- The effectiveness of different types of tubes
- General remarks
- Flat solar collectors:
- Vacuum solar collectors:
- Main recommendation
- What types of solar collectors exist
- flat
- vacuum
- Types of heat-removable elements (absorbers), out of 5
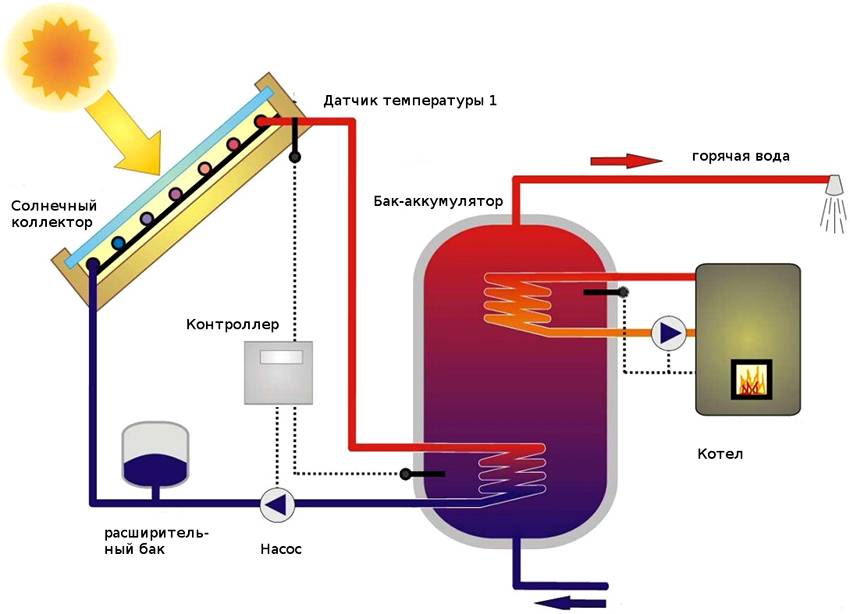
- Systems with flow heaters or thermosyphon
- Types of vacuum collectors
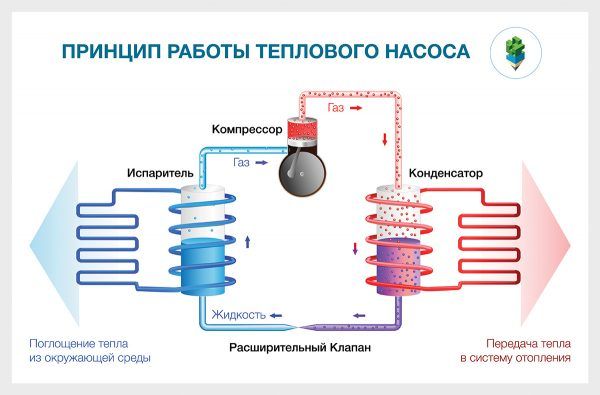
- Working principle of solar heaters
- Tubular solar heaters
- Tube types
- Types of thermal channels
- How to assemble an air manifold
- What will be required in the work
- Assembly technology
- System stagnation
- Additional operating costs
- Results
The effectiveness of different types of tubes
Efficiency rating of vacuum manifolds depending on the type of tubes installed:
- U-shaped (U-type);
- Twin coaxial;
- Feather;
- Coaxial (Heat Pipe);
- Thermosiphon (open).
This rating characterizes different systems in general, because the performance depends on the design features, the properties of the materials used and design solutions. The following factors influence the efficiency level of the vacuum manifold:
- Absorption and emissivity coefficients of the absorber;
- Maximum working pressure in the system;
- Quality and thermal conductivity of materials at the joints;
- The presence and properties of the metal absorber along the inner perimeter of the glass wall;
- Resistance of glass to mechanical stress;
- Design features - wall thickness, quality of metals, etc.
Important!
Many manufacturers of vacuum tubes and collectors overestimate their performance. The actual amount of heat that can be obtained depends on many factors and must be calculated individually.
General remarks
All of the above applies to expensive and high-quality solar collectors. Meanwhile, a large number of systems from different manufacturers have now appeared on the Russian market. What are solar collectors and what is better to choose? How not to be deceived in expectations and choose the right option?
Flat solar collectors:
Flat solar collectors are European, Russian and Chinese. Dimensions may vary, power is estimated as a standard by collector area.
1. European. Usually shipped from Germany, rarely from Italy or other European countries. Almost all manufacturers of collectors are of high quality workmanship and the highest possible efficiency for flat-plate collectors. The price is high.
2. Russian. The quality depends on the manufacturer. The best samples are still inferior to European models. The worst ones are comparable to cheap Chinese options. Efficiency also varies. Before installation, it is better to ask for feedback on this type of collectors and evaluate applicability to your project. The price is average.
3. Chinese. The quality depends on the manufacturer. The best samples from well-known companies are inferior to European models and are comparable to Russian ones.There are cheap flat-plate collectors without a brand - the quality is usually low and the efficiency is also low, although it is possible to use them in water heating systems. The price is low.
Vacuum solar collectors:
Vacuum solar collectors are supplied almost exclusively from China, they are not produced in Russia. In Europe, they are produced in a relatively small volume, but they are practically not supplied to Russia.
