- Requirements for types and methods of attaching tags
- Ley line markers
- Labels for low power circuits
- The difference between cables and wires depending on the core material
- Aluminum conductors
- Copper conductors
- Computer
- Wire marking
- Cable and wire marking table
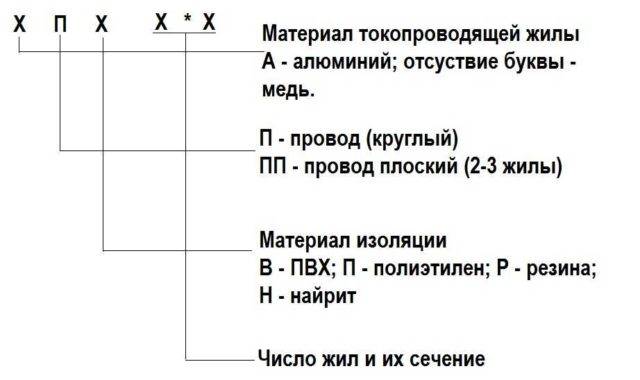
- Types of power copper cables
- Power cables
- Copper or aluminum?
- Product types
- Cords
- Cables
- Types of cables
- wires
Requirements for types and methods of attaching tags
In addition to the placement of tags, all information about the designations made on cable lines and communication devices is recorded in a special journal. Such records are regularly updated depending on the changes that have taken place in the structure of the network.
Like cable, tags are made in a certain shape from various materials. These can be ordinary labels, self-adhesives, plastic seals or polymer products used for high-quality and reliable marking of a bundle of several cores or one wire.
Ley line markers
In accordance with GOST, plastic plaques are made in square, round or triangular shapes. They are used in open areas of cable routes and circuit components. There are two holes on the tags through which the wire or core should be passed, after which it is securely clamped and fixed in the desired position.

