- The use of circulation pumps in home heating
- closed system
- Open heating system
- Underfloor heating system
- Calculation of pump parameters
- Power connection
- How to choose a circulation pump for heating: tips
- How to choose a circulation pump for heating, depending on performance
- Functions
- How to choose the right pump for the heating system
- Main characteristics
- Auxiliary characteristics
- Surface vortex
- Glandless heating pump
- The device and principle of operation of the circulation pump
- Dry rotor heating pumps
- Site preparation and installation
The use of circulation pumps in home heating
Since some features of the operation of circulation pumps for water in various heating schemes have already been mentioned above, the main features of their organization should be touched upon in more detail. It is worth noting that in any case, the supercharger is placed on the return pipe, if home heating involves raising the liquid to the second floor, another copy of the supercharger is installed there.
closed system
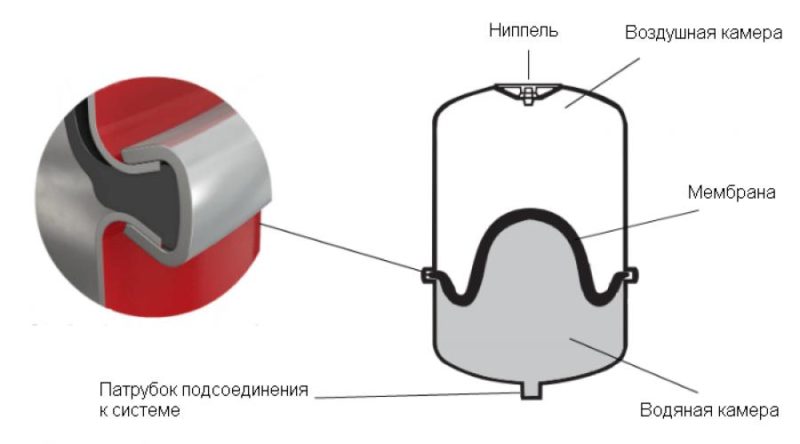
The most important feature of a closed heating system is sealing. Here:
- the coolant does not come into contact with the air in the room;
- inside the sealed piping system, the pressure is higher than atmospheric pressure;
- the expansion tank is built according to the hydraulic compensator scheme, with a membrane and an air area that creates back pressure and compensates for the expansion of the coolant when heated.
The advantages of a closed heating system are many. This is the ability to carry out desalination of the coolant for zero sediment and scale on the boiler heat exchanger, and filling in antifreeze to prevent freezing, and the ability to use a wide range of compounds and substances for heat transfer, from a water-alcohol solution to machine oil.
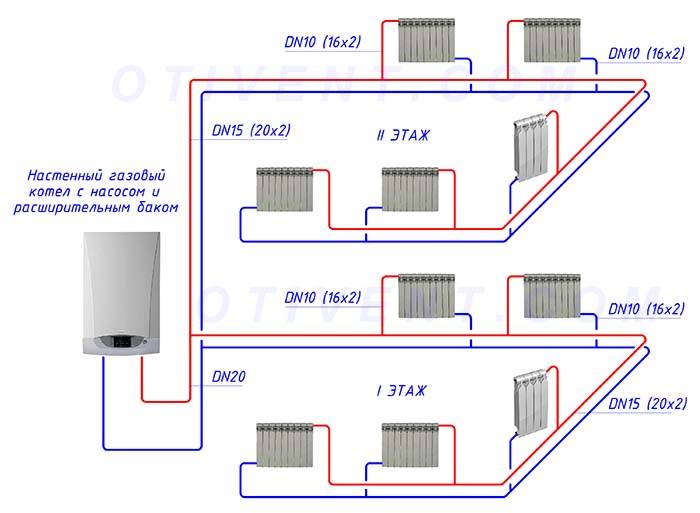
The scheme of a closed heating system with a single-pipe and two-pipe type pump is as follows:
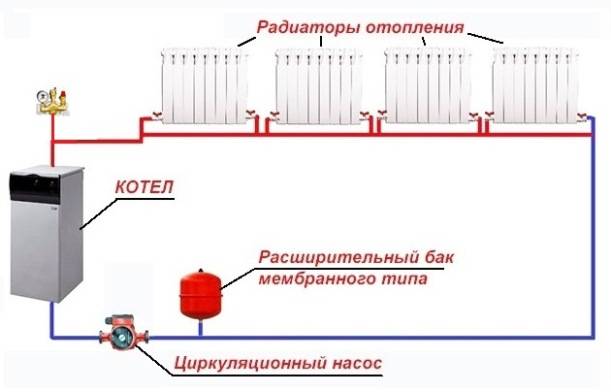
When installing Mayevsky nuts on heating radiators, the circuit setting improves, a separate air exhaust system and fuses in front of the circulation pump are not needed.
