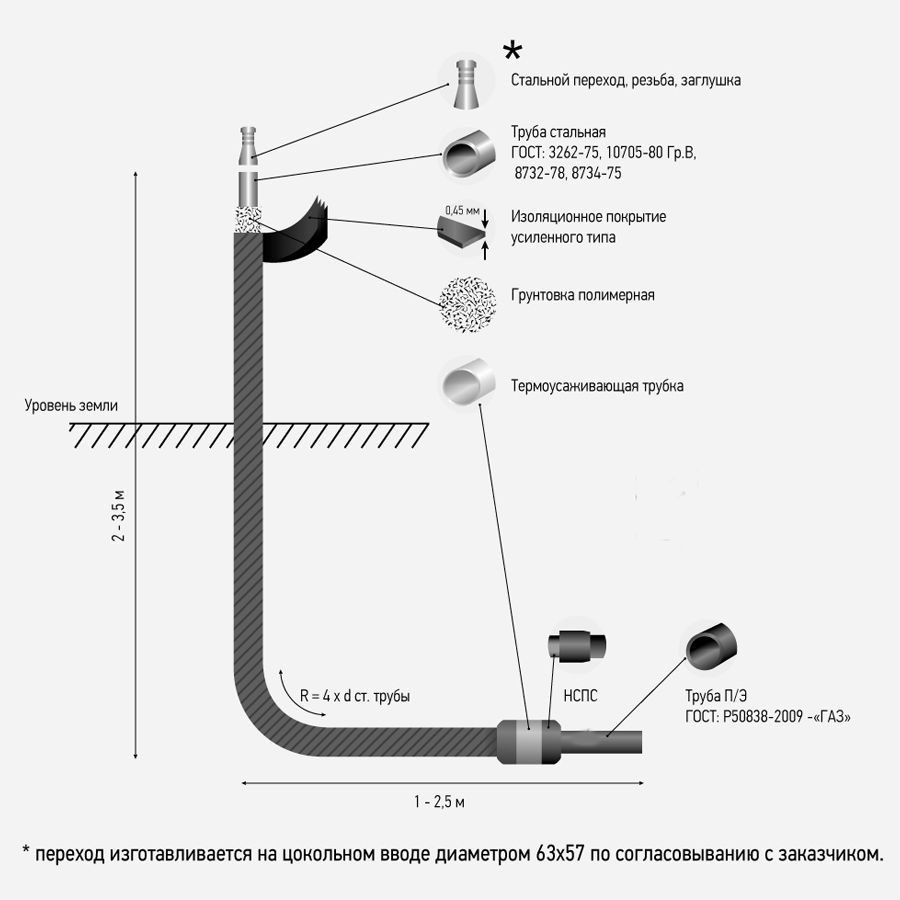
Gas base inlets
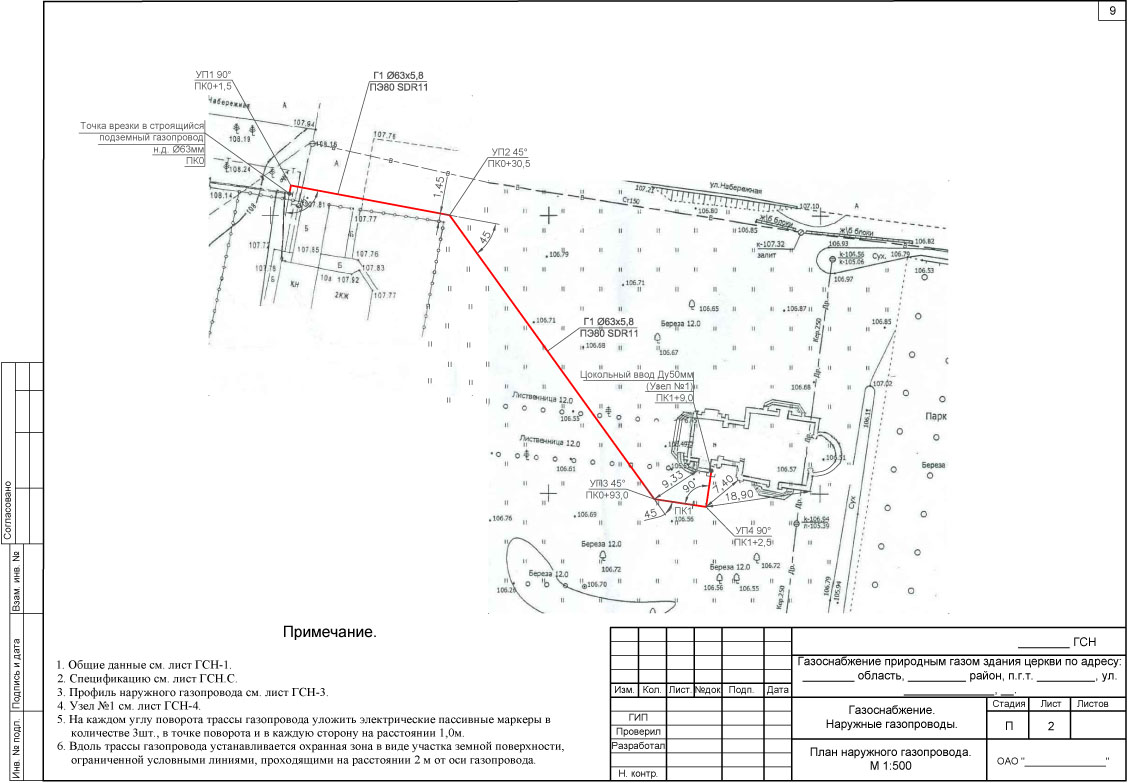
Description and application of gas base inlets
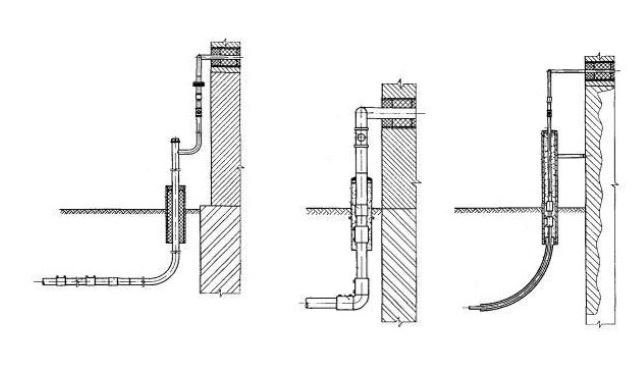
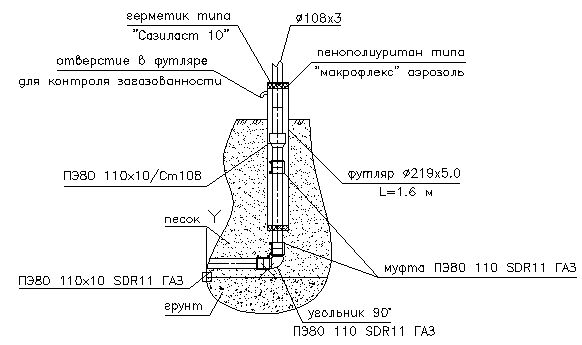
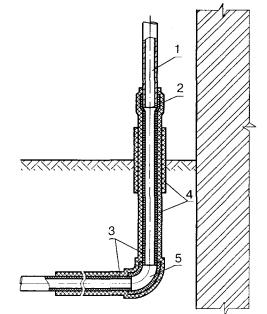
Gas socle inlets are installed at the points of transition of the external underground gas pipeline to the above-ground position, as well as where the exit is located in close proximity to the building.
The gas base inlet can be made by bending a plastic pipe with a polyethylene-steel connection in a protective case (Fig. b).
