- Blue fuel extraction process
- Mining using coal mines
- Hydraulic fracturing method
- Features of underwater production
- Origin of natural gas:
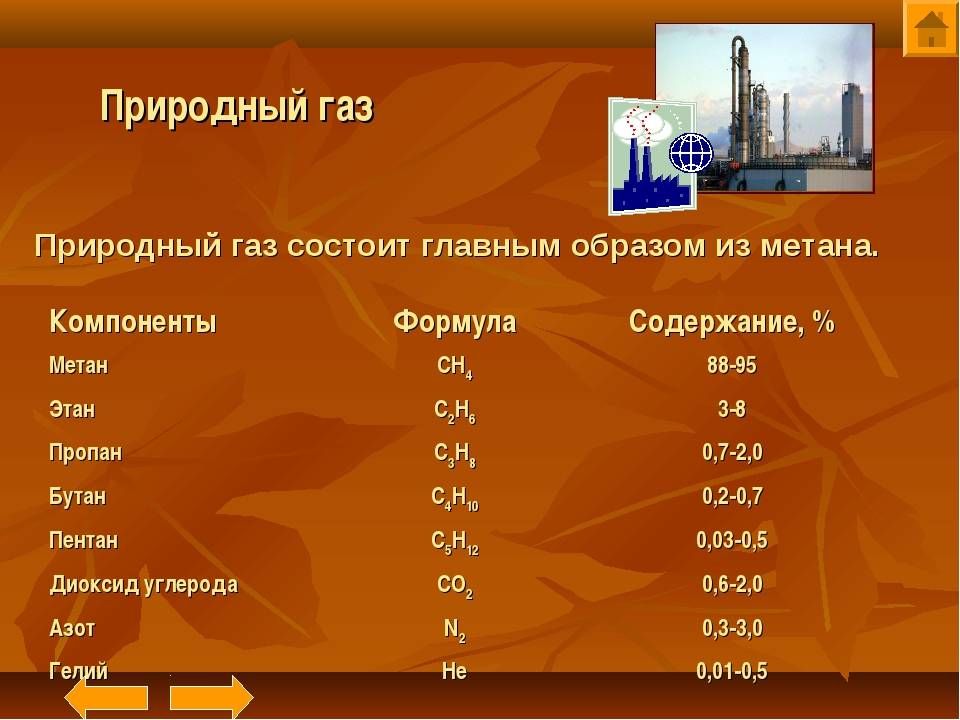
- Methane
- Transportation
- Gas preparation for transportation
- gas pipeline
- LNG transportation
- Where does the gas in the bowels of the earth come from?
- Major origin theories
- Interesting facts and hypotheses
- Classification and properties
- Natural gas processing methods
- physical processing
- Use of chemical reactions
Blue fuel extraction process
Prior to gas production is the process of geological exploration. They allow you to accurately determine the volume and nature of the occurrence of the deposit. Currently, several methods of reconnaissance are used.
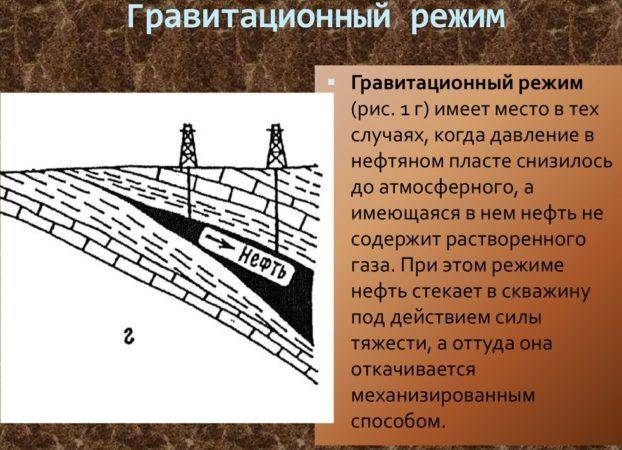
Gravity - based on the calculation of the mass of rocks. Gas-containing layers are characterized by a significantly lower density.
Magnetic - takes into account the magnetic permeability of the rock. By means of aeromagnetic survey it is possible to obtain a complete picture of deposits up to 7 km deep.
 The purpose of this technique
The purpose of this technique
Seismic - uses radiation that is reflected when passing through the bowels. This echo is able to catch special measuring instruments.
Geochemical - the composition of groundwater is studied with the determination of the content in them of substances associated with gas fields.
Drilling is the most effective method, but at the same time the most expensive of those listed. Therefore, prior to its use, a preliminary study of the rocks is required.
