- The role of multiplicity in industrial buildings
- Classification of industrial ventilation
- Industrial premises with natural ventilation
- 1 Conditioning process
- Ventilation efficiency
- Types of industrial ventilation
- Calculation of local exhaust
- Ventilation created artificially (mechanical) in production
- Supply ventilation in production
- Exhaust ventilation in production
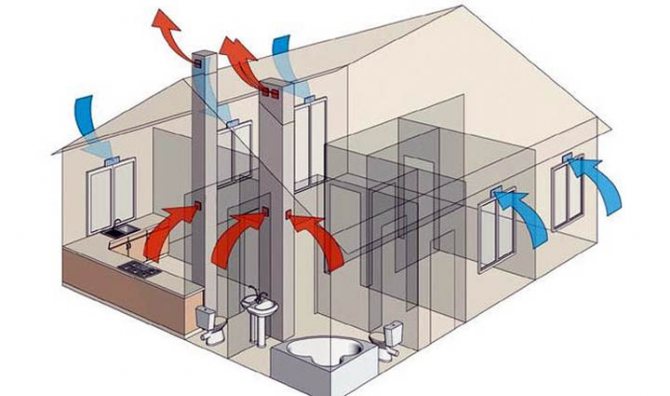
- Ventilation requirements for living quarters
- 3 Description of the supply system
The role of multiplicity in industrial buildings
Precisely selected expansion ratio allows for accurate calculation of air exchange in production rooms. Proper provision of air exchange is one of the main factors affecting the quality installation of equipment, including ventilation.
Air exchange indicators by multiplicity are used to improve the accuracy of determining the amount of heat released. Air of the required volume, allocated to the workshop of the production facility, allows you to provide working conditions that meet sanitary standards and prevent overheating of the equipment.
Classification of industrial ventilation
According to the method of supplying air masses, ventilation in the workshop is divided into natural and artificial:
- Natural.Air exchange is carried out according to the laws of physics and aerodynamics: the movement of air is induced due to the difference in temperature or pressure inside and outside the room. Street air is sucked into the workshop through the supply grilles. It "squeezes out" the exhaust air through the exhaust holes.
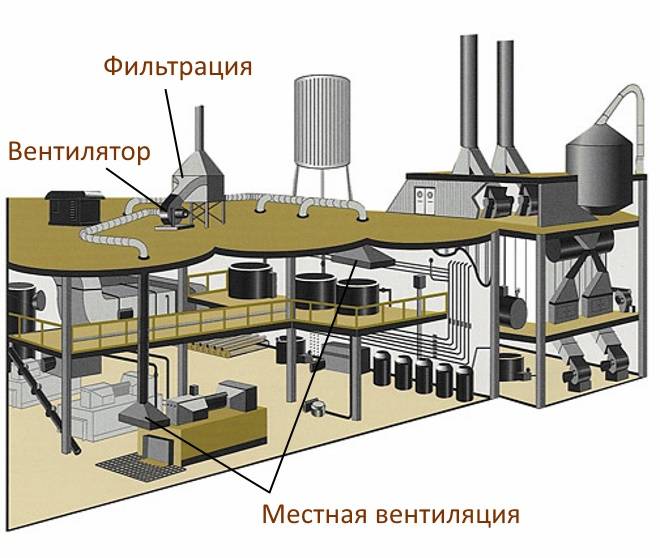
- Artificial. Air exchange is carried out due to mechanical stimulation with the help of fans. The main type of ventilation of industrial premises. Allows for preliminary preparation of incoming air, as well as filtration of the outgoing air.
