- Homemade from an old refrigerator
- The principle of operation of an air-to-air heat pump
- What is the difference between an air-to-air heat pump and an air conditioner
- Features of a competent calculation
- How to set the air conditioner for heating?
- How to choose an air conditioner
- What is a heat pump for heating a private house? How does it work?
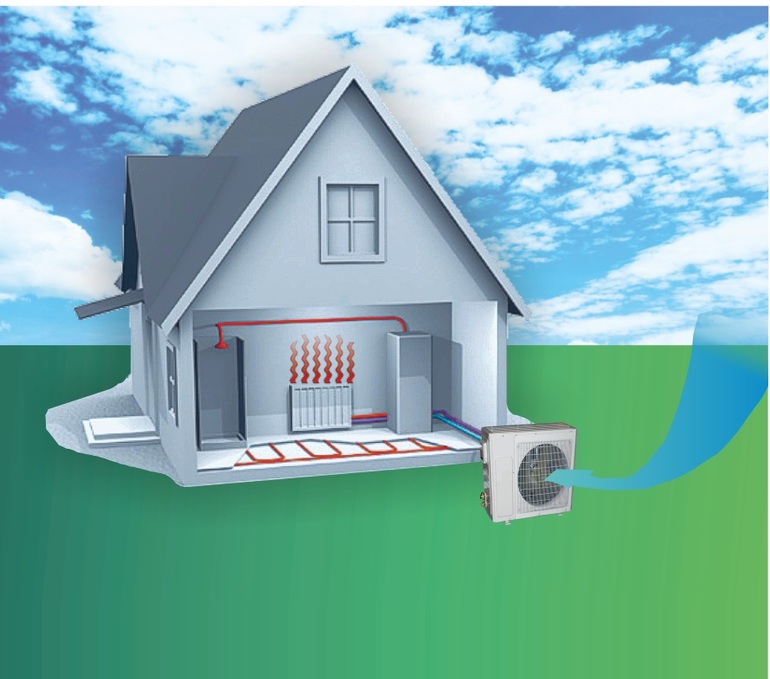
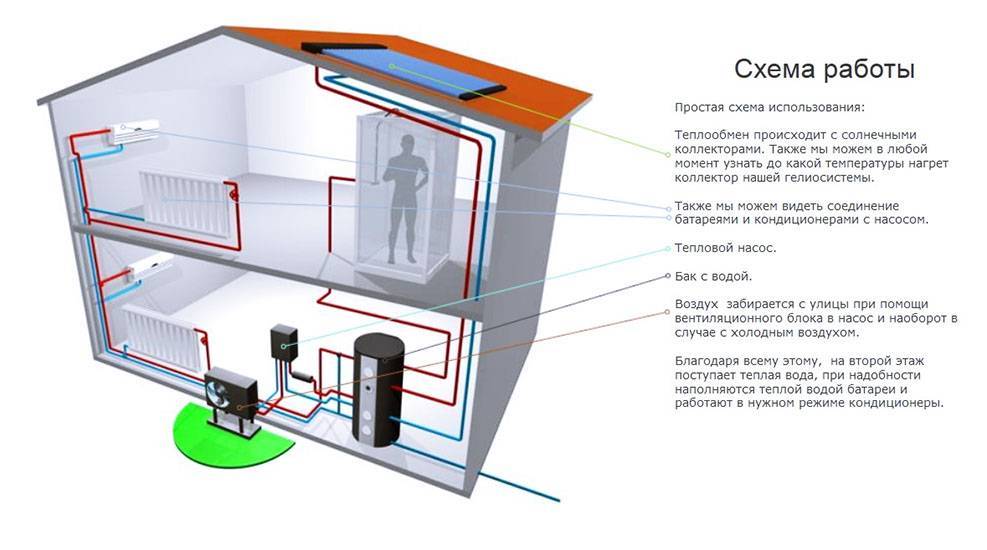
- Heat pump based heating system
- Heating with air - the principle of operation
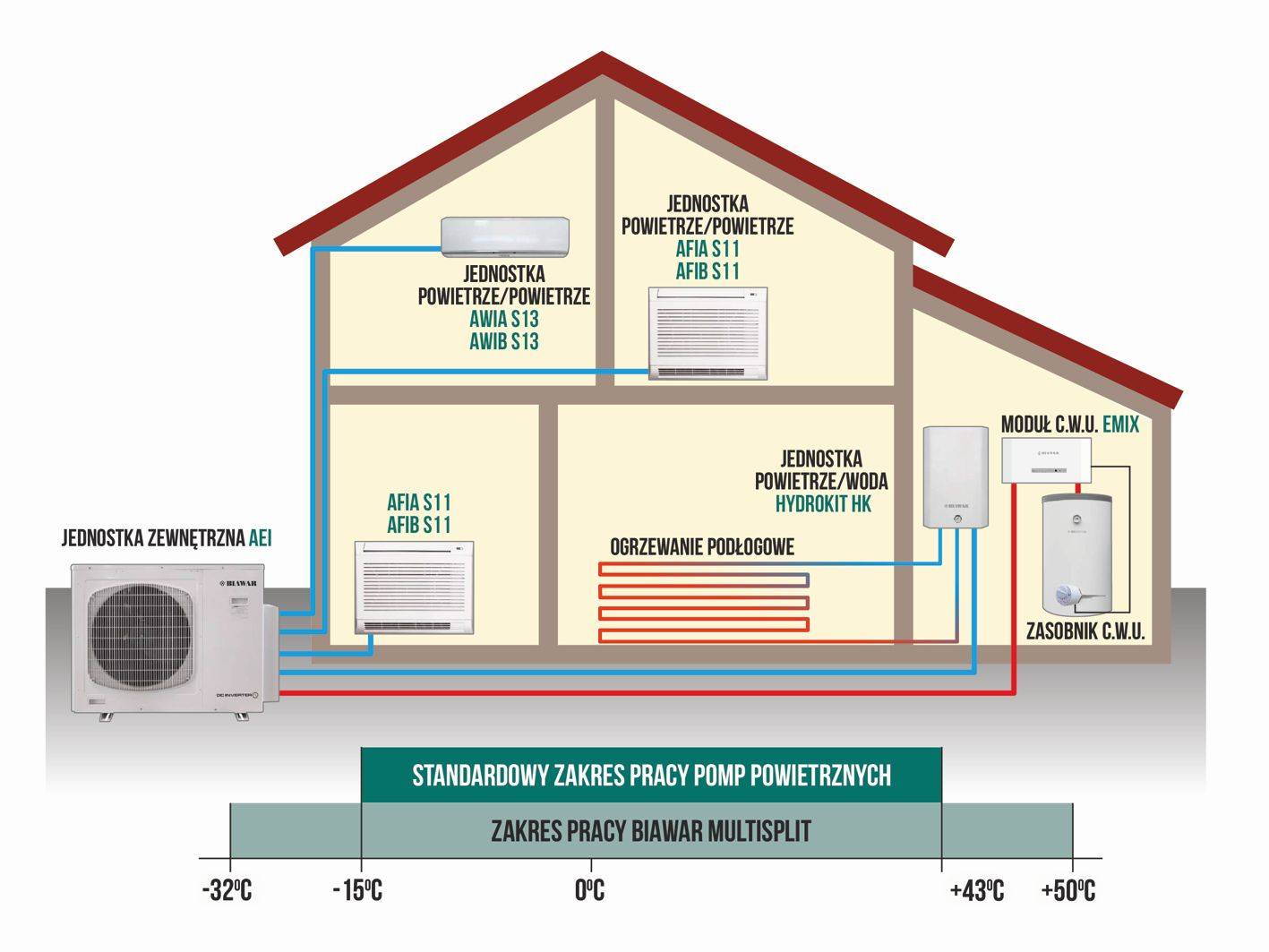
- Heat pumps - classification
- Geothermal pump - principles of design and operation
- Using water as a heat source
- Air is the most accessible source of heat
- Arguments for choosing an air system
Homemade from an old refrigerator
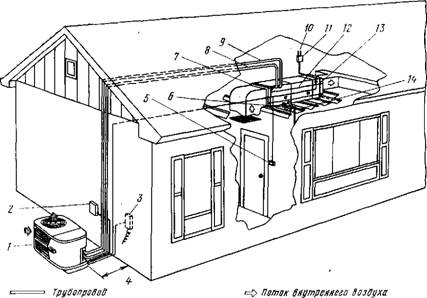
It is quite difficult to assemble an air-to-air heat pump from individual compressors and condensers with your own hands without specialized engineering knowledge. But for a small room or a greenhouse, you can use an old refrigerator.
 The simplest air heat pump can be made from a refrigerator by extending an air duct into it from the street and hanging a fan on the rear grille of the heat exchanger
The simplest air heat pump can be made from a refrigerator by extending an air duct into it from the street and hanging a fan on the rear grille of the heat exchanger
To do this, you need to make two holes in the front door of the refrigerator. Through the first in the freezer street air will be supplied, and on the second lower one - to be taken back to the street.
At the same time, during the passage through the inner chamber, it will give off part of the heat it contains to freon.
It is also possible to simply build the refrigeration machine into the wall with the door open to the outside, and the heat exchanger at the back into the room. But it should be borne in mind that the power of such a heater will be small, and it consumes a lot of electricity.
The air in the room is heated by a heat exchanger at the back of the refrigerator. However, such a heat pump is only able to operate at outdoor temperatures not lower than plus five Celsius.
This appliance is designed for indoor use only.