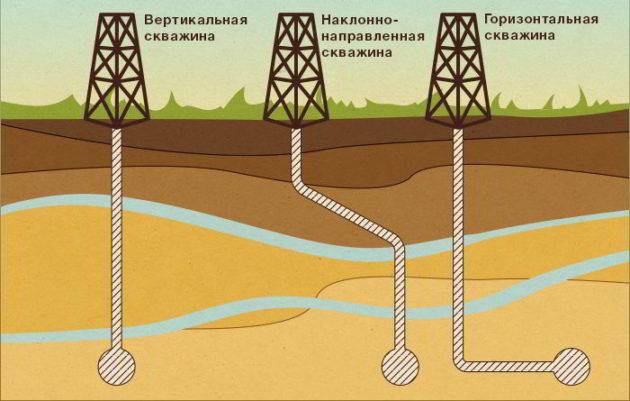 Well drilling methods for natural gas production
Well drilling methods for natural gas production
After the field is identified and the preliminary volumes of deposits are estimated, the process of gas production proceeds directly. Wells are drilled to the depth of the mineral layer. To evenly distribute the pressure of the rising blue fuel, the well is made with a ladder or telescopically (like a telescope).
The well is reinforced with casing pipes and cemented. To evenly reduce pressure and speed up the process of gas production, several wells are drilled at once in one field. The rise of gas through the well is carried out in a natural way - the gas moves to a zone of lower pressure.
Since the gas contains various impurities after extraction, the next step is its purification. To ensure this process, appropriate industrial facilities for gas purification and processing are being built near the fields.
Natural gas purification system
Mining using coal mines
Coal seams contain a large amount of methane, the extraction of which not only makes it possible to obtain blue fuel, but also ensures the safe operation of coal mining enterprises. This method is widely used in the USA.
The main directions of use and processing of methane
Hydraulic fracturing method
When gas is produced by this method, a stream of water or air is injected through the well. Thus, the gas is displaced.
This method can cause seismic instability of broken rocks, so it is prohibited in some states.
Features of underwater production
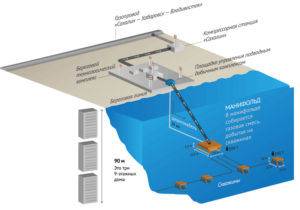 For the first time in Russia, gas production at the Kirinskoye field is carried out using an underwater production complex
For the first time in Russia, gas production at the Kirinskoye field is carried out using an underwater production complex
Gas reserves are present, except for land, and under water. Our country has extensive underwater deposits. Underwater production is carried out using heavy gravity platforms. They are located on a base resting on the seabed. Well drilling is carried out with columns located on the base. Tanks are placed on the platforms to store the extracted gas. It is then transported to land via a pipeline.
These platforms provide for the constant presence of people performing maintenance of the complex. The number can be up to 100 people. These facilities are equipped with autonomous power supply, a platform for helicopters, and staff quarters.
When deposits are located near the shore, wells are performed obliquely. They begin on land, leaving the base under the sea shelf. Gas production and transportation is carried out in a standard manner.
Origin of natural gas:
There are two theories of the origin of natural gas: the biogenic (organic) theory and the abiogenic (inorganic, mineral) theory.
For the first time, the biogenic theory of the origin of natural gas was expressed in 1759 by M.V. Lomonosov. In the distant geological past of the Earth, dead living organisms (plants and animals) sank to the bottom of water bodies, forming silty sediments. As a result of various chemical processes, they decomposed in an airless space.Due to the movement of the earth's crust, these remnants sank deeper and deeper, where, under the influence of high temperature and high pressure, they turned into hydrocarbons: natural gas and oil. Low molecular weight hydrocarbons (i.e. natural gas proper) were formed at higher temperatures and pressures. High-molecular hydrocarbons - oil - at smaller. Hydrocarbons, penetrating into the voids of the earth's crust, formed deposits of oil and gas fields. Over time, these organic deposits and hydrocarbon deposits went deep down to a depth of one kilometer to several kilometers - they were covered with layers of sedimentary rocks or under the influence of geological movements of the earth's crust.
The mineral theory of the origin of natural gas and oil was formulated in 1877 by D.I. Mendeleev. He proceeded from the fact that hydrocarbons can be formed in the bowels of the earth at high temperatures and pressures as a result of the interaction of superheated steam and molten heavy metal carbides (primarily iron). As a result of chemical reactions, oxides of iron and other metals are formed, as well as various hydrocarbons in a gaseous state. In this case, water enters deep into the bowels of the Earth through cracks-faults in the earth's crust. The resulting hydrocarbons, being in a gaseous state, in turn rise up through the same cracks and faults to the zone of least pressure, eventually forming gas and oil deposits. This process, according to D.I. Mendeleev and supporters of the hypothesis, happens all the time. Therefore, the reduction of hydrocarbon reserves in the form of oil and gas does not threaten mankind.
