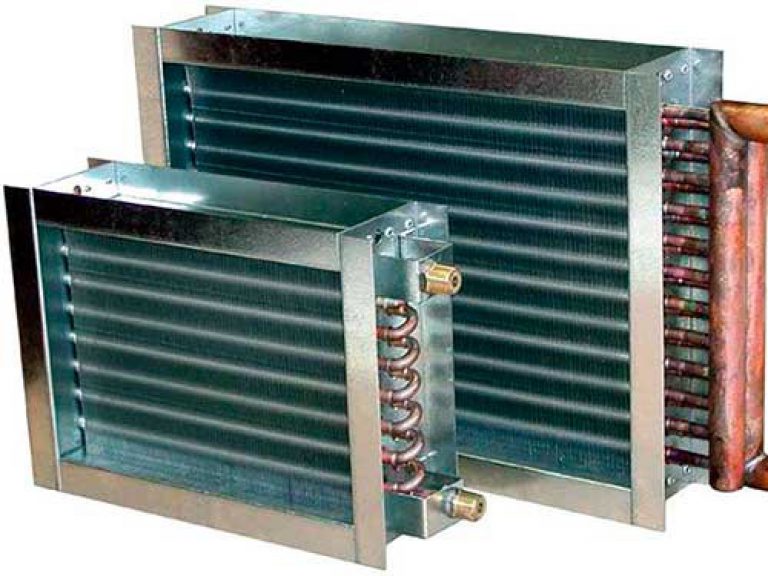
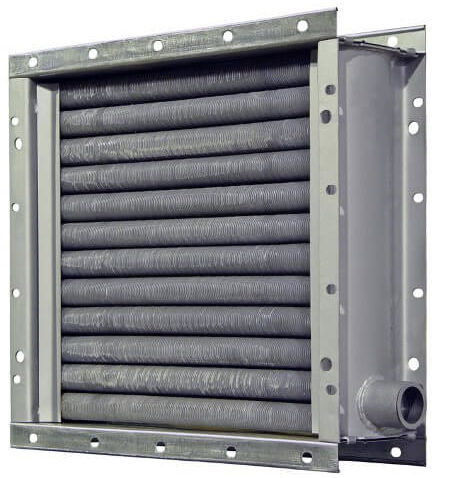
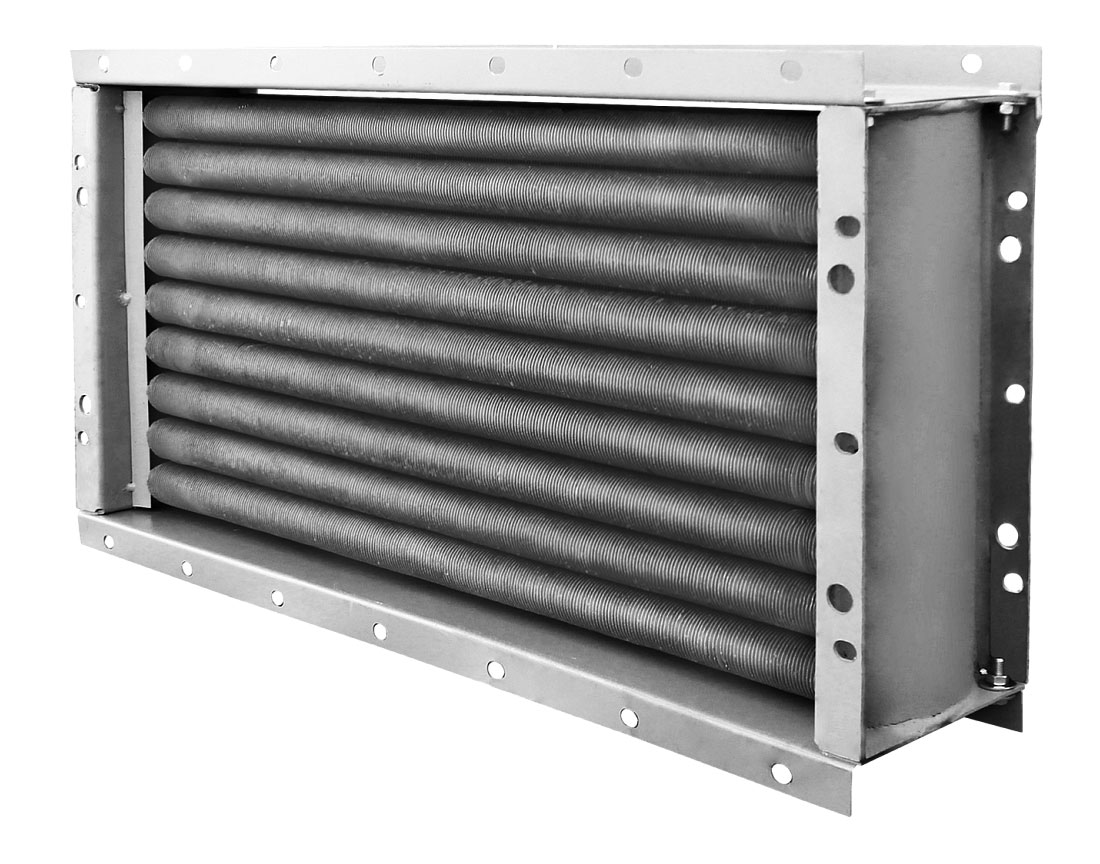
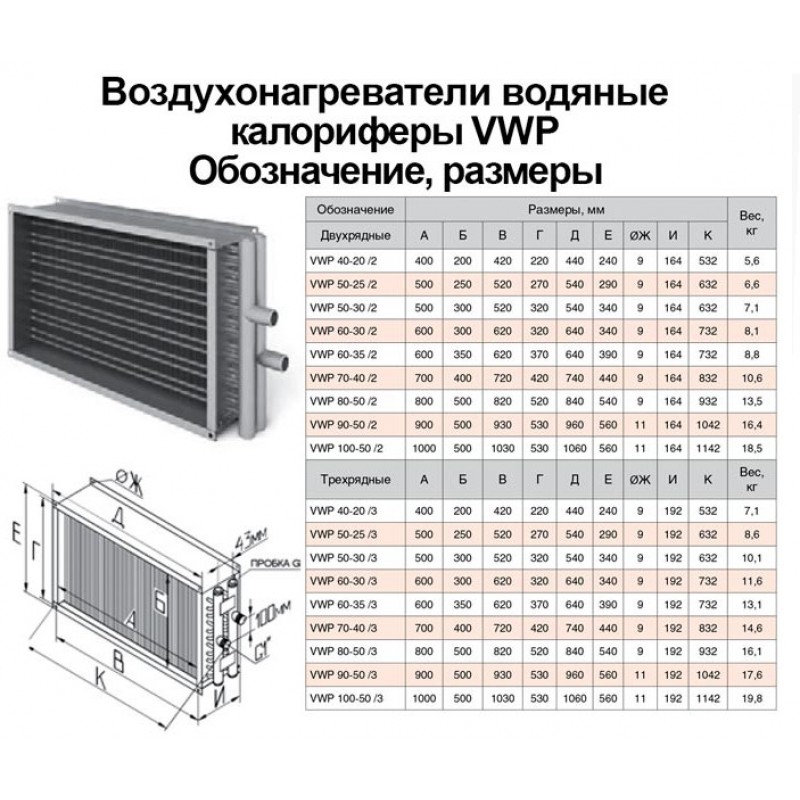
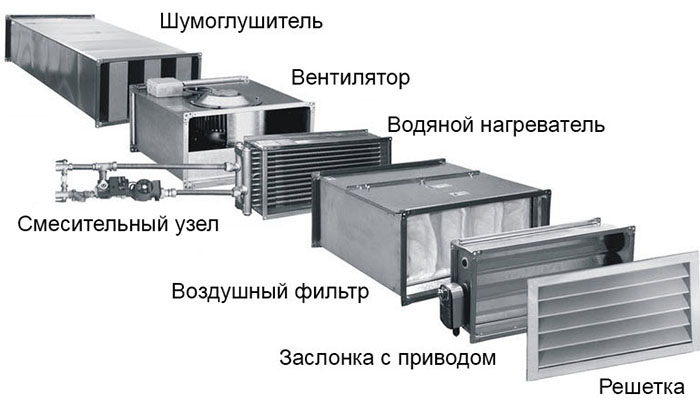
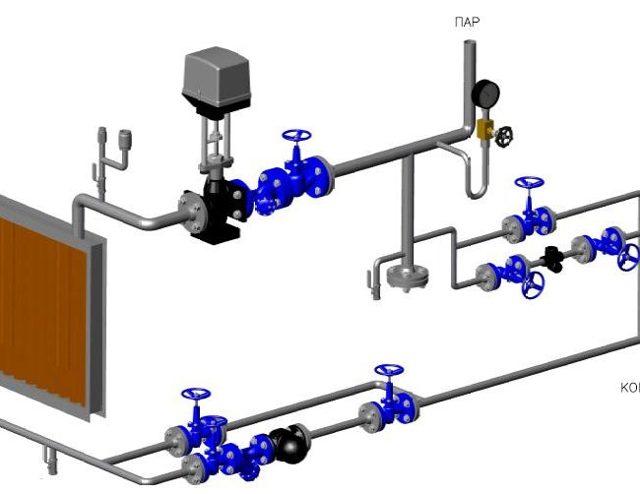
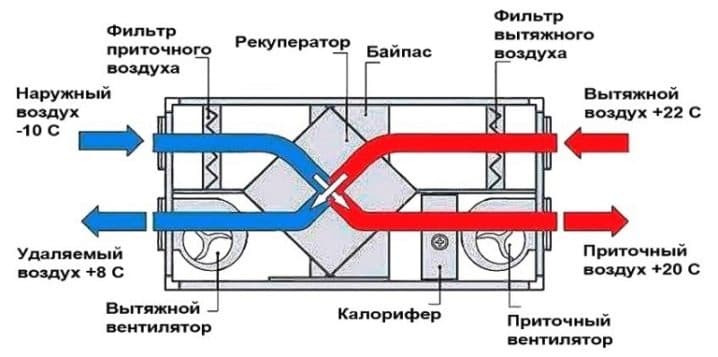
- Pros and cons of using
- Connection
- Rules for the operation of the heater
- Heating of supply air masses by means of recirculation
- Coolant speed
- What is a heater and why is it needed
- The principle of operation of the water heater
- Advantages and disadvantages
- Kinds
- Heat source
- materials
- non-standard version
- Types of systems
- Brief overview of modern models
- 1 Features and principle of operation
- Calculation-online of electric heaters. Selection of electric heaters by power - T.S.T.
Pros and cons of using
If the enterprise has its own heat supply system, the use of air heaters for forced ventilation is the most cost-effective.
A set of water heaters for maintenance of a warehouse. Heaters with an air flow rate of 5200 m³/h and a coolant temperature of + 130ºС heat the air and maintain the set temperature
Advantages of devices connected to a centralized system:
- simple installation, not differing in complexity from the installation of heating pipes;
- rapid heating of a large room;
- the safety of all nodes;
- the ability to adjust the flow of heated air;
- strict industrial design.
But the main advantage is the absence of regular financial investments - payment occurs only when buying new equipment.
Current prices for water bimetallic heaters KSK manufactured by the Novosibirsk company T.S.T., which manufactures thermal equipment. The final price depends on the basic configuration and technical characteristics (+)