Open heating system
The external characteristics of an open system are similar to a closed one: the same pipelines, heating radiators, expansion tank. But there are fundamental differences in the mechanics of work.
- The main driving force of the coolant is gravitational. Heated water rises up the accelerating pipe; to increase circulation, it is recommended to make it as long as possible.
- The supply and return pipes are placed at an angle.
- Expansion tank - open type. In it, the coolant is in contact with air.
- The pressure inside an open heating system is equal to atmospheric pressure.
- The circulation pump installed on the feed return acts as a circulation amplifier. Its task is also to compensate for the shortcomings of the pipeline system: excessive hydraulic resistance due to excessive joints and turns, violation of tilt angles, and so on.
An open heating system requires maintenance, in particular, a constant topping up of coolant to compensate for evaporation from an open tank. Also, corrosion processes are constantly taking place in the network of pipelines and radiators, due to which the water is saturated with abrasive particles, and it is recommended to install circulation pump with dry rotor.
The scheme of an open heating system is as follows:
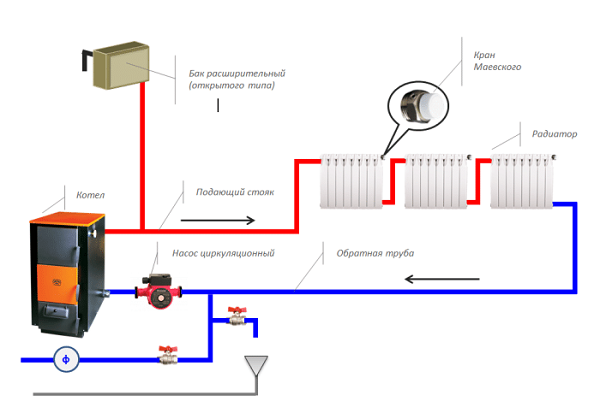
An open heating system with the correct angles of inclination and a sufficient height of the accelerating pipe can also be operated when the power supply is turned off (the circulation pump stops working). To do this, a bypass is made in the pipeline structure. The heating scheme looks like this:
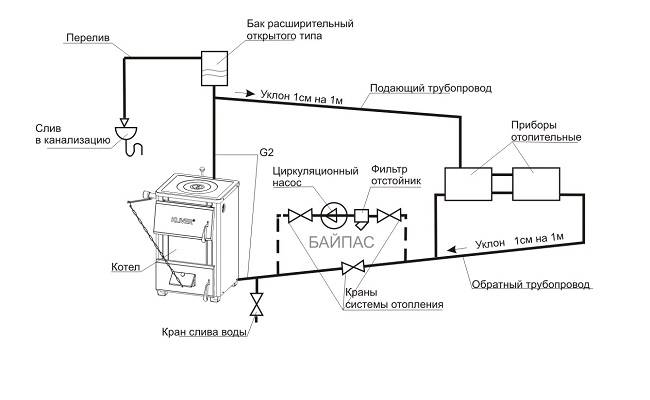
In the event of a power outage, it is enough to open the valve on the bypass bypass loop so that the system continues to work on the gravitational circulation circuit. This unit also makes the initial start-up of the heating easier.