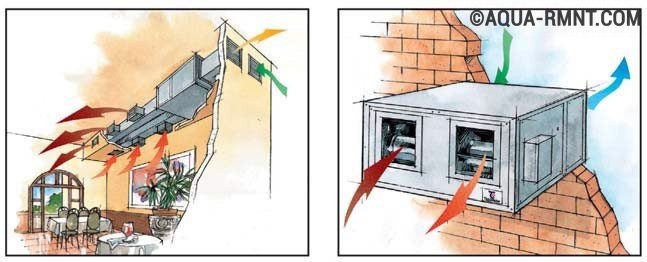
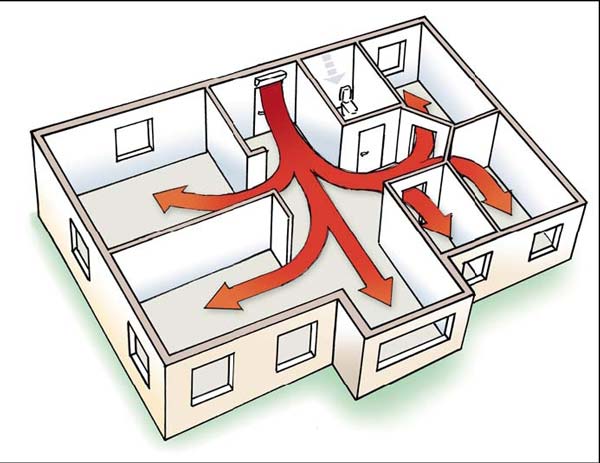
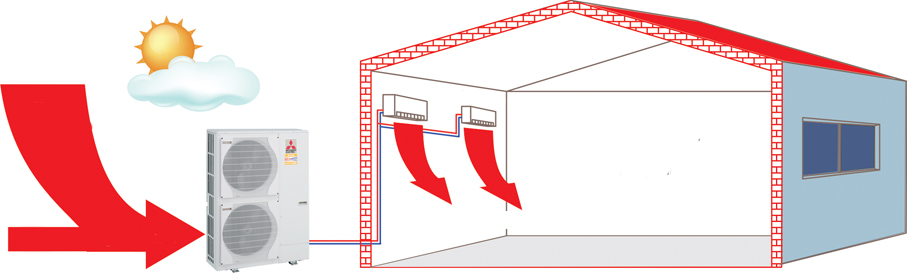
 In a large cottage, the air heating system will have to be supplemented with air ducts that distribute warm air evenly throughout all rooms.
In a large cottage, the air heating system will have to be supplemented with air ducts that distribute warm air evenly throughout all rooms.
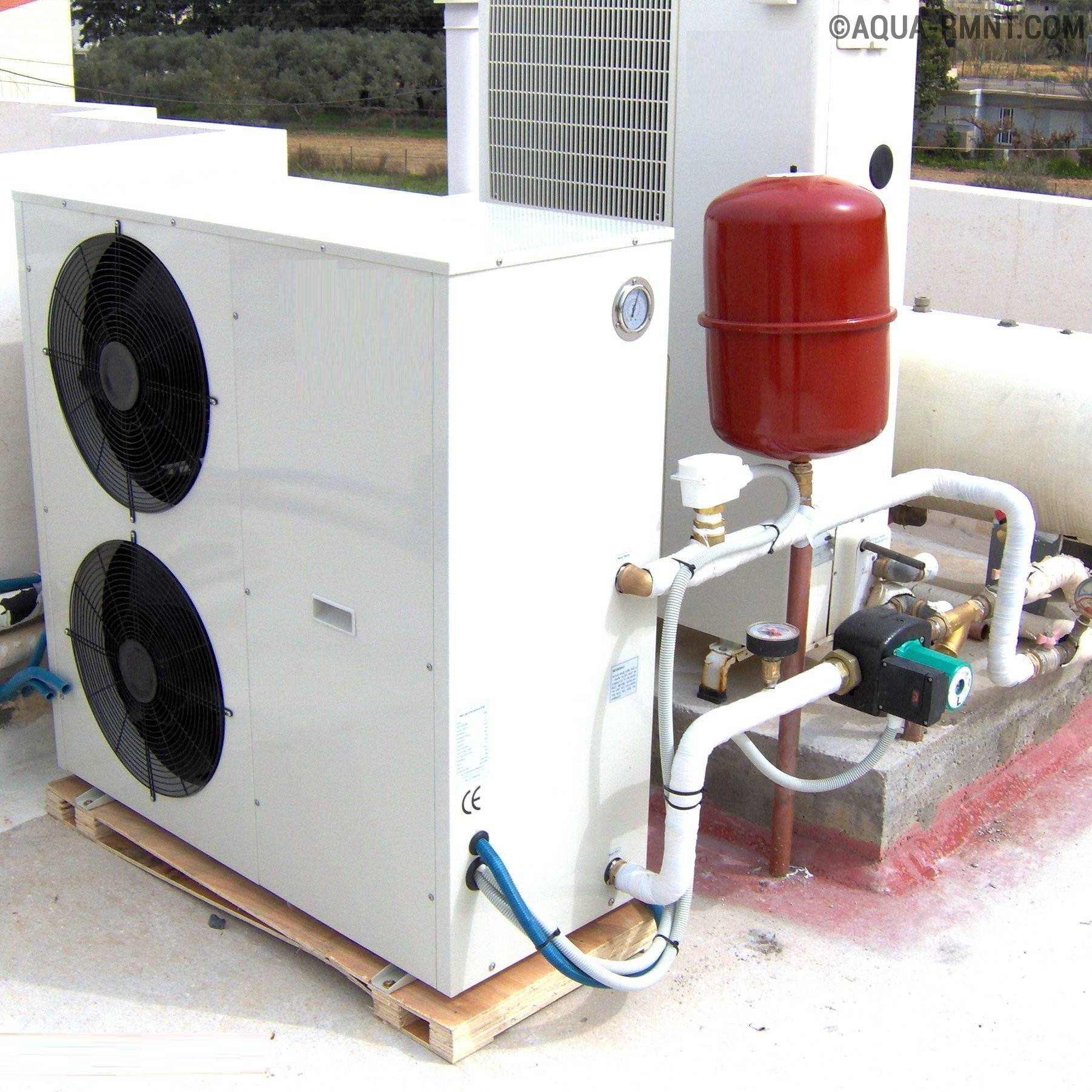
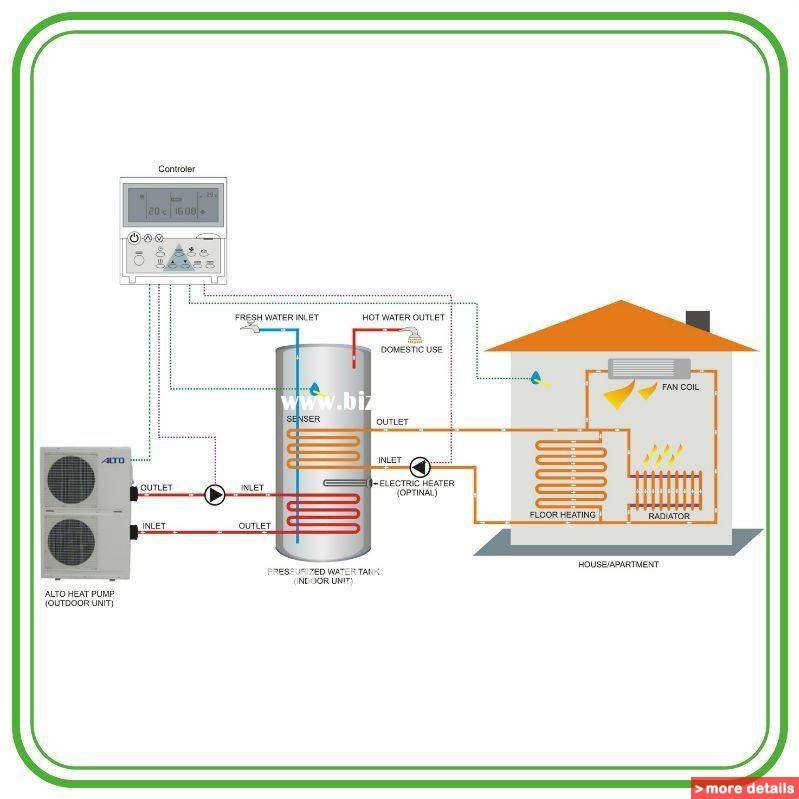
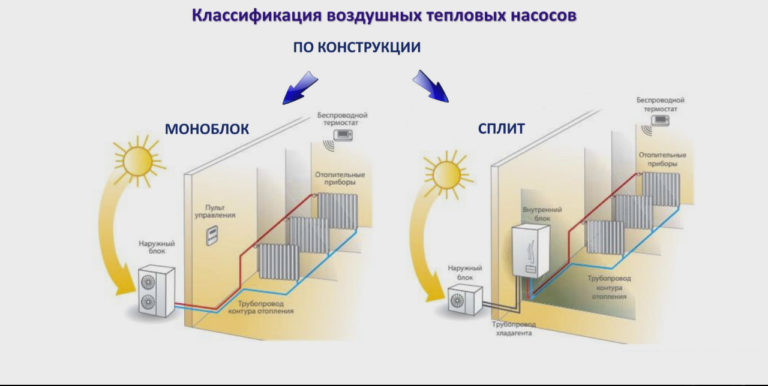
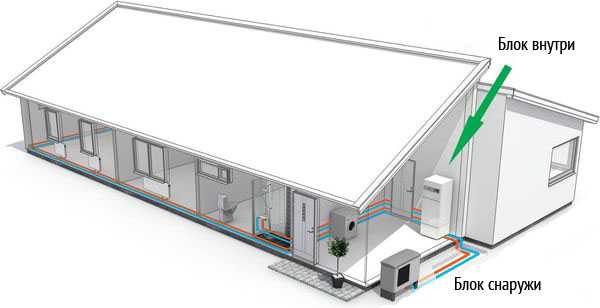
The installation of an air-to-air heat pump is extremely simple. It is necessary to install the external and internal units, and then connect them to each other with a circuit with a coolant.
