- Energy-saving lamps: how to choose and types of devices
- Halogen devices
- Fluorescent
- LED
- What to look for when buying
- Design features of LED lamps
- Low pressure sodium lamps (NLND)
- Types of energy saving lamps
- Types of lamps
- 8 best lamps for 12 V with a power of 5-8 W
- Why LED lamps flash: causes and solutions
- Why do LED lights blink when on?
- Why do LED lamps blink or glow when the light is off?
- Why do LED bulbs burn out
- Lists of the best
- Halogen – Uniel led-a60 12w/ww/e27/fr plp01wh
- Fluorescent – OSRAM HO 54 W/840
- LEDs – ASD, LED-CANDLE-STD 10W 230V E27
- No. 5. Lamp power and luminous flux
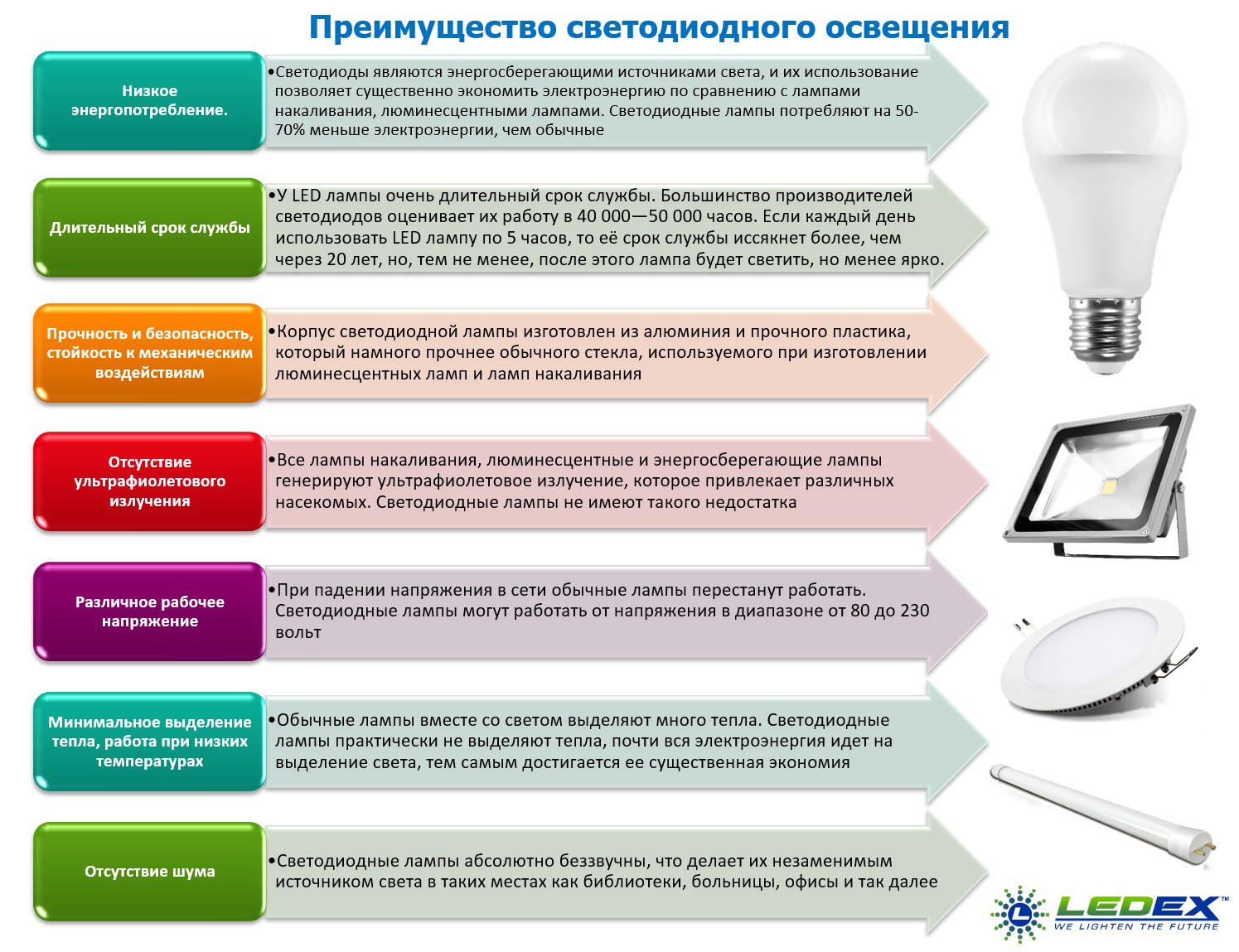
- Benefits of energy saving lamps
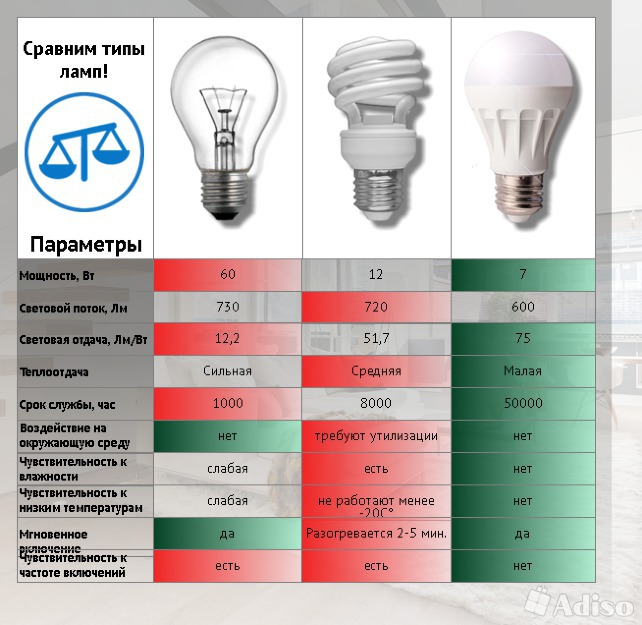
- Energy saving devices. Comparison
Energy-saving lamps: how to choose and types of devices
Halogen devices
Thanks to the technology of filling the lamp bulb with halogen vapors, a number of operational difficulties are solved and the range of modern illuminators is expanding.
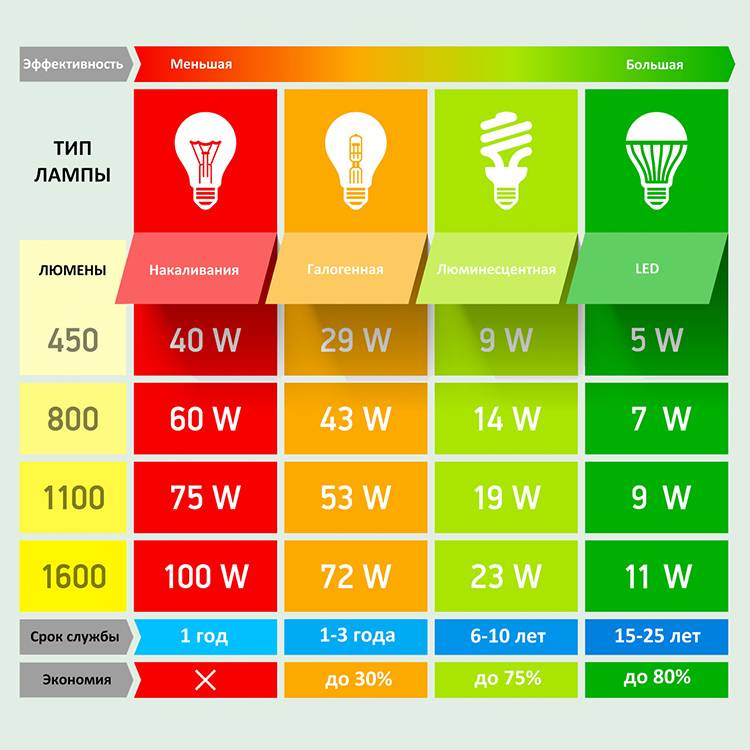
Efficiency and power of various types of lamps
Halogens provide a longer filament life and prevent tarnishing.
The advantages also include improved luminous efficacy and small bulb sizes.
A significant proportion of halogen lamps have a pin base, but models with a traditional threaded base are also available.
When installing halogen lamps, it is required to control the voltage, which is due to the impossibility of using low-voltage models without the use of step-down transformers.
Fluorescent
 Compact fluorescent lamps with a curved bulb shape are especially popular at present.
Compact fluorescent lamps with a curved bulb shape are especially popular at present.
Thanks to this form, it is possible to install the lamp in a lighting fixture of small dimensions.
Often, a design feature of a fluorescent lamp is the presence of a built-in electronic choke.
The main advantages of a fluorescent lamp are represented by high luminous efficiency, the absence of point emission of the light flux and a long service life under continuous operating cycle conditions. Also, the advantage of such a lighting device is the different values of color temperature while maintaining a high efficiency.
A significant difference between a luminescent light source and a traditional fluorescent lamp, which has an electromagnetic choke and is powered by alternating voltage, is the inability to produce a stroboscopic effect under certain conditions.