For lines whose voltage does not exceed 1000 V, square tags are used. If the operating voltage is higher than 1000 V, then round plastic plates are taken. Triangular products are necessary for control power lines.
Labels for low power circuits
For such purposes, small plates made of polymeric materials can be used, which indicate information about the electricity consumption of the subscriber of the circuit and other data.
Important! Cable tags must be used even for hidden lines located inside pipes, manholes and blocks
The difference between cables and wires depending on the core material
Cores of wires and cables for specialized purposes can be made of various metals, but aluminum and copper are mainly used in electrical engineering. Each of them has its own specific properties, advantages and disadvantages, which must be taken into account when selecting a core material for a specific purpose.
Aluminum conductors
The invention of a relatively inexpensive way to extract aluminum made a revolution in the global development of electrification, because in terms of electrical conductivity, this metal is in fourth place, skipping ahead only silver, copper and gold. This allowed the production of wires and cables to be as cheap as possible and made universal electrification a reality.
Such electrical wires and their types are distinguished by their low cost, chemical resistance, high level of heat transfer and low weight - they have determined the mass character of electrification in industrial and domestic conditions for more than half a century.
In the light of the relatively recent dominance of aluminum in the wire market, it may seem strange to the uninitiated that the provisions of the PUE prohibit the use of this material in everyday life.More precisely, you can not use aluminum wires with a cross section of less than 16 mm², and these are the most common ones for installing home electrical wiring. To understand why there is a ban on the use of these wires, you can familiarize yourself with their advantages and disadvantages.
+ Advantages of aluminum wires
- Lighter than copper.
- Significantly cheaper.
- Cons of aluminum wires
- Aluminum conductors with a cross section of up to 16 mm² can only be single-wire, which means that they can only be used for laying fixed wiring and without bending at an acute angle. All flexible wires and cables have always been made of copper.
- The chemical resistance of aluminum is determined by the oxide film that forms when it comes into contact with air. Over time, with constant heating of the contact due to the flow of electric current through it, this film worsens the electrical conductivity, the contact overheats and fails. That is, aluminum wires require additional maintenance, and contacts through which powerful currents pass are coated with a special lubricant.
- Amorphousness of the material - if you clamp two aluminum wires together, then over time the contact will weaken, since the aluminum will partially “leak out” from under the yoke.
- Soldering can only be carried out using special tools, and welding can be done in an inert gas chamber.
- Good electrical conductivity is observed only in pure aluminum, and impurities that inevitably remain during production worsen this indicator.
As a result, aluminum is a good choice if you need to save money here and now, but in the long run it will cost more due to the relatively short service life and the need for regular maintenance.For this reason, and for additional security reasons, the PUE categorically prohibits using it for laying new power lines.
Copper conductors
In terms of electrical conductivity, copper is in second place, only 5% inferior to silver in this indicator.
Compared to aluminum, copper has only 2 significant drawbacks, due to which it was used much less frequently for a long time. Otherwise, copper wins in all respects.
+ Advantages of copper wires
- The electrical conductivity is 1.7 times higher than aluminum - a smaller wire section will pass the same amount of current.
- High flexibility and elasticity - even single-core wires can withstand a large number of deformations, and cords for electrical appliances of increased flexibility are obtained from stranded wires.
- Soldering, tinning and welding are carried out without the use of additional materials.
- Cons of copper wires
- The cost is several times more expensive than aluminum.
- High density - a coil of copper wire, the same length and cross section as aluminum, will weigh 3 times more.
- Copper wires and contacts oxidize in the open air. However, this practically does not affect the contact resistance and, if necessary, is “treated” by lubricating the surface of an already tightened contact.
As a result, although copper is a more expensive material, in general its use is more cost-effective, as it is more durable, requires less effort during installation and attention during maintenance.
This is interesting: Technical tricks of household sockets: we understand the essence
Computer
Computer cables and their varieties are made to form computer networks, to connect a PC to the Internet or to connect machines to each other. The modification most known to many specialists is twisted pair.It is made from a number of wires intertwined in pairs for the efficiency of receiving / transmitting signals.
Computer cables
This type of wire is divided into 2 main structural types - copper and optical. The second one has the highest bandwidth and stability in relation to external interference. At the same time, copper "twisted pair" is still more often used for home and office local area networks.
Electricity is needed always and everywhere, many devices and devices that make the life of a modern person more diverse and interesting will not work without it. The transmission of electrical energy to consumers is carried out using an electrical cable, and every competent electrician must be able to know and distinguish between the types of electrical wires and cables.
Wire marking
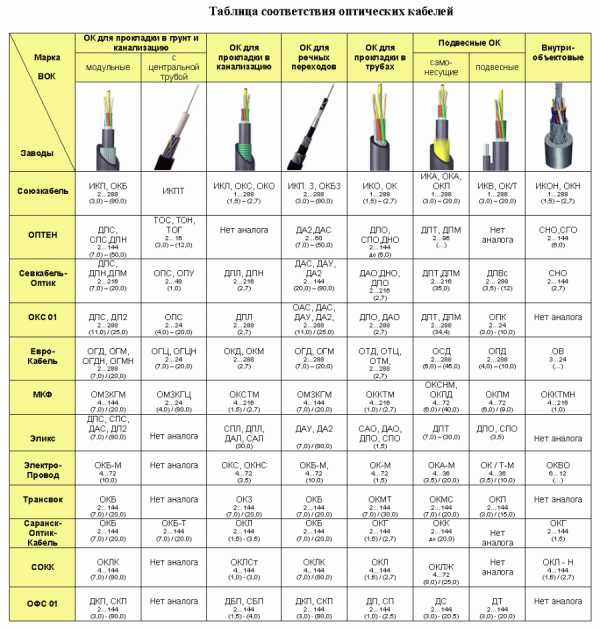
Wires are marked in the same way as cables. The first position also indicates the material of the cores - A - aluminum, and its absence - copper. The second position can be either P (wire), or PP - flat wire, Ш - cord. In the first case, it can be single-core, in the second, it usually consists of two or three (rarely more) cores. Recently, a new type has appeared - heating wires. They are designated PN.
Wire marking - which letter means what
And the last - third - position with letters is the insulation material. Everything is standard here:
- B - PVC;
- P - polyethylene:
- R - rubber;
- N - nayrit;
- L - cotton sheath, varnished;
- O - impregnated cotton braid;
- M - from oil-resistant rubber;
But this position may contain information about the design or purpose of the wire:
- G - flexible;
- T - for laying in pipes;
- C - connecting;
The letters are followed by numbers. This is the number of conductors (first digit) and their cross section (second).