The first part of the system is installed outdoors: directly on the facade, roof or next to the building. The second in the house can be placed on the ceiling or wall.
It is recommended to mount the outdoor unit a few meters from the entrance to the cottage and away from the windows, do not forget about the noise produced by the fan.
And the internal one is installed so that the flow of warm air from it is evenly distributed throughout the room.
If you plan to heat a house with several rooms on different floors with an air-to-air heat pump, you will have to equip ventilation duct system with forced injection.
In this case, it is better to order a project from a competent engineer, otherwise the power of the heat pump may not be enough for all the premises.
The electricity meter and protective device must be able to withstand the peak loads generated by the heat pump. With a sharp cold snap outside the window, the compressor begins to consume electricity many times more than usual.
It is best to lay a separate supply line from the switchboard for such an air heater.
Particular attention should be paid to the installation of pipes for freon. Even the smallest chips inside can damage compressor equipment
Here you can not do without copper soldering skills. Refilling refrigerant should generally be entrusted to a professional in order to avoid problems with its leaks later.
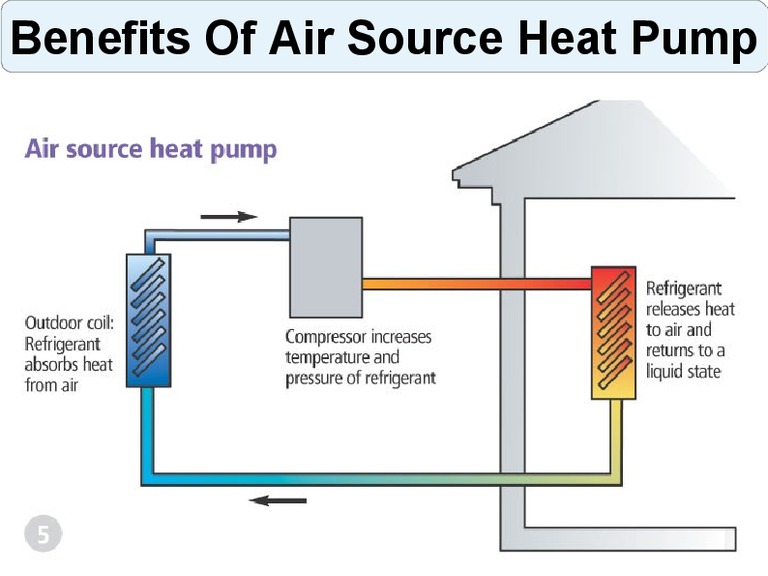
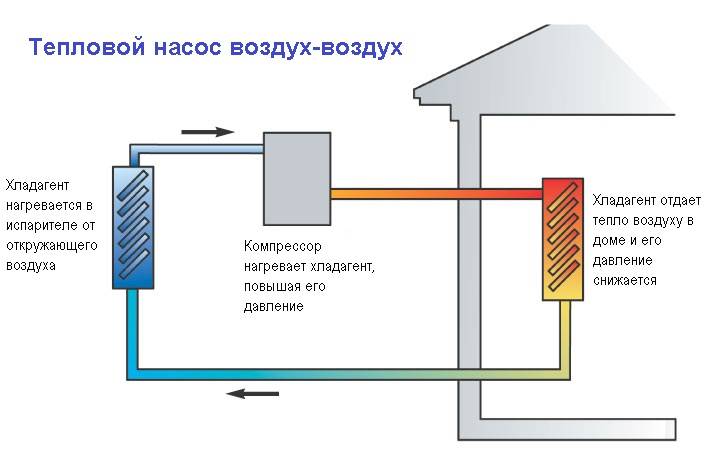
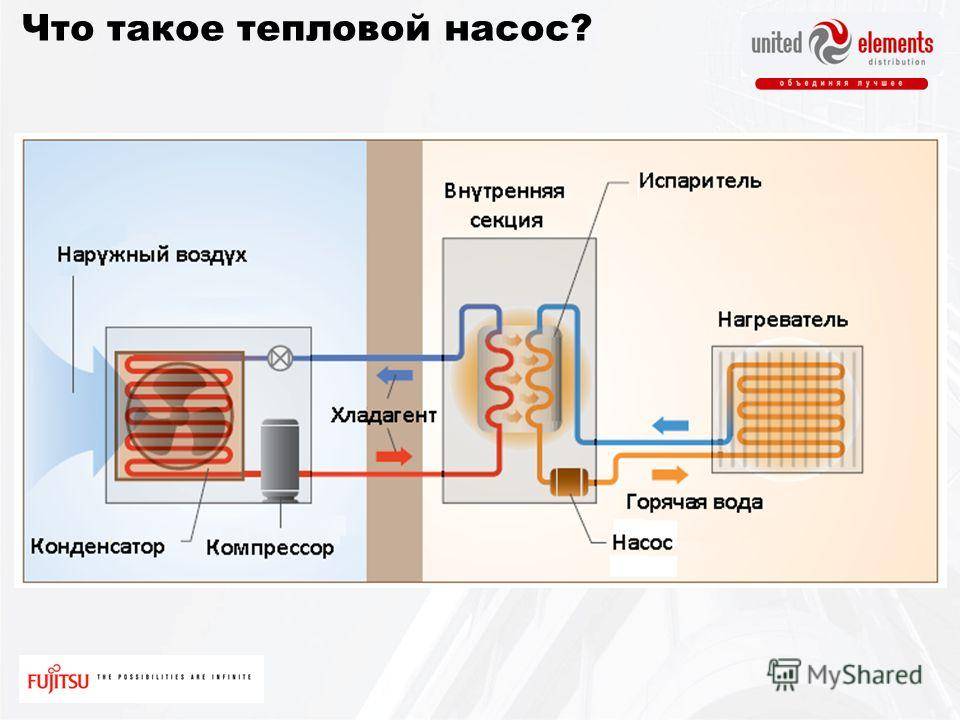
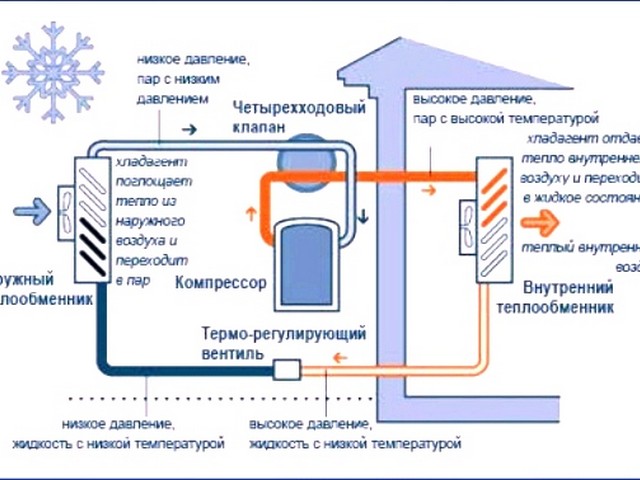
The principle of operation of an air-to-air heat pump
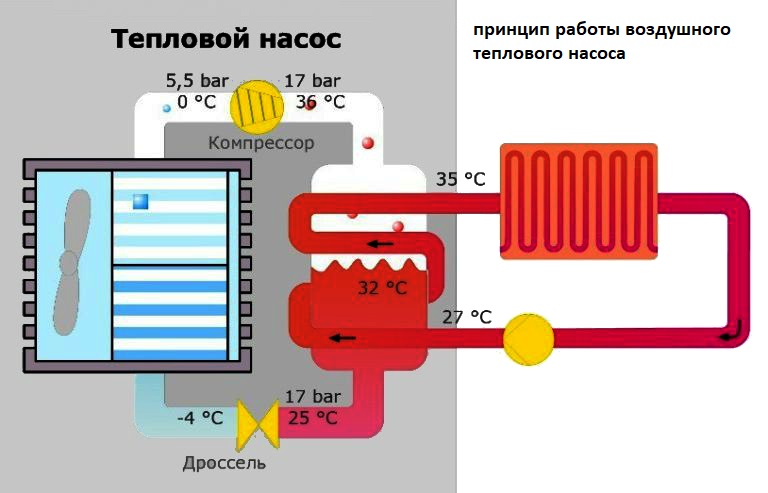
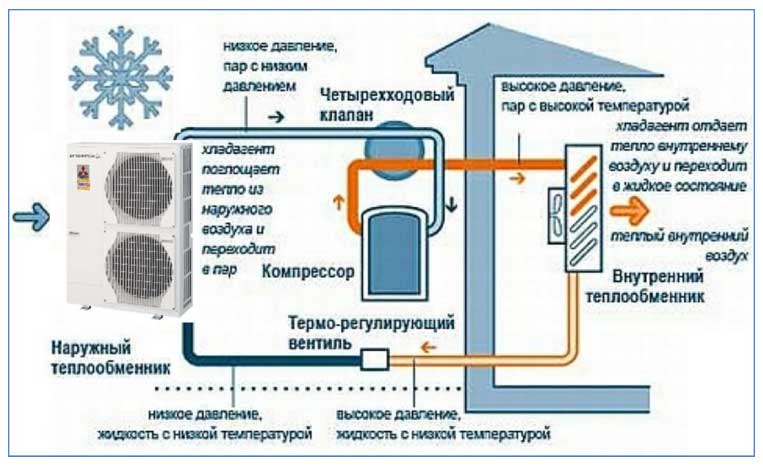
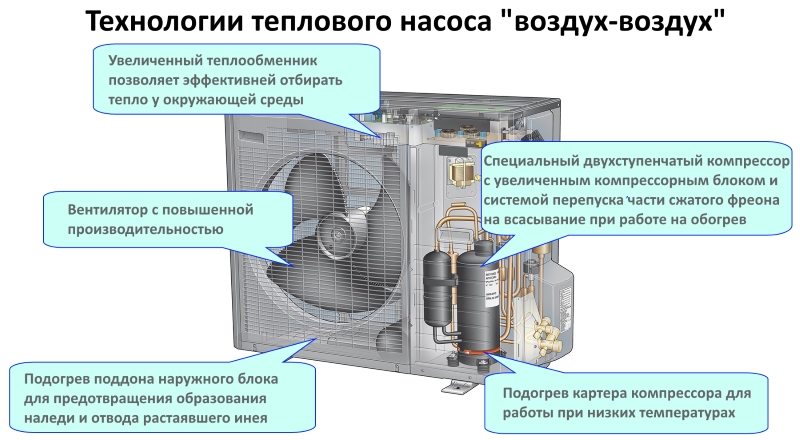
The general principle of operation of the HP is in many respects similar to that used in the air conditioner, in the “space heating” mode, with the only difference. The heat pump is “sharpened” for heating, and the air conditioner for cooling rooms. During work low-potential air energy is used. As a result, electricity consumption decreased by more than 3 times.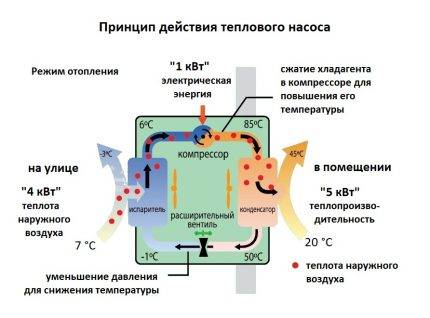 The principle of operation of an air-to-air heat pump installation, without going into technical details, is as follows:
The principle of operation of an air-to-air heat pump installation, without going into technical details, is as follows:
- Air, even at negative temperatures, retains a certain amount of thermal energy. This happens until the temperature readings reach absolute zero. Most HP models are able to extract heat when the temperature reaches -15°C. Several well-known manufacturers have released stations that remain operational at -25 ° C and even -32 ° C.