As well as gas base inlets are made using a branch and embedded heaters (Fig.in)
Gas socle inputs are covered with a reinforced insulating coating in accordance with GOST 9.602-2005 and RD 153-39.4-091-01.
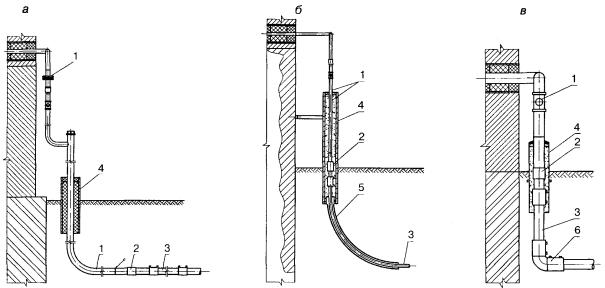
Varieties of gas base inlets
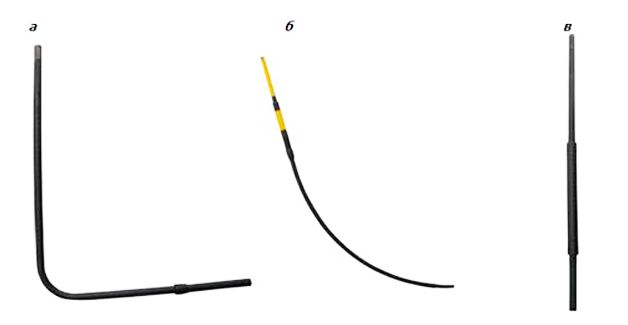
According to the Code of Rules for the design and construction of gas pipelines from polyethylene pipes SP 42-103-2003 ″, it is possible to use three types of gas base inlets:
a - steel gas base inlet;
b - polyethylene gas base inlet, with a free bend of the pipe;
c - polyethylene gas base inlet, using an outlet with embedded heaters.
1 - steel section of the basement input; 2 - transition "steel-polyethylene"; 3 - polyethylene gas pipeline; 4 - case; 5 - curved polyethylene case; 6 - outlet with embedded heaters; 7 - electrical insulating device
LLC "NIZHPOLYMER" offers all types of gas base inlets, in accordance with the set of rules SP 42-103-2003.
a - L-shaped (bent) gas base inlet from a steel insulated pipe.
Such a gas base inlet is a very reliable and time-tested product that can be used in the cold season at low temperatures, due to the fact that the permanent connection is underground. Such a gas base inlet has a diameter of 32x34 (Dn25) and 63x57 (90x89, 110x108) and is manufactured without a welded joint.
Gas socle inlets with a diameter of 160x159, 225x219, 315x273 and above are manufactured with a welded joint with a protocol for their verification. The steel part is insulated with a four-layer tape "Polylen" based on thermolight-stabilized polyethylene and butyl rubber. The insulation layer is more than 1.8 mm.
b - Direct gas base inlet with a free bend of a polyethylene pipe.
The diameter of direct gas socle inlets is 32x34(Dn25)mm.
c - Gas base inlet of a gas pipeline with a straight section of a polyethylene pipe and a steel insulated pipe (i-shaped base inlet).
Such a gas base inlet is used in various climatic zones, due to the underground location of 0.5 m. The upper part of such an input is also reinforced with a four-layer Polylen tape based on thermo-light-stabilized polyethylene and butyl rubber. The insulation layer is more than 1.8 mm.