The main disadvantage is the impossibility of using water models in everyday life, especially in urban housing. An alternative is the use of electrical appliances. Another nuance concerns negative temperatures: the equipment must be installed in rooms where the minimum threshold does not fall below 0ºС.
There are practically no wearing parts in the design of the water heater. They rarely fail and require major repairs, which should also be attributed to the “piggy bank” of equipment advantages (+)
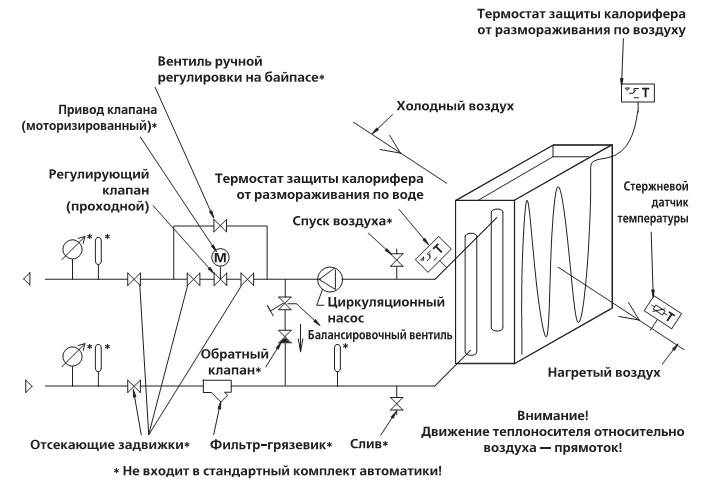
Connection
The intake of air masses can be carried out in one of two ways:
- Left execution: the mixing unit and automatic control are installed on the left side, the water supply is from above, the outflow is at the bottom.
- Right execution: these mechanisms are on the right, the water supply tube is at the bottom, the “return” is at the top.
The tubes are placed on the side where the air valve is installed.
Water heaters are divided into 2 types according to the type of valve:
- two-way - when connected to the general heat supply;
- three-way - with a closed method of supplying heat (for example, when connected to a boiler).
The type of valve is determined by the characteristics of the system supplying heat. These include:
- Type of system.
- Water temperature at the beginning of the process and at the outflow.
- With central water supply - the difference between the pressure in the pipes for supplying water and its outflow.
- With autonomous - the presence or absence of a pump installed on the inflow circuit.