1. With heating tubes. The most common type of vacuum collectors. Inside the glass vacuum tubes are special copper tubes that transfer energy to the coolant. The quality varies from very high in the best factories in China to very low in small and handicraft industries. High-quality collectors are distinguished by high glass strength and an increased level of solar energy absorption due to special selective nano-coatings. Low-quality tubes are brittle and have poor heat absorption. Visually distinguishing high-quality from low-quality is difficult, so you should focus on well-known brands. The largest manufacturer of vacuum manifolds in China is Himin Solar, whose products are of the highest quality.
2. With U-tubes. In these collectors, solar energy is transmitted through mini-copper circuits (U-tubes) located inside each glass bulb. Compared to heating tubes, this results in a 10-15% increase in efficiency. The production of such collectors is more technologically advanced, so usually these are high-quality solar collectors produced by well-known companies, the largest of which is Himin Solar.

Main recommendation
If you only need hot water, you can choose both flat and vacuum solar collectors. A vacuum manifold will only have higher efficiency in winter and cloudy weather.
For heating in the Russian climate, only vacuum collectors should be used.
Remember that magic does not happen and regardless of the type of collector, an additional source of energy is required in case of prolonged cloudy weather.
And most importantly, do not buy products of dubious production and unknown quality, trust only well-known brands.
This article has been read 6137 times!
What types of solar collectors exist
Such systems are of two types: flat and vacuum. But, in essence, their principle of operation is similar. They use the sun's heat to heat water. They differ only in the device. Let's look at the principles of operation of these types of solar systems in more detail.
flat
This is the simplest and cheapest type of collector. It works as follows: Copper tubes are located in the metal case, which is internally treated with a highly efficient feather absorber to absorb heat. A coolant (water or antifreeze) circulates through them, which absorbs heat. Further, this coolant passes through a heat exchanger in the storage tank, where I transfer heat directly to the water that we can use, for example, for heating a house.
The upper part of the system is covered with high-strength glass. All other sides of the case are insulated with insulation to reduce heat loss.
| Advantages | Flaws |
| Low cost panels | Low efficiency, about 20% lower than vacuum |
| Simple design | Large amount of heat loss through the body |
