- Regulatory documents of GOST for water supply and SanPiN
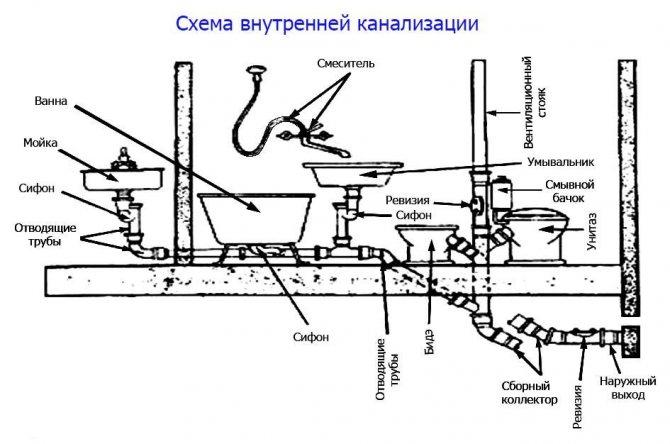
- Internal sewerage
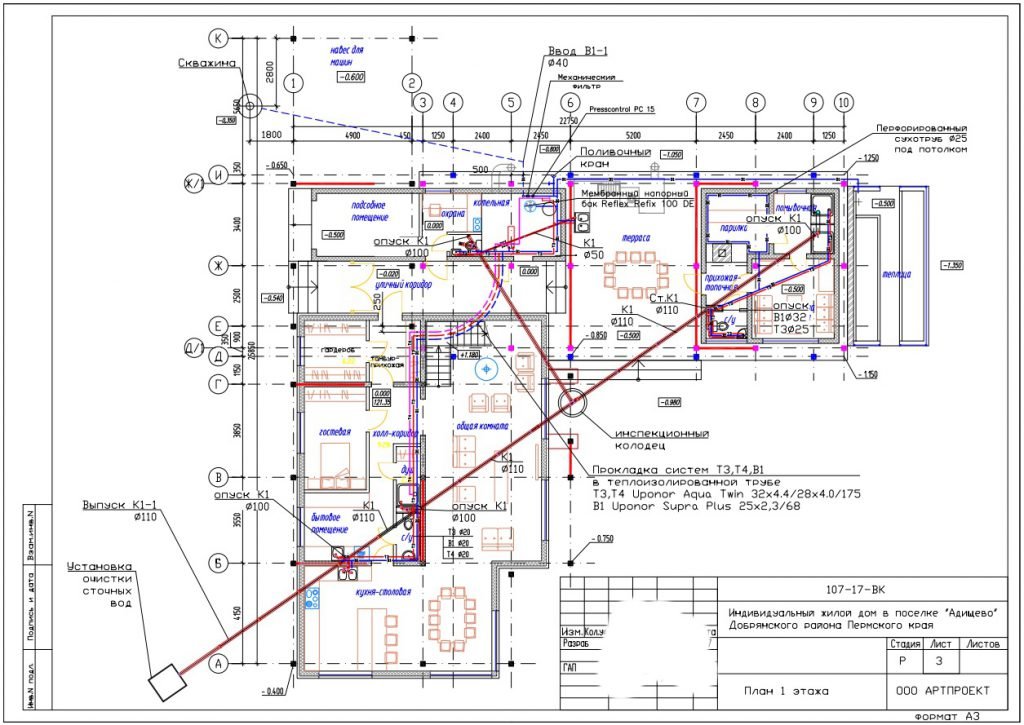
- The composition of the working drawings
- Pipe materials and valves
- Installation options for water pipes for suburban areas
- Internal water supply and sewerage - snip, requirements and installation rules
- What is plumbing?
- Main characteristics
- General provisions of the document
- Exceptions
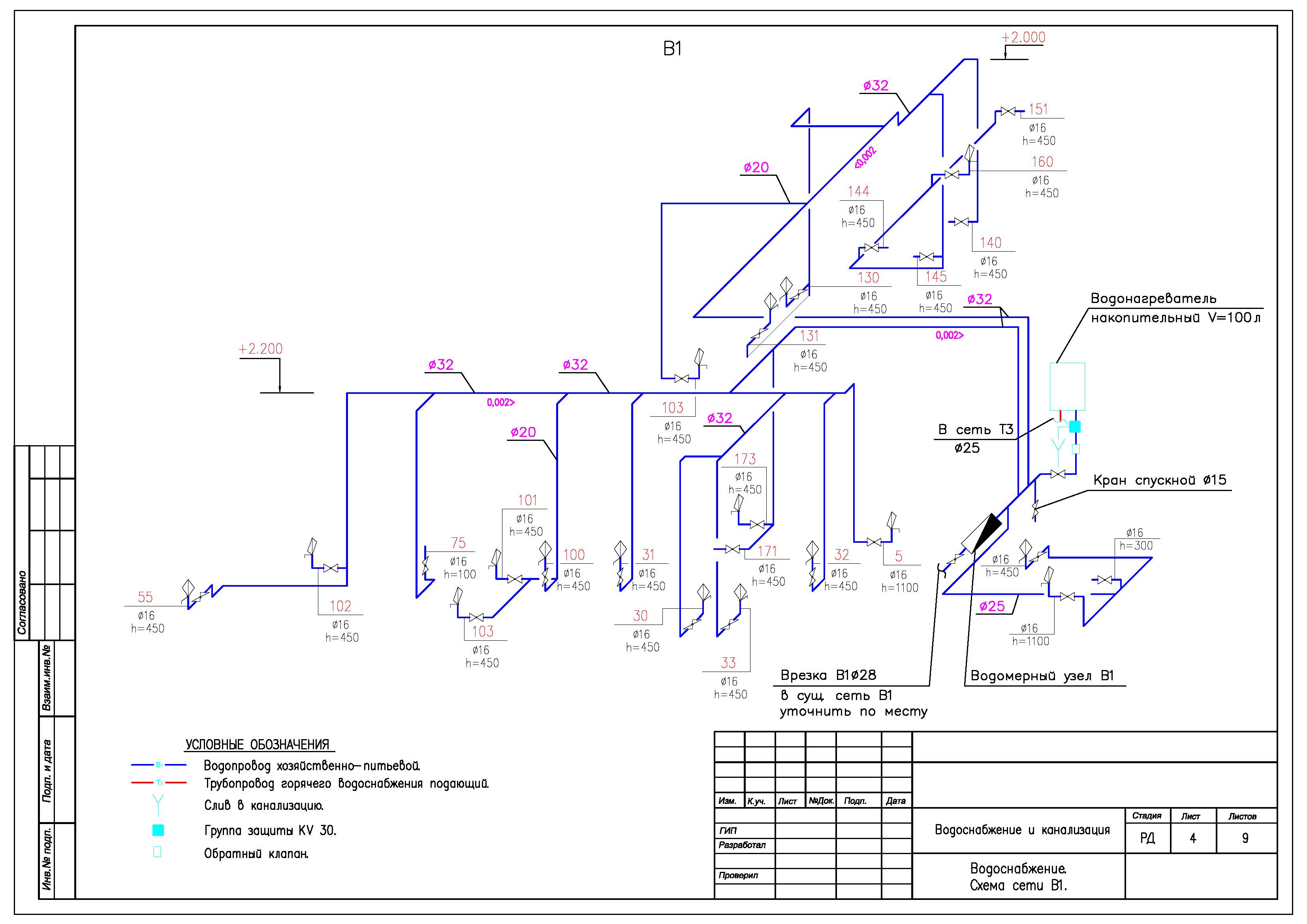
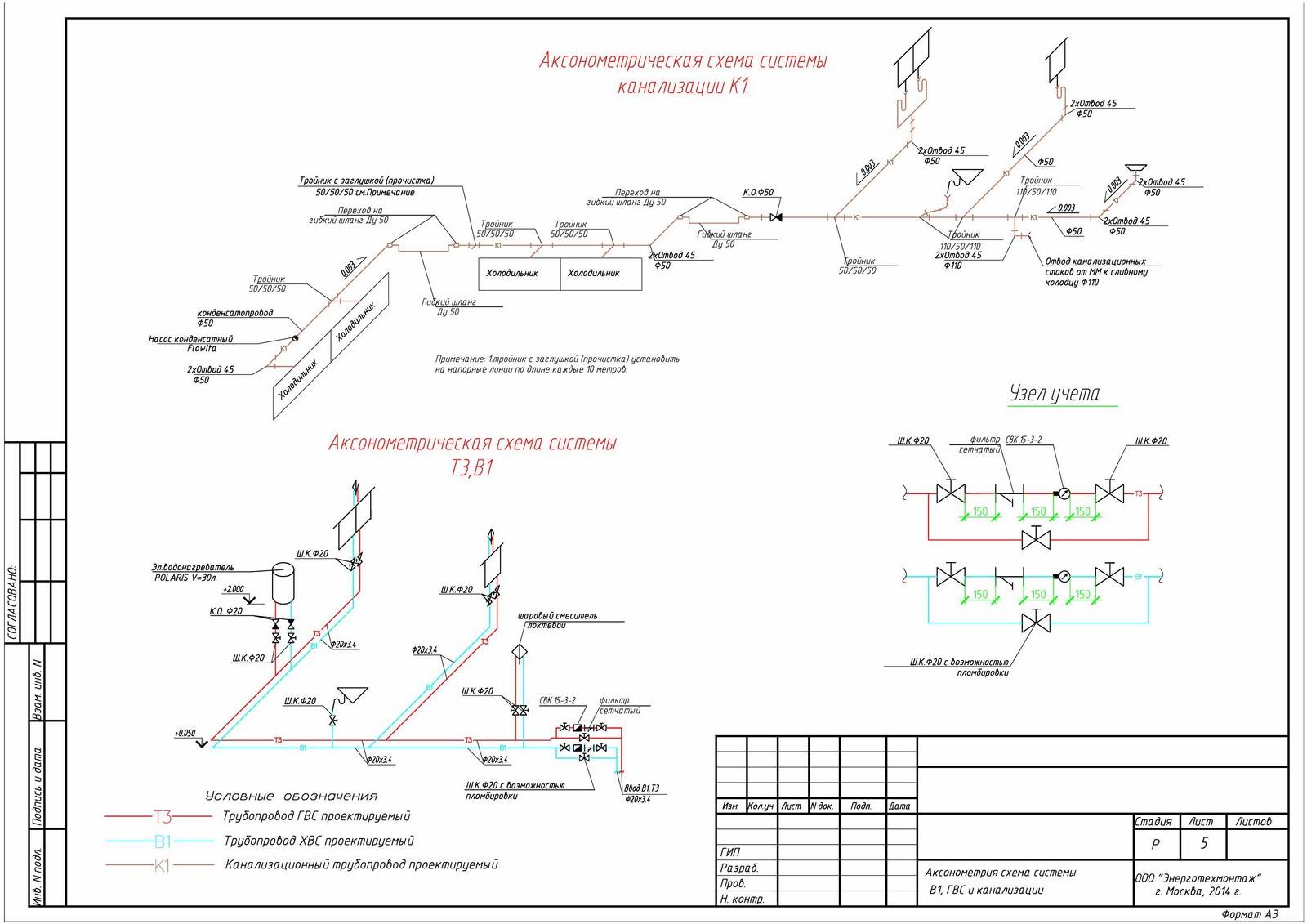
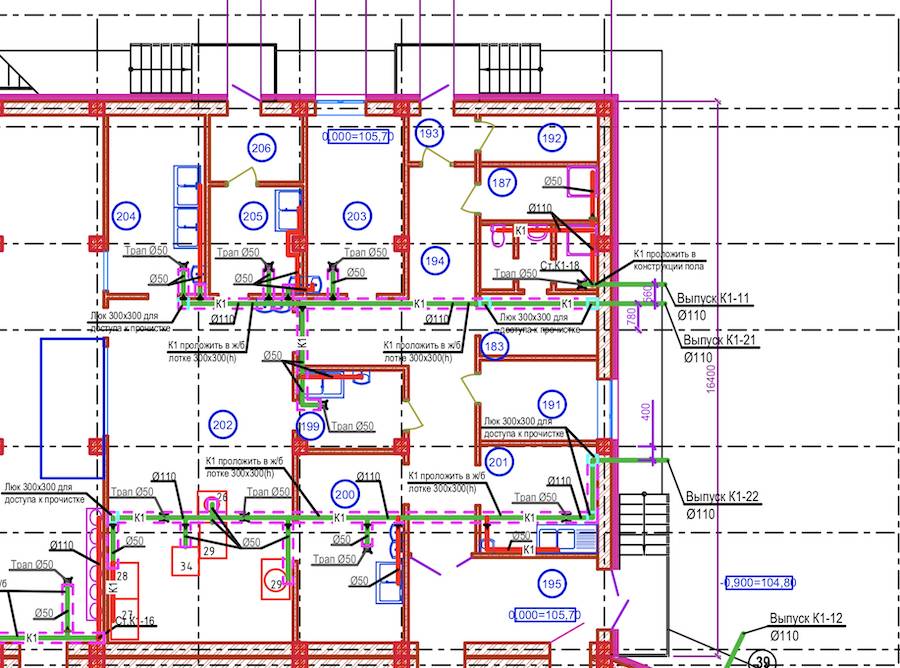
- 6.1 System plans
- Plumbing installation
- Internal water supply and sewerage: design, installation and maintenance
- External and internal water supply and sewerage of buildings
- Requirements for internal water supply and sewerage inside buildings
- Consumption norms and SNiP for water supply
- Calculation of water networks
- Internal sewerage: norms and rules
- Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Regulatory documents of GOST for water supply and SanPiN
The current norms apply to the drafting of systems for reconstructed or under construction for internal hot and cold water supply, directed drains and sewerage. In the process of designing water supply systems, both hot and cold, as well as sewage, it is necessary to comply with the requirements of various regulatory documents that are agreed and approved by the Ministry of Construction of Russia.