LED
 All types of LED lamps are equipped with a special semiconductor diode based on the principle of p / n junction as a light emitting element.
All types of LED lamps are equipped with a special semiconductor diode based on the principle of p / n junction as a light emitting element.
LED lamps do not contain mercury vapor, therefore they are completely safe, and they also have many advantages, represented by a low level of electrical energy consumption and a long service life.
Such lamps form a fairly bright light and do not emit warm energy during operation, and the plastic bulb has increased resistance to various mechanical damage.
From the point of view of operating comfort and energy efficiency, LED light sources are more profitable, but to obtain diffused lighting, it is necessary to use a large number of bulbs, which is due to the directional diode light flux.
What to look for when buying
Parameters that are taken into account when buying energy-saving light bulbs:
- Power. To determine the required power, it is enough to divide the required power by five. For example, if the required power is 100V, then the light bulb should be taken with a power of 20V. This definition of power is not suitable for all types.
- Light color and temperature. For the office, a cold shade with blueness and a temperature of up to 6.5 thousand K is suitable. In the children's room, a natural shade with a temperature of 4.2 thousand K is desirable.
- Lifetime. Each type and manufacturer has its own term. On average, from 3 to 15 thousand hours.
- Warranty obligations. Each manufacturer sets its own guarantees. Generally six months to three years.
- Product form. The choice of form is individual. It must match the size of the lighting fixture, the design of the room.
We recommend watching a video review:
Design features of LED lamps
According to the design scheme, such light bulbs are similar to fluorescent ones, as can be seen from the illustration below.
The key components are:
- Flask diffuser.It is used for mechanical protection of LEDs and uniform distribution of the luminous flux,
- LEDs. Semiconductor, light generating elements,
- Pay. Printed wiring diagram for switching diodes,
- Radiator housing. Provides sufficient heat dissipation during lamp operation,
- Driver. The electronic unit that generates the supply voltage of the diodes,
- Protective driver case,
- Plinth.

