- Warm floor power calculation
- System load
- Calculation of heat transfer power: calculator
- Some Tips
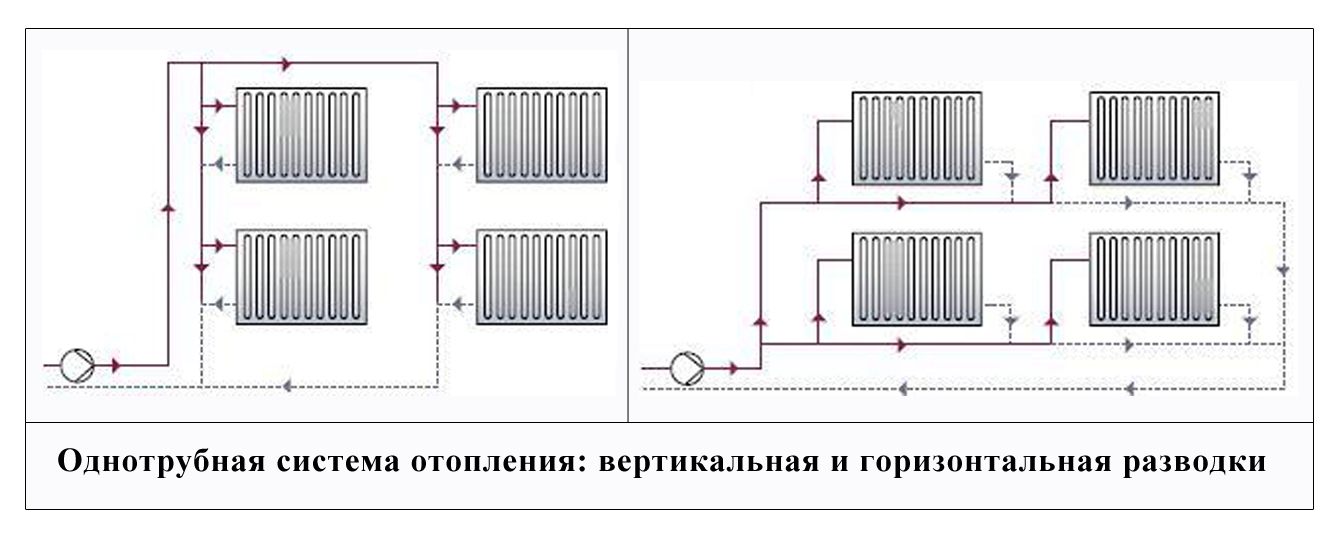
- Calculation of different types of radiators
- Scheme of connecting a water heated floor to a boiler
- Diagram with a three-way valve
- Scheme with a mixing unit
- Scheme with an electronic thermostat
- Direct Connection Diagram
- Recommendations for the selection of materials
- How many meters is the optimal length of the circuit
- Calculation of energy consumption in one room
- Design Features
- Pressure in the heating system of a multi-storey building
- We calculate the circulation pump
- What is required for the calculation
- Which gender to choose?
- Conclusion
- Methods for calculating the heat transfer of heating pipes
Warm floor power calculation
The determination of the required power of a warm floor in a room is influenced by the heat loss indicator, for an accurate determination of which it will be necessary to make a complex heat engineering calculation using a special method.
- This takes into account the following factors:
- the area of the heated surface, the total area of the room;
- area, type of glazing;
- presence, area, type, thickness, material and thermal resistance of walls and other enclosing structures;
- the level of penetration of sunlight into the room;
- the presence of other sources of heat, including the heat emitted by equipment, various devices and people.
