- 5 Checking the performance of the ventilation system
- Technology for creating a ventilation system
- 2 How the system works
- When is a regular hood not enough?
- An example of a simple basement ventilation calculation
- Natural system calculation
- Calculation of the forced system
- How to make ventilation in the cellar
- Why is a cellar ventilation system necessary?
- Calculation and device
- Do-it-yourself installation
- Kinds
- Natural supply ventilation
- Natural exhaust ventilation
- Forced
- Supply and exhaust ventilation with heat recovery
- Installation nuances
- Video description
- Conclusion
- Combined system type
5 Checking the performance of the ventilation system
You can test any type of system in a very simple way - a piece of paper attached to the hole in the exhaust pipe must be held by the exhaust air stream, as if glued.
By installing an ordinary outdoor (alcohol) thermometer in the basement, you can monitor temperature changes and, if necessary, make adjustments - close or open valves, turn on the fan additionally. The optimum temperature for a room used for storing vegetables is about 3-5 ° above zero; for a gym, a billiard room, comfortable indicators are + 17-21 °. Humidity within 85-90% and 60% respectively.

With its increase over 90% in the room, approximately in the middle, a box filled with sawdust, salt, and quicklime is installed. These materials, absorbing moisture well, will reduce its content in the air. If they are then dried in the sun or otherwise, they can be reused.
In difficult cases, when mold has appeared on the walls, they are cleaned, treated with special antiseptics or whitewashed with lime. The use of bleach is not recommended. After completing the treatment, the movement of air is temporarily increased. This procedure is recommended to be carried out every year before laying the fruit for the winter.
Another important point is that in order to improve the quality of ventilation, at the construction stage, mandatory waterproofing of the walls from the outside and inside is carried out. When planning the location of a workshop or a rest room, they provide for the possibility of insulation, connecting heating.
Technology for creating a ventilation system
Although there are several varieties of plinth ventilation systems, there is no variety of schemes and technologies. The basis of any hood is natural supply and exhaust air exchange.
The scheme of arrangement of any method is similar. That is, it all starts with the planning and placement of air vents, ventilation pipes.
If the area of the room is large (over 50 m²), then a fan of sufficient power should be added to the design. In this case, the inlets must provide a supply of clean air.
If there are several rooms and in each of them it is necessary to maintain a separate microclimate, then it will be necessary to create complex ventilation systems.
Which involve the use of natural or forced exhaust in separate rooms, and a large number of additional equipment can be used for its implementation.
 To replace polluted air masses, special ventilation openings are used, which are usually distributed on all sides of the building. Which in itself makes the method more effective
To replace polluted air masses, special ventilation openings are used, which are usually distributed on all sides of the building. Which in itself makes the method more effective
The most important point is the number of ventilation holes. With their shortage, the system will not be able to cope with the task even in a small basement.
Since numerous stagnant zones with high humidity and other negative phenomena will form.
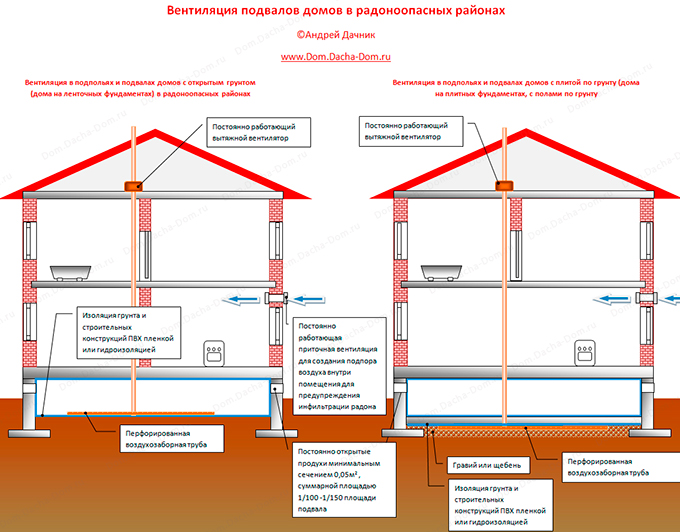
This indicates that there should be a lot of air ducts, and their exact parameters are indicated by the profile Code of Rules - SP 54.13330.2011. Where it is clearly noted that the total area of the ventilation openings should be 1/400 of the total area of the basement.
 Despite the characteristics of each type basement ventilation systems the most important issue is still the correct use of exhaust pipes and openings. So, in the latter case, the air ducts should be located at least 1.5-2 m apart, otherwise it will be difficult to achieve the expected result even when using modern equipment
Despite the characteristics of each type basement ventilation systems the most important issue is still the correct use of exhaust pipes and openings. So, in the latter case, the air ducts should be located at least 1.5-2 m apart, otherwise it will be difficult to achieve the expected result even when using modern equipment
The same document says that these elements should be evenly spaced around the entire perimeter. Another rule contained in the SP is the indication of the exact area of each duct, which should not be less than 0.05 m².
The most important and most frequently used element in any basement ventilation scheme is the exhaust opening, called the vent.For maximum efficiency, there should be a lot of them, and around the entire perimeter of the building
It is also important to understand that these structures are divided into supply and exhaust. And they must be placed on opposite walls, opposite each other.
And then, to determine the parameters and draw up a ventilation scheme, it remains only to perform a simple calculation.
What do you need:
- The area of the basement divided by 400. The result is the total area of the openings in the base;
- The resulting value should be divided by 2 (pairs of supply and exhaust structures) and placed evenly around the entire perimeter of the building.
At the same time, it should be remembered that, according to the joint venture, it is not necessary to make a round hole with a diameter less than 25 cm, and the minimum size of a rectangular hole should be 20 × 22 cm.
An exception may be situations where several smaller ducts are placed side by side - if round ducts are made, their diameter may not be 25 cm, but 11 cm.
Do not make the ventilation holes as large and rare as possible. For example, in a house, the area of \u200b\u200bthe basement of which is 100 m² with a prescribed air volume of 250 cm², they should not be divided between 4 large ones, as many developers do, but divided into 10 small ones.
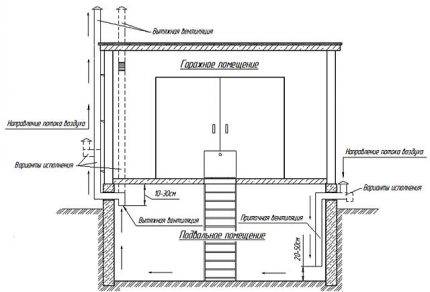 The scheme in which air exchange is provided with the help of inlet and outlet openings is considered classical or typical. Since it is suitable in most cases, and without any changes
The scheme in which air exchange is provided with the help of inlet and outlet openings is considered classical or typical. Since it is suitable in most cases, and without any changes
And it’s even more practical to make two dozen minimum allowable holes, for example, round ones with Ø 11 cm, and place them approximately every one and a half meters along the entire perimeter. And such a ventilation scheme of any basement floor will be as efficient and profitable as possible.
If the air ducts do not cope with the function of replacing the air in the basement room, then air ducts are added to the ventilation system - pipes that are additionally equipped with fans and other additional equipment characteristic of a forced system.
2 How the system works
The principle of operation of the system is based on the basic laws of physics. Having carefully looked at the ventilation scheme in the cellar, one can state the fact that it is extremely simple, but at the same time reliable.