The driver and heatsink are necessary to ensure the normal operation of the device: the first in terms of voltage drop, and the second in terms of overheating. Both of these conditions adversely affect lamp life.
Low pressure sodium lamps (NLND)
These are the brightest light sources, with a light output of 200 Lm/W. The principle of operation of the device: sodium vapor, passing an electric current through itself, begins to shine in a yellow-orange color. The NLND inner flask is made of borosilicate glass resistant to aggressive environments.
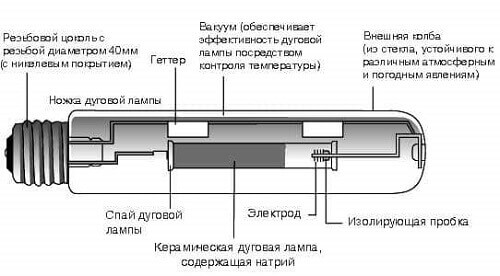
Positive traits:
- high light output;
- long service life up to 28,000 hours;
- comfort of color radiation;
- a wide range of operating temperatures, from - 60 to + 40 degrees Celsius;
Negative qualities:
- the presence of mercury;
- explosive, contact with air may ignite;
- inertia when turned on;
- complexity of connection and maintenance;
- low level of color rendering;
- increased pulsation of the light flux in the network 50 Hz;
- high ignition voltage and even higher at restart;
- increase in power consumption during operation.
Despite the fact that low-pressure sodium lamps can shine brighter than others, and in terms of efficiency they are in first place, they are used only in places of temporary stay of people, illuminating:
- open spaces, streets, highways,
- tunnels, sports facilities, squares,
- architectural structures, airports.
NLND is used in automobile fog lamps, to improve visibility on roads, in warehouses and in other places where there is no need for high color rendering.
Types of energy saving lamps