The technique for performing such accurate calculations requires deep theoretical knowledge and experience, and therefore it is better to entrust heat engineering calculations to specialists.
After all, only they know how to calculate the power of a warm water floor with the smallest error and optimal parameters.
This is especially important when designing heated built-in heating in rooms with a large area and high height.
Laying and efficient operation of a heated water floor is possible only in rooms with a heat loss level of less than 100 W / m². If the heat loss is higher, it is necessary to take measures to insulate the room in order to reduce heat loss.
However, if the design engineering calculation costs a lot of money, in the case of small rooms, approximate calculations can be carried out independently, taking 100 W / m² as an average value and the starting point in further calculations.
- At the same time, for a private house, it is customary to adjust the average heat loss rate based on the total area of \u200b\u200bthe building:
- 120 W / m² - with a house area of up to 150 m²;
- 100 W / m² - with an area of 150-300 m²;
- 90 W/m² - with an area of 300-500 m².
System load
- The power of a water heated floor per square meter is influenced by such parameters that create a load on the system, determine the hydraulic resistance and the level of heat transfer, such as:
- the material from which the pipes are made;
- circuit laying scheme;
- the length of each contour;
- diameter;
- distance between pipes.
Characteristic:
Pipes can be copper (they have the best thermal and operational characteristics, but they are not cheap and require special skills, as well as tools).
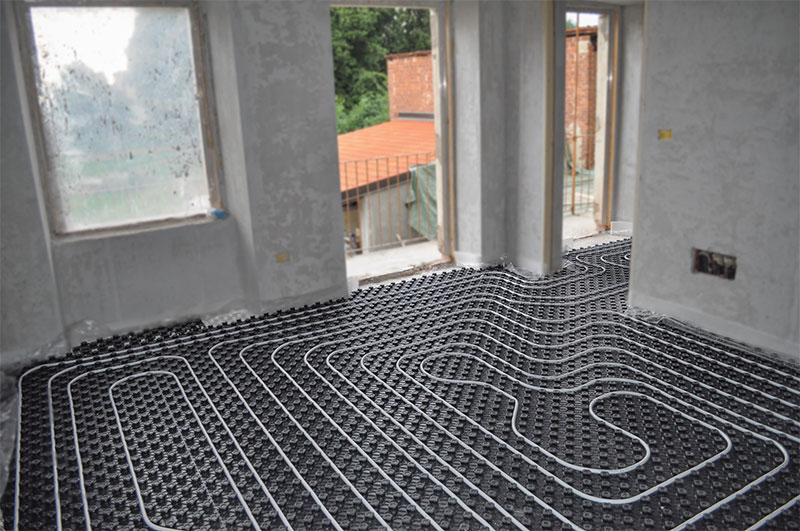
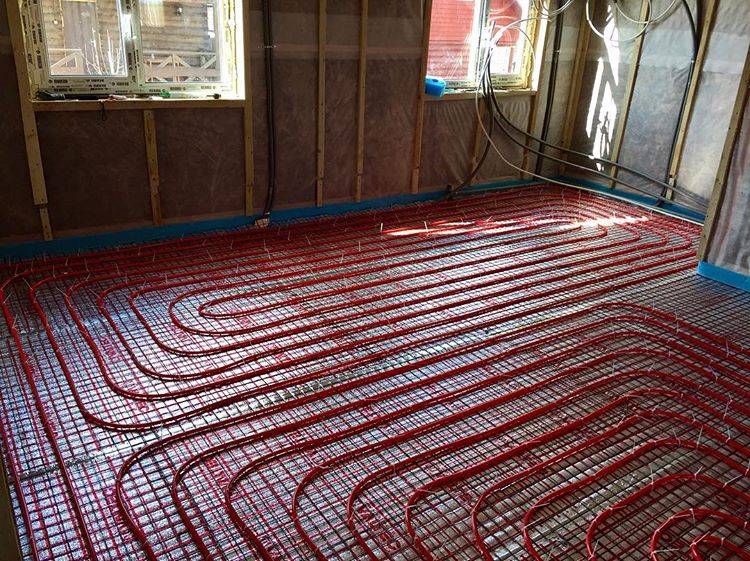
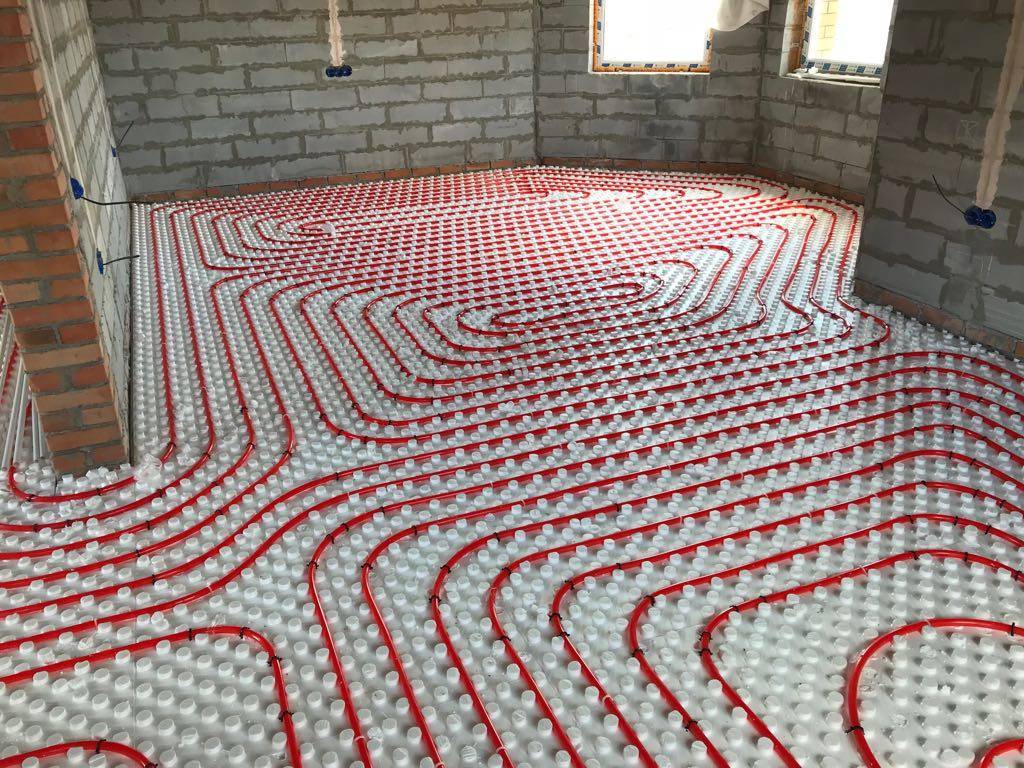
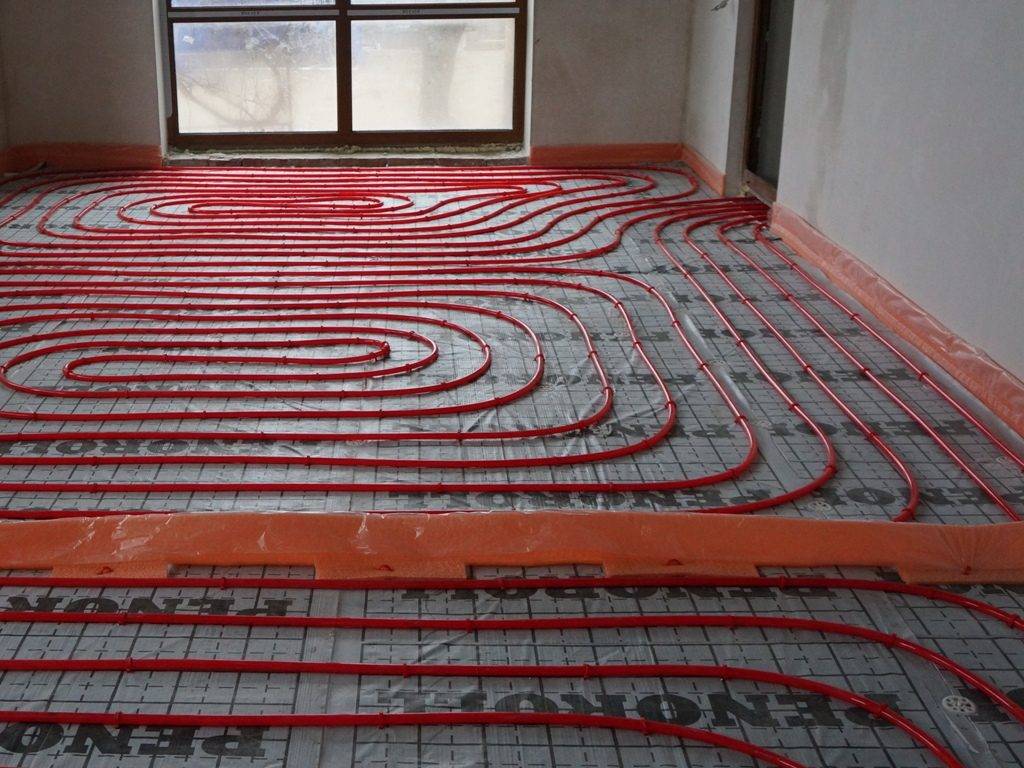
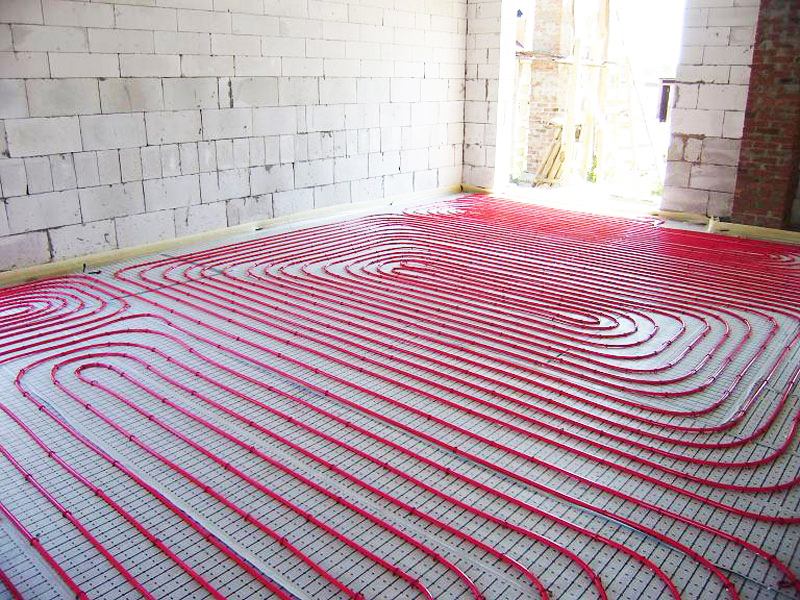
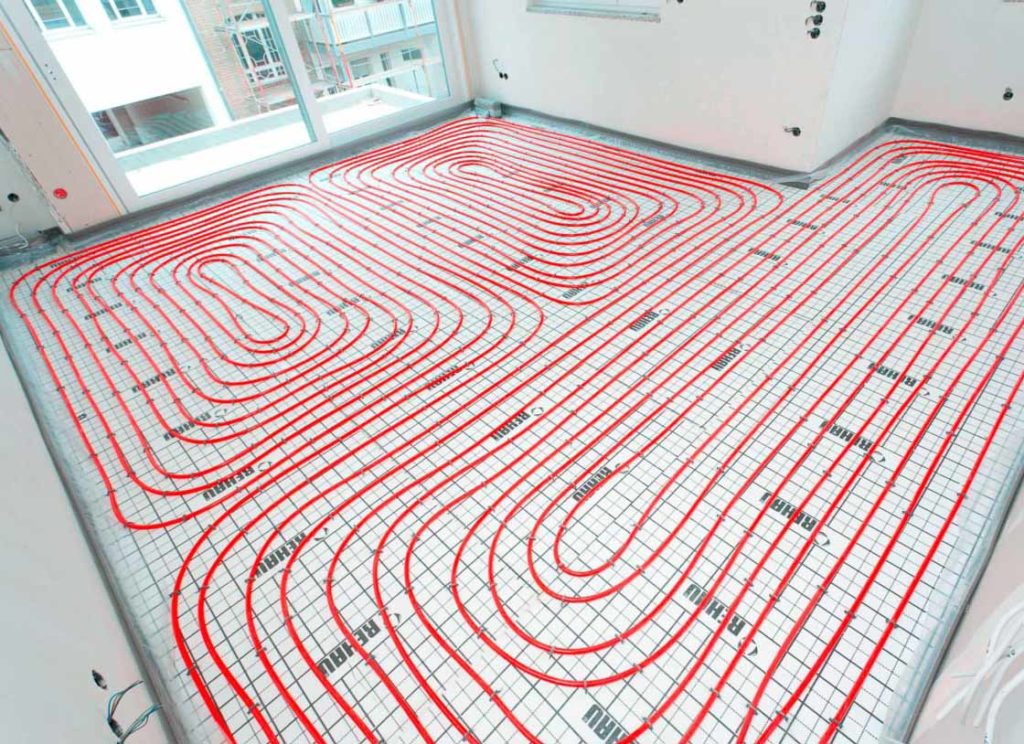
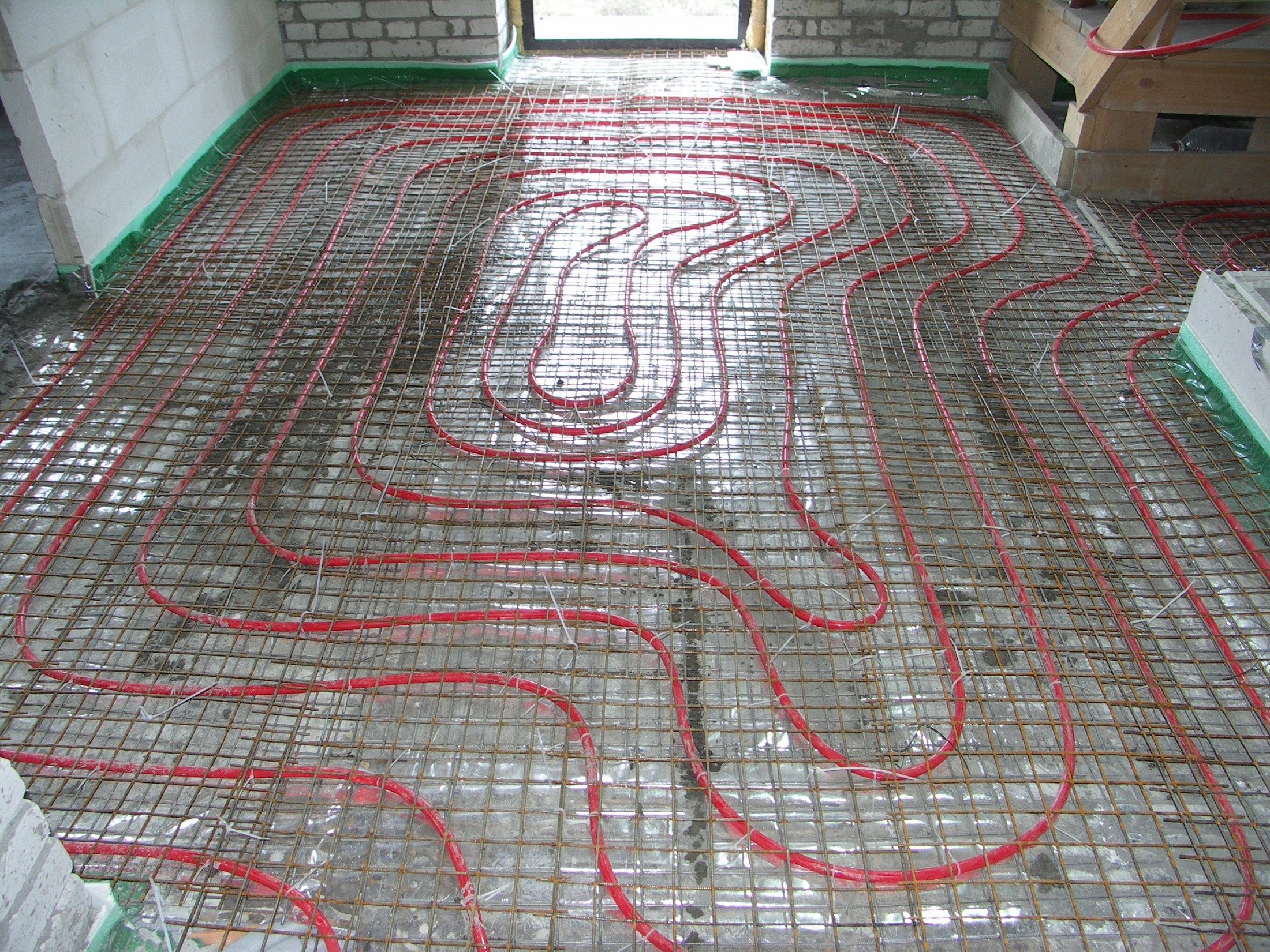
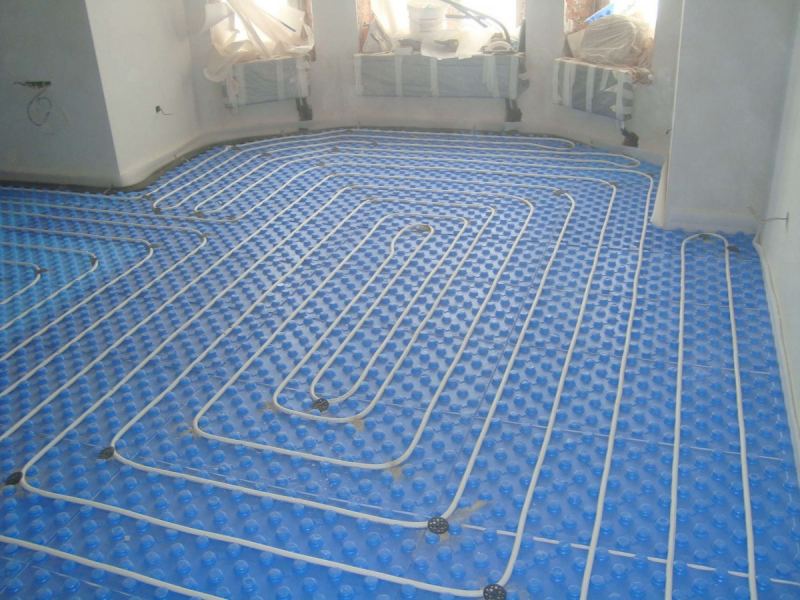
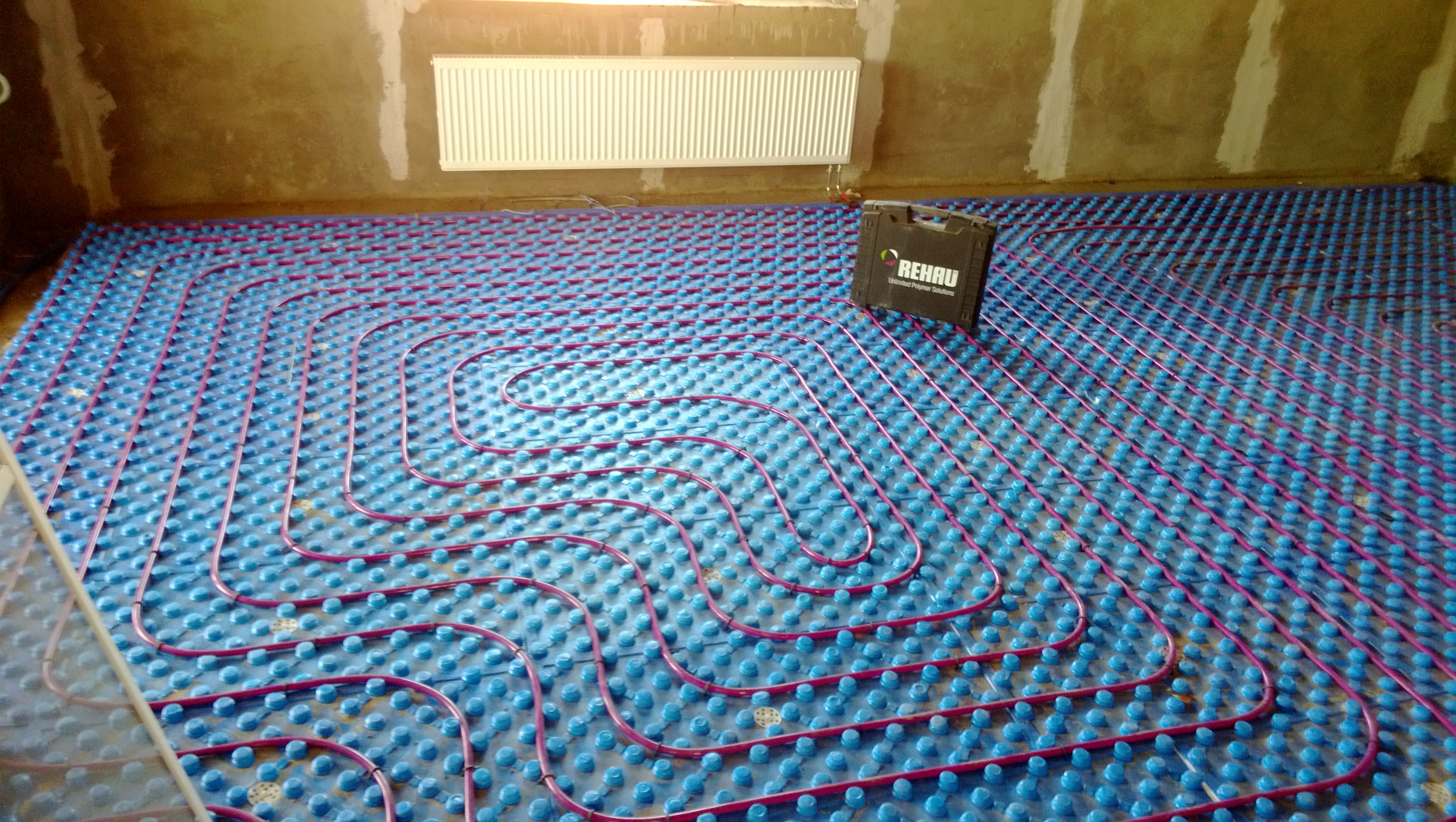
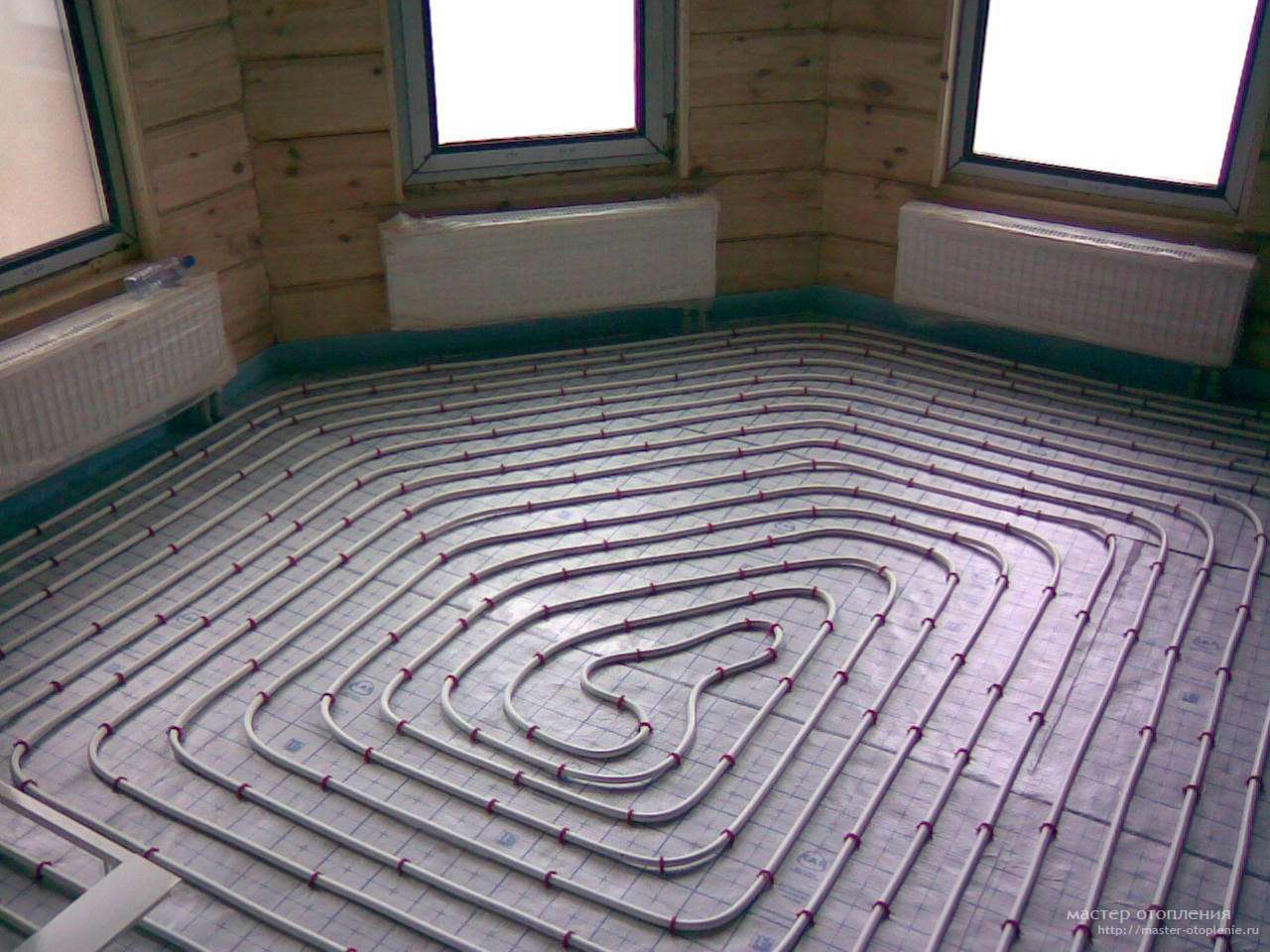
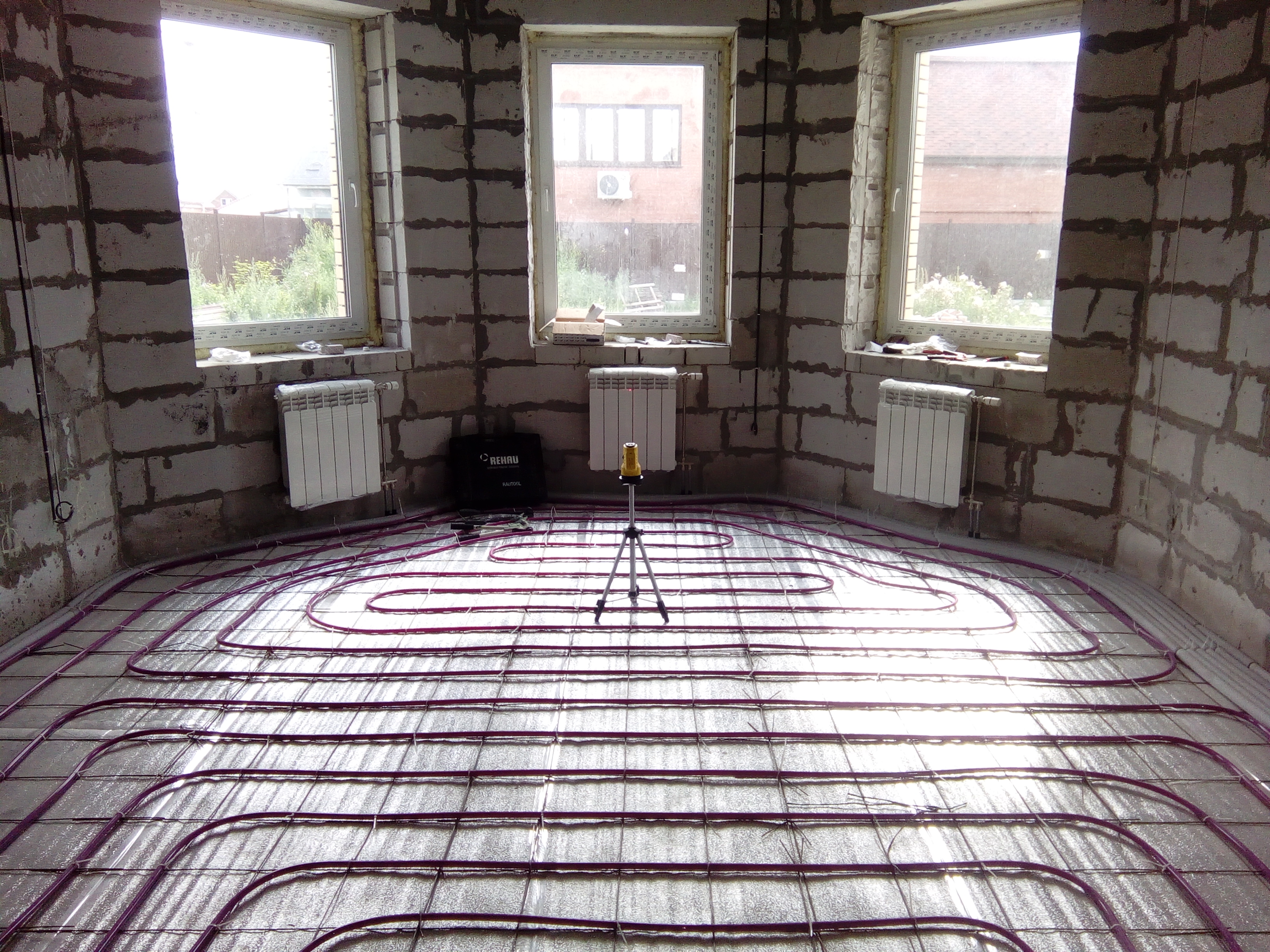
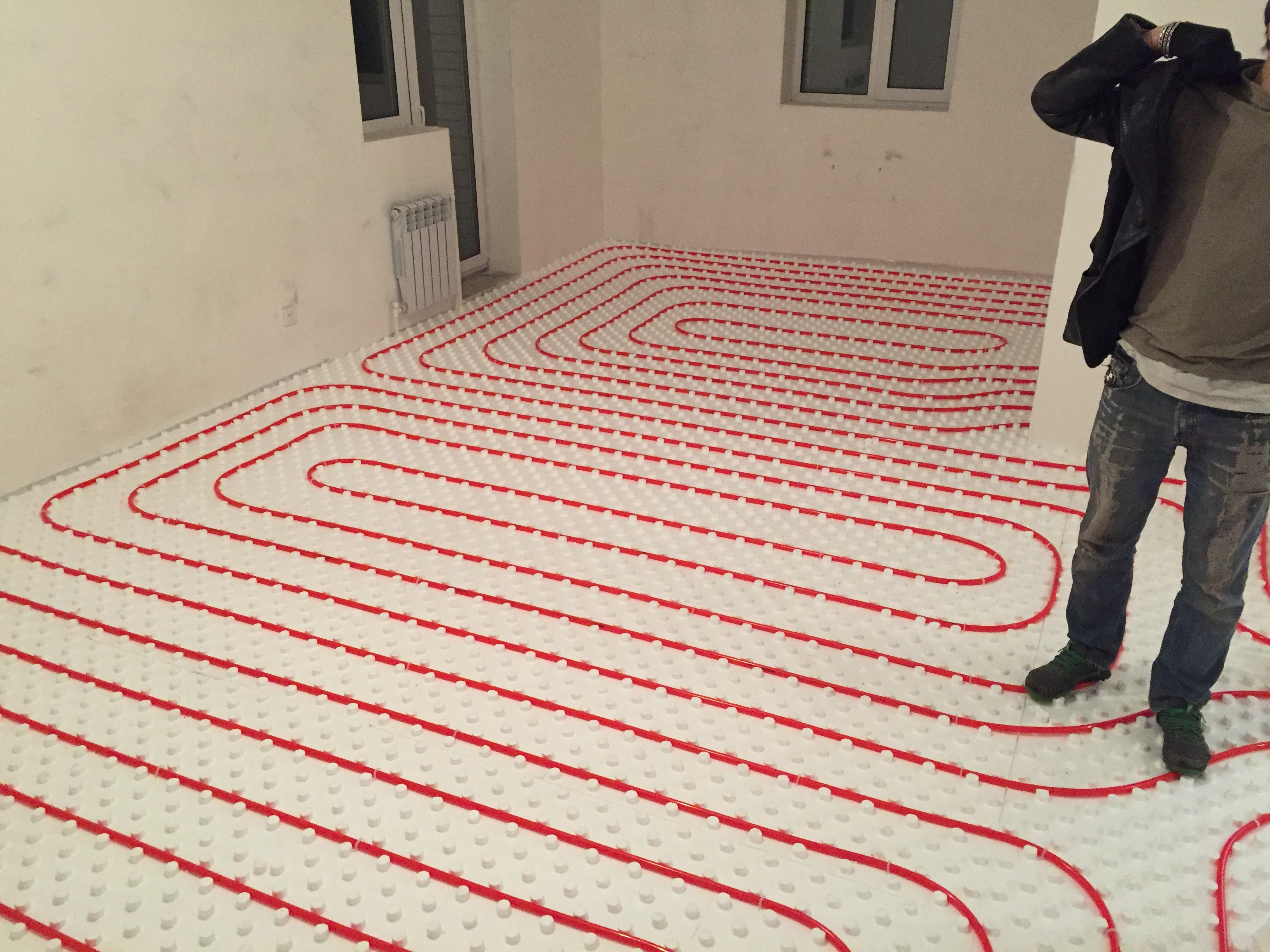
There are two main contour laying patterns: a snake and a snail.The first option is the simplest, but less effective, as it gives uneven floor heating. The second one is more difficult to implement, but the heating efficiency is an order of magnitude higher.
The area heated by one circuit must not exceed 20 m². If the heated area is larger, then it is advisable to divide the pipeline into 2 or more circuits, connecting them to a distribution manifold with the ability to control the heating of floor sections.
The total length of the pipes of one circuit should be no more than 90 m. In this case, the larger the diameter chosen, the greater the distance between the pipes. As a rule, pipes with a diameter of more than 16 mm are not used.
Each parameter has its own coefficients for further calculations, which can be viewed in reference books.
