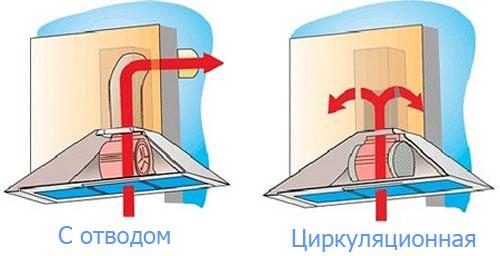
- Other ways to ventilate a cold attic
- Properly arranged attic roof
- Ventilation calculation
- Roof ventilation methods
- Roof ventilation from metal tiles and corrugated board
- Is it necessary to ventilate the attic floor, and why?
- How to ensure air exchange in a cold attic
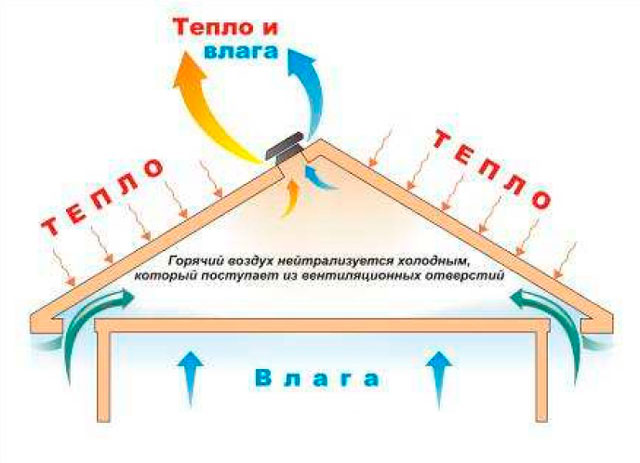
- Why do you need ventilation for the attic and roof
- Ventilation of problem areas
- Three main misconceptions and elimination of consequences
- The first misconception is about the seasons
- The second misconception - it will be cold in the house ↑
- Misconception three - size does not matter ↑
- Exit with poor ventilation ↑
Other ways to ventilate a cold attic
It is very common for domestic and European builders of private houses to use special vents for organizing ventilation in the attic. Vents or vents in the roof of a private house are called holes into which gratings are mounted, protected from atmospheric precipitation. Also, deflectors, aerators and pitched exits can be used as vents.
 Products are ridge or eaves. The name of each type tells about their location. Eaves products are of two types: slotted and point.Cornice-slit vents are a gap between the wall of the house and the cornice, 2 cm wide, closed with a metal mesh. Cornice-point vents are made in the form of holes, the diameter of which depends on the angle of the roof slope, but not more than 2.5 cm.
Products are ridge or eaves. The name of each type tells about their location. Eaves products are of two types: slotted and point.Cornice-slit vents are a gap between the wall of the house and the cornice, 2 cm wide, closed with a metal mesh. Cornice-point vents are made in the form of holes, the diameter of which depends on the angle of the roof slope, but not more than 2.5 cm.
Ridge vents are slots along the roof ridge, closed with perforated metal, 5 cm wide. For better air exchange, they are arranged on both sides of the ridge along the entire length of the roof. Ridge vents can be purchased with roofing material.
An equally popular solution for arranging ventilation of a cold attic is the installation of deflectors and ventilation turbines, which provide traction quite well.
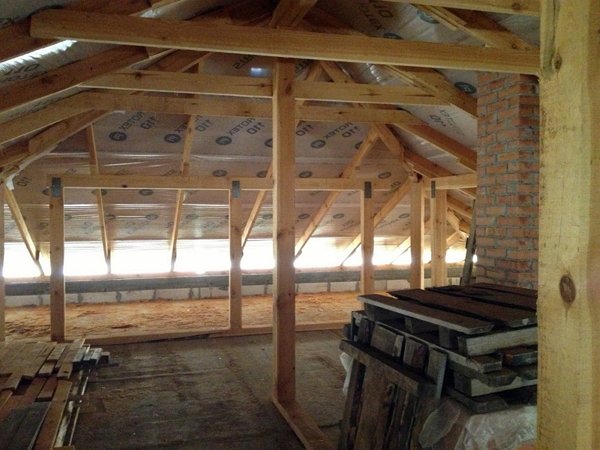
Properly arranged attic roof
In modern construction, they try to provide all structures with maximum thermal insulation, seal them in order to reduce heat loss. The structures enclosing the attic, this concerns, perhaps, the most. After all, it is through the roofing system that the greatest amount of heat can escape.
If the layers of hydro, steam and thermal insulation in the roofing pie are stacked without ventilation gaps, the insulation system will practically not work. Moisture falling in the form of condensate due to temperature differences, household fumes, rainwater that has penetrated under the roof will not have the opportunity to go outside.