The installation scheme must provide for the inadmissibility of installation in the following cases:
- with vertical input and output of the pipe;
- with top air intake.
Such restrictions are due to the possibility of snow masses getting into the inflow of equipment and further leakage of melt water into the electronic unit.
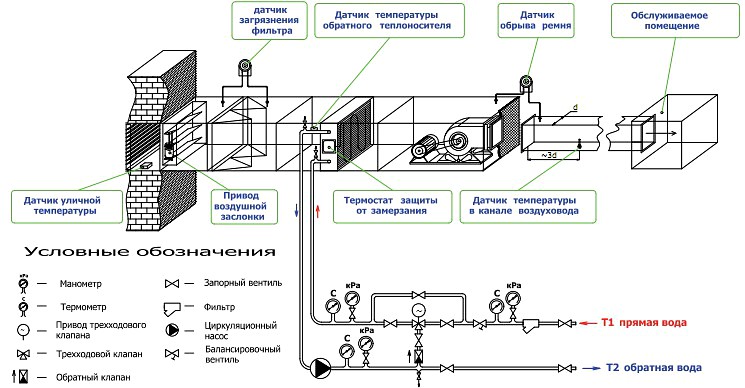
To avoid malfunctions of the automation unit, the temperature sensor must be located in the inner part of the air blowing element at a distance of at least 0.5 m from the inflow mechanism.
Rules for the operation of the heater
For long and trouble-free operation, it is important to adhere to the following operating rules:
It is impossible to exceed the pressure in the pipelines above the normalized indicators, which are indicated for each device in the technical documentation.
Composition of air masses indoors must meet the requirements of GOST 12.1.005-88.
During installation, it is important to follow the instructions and recommendations of the manufacturer.
It is forbidden to use a heat carrier with a temperature exceeding +190 degrees.
The cooled air in the room is warmed up gradually. The temperature should rise every hour by 30 degrees.
To protect the heat exchanger tubes from rupture, temperature readings cannot drop to minus values.
In a production room with very humid or dirty air, heaters with a protection level of at least IP 66 are installed. It is forbidden to repair heating equipment on your own
This must be done by qualified service personnel.Compliance with all of the above rules will help extend the service life and protect against emergencies. water heater for supply ventilation
It is forbidden to repair heating equipment by yourself. This must be done by qualified service personnel. Compliance with all of the above rules will help extend the service life and protect against emergencies. water heater for supply ventilation
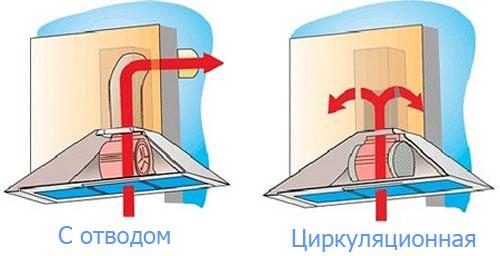
Heating of supply air masses by means of recirculation
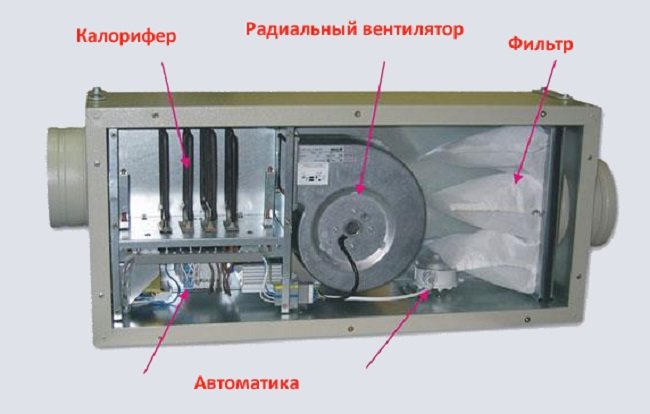

An obligatory component of ventilation is an electric heater
Recirculation heated ventilation, in general terms, works according to the following principle:
- air enters the house through the inflow of the ventilation system;
- after a certain period of time, it enters the exhaust system, where part of the incoming air masses is removed outside the house;
- the rest of the air enters the mixing chamber.
In the mixing compartment, fresh air is mixed with “exhaust air”, thus heating cold wind masses (if the system is set in the air heating mode in the control settings, and not vice versa). Further, the air flow is directed to the heater or air conditioner, then through the ventilation ducts to the house.
Coolant speed
5. Calculation of the speed of water movement in the tubes of the received heater. Gw is the coolant flow rate, kg/s; pw is the density of water at an average temperature in the air heater, kg/m³;
fw is the average open area of one pass of the heat exchanger (accepted according to the selection table for heaters KSK), m².
| Density of water as a function of temperature | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| temperature, °С | +5 | +10 | +15 | +20 | +25 | +30 | +35 | +40 | +45 | +50 | +55 | +60 | +65 | +70 | |
| density, kg/m³ | 999 | 999 | 999 | 999 | 998 | 997 | 996 | 994 | 992 | 990 | 988 | 986 | 983 | 981 | 978 |
| temperature, °С | +75 | +80 | +85 | +90 | +95 | +100 | +105 | +110 | +115 | +120 | +125 | +130 | +135 | +140 | +150 |
| density, kg/m³ | 975 | 972 | 967 | 965 | 962 | 958 | 955 | 951 | 947 | 943 | 939 | 935 | 930 | 926 | 917 |
| Heat capacity of water as a function of temperature | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| temperature, °С | +5 | +10 | +15 | +20 | +25 | +30 | +35 | +40 | +45 | +50 | +55 | +60 | +65 | +70 | |
| heat capacity, J/(kg•°С) | 4217 | 4204 | 4193 | 4186 | 4182 | 4181 | 4179 | 4178 | 4179 | 4181 | 4182 | 4183 | 4184 | 4185 | 4190 |
| temperature, °С | +75 | +80 | +85 | +90 | +95 | +100 | +105 | +110 | +115 | +120 | +125 | +130 | +135 | +140 | +150 |
| heat capacity, J/(kg•°С) | 4194 | 4197 | 4203 | 4205 | 4213 | 4216 | 4226 | 4233 | 4237 | 4240 | 4258 | 4270 | 4280 | 4290 | 4310 |
If two or more heaters are taken for calculation, this formula is valid only if they are consecutive
heating medium connection. That is, the heaters are connected so that hot water, having passed through the contours of one
heat exchanger, fed into the second, etc. When connecting in parallel, for example, two KSK air heaters
coolant, the value of fw will be 2fw, etc. For example, to heat the air, we need two heat exchangers Ksk 3-9 s
with an area of 0.455 m² (in total this gives 0.910 m²). The coolant flow rate was 0.600 kg/s. Calculate movement speed
one stroke of the heaters. When connected in series through the coolant, the formula will look like - W (m / s) \u003d Gw /
(pw • fw), with parallel (the heat pipe is connected to each air heater separately) - W (m / s) = Gw / (pw • 2fw).