Table of gas base inlets at NizhPolymer:
| Name | Weight, kg | Pipe PE GOST 50838-95 | Steel pipe | L1, not less than mm | L2, not less than mm | L3 no more than mm | dmm | d1mm |
| VCG PE 80 GAS SDR 11 32/st25 GOST 3262-75 (2х1)** | 6,96 | 32x3.0 | 25x3.2 | 1800 | 1100 | 300 | 32 | 32 |
| VCG PE 80 GAS SDR 11 32/st32 GOST 8732-78 (2х1) | 6,47 | 32x3.0 | 32x3.0 | 1800 | 1100 | 300 | 32 | 32 |
| VCG PE 80 GAS SDR 11 32/st25 GOST 3262-75 (2х2)*** | 9,87 | 32x3.0 | 25x3.2 | 1800 | 2100 | 300 | 32 | 32 |
| VCG PE 80 GAS SDR 11 32/st32 GOST 8732-78 (2x2) | 9,17 | 32x3.0 | 32x3.0 | 1800 | 2100 | 300 | 32 | 32 |
| VCG PE 80 GAS SDR 11 40/st32 GOST 3262-75 (2х1) | 9,00 | 40x3.7 | 32x3.2 | 1800 | 1100 | 300 | 40 | 38 |
| VCG PE 80 GAS SDR 11 40/st38 GOST 8732-78 (2х1) | 7,73 | 40x3.7 | 38x3.0 | 1800 | 1100 | 300 | 40 | 38 |
| VCG PE 80 GAS SDR 11 40/st32 GOST 3262-75 (2x2) | 12,74 | 40x3.7 | 32x3.2 | 1800 | 2100 | 300 | 40 | 38 |
| VCG PE 80 GAS SDR 11 40/st38 GOST 8732-78 (2x2) | 10,92 | 40x3.7 | 38x3.0 | 1800 | 2100 | 300 | 40 | 38 |
| VCG PE 80 GAS SDR 11 63/st57 GOST 10705-80 (2x1) | 13,24 | 63x5.8 | 57x3.5 | 1800 | 1100 | 300 | 63 | 38 |
| VCG PE 80 GAS SDR 11 63/st57 GOST 10705-80 (2x2) | 18,82 | 63x5.8 | 57x3.5 | 1800 | 2100 | 300 | 63 | 38 |
| VCG st57 GOST 10705-80 (2x3) | 25,38 | – | 57x3.5 | 1800 | 3000 | 300 | 57 | 38 |
Additional complete set of gas socle inputs
, if necessary, is ready to supply gas base gas pipeline inlets in the following configurations:
1) Mounted gas valves;
2) Bellows expansion joints insulating joints;
3) Electrofusion bends.
And also various standard sizes are possible (2x1, 2.5x1.3, 2x1.5, 2x2, etc.)
High-pressure gas pipeline security zone: how many meters according to SNiP (SP)
According to SP 62.13330.2011, this parameter is the largest. The gas pipeline area should ideally occupy sufficient space to secure the surrounding facilities and provide quick access for repairs.
 gate valve
gate valve
Indeed, in a gas pipeline with high pressure, all kinds of risks are higher. In the event of some kind of emergency, the gas abruptly breaks out, pushed out by itself, and also due to factors that tell the substance the speed (as a result of which it moves).
Whence it follows that for category 2 (with a head of 0.3-0.6 MPa inclusive), the security zone of the high-pressure gas pipeline is 7 meters in each direction. Thanks to this, it is possible to avoid problems in the maintenance of communications or any emergency situations.
Such measures are justified, and it is believed that the protection zone for category 2 high pressure pipes should even be larger. At least 7.4–7.8 meters. But so far this is just a theory.
 Above ground pipeline
Above ground pipeline
The accumulated experience is sufficient to state that these standards for gas pipelines of various pressures meet modern needs. And they are unlikely to change in the next few decades.
At least until 2022, no changes are expected. Below are the norms that are relevant both for settlements, including cities and villages, and for the private sector.
Composition of natural gas
These figures were derived in the course of many years of operation of gas pipelines and gas communications. According to them, excavation and other works, construction may or may not be allowed in the end.
| An object | Distance from the gas pipeline (0.3–0.6 MPa inclusive) |
| House (to the foundation, not to the facade) | 7 meters |
| Road | 7 meters |
| Water pipes | 1.5 meters |
| Sewerage | 2 meters |
| Power lines (1–35 kV) | 5 meters |
It is important to take into account that the pressure in the category 2 pipeline is 0.3–0.6 MPa. So maintenance work on this gas pipeline system is characterized by increased danger.