Calculation of heat transfer power: calculator
To determine the power of the water floor, it is necessary to find the product of the total area of \u200b\u200bthe room (m²), the temperature difference between the supply and return fluid, and coefficients depending on the material of the pipes, flooring (wood, linoleum, tiles, etc.), other elements of the system .
The power of a water heated floor per 1 m², or heat transfer, should not exceed the level of heat loss, but not more than 25%. If the value is too small or too large, it is necessary to recalculate by choosing a different pipe diameter and distance between the contour threads.
The power indicator is the higher, the larger the diameter of the selected pipes, and the lower, the larger the pitch is set between the threads. To save time, you can use electronic calculators for calculating the water floor or download a special program.
Some Tips
Before calculating the need for heat transfer, you need to take into account some points.Initially, it is necessary to determine the maximum thermal conductivity of the material that are located above the pipes, films and cables that act as heating elements. The efficiency of heat transfer depends directly proportional to the heat power, inversely proportional to the resistance of the coating.
All pipes and materials that will be located below the level of the heating element must be highly thermally insulated. This will eliminate possible heat loss through the coatings. If the installation and calculation are carried out correctly, then the thermal insulation will block the transfer of heat and reflect thermal radiation.
The need for thermal power is determined by thermal insulation and its quality. It is preferable to adhere to standards that will guarantee high performance and comfort.
Remember that if you have chosen a warm floor, you should not clutter it up with massive furniture designs. This will not bring the proper result of heating, and overheating and damage to furniture under the influence of temperatures is also possible.
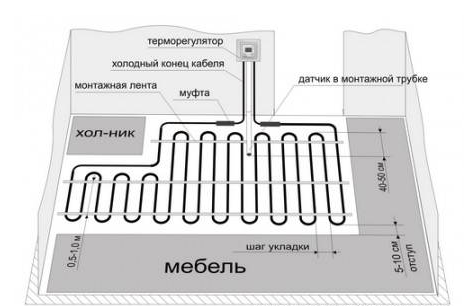
An example of laying a warm floor in the kitchen
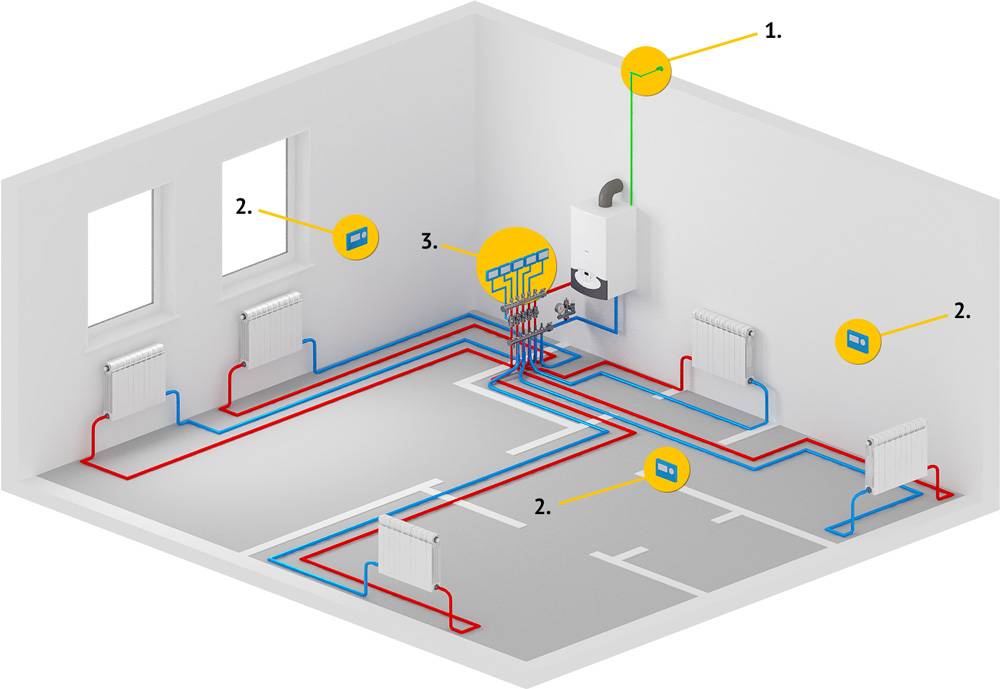
Calculation of different types of radiators
If you are going to install sectional radiators of a standard size (with an axial distance of 50 cm in height) and have already chosen the material, model and the desired size, there should be no difficulty in calculating their number. Most of the reputable companies that supply good heating equipment have the technical data of all modifications on their website, among which there is also thermal power. If not power is indicated, but the flow rate of the coolant, then it is easy to convert to power: the coolant flow rate of 1 l / min is approximately equal to the power of 1 kW (1000 W).
The axial distance of the radiator is determined by the height between the centers of the holes for supplying/removing the coolant
To make life easier for buyers, many sites install a specially designed calculator program. Then the calculation of sections of heating radiators comes down to entering data on your room in the appropriate fields. And at the output you have the finished result: the number of sections of this model in pieces.