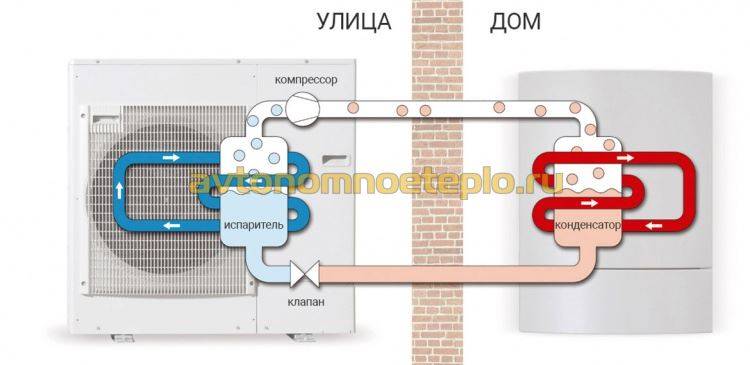
- The intake of low-grade heat occurs due to the evaporation of freon circulating through the internal circuit of the HP.For this, an evaporator is used - a unit in which optimal conditions are created for converting the refrigerant from a liquid to a gaseous state. At the same time, according to physical laws, a large amount of heat is absorbed.
- The next unit located in the air-to-air heat supply system is the compressor. It is here that the refrigerant in the gaseous state is supplied. Pressure is built up in the chamber, which leads to a sharp and significant heating of freon. Through the nozzle, the refrigerant is injected into the condenser. The heat pump compressor has a scroll design, which makes it easier to start at low temperatures.
- In the indoor unit, located directly in the room, there is a condenser that simultaneously performs the function of a heat exchanger. Gaseous heated freon purposefully condenses on the walls of the module, while giving off thermal energy. HP distributes the received heat in a manner similar to a split system.
Channel distribution of heated air is allowed. This solution is especially practical when heating large multi-apartment buildings, warehouses and industrial premises.
The principle of operation of an air-to-air heat pump and its efficiency are directly related to the ambient temperature. The colder "outside the window", the lower the performance of the station. Operation of the heat pump air-air at temperature minus -25°C (in most models) stops completely. To compensate for the lack of heat, a backup boiler is installed. The simultaneous use of an electric heating element is optimal.
Thermal air-to-air pumps consist of two blocks of outdoor and indoor placement.The design is in many ways reminiscent of a split system and is installed in a similar way. The indoor unit is mounted on wall or ceiling. The settings are set using the remote control.
What is the difference between an air-to-air heat pump and an air conditioner
An air-to-air heat pump works like an air conditioner, but has significant differences in terms of design and performance
Although there is an external similarity, in fact, the differences, if you pay attention to the technical characteristics, are significant:
- Productivity - air-to-air heat pump for home heating, works as efficiently as possible to heat the room. Some models are capable of cooling the air. During air conditioning, the energy efficiency is significantly inferior to conventional air conditioners.
- Economical - even inverter air conditioners consume more electricity during operation than is required for heating with an air-to-air heat pump. When switching to heating mode, the cost of electricity increases even more.
For HP, the energy efficiency coefficient is determined according to the COP. The average indicators of stations are 3-5 units. The cost of electricity in this case is 1 kW for every 3-5 kW of heat received. - Scope of application - air conditioners are used for ventilation and additional heating of the premises, provided that the ambient temperature is not less than +5°C. Air-to-air heat pumps are used as the main source of heating throughout the year in mid-latitudes. With a certain modification, they can be used to cool rooms.
World experience in the use of thermal heating pump systems air-to-air, convincingly proved that the use of renewable energy sources is not only possible, but also cost-effective, despite the need for upfront investment.
Features of a competent calculation
Despite the assurances of unfortunate masters, it is very difficult to independently calculate air heating. Such a task is only possible for specialists.
The customer can only check the availability of all items of the project, which include:
- Determination of heat losses of each of the heated premises.
- Type of heating equipment indicating the required power, which should be calculated based on real heat losses.
- The required amount of heated air, taking into account the power of the selected heater.
- Required section of air ducts, their length, etc.
These are the main points for calculating the heating system. It will be right to order a project from specialists. As a result, the customer will receive several calculation options, from which it will be possible to choose and translate into reality the most liked solution.
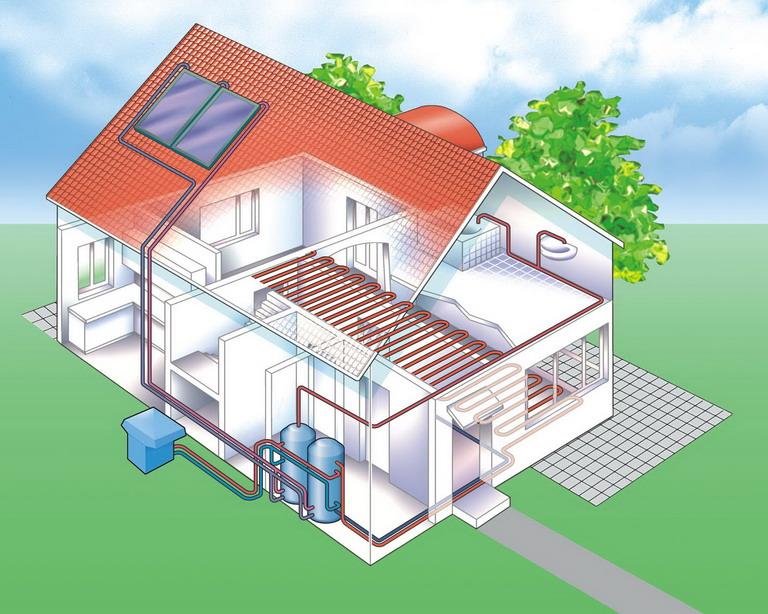
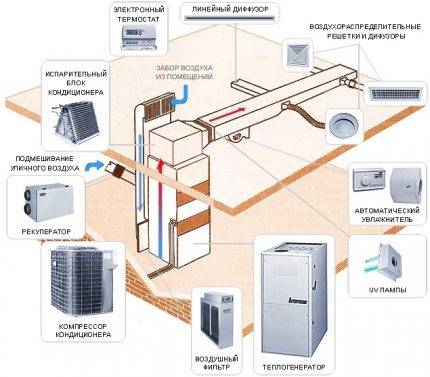 The air heating system is a complex structure consisting of many elements. To calculate it, it is better to involve professionals; to get acquainted with the components, it is worth studying the scheme in detail (+)
The air heating system is a complex structure consisting of many elements. To calculate it, it is better to involve professionals; to get acquainted with the components, it is worth studying the scheme in detail (+)
How to set the air conditioner for heating?
Before turning on conventional split system for heating, you should make sure that this option is provided in the equipment.
Before starting operation, it is imperative to study the instructions in which the presence of this mode is indicated by the sun icon or the “Heat” key. If the option is provided, see the lower temperature threshold

Stages of connecting the air conditioner to heating using the control panel.