Water is an excellent conductor, because of its content in the insulation, heat waves will freely pass to the street. In addition, it provokes rotting of the wood from which the truss frame is made, and often the attic sheathing.
Drainage of a roofing pie is perhaps a separate extensive topic.However, its effectiveness significantly affects the microclimate of the attic, especially in the summer heat, when the top layer of the roof warms up to + 100C. Therefore, we will briefly describe how this should be arranged.
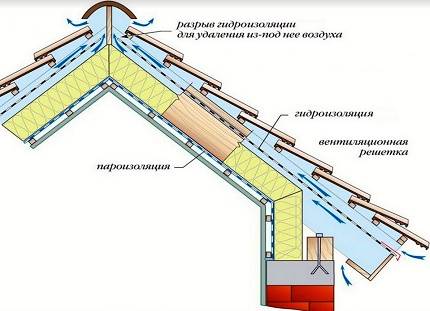
With the competent organization of the roofing pie, with the installation of ventilation ducts of the required section, the insulated slopes are regularly washed by air currents. As a result, the dried roof does not let heat waves through, does not get wet and building structures do not fail.
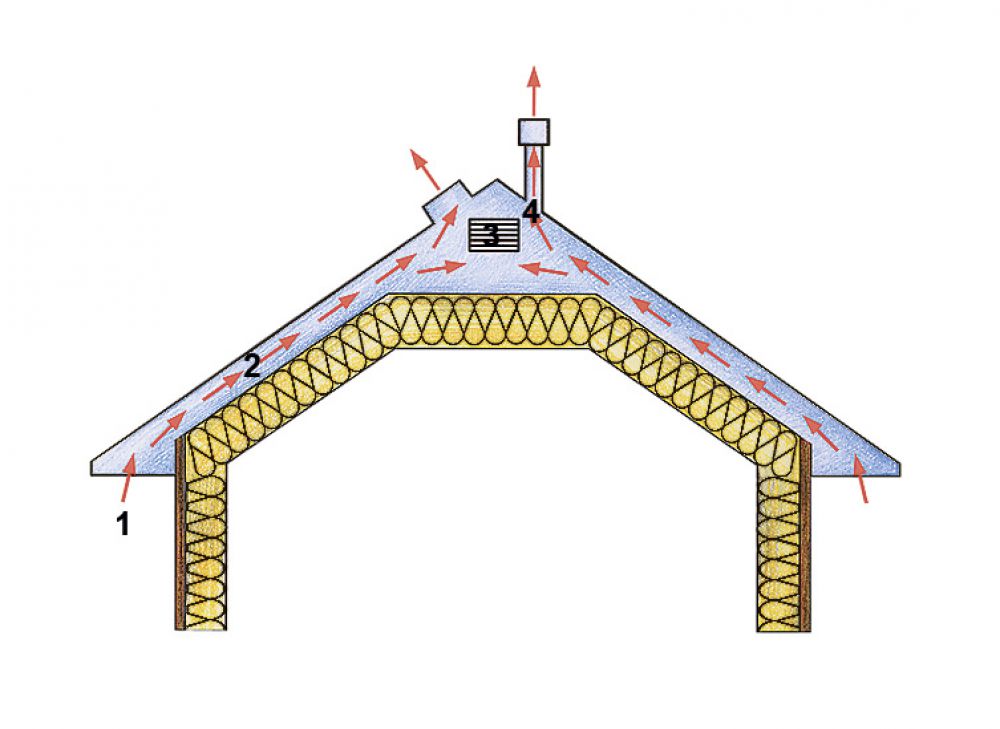
The purpose of any roof ventilation device is to ensure the movement of air from the overhangs to the ridge. The easiest way to arrange this is under a roof made of slate or ondulin: under the waves of the roofing material, the air freely rises to the ridge, in this case the overhangs are not tightly hemmed.
With metal tiles and corrugated board, the situation is almost the same, but it is desirable to equip their cornices with ventilation grilles or close them with an air-permeable seal. The relief roof must be separated from the waterproofing with a distance bar - it forms the ventilation gap required to remove fumes and atmospheric water accumulated under the coating.
Other materials, in particular, soft tiles or sheet metal, need to artificially create 1 or even 2 ventilation layers of 3-5 cm, separating the vapor barrier from the insulation, and the waterproofing film from the coating.
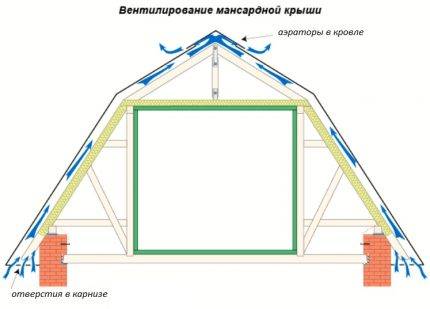 For the inflow and exit of air flows into the roofing system, holes must be arranged to allow the flow to move freely.