Due to their ease of manufacture, such systems are often made even with their own hands. You can buy the necessary materials in construction stores.
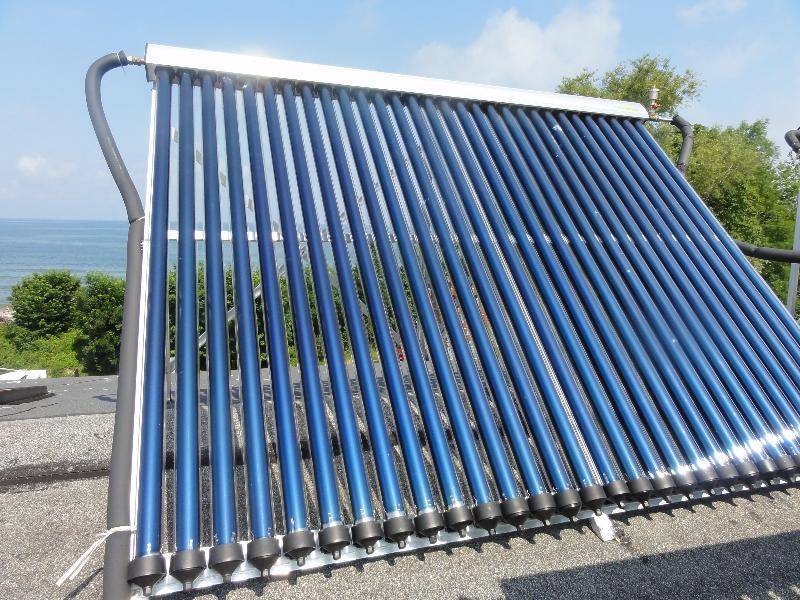
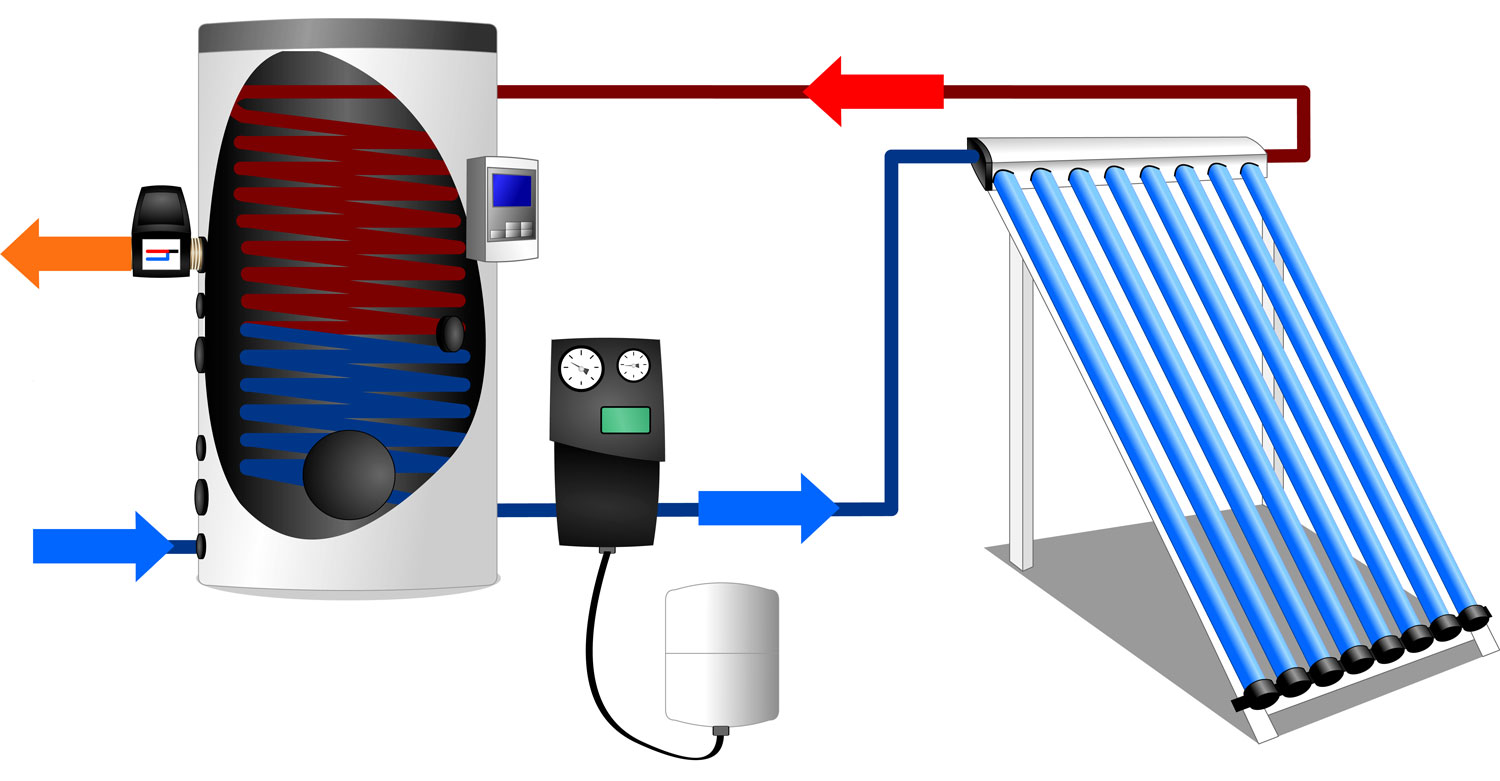
vacuum
These systems work a little differently, this is due to their design. The panel consists of double tubes. The outer tube plays a protective role. They are made of high strength glass. The inner tube has a smaller diameter and is covered with an absorber that accumulates solar heat.
Further, this heat is transferred to heat by strippers or rods made of copper (they come in several types and have different efficiency, we will consider them a little later). Heat removers transfer heat with the help of a heat carrier to an accumulating tank.
There is a vacuum between the tubes, which reduces heat loss to zero and increases the efficiency of the system.
| Advantages | Flaws |
| High efficiency | Higher price relative to flat |
| Minimum heat loss | The impossibility of repairing the tubes themselves |
| Easy to repair, tubes can be changed one at a time | |
| Large selection of species |
Types of heat-removable elements (absorbers), out of 5
- Feather absorber with direct-flow thermal channel.
- Feather absorber with heat pipe.
- U-shaped direct-flow vacuum manifold with coaxial bulb and reflector.
- System with a coaxial flask and a heat pipe "heat pipe".
- The fifth system is flat collectors.
Let's take a look at the efficiency of different absorbers, and also compare them with flat-plate collectors. Calculations are given for 1 m2 of the panel.
This formula uses the following values:
- η is the efficiency of the collector, which we calculate;
- η₀ - optical efficiency;
- k₁ - heat loss coefficient W/(m² K);
- k₂ - heat loss coefficient W/(m² K²);
- ∆T is the temperature difference between the collector and air K;
- E is the total intensity of solar radiation.
Using this formula, using the data above, you can do the calculations yourself.
Put simply, the efficiency depends on the amount of heat that the copper heat sinks absorb and the amount of heat loss in the system.
Systems with flow heaters or thermosyphon
According to their structure, they can be both flat and vacuum. The same operating principles are used. However, they have one significant difference in the technical device.
This system can operate without an additional backup storage tank and pump group.
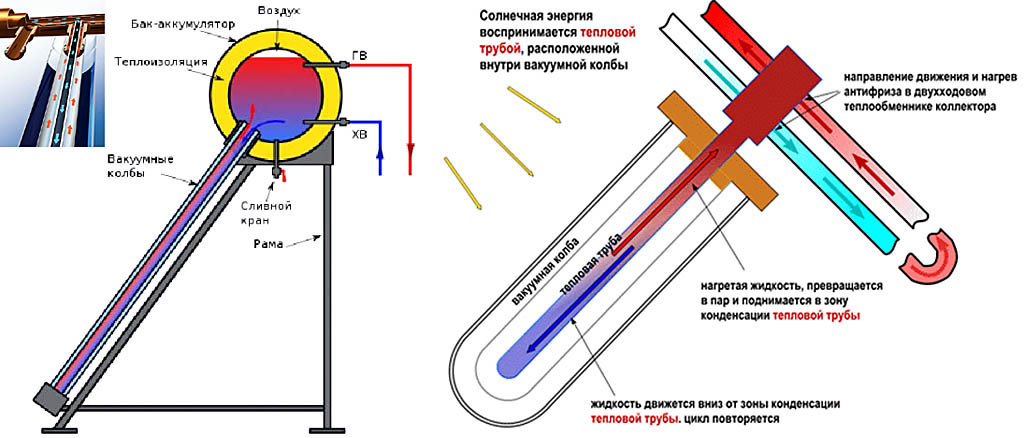
The principle of operation is the following. The heated coolant is accumulated in the base tank, which is located in the upper part of the system, usually 300 liters. A coil passes through it, through which water circulates from the pressure of the house's plumbing system itself. It warms up and goes to the consumer.