Scheme of ventilation systems
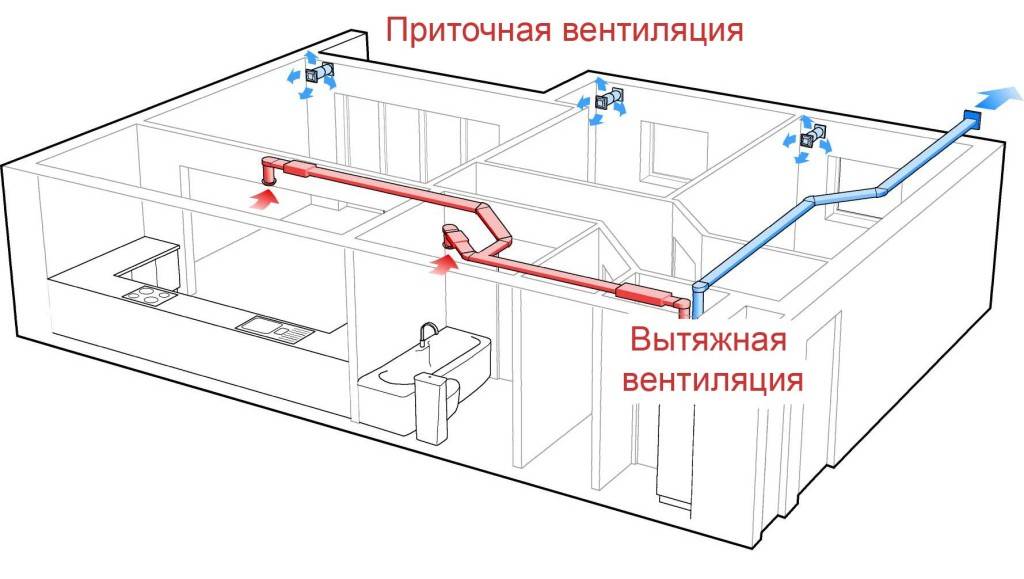
In the direction of air movement, the ventilation system is divided into supply and exhaust:
- Supply. The main task is to supply fresh air inside the workshop. Can be with artificial and natural urge. It is represented by duct fans sucking in air from outside. Often equipped with heaters.
- Exhaust. The main task is to remove the exhaust air through the exhaust openings. Often equipped with filters to prevent waste products from entering the atmosphere.
Together they make up the supply and exhaust ventilation system. This is the basis of a high-quality microclimate of any room.
By scope, it is divided into general and local:
General exchange. The main task is to ventilate the entire workshop. In its pure form, it is used when harmful chemical compounds are not released during production. Often combined with local.
General ventilation
Local. Point system for removing polluted air from a specific area of the production facility. The classic option is local hoods installed above a specific workplace or machine.The supply ventilation system can be made in the form of an air shower, a curtain or a separate zone with a controlled air composition.
Any ventilation system in production works according to two main principles:
- Mixing. Air is supplied through ceiling or wall supply openings, mixed with exhaust air and removed by means of hoods.
- Crowding out. The mechanical supply ventilation system is mounted at the floor level. Colder outdoor air is supplied, displacing the exhausted warm air to the top, where the hoods are installed.
displacement ventilation
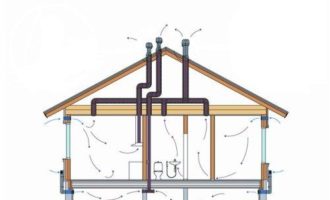
Industrial premises with natural ventilation
Natural ventilation is based on air exchange based on temperature differences. This indicator affects, first of all, the different specific gravity of air, inside the production hall and outside. The efficiency of such a system depends on the difference between these parameters. That is, the greater the difference in specific gravity and temperature, the greater the efficiency of this system.
Scheme of industrial ventilation
This ventilation system can be organized and unorganized. In the first variant, the flow of air volumes is carried out through non-densities between windows or doors, as well as when opening vents or doors. The inflow of fresh air is improved by the device of special ventilation shafts, and the shafts or channels themselves are additionally supplied with special nozzles, they are also called deflectors.
This system, even of an organized type, can only be used in industrial buildings with a small area. Most often it is used in agricultural workshops or farms.
In workshops of a small area, natural ventilation is carried out by aeration. The calculation of the ventilation system for industrial premises using this method consists in the location of windows at a certain height, as well as special openings, the size of which depends on the size of the room itself.
For example, a small workshop in which ventilation will be carried out by aeration should be equipped with openings with special transoms. The openings themselves must be mounted in two levels. In this case, the height of the first level should vary from 1 to 1.5 meters from the floor, and the second level from 4 to 6 meters from the same floor.
Industrial ventilation system
Ceilings in the workshop should be equipped with transoms in the upper part, with the so-called aeration lamps with transoms opening to the required value.