Wires - P - regular, round, PP - flat
When deciphering the markings, the main thing is to understand where the cable is and where the wire is. After all, the letter "P" in the second position can denote polyethylene insulation of wires. You can navigate by the number of letters - wire marking usually contains 4 letters, and cables - more. Although this is not a clear sign, it helps in most cases. But the rest of the decoding of wire markings is much easier than cable products. Here are some examples:
- APPV:
- A - aluminum conductors;
- PP - flat wire;
- B - vinyl insulation;
- PNSV:
- letters A no - copper wires;
- PN - heating wire;
- C - steel core, round;
-
B - PVC sheath;
- PV. For wires of this brand, a number is written through the dash, indicating the number of conductors in the wire (PV-1, PV-3):
- P - wire;
- B - vinyl sheath (PVC).
- A and AC - uninsulated aluminum wire, AC - twisted.
- PR - wire with rubber insulation.
Often the question still arises: what is the difference between a wire and a cable. Basically - the number of conductors. The wire most often has one core. Two- and three-core wires differ from cables in that it has only one thin sheath. Cables usually have several.
Cable and wire marking table
Using this table, you can determine the main classifications of products and select the required section.
| Abbreviation | Permissible cross section of conductive core, mm | Flexibility category |
| APW, APPW | 1.5 to 15.0 | 1 |
| PV1, PPV | 25.0 and more | 2 |
| PV1 | from 0.7 to 11.0 | 1 |
| PV3 | 15.0 and up | 2 |
| PV4 | from 3.5 and more | 2 |
| VVG | from 1 to 1.5 | 2,3,4 |
| VVGng | 5.0 and up | 4 |
| PUNP | 0.5 and 1.0 | 3 |
| APPV | 1.0 and 1.5 | 5 |
| PVA | 2.5 and 3.5 | 3,4 |
| SHVVP | 6.0 and 11.0 | 5 |
| VBbShv | 4.0 and 4.5 | 4 |
Useful tips when working with wires:
if a mixed type of cable is used (copper and aluminum), then terminal blocks must be used. When two different metals come into contact with each other, oxidation occurs, as a result of which the cable overheats, and a short circuit or fire occurs at the point of contact;
Color coding
- if the cross-sectional area is not selected correctly, then when powerful devices are connected to the network, the wiring may burn out. In order to correctly calculate the cross-sectional area, it is necessary to calculate the power of all devices that will be connected;
- for laying in the ground, it is recommended to use a product with an armored insulation layer. It will save the cable from constant loads;
 Short circuit result
Short circuit result
- laying is permissible only at a temperature not lower than 15 degrees, otherwise you will have to preheat the wire with a special gun;
- if the external insulation has been subjected to mechanical damage, then such a product cannot be laid on the line. Quickly enough, the PVC will weaken and the strands will bend to overheat. The result is a short circuit;
- if the wire is not enough, then you need to use a cable sleeve. Only an experienced person should work with it;
- marking of wires and cables during installation will help to find out the content of the product and its parameters;
- when laying in strobes, it is necessary to use corrugations or cable channels that will protect the product from external influences.
 Protective corrugations
Protective corrugations
Marking helps to choose the right product. But besides it, you need to know the general set of rules for any wire.
The first step is to decide which composition to choose from.
Most electricians prefer copper conductors.The main advantage is that copper consumes less aluminum and also has a longer service life. Copper products will be more expensive, but they fully pay for themselves with their safety.
Next, the wire is selected for flexibility and rigidity. A rigid product usually consists of a single core, while a flexible one consists of many. The more wires inside the cable and the smaller each wire, the softer the product will be.
Flexibility can be divided into 7 categories, single-core is the 1st category, and stranded is the 7th.
 What does the section look like?
What does the section look like?
Knowing the decoding of markings is necessary not only for an electrician, but also for an ordinary person. Thus, it will be easier to purchase cable products. When laying, it is imperative to comply with all safety rules and the technology for installing cable products. Even with correct decryption, incorrect wiring can lead to consequences.
Types of power copper cables
There are various types of copper cables used to bring electricity to the house. Recently, the most commonly used cable is VVG and its modifications. The following are the different types of power cables and their brief characteristics.