| Advantages | Flaws |
| Low cost due to the absence of part of the equipment. | Low system efficiency in the winter season and at night |
| Ease of installation, minimum effort is required, as the system is equipped with everything necessary |
Types of vacuum collectors
Solar collectors of different types contain vacuum tubes of different sizes. The larger the tube, and the thicker it is, the more energy the collector will supply. The length of the tubes is at least 1 meter, the maximum length is more than two meters. Tubing less than 58 mm in diameter is not welcome as it is less efficient.
Water heaters need to be cleaned from time to time, but how to do this, read the article draining water from a water heater. About Termex storage water heaters, see reviews here.
Heat pipes are also different:
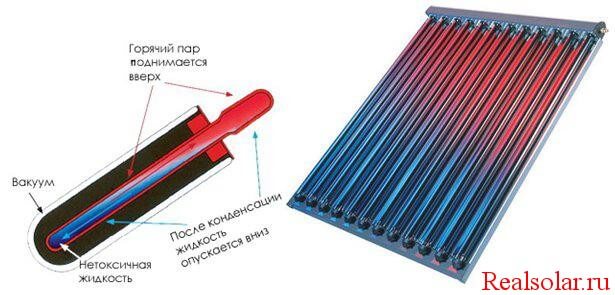
- Copper tubes, being in glass tubes, heat up. The heat is evaporated by the coolant, rises to the top of the tube and condenses.
- In a system with U-tubes, the coolant, passing through the lower part of the tube, heats up and quickly passes through its upper part - this is a closed circuit system. It features accelerated heat transfer and is 15-20% more efficient than standard systems.
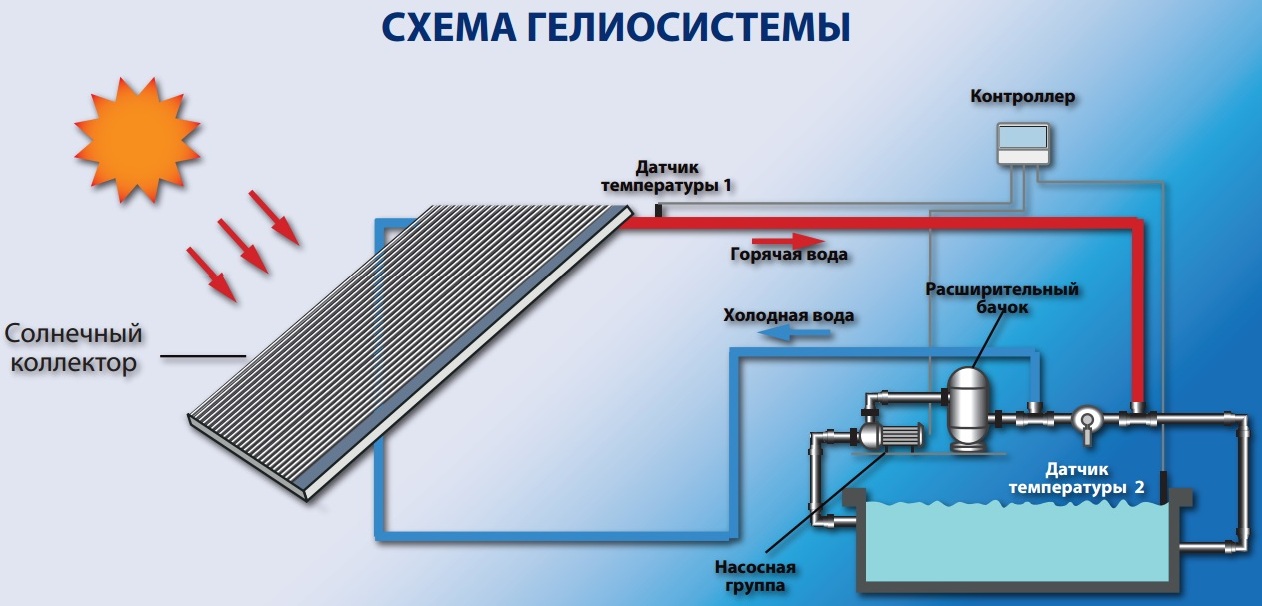
Working principle of solar heaters
Before embarking on the manufacture of a home-made solar system, it is worth studying the design of factory-made solar collectors - air and water. The former are used for direct space heating, the latter are used as water heaters or non-freezing coolant - antifreeze.