Methane
In addition, methane is also found in coal mines, where, due to its explosive nature, it poses a serious threat to miners. Methane is also known in the form of excretions in swamps - swamp gas.
Depending on the content of methane and other (heavy) hydrocarbon gases of the methane series, gases are divided into dry (poor) and fatty (rich).
- Dry gases include gases mainly of methane composition (up to 95 - 96%), in which the content of other homologues (ethane, propane, butane and pentane) is insignificant (fractions of a percent). They are more characteristic of purely gas deposits, where there are no sources of enrichment in their heavy components that are part of the oil.
- Wet gases are gases with a high content of "heavy" gas compounds. In addition to methane, they contain tens of percent of ethane, propane and higher molecular weight compounds up to hexane. Fatty mixtures are more characteristic of associated gases accompanying oil deposits.
Combustible gases are common and natural companions of oil in almost all of its known deposits, i.e. oil and gas are inseparable due to their related chemical composition (hydrocarbon), common origin, conditions of migration and accumulation in natural traps of various types.
An exception is the so-called "dead" oils. These are oils close to the day surface, completely degassed due to evaporation (volatilization) of not only gases, but also light fractions of the oil itself.
Such oil is known in Russia at Ukhta. It is a heavy, viscous, oxidized, almost non-fluid oil that is produced by unconventional mining methods.
Purely gas deposits are widespread in the world, where there is no oil, and gas is underlain by formation waters.In Russia, super-giant gas fields have been discovered in Western Siberia: Urengoyskoye with reserves of 5 trillion cubic meters. m3, Yamburgskoye - 4.4 trillion. m3, Zapolyarnoye - 2.5 trillion. m3, Medvezhye - 1.5 trillion. m3.
However, oil and gas and oil fields are the most widespread. Together with oil, gas occurs either in gas caps, i.e. over oil, or in a state dissolved in oil. Then it is called dissolved gas. At its core, oil with gas dissolved in it is similar to carbonated drinks. At high reservoir pressures, significant volumes of gas are dissolved in the oil, and when the pressure drops to atmospheric pressure during the production process, the oil is degassed, i.e. gas is rapidly released from the gas-oil mixture. Such gas is called associated gas.
The natural companions of hydrocarbons are carbon dioxide, hydrogen sulfide, nitrogen and inert gases (helium, argon, krypton, xenon) present in it as impurities.
Transportation
Gas preparation for transportation
Despite the fact that in some fields the gas has an exceptionally high quality composition, in general, natural gas is not a finished product. In addition to target component levels (where target components may vary depending on the end user), the gas contains impurities that make it difficult to transport and are undesirable in use.
For example, water vapor can condense and accumulate in various places in the pipeline, most often bends, thus hindering the movement of gas. Hydrogen sulfide is a highly corrosive agent that adversely affects pipelines, associated equipment and storage tanks.
In this regard, before being sent to the main oil pipeline or to the petrochemical plant, the gas undergoes the procedure of preparation at the gas processing plant (GPP).
The first stage of preparation is cleaning from unwanted impurities and drying. After that, the gas is compressed - compressed to the pressure required for processing. Traditionally, natural gas is compressed to a pressure of 200-250 bar, which results in a 200-250 times reduction in the occupied volume.
Next comes the topping stage: at special installations, the gas is separated into unstable natural gasoline and stripped gas. It is the stripped gas that is sent to main gas pipelines and petrochemical production.
Unstable natural gasoline is fed to gas fractionation plants, where light hydrocarbons are extracted from it: ethane, propane, butane, pentane. These substances are also valuable raw materials, in particular for the production of polymers. And a mixture of butane and propane is a ready-made product used, in particular, as a household fuel.
gas pipeline
The main type of natural gas transportation is its pumping through the pipeline.
The standard diameter of the pipe of the main gas pipeline is 1.42 m. The gas in the pipeline is pumped under a pressure of 75 atm. As it moves along the pipe, the gas, due to overcoming frictional forces, gradually loses energy, which is dissipated in the form of heat. In this regard, at certain intervals, special pumping compressor stations are being built on the gas pipeline. On them, the gas is compressed to the required pressure and cooled.
For delivery directly to the consumer, pipes of smaller diameter are diverted from the main gas pipeline - gas distribution networks.

gas pipeline
LNG transportation
What to do with hard-to-reach areas located far from the main main gas pipelines? In such areas, gas is transported in a liquefied state (liquefied natural gas, LNG) in special cryogenic tanks by sea and by land.