For the inflow and exit of air flows into the roofing system, holes must be arranged to allow the flow to move freely.
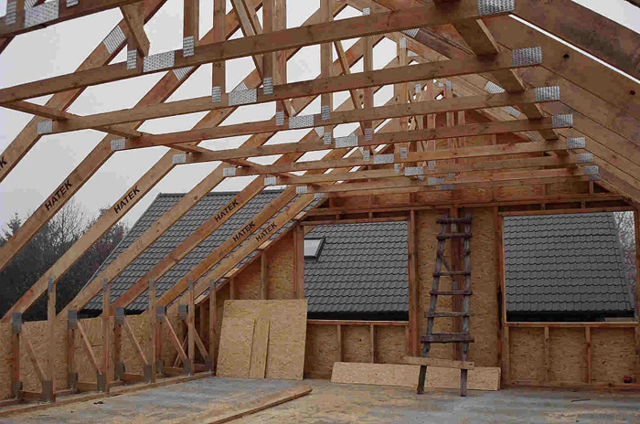
Ventilation ducts for this are arranged by laying the battens and counter battens. Air will rise between the slats.If the thickness of the rafters is not enough to lay all the layers of the roofing cake and provide ventilation gaps, the rafter legs are built up with bars.
For inflow in the hemming of the roof overhangs, perforated inserts are used - spotlights or ventilation grilles, at regular intervals along the entire length of the overhang. For the hood, a special ridge with aeration or point aerators is installed.
The total cross-sectional area of all holes for roof space ventilation should be 1m2 for every 300 - 500m2 roof slope area.

Both the under-roof space and the pediment sheathing can be ventilated through point aerators if the organization of long aerators or slots is not possible
Ventilation of the gables is carried out between the crate and the facade cladding material. If the sheathing is installed horizontally, then the supports of the crate are vertical, and they do not interfere with natural ventilation.
If the frame rails need to be fixed horizontally, there are several solutions for gable ventilation:
- Fasten small sections of rails horizontally in a checkerboard pattern. It's economical and efficient, but it can be tricky to level everything.
- Install long rails, but make holes in them in a checkerboard pattern.
- Build a vertical counter-batten. Ventilation in this case will be the most effective, but the material will also need the most.
If the sheathing is diagonal, preference should be given to the vertical arrangement of the rails.
Ventilation calculation
The air flow, in accordance with the regulations, should go around the attic space 2 times in 1 hour.In order for attic ventilation to function normally, the ratio of the area of \u200b\u200bthe room and the area of \u200b\u200bholes should be adhered to - 1:400.
The area of cornice vents should be 12-15% less than the area of ridge and pitched ones. The calculation of the elements of the ventilation system is carried out taking into account:
- attic area;
- type of material of the insulating layer;
- the volume of warm air that enters the attic from the living quarters.
It is not allowed to reduce or increase the area of holes, vents. If they are not enough, then the air will not flow in the required volume.
Otherwise, the necessary protection of the room from the penetration of snow flakes and raindrops into it will not be provided.
Calculation sequence:
- measurement of the attic area;
- determining the size of the ventilation holes.
If the area of the attic is significant, then you can arrange several products. The same applies to the dormer, ventilation window - instead of one, you can install 2 smaller ones.
The calculation of ventilation for a house with an attic is carried out taking into account its volume and the number of people in it at a time.
The norm is laid down in the SNiP "Heating, ventilation and air conditioning", which regulate the issues of the system design, regardless of the type of roof. In the calculations, the air exchange rate indicator is used.
Roof ventilation methods
For the implementation of air circulation in the under-roof space, apply:
- roof ventilation outlets;
-
piece roof covering with ventilation holes;
- roof fans;
-
ventilation gap of the roofing cake;
- dormer windows.
Now there are many roof outlets and ventilation ducts of a continuous and point type.

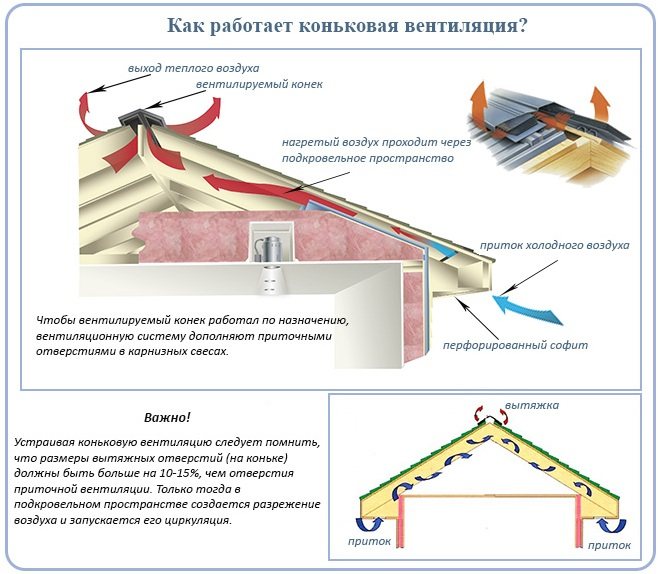
Aerators for continuous roof ventilation
Continuous aerators include ridge and eaves vents, their combination brings maximum efficiency.