The current standards apply when designing:
- Automatic fire extinguishing systems;
- Hot water treatment plants;
- Plumbing systems of firefighting enterprises that produce or store explosives;
- Thermal points;
- Hot water supply systems that supply water to industrial enterprises for technological needs;
- Industrial special water supply systems.
Also, the development of rules may relate to projects of water supply systems for one technological equipment.
GOST 2874-82 applies to drinking water. Regulates hygiene requirements and controls its quality. GOST R 51232 and SanPin "Drinking water" regulate the rationing of the concentration of microelements and pathogenic substances in liquids.
The internal pipeline is a system of devices and pipes that provide water supply to various sanitary appliances, equipment, fire hydrants.
GOST R 53630-2009 regulates the rules and regulations regarding multilayer pressure pipes for heating and water supply systems.
The water supply system serves one building or a whole group and at the same time has a common measuring device from the water supply network of an industrial organization or a settlement. If water will be supplied from external fire extinguishing systems and the pipeline will be laid outside buildings, then it is necessary to fulfill the requirements in accordance with SNiP 2.04.02-84.
Internal sewerage
Internal sewerage includes pipes and auxiliary fittings. This communication performs a very important function - the removal of wastewater from plumbing fixtures and rain inlets outside the buildings. The end point, as a rule, is a treatment plant that filters the water and disposes it in the nearest body of water.After that, the water can be reused for different needs.
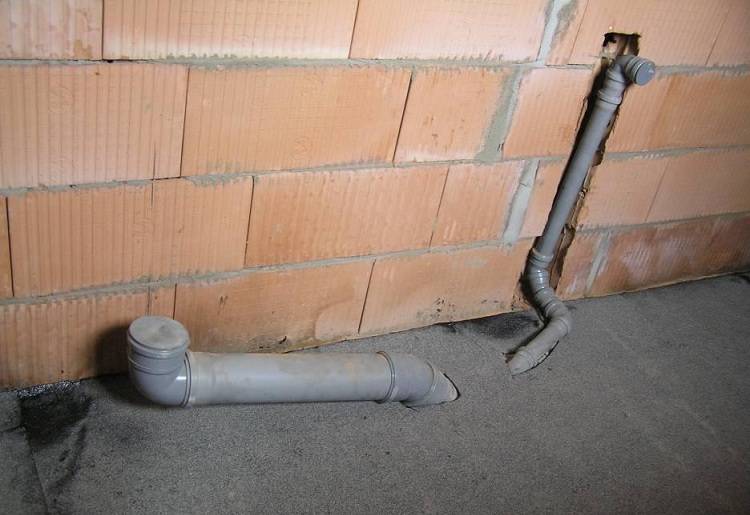

The internal sewerage system collects and diverts wastewater from consumer devices to the general network
The main types of internal sewage:
- economic;
- sewerage at enterprises;
- combined (combined) sewer network;
- rain.
Consider the cases in which a separate sewer system is installed:
- for facilities whose wastewater needs additional treatment measures;
- for buildings that have treatment facilities;
- for various industrial buildings, as well as for buildings related to the food industry (cafes, restaurants, etc.).
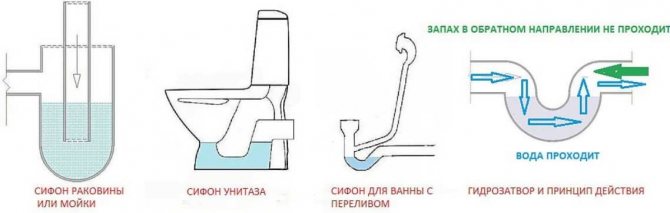
The main requirements for plumbing fixtures and wastewater receivers are as follows:
- at the point of release, a siphon or water seal must be located;
- each toilet must be equipped with a flush tank;
- urinals must be present in men's toilets.
The installation of all devices is subject to certain rules outlined in SNiP. The height of the devices and other parameters must be strictly observed.
It is also worth noting that for the organization of connections in the sewer structure, special devices are used - fittings. Sewer fittings are distinguished by their constructive diversity, which determines their high popularity and functionality.
Pipe materials that are allowed to be used when installing non-pressure sewer communications of an internal type:
- polymeric (usually polyethylene pipes);
- cast iron (mainly from durable gray cast iron);
- asbestos-cement.
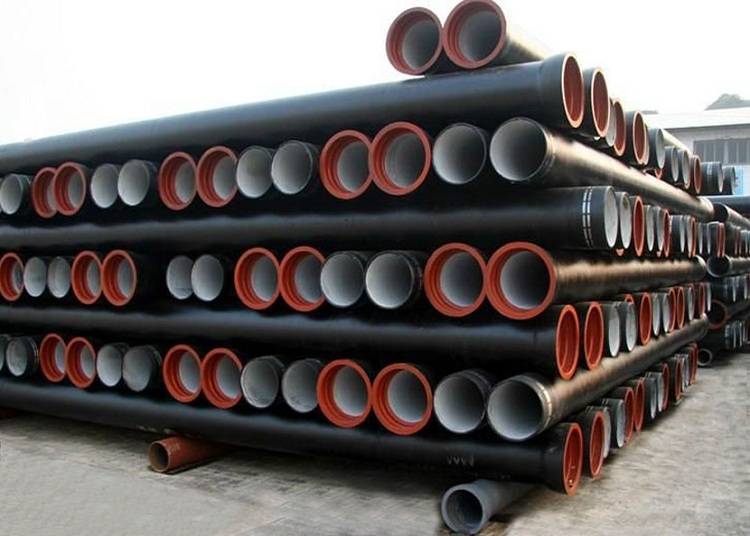

For non-pressure sewage systems, cast-iron, asbestos-cement or polymer pipes are used.