Underfloor heating system
In the underfloor heating system, the correct calculation of the circulation pump and the choice of a reliable model are a guarantee of stable operation of the system. Without forced water injection, such a structure simply cannot work. The pump installation principle is as follows:
- hot water from the boiler is supplied to the inlet pipe, which is mixed through the mixer block with the return flow of the underfloor heating;
- the supply manifold for underfloor heating is connected to the pump outlet.
The distribution and control unit of the underfloor heating is as follows:
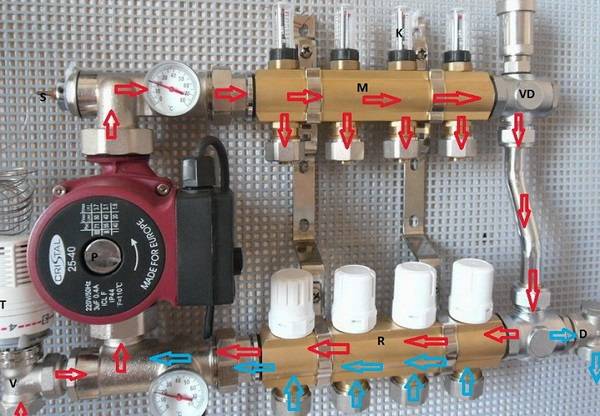

The system works according to the following principle.
- At the pump inlet, a main temperature controller is installed that controls the mixing unit. It can receive data from an external source, such as remote sensors in the room.
- Hot water of the set temperature enters the supply manifold and diverges through the floor heating network.
- The incoming return has a lower temperature than the supply from the boiler.
- The thermostat with the help of the mixer unit changes the proportions of the hot flow of the boiler and the cooled return.
- Water of the set temperature is supplied through the pump to the inlet distribution manifold of the underfloor heating.
Calculation of pump parameters
Circulation pumps are installed in heating systems. They do not create excess pressure, but simply push the coolant at a certain speed. Since the need for heat varies depending on weather conditions, the speed of the coolant must also change. Therefore, it is better to install adjustable pumps - three-speed.
Before buying, you should decide on two main parameters: performance (flow) and pressure. If water is the coolant, the pump performance is calculated using the following formula:
Q \u003d 0.86 * Pn / (tpr.t - trev.t)
- Pn is the power of the heating circuit, kW;
- tareb.t - temperature of the coolant in the return
- tpr.t - supply temperature.
The temperature difference in water heating systems is usually 5 ° C, the circuit power most often depends on the heated area, therefore, to simplify the selection of a pump for a water heated floor, you can use the table. But it must be taken into account that the average figures for central Russia were taken in the calculations. Therefore, if your house does not have the best insulation, or you live much north or south of the middle lane, you will have to adjust the result (or calculate it yourself). In general, this parameter is taken with a margin of 15-20% in case of abnormal cold weather.
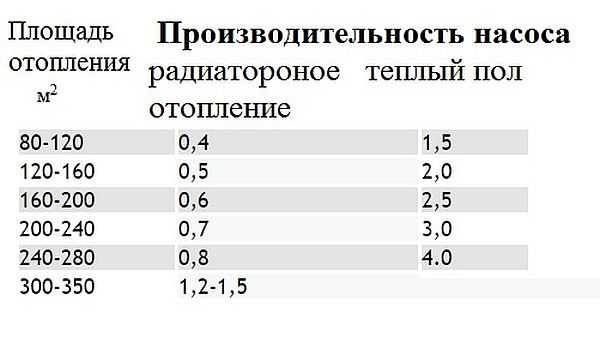
Table for determining pump performance depending on the heated area
The second characteristic by which the pump is selected is the pressure that it can create. The pressure is necessary to overcome the hydraulic resistance of pipes, fittings, and other components of the system. The resistance of the system depends on the material of the pipe and its diameter. The value of the hydraulic resistance of the pipe is available in the accompanying documents for them (you can use averaged data). Also, an increase in resistance on the valve (1.7), on fittings and fittings (1.2) and on the mixing unit (required when using a high-temperature boiler and the coefficient for it is 1.3) is taken into account.