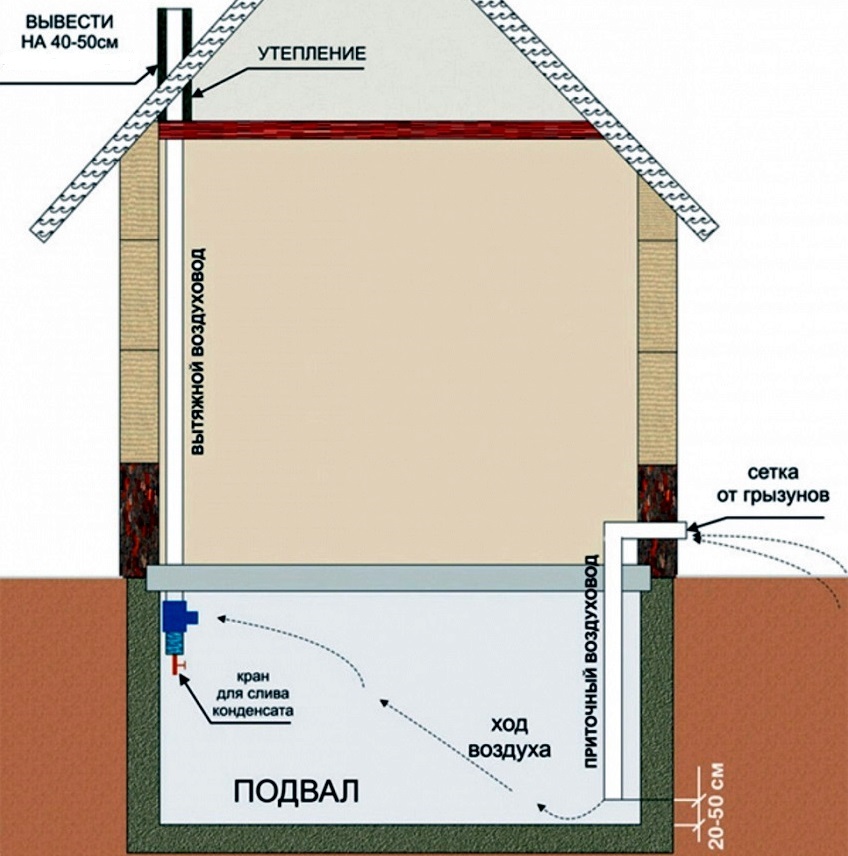
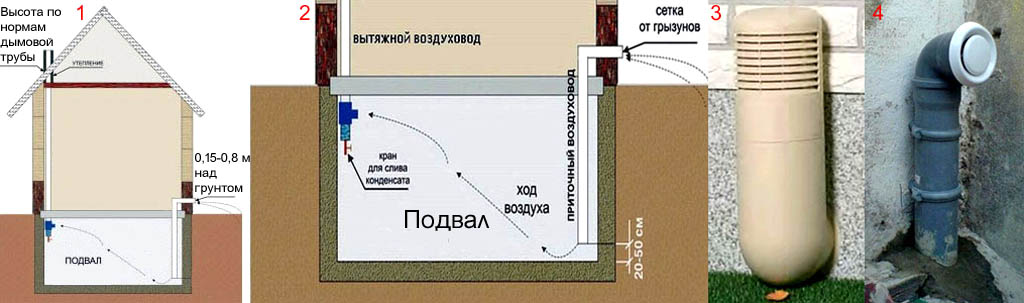
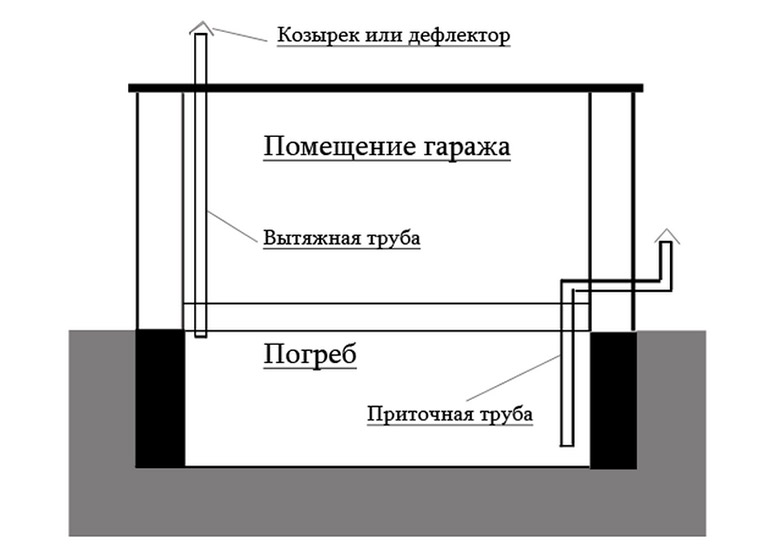
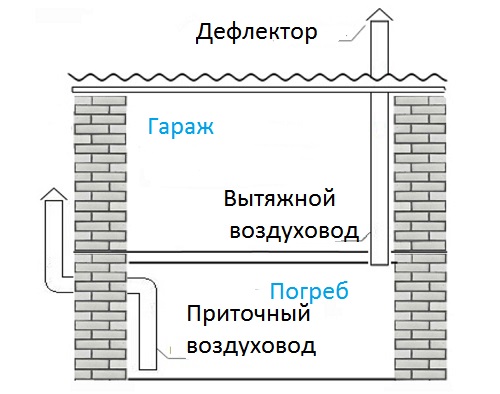
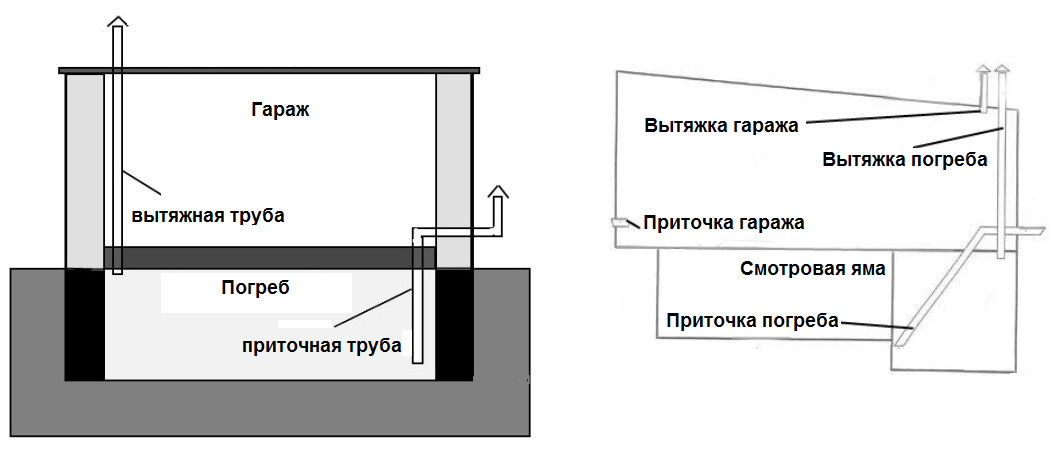
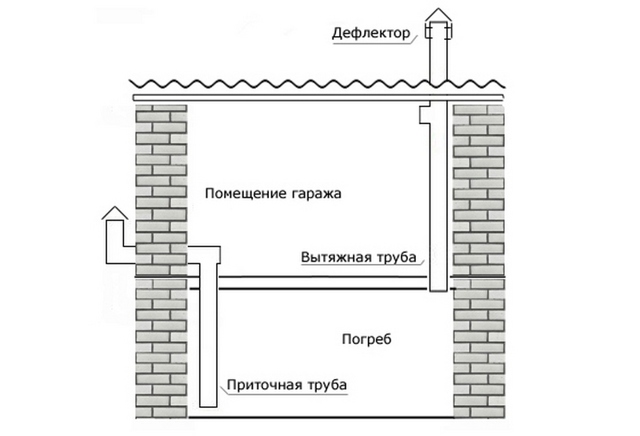
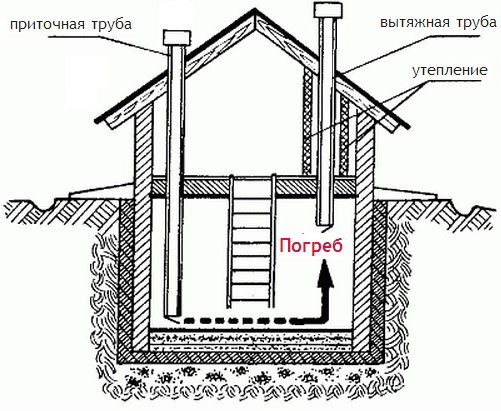
To organize a complete system, it is enough to provide 2 ventilation holes for the basement. One of them is necessary to remove excess fumes and air from the room, and the second is to ensure the flow of pure and fresh oxygen. To ensure optimal efficiency, such a system requires two pipes, supply and exhaust.
