- Design principles
- Ways to adjust contours
- insulation
- Collector-mixing unit
- Types of water floors and device features
- Advantages and disadvantages
- Wooden heated floor with liquid coolant
- Features of the installation
- Rules for the device cable version
- Installation of infrared film floor
- Floor water heating system
- Calculation of a warm water floor
- An example of a warm water floor
- Working with the base
- Laying the contour
- Manifold installation
- Cabinet connection
- Laying a layer of thermal insulation and waterproofing
- Checking the work and making concrete screed
- Mixture for pouring screed
- Materials for a warm water floor
- Underfloor heating pipes and laying schemes
- Screed
- Pipe selection and installation
- Why air must be removed
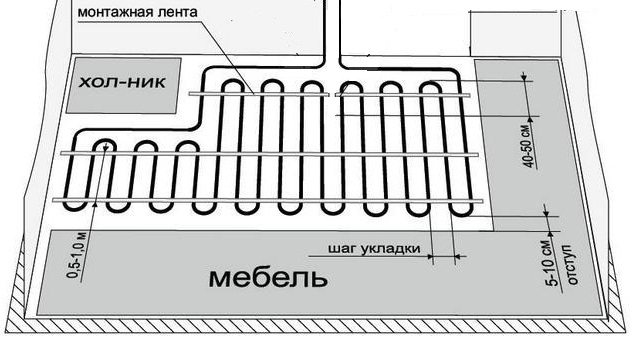
- Choosing the optimal step
- Video - Warm floor "Valtek". Mounting instruction
Design principles
When calculating a water heated floor, you must consider:
- only the active area of the system, under which the heated pipes are located, and not the entire quadrature of the room;
- step and method of laying a pipeline with water in concrete;
- screed thickness - a minimum of 45 mm above the pipes;
- requirements for the temperature difference in the supply and return - 5–10 0С are considered optimal values;
- water should move in the system at a speed of 0.15–1 m / s - a pump should be selected that meets these requirements;
- the length of the pipes in a separate TP circuit and the entire heating system.
Every 10 mm of screed is approximately 5–8% of heat loss for concrete heating. It is worth pouring it with a layer of more than 5-6 cm above the pipes only as a last resort, when increased strength of the rough base is required.
Ways to adjust contours
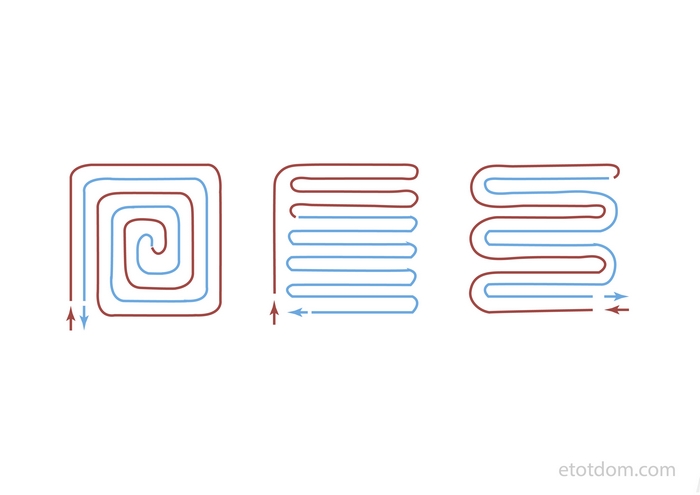
Pipes in the floor heating circuit are laid:
- snake (loops);
- spiral (snail);
- double helix;
- in a combined way.
The first option is the easiest to implement. However, when laying pipes with a “snake”, the water temperature at the beginning of the circuit and at the end will differ by 5–10 0С. And this is a fairly noticeable difference, which is felt with bare feet. Therefore, in most cases, it is recommended to choose a "spiral" or combine methods to ensure approximately equal temperature conditions throughout the floor.
Laying methods
insulation
As a heat-insulating material under the pipes, it is best to put extruded polystyrene foam (EPS). This is a moisture-resistant and durable insulation that is easy to install and easily tolerates contact with an alkaline cement mortar.
The thickness of the XPS boards is selected as follows:
- 30 mm - if the floor below is a heated room;
- 50 mm - for the first floors;
- 100 mm or more - if the floors are laid on the ground.

Floor insulation
Collector-mixing unit
One of the main elements of the water floor is a mixing unit with a manifold, shut-off valves, an air vent, a thermometer, a thermostat and a bypass. A circulation pump is placed directly in its composition or in front of it.
If the TP is adjusted manually in the plans, then the connection of the circuits to the collector can be done through simple valves. Otherwise, you will have to install thermostats and electric valves on each outlet.
The manifold and mixing unit allows precise control of the water temperature in each circuit and, thanks to the bypass, protects the boiler from overheating. It is installed in a special closet or a niche in a room with a warm floor. Moreover, if the setting of this unit is performed incorrectly, then a hot frying pan may turn out under your feet, but there will not be enough heat in the room. It is on him that the efficiency of the entire floor heating system depends.