The main element of the solar system is the solar collector itself, which is offered in 3 versions:
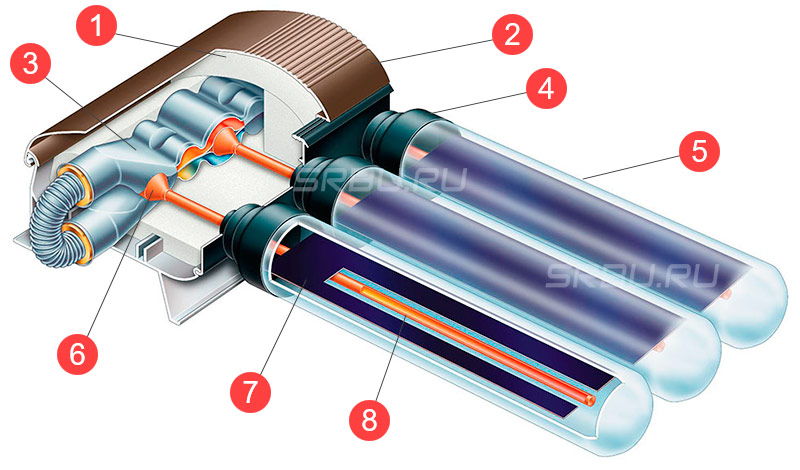
- Flat water heater. It is a sealed box, insulated from below. Inside there is a heat receiver (absorber) made of a metal sheet, on which a copper coil is fixed. From above the element is closed by strong glass.
- The design of the air-heating manifold is similar to the previous version, only the air pumped by the fan circulates through the tubes instead of the coolant.
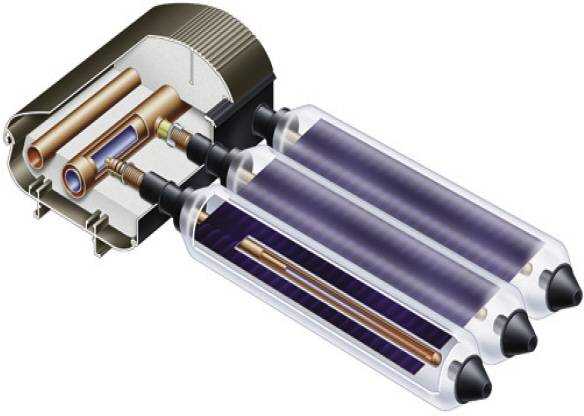
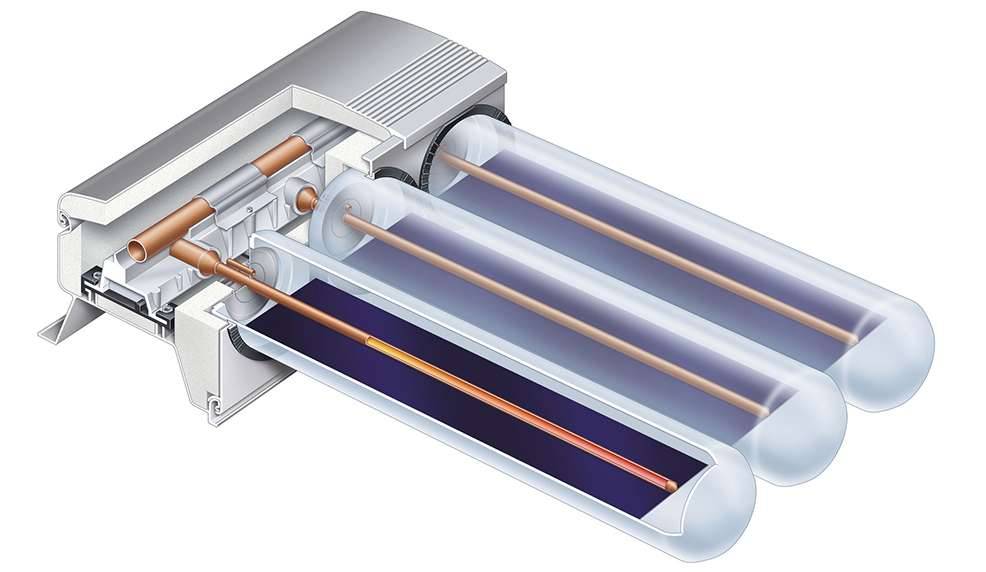
- The device of a tubular vacuum collector is fundamentally different from flat models. The device consists of durable glass flasks, where copper tubes are placed. Their ends are connected to 2 lines - supply and return, the air is pumped out of the flasks.
Addition.There is another type of vacuum water heaters, where glass flasks are tightly sealed and filled with a special substance that evaporates at a low temperature. During evaporation, the gas absorbs a large amount of heat transferred to the water. In the process of heat exchange, the substance condenses again and flows to the bottom of the flask, as shown in the picture.
Device of a directly heated vacuum tube (left) and a flask powered by liquid evaporation/condensation
The listed types of collectors use the principle of direct transfer of the heat of solar radiation (otherwise - insolation) to a flowing liquid or air. A flat water heater works like this:
- Water or antifreeze pumped by a circulation pump moves through a copper heat exchanger at a speed of 0.3-0.8 m / s (although there are also gravity models for an outdoor shower).
- The rays of the sun heat up the absorbent sheet and the coil tube tightly connected to it. The temperature of the flowing coolant rises by 15-80 degrees depending on the season, time of day and street weather.
- To exclude heat losses, the bottom and side surfaces of the body are insulated with polyurethane foam or extruded polystyrene foam.