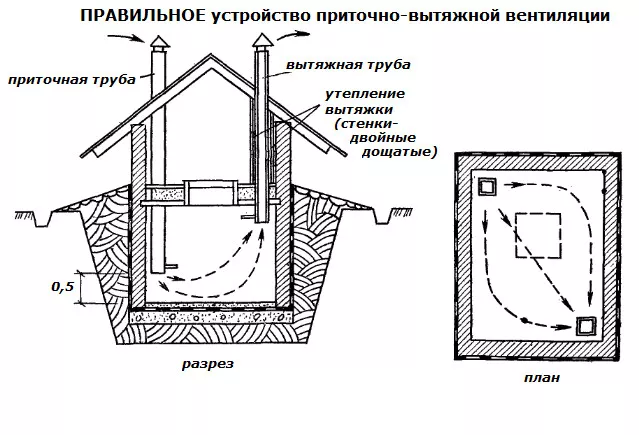
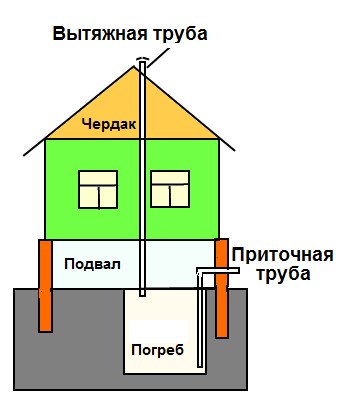
Ventilation in the cellar under the house
An equally important stage is the installation of pipes at the optimum height from the floor and their subsequent withdrawal into the external space. Incorrectly placed air ducts can bring in too much air, which is extremely undesirable for fresh food and vegetables stored on the shelves. Too small a diameter of the pipes will not allow you to quickly remove musty air masses from the room.
We recommend watching a short video that will explain the principle and operation of the cellar
When is a regular hood not enough?
In a number of situations, you can get by with the usual natural supply ventilation, which is so popular with suburban homeowners.It will not require serious costs for the arrangement and operation, however, one can argue about the effectiveness of its work (especially in the summer). A natural hood does not need additional fans in the cellar, so the installation costs are really minimal (you only need to buy pipes and protective caps).
Air ducts fixed on the wall of the cottage.
However, natural ventilation will not give the desired effect if:
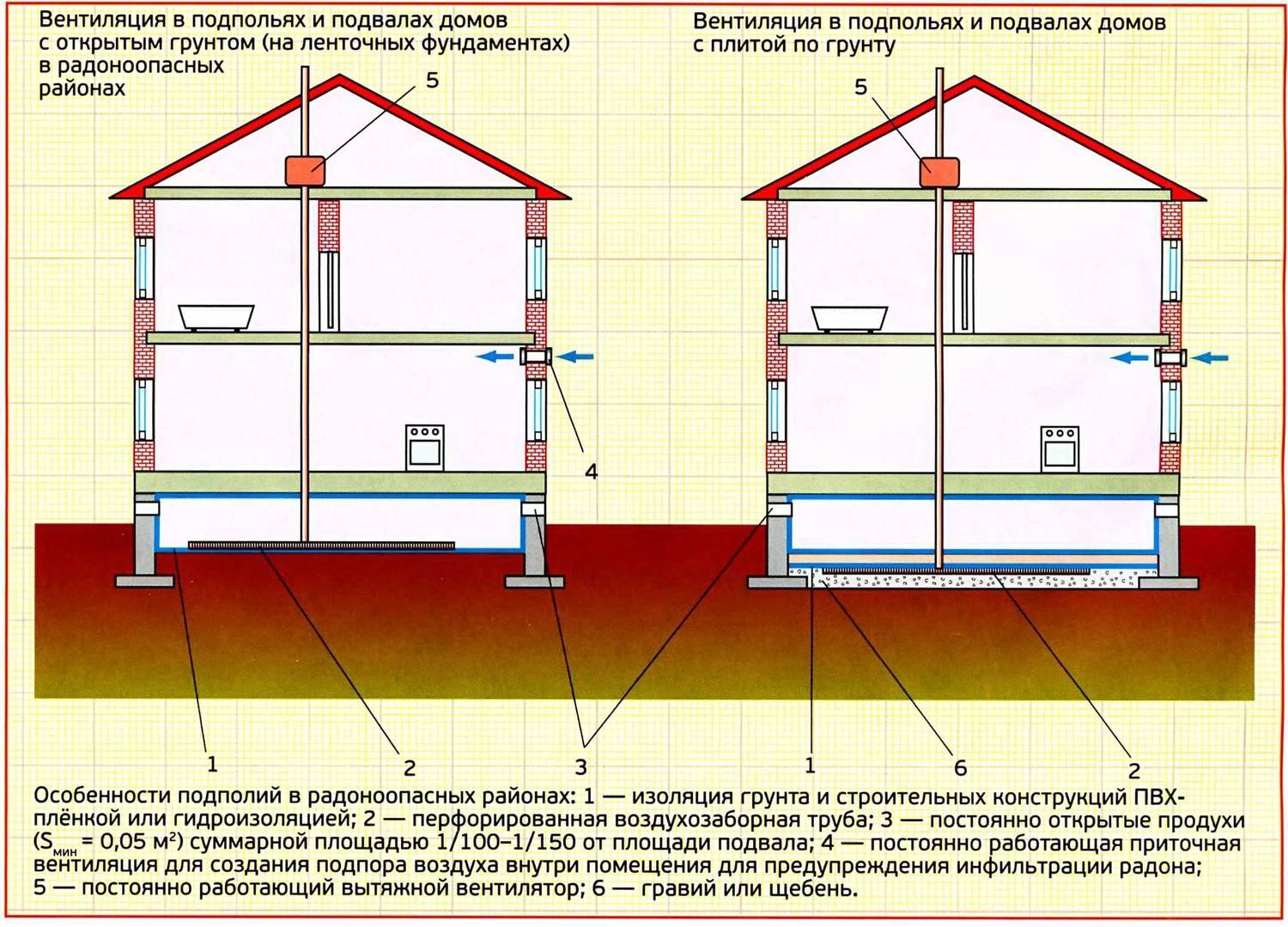
- The basement has an area of 40 sq.m. and more. In large storage facilities, in the absence of good ventilation during the winter months, the warm air inside is saturated with moisture. In the chimney, moisture condenses and remains on its walls (this happens according to the laws of physics, due to the temperature difference). Drops of condensate quickly accumulate, and due to the negative temperature they soon turn into frost. When frosts last for several days, frost closes the exhaust pipe with a dense layer, which excludes the normal movement of air outside. This moisture can be eliminated only with the help of fans in the cellar, which are placed inside the supply and exhaust pipes. An exception is the situation when the basement is divided into several rooms and natural ventilation pipes are installed in each. Then a forced ventilation device in the basement is not required.