Conventional incandescent lamps are not famous for their efficiency and durability, so the emergence of alternative light sources was only a matter of time. Now there are three options for energy-saving lamps, one of them is not entirely fair to refer to this category. Their price, of course, is higher, but the long service life allows us to expect a quick payback for these products.
- Halogen, or halogen - gas-filled. These devices cannot be called energy-saving, since, in fact, they are the same "Ilyich's bulbs", but with a different "stuffing". Their flask is filled with boron or iodine vapor. Both chemical elements are halogens, hence the name of these lamps. They differ from conventional incandescent appliances in a long service life, however, in terms of durability and power consumption, they are much inferior to the following two competitors.
- Luminescent. These products are real energy-saving light sources. The principle of their operation is very different from the functioning of previous devices. In this case, ultraviolet radiation is formed, which acts on a substance that can convert it into light. Fluorescent lamps are in demand to a greater extent than diode "colleagues".
- LED lamps are now considered ideal devices. They are as durable as possible (even in comparison with fluorescent devices), devoid of the disadvantages inherent in lamps with a phosphor.The light source in them is an LED diode, an electronic circuit is responsible for its operation. A significant drawback of these products is their high price.
Since the most popular fluorescent lamps (CFLs) can rightfully be considered the “popular” choice, their characteristics will have to be considered in more detail. Getting to know the advantages and disadvantages will allow the potential buyer to make the final choice and not regret it.
Types of lamps
On sale there are many types with different characteristics. This article will help you make the right choice.
To choose the right light bulb, you need to know that they are divided into two main types: fluorescent and LED. Let's talk about each of them.
Fluorescent lamps emit light by passing an electrical current through mercury vapor. Due to this, ultraviolet begins to be emitted, which falls on the phosphor coating and turns into daylight. In the case of light-emitting diode light bulbs (LED lamps), the source of light is LEDs. They gained their popularity because of the light in various colors, they are long-lasting and not dangerous for the environment.
Energy-saving lamps are divided into the following types:
- in shape - in the form of a spiral, circle, square;
- by type of base - E14, E27, E40;
- by the type of flask - in the form of a pear, a candle, a ball;
- adjust the brightness if possible.
It should be noted that for fluorescent lamps, the most common shape is the two-tube (U-shape) bulb.
8 best lamps for 12 V with a power of 5-8 W
The review is based on a comparison of technical and economic indicators and customer reviews. Is not advertising.
OSRAM LED Star 850 4052899971684