The axial distance is determined between the centers of the holes for the coolant
But if you are just considering possible options for now, then it is worth considering that radiators of the same size made of different materials have different thermal output. The method for calculating the number of sections of bimetallic radiators is no different from the calculation of aluminum, steel or cast iron. Only the thermal power of one section can be different.
To make it easier to calculate, there are average data that you can navigate. For one section of the radiator with an axial distance of 50 cm, the following power values are accepted:
- aluminum - 190W
- bimetallic - 185W
- cast iron - 145W.
If you are still only figuring out which material to choose, you can use these data. For clarity, we present the simplest calculation of sections of bimetallic heating radiators, which takes into account only the area of \u200b\u200bthe room.
When determining the number of bimetal heaters of a standard size (center distance 50 cm), it is assumed that one section can heat 1.8 m 2 of area. Then for a room of 16m 2 you need: 16m 2 / 1.8m 2 \u003d 8.88 pieces. Rounding up - 9 sections are needed.
Similarly, we consider for cast-iron or steel bars. All you need is the rules:
- bimetallic radiator - 1.8m 2
- aluminum - 1.9-2.0m 2
- cast iron - 1.4-1.5m 2.
This data is for sections with a center distance of 50cm. Today, there are models on sale with very different heights: from 60cm to 20cm and even lower. Models 20cm and below are called curb. Naturally, their power differs from the specified standard, and if you plan to use "non-standard", you will have to make adjustments. Or look for passport data, or count yourself. We proceed from the fact that the heat transfer of a thermal device directly depends on its area. With a decrease in height, the area of \u200b\u200bthe device decreases, and, therefore, the power decreases proportionally. That is, you need to find the ratio of the heights of the selected radiator to the standard, and then use this coefficient to correct the result.

Calculation of cast iron radiators. Can count on area or volume premises
For clarity, we will calculate aluminum radiators by area. The room is the same: 16m 2. We consider the number of sections of a standard size: 16m 2 / 2m 2 \u003d 8pcs. But we want to use small sections with a height of 40 cm. We find the ratio of radiators of the selected size to the standard ones: 50cm/40cm=1.25. And now we adjust the quantity: 8pcs * 1.25 = 10pcs.
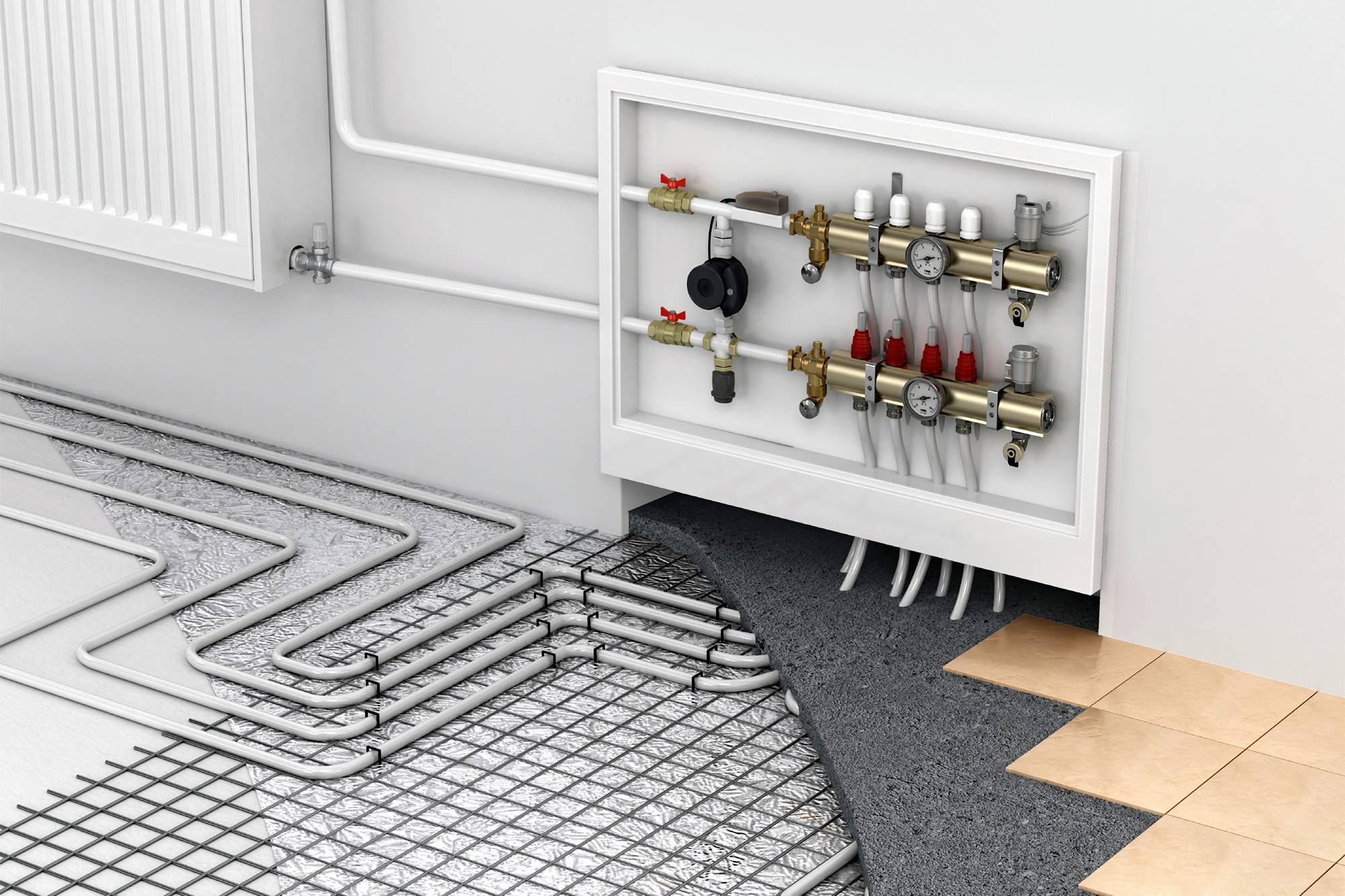
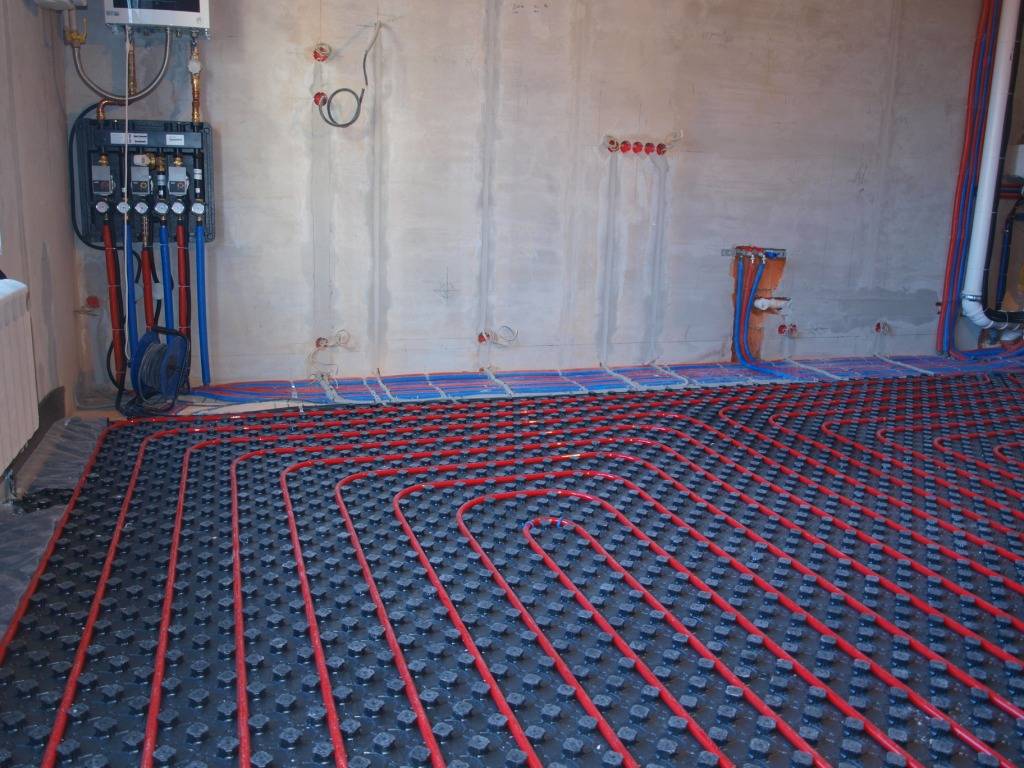
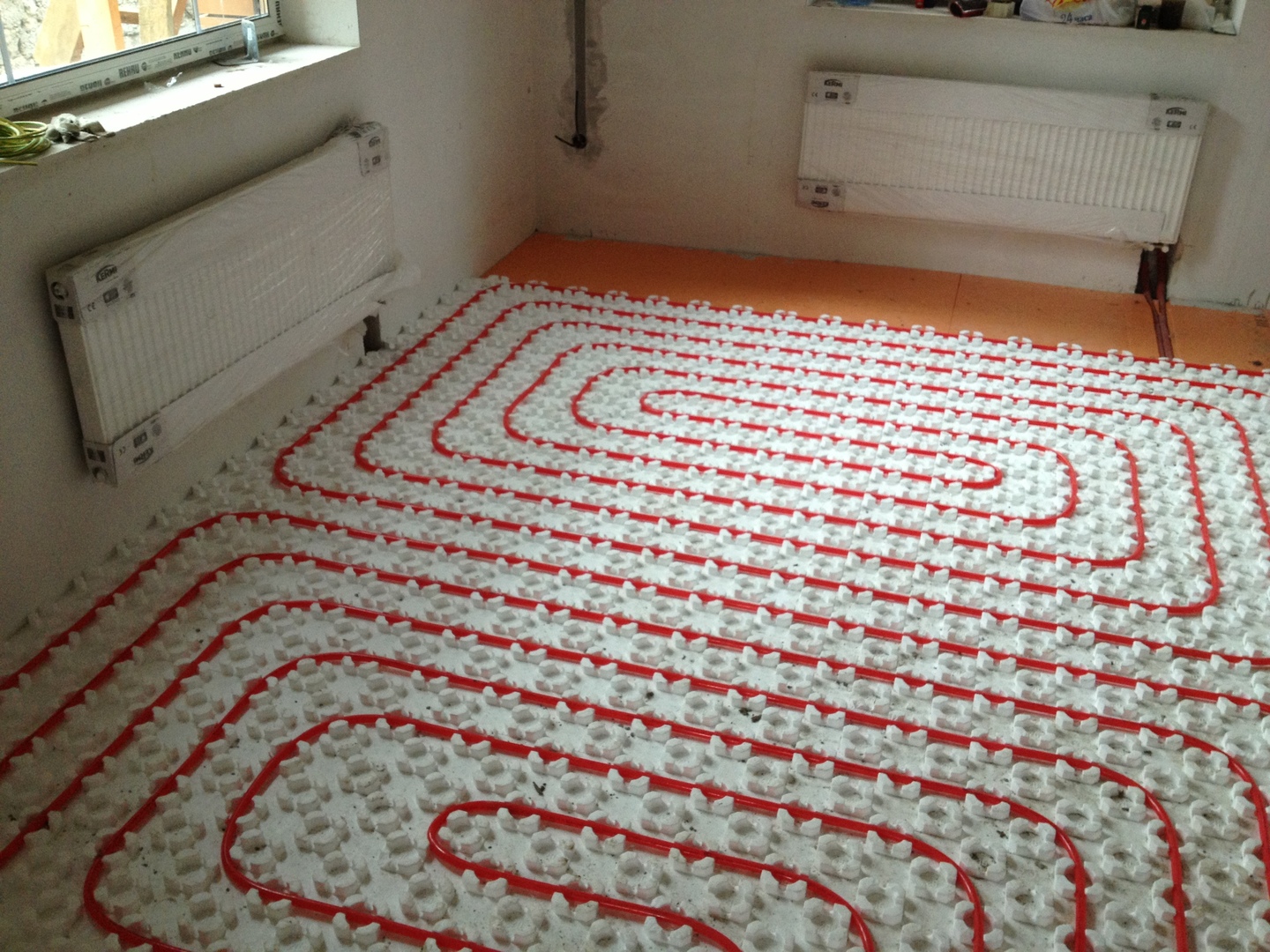
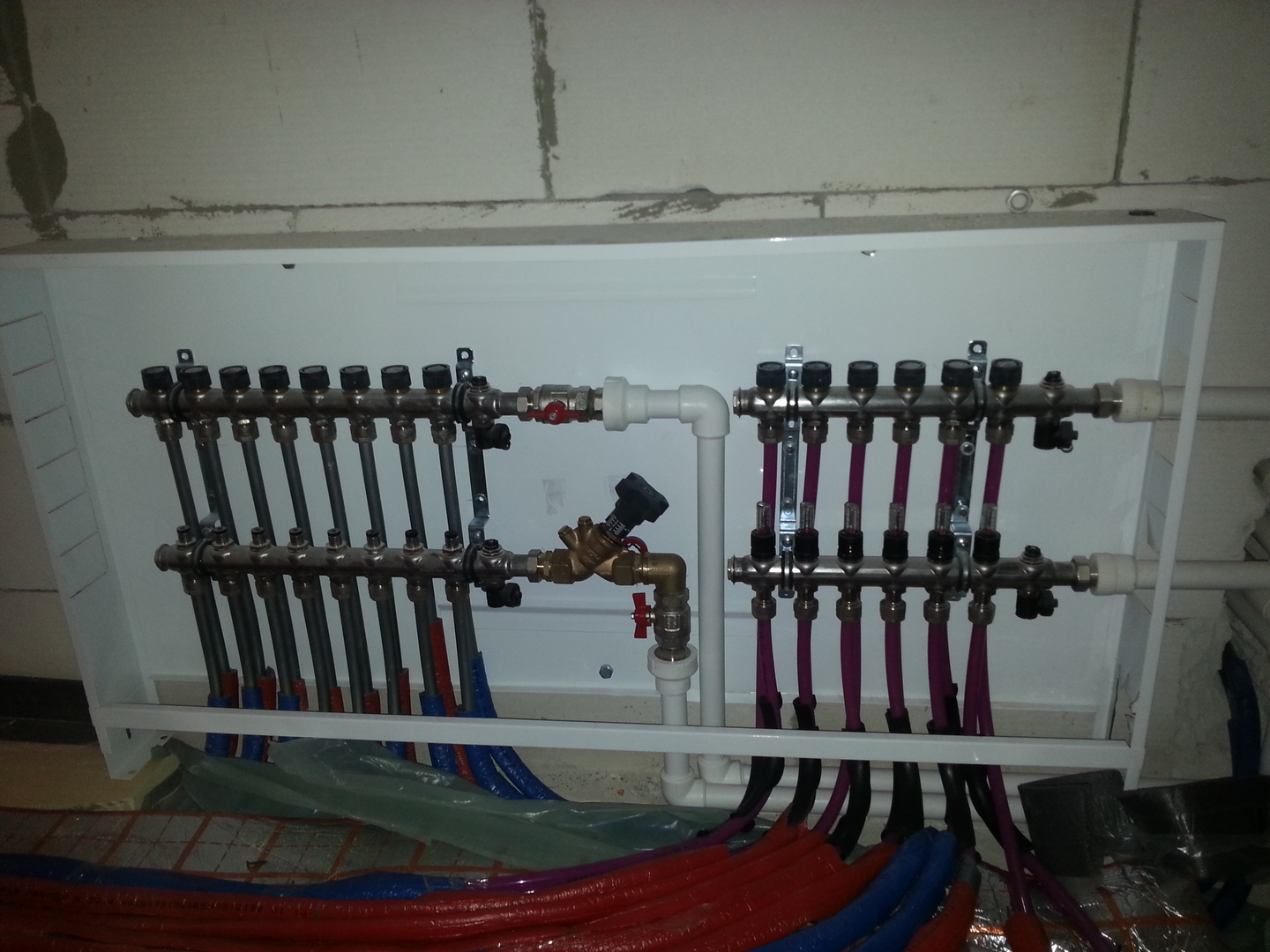
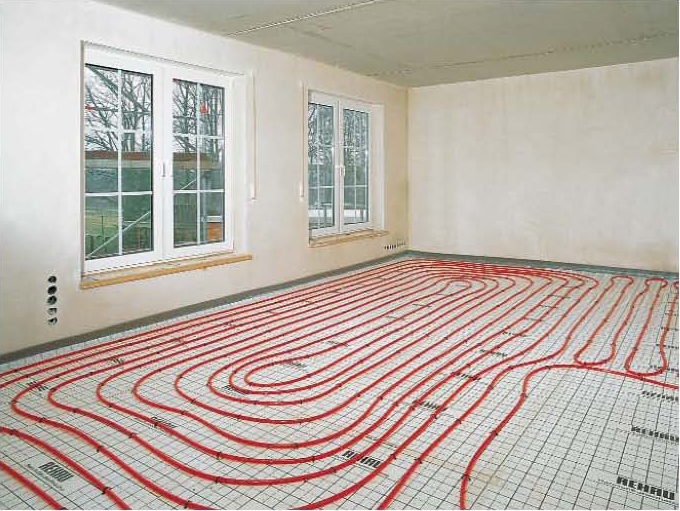
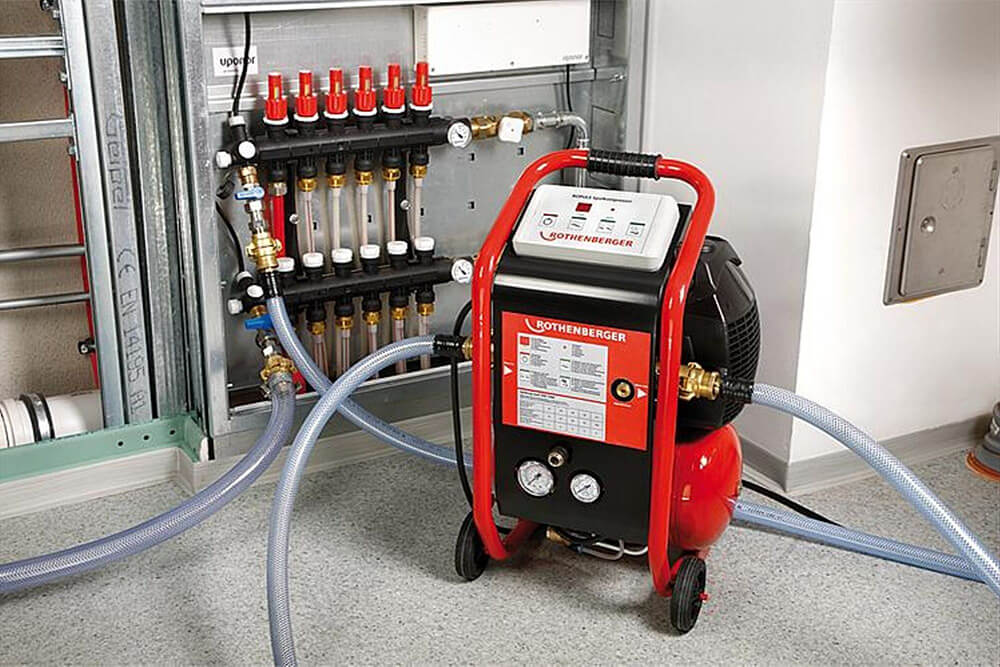
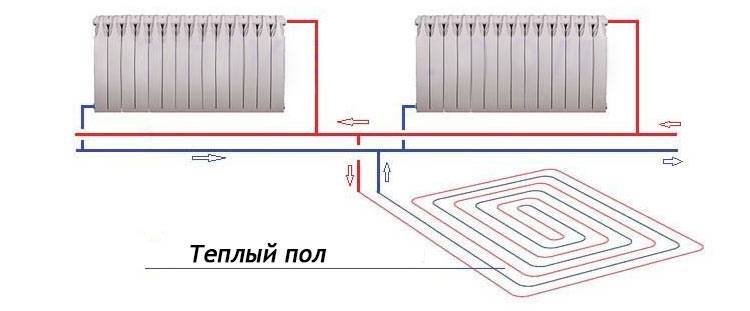
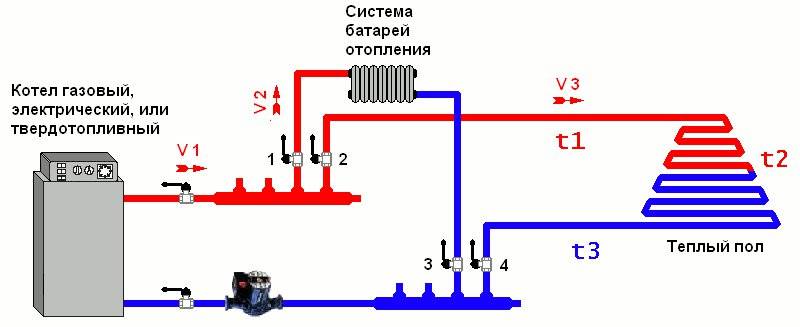
Scheme of connecting a water heated floor to a boiler
There are different ways to tie a boiler with a warm floor. All of them have positive and negative sides, and are designed for certain conditions. Consider popular connection schemes water heated floors to the boiler.