Installation of the above pipes can be done in two ways:
- open;
- closed.
The open method involves the use of special elements for fixing. Through these elements, the pipes are attached to the working surfaces. It is recommended to install sewer pipes in places where the probability of their mechanical damage is the smallest. The hidden method of laying sewer communications involves the installation of its structural elements so that the pipes are not visible (under the floor, in the wall, etc.).
The composition of the working drawings
Project documentation system
for construction (abbreviated as SPDS) defines the rules for drawing elements
plumbing and sewerage, as well as the overall composition of the package. He is the main
part of the working documentation of the VK brand. The full package of documents considers all
sewer network, internal and external. In this case, both parts are displayed in
different drawings, since the specifics of their work differ from each other.
SPDS water supply and sewerage
internal networks considers the specifics of constructing diagrams and drawings of internal
lines. If necessary, they can be combined with water or
gas pipelines. All symbols used are also defined by the regulations,
deviation from which is unacceptable.
The package consists of the following documents:
- general schemes of sewer lines;
- sketches of non-standard structures;
- drawings of atypical units of the complex;
- tables showing the list of materials needed to create networks;
- specification for the equipment used.
General instructions are also given here, explaining or clarifying the data of diagrams or drawings.
These include:
- information about the documents on the basis of which
RD was developed; - confirmation of compliance of the RD with all applicable
regulations, standards; - list of documentation, technical regulations,
determining the order of work; - the level of the mark conditionally taken as zero;
- list of hidden (underground) works;
- regulations that have been used
when performing calculations; - geological characteristics of the site;
- special requirements for the performance of work,
thermal insulation.
On the engineering diagrams of communications are noted:
- axes of pipelines and distances between branches;
- coordinates and depth levels of wells or
collectors; - technological units, operating equipment;
- diameters of outlets of sewer lines;
- marks of the level of branches, ceilings, risers,
other elements.
The focus should be on the capacity and configuration of all lines. These are the main indicators that determine the efficiency and operating parameters of the complex
In addition, an important point is the geological situation, the level of soil water, the presence of seasonal fluctuations or the possibility of flooding. Impacts on the underground part of the system are dangerous because they manifest themselves in a developed state, when all problems have already arisen. Competent design allows you to calculate all the hazards and impacts in advance. GOST water supply and sewerage external networks is a set of rules according to which technical documentation is drawn up.
Pipe materials and valves
SNiP for water supply and sewerage of internal networks indicates a list of materials from which it is recommended to install pipelines for hot and cold water. These rules also apply to fittings required for the construction of engineering systems. Recommended materials include:
Polymers:
- polyethylene;
- polyvinyl chloride;
- polypropylene;
- metal-plastic;
- fiberglass.
Plastic pipes are recommended to be used for concealed wiring, they are walled up in strobes, covered with skirting boards, placed in channels when pouring the floor. Open wiring is installed in areas where the pipeline is not threatened by mechanical damage.
Cold water pipes
Metals:
- Cink Steel;
- copper;
- bronze;
- brass.
Pipes and fittings for hot water
Pipes and fittings must withstand:
- test pressure not lower than 0.68 MPa;
- test pressure of hot water 0.45 MPa at a temperature of 90;
- working pressure is not lower than 0.45 MPa for cold water temperature 20, and hot - 75.
Shut-off valves (faucets, gate valves) are installed on the branches of the main line to the building or sectional nodes, as well as on the branch extending from the riser to the apartment. Fittings with plugs for draining water are installed at the upper and lower points of the riser. This allows pipe repair.
Installation options for water pipes for suburban areas
Pipe installation can be done by two common methods:
- Serial connection of consumers.
- collector connection.
As a rule, the first option is suitable for a small country house. For country houses in which people constantly live, the first option is not suitable. When connected in series, each transition contributes to a pressure loss. In this case, the need is collector wiring, which involves the removal of the pipe from the main collector to the consumer. Thus, the water pressure for each consumer will be the same.
Water is usually taken from a well or well. A pipe is laid from the well using a closed method (in the ground). Such a pipe is connected to the pumping equipment, but before that it is necessary to install a check valve in it, which will regulate the direction of water movement and will not allow it to move in the opposite direction. The water pipe that transports hot water must be connected to a suitable water heater.
Internal water supply and sewerage systems are subject to certain rules, which are established by the competent state institutions. Compliance with these rules is not only recommended, but is also a mandatory item when installing these communications.
Internal water supply and sewerage - snip, requirements and installation rules

What is plumbing?
Water pipeline - a system of continuous water supply to consumers, designed to carry water for drinking and technical purposes from one place (usually water intake facilities) to another - to the water user (city and factory premises) mainly through underground pipes or channels; at the final point, often purified from mechanical impurities in the filter system, the water is collected at a certain height in the so-called water-lifting towers, from where it is already distributed through the city water pipes. The volume of water intake is determined by water meters (so-called water meters, water meters). The water-pressure power of the water supply is also used for hydraulic purposes.
HistoryAqueduct inside the Pont du Gard, middle of the 1st c. n. e.
Known from the 1st millennium BC. e., are mentioned in the Bible (2 Kings, Is. VII, 3, II Chr. XXXII, 30). In ancient Rome, aqueducts were called aqueducts.The first water supply systems in Russia appeared in Bolgar.
In the 11th or early 12th century, the first water supply system made of wooden pipes appeared at Yaroslav's Court in Novgorod.
Important
The Moscow Kremlin has had running water since the 15th century. The first urban water supply system in Moscow (Mytishchi-Moscow water supply system) appeared in 1804.
Clay, wood, copper, lead, iron, steel were used as a material for plumbing, and with the development of organic chemistry, polymers began to be used. Pipelines of large diameters have also been made from cement, reinforced concrete, asbestos cement, and in recent years from various types of plastic.
Due to the increased mechanical strength and resistance to elevated temperatures in domestic water supply, metal water pipes are most widely used - made of steel, stainless steel, cast iron, high-strength cast iron with nodular graphite (VCSHG) and copper. Pipes made of synthetic materials, such as polyethylene of various densities, are also used.
In the 20th century, in developed countries, copper pipelines became widespread in the water supply of buildings due to a combination of factors that provide extended periods of trouble-free operation.