The work of this scheme is in the wind and thermal pressure. With proper roof ventilation for an hour, the air flow passes through the entire surface of the roof twice.
At the top, the vents are applied with roofing material so that they do not spoil the appearance and do not let precipitation through.
Roof ventilation from metal tiles and corrugated board
These are the most common roofing materials in our country. They are very convenient in technology of application and price. They are made using the same technology and differ primarily in shape. The corrugated board looks less impressive, but at the same time it has stiffeners along the entire length.
In the process of arranging a metal-tiled or corrugated roof, difficulties arise with ventilation. The fact is that these materials are absolutely vapor-tight and thermally conductive. They heat up and cool down quickly, causing a lot of condensation to collect on the inside. But even these materials make it possible to create high-quality roof ventilation - roof ventilation, which extends the operational life of the entire building.

Decking and metal tiles
Manufacturers of metal tiles and corrugated board produce special additional elements with which ventilation passages are equipped. The main thing is to entrust the arrangement of the roof to specialists who will think over a good ventilation system.Since these materials do not retain heat very well, additional layers of hydro and thermal insulation are provided when they are used. In addition, these roofing materials themselves must be protected from moisture with special care. Due to these features roofs made of metal tiles and corrugated board often equipped with forced ventilation.
Is it necessary to ventilate the attic floor, and why?
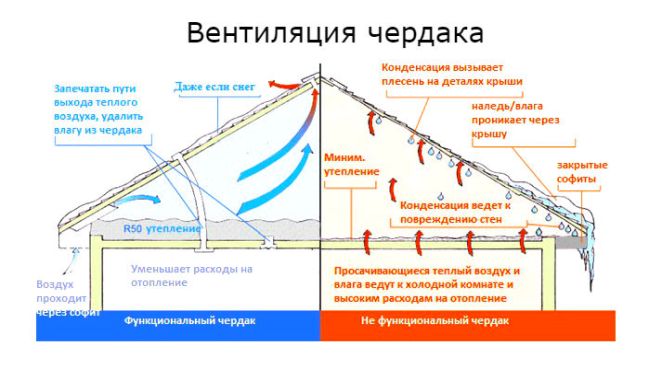
It is imperative to equip a ventilation system in the attic space, as it allows you to solve several very serious problems with the microclimate at once. At the same time, you can equip it with your own hands with a relatively small budget for work.
Consequences of lack of ventilation in the attic
Properly made attic ventilation solves the following problems:
- Elimination of excess moisture and prevention of the appearance of dampness in heat-insulating (insulating) materials. That is, ventilation protects heat-insulating materials from wear and functional damage.
- Significant reduction in the likelihood of the appearance and accumulation of fungal and mold colonies, which creates additional protection for the wooden roofing items (and also protects the health of those living in the building).
- Protection against the introduction of too hot air masses into the building during periods of intense heat (heat) in the external environment (outdoors).
- Protection against accumulation of moisture, and, as a result, protection of corrosive phenomena that can damage metal structures.
- Protection against the appearance of icicles under the eaves in the winter (especially during severe frosts).
- Significant savings on electricity required for optimal heating of the attic for the winter and, sometimes, autumn periods (in general, during the cold season).