Diagram with a three-way valve
A common scheme for a multi-circuit system with different heating devices is with a three-way valve.Suitable for combined heating - radiators, water temperature 80 degrees, and underfloor heating - 45.
To ensure such a temperature difference, the installation of a three-way valve with a circulation pump will help. The required level of heating of the coolant is achieved by mixing water from the boiler with the water coming from the return. Portions of cold liquid admixture are regulated by opening or closing the valve.
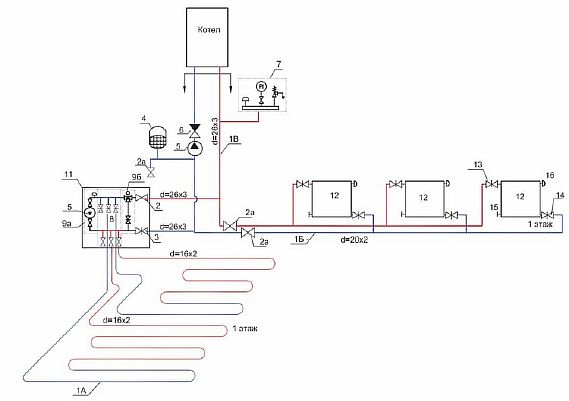
Scheme with a mixing unit
The method is intended for combined systems - batteries and TP. Here, instead of a thermostatic valve, a pump-mixing unit is mounted.
Connecting the collector to the boiler is an energy-efficient scheme, in which, with the help of a balancing valve, hot and chilled water is mixed in strict proportions.
Scheme with an electronic thermostat
The TP supply system functions with the help of small-sized thermoelectronic sets, they can ensure the operation of only one loop heating an area of no more than 20 m2.
The thermostat is a small device with a plastic case that contains:
The principle of operation of the circuit is simple - the heated liquid is sent to the circuit directly from the boiler, without admixture. Temperature control is carried out by a built-in regulator.
He gives the command to the electromechanical valve, which is responsible for supplying gas to the boiler. Water moves along the circuit without the action of the pump, and is cooled directly inside the loop.
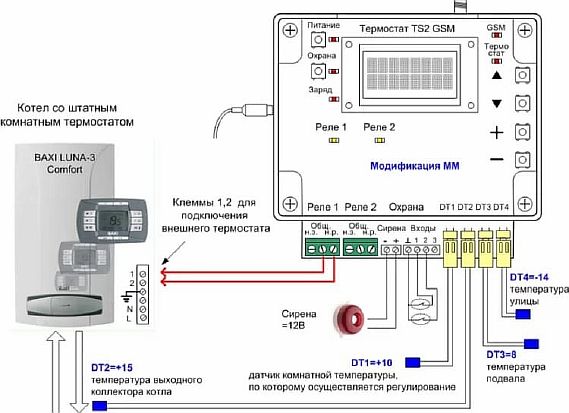
The circuit is simple and such a strapping is not expensive, but it does not allow fine-tuning. She fits:
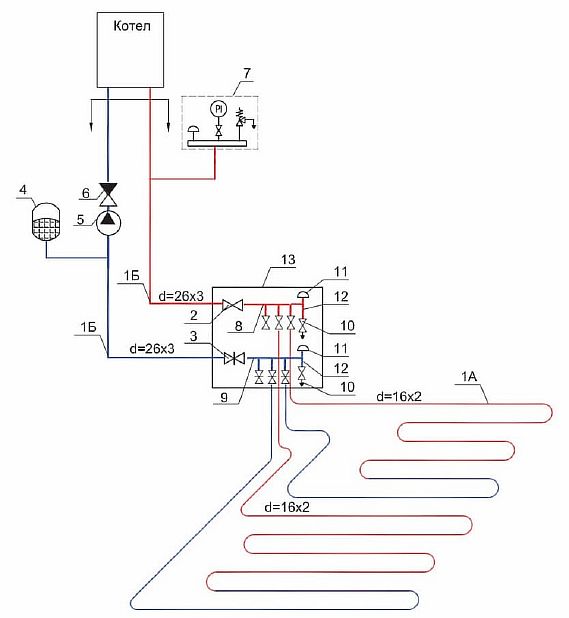
Direct Connection Diagram
To power the floor according to this scheme, a hydraulic arrow is used.The method differs in that when connecting a heated floor to a boiler with a pump, its circuit must have a pumping unit that works together with a thermostat. They will regulate the speed of movement of the liquid, taking into account the air temperature.
The process is as follows - the heated water from the boiler moves into the hydraulic collector, where it is distributed along the contours of the floor. After passing through the loops, it returns to the heater through the return pipe.
This method is mainly used only on condensing devices, since with this scheme, the temperature does not drop on the supply pipe. If you install a conventional gas boiler, then working in this mode will lead to a quick breakdown of the heat exchanger.
When installing a solid fuel boiler, in order for the system to function correctly, it will be necessary to install a buffer tank, and this will limit the temperature level.
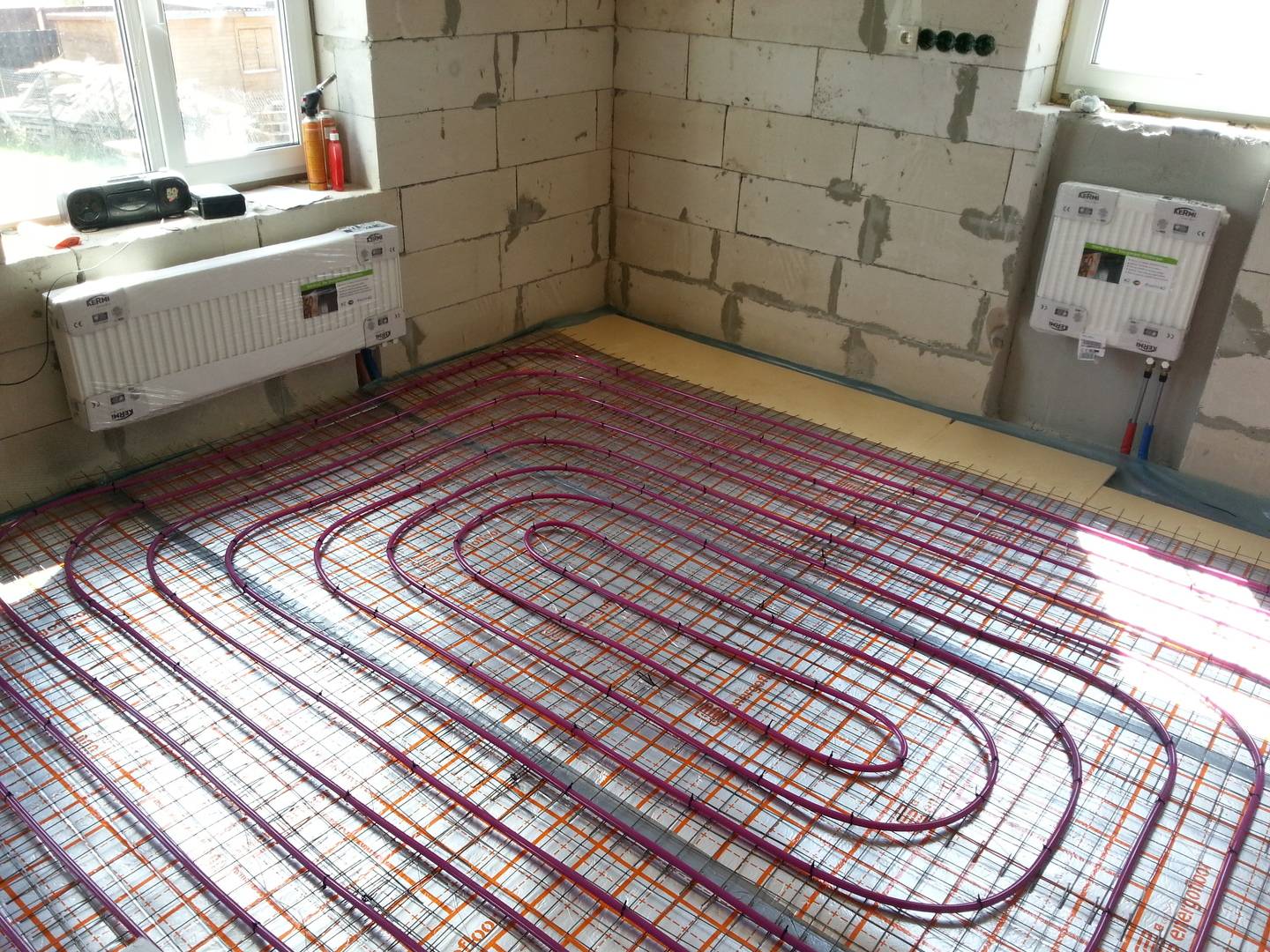
Recommendations for the selection of materials
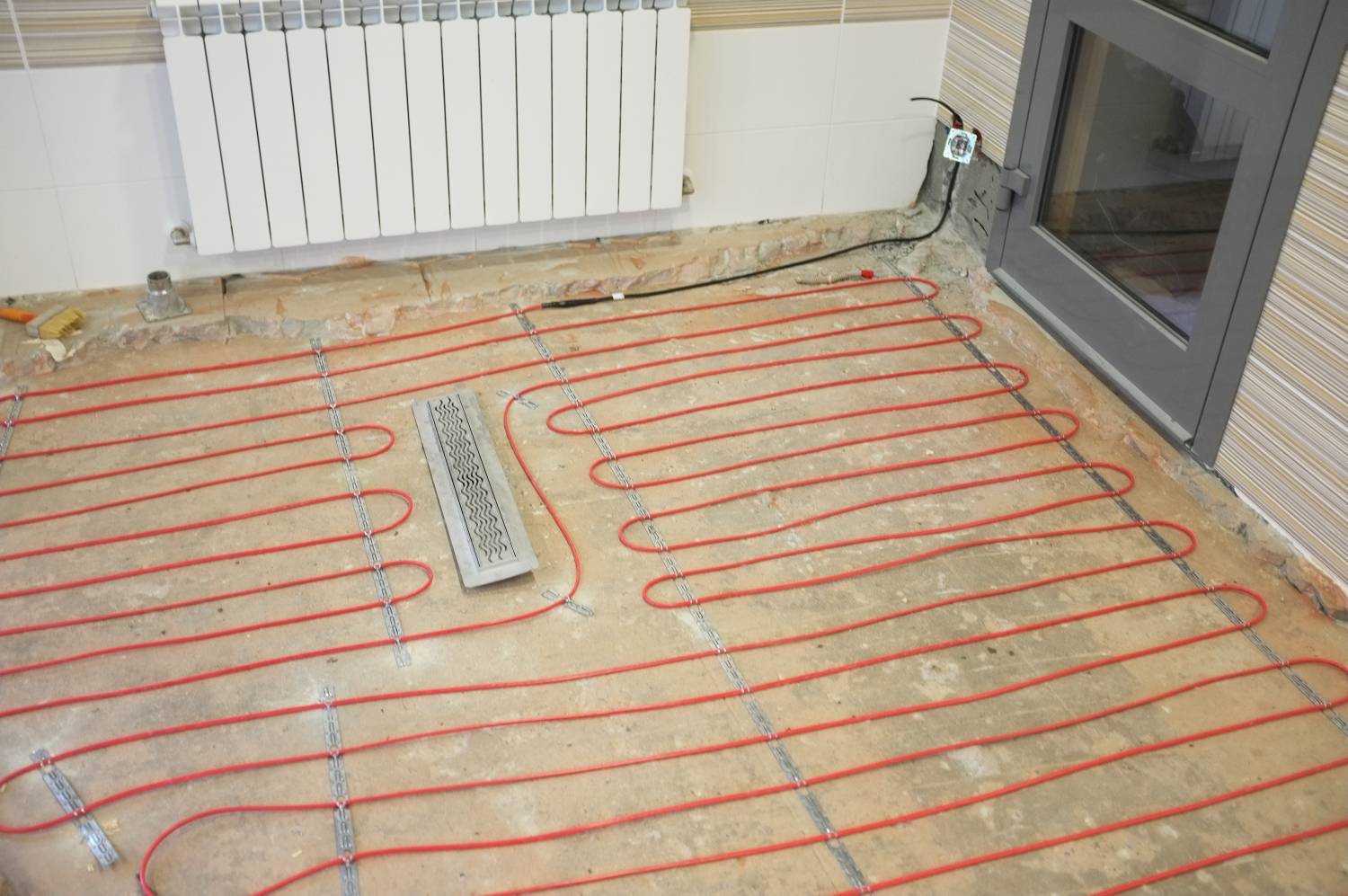
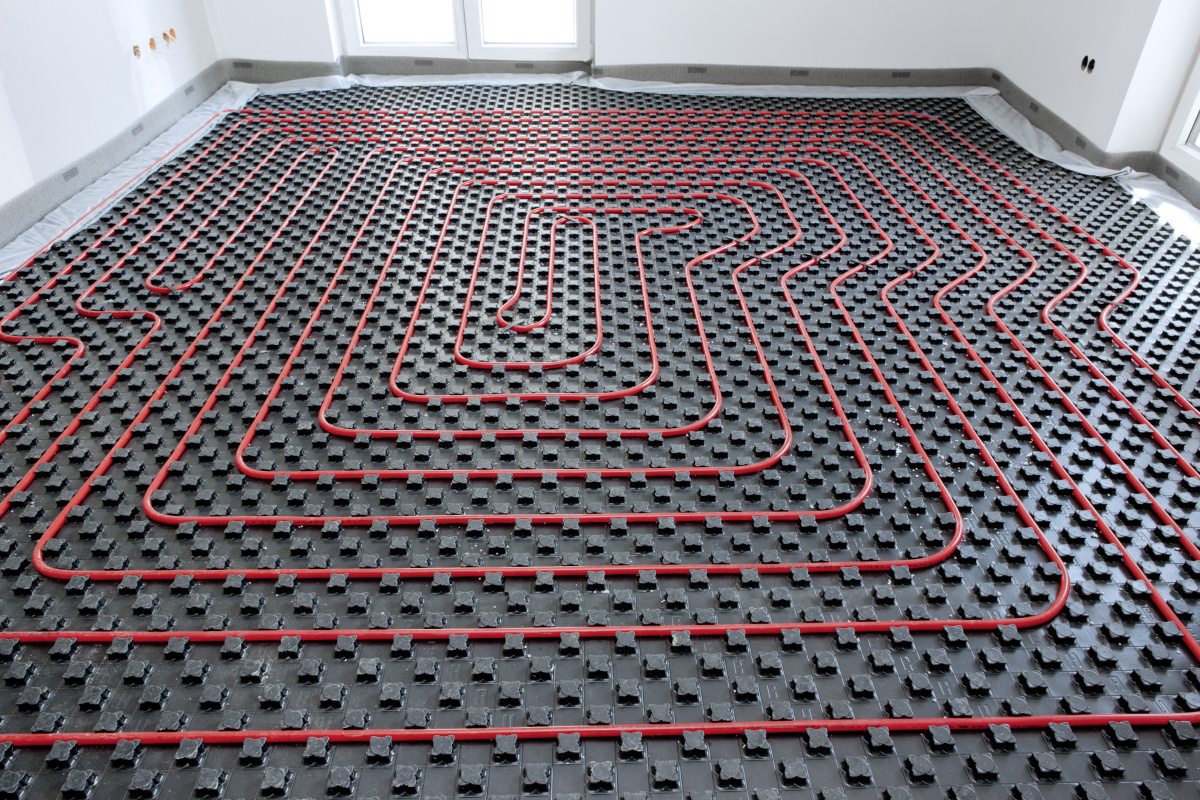
Here is a list of equipment and building materials that will be used for the installation of a water heated floor:
- pipe with a diameter of 16 mm (internal passage - DN10) of estimated length;
- polymer insulation - foam plastic with a density of 35 kg / m³ or extruded polystyrene foam 30-40 kg / m³;
- damper tape made of polyethylene foam, you can take "Penofol" without foil 5 mm thick;