Accordingly, the speed of movement of water in the tubes, in the first case, will be of greater importance than in the second. Recommended
the speed of the coolant in water heaters of the KSK type is (0.2 - 0.5) m / s. Exceeding this speed is associated with an increase
hydraulic resistance. Permissible values are from 0.12 to 1.2 m/s.
What is a heater and why is it needed
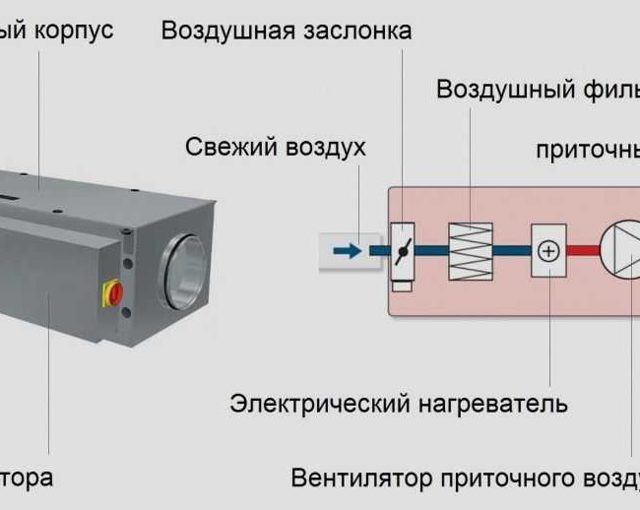
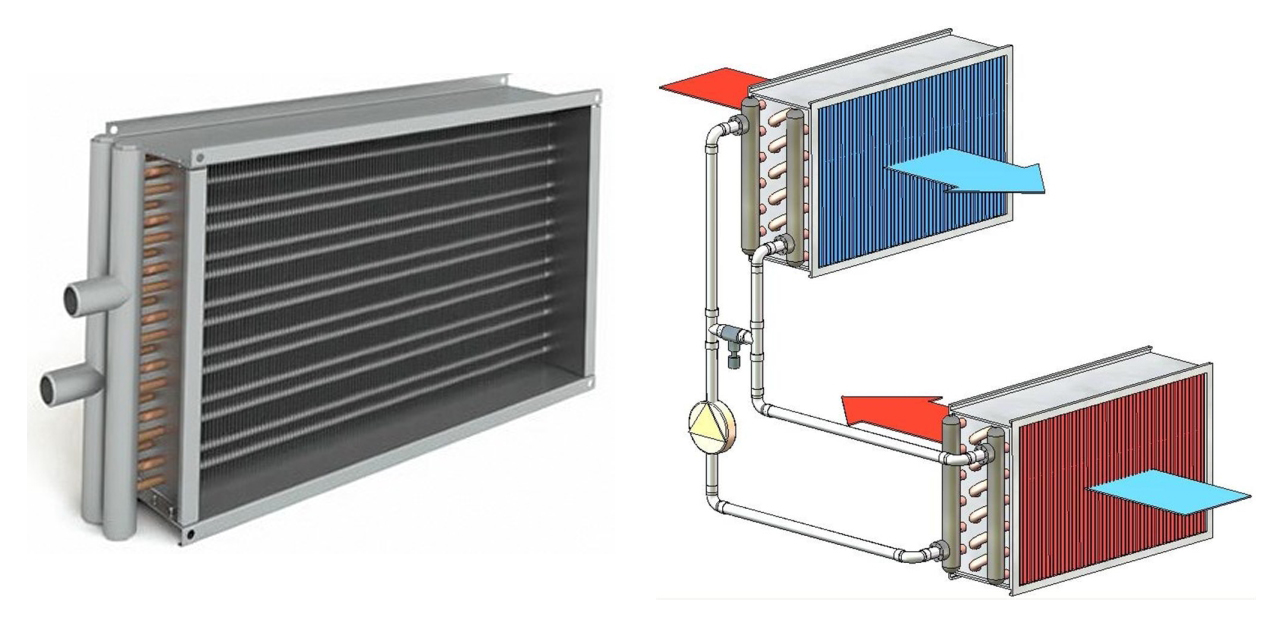
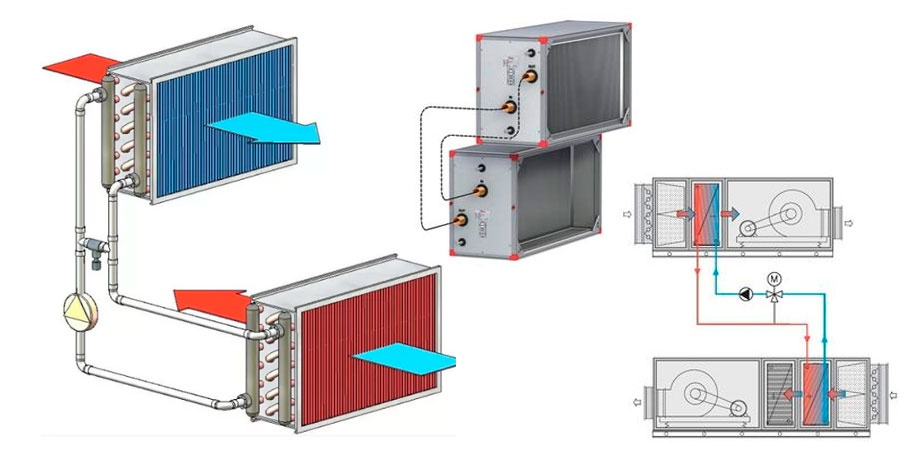
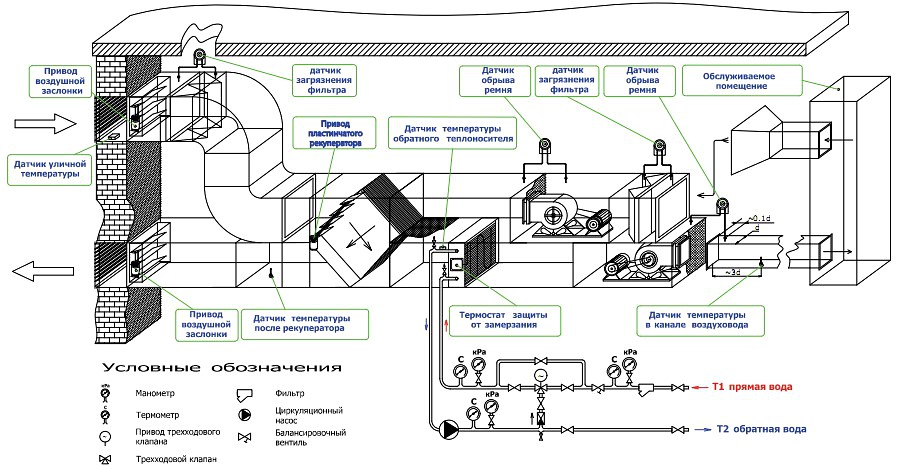
It is a kind of heat exchanger in which the heat source is air flows in contact with the heating elements.By means of the device, the supply air is heated in ventilation systems and drying equipment.