- Natural ventilation is indispensable in those basements where it is planned to make living rooms, or rooms in which people will stay for a long time (workshop, bathhouse, gym, etc.). Only an extractor hood based on the operation of a cellar fan will be able to supply oxygen in sufficient quantity for a comfortable stay of people.
- Also, good fans in the cellar are needed if there is a large amount of food in the storage. In the case of a vegetable cellar, the hood will fight not only with humidity, but also with unpleasant odors.
An example of a simple basement ventilation calculation
Natural system calculation
It is based on the following rule - air exchange per 1m2 of the basement provides 25 cm2 of the flow area of the air line.
EXAMPLE: To ventilate a basement with an area of 15 m2, it is necessary to use a 375 cm2 main.
Circle area formula:
Substituting the appropriate values, we get, see:
Rounding the value, we obtain the estimated diameter of the air line pipe 20 cm.
Calculation of the forced system
For air ducts in operated basements (cellars) with forced ventilation, it is based on the intensity of air exchange. According to the standards, it is accepted that the air in the basement, occupied by the storage of vegetables, is completely replaced twice within an hour. The need for air exchange will be calculated by the formula:
where:
-
- L is the need for air exchange, m3/hour;
- Vp - the volume of the basement, m3;
- Kkr - the coefficient of the frequency of air replacement.
EXAMPLE: Basement with an area of 15 m2, a height of 2 m, a volume of 30 m3. Therefore, the need for air exchange will be 60 m3/hour.