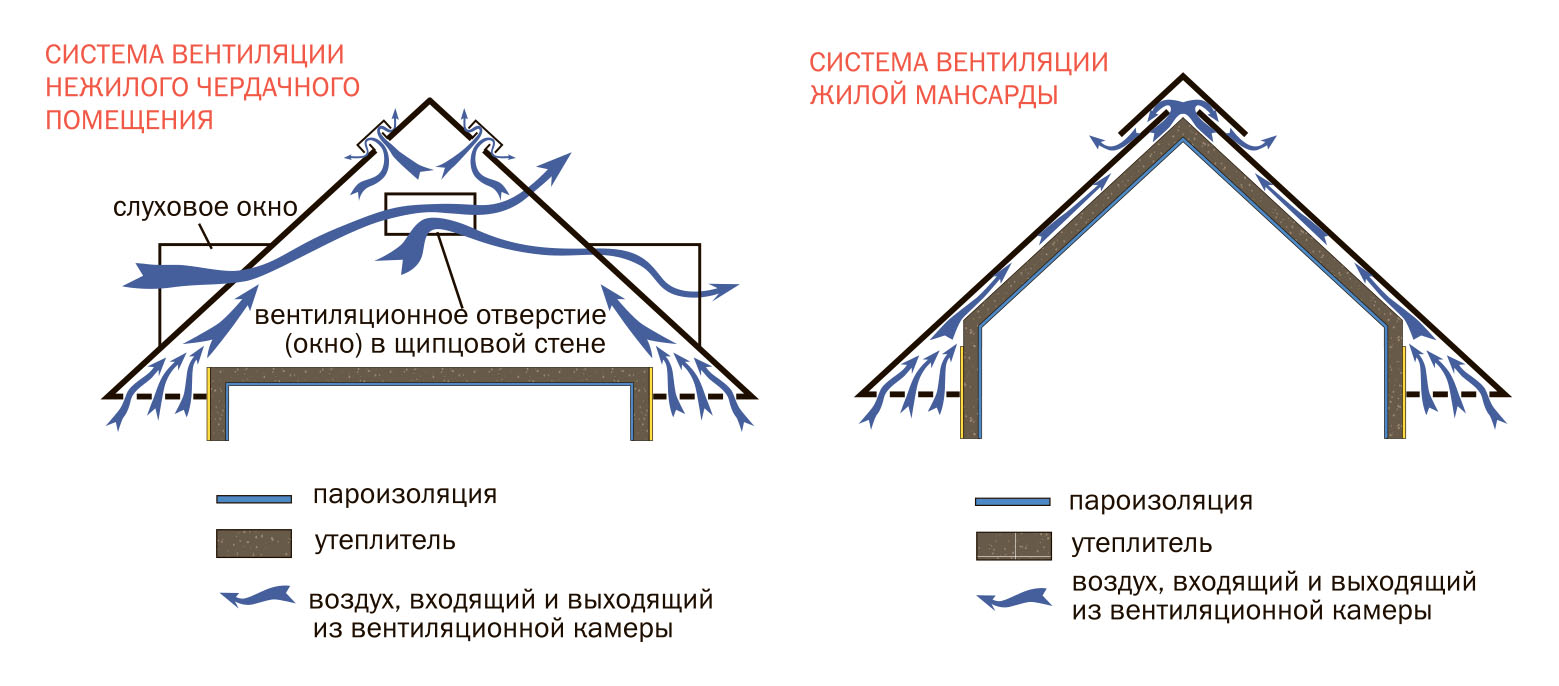
How to ensure air exchange in a cold attic
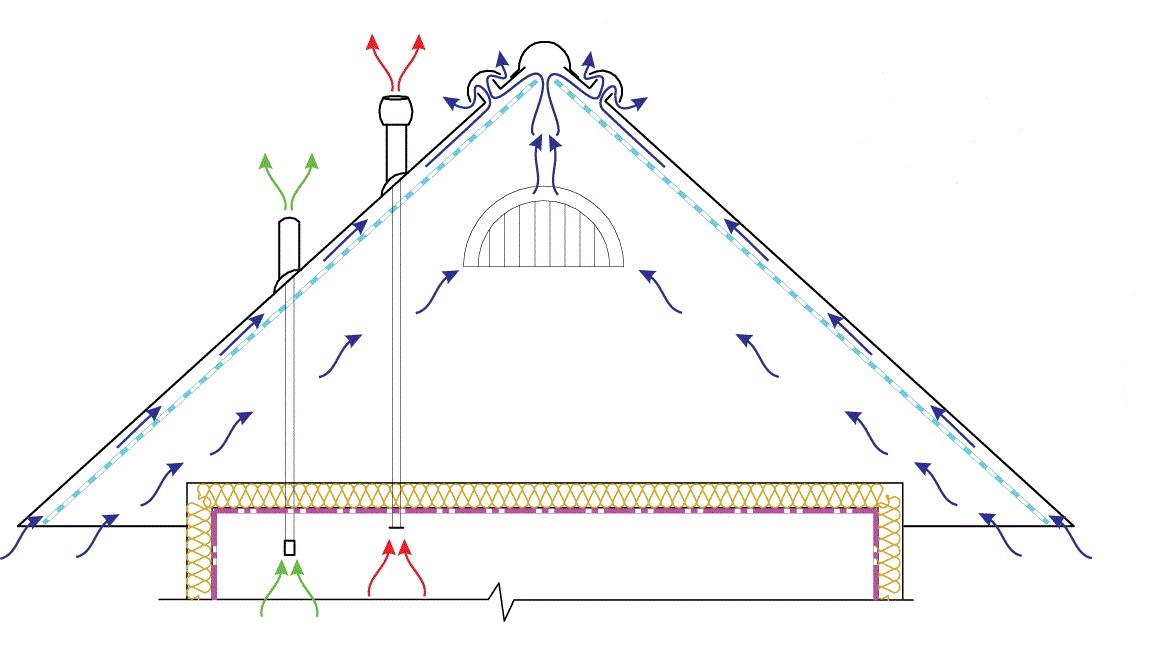
Cold attic ventilation can be arranged in many ways. In this case, all possible options are suitable:
- Soffits.