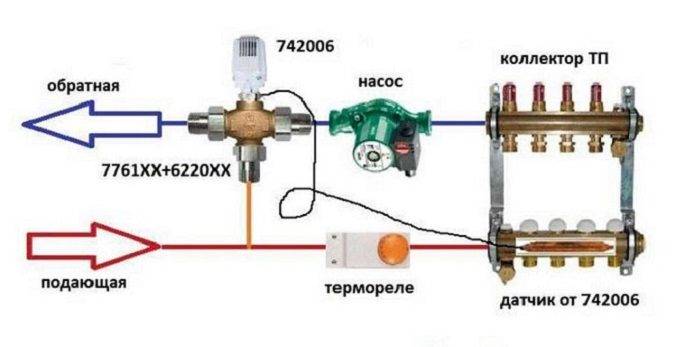
Collector assembly
Types of water floors and device features
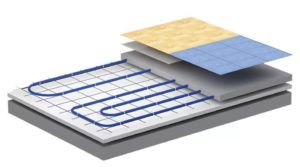
The main element of the system of such floor heating is the pipes through which the coolant-water circulates. They can be both metal and made of polymeric materials. The former are distinguished by a high price and the complexity of the connections, while the latter are much easier to lay, and they are cheaper. In addition to pipes, other elements of this system will be needed. This is a base in the form of a concrete slab or polystyrene, a waterproofing layer, a thermal insulation layer, a concrete screed. On top of this cake, the finishing coating is laid directly. In general, the thickness of the entire structure will be about 7-15 cm.
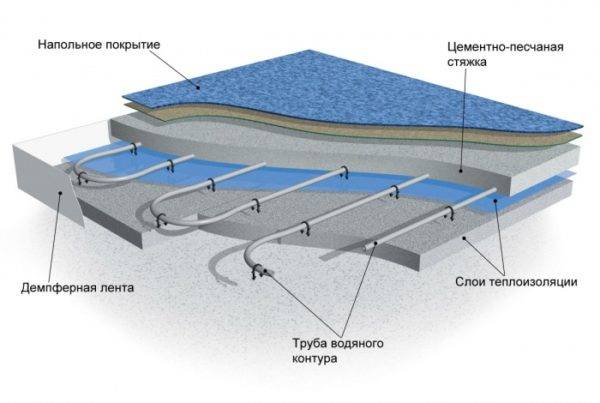
The structure of the water floor heating
Depending on how the arrangement of underfloor heating is carried out, there are several basic types of construction.
Table. Types of water floors.
Heavy
This is the most common option, characterized by high reliability.
Here it is important to carefully prepare the rough surface (rough floor or floors), then lay the heat and waterproofing layers, and then the reinforcing mesh layer, to which the heating circuit itself from the pipes will be attached with clamps. After that, it remains to fill everything with a screed, dry it, and the warm floor is ready for use.
Heavy water floors are also called concrete or wet floors. The latter is due to the fact that it is required to carry out work on pouring the screed. It is important to understand that the screed layer above the pipes themselves should not be less than 3 cm.
Lungs
In this case, a special polystyrene foam plate is used as the basis for the pipes. It is sold ready-made. During installation, it must be laid on the subfloor and laid along it in accordance with the scheme of the underfloor heating pipe. They will not need additional fixation, since there are special protrusions on the plate itself that allow you to securely fix the pipes. Then, special heat-distributing plates are placed on top, on top of which the finishing coating is mounted. it good option for furnishing water floor in the conditions of the impossibility of mounting it according to the standard scheme due to the heavy weight of the standard screed.

The installation of a warm floor in itself is considered a complex engineering task.
There is also another option for arranging a floor heating system - along wooden slats. That is, a tree will be used as the basis for such a floor, to which the pipes are attached, and from above they are covered with gypsum fiber and a finish coating. This option is used extremely rarely and it is not reliable.
Advantages and disadvantages
If we compare water heating with standard heaters and convectors, then the warm floor has a number of undeniable advantages: efficiency, safety, comfort and aesthetics of the interior.
- Since the average temperature of the heat carrier is low, and this is up to 50 ºС, energy consumption is reduced by 25%. In rooms equipped with high ceilings, this figure reaches more than 55% due to the fact that heating is carried out only to a height of 2.5 m. Economy is the main advantage of this system.
- The inaccessibility of the heating elements, there is no possibility of getting burned or injured on the coolant, even for children.
- Warming up is carried out gradually and evenly over the entire surface, creating comfortable and healthy conditions for staying in the room. A small child will not be cold playing on the floor.
- When planning and designing a room, there will be no interference in the form of convectors or other heating elements that have to be hidden behind decorative panels or changed depending on the style.

water floor
It should be noted that underfloor heating has its drawbacks.
- The main disadvantage is the complexity of installation. The surface of the base must be pre-prepared and leveled. The multi-layer design also does not add ease of installation.
- Possibility of leakage. The search for a leak can be difficult due to the length of the pipes, sometimes it can reach 70-80m. To fix this problem, you will need to remove the floor covering.
- This type of heating can effectively serve as the main source of heat only in rooms with good thermal insulation, reliable double-glazed windows and doors.If heat loss cannot be minimized, and also in places where it is impossible to lay a water floor (stairs, corridors), additional heat sources will have to be installed.
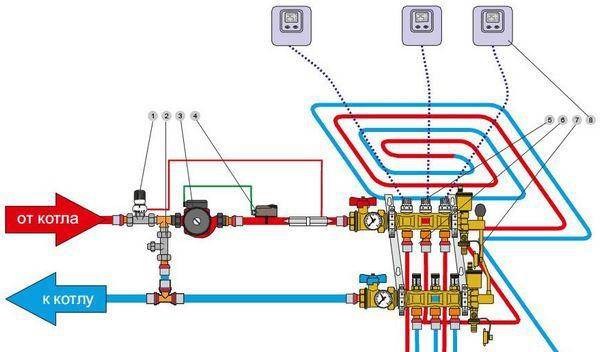
Scheme of connection to a water heated floor boilerScheme of connection to a water heated floor boiler
Wooden heated floor with liquid coolant
In the event that you have wooden floors, it is advisable to use a different design of the warm floor.
There are two main types of warm wood flooring: slatted and modular.
When laying a modular floor, prefabricated elements made of chipboard are used, in which grooves are already made in the factory for installing heat carrier pipes.
Installation of a slatted floor with underfloor heating is as follows:
- First, strips of chipboard with a width of 15 to 40 centimeters are laid on the floor. The slabs are fastened to the ceiling with self-tapping screws with a step of about 2 centimeters.