- mounting polyurethane foam;
- film 200 microns thick, adhesive tape for sizing;
- plastic staples or clamps + masonry mesh at the rate of 3 attachment points per 1 meter of pipe (interval 40 ... 50 cm);
- thermal insulation and protective covers for pipes crossing expansion joints;
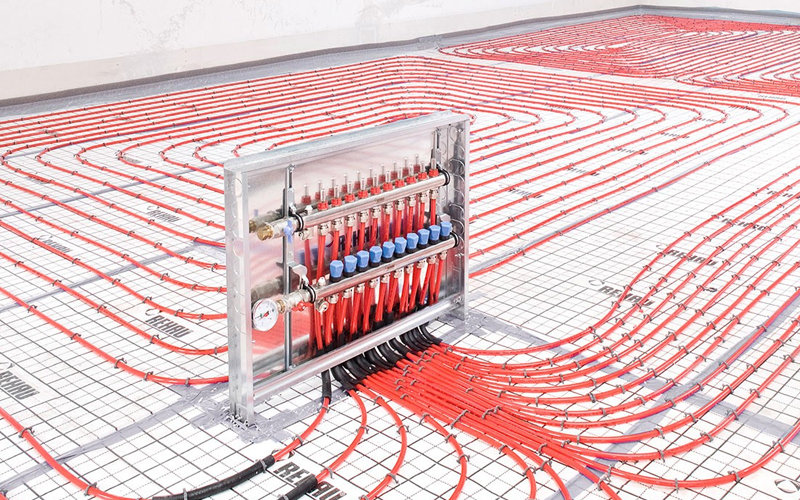
- a collector with the required number of outlets plus a circulation pump and a mixing valve;
- ready-made mortar for screed, plasticizer, sand, gravel.
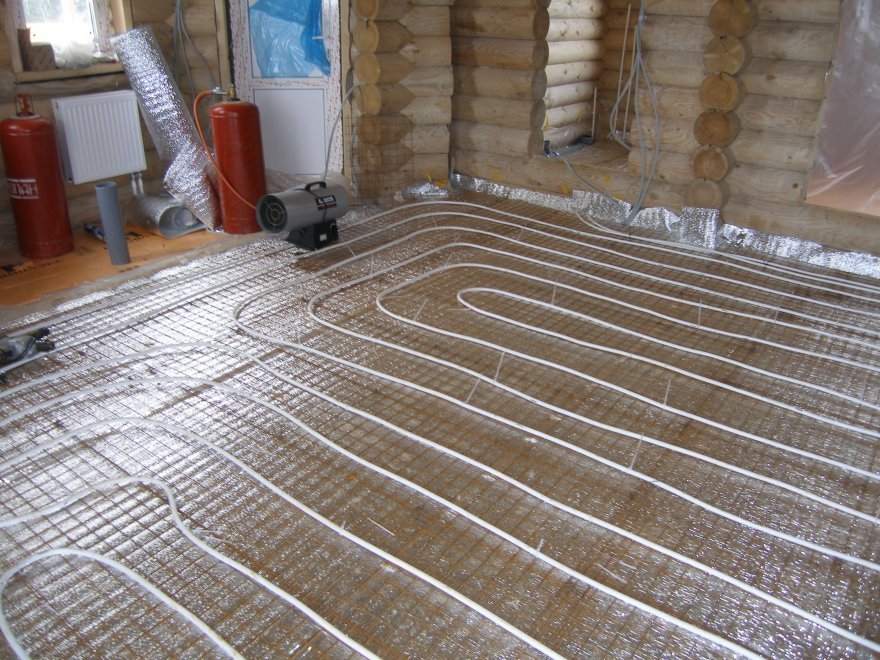
Why you should not take mineral wool for thermal insulation of floors.Firstly, expensive high-density slabs of 135 kg / m³ will be needed, and secondly, the porous basalt fiber will have to be protected from above with an additional layer of film. And the last thing: it is inconvenient to attach pipelines to cotton wool - you will have to lay a metal mesh.
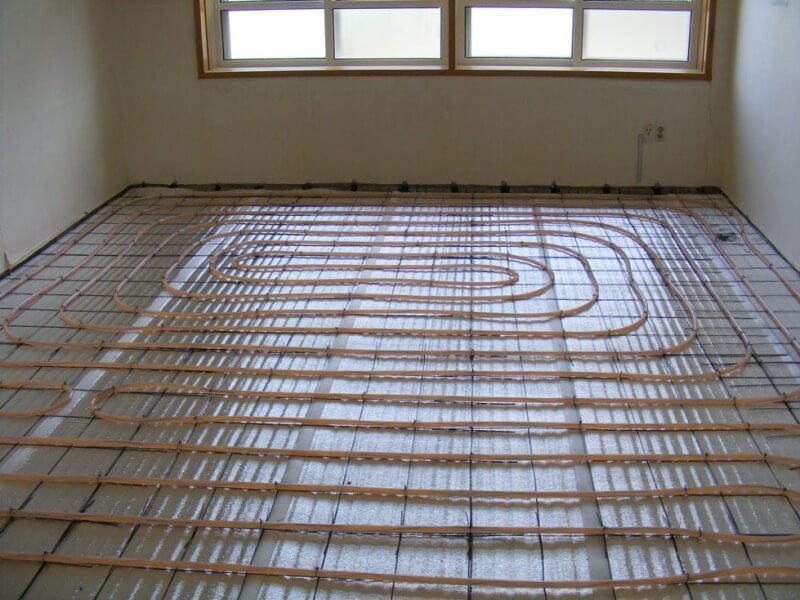
Explanation about the use of masonry welded wire mesh Ø4-5 mm. Remember: the building material does not reinforce the screed, but acts as a substrate for reliable fastening of pipes with plastic clamps when the “harpoons” do not hold well in the insulation.
Option of fastening pipelines to a grid of smooth steel wire
The thickness of thermal insulation is taken depending on the location of underfloor heating and the climate in the place of residence:
- Ceilings over heated rooms - 30 ... 50 mm.
- On the ground or above the basement, the southern regions - 50 ... 80 mm.
- The same, in the middle lane - 10 cm, in the north - 15 ... 20 cm.
In warm floors, 3 types of pipes with a diameter of 16 and 20 mm (Du10, Dn15) are used:
- from metal-plastic;
- from cross-linked polyethylene;
- metal - copper or corrugated stainless steel.
Pipelines made of polypropylene cannot be used in TP. Thick-walled polymer does not transfer heat well and elongates significantly when heated. Soldered joints, which will necessarily be inside the monolith, will not withstand the resulting stresses, deform and leak.

Usually metal-plastic pipes (left) or polyethylene pipes with an oxygen barrier (right) are laid under the screed
For beginners, we recommend using metal-plastic pipes for an independent installation of underfloor heating. The reasons:
- The material is easily bent with the help of a restrictive spring, after bending the pipe "remembers" the new shape.Cross-linked polyethylene tends to return to the original radius of the bay, so it is more difficult to mount it.
- Metal-plastic is cheaper than polyethylene pipelines (with equal quality of products).
- Copper is an expensive material, it is connected by soldering with heating of the joint with a burner. Quality work requires a lot of experience.
- Corrugation made of stainless steel is mounted without problems, but has increased hydraulic resistance.
For the successful selection and assembly of the manifold block, we suggest that you study a separate manual on this topic. What's the catch: the price of the comb depends on the method of temperature control and the mixing valve used - three-way or two-way. The cheapest option is RTL thermal heads that work without admixture and a separate pump. After reviewing the publication, you will definitely make the right choice of the underfloor heating control unit.