VVG - a power cable with a copper core, PVC insulation TPZh, a PVC sheath (cambric), which does not have external protection, is not flammable. It is used for transmission and distribution of electric current with an operating voltage of 660 - 1000 V and a frequency of 50 Hz.
The outer shell is usually black, although white can sometimes be found. TPG insulation is marked with different colors - blue, yellow-green, brown, white with a blue stripe, red and black.It is usually packed in coils of 100 and 200 m.
The number of cores varies from one to five. The core cross section is from 1.5 to 240 mm2. In domestic conditions, a cable with a core cross section of 1.5 - 6 mm2 is used, in the construction of a private house - up to 16 mm2. The cores can be either single or multi-wire.
VVG is used in a wide temperature range: from -50 to +50 °C. Withstands humidity up to 98% at temperatures up to +40 °C. Resistant to aggressive chemicals, strong enough to break and bend. During installation, it should be remembered that each cable or wire has a certain bending radius; in the case of a flat cable or wire, the width of the plane is taken into account. So, to turn the VVG by 90 ° C, the radius of its bend must be at least 10 diameters of the cable section.
Varieties of VVG:
- AVVG (aluminum is used instead of a copper core);
- VVGng (cambric with increased incombustibility);
- VVGp (flat cable section);
- VVGz (the space between the TPG insulation and the cambric is filled with PVC bundles or a rubber mixture).


NYM (there is no letter designation in Russian) is a copper power cable with TPZh PVC insulation and an outer sheath of non-combustible PVC. Between the layers of insulation there is a filler in the form of coated rubber, which gives the cable increased strength and heat resistance. Stranded conductors, always copper.
The number of cores is from two to five, the core cross section is from 1.5 to 16 mm2. Designed for lighting and power networks with a voltage of 660 V. It can be used for laying outdoors. It has high moisture resistance and heat resistance. Operating temperature range - from -40 to +70 °C. At the same time, the cable does not tolerate exposure to sunlight, so it must be covered.Bending radius - 4 diameters of the cable section. Compared to VVG of any kind, the NYM cable is more resistant and easy to use. However, it is significantly more expensive than VVG and can only be of round section, so it is inconvenient to lay it in plaster or concrete.

KG - flexible cable. This conductor is suitable for AC voltage up to 660V and frequency up to 400Hz or DC voltage 1000V.
Copper conductors, flexible or increased flexibility, from one to six.
The TPZh insulation and outer sheath are made of rubber. Operating temperature range - from -60 to +50 °C. This cable is mainly used for connecting various portable devices, such as welding machines, generators, heat guns, etc. There is a type of KGNG with non-combustible insulation.


VBBSHv is an armored power cable with copper single-wire or multi-wire conductors. The number of cores can be from one to five. The core cross section is from 1.5 to 240 mm2. PVC is used as a material for the insulation of the TPG, the outer sheath and filling the space between the insulation and the cambric. The cable is armored with two tapes, which are wound one on top of the other in such a way that the upper one covers the gaps between the turns of the lower one. A protective PVC hose is put on top of the armor on the cable; in the VBBSHvng modification, PVC of low flammability is used.
VBBSHv is designed for alternating rated voltage of 660 and 1000 V. Single-core modifications are used for conducting direct current. Operating temperature range - from -50 to +50 °C. Moisture resistant: at a temperature of +35 °C withstands humidity of 98%. The bending radius is at least 10 cable diameters. VBBSHv is laid in pipes, ground and outdoors with sun protection.It is used when conducting electricity for stationary installations, as well as for underground supply of electricity to separate objects.
VBBSHv cable modifications:
- AVBBSHv - cable with aluminum core;
- VBBSHvng - non-flammable cable;
- VBBSHvng-LS is a non-combustible cable with low smoke emission and gas emission at elevated temperatures.
Power cables
Power cable for electric power lines - an electrical product for single or multi-core construction. Applications: individual housing construction, apartments in a multi-storey housing sector, country house or mobile electrical equipment. The purpose of the power cable is to connect the house switchboard and the consumer's electrical wiring. In order to choose the right product for your own needs, you need to know what the cable consists of.