- A gap is left between the plates for thermal deformation and for laying coolant pipes. The same gap remains between the plates and the walls of the room.
- An aluminum profile is placed in the grooves between the chipboard plates, which is the basis for the heat carrier pipes.
- Underfloor heating pipes are located inside the aluminum profile.
There is also the option of laying water heating pipelines in the floor on logs.
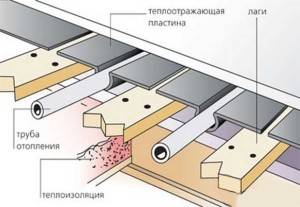
Laying a water-heated floor on a floor on logs
1. The first stage in the construction of such a floor is the laying of a layer of thermal insulation made of foamed polymer.
2. Then wooden logs are installed.
3.According to the planned scheme, a curly aluminum structure is laid, which will serve as a bed for the coolant and at the same time will reflect the heat flow.
4. Additional thermal insulation is laid between the lags and pipes.
5. A moisture-absorbing layer is placed on top of this structure. As it can be used foamed polyethylene or ordinary cardboard.
6. On top of the structure of wooden logs, aluminum profiles and heat carrier pipes, a draft floor is laid, for example, from chipboard or gypsum-fiber sheets. Be sure to leave a gap between the plates for thermal expansion. A similar gap must be left between the plates and walls.
7. A finishing coating is mounted on the subfloor - tiles.
In order to learn more about the step-by-step algorithm for installing a water-heated floor under a tile with your own hands, we suggest you watch the video instructions:
Features of the installation
Having learned how much it will cost to make a warm floor, many people think about how to do this work on their own. There is a rational grain in this desire, but in reality one will have to face rather difficult tasks of a technical nature that will require both knowledge and practical skills. Due to the technological differences between different types of underfloor heating, their installation is also different. We offer to understand the features of arranging a warm floor in each case.
Any of the above systems will consist of heating elements, temperature sensors and thermostats. Installation is more convenient to perform either immediately during the construction of the house, or during major repairs.
Rules for the device cable version
As mentioned above, different types of cables serve as a heating element in this system. They are laid either in a screed or in a layer of tile adhesive if a cable fastened with a special mesh is used. Installation is carried out in the following sequence:
- At the initial stage, a cable laying diagram is drawn up and the location of the sensor, thermostat, as well as the connection point for the underfloor heating is determined.
- Next, thermal insulation with a reflector is mounted on the base.
- Then, according to the scheme, cables are laid and a thermoregulation system is installed, which will protect the system from overheating.
- After that, the floor is filled with cement mortar. The main requirement at this stage is to avoid the formation of voids.
- After 30 days (at least) after the screed is completed, the system is checked for operability.
Cable underfloor heating is laid either in a screed or in a layer of tile adhesive
Installation of infrared film floor
Installation of this system is perhaps the best option for those who do not know how to make a wooden floor warm, although it is also a great solution for concrete floors. It is also captivating that you can lay on top of it those types of floor coverings that you like, without limiting your imagination. And the best part is that even a person who is not very experienced in repair matters will cope with the installation.
Main stages of work:
- Dismantling of existing flooring and preparation of the base. In case of serious surface defects, it is better to make a screed and wait for it to dry completely.
- Next, a film with heating elements is laid and a thermostat and sensor are connected.
- The next step is to check the performance of the system and troubleshoot if any.
- After checking, the thermal elements are covered with a protective film (dry installation) or filled with a solution (wet). When pouring, you must wait a month until it dries completely.
- The final stage is the installation of flooring, according to the technology.
This is just a brief description of the process, a specialist consultation will provide much more information, but if this is not possible, then it will be useful to watch the video below:
Floor water heating system
This option of underfloor heating, although captivating with its practicality and efficiency, is not very common in apartments, since the coolant (hot water) is taken from central water heating pipes, which can negatively affect the temperature of the radiators. In addition, this type of underfloor heating is quite laborious in terms of installation, requires professional skills and serious material costs. Another small minus, which can also play a role - when performing a screed, up to 10 cm of the height of the room is hidden.
Installation of a water heated floor is quite laborious, requires professional skills and serious material costs.
If you are still interested in how to carry out all the work, then we will list the main stages:
- They all start with the installation of a polypropylene riser, if the replacement has not been completed before.
- Next, a piping layout is drawn up.
- After that, another important point is the laying of a special reliable waterproofing, the strips of which are best overlapped, and the seams are connected extremely tightly.
- Next, a rough screed is made, the level of which should be approximately 5 cm below the expected level of the finished floor, and allowed to dry.
- The next stage is foil insulation, the joints of which must be glued with aluminum tape.
- And, finally, the installation of a polypropylene pipe according to the scheme, connecting it to the supply and return risers through a control valve.
- Checking the system for leaks. Then the water must be drained.
- Perform the final screed, which should be perfectly even. Let it dry and acquire the necessary strength.
Calculation of a warm water floor
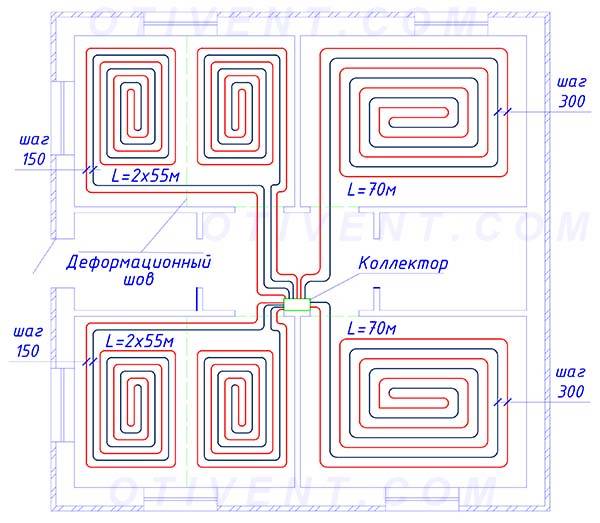
Before installation and purchase of materials, it is imperative to calculate the underfloor heating. To do this, they draw a diagram with contours, which will then come in handy during repair work in order to know the position of the pipes.