Nowadays, polymer pipelines are becoming more widespread due to the ease of their installation and the low cost of products coming from developing countries.
Due to the variety of types of polymer pipelines themselves, connection methods, their performance continues to be a subject of controversy, and prices vary greatly. A lot of experience has already been accumulated in the use of polymeric water pipes.
So, after a series of massive accidents in North America, the use of polybutene pipelines was completely stopped.
Plumbing elements
Water pipelines are internal, located inside buildings and structures, and external - laid outside buildings and structures, usually underground.
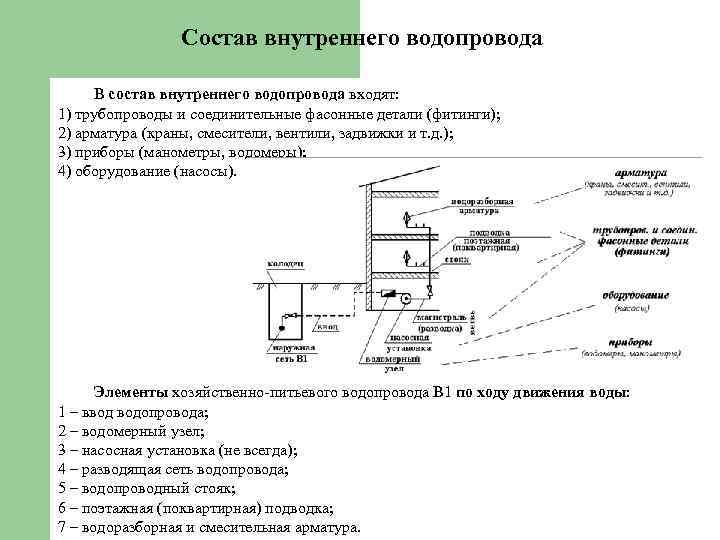
Internal water supply is regulated by SNiP 2.04.01-85 “Internal water supply and sewerage of buildings”. The main elements of the internal plumbing are:
Advice
input of a water supply system - the pipeline connecting a city water supply system with internal; water metering unit - a water consumption metering unit, the main element of which is a water meter; installations for increasing pressure (booster pumps); pipeline distribution networks; water fittings and shutoff valves; fire hydrants;
watering taps, etc.
Outdoor plumbing
Main characteristics
Internal networks of water supply and sewerage should be installed in accordance with a pre-drawn project. Drawing up a project is a mandatory norm, which is necessary for high-quality installation of communications. The effectiveness of a particular communication, as well as the duration of its operation, will depend on how the installation is carried out.
Water supply systems, as well as sewerage networks, are laid to provide maintenance for private houses, multi-storey residential buildings, small and large enterprises, as well as administrative buildings and other buildings.
The method of installation of internal water supply and sewerage can be of two types:
- interior;
- outer;
Communications laid inside buildings, in most cases, are made of metal-plastic or plastic pipes.However, SNiP allows you to lay pipelines from other materials. For example, for a water supply network, the use of steel or copper pipes is allowed.
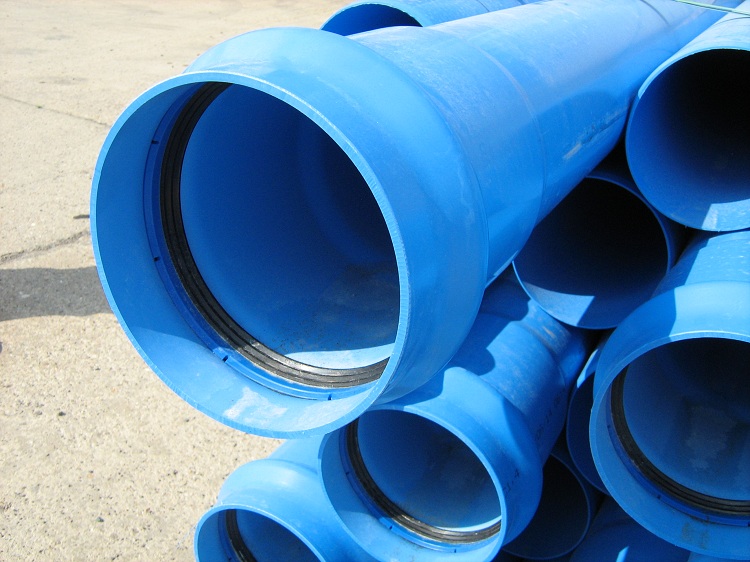

Modern plumbing and sewer systems are often mounted from polymer pipes, which have a lot of advantages over metal ones.
In addition, it is worth noting that steel pipes have low resistance to corrosive effects and are prone to blockages due to insufficiently smooth inner surfaces. As for copper products, they are perhaps the most expensive and, despite their excellent technical characteristics, are installed extremely rarely.
Modern projects should contribute to the improvement of construction work, as well as widely introduce the following points:
- maximum automation of all processes;
- mechanization of labor-intensive stages of installation;
- standardization of communications through the use of pipes and accessories for them of the same (standard) sizes;
- reduction of financial, energy and labor costs during the installation of any communication.
For external communications, there are own standards prescribed in the SNiP "external water supply and sewerage of buildings."
General provisions of the document
First, a little about the scope of SNiP. It is relevant for hot and cold water supply systems being designed and to be reconstructed (hereinafter - cold water and hot water supply), internal sewerage of buildings and drainage systems.

The main content of SNiP - rules for the installation of water supply and sewerage
What information you will not find in the text of the document:
- Manuals for the design of elevator units and installations for the preparation and treatment of hot water;
- Descriptions of specialized cold water and hot water systems, subject to separate regulatory documents (including engineering systems of medical institutions;
- Diagrams of any automatic fire extinguishing systems and fire water pipelines of enterprises producing combustible and explosive substances (see Requirements for fire water supply: an overview of current regulations).
Internal water supply and sanitation systems should be provided for:
In all buildings erected in areas with central sewerage;

If there is a central sewer in your area of the settlement, the house must be connected to it
- In residential buildings above two floors;
- in hotels;
- In medical institutions and nursing homes;
- In sanatoriums, boarding houses and rest houses;
- In kindergartens, schools and children's holiday camps;
- In canteens and other catering establishments;
- In sports complexes;
- In laundries and baths.