The cross-sectional area of the duct is determined by the formula:
where:
-
- S is the cross-sectional area of the duct, m2;
- L – air consumption (air exchange), m3/hour;
- W is the air flow velocity, m/s. It is taken from the technical passport of the fan (we accept 1 m / s).
Substituting all the values into the formula and using the previous formula for determining the radius, we get a pipe radius of 7.4 cm.Therefore, when using a fan capable of creating an air flow at a speed of 1 m / s for ventilation of the basement, a pipe with a diameter of 15 cm is sufficient.
In the case of intensive use of the basement floor, for example, there is a gym in it, the air exchange rate should take into account excess heat and moisture in the room. The formula for calculating the expense will look like this:
where:
-
- p is the air density (at t 20°C it is equal to 1.205 kg/m3);
- Тв is the heat capacity of air (at t 20°С it is equal to 1.005 kJ/(kg×K));
- q - the amount of heat generated in the basement, kW;
- ti – outgoing air temperature, °C;
- tv is the temperature of the incoming air, °C.
All coefficients used in the calculations are regulated by the normative document SNiP 41-01-2003 "Heating, ventilation and air conditioning".
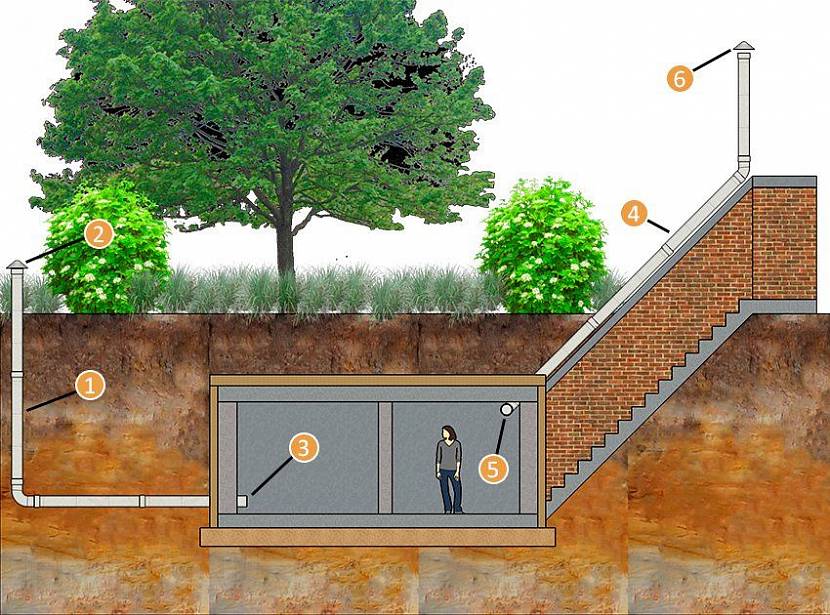
How to make ventilation in the cellar
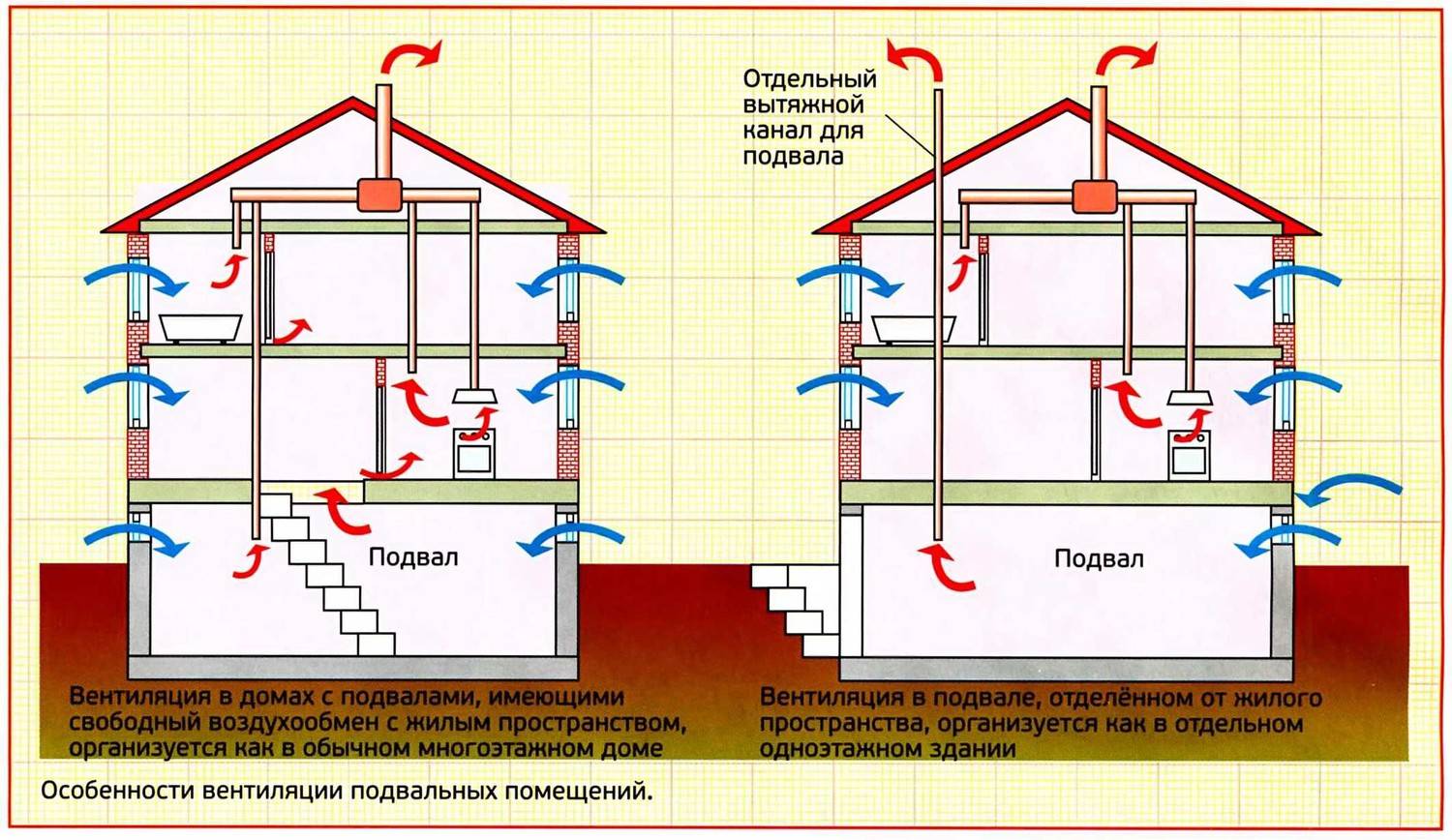
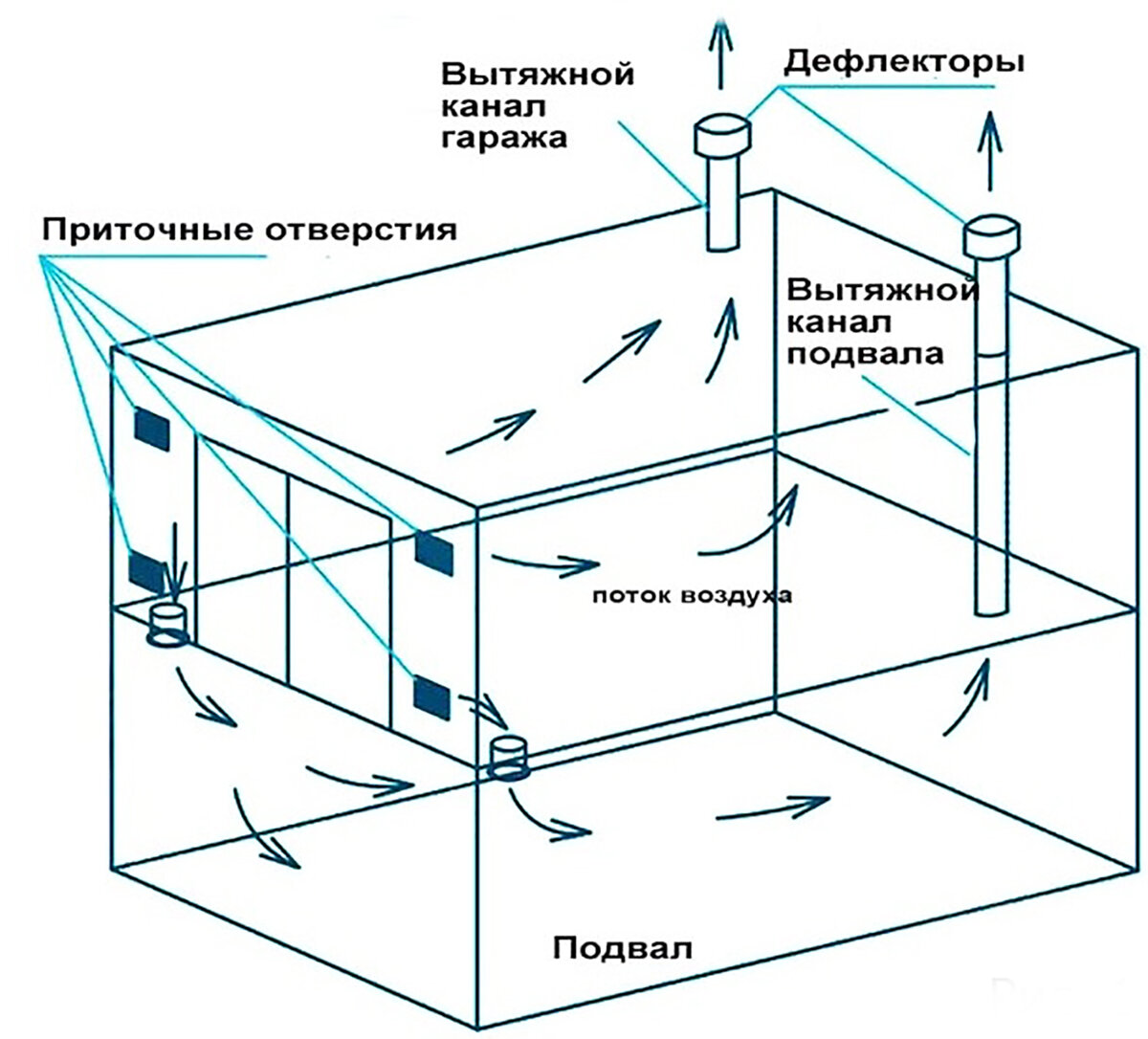
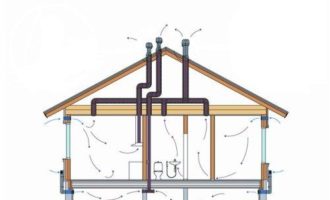
Air circulation in the underground storage can be provided naturally or artificially. In the first case, air enters through special openings, and in the second - with the help of fans (Figure 1).