- If you are sure that furniture or plumbing will always stand in a certain place, pipes are not laid in this place.
- The length of the circuit with a diameter of 16 mm must not exceed 100 m (maximum for 20 mm is 120 m), otherwise the pressure in the system will be bad. Thus, each circuit approximately occupies no more than 15 square meters. m.
- The difference between the length of several circuits should be small (less than 15 m), that is, they should all be of uniform length. Large rooms, respectively, are divided into several circuits.
- The optimum pipe spacing is 15 cm when using good thermal insulation. If in winter there are often frosts below -20, then the step is reduced to 10 cm (only possible at the outer walls). And in the north you can not do without additional radiators.
- With a laying step of 15 cm, the consumption of pipes is approximately 6.7 m for each square of the room, when laying every 10 cm - 10 m.
In general, the question of how to calculate a warm water floor requires separate consideration, because many nuances are taken into account when designing: heat loss, power, etc.
The graph shows the dependence of the flux density on the average coolant temperature.Dotted lines indicate pipes with a diameter of 20 mm, and solid lines - 16 mm.
- To find the flux density, the sum of the heat loss of the room in watts is divided by the pipe laying area (the distance from the walls is subtracted).
- The average temperature is calculated as the average value at the inlet to the circuit and the outlet from the return.
To calculate the length of the circuit, the active heating area in square meters is divided by the laying step in meters. To this value is added the size of the bends and the distance to the collector.
According to the above diagram, you can only perform a rough calculation and make the final adjustment due to the mixing unit and thermostats. For accurate design, be sure to contact professional heating engineers.
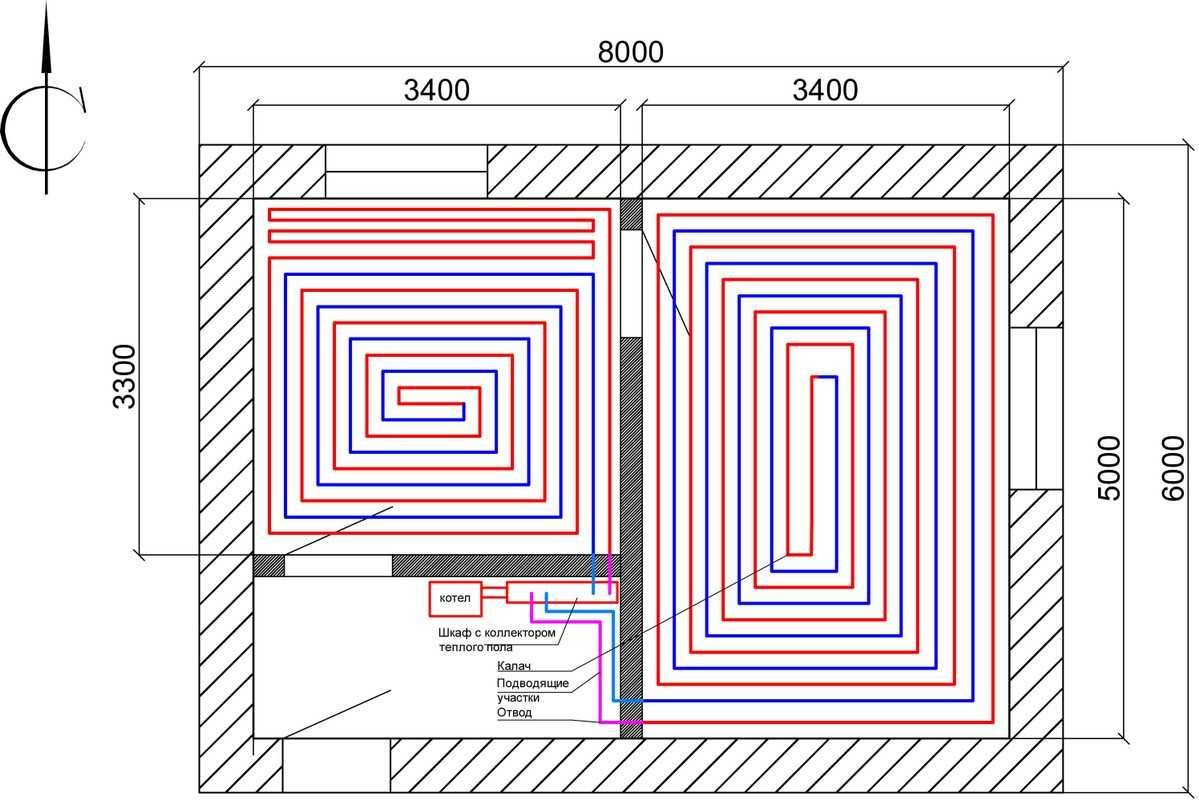
An example of a warm water floor
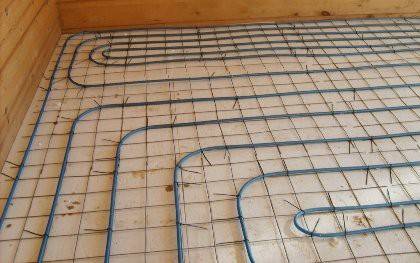
An example of a warm water floor
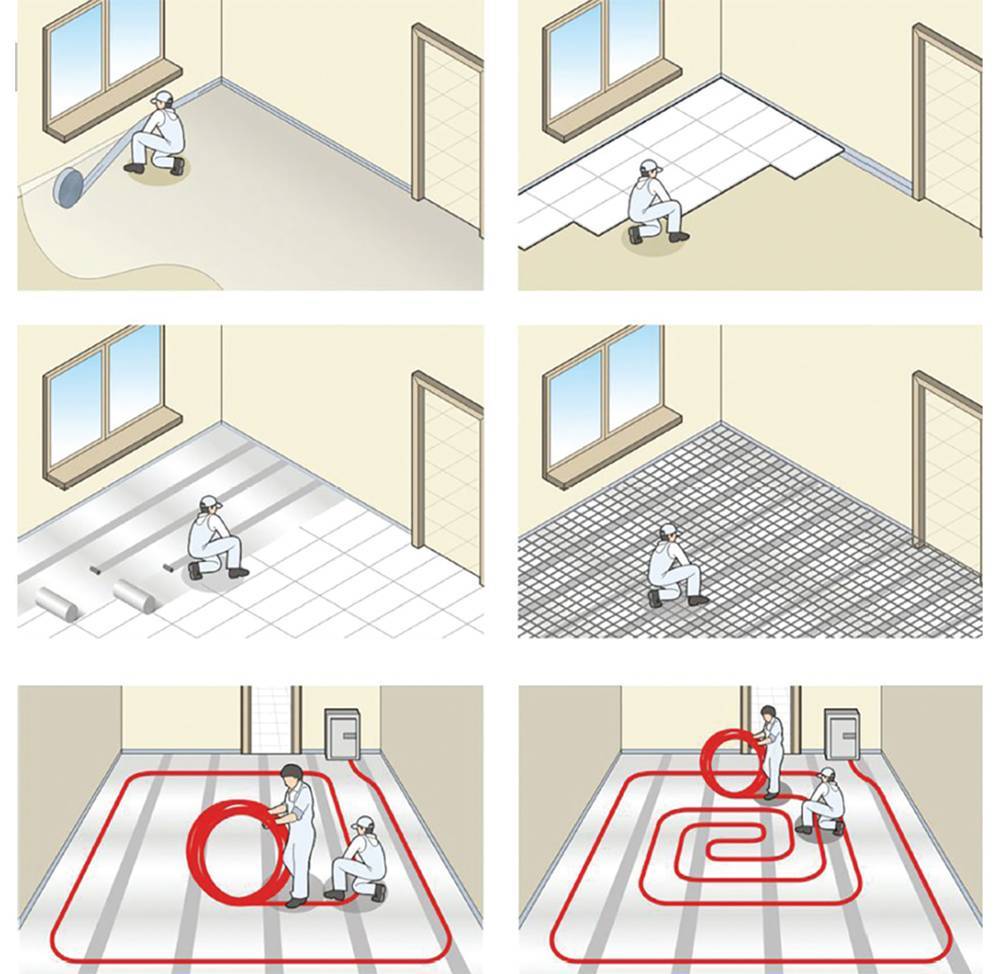