- Ventilated skate.
- Gable windows.
- Dormer windows.
For a gable roof, all ventilation methods are suitable. The simplest and most effective is based on the natural movement of air masses due to the difference in temperature and pressure at different heights.

On the roof overhangs, sheathing is made of wooden slats, leaving gaps between them, or spotlights are used - perforated metal or PVC siding.
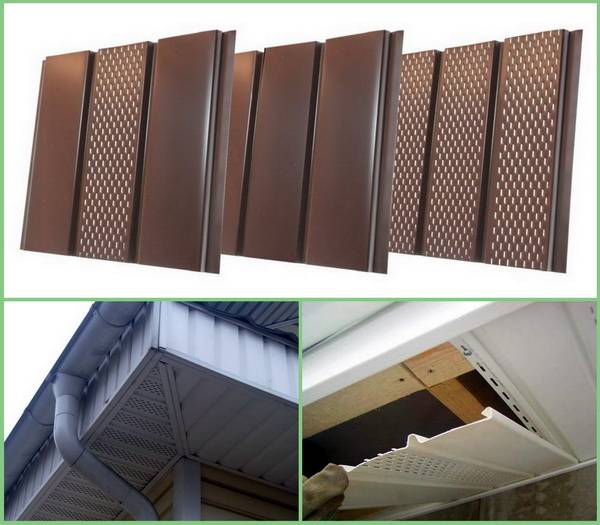

If the sheathing is made close and does not have ventilation holes, it is possible to arrange vents under the cornices in the form of ordinary gratings mounted every 90 cm. Air exits through the vents in the ridges. And also used point aerators.
Another simple and inexpensive option is the installation of lattices (windows) on the gables. The optimal size of windows for ventilation of the roof is 60x80 cm. When choosing their location, you should keep an equal distance from the ridge, overhang and sides of the house. There should be two lattices - one each from opposite gables.
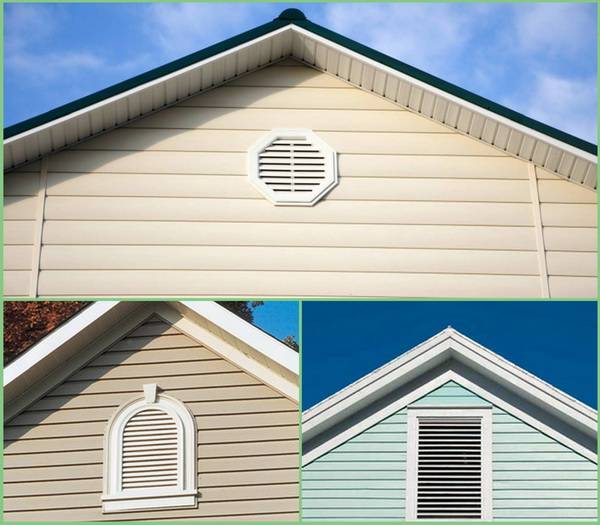

Dormer windows are the most difficult way to ventilate the under-roof space. But such a ventilation window in the attic will serve as both a natural source of light and an exit to the roof.

For normal air exchange under a hip roof without gables, soffits and ridges with holes for air inlet and outlet and air vents in the roof in the form of dormer windows located on opposite sides of the building are suitable.
In a cold attic with sheathing made of ondulin, metal tiles, corrugated board or slate, the ventilation of the ridge is provided by the space between the waves of the material, so there is no need to equip it additionally.
If ventilation pipes are installed in an unheated attic, then over time they can become clogged with frost, reducing efficiency to zero. Therefore, insulation of ventilation pipes is a mandatory step.

It is best to use foil insulation. And outside, you need to equip the pipes with gratings or diffusers so that debris and insects do not get into them.
This is interesting: Insulation of the foundation with polystyrene foam: we consider in detail
Why do you need ventilation for the attic and roof
In modern building architecture, an attic is understood as a floor in an attic space, the facade of which is completely or partially formed by an inclined or curved roof surface. This space can be residential or non-residential.
The features of the air exchange system depend on the nature of use and purpose. As in all other rooms, two types of ventilation are used:
- natural;
- forced.
In its natural form, air circulation occurs without the use of additional ventilated equipment. The movement of air flows is carried out due to the difference in temperature and pressure in the room and outside it. The disadvantage of natural ventilation is the dependence on weather conditions. In winter, the draft can be strong, and in summer, in hot weather, the functioning of air exchange can stop.