The diagram shows the position of the air heater in a duct ventilation unit.
The device to be mounted can be presented as a separate module or be part of a monoblock ventilation unit. The scope of application is presented:
- initial air heating in supply ventilation systems with air flow from the street;
- secondary heating of air masses during recuperation in supply and exhaust type systems that regenerate heat;
- secondary heating of air masses inside individual rooms to ensure individual temperature conditions;
- heating the air to supply it to the air conditioner in winter;
- backup or additional heating.
The energy efficiency of a duct air heater of any design is determined by the heat transfer coefficient under conditions of certain energy costs, therefore, with significant heat transfer rates, the device is considered to be highly efficient.
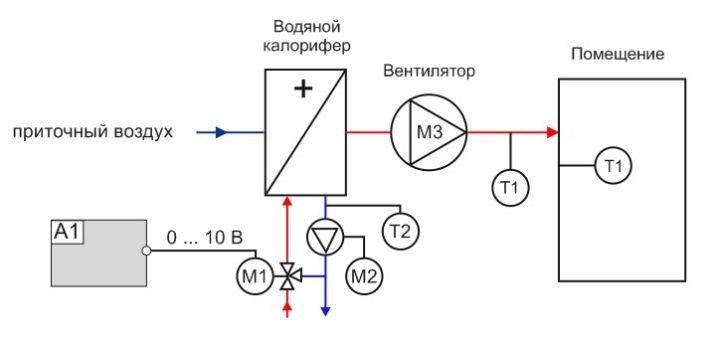
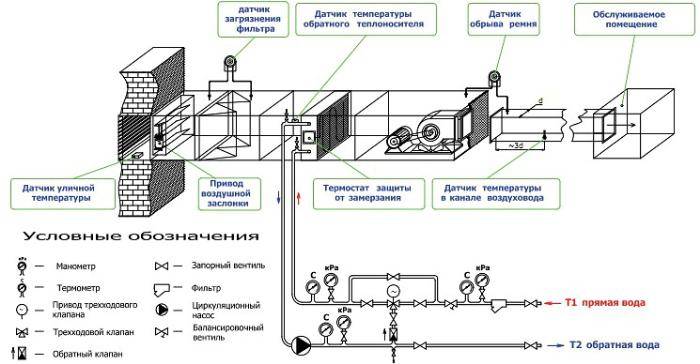
The binding in the supply ventilation system of the regulating reinforcing cage is carried out by means of two-way valves in the city network, as well as three-way valves when using a boiler room or boiler. With the help of the installed strapping unit, the performance of the equipment used is easily controlled and the risk of freezing in winter is minimized.
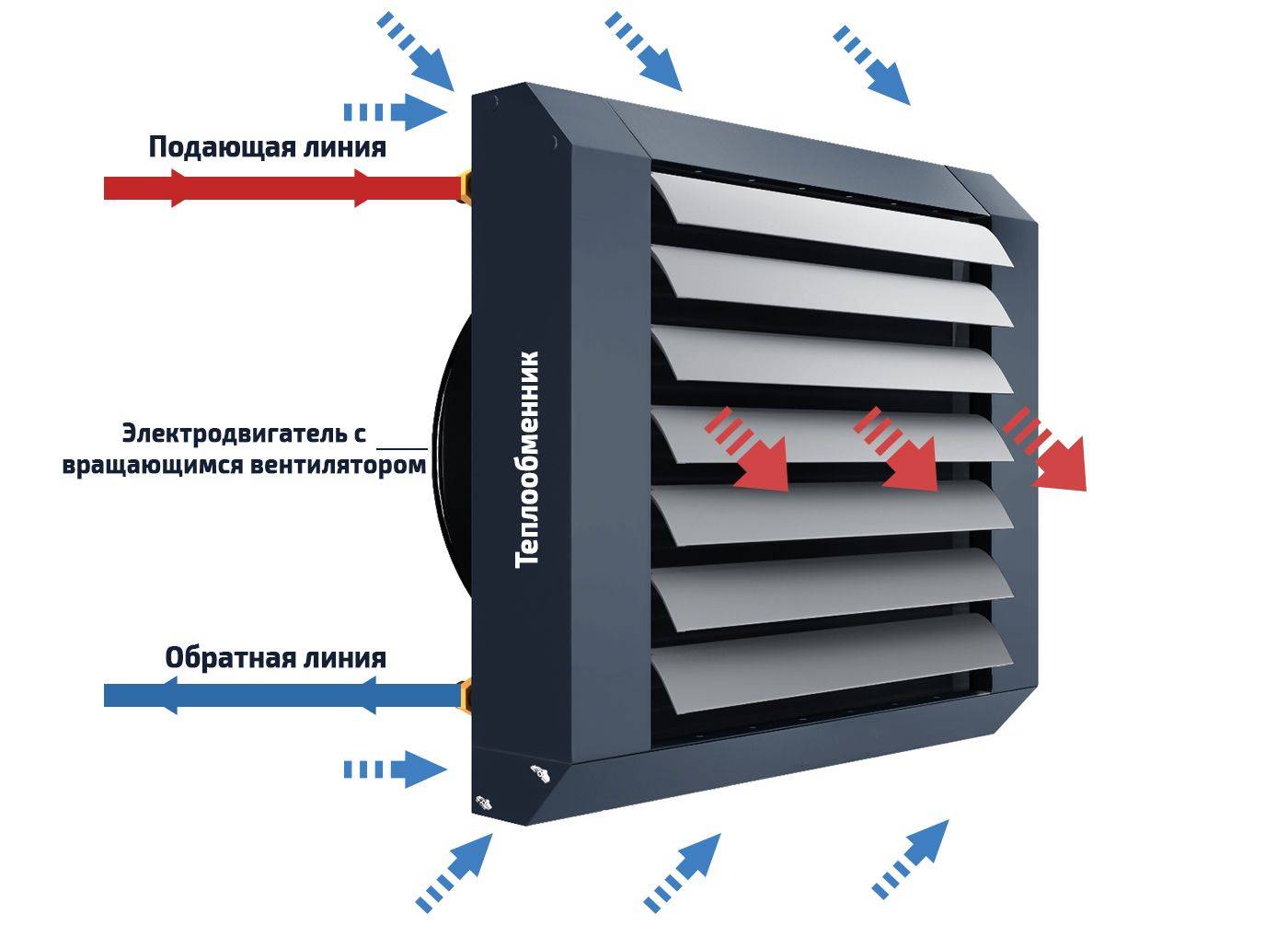
The principle of operation of the water heater
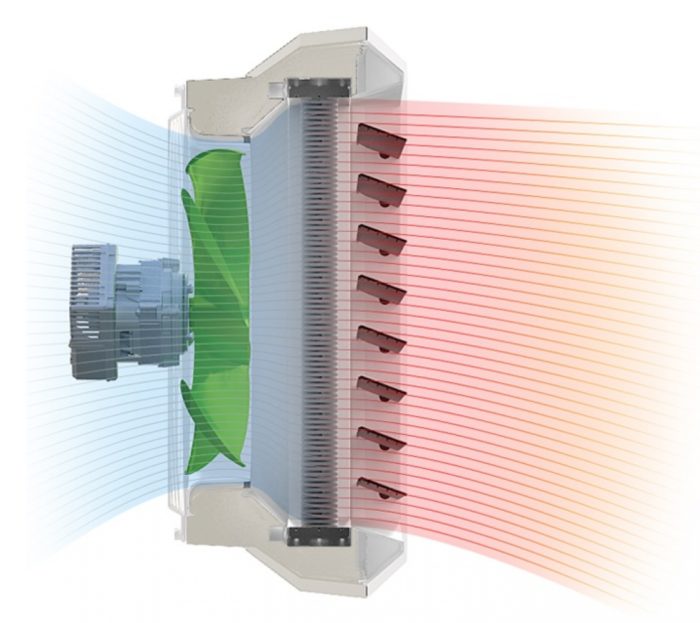
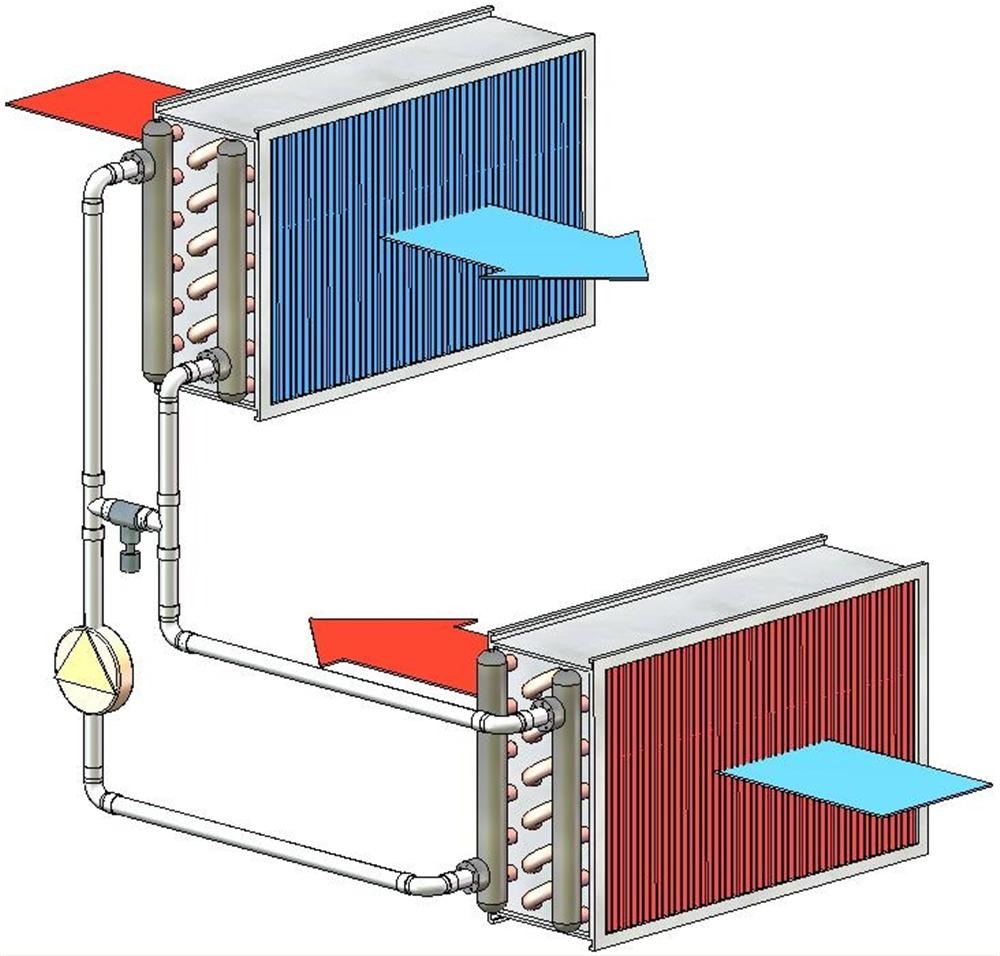
Devices for the ventilation system that operate using water are installed only if there is an adjusted and adjusted operation of the heat supply system or hot water supply. The unit can heat air masses up to a temperature of +70…+100°C.Heated air is used as a source of additional heat in large areas - gyms, warehouses, supermarkets, pavilions, industrial premises and greenhouses.