This method is not applicable to production areas that contain harmful substances or exhaust gases that pollute the atmosphere. Natural circulation does not provide for air purification, therefore, for such premises, more complex ventilation systems should be installed with mandatory filters for air purification, both in the room and at the exit from it.
1 Conditioning process
Constant replacement of air can prevent some pathologies of the nervous and cardiovascular systems. It is also necessary for people who have chronic diseases.
Today, the ventilation system can achieve the following:
- 1. Reduce the concentration of dust and various suspended particles.
- 2.Select a comfortable operating temperature.
- 3. Remove combustion products and other aggressive components that can lead to allergic reactions from the production area.

In winter, the temperature and humidity are much lower. A heater can be used for heating and humidification. This is done by mixing streams with different temperatures. The air is cooled in the chambers with the help of small water droplets. There are rooms that require the organization of a special ventilation and air conditioning system. For example, these include swimming pools, where there is a constantly high level of humidity.
Such problems are solved with the help of special dehumidifiers. But unfortunately, they have one serious drawback - the lack of ventilation. It is necessary to additionally equip the air exchange system. Otherwise, the concentration of oxygen will fall, which adversely affects the well-being of people.
Ventilation efficiency
Regardless of the type of ventilation, it must first of all be of high quality and efficient. To fulfill these conditions, it is necessary that some recommendations be followed at the design stage:
- The volume of incoming air must correspond to the amount of air that is removed from the premises. There are cases when it is necessary to make these volumes different, but all this is foreseen in advance.
- Supply ventilation system and exhaust must be positioned correctly. Clean air should come, first of all, where there are no harmful emissions, and the outflow should be maximum in places where toxic substances are formed.
- The ventilation system should not significantly affect the temperature regime of industrial premises.
- The noise emitted by the ventilation devices must not exceed the permissible limits.
- Installation must necessarily provide for fire safety issues.
- Ventilation should be easy to maintain.
- The efficiency of the system should be maximum.
Types of industrial ventilation
There are several features by which several types of ventilation of industrial premises can be distinguished.
According to the principle of operation - on natural and mechanical. Natural ventilation occurs due to the temperature difference between different air flows or due to the special arrangement of windows in the room. But this system is not efficient, so mechanical ventilation is used in industries that emit harmful substances. It not only purifies the air, but also prevents the ingress of harmful fumes into the working premises, guarantees the safety of workers.
Natural ventilation in production