OSRAM LED Star 850 4052899971684
| Power | 5 W |
| Plinth type | Gu5,3 |
| Flask shape | Reflector |
| Colorful temperature | 5000 K |
| Light flow | 370 lm |
| Color rendering index | 89 |
| Dimensions | 45×50 |
| Life time | 15000 h |
| Price | 180 rub |
pros
Good light quality. Suitable for spots and spot lighting.
Minuses
Low degree of dust and moisture protection for use in bathrooms: ip20.
LED ERA B0020546

LED ERA B0020546
| Power | 8 W |
| Plinth type | Gu5,3 |
| Flask shape | Soffit |
| Colorful temperature | 2700 K |
| Light flow | 640 lm |
| Color rendering index | 80 |
| Dimensions | 50×50 |
| Life time | 30000 h |
| Price | 60 rub |
pros
Low price. Bright. Suitable for spots and spot lighting.
Minus
Users note that the service life is lower than stated.
Philips Ultinon LED 11366ULWX2

Philips Ultinon LED 11366ULWX2
| Plinth type | H8/H11/H16 |
| Colorful temperature | 6200 K |
| Life time | 8 years |
| Price | 4155 rub (2 pcs) |
pros
Fog lights. increased brightness, resistance to power surges and vibrations.
Minuses
High price.
Incandescent lamp OSRAM W5W 12V 5W

Incandescent lamp OSRAM W5W
| Power | 5 W |
| Plinth type | W2.1×9.5d |
| Flask shape | Transparent capsule |
| Dimensions | 45×50 |
| Price | 76 rub (2 pcs) |
pros
Low price. Designed for position lights, direction indicators, license plate lights.
Minuses
Lamp type.
LED ASD LED-STD

LED ASD LED-STD
| Power | 5 W |
| Plinth type | G4 |
| Flask shape | Transparent capsule |
| Colorful temperature | 3000 K |
| Light flow | 450 lm |
| Dimensions | 16×62 |
| Life time | 30000 h |
| Price | 90 rub |
pros
Bright, suitable for spot lighting.
Minuses
Thin contacts - unreliable contact.
LED Gauss 107807105

LED Gauss 107807105
| Power | 5.5W |
| Plinth type | G4 |
| Flask shape | Transparent capsule |
| Colorful temperature | 3000 K |
| Light flow | 480 lm |
| Dimensions | 16×58 |
| Life time | 35000 h |
| Price | 250 rub |
pros
Bright, suitable for spot lighting.
Minuses
High price.
LED OSRAM Parathom PRO 50 24 930

OSRAM Parathom PRO 50 24 930
| Power | 8.5W |
| Plinth type | G53 |
| Flask shape | Matte tablet |
| Colorful temperature | 3000 K |
| Light flow | 450 lm |
| Dimensions | 55×111 |
| Life time | 45000 h |
| Price | 1200 rub |
pros
Compatible with dimmer. Suitable for spot lighting, emergency lighting.
Minuses
Not very bright, high price.
LED Uniel UL-00002381

Uniel UL-00002381
| Power | 10 W |
| Plinth type | E27 |
| Flask shape and color | Matte pear |
| Colorful temperature | 4000 K |
| Color rendering index | 80 |
| Light flow | 850 lm |
| Dimensions | 60×110 |
| Life time | 30000 h |
| Price | 190 rub |
pros
Small, bright, standard base. Suitable for general lighting and spot lighting.
Why LED lamps flash: causes and solutions
Some consumers, having installed LED lamps in the house, notice that their operation is accompanied by flickering. Such lighting tires the eyes and harms vision in general. Having understood the reasons for such a negative effect, you can find ways to eliminate it.
Why do LED lights blink when on?
There are several reasons why LED lamps blink when on. Why is this happening:
- incorrect installation - it is necessary to check all the contacts of the circuit, they must be strong;
- adapter power mismatch with the lamp used - you can replace the power supply with a new one that matches the power;
- significant power surges - the driver may not be able to cope with surges, the level of which is beyond the permissible;