Before performing work, you need to know that the device of such a system will take a space of about 8 cm from the floor from the room. The phased arrangement of a warm floor consists of the following points:
Working with the base
Initially, all dirt, debris, grease and oil stains are removed from the surface of the subfloor, and then they begin to arrange the first layer. As a rule, a screed based on a mixture of sand and cement is used in the house. It is laid in strict accordance with horizontality - along the lighthouses. It is allowed to install self-leveling floors using modern self-leveling mixtures. In order for the heat to be distributed evenly, you need to make the surface perfectly flat.
Laying the contour

Laying the contour
According to the scheme you have drawn up, lay out the pipes. Initially, do not fasten them too tightly.
Manifold installation
Scheme-example of connecting a water-heated floor
The allocated space for the docking components that connect the heating pipes and the house's heat supply system should be hidden in a special cabinet. It is best to make a niche in order to save space. Approximate cabinet dimensions: 600x400x120 mm. These are standard commercially available manifold cabinets. Both joints and certain regulatory systems can be placed in them.
Cabinet connection
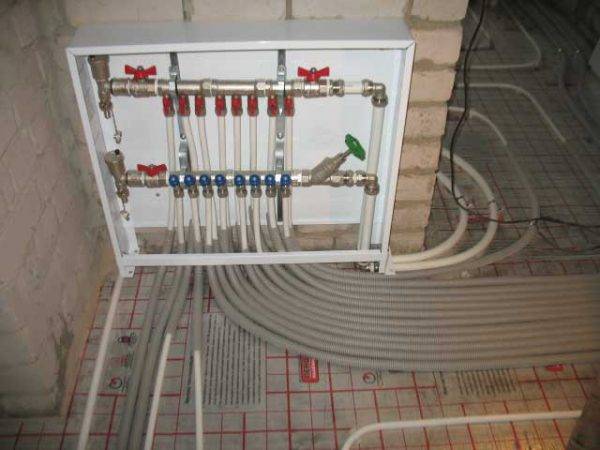

Collector group of a warm water floor
Make access to the return hose and the boiler feed pipe in the cabinet. Attach shut-off valves to them. Connect the manifold and put a plug on its end. A great option would be to install a splitter.
Laying a layer of thermal insulation and waterproofing
- It is necessary to lay sheets of aluminum foil or polyethylene on a concrete base:
- Fasten the damper tape along the perimeter 2 cm above the level of the screed.
- As a heat-insulating material, take slabs of mineral wool, polystyrene foam, polystyrene foam, cork, foam concrete, foam plastic. According to your desire, the selected component should be characterized by a sufficient value of temperature resistance, which will generally exceed all the indicators of the heating layers.
- Additional waterproofing is not required if you took polystyrene with foil as a heat-insulating material.