On the organization of air exchange - for general and local. General ventilation of industrial premises creates uniform air exchange, while all parameters: temperature, humidity, air velocity become the same at any point in the room. This system allows you to quickly get rid of small contaminants.
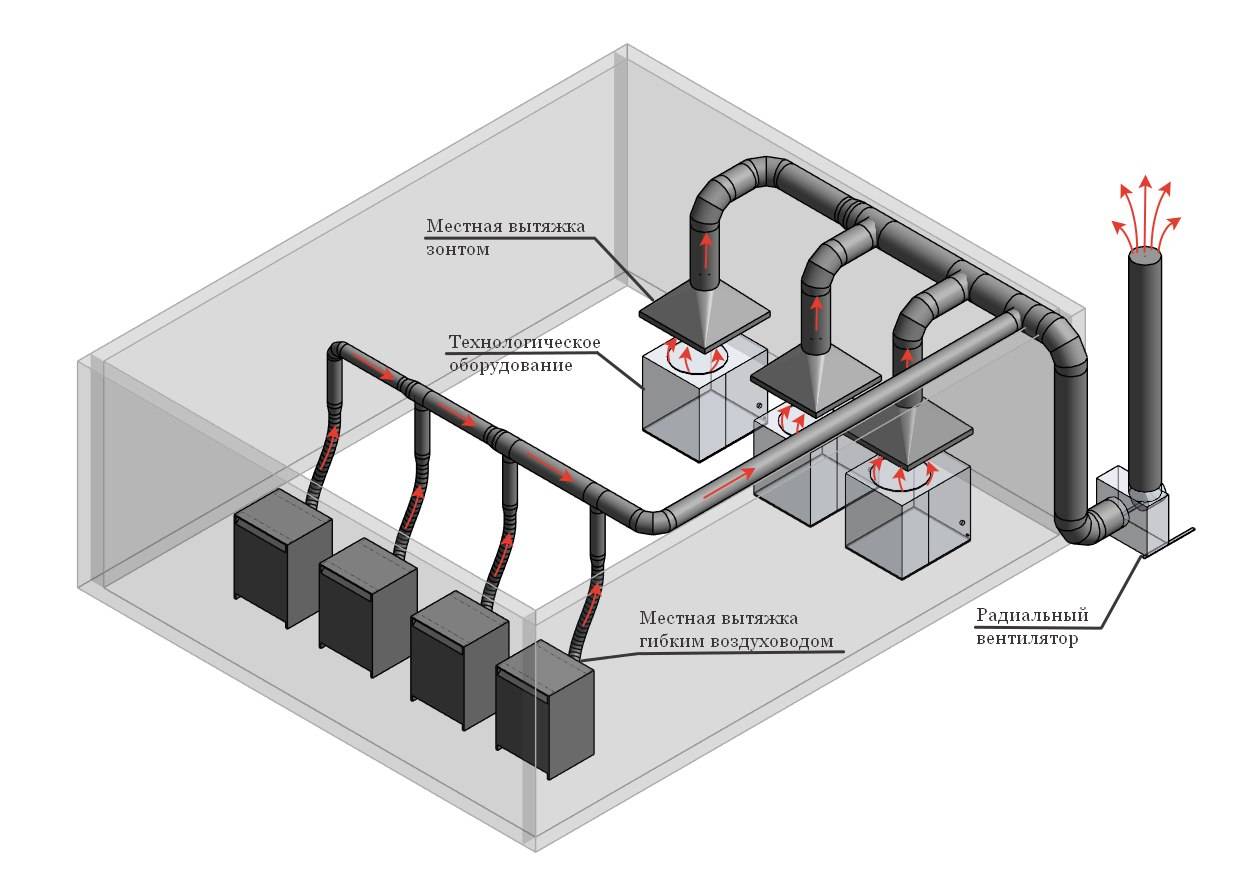
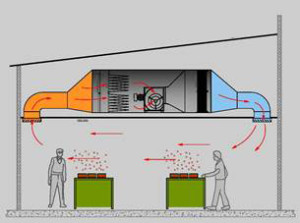
If a lot of harmful substances and fumes are released in a certain place, then local ventilation is simply necessary. It is designed to purify a small volume of air, located next to the device that pollutes the air. It can be combined with general ventilation for better results.Local exhaust is carried out either by an exhaust hood installed directly above the equipment, or by a flexible duct connected to the exhaust outlet on the equipment. Local exhaust through the exhaust hood Local exhaust from the equipment
If harmful substances are emitted at several points in the room, then a more local ventilation system will work much more efficiently. It is an exhaust hood, mounted in close proximity to the source of emissions.
In order to calculate extractor power, you need to know the size of the emission source, as well as its technological characteristics: electrical / thermal power, concentration of emitted harmful substances, etc. The dimensions of the umbrella must exceed the dimensions of the source of emission by 10-20 cm on each side. By type of device - for supply, exhaust and supply and exhaust.
It is the latter type that is most often used at enterprises: it is a combination of the functions of exhaust, supply ventilation of industrial premises, that is, it provides a full-fledged air exchange, and not just the removal of polluted air masses or the supply of clean air.
- Exhaust ventilation of industrial premises forcibly removes air from the premises, there is no organized air flow. The system provides only air outlet, removal of contaminants, and air is supplied through slots, vents, doors.
- With supply systems, this principle works exactly the opposite: the air supplied from the outside causes too much pressure in the room and the excess air itself is removed through the same gaps in the walls, door and window openings.
Both of these systems are not very effective, and for production, in the process of work which emit hazardous substances they cannot be applied, because there is a high probability that harmful air will enter the working area. In addition, to organize a working exhaust system in production, it will be necessary to use equipment of high electrical power, because they will be subjected to serious loads. It will also require the organization of a distribution duct system. Industrial exhaust system
Calculation of local exhaust
If emissions of harmful substances occur in production, they must be captured directly at the closest possible distance from the source of pollution. This will make their removal more efficient. As a rule, various technological capacities become sources of emissions, and operating equipment can also pollute the atmosphere. To capture the emitted harmful substances, local exhaust devices are used - suction. Usually they have the form of an umbrella and are installed above a source of vapors or gases. In some cases, such installations are included with the equipment, in others, the capacities and dimensions are calculated. It is not difficult to perform them if you know the correct calculation formula and have some initial data.