LED lamps are able to work without problems with power surges
- defective product during production - it is necessary to replace the light bulb, since this product is accompanied by a guarantee;
- illuminated switch - it is not recommended to use such switches in conjunction with an LED light source, since when such a device is turned off, the circuit is in a closed state and contributes to the glare of the lamp;
- wire connection mismatch - the “zero” phase should be output to the lighting device, and the wire with the phase to the switch;
- the presence of household electrical appliances that create high-frequency interference;
- the life of the LED lamp has expired.
But many people also face another problem when LED lamps glow after being turned off. You can find out why this happens by familiarizing yourself with the functional features of led lamps.
Why do LED lamps blink or glow when the light is off?
The reason why the LED lamp is on with the switch off or flickering intermittently, an LED light switch can be used. If you replace the illuminated appliance with a conventional switch, the lamp should stop flashing.

Spectrum of different light sources
The fact is that in the off state, the electrical installation device does not completely open the circuit: the main supply of electricity stops, and the backlight LED closes the circuit. The current passing through the diode charges the driver capacitor of the LED lamp, as a result of which it either blinks or emits a dim light.
Another reason why the LED lamp is on when the light is off is a poor-quality product. If you purchased an LED lamp at a low price and the manufacturer is unknown, it is likely that low-power components are installed in such a device. Light sources offered by leading manufacturers usually use capacitive capacitors. Of course, their cost is high, but they do not blink even when paired with a switch with LED backlight.
Why do LED bulbs burn out
The main reasons for the failure of LED light sources are poor product quality or external influences. The latter include:
a significant excess of the supply voltage - if there are power surges in the mains, you should give preference to models designed for 240V or more. You can also resort to the use of protective blocks and rectifiers;

To avoid problems, it is best to choose products from trusted manufacturers.
- poor-quality lampholders - poor-quality material of the cartridges tends to break down when overheated, the contacts are oxidized, thereby creating even more heating of the LED lamp base;
- the use of powerful lamps in closed-type plafonds that are not intended for the use of powerful light sources;
- use of the mode of frequent on-off of LED lamps - the working life of the lamps is noticeably reduced;
- incorrect connection diagram - if one lamp fails, the malfunction is transmitted to other light sources in the common circuit;
- poor-quality connection of wires at the nodal points of the electrical network - when connecting, it is recommended to use terminals, soldering or other modern connection options.