- Plug the equipment into the mains.
- Press the on/off button once. Most often, it differs from other buttons in color.
- Press the "Mode / Heat" key or the button with the image of a droplet, sun, snowflake. After that, the image of the sun appears on the display.
- Set the desired temperature.
Warm air will begin to flow after 5-10 minutes.
By means of the control panel it is possible to adjust the position of the blinds and the fan speed.

If there is no "HEAT" button or the sun on the remote control, at the same time other modes are provided, then your device is not intended for space heating
Steps for connecting an air conditioner to heating using the buttons on the device itself:
- Plug the equipment into the mains.
- Click on "on/off". The button is located on the indoor unit or under the plastic panel. By short pressing the modes change (from cold to warm). A long press turns off the device.
- The temperature can only be adjusted using the remote control.
A more detailed guide on turning on the air conditioner for heating is in the instructions.
How to choose an air conditioner

The “sun” icon is the heating mode.
Choosing an air conditioner for heating in winter should be based on the area of \u200b\u200bthe room and the temperature regime of operation. So, there are models that work up to -5, -15, -20 and -25 degrees. Prices also vary greatly. A powerful system for a full-fledged winter costs about 100 thousand rubles. An interesting article: “What are the benefits of heat pumps for the organization of the heating system at home?”.
You can take any manufacturer, preferably a well-known one.In order not to buy anyhow, see if the manufacturer has a website, what guarantees it gives, if there are service centers in your city. Well-known (verified) brands:
- LG;
- Samsung;
- Toshiba;
- Mitsubishi;
The fact is that some manufacturers do not emphasize this and the air flow direction curtains move in all modes in the same way. Naturally, it is better to direct the cold air upwards and it will descend to the floor on its own. In this way, the temperature will be uniform throughout room. With heat, it's the other way around. It must be directed perpendicularly down, and for some models of air conditioners this is simply not possible.
Now let's briefly talk about how to put the air conditioner on heating. Do you have a manual for the unit, read it everything is written there. If there is no instruction, look for the "sun" button on the control panel - this is the heating mode. If there is no such button, then go to the menu and look for the "sun" there.
What is a heat pump for heating a private house? How does it work?

A special device that is able to extract heat from the environment is called a heat pump.
Such devices are used as the main or additional method of space heating. Some devices also work for passive cooling of the building - while the pump is used for both summer cooling and winter heating.
The energy of the environment is used as fuel. Such a heater extracts heat from air, water, groundwater, and so on, so this device is classified as a renewable energy source.
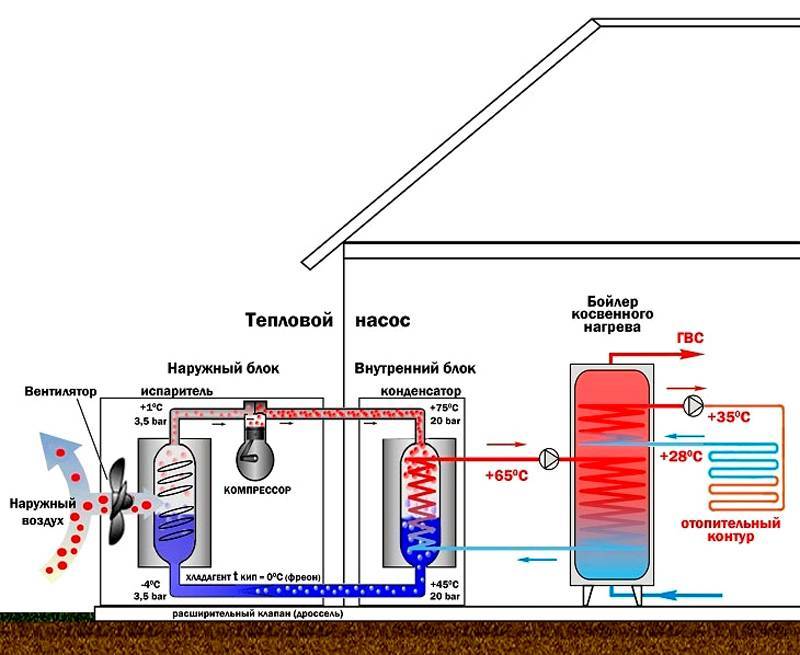
Important! These pumps require an electrical connection to operate. All thermal devices include an evaporator, a compressor, a condenser and an expansion valve.Depending on the heat source, water, air and other devices are distinguished.
The principle of operation is very similar to the principle of the refrigerator (only the refrigerator throws out hot air, and the pump absorbs heat)
Depending on the heat source, water, air and other devices are distinguished. The principle of operation is very similar to the principle of the refrigerator (only the refrigerator throws out hot air, and the pump absorbs heat)
All thermal devices include an evaporator, a compressor, a condenser and an expansion valve. Depending on the heat source, water, air and other devices are distinguished. The principle of operation is very similar to that of a refrigerator (only the refrigerator throws out hot air, and the pump absorbs heat).
Most devices operate both at positive and negative temperatures, however, the efficiency of the device directly depends on external conditions (i.e., the higher the ambient temperature, the more powerful the device will be). In general, the device works as follows:
- The heat pump comes into contact with the surrounding conditions. Typically, the device extracts heat from the ground, air or water (depending on the type of device).
- A special evaporator is installed inside the device, which is filled with refrigerant.
- Upon contact with the environment, the refrigerant boils and evaporates.
- After that, the refrigerant in the form of vapor enters the compressor.
- There it shrinks - due to this, its temperature rises seriously.
- After that, the heated gas enters the heating system, which leads to the heating of the main coolant, which is used for space heating.
- The refrigerant cools down little by little. In the end, it turns back into a liquid.
- Then the liquid refrigerant enters a special valve, which seriously lowers its temperature.
- At the end, the refrigerant enters the evaporator again, after which the heating cycle is repeated.
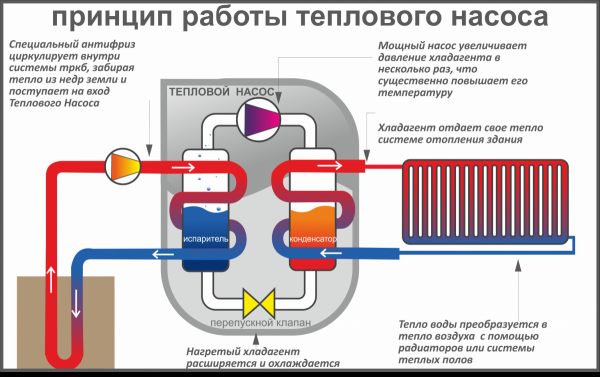
Photo 1. The principle of operation of the thermal ground water pump. Blue indicates cold, red indicates hot.
Advantages:
- Environmental friendliness. Such devices are renewable energy sources that do not pollute the atmosphere with their emissions (whereas natural gas produces harmful greenhouse gases, and electricity is often used to burn coal, which also pollutes the air).
- Good alternative to gas. A heat pump is ideal for space heating in cases where the use of gas is difficult for one reason or another (for example, when the house is far from all major utilities). The pump also compares favorably with gas heating in that the installation of such a device does not require state permission (but when drilling a deep well, you still have to get it).
- Inexpensive additional heat source. The pump is ideal as a cheap auxiliary power source (the best option is to use gas in winter and a pump in spring and autumn).
Flaws:
- Thermal restrictions in case of using water pumps. All thermal devices function well at positive temperatures, while in the case of operation at negative temperatures, many pumps stop working.This is mainly due to the fact that the water freezes, which makes it impossible to use it as a heat source.
- There may be problems with devices that use water as heat. If water is used for heating, then a stable source will need to be found. Most often, a well must be drilled for this, due to which the installation costs of the device may increase.
Attention! Pumps usually cost 5-10 times more than a gas boiler, therefore, the use of such devices in order to save money in some cases may be impractical (for the pump to pay off, you will need to wait several years)
Heat pump based heating system
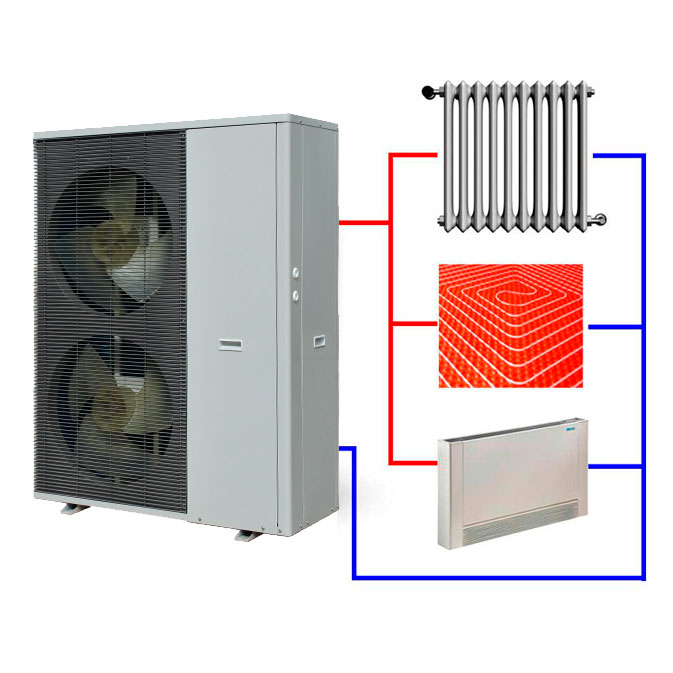
The heat energy produced by the heat pump can be used in any way. Typically, this equipment is used for water heating, which goes on for hot water needs (kitchen, bathroom, sauna) and heating.