By sea, liquefied gas is transported on gas carriers (LNG tankers), ships equipped with isothermal tanks.
LNG is also transported by land transport, both rail and road. For this, special double-walled tanks are used that can maintain the required temperature for a certain time.
Where does the gas in the bowels of the earth come from?
Although people learned to use gas more than 200 years ago, there is still no consensus on where the gas in the bowels of the earth comes from.
Major origin theories
There are two main theories of its origin:
- mineral, explaining the formation of gas by the processes of degassing hydrocarbons from deeper and denser layers of the earth and raising them to zones with lower pressure;
- organic (biogenic), according to which gas is a decomposition product of the remains of living organisms under conditions of high pressure, temperature and lack of air.
In the field, gas can be in the form of a separate accumulation, a gas cap, a solution in oil or water, or gas hydrates. In the latter case, deposits are located in porous rocks between gas-tight clay layers. Most often, such rocks are compacted sandstone, carbonates, limestones.
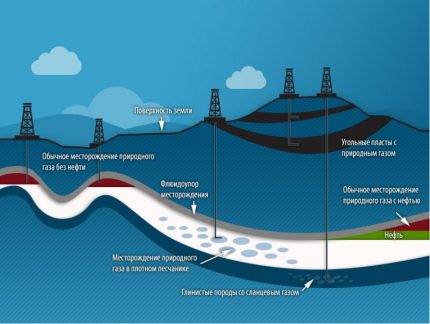 The share of conventional gas fields is only 0.8%.A slightly larger percentage is accounted for by deep, coal and shale gas - from 1.4 to 1.9%. The most common types of deposits are water-dissolved gases and hydrates - approximately in equal proportions (46.9% each)
The share of conventional gas fields is only 0.8%.A slightly larger percentage is accounted for by deep, coal and shale gas - from 1.4 to 1.9%. The most common types of deposits are water-dissolved gases and hydrates - approximately in equal proportions (46.9% each)
Since gas is lighter than oil and water is heavier, the position of fossils in the reservoir is always the same: gas is on top of oil, and water is propping up the entire oil and gas field from below.
The gas in the reservoir is under pressure. The deeper the deposit, the higher it is. On average, for every 10 meters, the pressure increase is 0.1 MPa. There are layers with abnormally high pressure. For example, in the Achimov deposits of the Urengoyskoye field, it reaches 600 atmospheres and higher at a depth of 3800 to 4500 m.
Interesting facts and hypotheses
Not so long ago, it was believed that the world's oil and gas reserves should be exhausted already at the beginning of the 21st century. For example, the authoritative American geophysicist Hubbert wrote about this in 1965.
To date, many countries continue to increase the pace of gas production. There are no real signs that hydrocarbon reserves are running out
According to the doctor of geological and mineralogical sciences V.V. Polevanov, such misconceptions are caused by the fact that the theory of the organic origin of oil and gas is still generally accepted and owns the minds of most scientists. Although D.I. Mendeleev substantiated the theory of the inorganic deep origin of oil, and then it was proved by Kudryavtsev and V.R. Larin.
But many facts speak against the organic origin of hydrocarbons.
Here is some of them:
- deposits were discovered at depths of up to 11 km, in crystalline foundations, where the existence of organic matter cannot even theoretically exist;
- using organic theory, only 10% of hydrocarbon reserves can be explained, the remaining 90% are inexplicable;
- The Cassini space probe discovered in 2000 on Saturn's moon Titan giant hydrocarbon resources in the form of lakes several orders of magnitude larger than those on Earth.
The hypothesis of an originally hydride Earth put forward by Larin explains the origin of hydrocarbons by the reaction of hydrogen with carbon in the depths of the earth and the subsequent degassing of methane.
According to her, there are no ancient deposits of the Jurassic period. All oil and gas could have formed between 1,000 and 15,000 years ago. As the reserves are withdrawn, they can gradually replenish, which is seen in long-depleted and abandoned oil fields.
Classification and properties
Natural gas is divided into 3 main categories. They are described by the following characteristics:
- Excludes the presence of hydrocarbons in which more than 2 carbon compounds. They are called dry and are obtained only in those places that are intended for extraction.
- Along with primary raw materials, liquefied and dry gas and gaseous gasoline mixed with each other are produced.
- It contains a large amount of heavy hydrocarbons and dry gas. There is also a small percentage of impurities. It is extracted from gas condensate type deposits.