In the photo - a station for deep biological wastewater treatment
Exceptions
In the absence of a central sewage system, cesspools or backlash closets (toilets with the collection of sewage into an external cesspool) can be equipped with:
- Separate buildings of enterprises with the number of workers simultaneously involved in one shift of 25 or less;
- Residential buildings not higher than 2 floors;

Ageless classic: backlash closet in the yard
- Dormitories up to two floors inclusive (with the number of residents not more than 50);
- Summer camps for 240 or less places;
- Outdoor stadiums, football fields, volleyball courts, tennis courts and treadmills;
- Catering establishments serving no more than 25 people at the same time.
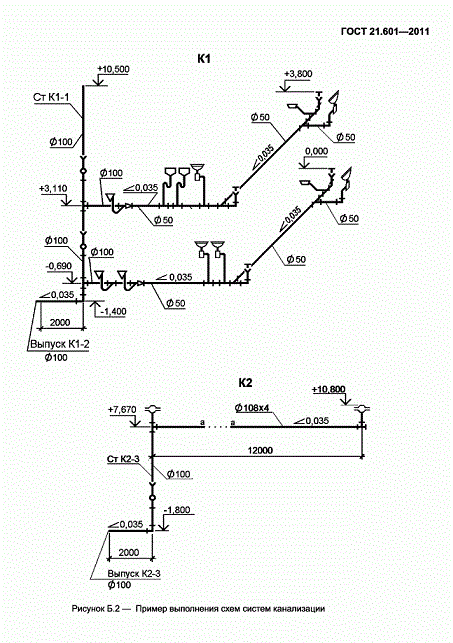
6.1 System plans
6.1.1
Plans for water supply systems (including hot water supply), as a rule,
combined with the plans of sewerage systems.
6.1.3
On the systems plans, the equipment of the systems (for example, pumps, tanks) and installations
indicate with simplified graphic images, pipelines and other
elements of systems - conventional graphic symbols.
pipelines,
made by conditional graphic symbols in one line and located
one above the other in the same plane, on the plans of systems they are conditionally depicted as parallel
lines.
6.1.5
On the plans of the systems apply and indicate:
—
coordination axes of the building (structure) and the distance between them (for residential
buildings - the distance between the axes of the sections);
—
building structures and technological equipment, to which they bring
water or from which waste water is diverted, as well as affecting the gasket
pipelines;
—
marks of clean floors of floors and main platforms;
—
dimensional bindings of system installations, water supply inlets and outlets
sewers, main pipelines, system risers (on basement plans,
technical underground), sanitary appliances, fire and watering taps,
trays and channels to coordination axes or structural elements;
—
alphanumeric designations of pipelines;
—
designations of installations and risers of systems on the shelves of leader lines;
—
diameters of pipelines, water supply inlets and sewer outlets.
On the
plans, in addition, indicate the names of the premises and the categories of premises according to
explosion and fire hazard. Room names are allowed
categories of premises in terms of explosion and fire hazard should be brought to
explication of premises according to form 2 GOST
21.501.
6.1.6
The names of the system plans indicate the mark of the finished floor of the floor or the number
floors.
Example — Plan for
elev. 0.000; Elevation plan +3.600; Plan 2 — 9 floors
At
execution of a part of the plan in the name indicate the axes that limit this part
plan.
Example — Plan for
elev. 0.000 between axles 1 — 8 and A - D
At
separate implementation of plans for water supply systems and plans for sewerage systems in
the names of the plans also indicate the designations or names of the systems.
Example — Systems plan
B1, B2 at el. 0.000; Sewerage. Elevation plan 0.000
6.1.7
In necessary cases, cuts are made along the technical underground (basement).
6.1.8
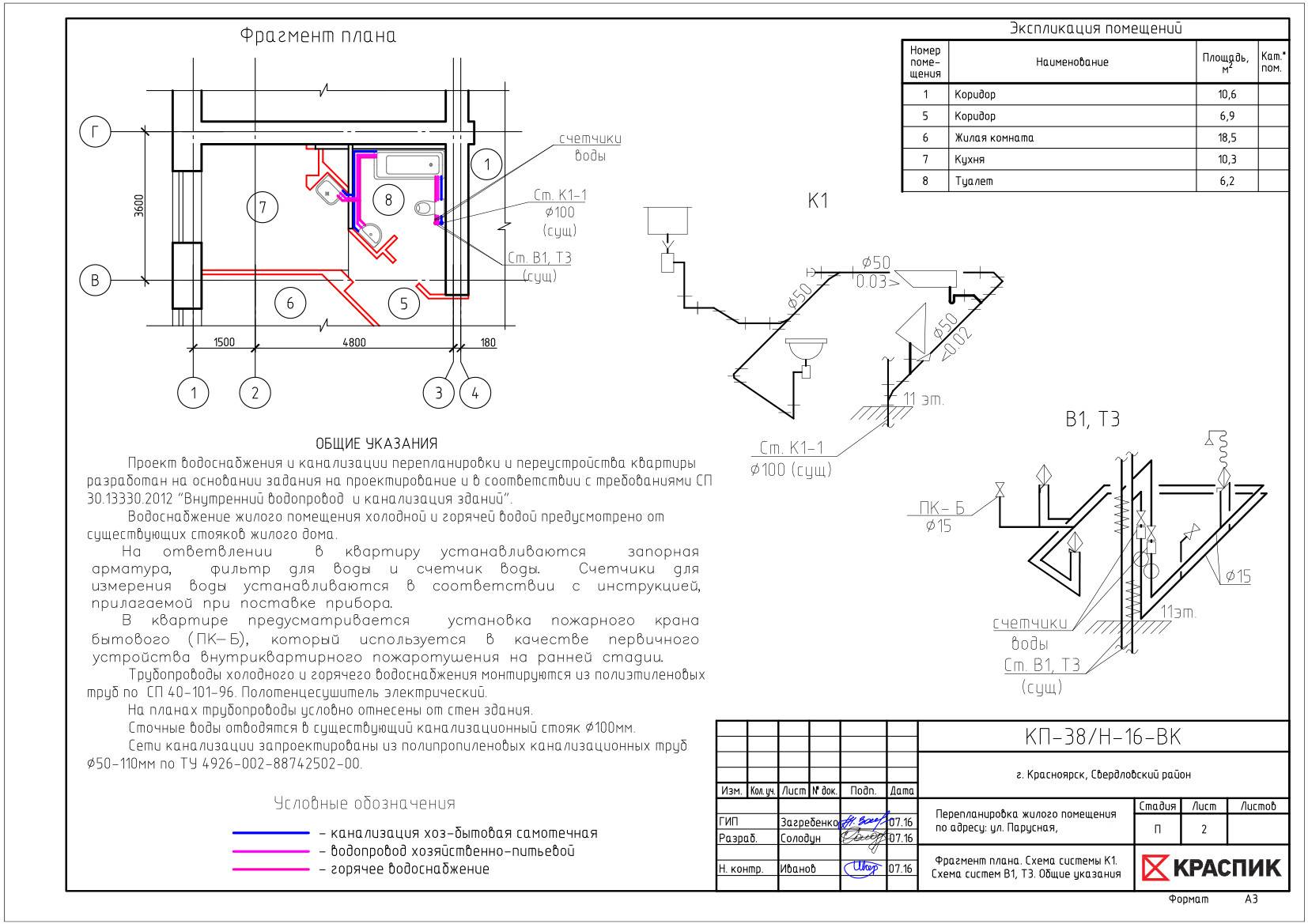
Examples of the implementation of system plans are shown in the figures and (Appendix),
fragment of the plan - in the figure (application).