The principle of operation of supply ventilation with a water heater is similar to the operation of a similar household appliance for space heating, only instead of an electric spiral, a coil made of metal tubes in which the coolant circulates acts as a heat exchanger.
In this case, the process of heating the air masses is as follows:
- hot liquid from the heating system or DHW networks, heated to 80-180 degrees, goes to a tubular heat exchanger, which is made of copper, steel, bimetal or aluminum;
- the coolant heats the tubes, and they, in turn, give off thermal energy to the air masses passing through the heat exchanger;
- for uniform distribution of heated air throughout the room, there is a fan in the device (it is also responsible for the return supply of air masses to the heater).
If everything is already tired and you don’t know what else to play, then you can try downloading 1xBet slot machines and enjoy new experiences with the popular bookmaker.
Thanks to the use of already heated air from the heating system, the unit saves money. A water heater for ventilation networks can be called a device that combines the qualities of a convector, a fan and a heat exchanger.
Heaters for ventilation networks work only with air, the degree of dust content of which does not exceed 0.5 mg/m³, and the minimum temperature is not lower than -20°C. The device is mounted inside the ventilation shaft and selected according to its parameters (section and shape).Sometimes, to achieve the desired air temperature, several less powerful devices are installed in series, if one design of suitable performance cannot be built into the duct.
Advantages and disadvantages
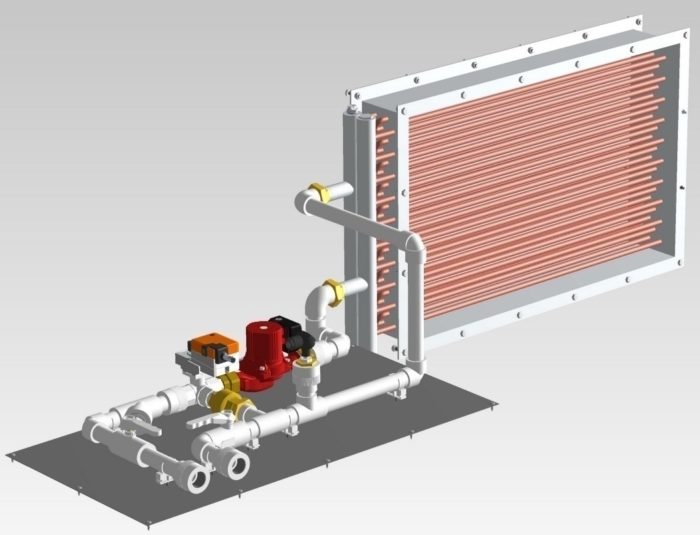
It is advisable to use water heaters in industrial enterprises that have their own heat supply communications. In this case, the unit will be as profitable as possible.