- The thickness of the layer is taken depending on the power of the autonomous heating system, the presence or absence of a heated room on the floor below, and the thermal resistance of the floor.
- It makes sense to purchase a heat insulator for warm water floors, since it has protrusions for pipes on one side.
Checking the work and making concrete screed
It is important to check the functionality of the system before performing the screed.Only after checking the correct operation of the entire system can the self-leveling floor or cement mortar be laid, making the surface perfectly flat along the installed beacons.
After the mixture has hardened, one more check of the operation of the system must be done and only then take up the flooring device.

Enjoy the warmth of the floor
Mixture for pouring screed
Filling the floor or screed is a procedure that requires great care and accuracy. It is possible to avoid cracking of the floor during drying and during the operation of the system by carefully observing the temperature regime and strictly following the instructions for preparing solutions.
For pouring, ready-made self-leveling mixtures are used. for underfloor heating or self-mixed on a concrete base.
In the first case, the mixtures are made on the basis of gypsum, they require dilution with water to the consistency of sour cream. The floor drying time in this case is from 3 to 5 days. During this period, it is recommended to minimize air humidity.
From the use of these solutions for floor screed in rooms that are constantly exposed to water (bathroom, cellar), it is better to refrain.
Homemade mixtures are made on the basis of cement. The recommended brand is M300 and above. The composition of the mixture is as follows:
- Cement - 1 part.
- Fine-grained sand - 4 parts.
- Water. Water is added until the mixture has the consistency of dough. When adding water, constant stirring is necessary.
- plasticizer. It facilitates the screeding, is applied in concentrations recommended by the manufacturer, ranging from 1 to 10% by volume.
The criterion for the correct consistency of the mixture is the ability to sculpt lumps from it that do not crumble and do not spread.If the plasticity of the composition is not sufficient, the ball cracks, which means that there is little liquid in the mixture. If the mixture is too liquid, it is necessary to add sand with cement.
Before pouring, the perimeter of the room is covered with a damper tape, which serves to soundproof and prevent cracking of the floor when heated.
Pipes and cables are fixed with rigid clamps.
The screed is produced at an air temperature of 5 ° to 30 ° (a number of professional mixtures allow laying at lower temperatures, they have a special marking).
The maximum area for a one-time pour is 30 sq. m. It is better to divide large spaces into sections. In places where the surface is divided into sections, protective corrugated hoses are put on the pipes.
The shelf life of the finished solution is 1 hour, after which it can not be used.
The filling of one section is carried out promptly and in one step.
Immediately after the procedure, the mixture should be pierced in several places with an awl or a thin knitting needle to ensure the release of air bubbles. For the same purposes and additional alignment, a spiked roller or a stiff brush is used. The needle should be longer than the thickness of the solution layer.
Drying home-made mixtures occurs within 20-30 days and has a number of features:
- Sudden temperature changes in the room, exposure to direct sunlight are unacceptable. This is fraught with uneven drying and subsequent deformation.
It is better to cover the floor surface with plastic wrap and periodically (every few days) moisten with liquid.
After drying, it is recommended to turn on the heating system for several hours in the mode of moderate heat supply.
The recommended air humidity is 60-85%.
Before laying tiles, linoleum, parquet or wooden flooring, the heating must be switched off.
When using materials prone to cracking and swelling, the air humidity must be reduced to 65%.
The tile keeps within on tile glue, a carpet, linoleum and a laminate directly on a coupler.
Self-installation of a warm water floor is possible only if there is enough time, accurate and precise compliance with all instructions and rules.
We offer you to watch a video that tells in detail about the installation of water heated floors:
Materials for a warm water floor
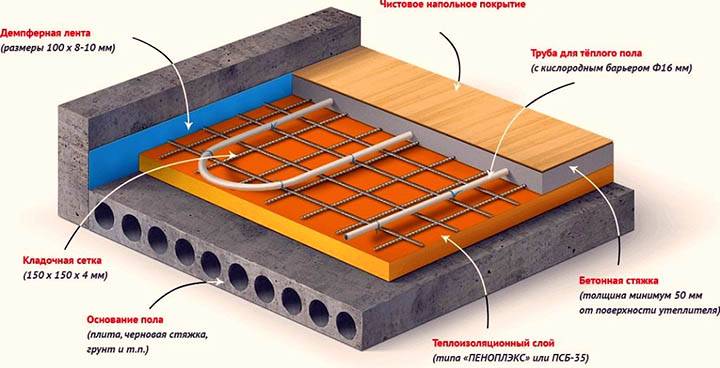
Most often they make a water-heated floor in a screed. Its structure and necessary materials will be discussed. The scheme of a warm water floor is presented in the photo below.
Scheme of a warm water floor with a screed
All work begins with leveling the base: without insulation, heating costs will be too high, and insulation can only be laid on a flat surface. Therefore, the first step is to prepare the base - make a rough screed. Next, we describe step by step the procedure for work and the materials used in the process:
- A damper tape is also rolled around the perimeter of the room. This is a strip of heat-insulating material, no more than 1 cm thick. It prevents heat loss for wall heating. Its second task is to compensate for the thermal expansion that occurs when materials are heated. The tape can be special, and you can also lay thin foam cut into strips (no more than 1 cm thick) or other insulation of the same thickness.
- A layer of heat-insulating materials is laid on the rough screed. For underfloor heating, the best choice is polystyrene foam. The best is extruded. Its density must be at least 35kg/m2.It is dense enough to support the weight of the screed and operating loads, has excellent performance and a long service life. Its disadvantage is that it is expensive. Other, cheaper materials (polystyrene, mineral wool, expanded clay) have a lot of disadvantages. If possible, use polystyrene foam. The thickness of the thermal insulation depends on many parameters - on the region, the characteristics of the foundation material and insulation, the method of organizing the subfloor. Therefore, it must be calculated for each case.