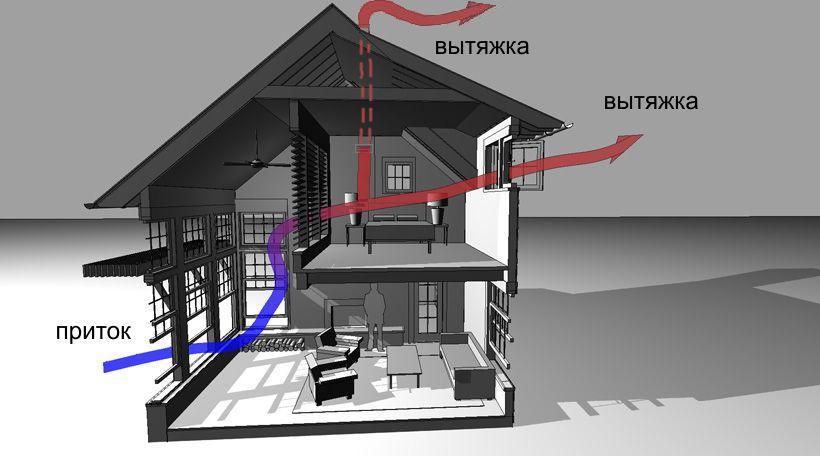
The most simple, inexpensive, but at the same time effective method of ventilation is the supply and exhaust system. For its arrangement, two pipes are installed at different levels, the ends of which are led out into the street. Warm air is exhausted through one of the rooms, and cool air enters through the other. Next, we will consider in more detail how to equip various ventilation systems in basements.
Why is a cellar ventilation system necessary?
Many owners of personal plots believe that it does not make sense to equip any kind of hood in the basement.There is also an erroneous opinion that the presence of holes in the walls or roof of the vault will disturb the stable microclimate. In fact, everything happens the other way around.
Figure 1. The principle of operation of the hood in the basement
In residential areas, the temperature is too high for storing fresh vegetables and preparations in jars, and it is too cold outside (in winter). In the underground storage, subject to proper ventilation, not only a stable temperature is maintained, but the humidity is optimal for storing vegetables. It is with this task that a high-quality hood successfully copes, through which warm air is removed and a moderate amount of fresh oxygen enters.
Calculation and device
For small cellars, one or more holes in the walls, brought out with pipes, will suffice. However, if the storage is large enough, it is better to equip the supply and exhaust system that will effectively cope with maintaining the microclimate.
To determine how many channels you need for your basement, you need to do some calculations. First, calculate the area of \u200b\u200bthe room by multiplying the width by the length. Secondly, it should be borne in mind that for each square meter of area, 26 square centimeters of the exhaust duct are needed. For example, if the cellar area is 6 square meters, this figure must be multiplied by 26. The resulting number (156 square centimeters) will mean the total area of \u200b\u200bvents. To determine which diameter will be optimal, you need to take the square root of this number divided by the number Pi. In our example, this indicator will be 14 cm.However, for a better removal of warm air and the inflow of fresh air, this figure can be independently increased by 10-15%.
Do-it-yourself installation
After you have made all the necessary calculations and decided on a suitable diameter, you can proceed with the direct installation of the system.
Installing the hood in the cellar is carried out as follows:
- If the hood is mounted in an already finished storage, it is necessary to make several holes in the roof.
- An exhaust pipe is inserted through one hole and fixed so that the lower edge is 10-15 cm below the ceiling, and the upper part protrudes 70-80 cm above the ground.
- A hole is also made in the opposite corner and a supply pipe is inserted into it. It must be fixed in such a way that the lower edge does not reach the floor by 15-20 cm, and the upper one only protrudes 20-25 cm above the soil surface.
After installation, it is desirable to cover the outer parts with visors and gratings so that atmospheric precipitation does not get inside. Checking the draft intensity is very simple: just attach a sheet of paper to the supply channel. If it fluctuates intensively, then the air flow into the room is good.
Kinds
All types of ventilation are divided into several types, depending on its purpose, the complexity of the arrangement and the principle of operation. But the principle of operation of any of them will be based on the laws of physics on the movement of air masses. Cold air goes down and warm air goes up.
Natural supply ventilation
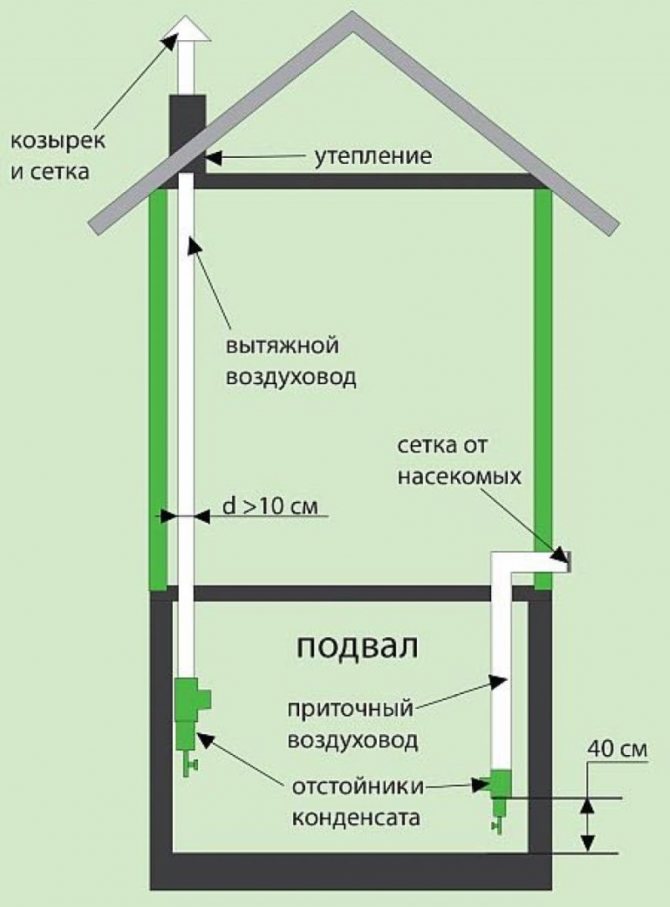
The simplest, airflow system in the foundation or basement. It is equipped at the stage of building a house and is a small hole in the upper part of the basement.
If the basement is below ground level, then the hood is equipped with plastic or asbestos-cement pipes with a diameter of 10-15 cm. They are brought out above the surface to a height of 30 cm and covered with bars from debris and rodents. This method is natural and depends on fluctuations in street temperature, wind strength, and humidity.
When calculating its throughput, 1/400 of the total area of \u200b\u200bthe basement is taken - this is how we get the total area of \u200b\u200ball products.
Openings should be located on the leeward side, the least exposed to precipitation. Houses with a complex foundation shape and located in low-lying places can have up to one hole for every 3-4 meters. We close the vents with gratings from the outside.
This inexpensive option is well suited for ventilating garages and non-residential basements, or as an addition to the main ventilation system.