Practice shows which is better to use underfloor heating than heating with radiators. In addition to the fact that this is soft heat and does not require heating water to a high temperature, there is a third, and important in terms of economy.
The lower the temperature of the water to be heated, the higher the efficiency of any heat pump. If for radiators the water should be warmed up to 50-55 degrees, then for warm floors - 30-35 degrees. Even if the inlet water temperature is 1-2 degrees, the difference in efficiency will be about 30%.
Air is often used for space heating. This is especially effective in regions where temperatures do not fall below 0, and also if a heat pump is used as an additional source of heat energy.
It is most convenient to use fan coil units for this, but for their installation you will either have to build a false ceiling or sacrifice aesthetics. If there is forced ventilation, you can use it to supply warm air.

Now heat pumps are not so widespread in the CIS than in other countries. We still have cheap traditional heat sources such as coal, gas and wood. But the situation is constantly changing and heat pumps are increasingly used for heating houses and non-residential buildings.
In this article, we tried to describe in detail the pros and cons of different types of heat pumps. We hope it was helpful to you. Don't forget to share the post with your friends!
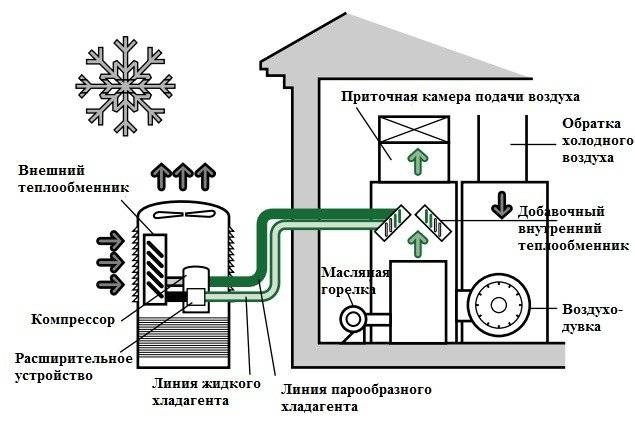
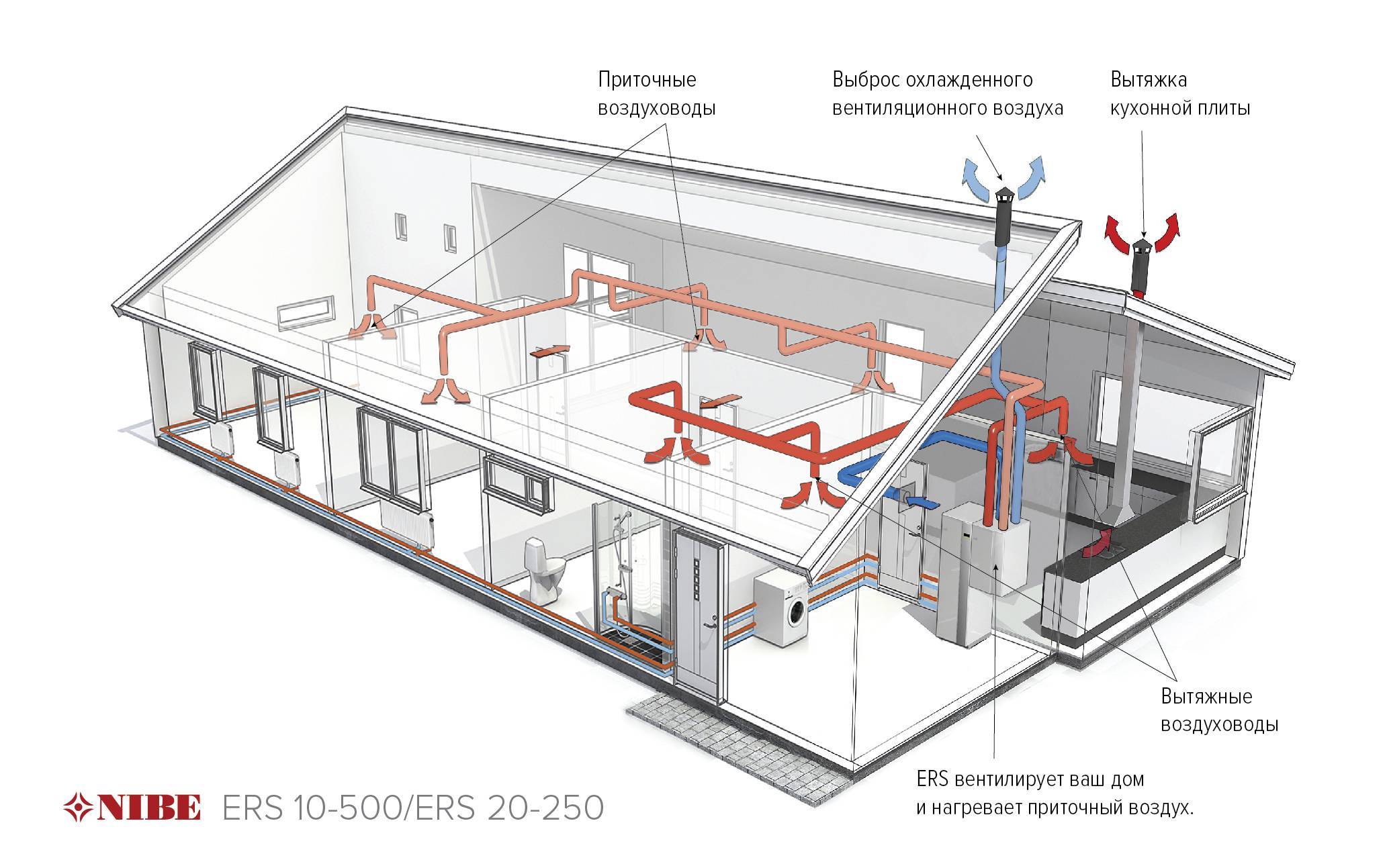
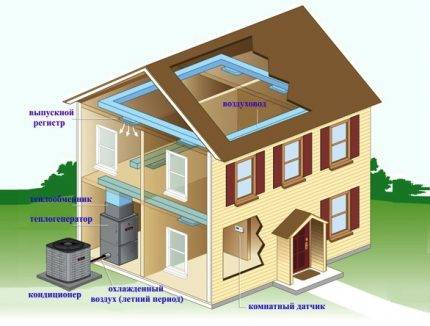
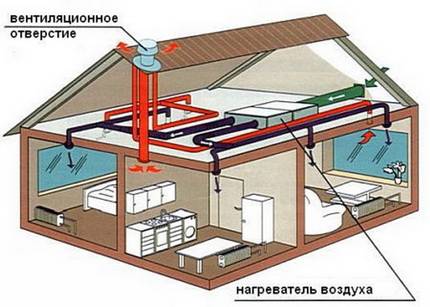
Heating with air - the principle of operation
Heating with the use of air mass entering the premises is based on the principle of thermoregulation. In other words, air heated or cooled to a certain temperature is supplied directly into the premises. Those. thus, heating of internal spaces and conditioning can be carried out.
The main element of the system is a heater - a channel-type furnace equipped with a gas burner. In the process of gas combustion, heat is generated, which enters the heat exchanger, and after that, the masses heated to a certain temperature enter the air space of the heated room. The air heating system must be equipped with a network of air ducts and a channel for the release of toxic combustion products to the outside.
Due to the constant supply of fresh air, the furnace receives an influx of oxygen, which is one of the main components of the fuel mass.Mixing in the combustion chamber with combustible gas, oxygen increases the intensity of combustion, thereby increasing the temperature of the fuel mass. In the old systems used by the ancient Romans, the main problem was the entry of harmful combustion products into the heated rooms along with the warm air.
Autonomous heating structures, built on the principle of heating air masses, have found their application in the heating system of large industrial buildings and facilities. With the advent of compact and easy-to-use air heaters that use gas, solid or liquid fuel, it has become possible to use such heating systems in everyday life. An ordinary, traditional air heater, which is commonly called a heat generator, has a combustion chamber, a heat exchanger of a recuperative type, a burner and a pressure group.
Furnace installation air heating in private and country houses is quite justified and cost-effective. This heating scheme is not suitable for an apartment, due to the need to lay a large number of bulky air ducts, the presence of technical noise and a high fire hazard.
Modern heating complexes are mainly built on a similar principle, however, in most designs, direct heating of the air mass is not provided. Heating is carried out with the help of heat generators, of which there are quite a lot today. Such units have recuperative heat exchangers in their design, due to which high-temperature flue gases are separated from heated air.Such a technological feature of modern air heating systems is to supply clean air heated to the required temperature into the premises.
The products of combustion in this case go through the chimney. Well-established operation of the hood and a clean chimney ensure the safety of the entire heating system of this type during operation.
Heat pumps - classification
 The operation of a heat pump for heating a house is possible in a wide temperature range - from -30 to +35 degrees Celsius. The most common devices are absorption (they transfer heat through its source) and compression (the circulation of the working fluid occurs due to electricity). The most economical absorption devices, however, they are more expensive and have a complex design.
The operation of a heat pump for heating a house is possible in a wide temperature range - from -30 to +35 degrees Celsius. The most common devices are absorption (they transfer heat through its source) and compression (the circulation of the working fluid occurs due to electricity). The most economical absorption devices, however, they are more expensive and have a complex design.
Classification of pumps by type of heat source:
- Geothermal. They take heat from water or earth.
- Air. They take heat from the air.
- secondary heat. They take the so-called production heat - generated in production, during heating, and other industrial processes.