To make a calculation, you need to take some measurements and find out the following parameters:
- the size of the emission source, the length of the sides, the cross section, if it has a rectangular or square shape (parameters a x b);
- if the pollution source is round, its diameter must be known (parameter d);
- the speed of air movement in the zone where the release occurs (parameter vв);
- suction speed in the area of the exhaust system (umbrella) (parameter vz);
- planned or existing installation height of the hood above the source of pollution (parameter z). At the same time, it must be remembered that the closer the hood is to the source of emission, the more efficiently pollutants are captured. Therefore, the umbrella should be placed as low as possible above the tank or equipment.
The calculation formulas for rectangular hoods are as follows:
A = a + 0.8z, where A is the side of the ventilation device, a is the side of the source of pollution, z is the distance from the source of emission to the hood.
B = b + 0.8z, where B is the side of the ventilation device, b is the side of the pollution source, z is the distance from the emission source to the hood.
If the exhaust unit will have a round shape, then its diameter is calculated. Then the formula will look like this:
D = d + 0.8z, where D is the hood diameter, d is the pollution source diameter, z is the distance from the emission source to the hood.
The exhaust device is made in the form of a cone, and the angle should be no more than 60 degrees. Otherwise, the efficiency of the ventilation system will decrease, as zones are formed along the edges where air stagnates. If the air velocity in the room is more than 0.4 m / s, then the cone must be equipped with special folding aprons to prevent the dispersion of released substances and protect them from external influences.
It is necessary to know the overall dimensions of the hood, since the quality of air exchange will depend on these parameters.The amount of exhaust air can be determined using the following formula: L = 3600vz x Sz, where L is the air flow rate (m3 / h), vz is the air velocity in the exhaust device (a special table is used to determine this parameter), Sz is the opening area of the ventilation unit .
If the umbrella has a rectangular or square shape, then its area is calculated by the formula S \u003d A * B, where A and B are the sides of the figure. If the exhaust device has the shape of a circle, then its size is calculated by the formula S = 0.785D, where D is the diameter of the umbrella.
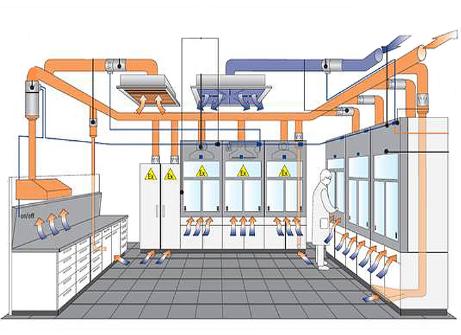
Ventilation created artificially (mechanical) in production
This type provides the intake and removal of air flows with the help of fans. The organization of a mechanical system requires the investment of large energy resources and economic costs. Despite this, it has several advantages:
- Allows air to be taken from the desired location
- It is possible to influence the physical properties: cool or heat the air flow, increase or decrease the humidity level
- It is possible to supply air directly to the workplace or exhaust with subsequent filtration
Purification of polluted air from the premises, a prerequisite for production. This factor is under strict control of environmental organizations.
The mechanical system, depending on the design, goals, and tasks assigned to it, differs:
- Supply
- exhaust
- Supply and exhaust
In production places, the air system is selected based on the needs and specifics of the place of operation.