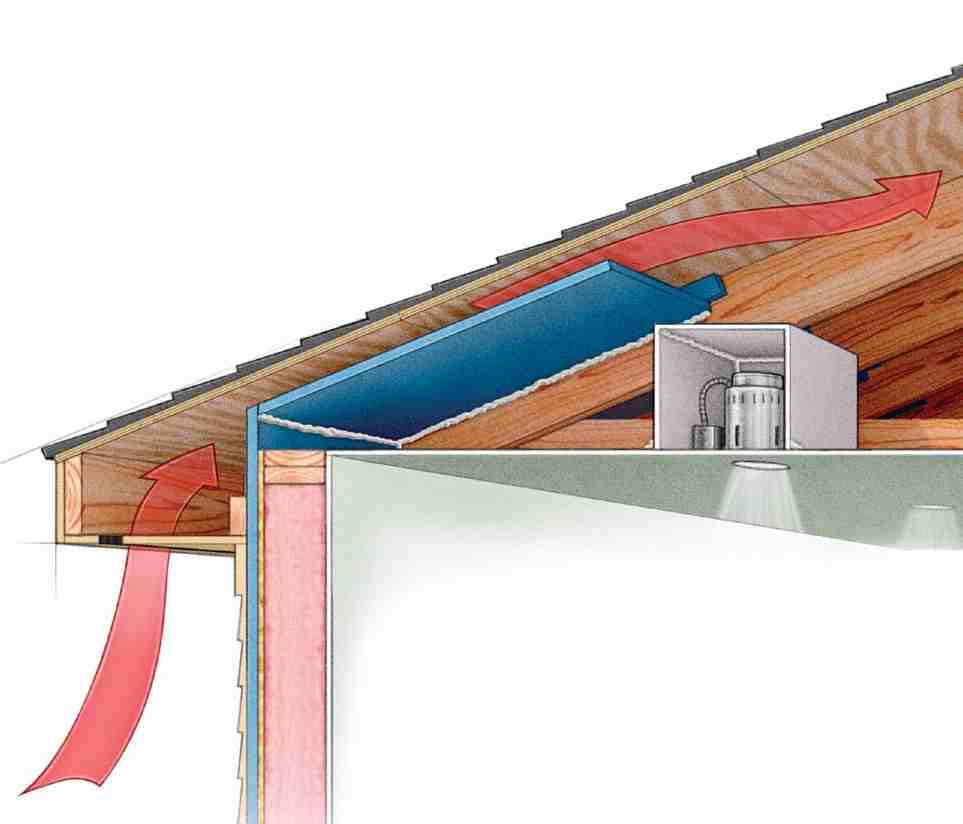
The forced ventilation system is based on the use of special ventilated equipment that artificially organizes the circulation of air masses at the desired speed.Forced air exchange is more efficient than natural, but also has disadvantages - higher cost, constant power consumption, dependence on the availability of electricity and the health of the device.
The best option for attic air exchange equipment is a mixed system. This design allows the use of natural and forced principles of air circulation, depending on external factors.
The optimal type of ventilation for the attic is supply and exhaust. This system has two blocks:
- working on the flow of air;
- working to remove waste air masses.
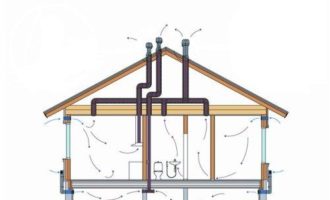
It is worth distinguishing and separating attic ventilation and roof ventilation. These are two separate systems, each solves its own problems.
Mansard roof ventilation is designed for:
- Ventilation of the under-roof space with insulation. Allows you to maintain an optimal level of humidity, protects against the development of fungi, bacteria, mold.
- Maintaining a favorable microclimate and increasing the life of the roof.
- Prevention of condensation on the inner surface of the roofing material.
- Protection of roof elements from overheating.
- Ensuring uniform snow melting, preventing the formation of ice and icicles on the eaves.
Attic ventilation is designed for:
- constant supply of fresh air;
- uninterrupted removal of waste air flows;
- maintaining favorable levels of humidity, temperature;
- reducing the overall cost of heating a house in winter and cooling it in summer.
Ventilation of the attic floor should not be combined with the air exchange of residential premises.

Attic ventilation should not be combined with air exchange in other living rooms.
Extraction from the toilet, bathroom, kitchen and other rooms is carried out using ventilation ducts that lead to the roof through the attic space.
Ventilation of problem areas
In addition to the ridge, the need for increased ventilation arises in areas where moisture accumulates on the roof: valleys, drain funnels, drips, this is especially felt on roofs with long slopes. It is strongly not recommended to drill rafters, this will not lead to the desired effect and will only reduce their bearing capacity.
On roofs with a large angle of inclination (above 45 °), special point aerators are installed along the valley; this method is not suitable for more gentle ones. In this case, the organization of forced ventilation is recommended (however, as for all roofs with a complex shape).
Regardless of location, all ventilation openings are protected by special elements from debris and are periodically checked.