- The transparent top glass performs 3 functions: it protects the selective coating of the absorber, it does not allow the wind to blow over the coil, and it creates an airtight layer that retains heat.
- The hot coolant enters the heat exchanger of the storage tank - buffer tank or indirect heating boiler.
Since the temperature of the water in the circuit of the device fluctuates with the change of seasons and days, the solar collector cannot be used for heating and domestic hot water directly.The energy received from the sun is transferred to the main coolant through the coil of the tank - accumulator (boiler).
The efficiency of tubular apparatuses is increased due to the vacuum and the internal reflective wall in each flask. The rays of the sun freely pass through the airless layer and heat the copper tube with antifreeze, but the heat cannot overcome the vacuum and go outside, so the losses are minimal. Another part of the radiation enters the reflector and is focused on the water line. According to manufacturers, the efficiency of the installation reaches 80%.
When the water in the tank is heated to the right temperature, the solar heat exchangers switch to the pool using a three-way valve
Tubular solar heaters
In heating systems, one of the primary tasks is to ensure the safety of heat and prevent its loss. For this, various heaters and media are used to prevent the dissipation of thermal energy. The most effective heat insulator is vacuum. This principle is used in tubular or, as they are also called, vacuum solar collectors. But vacuum solar collectors can be of four modifications. They have different type of glass tube and different heat channels.
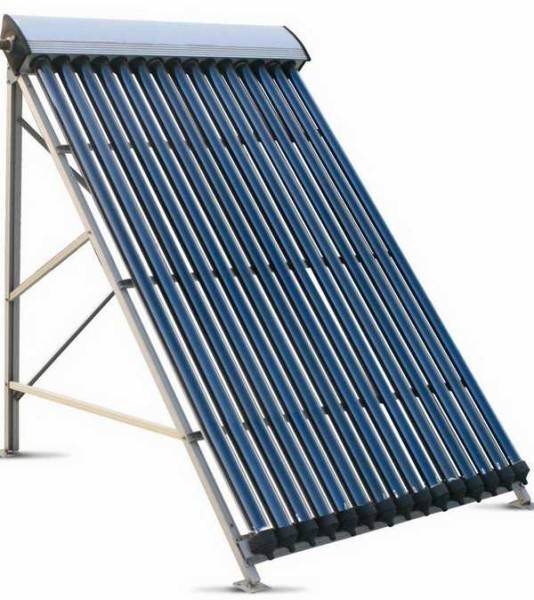

This is what tubular solar plants look like
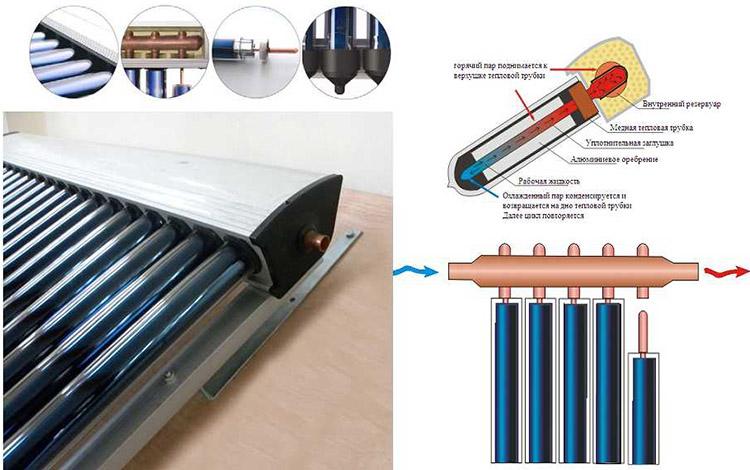
Tube types
Today, two types of tubes are mainly used: coaxial (pipe in tube) or feather tube. The structure of a coaxial tube resembles a thermos: two flasks are hermetically soldered together by one of the ends, between the walls there is a rarefied space - a vacuum. An absorbing layer is applied to the wall of the second flask. It converts the sun's rays into heat energy.The inner wall of the flask heats up, the air inside the flask heats up from it, and from it, in turn, the coolant is heated, which circulates through the heat channel. Due to the complex heat transfer system, heaters with such tubes do not have a very high efficiency. But they are used more often. For the reason that they can work at any time, even in severe frosts and have small heat losses (due to vacuum), which improves their efficiency.
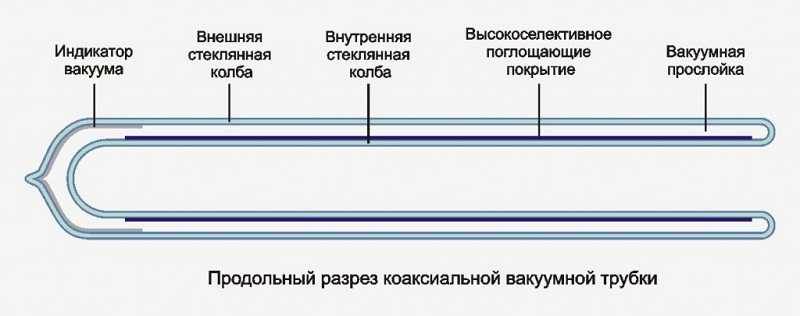
coaxial tube
A feather tube is just one flask, but with a thicker wall. A thermal channel is inserted inside, which, in order to improve heat transfer, is provided with a flat or slightly tortuous plate of absorbent material. Then the tube is evacuated. This type has a higher efficiency, but costs much more than coaxial ones. In addition, it is more difficult to replace when the tube fails.