- Further, a reinforcing mesh is often laid in increments of 5 cm. Pipes are also tied to it - with wire or plastic clamps. If expanded polystyrene was used, reinforcement can be dispensed with - you can fasten it with special plastic brackets that are driven into the material. For other heaters, a reinforcing mesh is required.
- Beacons are installed on top, after which the screed is poured. Its thickness is less than 3 cm above the level of the pipes.
- Next, a clean floor covering is laid. Any suitable for use in an underfloor heating system.
These are all the main layers that need to be laid when you make a do-it-yourself water-heated floor.
Underfloor heating pipes and laying schemes
The main element of the system is pipes. Most often, polymeric ones are used - made of cross-linked polyethylene or metal-plastic. They bend well and have a long service life. Their only obvious drawback is not too high thermal conductivity. This minus is not present in the recently appeared corrugated stainless steel pipes. They bend better, cost no more, but due to their low popularity, they are not often used yet.
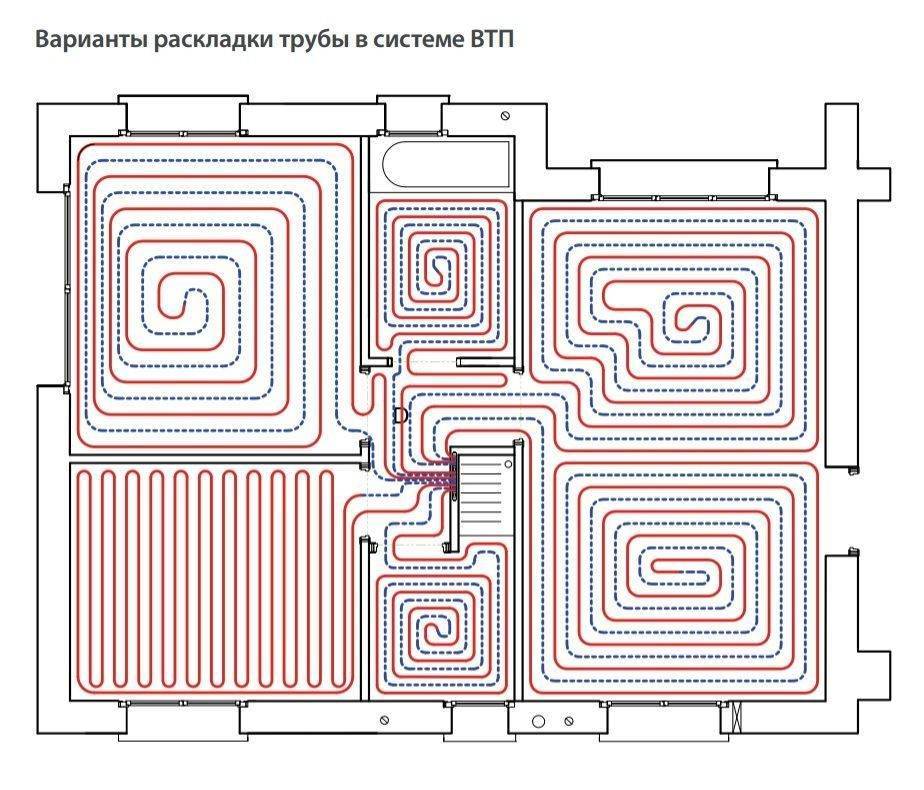
The diameter of pipes for underfloor heating depends on the material, but usually it is 16-20 mm. They fit in several schemes. The most common are spiral and snake, there are several modifications that take into account some features of the premises.
Schemes for laying pipes of a warm water floor
Laying with a snake is the simplest, but passing through the pipes the coolant gradually cools down and by the end of the circuit it is already much colder than it was at the beginning. Therefore, the zone where the coolant enters will be the warmest. This feature is used - laying starts from the coldest zone - along the outer walls or under the window.
This drawback is almost devoid of a double snake and a spiral, but they are more difficult to lay - you need to draw a diagram on paper so as not to get confused when laying.
Screed
Can be used for pouring hot water the floor is a conventional cement-sand mortar based on Portland cement. The brand of Portland cement should be high - M-400, and preferably M-500. Concrete grade - not lower than M-350.
Semi-dry screed for underfloor heating
But ordinary “wet” screeds gain their design strength for a very long time: at least 28 days. All this time it is impossible to turn on the warm floor: cracks will appear that can even break the pipes. Therefore, so-called semi-dry screeds are increasingly being used - with additives that increase the plasticity of the solution, significantly reducing the amount of water and the time for "aging". You can add them yourself or look for dry mixes with the appropriate properties. They cost more, but there is less trouble with them: according to the instructions, add the required amount of water and mix.
It is realistic to make a water heated floor with your own hands, but it will take a decent amount of time and a lot of money.
Pipe selection and installation
The following types of pipes are suitable for a water-heated floor:
- Copper;
- Polypropylene;
- Polyethylene PERT and PEX;
- metal-plastic;
- Corrugated stainless steel.
They have their strengths and weaknesses.
| Characteristic Material | Radius bending | Heat transfer | Elasticity | Electrical conductivity | Life time* | Price for 1 m.** | Comments |
| Polypropylene | Ø 8 | Low | high | Not | 20 years | 22 r | They only bend with heat. Frost-resistant. |
| Polyethylene PERT/PEX | Ø 5 | Low | high | Not | 20/25 years | 36/55 r | Can't withstand overheating. |
| metal-plastic | Ø 8 | Below the average | Not | Not | 25 years | 60 r | Bending only with special equipment. Not frost resistant. |
| Copper | Ø3 | high | Not | Yes, requires grounding | 50 years | 240 r | Good electrical conductivity can cause corrosion. Grounding required. |
| Corrugated stainless steel | Ø 2.5-3 | high | Not | Yes, requires grounding | 30 years | 92 r |
Note:
* characteristics of pipes are considered at operation in water heat-insulated floors.