Regardless of the scope of use and operational characteristics, structurally it is made of the following elements:
- Current-carrying conductors with a number from 1 to 5 units, made of aluminum / copper.
- The protective structure of the cores is in the form of an insulating coating.
- Protective structure of all elements in the form of an outer shell.
In addition to the main structural elements, the power cable has various auxiliary components: a waist outer cover, a screen, and armor. In addition, the design can be modified and supplemented with other elements, which will depend on the application and operating conditions. All characteristics of conductor products are displayed in color and alphanumeric markings, prescribed in its name.
Important! Today, VVG and its transformations are especially in demand. It is made in PVC insulation, copper conductive core, without external protection.The product is installed in networks for the transportation and distribution of electricity 660/1000 V and a current frequency of 50 Hz
The number of conductors is up to 5 units, with a cross section of 1.5 - 240.0 mm2. VVG can operate at ambient temperature from - 45 to + 45 C
The product is installed in networks for the transportation and distribution of electricity 660/1000 V and a current frequency of 50 Hz. The number of conductors is up to 5 units, with a cross section of 1.5 - 240.0 mm2. VVG can operate at ambient temperature from -45 to +45 C.
Copper or aluminum?
Again, this question is often asked by people who have nothing to do with electrical installation and do not know the EMP (electrical installation rules). If you do not go into details, then the answer will be the only and obvious one: copper. However, wires with aluminum strands are still in use. The main reason is their low cost. But whether it is necessary to save on this, the question is more interesting.
Consider the main disadvantages of aluminum:
- Lower conductivity (therefore, with similar current conductivity indicators, the cross section of aluminum wires and cables will be larger);
- Low strength, can not be repeatedly bent;
- Susceptibility to rapid oxidation, as a result - a short service life.
And of the advantages, we recall, only low price. But in the end, if we talk about savings, it is far from a fact that aluminum wires will be cheaper, since copper wires have a longer service life. And if we talk about the long term, then copper is more profitable. In any case, it is more reliable, so you should choose only copper wires.
It is also important to remember that not only the choice of the correct wire and cable is important, but also its quality installation. This is not only a question of service life, but also of safety.
If you do the wiring correctly and in compliance with all norms, then it can last for decades. Therefore, if you have no experience at all, then you can choose and buy wires yourself, but it’s better to entrust their laying to professionals. This is the case when saving is not worth it.
Product types
Today, when carrying out electrical work, craftsmen use wires, cables and cords. Before you start dealing with marking and decoding, it is worth understanding how these products differ and what they are in general.
Cords
Any cord always has several, at least a pair, elastic cores, with a total cross section of not more than 1.5 mm2. The cores of the cord are made of a large number of wires intertwined with each other, the insulation between which is realized using a non-metallic sheath. As a rule, cords are made with stranded wires, however, 2-core cords can also be found on sale, which are used when working with devices that do not need special grounding.
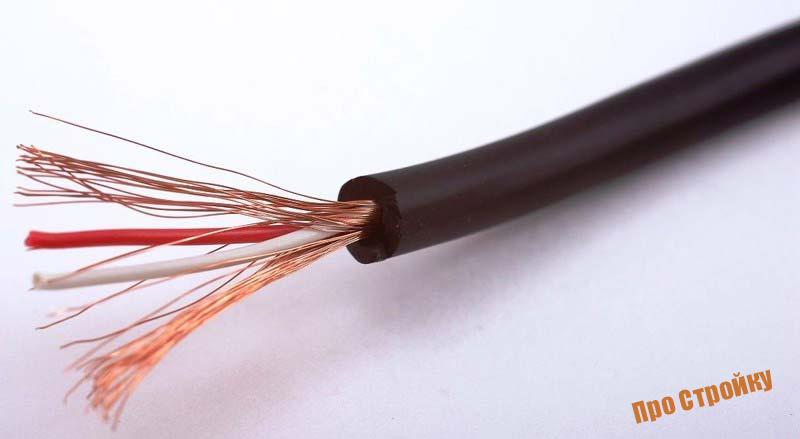
Today, cords are used to connect home appliances, whether it is a microwave or refrigerator, to the network.
Cables
An electrical cable consists of several wires located under a single insulating sheath, whether it be plastic, rubber or PVC. However, in addition to it, there may be one more protection - an armored shell made of steel tape or wire. It is necessarily reflected in the marking of the cable.