H= (P*L + ΣK) /(1000),
- H is the pump head;
- P - hydraulic resistance per linear meter of the pipe,
- Pa/m; L is the length of the pipes of the most extended circuit, m;
- K is the power reserve factor.
To calculate the required pressure in the circuit, the passport hydraulic resistance of a pipe meter is multiplied by the length of the circuit. Get the value in kPa (kilopascals). This value is converted into atmospheres (pump head is measured in atmospheres) 100 kPa = 0.1 atm. The found value, depending on the presence of fittings and valves, is multiplied by the corresponding coefficients. After all the operations, you have found the duty point of the pump.
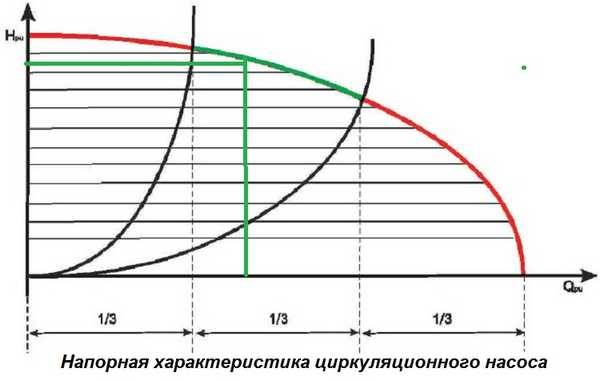
According to the graphic characteristics, choose a model
But the calculation of the pump for the warm floor has not yet been completed. Now you need to select a model. To do this, in the catalog of the manufacturer you like, find the characteristics of the pump. It is presented in the form of a graph. Select the model so that the found operating point is in the middle third of the characteristic.If you install a three-speed option, then select the model for the second speed - this will ensure the optimal, and not at the limit, operating mode and your pump will last a long time and provide normal temperature even on cold days.
Power connection
Circulation pumps operate from a 220 V network. The connection is standard, a separate power line with a circuit breaker is desirable. Three wires are required for connection - phase, zero and ground.
Electrical connection diagram of the circulation pump
The connection to the network itself can be organized using a three-pin socket and plug. This connection method is used if the pump comes with a connected power cable. It can also be connected via a terminal block or directly with a cable to the terminals.
The terminals are located under a plastic cover. We remove it by unscrewing a few bolts, we find three connectors. They are usually signed (pictograms are applied N - neutral wire, L - phase, and "earth" has an international designation), it is difficult to make a mistake.
Where to connect the power cable
Since the entire system depends on the performance of the circulation pump, it makes sense to make a backup power supply - put a stabilizer with connected batteries. With such a power supply system, everything will work for several days, since the pump itself and the boiler automation “pull” electricity to a maximum of 250-300 watts. But when organizing, you need to calculate everything and select the capacity of the batteries. The disadvantage of such a system is the need to ensure that the batteries are not discharged.
How to connect a circulator to electricity through a stabilizer
Hello.My situation is that a 25 x 60 pump stands right after the 6 kW electric boiler, then the line from the 40 mm pipe goes to the bathhouse (there are three steel radiators) and returns to the boiler; after the pump, the branch goes up, then 4 m, down, rings the house of 50 sq. m. through the kitchen, then through the bedroom, where it doubles, then the hall, where it triples and flows into the boiler return; in the bath branch 40 mm up, leaves the bath, enters the 2nd floor of the house 40 sq. m. (there are two cast-iron radiators) and returns to the bath in the return line; the heat did not go to the second floor; the idea to install a second pump in the bath for supply after a branch; the total length of the pipeline is 125 m. How correct is the solution?
The idea is correct - the route is too long for one pump.