As well as the operation of such a gas pipeline is generally more dangerous.
Of course, such a pipeline is much more difficult to lay in a place where there are many buildings and structures nearby, due to the guard distance. For example, even if this is a private sector, houses are often located close, which means that underground and aboveground structures are close, including communications with their security zones.
So it is worth considering several times whether the decision to lay a pipeline with high pressure will be justified. Even if there was agreement, approval, and in general the whole procedure was passed without complaints, perhaps this is not a reason to lay a gas pipeline with such parameters.
Norms for the location of communications in accordance with SNiP and SP
However, one should not forget that there are still high-pressure pipelines of the first class, from 0.6 to 1.2 MPa. In such systems, the security zone is 10 m in each direction. It will be 2 m to the water supply, 5 m to the sewer.
Indentation standards for high-pressure gas pipelines of category 1 (over 0.6 and up to 1.2 MPa) are presented in the table below.
| An object | Distance from the gas pipeline (over 0.6–1.2 MPa) |
| House | 10 meters |
| Road | 10 meters |
| Water pipes | 2 meters |
| Sewerage household | 5 meters |
Of course, more is possible. For example, 5.5 m to the sewer or 3 m to the water supply, including the well. But these are still the parameters applicable to GDS (as well as to ShRP and GRP) and nodes.So the restrictions are far from those that are imposed on the main pipelines.
The purpose of monitoring the condition of an underground gas pipeline
Gas pipelines laid in trenches need regular inspection no less than ground routes. Of course, they are not threatened with purely mechanical damage, as happens with open communications. However, gas workers have no less reason to worry about their condition.
If the pipe transporting blue fuel is immersed in the ground:
- It is difficult to monitor the mechanical condition of the gas pipeline, but its walls are affected by ground pressure, the weight of structures and pedestrians, as well as passing vehicles if the pipeline passes under a highway or a railway line.
- It is impossible to detect corrosion in a timely manner. It is caused by aggressive groundwater, directly the soil, which contains active components. The loss of initial technical characteristics is facilitated by technical fluids penetrating to the depth of the route.
- It is difficult to determine the loss of tightness due to a violation of the integrity of the pipe or welded assembly. The reason for the loss of tightness is usually the oxidation and rusting of metal pipelines, the banal wear of polymer structures, or a violation of assembly technology.
Despite the fact that the laying of gas pipelines in trenches provides for the complete replacement of aggressive soil with soil with neutral properties, and the device in places of possible spillage of technical liquids is completely prohibited, without special devices they cannot be considered completely protected from chemical aggression.
As a result of the loss of tightness, a gas leak occurs, which, as it should be for all gaseous substances, rushes up. Penetrating through the pores in the soil, the gaseous toxic substance comes to the surface and creates zones above the gas pipeline that are negative for all living things.
A gas leak can easily cause a serious catastrophe if the blue fuel that left the pipe “finds” any cavity in the ground for accumulation. When heated, for example, by elementary exposure to sunlight in a hot summer period, an explosion of accumulated gaseous fuel is almost inevitable.

The occurrence of a gas leak from the pipeline threatens not only with a violation of the ecological balance, but also with serious catastrophic consequences: explosions, destruction, fires
In addition, a gas leak entails considerable financial losses for the gas producing and gas transportation organization. Moreover, disagreements may arise between them, which it is not even worth going to court if a control tube for monitoring has not been installed on the gas pipeline case.