Natural exhaust ventilation
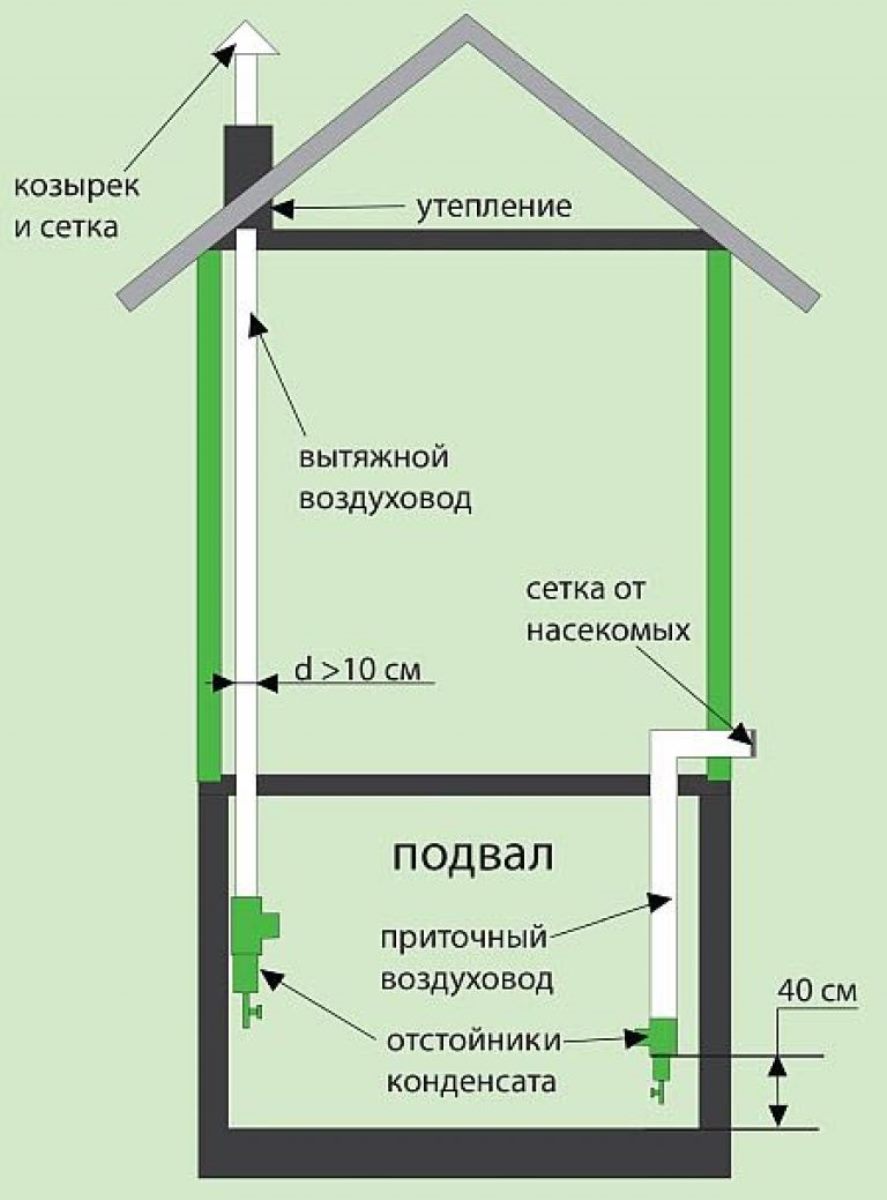
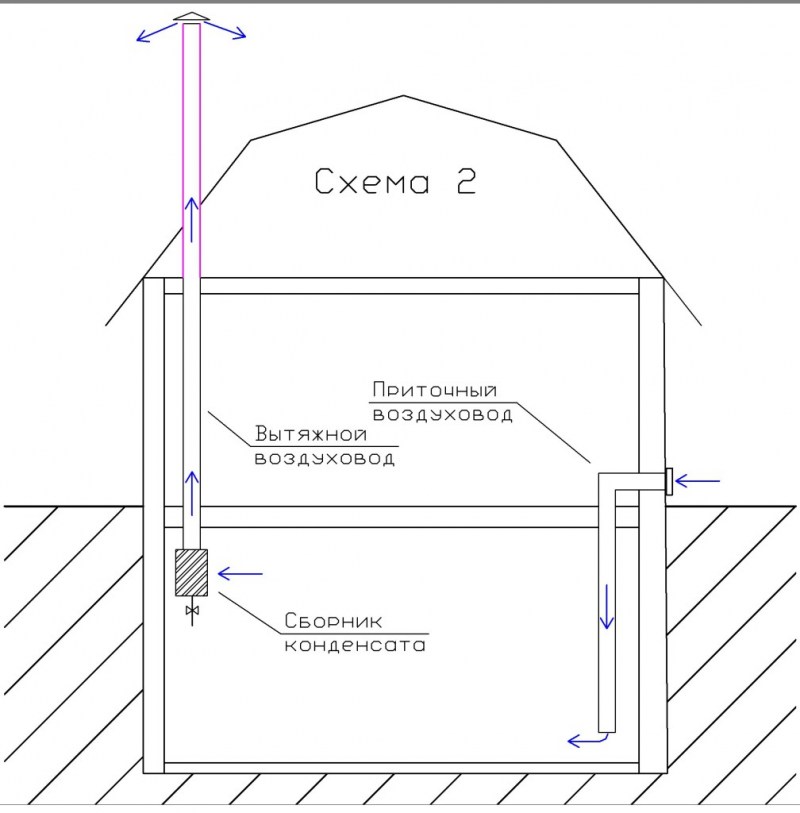
Supply and exhaust type. For proper operation, you will need to install two pipes for ventilation, and the supply and exhaust ventilation device looks like this.
- The first pipe is located under the very ceiling of the basement and is designed to drain warm air. We place the exhaust pipe as high as possible, preferably at the level of the roof ridge. This is necessary to ensure good traction. The part of the pipe that is in the open air must be insulated to prevent freezing in the winter and covered with a visor from precipitation.
- The second pipe for the influx of fresh air is located at a height of 30-40 centimeters from the floor level, and we place its entrance on the street a meter above the ground and cover it with a grate.Convection will occur due to the temperature difference between the outdoor and basement air. Such a system will work most efficiently when the supply channels are separated on different sides of the basement.
The disadvantage of all natural exhaust ventilation systems is one - it is dependent on weather conditions and prevailing winds. It will not work if the temperature in the basement and on the street is equal.
Forced
It is used if natural supply ventilation cannot cope or there is no physical possibility to use it. Usually used in the following cases:
- The basement area is from 40 m2 or has several rooms isolated from each other;
- High humidity of the room, when the condensate in the exhaust duct freezes in winter and impairs the permeability of air masses;
- The architecture of the house does not provide for high ventilation pipes;
- The basement is equipped with a sauna, cafe, gym, workshop or other source of unpleasant odors.