How to choose a circulation pump for heating: tips
Many are interested in the question of how to choose a circulation pump for heating
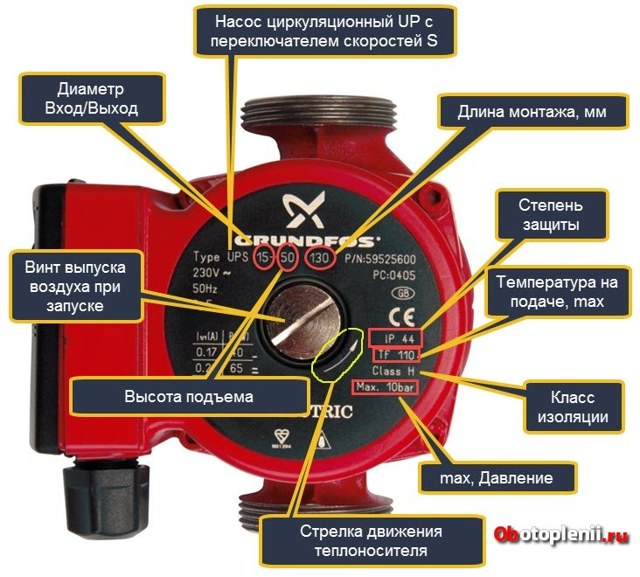
To select this product for a specific heating communication, it is necessary to pay attention to several factors. Most of these devices have a visual similarity to each other, however, they can differ greatly in their technical characteristics.
For private use, devices that operate from a standard network with a voltage of 220 V are chosen. A very important parameter is the power of the device. It depends on two main factors: the model and the mode in which the pump operates. Household appliances have a power rating that does not exceed 50-70 watts.
Also, experts recommend paying attention to the temperature of the coolant. All domestic circulation pumps have limitations on this indicator and can be used in heating systems with temperatures up to 110 ° C

Most pump models are mounted on pipes with union nuts.
How to choose a circulation pump for heating, focusing on geometric parameters? From the point of view of geometric indicators, the installation length of the device, as well as the cross-sectional index of the threaded part of the device, plays an important role. Most pumps are installed on pipes by means of union nuts, which are also called Americans. As a rule, such elements are included in the device package. The standard cross-sectional indicators that are applicable to domestic heating circuits are 25 and 32 mm. And the mounting length of the device can be 13 or 18 cm.
Among other things, you should pay attention to the markings that are applied to the pump housing. It often indicates the protection class of the electrical device, as well as the indicator of the maximum outlet pressure.
The first parameter is standard for most modern models and is designated IP44. The maximum outlet pressure in most cases is 10 bar.

An important factor when choosing a pump is the size of the installation length of the device.
If necessary, you can always consult with a specialist who will help you choose the right device for your heating design. And you can also ask a question that interests you on one of the specialized forums on the Internet.
How to choose a circulation pump for heating, depending on performance
Another important parameter to consider when choosing this equipment is its performance. This indicator indicates the amount of the working medium that the device is able to pump over in a certain unit of time (m³ / hour).And also it is worth considering the amount of pressure that the pump is able to create, calculated in meters.
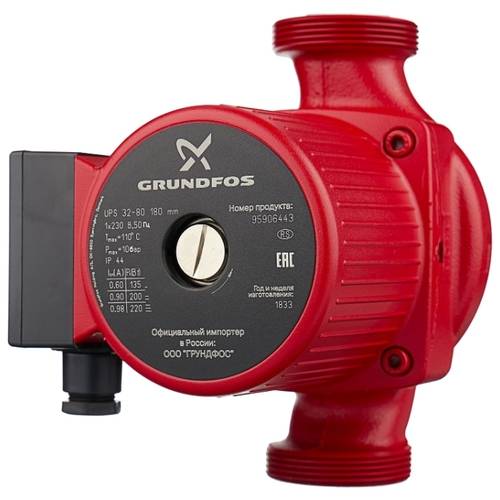
In most cases, the main technical characteristics of such devices are indicated in their name. For example, if you disassemble the name of the Grundfos UPS 32-80 device, then the first two digits indicate the diameter of the nozzles (32 mm), and the second - the head value, which is 8 m.
Note! When choosing the necessary device, it is imperative to carry out its calculation for a particular heating system. This will allow you to purchase the most suitable circulation device.