Plumbing installation
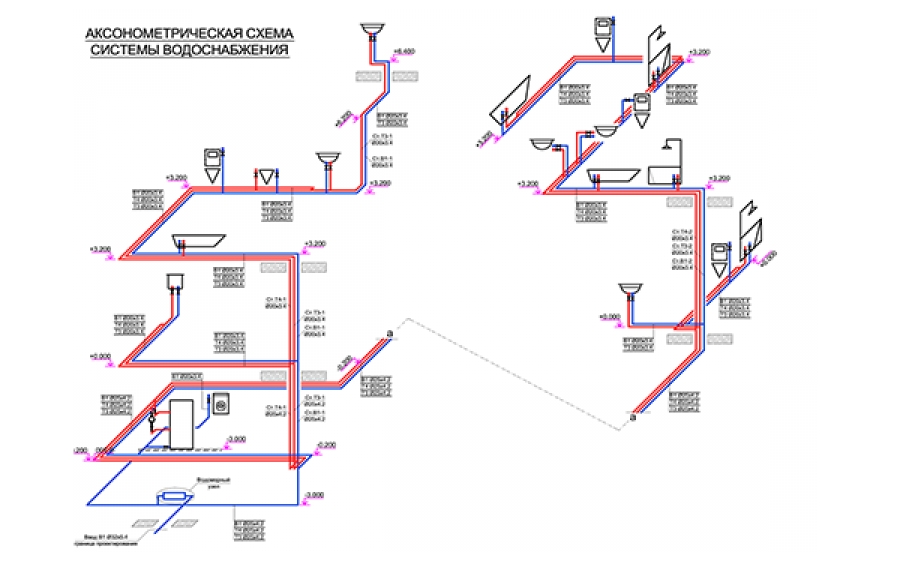
There are several schemes for organizing internal water supply:
- Lower wiring (in the basement) without installation of water lifting devices. In this case, the pressure parameters of the external network must ensure the flow of water to all consumers.
- Upper wiring with a water tank - mounted with insufficient pressure.
- Lower wiring with the installation of a booster pump.
- Ring scheme - differs in the installation of 2 or more inputs, provides uninterrupted water supply.
Cold water is supplied through dead-end and ring systems. A ring network with multiple inputs is used in several cases:
- in buildings with more than 400 apartments;
- when installing more than 12 fire hydrants;
- in theaters and clubs;
- in cinemas for 300 or more people;
- in baths for 200 people.
When installing a hot water pipeline, use:
- dead-end system - for low-rise buildings;
- circulation system - for high-rise buildings.
If the pressure created in the external pipeline is not sufficient to supply water to the upper floors, then a pressure tank is installed (at the highest point of the building) or a booster pump at the inlet.
SNiP requirements for the installation of internal plumbing:
- The entry of the pipeline through the basement wall is carried out with a gap of 20 cm, which is closed with an elastic waterproof material.
- Distribution networks are laid in basements, on technical floors, attics, in underground channels of the first floor. According to building structures.
- Hidden laying is carried out in rooms with special requirements for finishing. Plastic pipes are mounted hidden, and steel pipes are only open.
- When installed together, the cold water supply is installed below the hot one.
- The slope of the water supply is not less than 0.002.
- If cold water pipes pass in a room where the temperature drops below 2, then they must be insulated.
- The design process provides for measures to reduce noise and vibration of water pipes.
Internal water supply and sewerage: design, installation and maintenance

Internal plumbing and sewerage are an integral and important part of any home. Improper equipment of this system may not have the best effect on the comfort of using the room. Correcting errors in it is long, difficult and expensive. For this reason, the design and installation of plumbing and sewer systems require special attention and a responsible approach.
Issues discussed in the material:
- What are the differences between external and internal water supply and sewerage of buildings?
- What regulations regulate the installation and design of internal water supply and sewerage?
- What does SNiP internal water supply and sewerage contain?
- What rules must be observed in the design?
- What does the internal water supply and sewerage consist of?
- How are internal plumbing and sewerage designed?
- How is the installation of internal water supply and sewerage?
- Who should carry out the repairs?
External and internal water supply and sewerage of buildings
When building new buildings and improving the living conditions of old buildings, one of the most important issues is the equipment of engineering networks.
Indeed, it is difficult to imagine comfortable modern housing without internal water supply and sewerage networks in it, and it doesn’t matter if we are talking about an apartment building or a house in a summer cottage
Here are collected bills that will affect the work of the MA, HOA, housing cooperative.
The plumbing system provides a stable supply of water with the preservation of its necessary characteristics to the point of draw-off in the house. To perform these tasks, the system is equipped with the necessary devices: downhole pumps, storage tanks, filters.
The sewerage network is designed for the uninterrupted removal of used water from the premises to the treatment plant, followed by proper purification of the resulting effluents.
Private houses can be equipped with internal water supply and sewerage in one of the following ways:
- through centralized networks;
- using individual facilities.
The first method is simpler, since you only need to connect the room to the general system using a pipeline. A prerequisite will be obtaining permission to connect to centralized networks and technical conditions for the performance of work.
Owners of houses in settlements that are not equipped with a water supply and sewerage network have no choice but to create their own facilities, including autonomous treatment devices (septic tanks) and installations for drawing water from a well or well.
Wastewater disposal systems are classified according to several criteria. So, according to the method of moving the liquid, non-pressure and pressure systems are distinguished.
- In non-pressure systems, the liquid moves in the pipes itself, without the help of any devices, which involves placing the pipeline at an appropriate angle.