The advantages of air heating devices include the following:
- In terms of complexity and laboriousness, the installation of a water heat exchanger can be compared with the laying of heating pipes. In other words, there will be no installation problems.
- Heated air masses quickly heat even a large area.
- The absence of complex mechanical and electrical components ensures safe operation.
- The direction of the warm air flows can be controlled.
- During operation, there are no increased loads on the power grid, and a breakdown will not provoke a fire. By the way, the unit very rarely fails, because it does not have wear parts.
- Thanks to the use of hot liquid from the heating network, the equipment does not require regular financial investments.
The main disadvantage is that the heater cannot be used for domestic purposes in apartment buildings. But alternatively, similar electrical devices are used. The equipment has impressive dimensions and requires control over the temperature of the coolant in the heating network to which it is connected.Such ventilation equipment is allowed to be installed only in places where the ambient temperature does not fall below zero degrees.
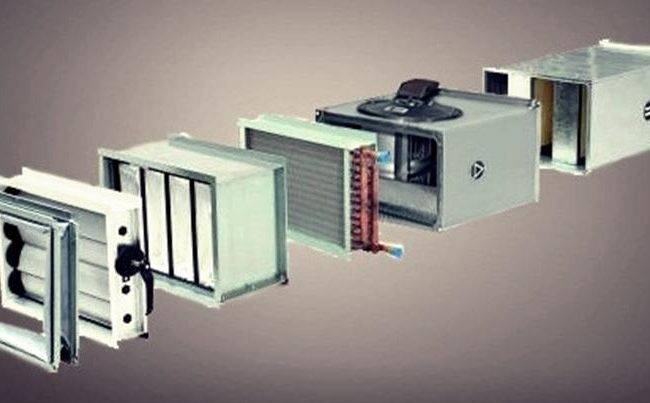
Kinds
On what grounds can heaters be classified?
Heat source
It can be used as:
- Electricity.
- Heat generated by an individual heating boiler, boiler house or CHP and delivered to the heater by a coolant.
Let's analyze both schemes in a little more detail.
An electric air heater for forced ventilation is, as a rule, several tubular electric heaters (heaters) with fins pressed onto them to increase the heat exchange area. The electric power of such devices can reach hundreds of kilowatts.
With a power of 3.5 kW or more, they are connected not to a socket, but directly to the shield with a separate cable; from 7 kW power supply from 380 volts is highly recommended.
In the photo - domestic electric heater ECO.
What are the advantages of an electric heater for ventilation against the background of a water one?
- Ease of installation. Agree that it is much easier to bring a cable to a heating device than to organize the circulation of a coolant in it.
- The absence of problems with the thermal insulation of the eyeliner. Losses in the power cable due to its own electrical resistance are two orders of magnitude less than heat losses in a pipeline with any coolant.
- Easy temperature setting. In order for the supply air temperature to be constant, it is enough to mount a simple control circuit with a temperature sensor in the power supply circuit of the heater. For comparison, a system of water heaters will force you to solve the problems of coordinating the air temperature, coolant and boiler power.
Does the power supply have disadvantages?
- The price of an electric device is slightly higher than a water one. For example, a 45-kilowatt electric heater can be bought for 10-11 thousand rubles; a water heater of the same power will cost only 6-7 thousand.
- More importantly, when using direct heating with electricity, the operating costs are outrageous. To heat the coolant that transfers heat to the air heating water system, the heat of combustion of gas, coal or pellets is used; this heat in terms of kilowatts is much cheaper than electricity.
| Thermal energy source | The cost of a kilowatt-hour of heat, rubles |
| main gas | 0,7 |
| Coal | 1,4 |
| Pellets | 1,8 |
| Electricity | 3,6 |
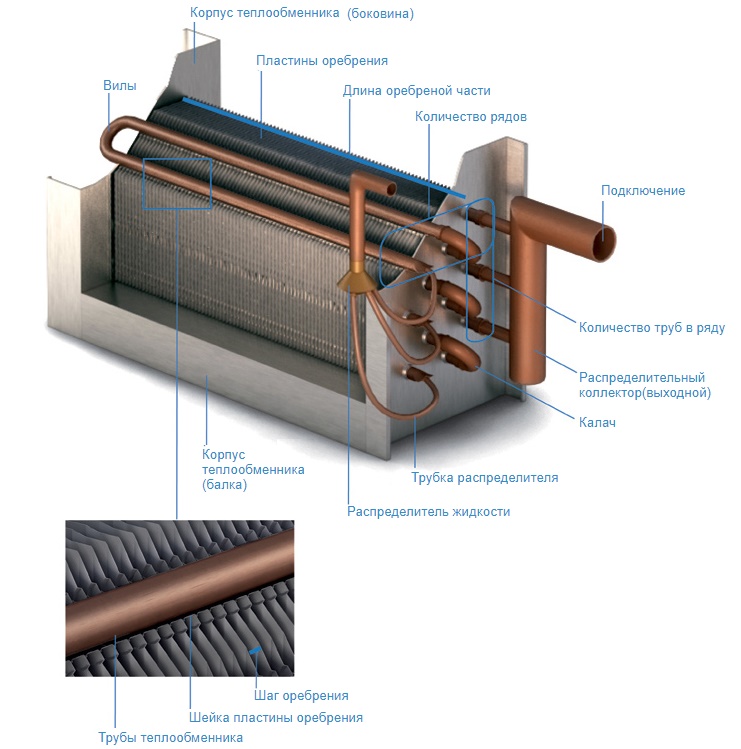
Water heaters for forced ventilation are, in general, ordinary heat exchangers with developed fins.
Water heater.
The water or other coolant circulating through them gives off heat to the air passing through the fins.
The advantages and disadvantages of the scheme mirror the features of the competing solution:
- The cost of the heater is minimal.
- Operating costs are determined by the type of fuel used and the quality of insulation of the coolant wiring.
- Air temperature control is relatively complex and requires a flexible circulation and/or boiler control system.
materials
For electric heaters, aluminum or steel fins are usually used on standard heating elements; somewhat less common heating scheme with an open tungsten coil.
Heating element with steel fins.
For water heaters, three versions are typical.
- Steel pipes with steel fins provide the lowest cost of construction.
- Steel pipes with aluminum fins, due to the higher thermal conductivity of aluminum, guarantee a slightly higher heat transfer.
- Finally, bimetallic heat exchangers made of copper tube with aluminum fins provide maximum heat transfer at the cost of a slightly lower resistance to hydraulic pressure.
non-standard version
A couple of solutions deserve special mention.
- Supply units are a heater with a pre-installed fan for air supply.
Supply ventilation unit.
- In addition, the industry produces products with heat recuperators. Part of the thermal energy is taken from the air flow in the exhaust ventilation.