Scheme of heating a house with a floor-standing boiler, weather-dependent automation and a boiler: 1 - boiler; 2 - a set of safety devices; 3 - boiler; 4 - boiler safety group 3/4″ 7 bar; 5 - hydraulic accumulator 12l / 10 bar; 6 - pump; 7 - 3-circuit manifold; 8 - bracket with a set of fasteners; 9 - boiler connection kit (1.0 and 1.2 m); 10 - direct module; 11 - mixing module with electric drive; 12 - KTZ-20 Du 20; 13 - crane 11B27P Du 20; 14 — KEG 9720 valve DN 20 (220 V); 15 - signaling device; 16 - gas meter; 17 - expansion tank 35 l / 3 bar; 18 - make-up valve; 19 - cartridge fine filter 1″; 20 - water meter; 21 - filter with manual washing 1″; 22 - ball valve for water; 23 - polyphosphate dispenser
The selection of a circulation pump for a heating system must be approached as competently as possible. Therefore, it is worth considering even such moments as the condition of the premises and the characteristics of the climatic region in which you live. If your house has good thermal insulation, then it is enough to get by with a device with low power (and vice versa).
You also need to take into account the dependence of the pump power on the climatic region. In this case, the following pattern can be traced: the colder the climate of the area in which the residential building is located, the more powerful the circulation device is needed. If necessary, the question of how to choose a circulation pump for heating can be answered by specialists in specialized stores.
Functions
A water heated floor differs from a traditional heating system in that the length of the circuits is significant - up to 120 meters at the maximum, and the diameter of the pipes is usually small 16-20 mm. Each circuit has many turns. Therefore, it becomes clear that for normal operation of the heating, forced circulation will be required. And it is the pump for the water floor that provides the speed of movement of the coolant through the pipes sufficient for normal temperatures. Moreover, in order to maintain a stable temperature, it will be better if the pump has several speeds. Such devices are called adjustable and their operation can be controlled manually or use automation for this.

Choosing a pump for a warm floor is a rather difficult and responsible task.
How to choose the right pump for the heating system
The circulation pump is designed to periodically move the coolant through the pipeline: water or antifreeze, which ensures the optimum ambient temperature in the room. Choosing the right pumping equipment can significantly save on the consumption of gas and electricity.
When choosing a circulation pump for heating systems, it is necessary to take into account the main and auxiliary characteristics of the unit.
Main characteristics
Power
Basically, the power of the heat pump is in the range of 60-300 W
This is the main characteristic that you should pay special attention to, as it determines the overall temperature scheme of the heating system. When choosing a pump, it is not recommended to focus on units with maximum power, since pumping equipment is not designed to move a large number of cubic meters of hot liquid for heating large areas of premises
Performance
Productivity is the amount (volume) of fluid moved over a certain period of time. This characteristic directly depends on the power of the pumping equipment and the diameter of the pipeline of the heating system.
pressure
Head, in its essence, is hydraulic resistance. Its value is measured in meters and indicates to what height the pump can raise the entire volume of liquid.
Auxiliary characteristics
Connection dimensions
The dimensions of the connection and installation of the pump in the heating system are mainly selected based on the diameters of the pipelines and the dimensions of the unit itself.
Temperature
Since the pump is designed to provide heat to residential premises, its pipeline must withstand high temperature loads. This characteristic must be coordinated with the temperature characteristics of the heating boiler and pipes used in the heating system.
Surface vortex

Surface well pump
This type of water pump is used to increase the pressure in the system and heating, which makes it also suitable for fire fighting. Due to the high noise background, this type of pump is best used in a technical room.The principle of their work is to create a water funnel (vortex) using a special wheel.
Compared to the centrifugal type, the vortex model gives a more powerful pressure and at the same time differs in dimensions. Also a plus can be called its resistance to air ingress into the system. But there is also a drawback - the design is sensitive to impurities, including small ones, their ingress in large quantities usually leads to failure.