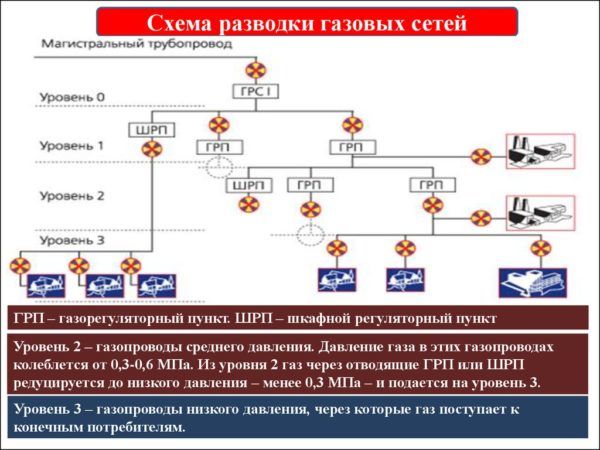
Varieties of gas pipelines
Gas pipeline communications are classified depending on pressure and location.
According to the level of pressure can be:
Gas pressure in the pipe
- low pressure (up to 5 kPa);
- medium pressure (up to 0.3 MPa);
- high pressure (up to 1.2 MPa).
Gas pipelines with medium and high pressure are designed to supply gas to industrial production enterprises and gas distribution stations, so it is advisable to build them as a resource for large-scale production.
The low pressure gas pipeline is used to supply gas directly to dwellings, so it is necessary to build it for settlements, residential and public facilities.
By location, they can be of the following type:
- underground;
- ground;
- outdoor;
- internal.
Installation of each type has its own characteristics and nuances. The choice of a method for laying a gas pipeline depends on many indicators, for example, the characteristic properties of the soil, climatic conditions.
Gas pipeline communications are divided into:
- main gas pipelines;
- gas pipelines of distribution networks.
Main gas pipelines. Designed to deliver gas over long distances. At certain distances, gas compressor stations should be installed, which are designed to maintain pressure.
Gas pipelines of distribution networks are designed to supply gas from gas distribution stations to consumers.
What determines the choice of communications
A special commission is responsible for the project of the new gas pipeline, which determines the route of the pipeline, the method of its construction, and the points for the construction of the GDS.
When choosing a laying method, the following criteria are taken into account:
- population of the territory where it is planned to stretch the gas pipeline;
- the presence on the territory of already extended underground utilities;
- type of soil, type and condition of coatings;
- characteristics of the consumer - industrial or household;
- the possibilities of various kinds of resources - natural, technical, material, human.
An underground laying is considered preferable, which reduces the risk of accidental damage to pipes and provides a stable temperature regime. It is this type that is practiced more often if it is necessary to supply gas to residential areas or detached buildings.
At industrial enterprises, highways are carried out above ground - on specially installed supports, along the walls. Open laying is also observed inside the buildings.
In rare cases, gas pipes are allowed to be masked under a concrete floor - in laboratories, places of public catering or public services. For safety reasons, the gas pipeline is placed in anti-corrosion insulation, poured with cement mortar, and placed in reliable cases at the exit points to ensure stability.
Which pipe to choose: types
Metal pipes for the fence are classified in two groups according to the profile section. The profile option is further subdivided into three groups:
According to the classification, round posts are suitable for mesh fences. Installation is carried out by means of hooks welded to the profile surface. The tension of the mesh is increased due to the fastening.
The profiled pipe is used when mounting solid sections: profiled sheets, fences made of wood or metal. Additionally, the frame is equipped with embedded parts for fastening the lag and ceilings.
Factors for choosing fence supports:
- Section diameter. Supports with insufficient section will fall under the weight of the cladding, or their own during the wind.
- Steel type. A lined steel support will last longer, but the cost of such pipes is higher. Steel pipes without spraying are often used, but with additional anti-corrosion treatment.
- Support length. The parameter depends on the section and weight of the fences, the soil - the amount of penetration is taken into account.
All parameters affect the wear resistance and service life of the fence. With the expected wind loads, the fourth factor is taken into account - windage.In other words, the ability of the supports to maintain the fence during a hurricane and a storm.