** Prices are taken from Yandex.Market.
The choice is very difficult if you try to save on yourself. Of course, you can not take copper for consideration - it is very expensive. But corrugated stainless steel, at a higher price, has exceptionally good heat dissipation. The temperature difference in the return and supply, they have the largest. This means that they give off heat better than competitors. Given the small bending radius, ease of operation and high performance, this is the most worthy choice.
Pipe laying is possible with a spiral and a snake. Each option has pros and cons:
- Snake - simple installation, almost always there is a "zebra effect".
- Snail - uniform heating, material consumption increases by 20%, laying is more laborious and painstaking.
But these methods can be combined within the same circuit. For example, along the walls "looking" at the street, the pipe is laid with a snake, and on the rest of the area with a snail. You can also change the frequency of turns.

There are generally accepted standards that professionals are guided by:
- Step - 20 cm;
- The length of the pipe in one circuit is not more than 120 m;
- If there are several contours, then their length should be the same.
Under stationary and large-sized interior items, it is better not to start pipes. For example, under a gas stove.
IMPORTANT: be sure to draw the laying diagram to scale. Laying starts from the collector
Unwinding the bay fix pipe according to the scheme. For fastening it is convenient to use plastic clamps
Laying starts from the collector. Unwinding the bay fix the pipe according to the scheme. For fastening it is convenient to use plastic clamps.
Corrugated stainless steel is produced in coils of 50 m. For its connection, branded couplings are used.

The last element laid between the turns of the pipes is the temperature sensor. It is pushed into the corrugated pipe, the end of which is plugged and tied to the mesh. The distance from the wall is at least 0.5 m. Do not forget: 1 circuit - 1 temperature sensor. The other end of the corrugated pipe is brought to the wall and then, along the shortest path, is brought to the thermostat.
Why air must be removed
The formation of voids reduces the efficiency of the heating system. Pumping equipment, like other components, works less efficiently. To provide comfortable temperature conditions for users in the premises, more resources have to be spent.
With an increase in such voids, the pressure gradually decreases. After reaching the limit minimum level, the corresponding signal is sent to the boiler control unit.In addition to electronic devices, mechanical means of a similar purpose are used. This is an emergency, so the automation turns off the supply of gas or other fuel.
For the subsequent inclusion it is necessary to manually raise the pressure. But there are a lot of gaseous inclusions in fresh water, so negative processes are accelerated. The equipment will turn off more often.
It should be remembered that oxidation, which destroys metals, occurs in the presence of water and oxygen. Adding a new coolant activates the corresponding negative processes. In this mode of operation, the durability of the heating equipment is reduced.
The appearance of air "plugs" in the heat exchange units of the boilers should be excluded. These parts are exposed to very high temperatures.
With insufficiently uniform heating, the heat exchanger will be damaged beyond repair
The reasons listed above are enough to understand the need for preventive measures. Their implementation will prevent complex breakdowns and costs associated with restoration work.
Choosing the optimal step
After selecting the material and method of placing pipes, you need to determine the distance between adjacent turns of the circuit. It does not depend on the type of placement of coolants, but is directly proportional to the diameter of the pipes. For large sections, too small a pitch is unacceptable, just like for pipes with a small diameter, a large one. The consequences may be overheating or thermal voids, which will no longer characterize the warm floor as a single heating system.
Video - Warm floor "Valtek". Mounting instruction
A correctly selected step affects the thermal load of the circuit, the uniformity of heating of the entire floor surface and the correct operation of the entire system.
- Depending on the diameter of the pipe, the pitch can be from 50 mm to 450 mm. But the preferred values \u200b\u200bare 150, 200, 250 and 300 mm.
- The spacing of heat carriers depends on the type and purpose of the room, as well as on the numerical indicator of the calculated heat load. The optimal step for a heating load of 48-50 W/m² is 300 mm.
- With a system load of 80 W / m² and more, the step value is 150 mm. This indicator is optimal for bathrooms and toilets, where the temperature regime of the floor, according to stringent requirements, must be constant.
- When installing a warm floor in rooms with a large area and high ceilings, the heat carrier laying step is taken equal to 200 or 250 mm.
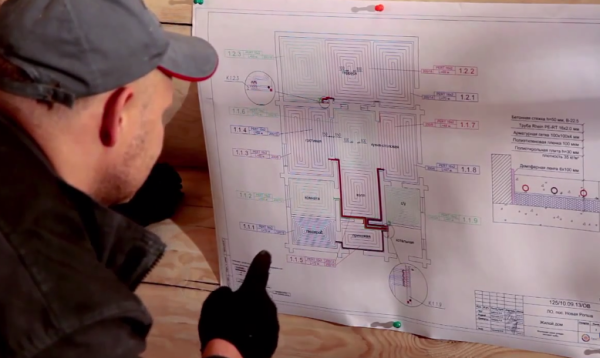
Underfloor heating installation project
In addition to a constant pitch, builders often resort to the technique of varying the placement of pipes on the floor. It consists in more frequent placement of coolants in a certain area. Most often, this technique is used along the line of external walls, windows and entrance doors - in these areas the maximum heat loss is noted. The value of the accelerated step is determined as 60-65% of the normal value, the optimal indicator is 150 or 200 mm with an outer diameter of the pipe of 20-22 mm. The number of rows is already determined during laying, and the calculated safety factor is 1.5.
Schemes for enhanced heating of external walls
Variable and combined laying pitch is practiced in external and edge rooms due to the urgent need for additional heating and large heat losses, in all internal rooms the usual method of placing heat carriers is used.
The process of laying underfloor heating pipes is carried out in strict accordance with the project