Three main misconceptions and elimination of consequences

The principle of roof ventilation
In order for attic ventilation in a private house to be done correctly, in addition to knowing the basic requirements, it is necessary to get rid of a misunderstanding of its purpose. There are three main misconceptions that have been falsely given the status of rules and applied in the design and construction of houses in the private sector.
The first misconception is about the seasons
It is generally accepted that flowing air circulation in the attic is needed only in the summer (hot) season:
- hot weather is not the only criterion for the need for attic ventilation.For unheated attics or for the ventilation gap of warm rooms, it is necessary to maintain a minimum difference between the internal and external temperatures;
- when it gets cold outside, the lack of flowing air circulation leads to the formation of condensate. This moisture contributes to the formation of dampness and fungal mold, and in winter - frost;
- this situation is extremely dangerous because spores of microorganisms can enter the living space through the ceiling. Dealing with the consequences will be extremely difficult.
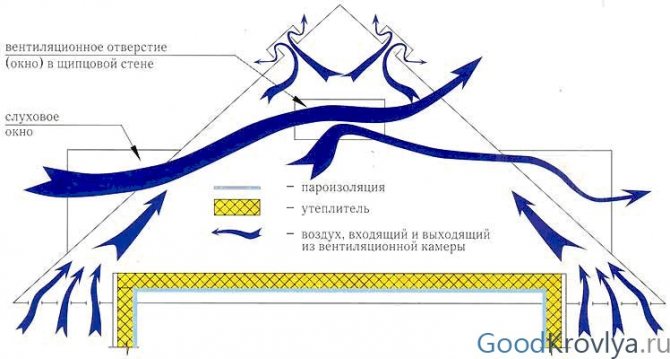
Air flow pattern
The second misconception - it will be cold in the house ↑
Ventilation in the attic contributes to the cooling of the living space, since warm air is consumed to heat the floors:
- in fact, the reason for the cooling of the rooms is the insufficient thermal insulation of the walls, floor and ceiling. The room, to a greater extent, is cooled not from the loss of warm air, but from the penetration of cold;
- in addition, in the absence of waterproofing on the floor, not only heat passes through it, but also moisture, which is an additional reason for the formation of condensate in the attic.
Misconception three - size does not matter ↑
The dimensions of the air circulation holes do not matter:
- this is not the case, and if we are talking about a ventilation gap under the roof, then the minimum distance to the insulation should be 20mm. It is set by choosing the cross-section of the rails for the counter-lattice;
- when arranging products for cold attics, one should adhere to the norm - 1 sq. m of ventilation openings (in total) per 500 sq. m of the total area of the premises;
- if you meet these requirements (vent gap or airflow area), then you can get rid of condensate, while avoiding critical losses of warm air.
Exit with poor ventilation ↑

Frozen condensate on the rafter system and crate
If the ventilation was done taking into account the above misconceptions, then in the cold season condensation will form, which freezes in winter, as shown in the top photo. In such cases, you have to correct the situation, but there is a way out, and it leads to good results with simple actions.

The simplest roof aerator
You can make additional vents or dormer windows, protecting them with bars so that pigeons do not fly into and nest in the attic (they can also nest in vents if there is room). But it is most convenient, especially if the roof is made of metal (corrugated board, metal tiles or rebate), to install the simplest passive aerator. If desired, of course, you can purchase and install an electric or turbine hood of this type.
Depending on the roofing material, the base of the hood is selected - it can be wavy, under slate or ondulin, or flat, under the corresponding roofing materials. As a rule, such devices are equipped with installation instructions from the manufacturer, a set of self-tapping screws, as well as street sealant for fasteners.
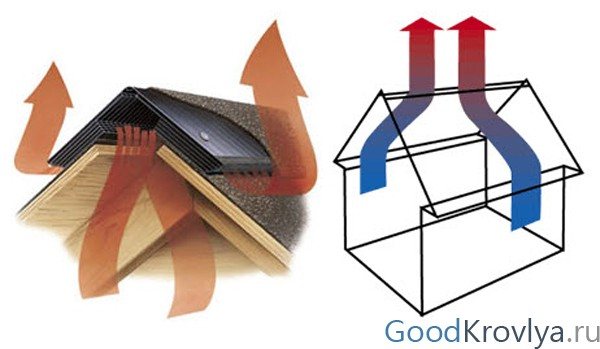
Attic ventilation is a must.
To install such a ventilation system in the attic, you need to cut a hole in the roof, the area of \u200b\u200bwhich should not be less than the hole in the hood, but not exceed the size of the mounting sole. For cutting, an angle grinder (grinder) is used, and the disc is selected in accordance with the roofing material (for metal or diamond-coated).
Summing up, we can say that ventilation in the attic is not an arrangement for elite houses, but an urgent need for each building, on which the comfort in the rooms depends. And the availability of do-it-yourself work significantly reduces the cost and allows you to quickly correct the situation with poor air circulation.