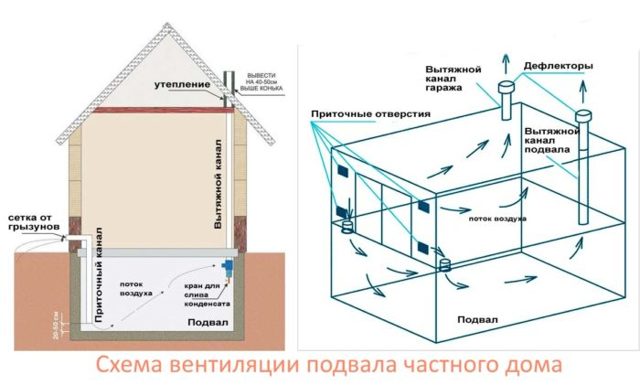
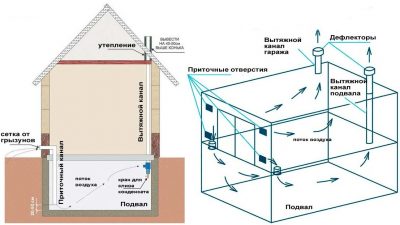
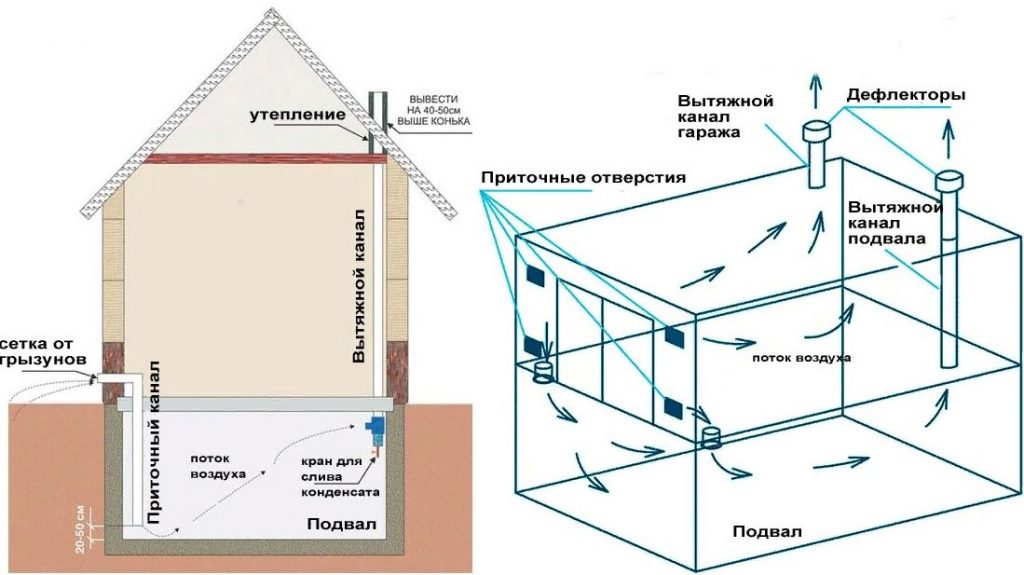
The device of forced supply and exhaust ventilation has a system of channels and fans that distill air.
The main condition is to make the air constantly circulate, which is ensured by the synchronous operation of the exhaust and supply fans. Their number is calculated depending on the volume of the cellar or basement and the capacity of the air ducts.
Supply and exhaust ventilation with heat recovery
For a basement floor where permanent residence is planned, it is not enough to simply install a forced ventilation system. The room must be insulated and waterproofed.The issue of heating and heating is also solved.
Increasingly, supply and exhaust with heat recovery is built into such schemes.
Already well-heated air enters the exhaust pipe, and in order not to throw ready-made calories into the atmosphere, the air is passed through a special ceramic heat exchanger. When heated, it gives off heat to fresh air. The air streams do not intersect. The efficiency of such a device is 50-90%, depending on the design of the heat exchanger. All heat recuperators are very reliable, do not require additional maintenance and can serve for decades.
It is equipped with moisture traps, dust filters, sensors that control humidity and air temperature. For a residential area, these figures lie in the range of 50-65% relative humidity and 18-220C. Such systems are most often found in "smart homes", and their installation is complicated and should only be carried out by professionals.
Installation nuances
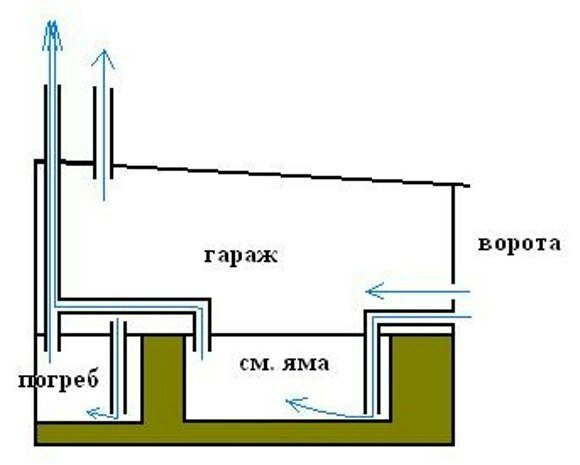
It is not always possible to provide air flow from the street, for example, in the box of a cooperative garage or built into the house. In such cases, the upper end of the supply pipe is led directly to the garage not far from the gate, and ventilation grilles are installed in them.
Scheme of natural ventilation without the outlet of the supply pipe to the street
Before making an vent in the cellar, it is necessary to determine the diameter of the pipes, which is especially important when arranging natural ventilation. The easiest way to calculate it is by the formula, according to which the cross-sectional area of \u200b\u200bthe pipe should be equal to 26 cm2 per square meter of the room .. For example, if the cellar area is 5 m2, then the cross section should be 130 cm2
Using the formula for the area of a circle, we find the diameter: 12 cm.If pipes of the required section are not found, products of a larger diameter are taken.
For example, if the cellar area is 5 m2, then the cross section should be 130 cm2. Using the formula for the area of a circle, we find the diameter: 12 cm. If the pipes of the desired section are not found, products of a larger diameter are taken.
In such rooms that are not demanding on aesthetics, such as basements, cellars and garages, you can install any pipes - asbestos-cement, sewer, special ventilation ducts. The latter have an antistatic layer on the inner surface, which does not allow dust to settle on the walls and gradually narrow the working lumen of the channel. But they are not cheap either.
Plastic air ducts come in round and rectangular sections
Therefore, the most popular option is polypropylene sewer pipes, which are attractive for their low price and ease of installation when using couplings, angles and tees with sealing rubber rings that ensure the tightness of the joints. But they do not differ in a wide variety of diameters. And this is one of the reasons why a mixed type of ventilation is preferred. In this case, the diameter of the duct is not so important, because the flow of air passing through it is accelerated due to artificially created traction.
During installation, you need to remember the following rules:
- the fewer turns the air duct has, the better it provides fresh air;
- diameter throughout should not change;
- the places where pipes pass through walls and ceilings must be sealed with mounting foam or cement mortar.
Video description
The installation option for a ventilation system made of asbestos-cement pipes is described in the video:
Conclusion
Knowing the physical principles of air movement, it is easy to understand how to make ventilation in the cellar of the garage. The circulation of air masses is provided by only two pipes installed at different levels. This is enough for small storages. By supplying the system with fans, it is possible to maintain a normal microclimate in large damp basements, thereby not only preserving the crop, but also not exposing the car to the risk of rusting ahead of time.
Combined system type
Combined ventilation is implemented mainly in the form of a scheme with natural inflow and mechanical, that is, forced, exhaust of waste masses.
Fresh air enters the rooms through the valves due to the rarefaction created by the exhaust fans. In this case, the preliminary heating of the supply air masses is not performed. But this is not a problem if you install a correctly selected heating element under the valve - an open radiator.
Mechanical exhaust in a private house is performed by fans, usually ducted. There may be several, but sometimes one is enough.
To ensure efficient circulation of air currents, exhaust fans must operate without interruption. In order to save energy resources, speed controllers with automatic / manual control are connected to the system.
The flow of air flows into the house is organized in a natural way. To do this, use wall or special window inlet valves. The design of such devices does not provide for the presence of moving parts.
Experts characterize combined ventilation as functional, relatively inexpensive and easy to operate.For the location of related equipment does not require a lot of space. In addition, all functional elements require minimal maintenance.
Among the disadvantages of the combined type of system, it is worth noting the lack of filtration and heating of the supply air, as well as the minimum air exchange rates.