- Pressure systems imply the presence in the plumbing and sewer systems of special installations - pumps for pumping out liquid. Such autonomous systems are equipped where it is impossible to provide the necessary slope, for example, due to the difficult terrain.
Depending on the location of the installations, the networks are internal and external. From the name it is obvious that the first type involves the location of equipment in the building, and the second - outside it.
Equipment and pipes of internal water supply and sewerage networks are placed in the building. The exit point of the internal sewerage pipeline from the foundation of the house is the final one. And the water supply, on the contrary, begins at the point where the pipe enters the building.
Internal sewerage consists of:
- pipes extending from the points of water intake;
- sewer riser to which pipes fit;
- point of exit of the sewer pipe from the building.
External networks include components such as:
- Pipeline located outside the house.
- Wells for various needs (differential, rotary, revision, etc.).
- Treatment plant (in the sewer).
- Equipped well or well (in the case of water supply).
- Pump installations.
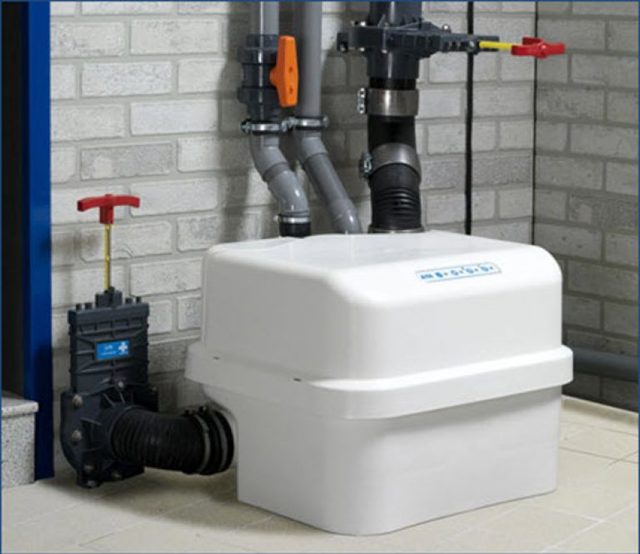
Pumping equipment is an obligatory component of almost all internal water supply and sewerage systems. The following types of pumping units are used in modern communications equipment:
- Submersible. These are water pumps.
- Surface. They are located on the surface and take water with the help of hoses.
- Fecal or sewer. They are a special type of pumping units designed to move liquid masses, including solid elements.
Requirements for internal water supply and sewerage inside buildings
There is a certain set of rules (SP), which must obey the internal networks of water supply and sewerage. Consider the list of basic requirements for these pipeline structures:
- when independently designing water supply and sanitation systems, it is recommended to combine them. This arrangement option is considered the most effective and allows to reduce the operating costs of these pipeline structures;
- water delivered through the domestic water supply must necessarily comply with all sanitary and hygienic standards. In order to achieve a certain quality standard, water must go through several mandatory procedures, including: purification, clarification, etc.;
- technical waters are not used for drinking, however, despite this, they must also undergo all necessary treatment measures. The degree of clarification of water is determined in accordance with its subsequent use (i.e. for which particular technological process it will be applied);
- for the transportation and delivery of water to the end consumer, communications made of environmentally friendly materials should be used, the material of which does not react with water and does not emit any foreign chemical impurities into it.
- according to SNiP, a necessary measure is to take into account the volume of water consumption, as well as the magnitude of the liquid pressure.
The material of pipes used for plumbing should not release any substances into drinking water that impair its quality.
Consider the minimum indicators of the free pressure of the liquid for different situations:
- one-story structures must have a free head, which is 10 m;
- each next floor must have a pressure increase of at least 4 m;
- in those cases when periods of minimum water consumption occur, the norm is to reduce the pressure on each subsequent floor after the first by 1 m.
Consumption norms and SNiP for water supply
Under the consumption rate, they represent the permissible maximum volume of water of the appropriate quality, which is necessary to meet the needs of ordinary consumers living in a particular housing. Water consumption rates are determined in accordance with building rules and regulations adopted by executive authorities.
The amount of water consumption will always depend on the quality and standard of living of people.
So, if 120 years ago the volume of water consumed per Muscovite was 11 liters of water per day, then 100 years ago this figure was 66 liters for everyday consumption. Today, the average volume of water per inhabitant of Moscow is 700 liters.
Water consumption depends on:
- The climate of the place of residence;
- Work activity performed.
For residents of the southern regions, the need for water will be much greater than for the northern ones.
Calculation of water networks
The main requirement for the calculation of domestic, industrial and fire water pipelines is to ensure the standard water pressure in the appliances. The calculation is based on the maximum water flow per second. If the system has 2 inputs, then each of them is calculated for full operation when the second is turned off. With multiple inputs - 50% liquid consumption.
The normative speed of water movement in the cold water pipeline is 3 m / s. The diameter of the pipes is selected based on providing the maximum pressure supplied from the external network. For hot water pipelines, the pressure loss that occurs in the supply and circulation lines for each branch of the system should not differ by more than 10%. The diameter of the circulation risers is selected in accordance with the requirements of SNiP.
Internal sewerage: norms and rules
Internal sewerage is a special system of devices and pipelines in a volume that is limited by the outer surfaces of adjacent structures and outlets to the first manhole. The internal sewerage system ensures the disposal of wastewater from sanitary appliances to local treatment facilities.
For all types of buildings that are being built in sewer areas, it is necessary to provide for sewerage and internal water supply.
As for settlements with non-sewerage areas, internal water supply systems should be provided with local treatment facilities.
Such an arrangement should be in:
- hotels;
- hospitals;
- nursing homes;
- maternity hospitals;
- outpatient clinics;
- Sanitary and epidemiological stations;
- Movie theaters;
- schools;
- Public catering establishments;
- baths;
- Sports facilities.
Such requirements also apply to residential buildings whose height is more than two floors.
Equipment with an internal sewerage system is allowed in buildings that are equipped with internal drinking and drinking facilities. In such settlements, there may be cesspools and backlash closets without a water drive input device.
It is allowed not to introduce sewerage and internal water supply systems in cases where there is no running water at the operating enterprise, and the number of employees does not exceed 25 people per shift.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Experience in arranging water supply and sewerage systems in a private house:
In the process of construction or repair of water and sewer networks, it is necessary to be guided by rules, norms, standards. Compliance with technological recommendations, adherence to standards and norms is the key to building effective and durable communications.
Do you have experience in arranging an internal water supply or sewer network? Please share information with our readers, tell us about the features of highway planning. You can leave comments in the form below.