Every year the price of LED lamps is getting lower.
Lists of the best
Above, we have presented you with a rating of the TOP 7 energy-saving lamps according to their characteristics and price. Now I would like to highlight the best in these categories:
- Halogen.
- Luminescent.
- LEDs.
Let's talk about another type of light bulbs - halogen lamps. They were created to replace incandescent lamps, and are distinguished by a high luminous flux. Their light is much brighter, and the service life is several times longer than that of conventional light bulbs. They have a standard base and are suitable for conventional cartridges. Halogen incandescent lamps consist of a bulb filled with gas (bromine or iodine) and a base. Flasks may vary in size. Usually they are used in car headlights or in lighting devices that require high brightness.
Halogen – Uniel led-a60 12w/ww/e27/fr plp01wh
Shaped like a pear. Small in size. Despite the frosted glass, it shines very brightly. Does not emit hazardous substances when lit. It has a standard base and is a good replacement for a conventional incandescent lamp. Its significant advantage is that it heats up much less, so it can be used in all ceiling lamps and lamps. The most important parameter of the lamp is its service life. It reaches up to 30 thousand hours. By all criteria, this is an ideal light source for those. who still misses the standard incandescent lamps, but still decided to save electricity.
Cost: 113 rubles.
lamp Uniel led-a60 12w/ww/e27/fr plp01wh
Fluorescent – OSRAM HO 54 W/840
Suitable for lighting offices, public buildings, shops and underground passages.It has a tubular shape, provides a uniform distribution of light. The lighting of such lamps can be of several shades: warm daylight and cold daylight. The service time is up to 24000 hours. Received their recognition due to high luminous efficiency, efficiency and long service life. They have a factory warranty.
Price: 268 rubles.
lamp OSRAM HO 54 W/840
LEDs – ASD, LED-CANDLE-STD 10W 230V E27
The shape of the flask is a candle. The base fits any standard cartridge. Fills the room with bright light, does not tire the eyes. Suitable for residential lighting. Electricity consumption is three times less than when illuminating with a conventional lamp. Service time is: 30 thousand hours. Good value for money.
Price: 81 rubles.
lamp ASD, LED-CANDLE-STD 10 W 230V Е27
No. 5. Lamp power and luminous flux
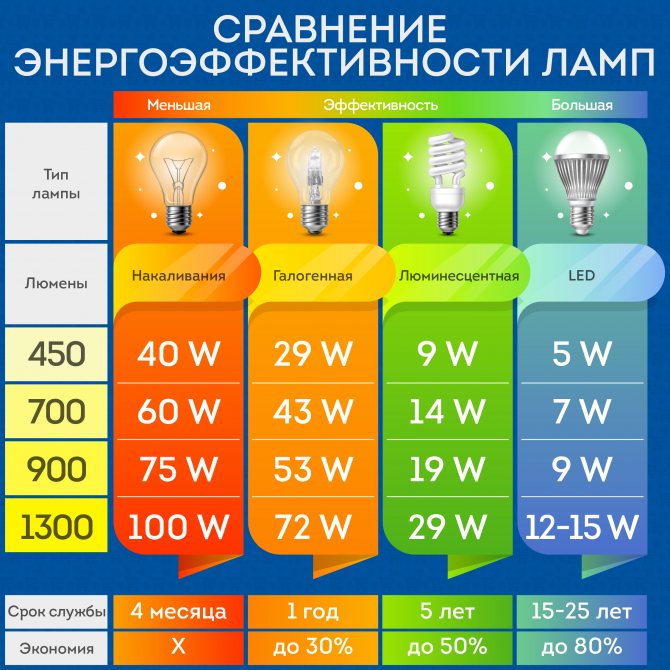
Conventional incandescent light bulbs have been around for so long that we tend to look primarily at wattage as a key metric when choosing. We all understand how a 40W or 60W lamp will shine. The power of energy-saving lamps is several times lower (4-25 W), so for many, buying a suitable lamp raises many questions. Manufacturers simplify this task for us and indicate on the packages the equivalent power, i.e. tell us how an economical light bulb will shine by comparing it with the luminous flux of an incandescent lamp of a certain power (for example, “8 W corresponds to 40 W” may be written on a fluorescent lamp).
The care of the manufacturer is pleasant, but educated people should understand that the power and light output of the lamp are not the same thing, and the familiar watts are a unit of power. Luminous flux is measured in lumens.To make it easier to understand: a 40 W incandescent lamp gives a luminous flux of 470-500 lm, 60 W - 700-850 lm, 75 W - 900-1200 lm. Now, when studying the packaging of an economical lamp, you can already roughly imagine how it will shine.
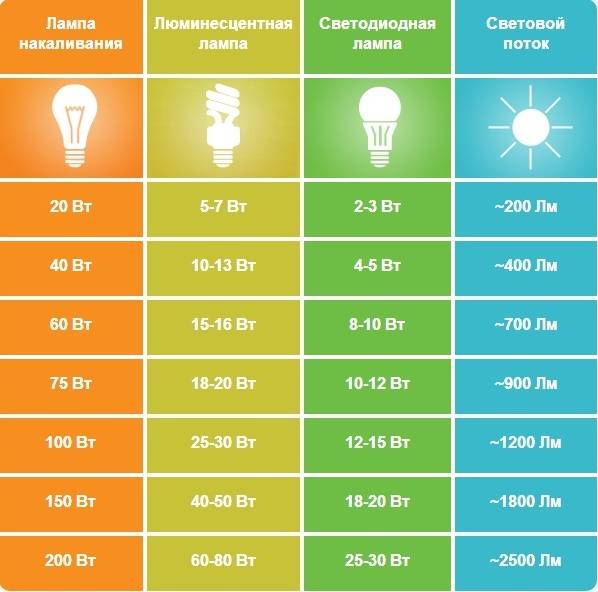
When choosing a lamp with the required level of brightness, you can also start from the equivalent power. For fluorescent lamps, you can use a factor of 5: if it is indicated that the lamp has a power of 12 W, then this means that it will shine like a 60 W incandescent lamp. For LED, this coefficient is about 7-8: a 10-12 W lamp will shine like a 75 W incandescent lamp.