Natural gas is considered a mixed composition, in which there are several subspecies of the substance. It is for this reason that there is no exact formula for the component. The main one is methane, which contains more than 90%. It is the most resistant to temperature. Lighter than air and slightly soluble in water. When burned in open air, a blue flame is produced. The most powerful explosion occurs if you combine methane with air in a ratio of 1:10.If a person inhales a large concentration of this element, then his health may be harmed.
It is used as raw material and industrial fuel. It is also actively used to obtain nitromethane, formic acid, freons and hydrogen. With the breakdown of hydrocarbon bonds under the influence of current and temperatures, acetylene, which is used in industry, is obtained. Hydrocyanic acid is formed when ammonia is oxidized with methane.
The composition of natural gas has the following list of components:

- Ethane is a colorless gaseous substance. When burning, it illuminates weakly. It practically does not dissolve in water, but in alcohol it can at a ratio of 3:2. It has not been used as a fuel. The main purpose of use is the production of ethylene.
- Propane is a well-used type of fuel that does not dissolve in water. During combustion, a large amount of heat is released.
- Butane - with a specific smell, low toxicity. It has a negative effect on human health: it can affect the nervous system, causes arrhythmia and asphyxia.
- Nitrogen can be used to maintain the appropriate pressure in boreholes. To obtain this element, it is necessary to liquefy the air and separate it by distillation. It is used for the manufacture of ammonia.
- Carbon dioxide - the compound can go into a gaseous state from a solid state at atmospheric pressure. It is found in the air and in mineral springs, and is also released when creatures breathe. It is a food additive.
- Hydrogen sulfide is a rather toxic element. It can negatively affect the functioning of the human nervous system.It has a smell of rotten eggs, a sweetish aftertaste and is colorless. Very soluble in ethanol. Does not react with water. Necessary for the production of sulfites, sulfuric acid and sulfur.
- Helium is considered a unique substance. It can accumulate in the earth's crust. It is obtained by freezing the gases in which it is included. When in a gaseous state, it does not manifest itself outwardly, in a liquid state it can affect living tissues. It is not capable of exploding and igniting. But if there is a large concentration of it in the air, it can lead to suffocation. Used to fill airships and balloons, when working with metal surfaces.
- Argon is a gas with no external characteristics. It is used when cutting and welding metal parts, as well as in order to increase the shelf life of food products (due to this substance, water and air are displaced).
The physical properties of a natural resource are as follows: the spontaneous combustion temperature is 650 degrees Celsius, the density of natural gas is 0.68-0.85 (in a gaseous state) and 400 kg / m3 (liquid). When mixed with air, concentrations of 4.4-17% are considered explosive. The octane number of the fossil is 120-130. It is calculated based on the ratio of flammable components to those that are difficult to oxidize during compression. The calorific value is approximately equal to 12 thousand calories per 1 cubic meter. The thermal conductivity of gas and oil is the same.
When air is added, a natural source can quickly ignite. In domestic conditions, it rises to the ceiling. That's where the fire starts. This is due to the lightness of methane. But air is about 2 times heavier than this element.
Natural gas processing methods
Before supplying natural gas to the main gas pipeline, this raw material does not need to be further purified, this advantage over oil (which must be subjected to primary treatment before being fed into the oil pipeline), resulting in significant savings in transportation costs.
Before obtaining the final chemical and production composition, the gas mixture is subjected to secondary processing at chemical industry plants, which, depending on the technologies used, is divided into main and secondary gas processing methods.
physical processing
This method is based on physical and energy indicators. Mined fossil material is subjected to deep compression and is separated into fractions by exposure to high temperatures.
During the transition from low to high temperatures, raw materials are intensively cleaned of impurities. The use of powerful compressors allows processing at the gas production site. When pumping gas from an oil-bearing formation, oil pumps are used, which are relatively cheap.
Properties of natural gas
Use of chemical reactions
During chemical-catalytic processing, processes occur associated with the transition of methane into synthesized gas, followed by processing. Chemical methods involve the use of two methods:
- steam, carbon dioxide conversion;
- partial oxidation.
The latter method is the most energy-saving and convenient, since the rate of chemical reaction during partial oxidation is quite high, and there is no need to use additional catalysts.
The use of high and low temperatures as a tool for influencing fossil raw materials is called a thermochemical method of processing natural gas. Under the influence of temperature on this raw material, chemical compounds such as ethylene, propylene, etc. are formed. The complexity of this type of processing lies in the use of equipment capable of producing heat up to 11 thousand degrees while increasing pressure up to three atmospheres.
Modern technologies for processing natural gas use the additional synthesis of methane, which doubles the amount of hydrogen produced. Hydrogen is a natural raw material from which ammonia is isolated, which is a material for the production of nitric acid, ammonium components, aniline, etc.