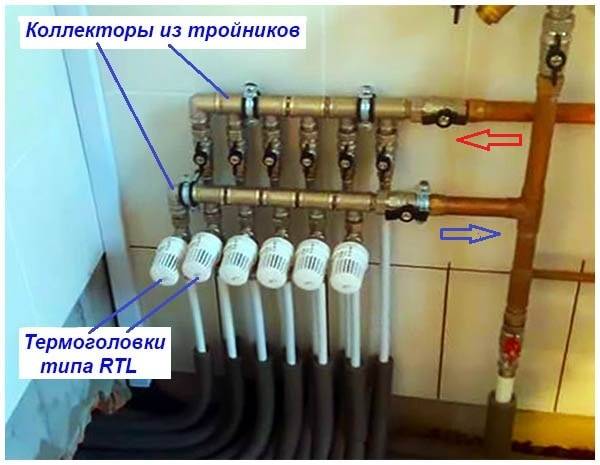

Homemade distribution block with RTL thermal heads that regulate the flow according to the return flow temperature
How many meters is the optimal length of the circuit
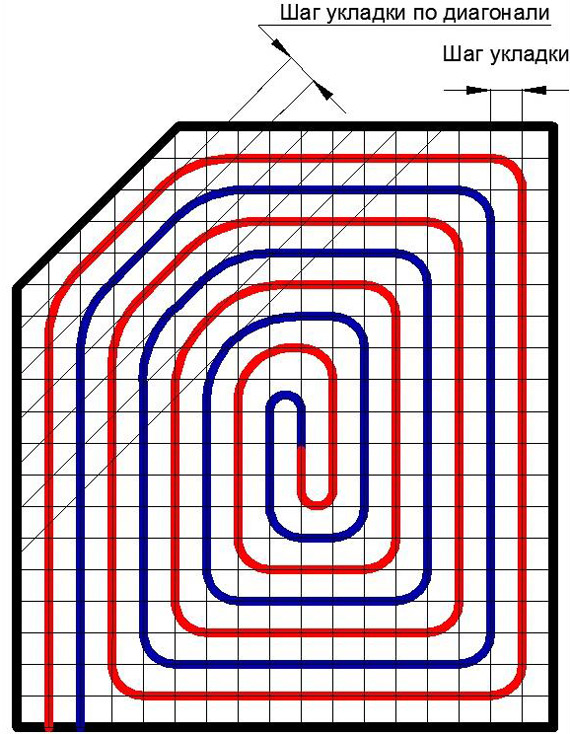 Often there is information that the maximum length of one circuit is 120 m. This is not entirely true, since the parameter directly depends on the diameter of the pipe:
Often there is information that the maximum length of one circuit is 120 m. This is not entirely true, since the parameter directly depends on the diameter of the pipe:
- 16 mm - max L 90 meter.
- 17 mm - max L 100 meter.
- 20 mm - max L 120 meter.
Accordingly, the larger the diameter of the pipeline, the lower the hydraulic resistance and pressure. And that means a longer contour. However, experienced craftsmen recommend not to "chase" the maximum length and choose pipes D 16 mm.
You also need to take into account that thick pipes D 20 mm are problematic to bend, respectively, the laying loops will be more than the recommended parameter. And this means a low level of system efficiency, because.the distance between the turns will be large, in any case, you will have to make a square contour of the cochlea.
If one circuit is not enough to heat a large room, then it is better to mount a double-circuit floor with your own hands. In this case, it is strongly recommended to make the same length of the contours so that the heating of the surface area is uniform. But if the difference in size still cannot be avoided, an error of 10 meters is allowed. The distance between the contours is equal to the recommended step.
Calculation of energy consumption in one room
For an average room area of 14 m2, it is enough to heat 70% of the surface, which is 10 m2. The average power of a warm floor is 150 W/m2. Then the energy consumption for the entire floor will be 150∙10=1500 W. With optimal daily energy consumption for 6 hours, the monthly electricity consumption will be 6∙1.5∙30= 270 kW∙hour. At a kilowatt-hour cost of 2.5 p. the costs will be 270 ∙ 2.5 \u003d 675 rubles. This amount is spent on constant round-the-clock operation of the warm floor. When the thermostat is set to a programmable economical mode with a decrease in heating intensity in the absence of owners in the house, energy consumption can be reduced by 30-40%.
You can check your calculation using an online calculator.
The calculation of the power of the warm floor is done with a small margin. In addition, it depends on the type of room. The real average annual calculation will be less, since the heating is turned off during the warm season (late spring, summer and early autumn).
You can check the actual energy consumption using the meter when the rest of the electrical appliances are turned off.
The power of water heated floors is more difficult to calculate. Here it is better to use the online calculator Audytor CO.
Design Features
All calculations of water heated floors must be made with the utmost care. Any flaws in the design can only be corrected as a result of the complete or partial dismantling of the screed, which can not only damage the interior decoration in the room, but also lead to significant expenditures of time, effort and money.
The recommended temperature indicators of the floor surface, depending on the type of room, are:
- living quarters - 29 ° C;
- areas near the outer walls - 35 ° C;
- bathrooms and areas with high humidity - 33 ° C;
- under parquet flooring - 27 °C.
Short pipes require the use of a weaker circulation pump, which makes the system cost effective. A circuit with a diameter of 1.6 cm should not be longer than 100 meters, and for pipes with a diameter of 2 cm, the maximum length is 120 meters.
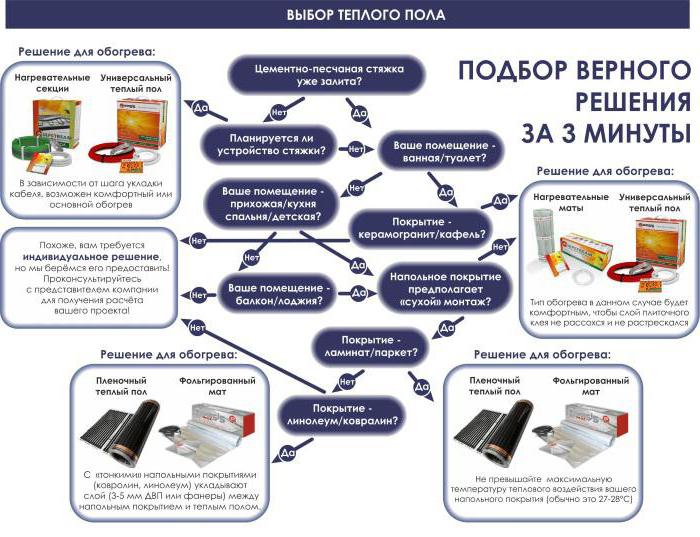
Decision table for choosing a water floor heating system
Pressure in the heating system of a multi-storey building
The following factors influence the actual pressure value:
- The condition and capacity of the equipment supplying the coolant.
- The diameter of the pipes through which the coolant circulates in the apartment. It happens that wanting to increase the temperature indicators, the owners themselves change their diameter upwards, reducing the overall pressure value.
- The location of a particular apartment. Ideally, this should not matter, but in reality there is a dependence on the floor, and on the distance from the riser.
- The degree of wear of the pipeline and heating devices. In the presence of old batteries and pipes, one should not expect that the pressure readings will remain normal. It is better to prevent the occurrence of emergency situations by replacing your old heating equipment.
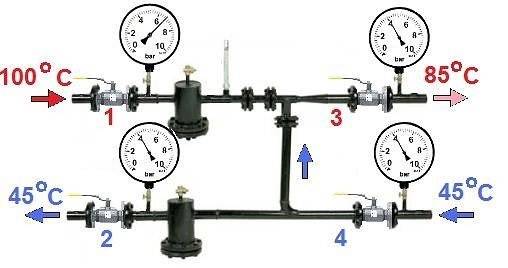
How pressure changes with temperature
Check the working pressure in a high-rise building using tubular deformation pressure gauges. If, when designing the system, the designers laid down automatic pressure control and its control, then sensors of various types are additionally installed. In accordance with the requirements prescribed in the regulatory documents, control is carried out in the most critical areas:
- at the coolant supply from the source and at the outlet;
- before the pump, filters, pressure regulators, mud collectors and after these elements;
- at the outlet of the pipeline from the boiler room or CHP, as well as at its entry into the house.
Please note: 10% difference between standard working pressure on the 1st and 9th floor is normal
We calculate the circulation pump
To make the system economical, you need to choose a circulation pump that provides the necessary pressure and optimal water flow in the circuits. The passports of pumps usually indicate the pressure in the circuit of the longest length and the total flow rate of the coolant in all loops.
The pressure is affected by hydraulic losses:
∆h = L*Q²/k1, where
- L is the length of the contour;
- Q - water flow l / s;
- k1 is a coefficient characterizing the losses in the system, the indicator can be taken from the reference tables for hydraulics or from the passport for the equipment.
Knowing the magnitude of the pressure, calculate the flow in the system:
Q = k*√H, where
k is the flow rate. Professionals take the flow rate for every 10 m² of the house in the range of 0.3-0.4 l / s.
Among the components of a warm water floor, a special role is given to the circulation pump.Only a unit whose power is 20% higher than the actual flow rate of the coolant will be able to overcome the resistance in the pipes
The figures relating to the magnitude of the pressure and flow indicated in the passport cannot be taken literally - this is the maximum, but in fact they are influenced by the length and geometry of the network. If the pressure is too high, reduce the length of the circuit or increase the diameter of the pipes.
What is required for the calculation
In order for the house to be warm, the heating system must compensate for all heat losses through the building envelope, windows and doors, and the ventilation system. Therefore, the main parameters that will be required for calculations are:
- the size of the house;
- wall and ceiling materials;
- dimensions, number and design of windows and doors;
- ventilation power (air exchange volume), etc.
You also need to take into account the climate in the region (minimum winter temperature) and the desired air temperature in each room.
These data will allow you to calculate the required thermal power of the system, which is the main parameter for determining the pump power, coolant temperature, pipe length and cross section, etc.
The calculator posted on the websites of many construction companies that provide services for its installation will help to perform a heat engineering calculation of a pipe for a warm floor.

Screenshot from calculator page
Which gender to choose?
Underfloor heating can be water or electric at the discretion of the owner. The first option is allowed to be used in private homes, since its connection to a centralized heating system is prohibited. For your home, a water floor is preferable, since using electricity for heating is more expensive.
In high-rise apartments, it is preferable to use electric underfloor heating. You can choose a small power, since floor heating is additional, and radiator heating is the main one. The choice of heater type depends on the type of coating being applied.
Conclusion
As you can see, in fact, there is nothing complicated in the correct calculation and increase in the efficiency of the system of discussed systems. The main thing is not to forget that in some cases, high heat transfer from heating pipes can lead to large annual costs, so you should not get carried away with this process either ().
In the presented video in this article you will find additional information on this topic.
In fact, you are a desperate person if you decide on such an event. The heat transfer of a pipe, of course, can be calculated, and there are a great many works on the theoretical calculation of the heat transfer of various pipes.
To begin with, if you started heating the house with your own hands, then you are a stubborn and purposeful person. Accordingly, a heating project has already been drawn up, pipes have been selected: either these are metal-plastic heating pipes or steel heating pipes. Heating radiators are also already looked after in the store.
But, before acquiring all this, that is, at the design stage, it is necessary to make a conditionally relative calculation. After all, the heat transfer of heating pipes, calculated in the project, is a guarantee of warm winters for your family. You can't go wrong here.
Methods for calculating the heat transfer of heating pipes
Why is the emphasis usually placed on the calculation of heat transfer of heating pipes. The fact is that for industrial heating radiators, all these calculations have been made, and are given in the instructions for the use of products.Based on them, you can easily calculate the required number of radiators depending on the parameters of your house: volume, coolant temperature, etc.
Tables. This is the quintessence of all the necessary parameters, collected in one place. Today, a great many tables and reference books are posted on the Web for online calculation of heat transfer from pipes. In them you will find out what is the heat transfer of a steel pipe or cast-iron pipe, the heat transfer of a polymer pipe or copper.
All that is needed when using these tables is to know the initial parameters of your pipe: material, wall thickness, internal diameter, etc. And, accordingly, enter the query "Table of heat transfer coefficients of pipes" into the search.
In the same section on determining the heat transfer of pipes, one can also include the use of manual Handbooks on the heat transfer of materials. Although they are getting harder and harder to find, all the information has migrated to the Internet.
Formulas. The heat transfer of a steel pipe is calculated by the formula
Qtp=1.163*Stp*k*(Twater - Tair)*(1-pipe insulation efficiency), W where Stp is the surface area of the pipe, and k is the heat transfer coefficient from water to air.
The heat transfer of a metal-plastic pipe is calculated using a different formula.
Where - temperature on the inner surface of the pipeline, ° С; t c - temperature on the outer surface of the pipeline, ° С; Q- heat flow, W; l — pipe length, m; t— coolant temperature, °C; t vz is the air temperature, °С; a n - coefficient of external heat transfer, W / m 2 K; d n is the outer diameter of the pipe, mm; l is the coefficient of thermal conductivity, W/m K; d in — pipe inner diameter, mm; a vn - coefficient of internal heat transfer, W / m 2 K;
You perfectly understand that the calculation of the thermal conductivity of heating pipes is a conditionally relative value. The average parameters of certain indicators are entered into the formulas, which can and do differ from the real ones.
For example, as a result of the experiments, it was found that the heat transfer of a polypropylene pipe located horizontally is slightly lower than that of steel pipes of the same inner diameter, by 7-8%. It is internal, since polymer pipes have a slightly larger wall thickness.
Many factors affect the final figures obtained in tables and formulas, which is why the footnote "approximate heat transfer" is always made. After all, the formulas do not take into account, for example, heat losses through building envelopes made of different materials. For this, there are corresponding Tables of amendments.
However, using one of the methods for determining the heat output of heating pipes, you will have a general idea of \u200b\u200bwhat kind of pipes and radiators you need for your home.
Good luck to you, builders of your warm present and future.