The heat carrier can be:
- Water from an artificial or natural reservoir, groundwater.
- Priming.
- Air masses.
- Combinations of the above media.
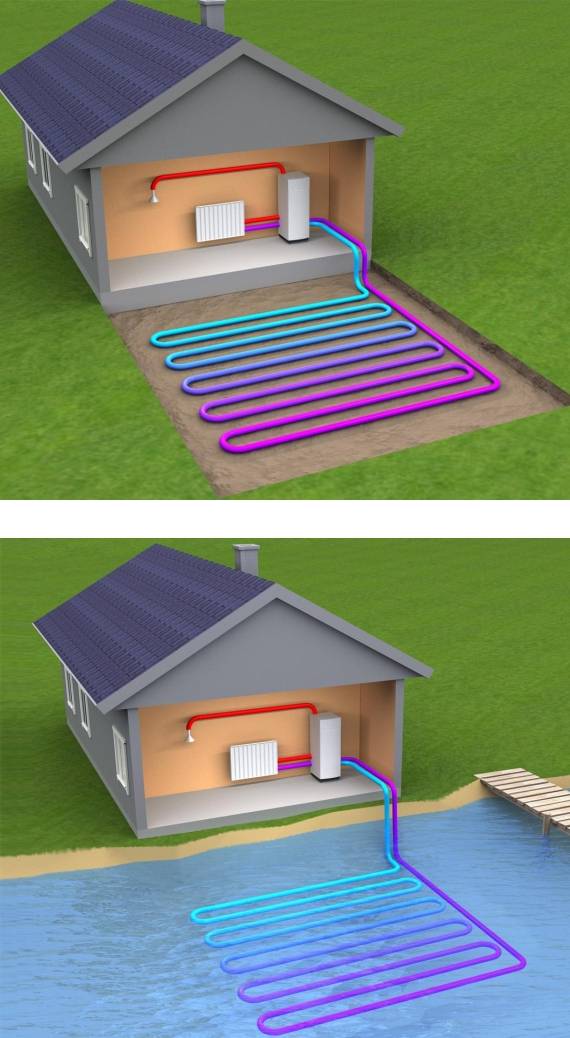
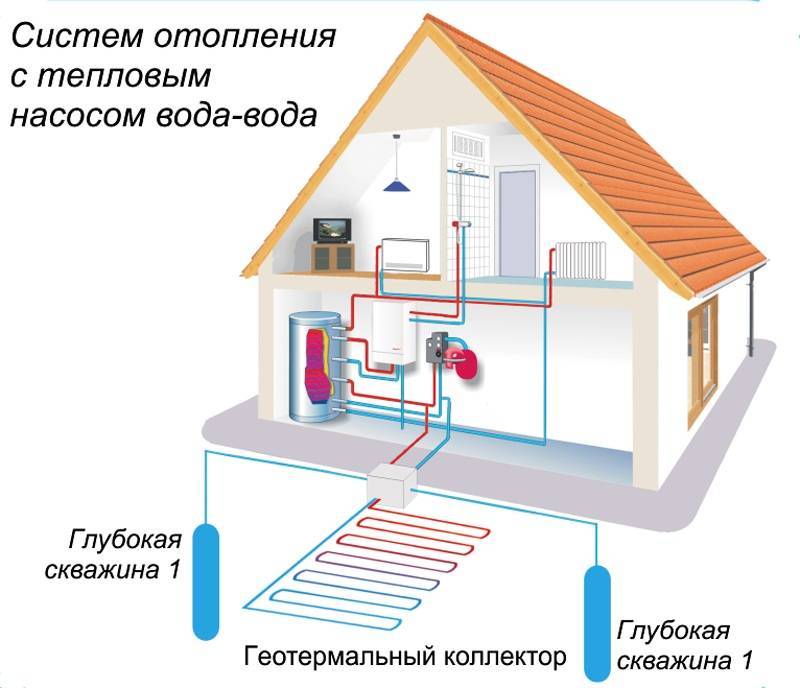
Geothermal pump - principles of design and operation
A geothermal pump for heating a house uses the heat of the soil, which it selects with vertical probes or a horizontal collector. Probes are placed at a depth of up to 70 meters, the probe is located at a small distance from the surface.This type of device is most efficient, since the heat source has a fairly high constant temperature throughout the year. Therefore, it is necessary to spend less energy on heat transportation.
 Geothermal heat pump
Geothermal heat pump
Such equipment is expensive to install. The high cost of drilling wells. In addition, the area allocated for the collector should be several times larger. heated house area or a cottage
It is important to remember: the land where the collector is located cannot be used for planting vegetables or fruit trees - the roots of the plants will be supercooled
Using water as a heat source
Pond - source a lot of heat. For the pump, you can use non-freezing reservoirs from 3 meters deep or groundwater at a high level. The system can be implemented as follows: the heat exchanger pipe, weighed down with a load at the rate of 5 kg per 1 linear meter, is laid on the bottom of the reservoir. The length of the pipe depends on the footage of the house. For a room of 100 sq.m. the optimal length of the pipe is 300 meters.
In the case of using groundwater, it is necessary to drill two wells located one after the other in the direction of groundwater. A pump is placed in the first well, supplying water to the heat exchanger. Chilled water enters the second well. This is the so-called open heat collection scheme. Its main disadvantage is that the groundwater level is unstable and can change significantly.
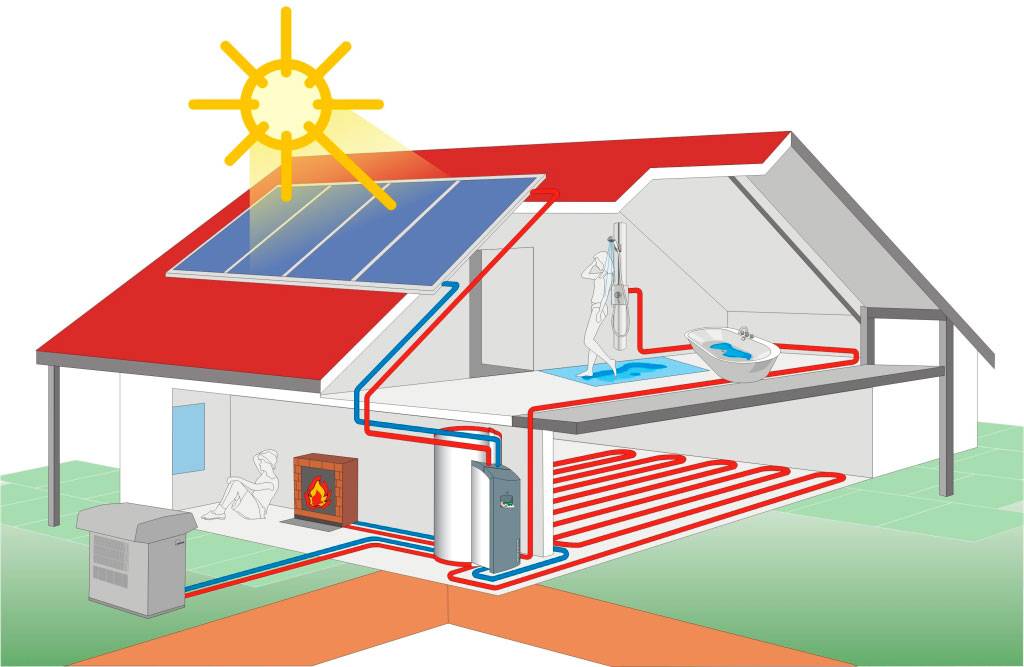
Air is the most accessible source of heat
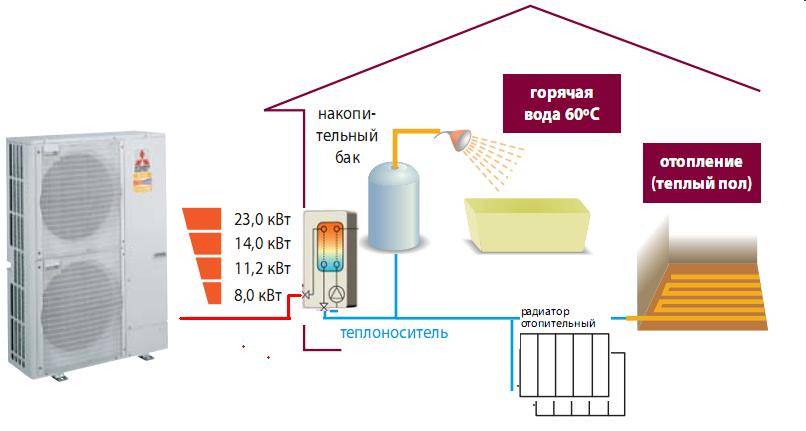
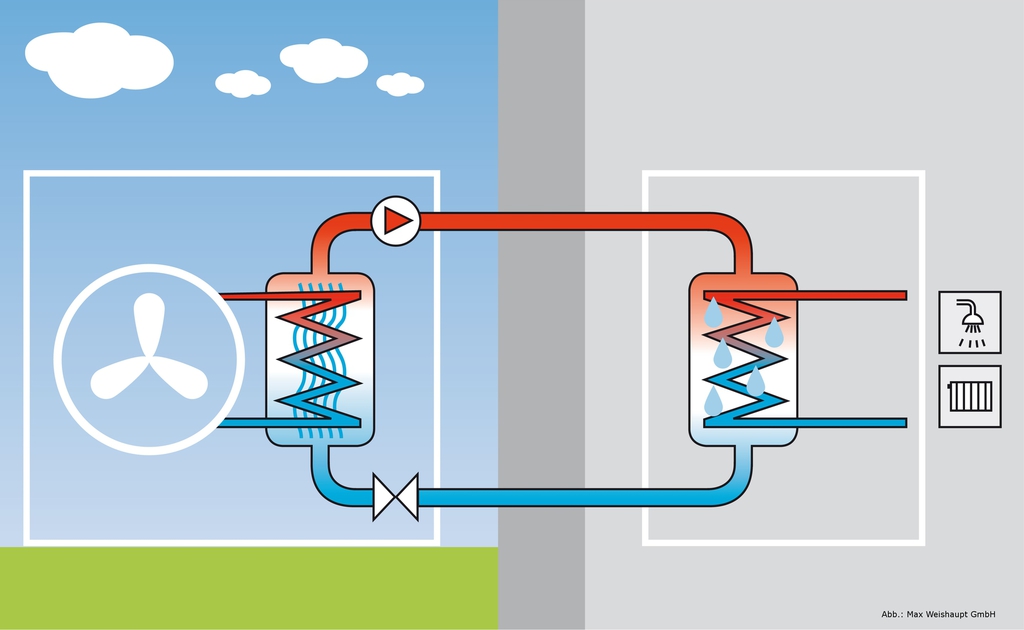
In the case of using air as a heat source, the heat exchanger is a radiator forcedly blown by a fan. If it works heat pump for heating a house using the air-to-water system, the user benefits from:
- Possibility to heat the whole house. Water, acting as a heat carrier, is diluted through heating devices.