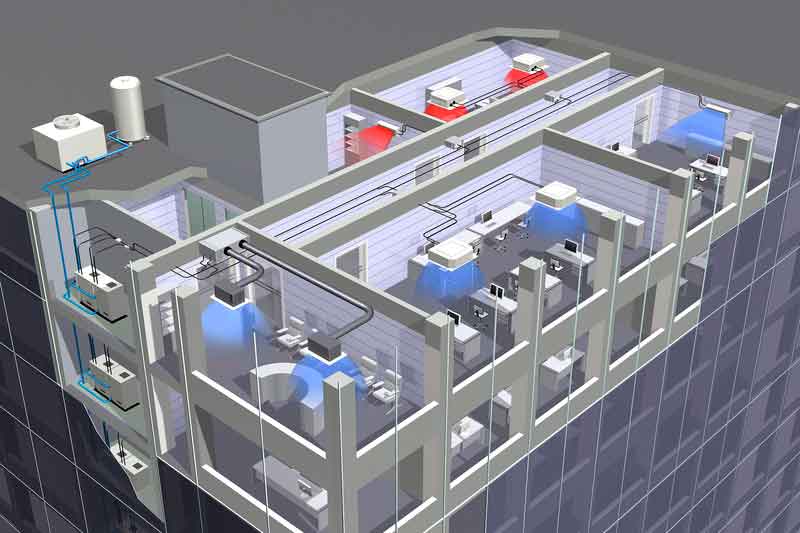
Supply ventilation in production
Designed to supply the production area with clean air. Installed mainly in places with elevated operating temperatures and low concentrations of harmful substances. Unclean air is removed through the natural ventilation outlets (transoms, ventilation shafts) supported additionally by the air flow of the supply ventilation.
According to the type of device, the following air handling units are distinguished:
- Monoblock. These devices are easy to operate and maintain, but are expensive. During installation, the main unit is fixed, to which air ducts are connected and electrical power is connected.
- Typesetting. Devices require special skills to install, are relatively inexpensive in price.
With forced ventilation can influence the environment and subjected to the necessary processing: heat, dry, moisten, depending on the type of production.

Exhaust ventilation in production
It performs the functions opposite to supply ventilation. Exhaust ventilation system for industrial premises provides ventilation. In production, it is independently used for small movements of the air flow. Depending on the prevalence, exhaust ventilation is distinguished:
- General exchange. Air movement covers the volume of the entire room
- Local. Designed to remove air from a specific workplace
It is mainly installed in warehouses, utility rooms, in places where there is no high concentration of harmful gases and impurities. The inflow in this case comes by infiltration through the frame of the building, windows, transoms.

Ventilation requirements for living quarters
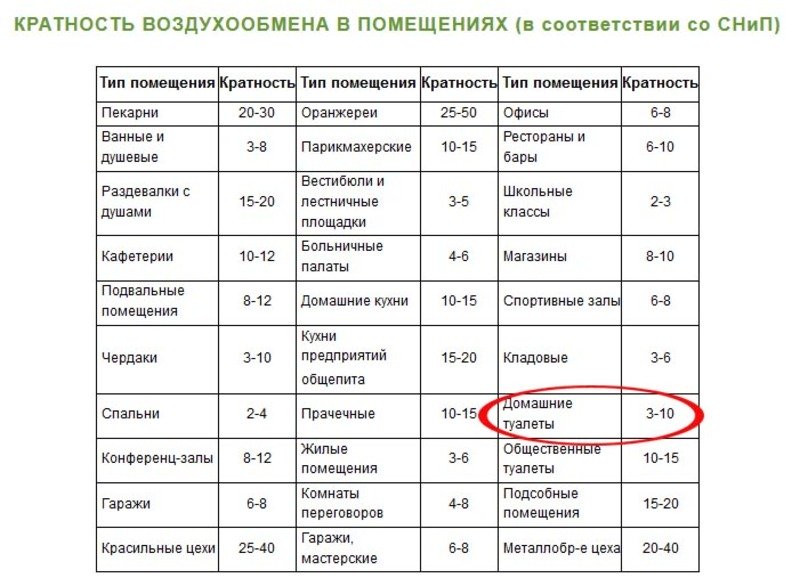
Among other things, optimal air exchange rates in the living area must be achieved. This indicator determines the number of air replacement cycles per hour. So according to the norms of SNIP for a room with an area of 30 sq.m. this value is 1.3 units.
In order to practically realize a full-fledged air exchange, two types of ventilation are used in the residential area: natural and forced supply. In the natural way, air circulation is provided through ventilation and due to the presence of gaps in doors and windows, and in log houses due to gaps between logs. However, such a measure does not allow for a full-fledged gas exchange and its multiplicity is quite low.