The dependence of the luminous flux on the power allows you to judge the efficiency of the lamp and its light output, which is measured in lm / W. Incandescent lamps for every 1 W of electricity consumed give only 10-16 lm of light ceiling, i.e. have a light output of 10-16 lm / W. Halogen lamps have a light output of 15-22 lm / W, fluorescent - 40-80 lm / W, LED - 60-90 lm / W.
Benefits of energy saving lamps
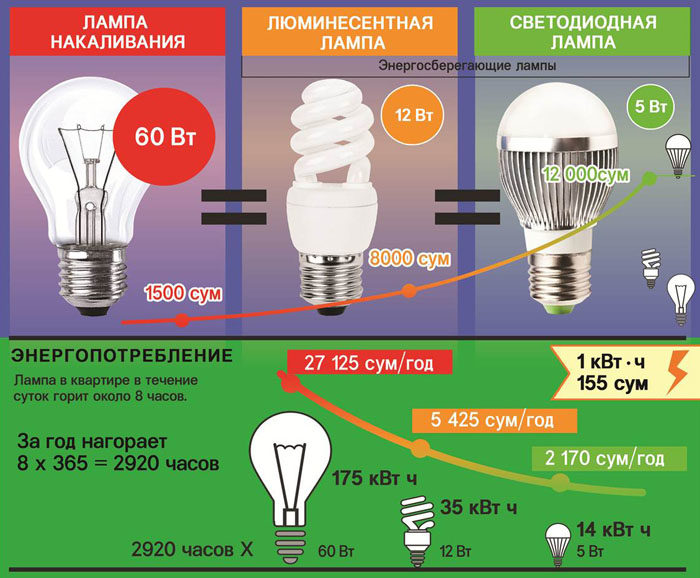
Low electrical energy consumption with equal light output. An ordinary incandescent light bulb, consuming 100 watts of energy, gives off only 18 watts in the form of light radiation, the rest of the energy is spent on heating the coil. Thus, the efficiency of a conventional lamp is only 18%.







An energy-saving lamp from the same consumed 100 W produces about 80 W of light radiation. It turns out that the efficiency of these lamps can be as much as 80%.

With proper operation, the lifespan significantly exceeds the lifespan of conventional light bulbs.

Fluorescent and LED lamps are safe to use, since the design features of these lamps exclude the possibility of a short circuit.

Energy saving devices. Comparison
Incandescent lamps consume a lot of energy. To avoid this, in 2020, consumers massively began to switch to energy-saving devices, the brightness of which cannot even be compared with incandescent filaments.
The amount of electricity consumed by energy-saving light bulbs compared to standard appliances will help determine the comparison table for incandescent lamps and energy-saving analogues of the luminescent type:
| Power of incandescent lamps (W) | Power of fluorescent lamps (W) | Luminous flux (Lumen) |
| 200 | 70 | 2650 |
| 150 | 45 | 1850 |
| 100 | 45 | 1850 |
| 75 | 19 | 955 |
| 60 | 15 | 720 |
| 40 | 11 | 430 |
| 25 | 6 | 255 |
The power equivalent of a 5w LED bulb to an incandescent bulb is 40W. Illumination is 450 lm. A similar 7W bulb corresponds to a 60W incandescent bulb.