- With minimal electricity consumption - the ability to provide residents with hot water. This is possible due to the presence of an additional heat-insulated heat exchanger with storage capacity.
- Pumps of a similar type can be used to heat water in swimming pools.
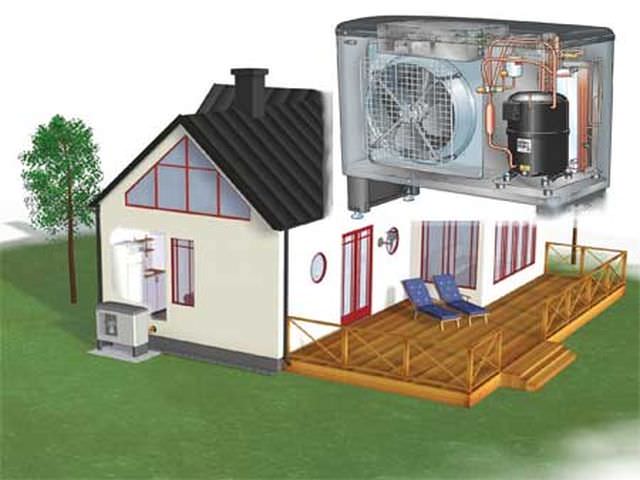
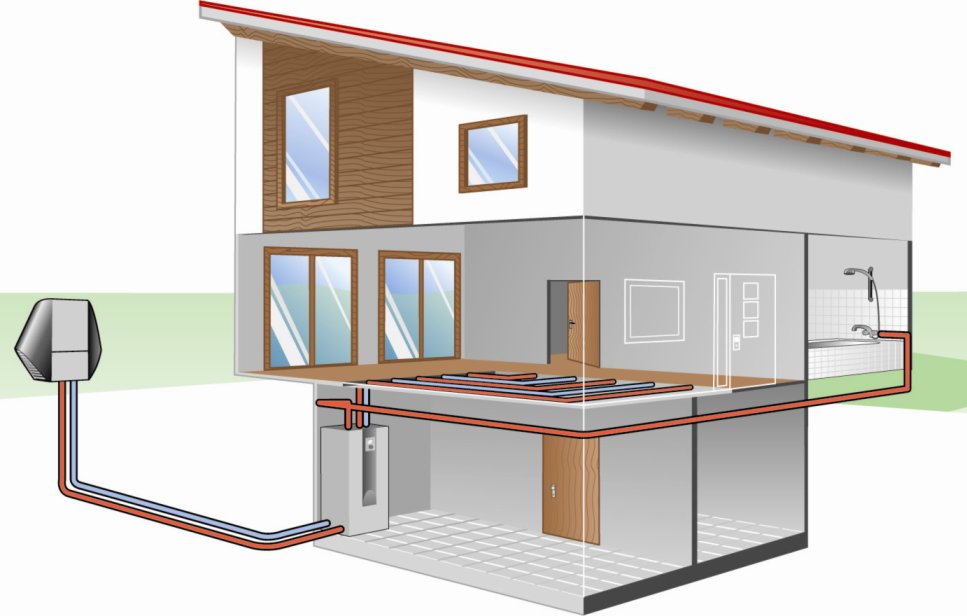
 Scheme of heating a house with an air source heat pump.
Scheme of heating a house with an air source heat pump.
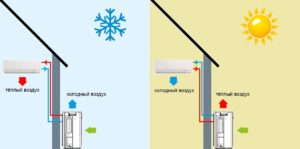
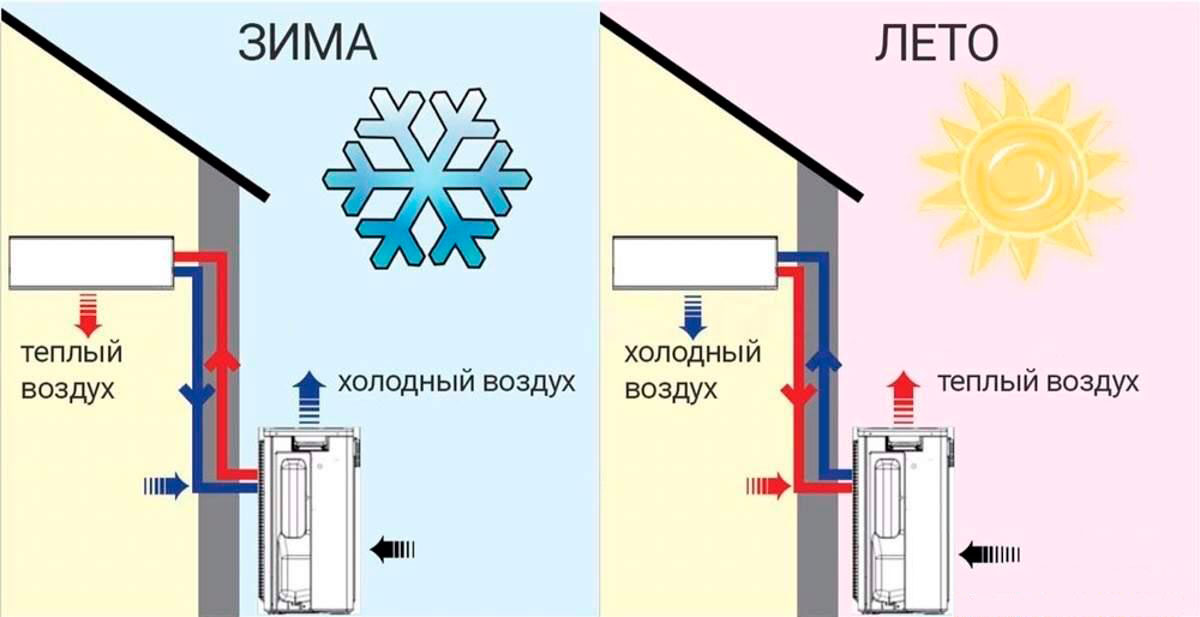
If the pump operates on an air-to-air system, no heat carrier is used to heat the space. Heating is produced by the received thermal energy. An example of the implementation of such a scheme is a conventional air conditioner set to heating mode. Today, all devices that use air as a heat source are inverter-based. They convert alternating current to direct current, providing flexible control of the compressor and its operation without stopping. And this increases the resource of the device.
Arguments for choosing an air system
Compared to conventional liquid heat transfer systems, air circuits have significant advantages. Let's consider them in more detail.
- High efficiency air systems. The performance of air heating circuits reaches about 90%.
- Possibility of turning off / on the equipment at any time of the year. Interruption of work is possible even in the most severe winter cold. This means that the disconnected heating system will not become unusable at negative temperatures, which, for example, is inevitable for water heating. You can turn it on at any time.
- Low operating cost of air heating. No need to purchase and install fairly expensive equipment: valves, adapters, radiators, pipes, etc.
- Possibility of combining heating and air conditioning systems. The result of the combination allows you to maintain a comfortable temperature in the building in any season.
- Low inertia of the system. This ensures extremely rapid heating of the premises.
- The possibility of installing additional equipment that is used to maintain an optimal microclimate. These can be ionizers, humidifiers, sterilizers, and the like. Thanks to this, it is possible to choose a combination of devices and filters that exactly matches the needs of the residents of the house.
- Maximum uniform heating of rooms without local heating zones. These problem areas are usually located near radiators and stoves. Due to this, it is possible to prevent temperature drops and their consequence - undesirable condensation of water vapor.
- Versatility. Air heating can be used to heat rooms of any size, located on any floor.
The system also has some disadvantages. Of the most significant, it is worth noting the energy dependence of the structure. Thus, when there is a power outage, the heating stops functioning, which is especially noticeable in areas with power outages. In addition, the system requires frequent maintenance and monitoring.
Air heating is very economical. The initial cost of its arrangement is small, operating costs are also low.
Another negative feature of air heating is that the installation of the structure must be carried out during the construction process. The installed system is not subject to modernization and practically does not change its operational characteristics.
If necessary, it is possible to install air heating in a constructed building, but in this case only suspended air ducts are used, which is not aesthetically pleasing and not always effective.