Types of cables
To date, there are 5 main types of electrical cables:
- RF;
- Power;
- For communication;
- Control;
- For management.
It is worth briefly talking about the features of the application of each type.
Radio frequency is mainly used to transmit radio and video signals and, as the name implies, is used in radio engineering devices.
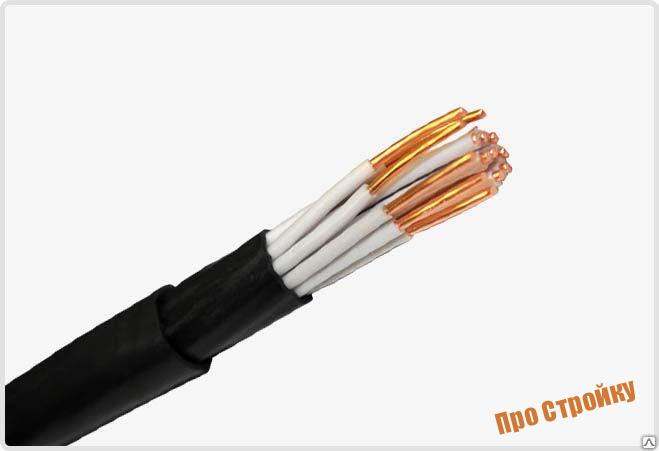

The communication cable is used to transmit information through currents of different frequencies. In this case, the transmission of long-distance communication lines is carried out at the expense of high-frequency conductors, and local - low-frequency.
The control cable is made in the form of a copper conductor equipped with a special protective screen. It has been widely used in various types of automatic systems. Here, the protective screen protects not only from mechanical damage, but also from interference.
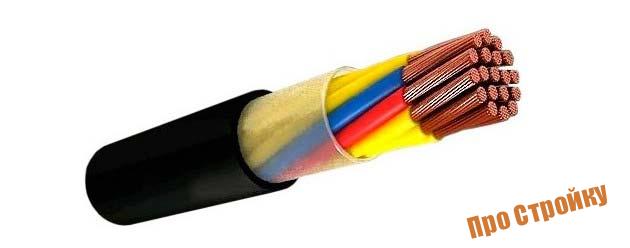
The control one is used for the operation of various electrical devices involved in signal transmission to control the main equipment. This type of cable can also be equipped with copper and aluminum conductors.
Power is designed to transfer energy to lighting and power electrical devices. Today on sale there are devices for various purposes and types. In most cases, power cables are used to implement internal (in houses) and external (underground or in the air) electrical wiring. They are made with both copper and aluminum conductors.
In this case, when choosing, pay attention to the first option. The insulating layer can be polyester, PVC, rubber, paper, etc.
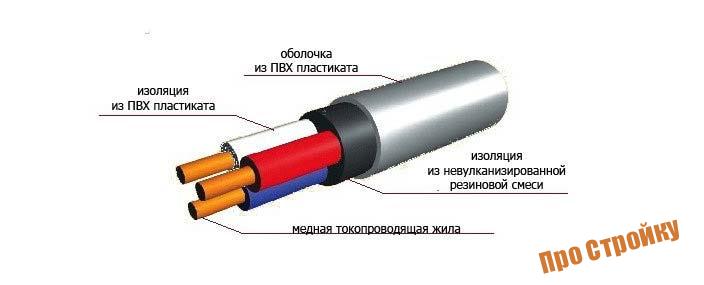
wires
Wires consist of one or more twisted wires with or without insulation. In this case, the sheath of the core is usually not made of metal, light, although it happens and happens to meet the winding with wire.
They are used when winding an electric motor, as well as when carrying out various electrical installation work, for example, laying electrical wiring in a private house. Wires with aluminum and copper conductors stand out. The latter option stands out in that it can pass more current through itself, but it is considered more expensive and starts to oxidize pretty soon in open space. At the same time, copper is a more elastic material, and therefore breakage does not occur so soon.

As for wires with aluminum conductors, they are cheaper and more fragile. They can only be connected to copper through terminals!
In the case of wires, the contacts can be made bare and insulated. The first option is usually used in the implementation of power lines. An insulated product can also be unprotected and protected - here the protection is an additional layer of insulation covering the core sheath. It is made of rubber or plastic.

Another classification is based on the purpose of the wires and divides products into installation, power and assembly. Installation and power are considered better known, since they are used in most cases inside buildings and outdoors. The mounting wire serves to connect the elements of the electrical circuit and must be made of copper without fail.
We have listed the main differences between these three electrical products. We recommend watching the following video, which more clearly presents the above information.