Perennial flowers (TOP 50 species): garden catalog for giving with photos and names | Video + Reviews
Glandless heating pump
In the body of such a heating device there is a rotor on which the impeller is fixed. Due to the movement of fluid in the heating system, it performs rotational movements. Water constantly circulates through the pump sleeve, cooling and lubricating all the bearings. In order for the fluid circulation to be the most optimal, the device must be fixed on a horizontal surface of the pipeline.
The efficiency of heating pumps of this type does not exceed 50%. When compared with a dry rotor pump, this figure is 30% less. But such pumps have a number of advantages.
- When working, it makes little noise;
- Its price is low;
- He has a small weight;
- It is easy and simple to install.
Such a device will last a long time without requiring frequent maintenance.

You can mount a pump with a wet rotor on any of the sections of the heating system. Installation can be done in two ways.
The first method allows installation in the pipeline itself,
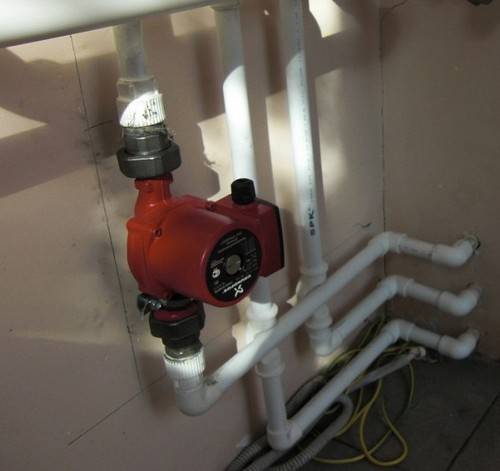

the second way is installation in the spare line.

The second installation method is more common, because in the event of an emergency power outage, all elements of the heating system will continue to work.
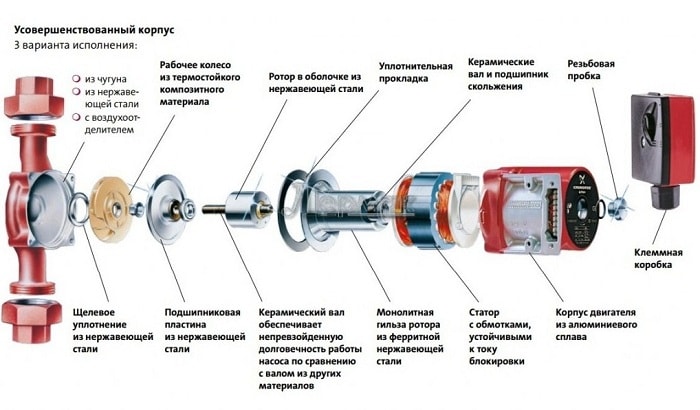
The device and principle of operation of the circulation pump
The device is one of the modifications of the hydraulic centrifugal machine and consists of the following main components:
- Metal or polymer case;
- Rotor, which ensures the rotation of the impeller;
- Trumpets;
- Lip, disc and labyrinth seals;
- An electronic control unit that allows you to control the parameters of the electric motor and set the required mode.
The inlet and outlet pipes can have a different location, which allows you to choose a circulation pump that fits optimally into the scheme of the designed circuit. Due to its small overall dimensions, the pump is often installed in the heat generator housing, which greatly simplifies the installation of the pipeline.
The principle of operation of the circulation pump
The process of forced submission can be divided into several stages:
- Suction of the liquid heat carrier through the inlet pipe;
- The rotating turbine throws the liquid against the walls of the housing;
- Due to centrifugal force, the working pressure of the coolant increases and it moves through the outlet pipe into the main pipeline.
In the process of moving the working medium to the edge of the turbine, the vacuum in the inlet pipe increases, which ensures continuous fluid intake.
If the power of the device built into the heat generator is not enough to ensure efficient circulation, the required parameters can be achieved by installing an additional circulation blower in the system.
Dry rotor heating pumps
The design of the unit in question is designed so that the pumped water does not have direct contact with the engine. That is why it is considered to be safer. In the design of the pump part, there are two rings that perform rotational movements between themselves. The pump part, in turn, is separated from the motor by the installed seal. With the help of the pumped liquid, the pump mechanisms are lubricated, thereby preventing its wear. The rings are tightly fastened together with a spring. This allows you to adjust the clamping force if abrasion occurs. All this helps to increase the life of the pump, and also makes it more reliable.