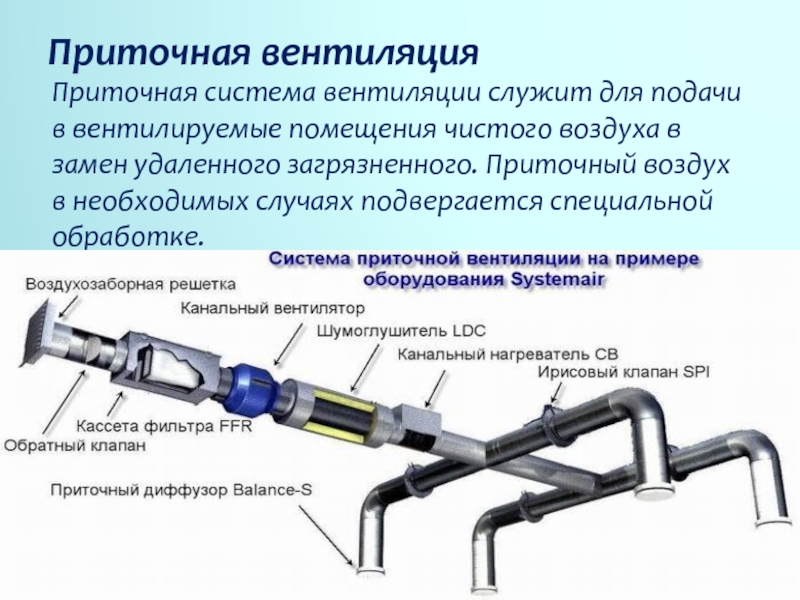
3 Description of the supply system
The main purpose of this type is to supply new air to the room. In order for the device to work at the proper level, additional elements are built into its design, for example, a filter or a humidifier. The disadvantage is the impossibility of taking in air masses. The room cannot be completely filled with fresh air.
The supply system includes a fan, which must be fixed to the window transoms. So the updated air enters the room. Gases are injected, which displace the waste masses through the exhaust holes.
The main parameter of the fan is its power. It determines the rate at which new air is forced into the room. Technical characteristics directly depend on the length of the channels. In addition to the main device, the system has the following elements:
- 1. Filters.
- 2. Air ducts.
- 3. Lattices.
- 4. Heaters.
- 5. Valves.
- 6. Distributors.
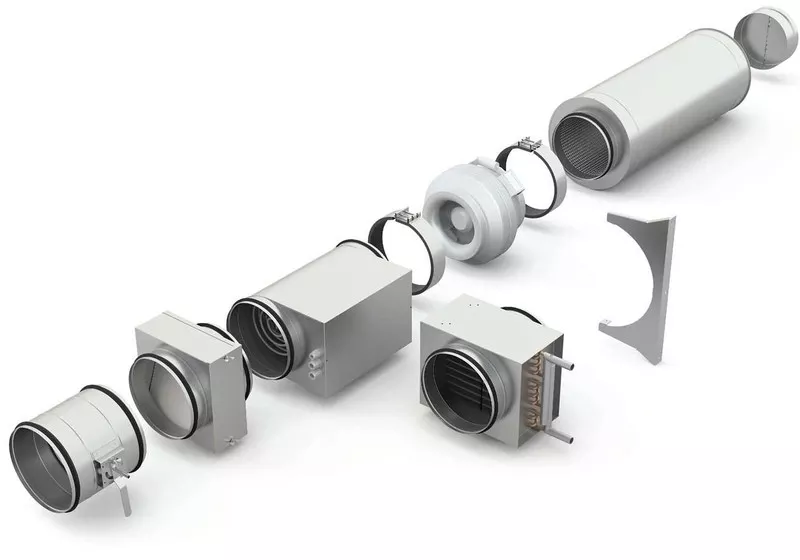

Filters clean fresh streams from various mechanical particles, for example, any debris or insects. Depending on the model, they can be coarse or fine cleaning.
Heaters increase the temperature of the feed streams. They are divided into electric and water types. Of the additional elements in the system, the following may be present:
- 1. Dehumidifiers.
- 2. Means of automation.
- 3. Recuperators.
- 4. Humidifiers.
The area of the system where fresh air will be supplied must be in a place protected from dust. The supply chamber is located near this element. This type of air exchange is suitable for any objects. It can provide flow to the entire building or a separate part of the room. Able to optimize temperature. With the help of the supply system, you can create various clean zones in the production.