Types of systems
The supply ventilation unit with air heating is available in several types. It can be central ventilation, which will heat a large industrial premises, or an office center, or it can be individual, for example, in an apartment or in a private house.
In addition, all heated ventilation systems are divided into the following types:
- With recovery. In fact, this is a heat exchange system, when the incoming masses come into contact with the outgoing masses and exchange heat. This option is suitable only for regions with not very cold winters. These systems are referred to as passive ventilation circuits. It is best to place them near the radiators.
- Water. Such a heated supply works either from a boiler or from a central heating battery. Its main advantage is energy savings. Supply ventilation with water heating of air is especially popular with consumers.
- Electrical. Requires significant electricity consumption.According to the principle of operation, this is a simple electric heating element that heats the air with its constant movement.
Supply ventilation can also differ in the way air is forced into the room. There are natural options, and there are forced ones, when air is taken in with the help of fans. The types of ventilation also differ according to the type of control. These can be manual models or automatic, which are controlled using a remote control or from a special application on the phone.
Brief overview of modern models
There are many models on the market mixing units from different manufacturers of climate equipment. Mixing units DEX, SMEX, MU, SUMX, as well as thermal control hydroblocks of the MST, UTK series are produced in various standard sizes with calculated weight and size indicators and connecting dimensions.
You can find out more about them using the links below:
-
Mixing units DEX
-
Mixing units MU
-
Mixing units WPG
-
Mixing units SME and SMEX
-
Mixing units MST
-
Mixing units SURP and SUR
-
Mixing units SWU
-
Mixing units VDL
-
Water mixing units UVS
-
Mixing units KEV-UTM
1 Features and principle of operation
The design of such a heater includes a housing inside which there is a fan and a heat exchanger. Management is carried out by means of a special block. When the device is turned on, the blades create an air flow that spreads throughout the room. Thanks to this, it is possible to achieve good heating in a short period of time.
In industrial enterprises, it is quite difficult to maintain a comfortable temperature only due to radiators. They are effective, but are usually less useful in these conditions. Installing heaters and other heaters is expensive. The cost of not only equipment is high, but also its subsequent maintenance, as well as payment for electricity. As a rule, such models are very energy-intensive. It is advisable to install fan heaters with a water heat source in the following rooms:
- large trading floors;
- greenhouses or greenhouses that operate during the cold season;
- production shops and warehouses with a large number of products;
- large car washes, as well as service stations;
- garages with a large area, hangars;
- large gyms.
Despite the fact that the device is intended for industrial use, some owners of cottages or large private houses use it for space heating. This is due to the simplicity of design and the possibility of self-manufacturing at home.
Calculation-online of electric heaters. Selection of electric heaters by power - T.S.T.
Skip to content This page of the site presents an online calculation of electric heaters. The following data can be determined online: - 1. the required output (heat output) of the electric air heater for the air handling unit. Basic parameters for calculation: volume (flow rate, performance) of the heated air flow, air temperature at the inlet to the electric heater, desired outlet temperature - 2. air temperature at the outlet of the electric heater.Basic parameters for calculation: consumption (volume) of the heated air flow, air temperature at the inlet to the electric heater, actual (installed) thermal power of the electrical module used
1. Online calculation of the power of the electric heater (heat consumption for heating the supply air)
The following indicators are entered into the fields: the volume of cold air passing through the electric heater (m3/h), the temperature of the incoming air, the required temperature at the outlet of the electric heater. At the output (according to the results of the online calculation of the calculator), the required power of the electric heating module is displayed to comply with the set conditions.
1 field. The volume of supply air passing through the electric heater (m3/h)2 field. Air temperature at the inlet to the electric heater (°С)
3 field. Required air temperature at the outlet of the electric heater
(°C) field (result). Required power of the electric heater (heat consumption for supply air heating) for the entered data
2. Online calculation of the air temperature at the outlet of the electric heater
The following indicators are entered into the fields: the volume (flow) of heated air (m3/h), the air temperature at the inlet to the electric heater, the power of the selected electric air heater. At the outlet (according to the results of the online calculation), the temperature of the outgoing heated air is displayed.
1 field. The volume of supply air passing through the heater (m3/h)2 field. Air temperature at the inlet to the electric heater (°С)
3 field. Thermal power of the selected air heater
(kW) field (result). Air temperature at the outlet of the electric heater (°С)
Online selection of an electric heater by the volume of heated air and heat output
Below is a table with the nomenclature of electric heaters produced by our company. According to the table, you can roughly select the electrical module suitable for your data. Initially, focusing on the indicators of the volume of heated air per hour (air productivity), you can choose an industrial electric heater for the most common thermal conditions. For each heating module of the SFO series, the most acceptable (for this model and number) range of heated air is presented, as well as some ranges of air temperature at the inlet and outlet of the heater. By clicking on the name of the selected electric air heater, you can go to the page with the thermal characteristics of this electric industrial air heater.
| Name of electric heater | Installed power, kW | Air performance range, m³/h | Inlet air temperature, °С | Outlet air temperature range, °C (depending on air volume) |
| SFO-16 | 15 | 800 — 1500 | -25 | +22 0 |
| -20 | +28 +6 | |||
| -15 | +34 +11 | |||
| -10 | +40 +17 | |||
| -5 | +46 +22 | |||
| +52 +28 | ||||
| SFO-25 | 22.5 | 1500 — 2300 | -25 | +13 0 |
| -20 | +18 +5 | |||
| -15 | +24 +11 | |||
| -10 | +30 +16 | |||
| -5 | +36 +22 | |||
| +41 +27 | ||||
| SFO-40 | 45 | 2300 — 3500 | -30 | +18 +2 |
| -25 | +24 +7 | |||
| -20 | +30 +13 | |||
| -10 | +42 +24 | |||
| -5 | +48 +30 | |||
| +54 +35 | ||||
| SFO-60 | 67.5 | 3500 — 5000 | -30 | +17 +3 |
| -25 | +23 +9 | |||
| -20 | +29 +15 | |||
| -15 | +35 +20 | |||
| -10 | +41 +26 | |||
| -5 | +47 +32 | |||
| SFO-100 | 90 | 5000 — 8000 | -25 | +20 +3 |
| -20 | +26 +9 | |||
| -15 | +32 +14 | |||
| -10 | +38 +20 | |||
| -5 | +44 +25 | |||
| +50 +31 | ||||
| SFO-160 | 157.5 | 8000 — 12000 | -30 | +18 +2 |
| -25 | +24 +8 | |||
| -20 | +30 +14 | |||
| -15 | +36 +19 | |||
| -10 | +42 +25 | |||
| -5 | +48 +31 | |||
| SFO-250 | 247.5 | 12000 — 20000 | -30 | +21 0 |
| -25 | +27 +6 | |||
| -20 | +33 +12 | |||
| -15 | +39 +17 | |||
| -10 | +45 +23 | |||
| -5 | +51 +29 |