Most often, this type of pump, with a dry rotor, is used in industrial enterprises with a large volume of water.
Site preparation and installation
A modern "wet" type circulation pump can be installed both on the supply and on the return section of the pipeline. Old-style models were installed only on the return pipe - so the cooled water extended the life of the mechanism.
On the part of the pipeline in front of the expansion tank and the section of the system after it, a different pressure level is created - compression and vacuum, respectively. The static pressure created by the tank will affect the functioning of the system with installed pumping equipment. The pump delivery zone is characterized by a hydrostatic pressure, which is an order of magnitude higher than usual, and on the heat carrier suction side it is characterized by a lower level, sometimes leading to a vacuum. If there is a large pressure difference in the system, the water may boil, or air may be formed when released and sucked.
To ensure the normal circulation of the coolant through the pipeline, an important condition should be taken into account: any point located within the suction boundaries must have excess hydrostatic pressure. You can control this process in the following ways: You can keep this process under control as follows:
You can keep this process under control as follows:
- install an expansion tank 80 cm above the highest point of the system. This method is the easiest and most convenient, especially if the heating system is retrofitted with a circulation pump. It will only take a sufficient height of the attic and insulation of the expansion tank;
- place the container at the top of the system so that the upper part of the pipeline is in the pump discharge zone. This method is applicable for modern heating systems, where the slope of the pipes to the boiler was originally equipped. The principle of operation is that air bubbles move in a stream of water under pressure created by the force of the pump;
- set the highest point of the system at the most remote riser. But there is one nuance here: the pipeline will have to be redone, and this is a very costly and complex undertaking;
- transfer the expansion tank and part of the pipe to the suction area of the pump, in front of the nozzle. Such a reconstruction will be optimal for operation under conditions of forced circulation of the coolant;
- installation of a circulation pump in the supply part of the pipe, immediately after the entry point of the expansion tank. However, this method is not suitable for all models of equipment, since the temperature in this zone will be quite high. The method is good for those pumps that are able to withstand such operating conditions.
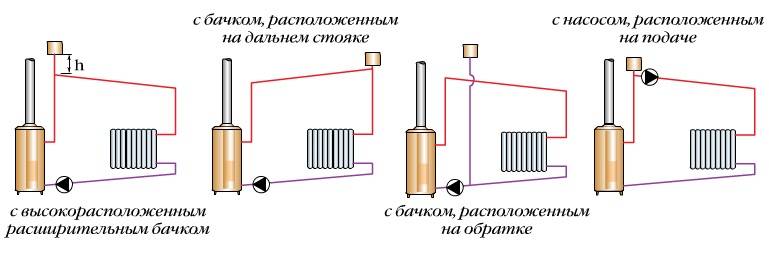
Schemes of mounting options for a circulation pump with an expansion tank
To install the pump, take into account its threaded diameter and purchase a filter element (coarse filter), check valve, bypass, wrenches ranging in size from 19 mm to 36 mm. On the main pipe, between the outlet and the inlet of the cut-in jumper, a shut-off valve of the appropriate diameter is installed. For ease of installation, a detachable thread is useful.
The task of the bypass, which is a small piece of pipe, is to switch the heating system from forced to natural circulation mode in the event of a pump failure, or a power outage. The diameter of the bypass must match the diameter of the riser in which it is installed.
The devices on the jumper must be mounted in the following order: first the filter element cuts in, then the valve, then the pump follows. Bypass inputs from the riser are carried out by means of shut-off valves that shut off the system in case of failures or breakdowns.

If a wet type pump is installed, the bypass must be cut horizontally to prevent air accumulation. Additionally, an automatic air outlet valve can be mounted in the system, always in a vertical position. The automatic tap has advantages over a conventional Mayevsky tap, which must be opened and closed manually.