Feather tube - inside a plate resembling a feather
Types of thermal channels
Two types of thermal channels are common today:
- heat pipe
- U-type or straight through channel.
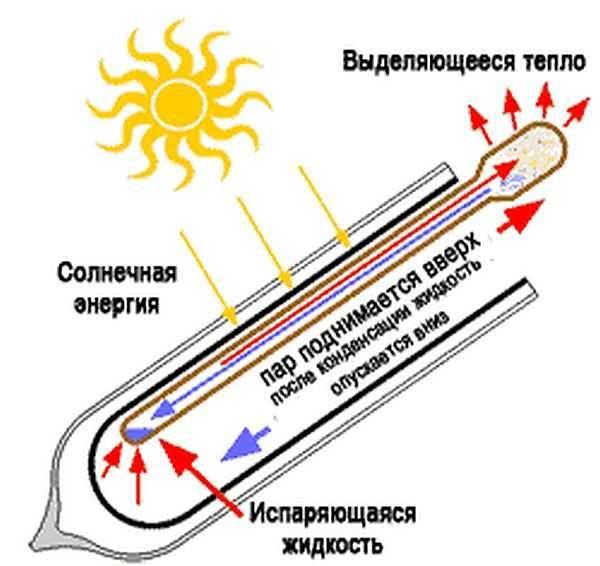
Scheme of operation of the Heat-pipe thermal channel
The Heat-pipe system is a hollow tube with a massive tip at one end. This tip is made of a material with good heat dissipation (most often copper). The tips are connected into a single bus - a manifold (manifold). Their heat is taken away by the coolant circulating through the manifold. Moreover, the circulation of the coolant can be organized through one or two pipes.
Inside the tube is a lightly boiling substance. As long as the temperature is low, it is in a liquid state at the bottom of the thermal channel.As it heats up, it begins to boil, part of the substance passes into a gaseous state, rises up. The heated gas gives off heat to the metal of the massive tip, cools down, turns into a liquid state and flows down the wall. Then it heats up again, and so on.
In tubular collectors with a once-through channel, a more familiar heat transfer scheme is used: there is a U-shaped tube through which the coolant moves. Passing through it, it heats up.
U-type heat exchangers show the best performance, but their main drawback is that they are an indivisible part of the system. And if one tube in the solar panel is damaged, you will have to change it completely.
Heat-pipe type heat exchangers are less efficient, but are used much more often due to the fact that the system is modular and any damaged tube is very easy to change. Just one gets out of the manifold, another one is put in its place. You can see how this happens in the video. Oddly enough, but this is how a vacuum tube for solar collectors is assembled. And there is no contradiction here. A coaxial flask is simply used and the vacuum is between its walls, and not around the thermal channel.
A separate type of solar tubular collectors are direct heating installations. They are also called "wet pipes". In this design, water circulates between two flasks, it heats up from their walls, then enters the tank. These plants are simple and cheap, but they cannot work under high pressure or at negative temperatures (water freezes and breaks the flasks). This option is unsuitable for heating, it can be used to heat water in the warm season.
How to assemble an air manifold
If you decide to assemble the solar system with your own hands, first take care of all the necessary tools.
What will be required in the work
1. Screwdriver.
2. Adjustable, pipe and socket wrenches.

Socket wrench set
3. Welding for plastic pipes.

Welding for plastic pipes
4. Perforator.

Perforator
Assembly technology
For assembly, it is desirable to acquire at least one assistant. The process itself can be divided into several stages.
First stage. First, assemble the frame, preferably immediately in the place where it will be installed. The best option is the roof, where you can separately transfer all the details of the structure. The very procedure for mounting the frame depends on the specific model and is prescribed in the instructions.
Second phase. Fasten the frame firmly to the roof. If the roof is slate, then use a sheathing beam and thick screws; if it is concrete, then use ordinary anchors.
Typically, frames are designed to mount on flat surfaces (maximum 20-degree slope). Seal the frame attachment points to the roof surface, otherwise they will leak.
Third stage. Perhaps the most difficult, because you have to lift a heavy and dimensional storage tank onto the roof. If it is not possible to use special equipment, wrap the tank in a thick cloth (to avoid possible damage) and lift it on a cable. Then attach the tank to the frame with screws.
Fourth stage. Next, you have to mount the auxiliary nodes. This may include:
- heating element;
- temperature sensor;
- automated air duct.
Install each of the parts on a special softening gasket (these are also included).
Fifth stage. Bring on the plumbing.To do this, you can use pipes made of any material, as long as it can withstand a temperature of 95 ° C heat. In addition, the pipes must be resistant to low temperatures. From this point of view, polypropylene is most suitable.
Sixth stage. After connecting the water supply, fill the storage tank with water and check for leaks. See if the pipeline is leaking - leave the filled tank for several hours, then carefully inspect everything and, if necessary, fix the problem.
Seventh stage. After making sure that the tightness of all connections is normal, proceed with the installation of the heating elements. To do this, wrap a copper tube with an aluminum sheet and place it in a glass vacuum tube. Place a retaining cup and a rubber boot on the bottom of the glass flask. Insert the copper tip at the other end of the tube all the way into the brass condenser.
It remains only to snap the cup-lock onto the bracket. Install the rest of the tubes in the same way.
Eighth stage. Install a mounting block on the structure and supply 220 volt power to it. Then connect three auxiliary nodes to this block (you installed them in the fourth stage of work). Despite the fact that the mounting block is waterproof, try to cover it with a visor or some other protection from atmospheric precipitation. Then connect the controller to the unit - it will allow you to monitor and regulate the operation of the system. Install the controller in any convenient place.
This completes the installation of the vacuum manifold. Enter all the necessary parameters in the controller and start the system.
System stagnation
Let's talk a little more about the problems associated with an excess of generated heat. So, suppose that you have installed a sufficiently powerful solar collector that can fully provide heat to the heating system of your home. But summer has come, and the need for heating has disappeared. If an electric boiler can be turned off the power supply, a gas boiler can be turned off the fuel supply, then we have no power over the sun - we can’t “turn it off” when it gets too hot.
System stagnation is one of the major potential problems for solar collectors. If insufficient heat is taken from the collector circuit, the coolant overheats. At a certain moment, the latter may boil, which will lead to the termination of its circulation along the circuit. When the coolant cools down and condenses, the system will resume operation. However, not all types of coolants easily transfer the transition from a liquid state to a gaseous state and vice versa. Some, as a result of overheating, acquire a jelly-like consistency, which makes it impossible to further operate the circuit.
Only a stable removal of heat produced by the collector will help to avoid stagnation. If the calculation of the power of the equipment is done correctly, the likelihood of problems is almost zero.
However, even in this case, the occurrence of force majeure circumstances is not excluded, therefore, methods of protection against overheating should be foreseen in advance:
1. Installation of a reserve tank for the accumulation of hot water. If the water in the main tank of the hot water supply system has reached the set maximum, and the solar collector continues to supply heat, a switchover will automatically occur and the water will begin to be heated already in the reserve tank.The created supply of warm water can be used for domestic needs later, in cloudy weather.
2. Heating water in the pool
The owners of houses with a swimming pool (whether indoor or outdoor) have a great opportunity to remove excess heat energy. The volume of the pool is incomparably larger than the volume of any household storage, which means that the water in it will not heat up so much that it will no longer be able to absorb heat
3. Draining hot water. In the absence of the ability to spend excess heat with benefit, you can simply drain the heated water in small portions from the storage tank for hot water into the sewer. The cold water entering the tank will lower the temperature of the entire volume, which will allow you to continue to remove heat from the circuit.
4. External heat exchanger with fan. If the solar collector has a large capacity, the excess heat can also be very large. In this case, the system is equipped with an additional circuit filled with refrigerant. This additional circuit is connected to the system by means of a heat exchanger equipped with a fan and installed outside the building. If there is a risk of overheating, excess heat enters the additional circuit and is “thrown” into the air through the heat exchanger.
5. Discharge of heat into the ground. If, in addition to the solar collector, the house has a ground source heat pump, the excess heat can be sent to the well. At the same time, you solve two problems at once: on the one hand, you protect the collector circuit from overheating, on the other hand, you restore the heat reserve in the soil depleted during the winter.
6. Isolation of the solar collector from direct sunlight. From a technical point of view, this method is one of the simplest.Of course, climbing onto the roof and hanging the collector manually is not worth it - it's hard and unsafe. It is much more rational to install a remotely controlled barrier, like a roller shutter. You can even connect a damper control unit to the controller - if the temperature rises dangerously in the circuit, the collector will close automatically.
7. Draining the coolant. This method can be considered cardinal, but at the same time it is quite simple. If there is a risk of overheating, the coolant is drained by means of a pump into a special container integrated into the system circuit. When conditions become favorable again, the pump will return the coolant to the circuit, and the collector will be restored.
Additional operating costs
The use of this does not imply any care or maintenance other than periodic cleaning of dirt and snow in winter (if it does not thaw itself). However, there will be some associated costs:
Repair, everything that can be changed under warranty, the manufacturer can be replaced without problems, it is important to buy an authorized dealer and have warranty documents.
Electricity, it is spent quite a bit on the pump and controller. For the first one, you can put only 1 solar panel at 300 W and it will be enough (even without a battery system).
Flushing of the coils, it will need to be done once every 5-7 years
It all depends on the quality of the water (if it is used as a heat carrier).
Results
In conclusion, I would like to note that the possible design of the collector is limited by the use of a copper coil.There are many different ways, for example, you can assemble a completely efficient, working collector using beer cans and other tin bottles as absorbent elements. There are many options. To do this, it is only worth studying the issue, collecting the required number of beer cans or tin bottles. Next, assemble them into a single design. The main thing is that even if you decide to collect beer collector cans or bottles, remember that all solar collectors work on the same principle. Qualitatively carry out the soldering of the joints of the connection of pipes and cans, create the proper vacuum conditions in the design and you will succeed. Get down to business boldly. As a result, you will receive not only a completely free and autonomous source of hot water. You will also get great psychological satisfaction from knowing that you have had a hand in increasing the share of renewable energy in today's globalized world. By creating a device that works on solar radiation, you will become more independent of the central supply systems for both electricity and gas. You will provide yourself with hot water for household needs. Good luck.
solar collector