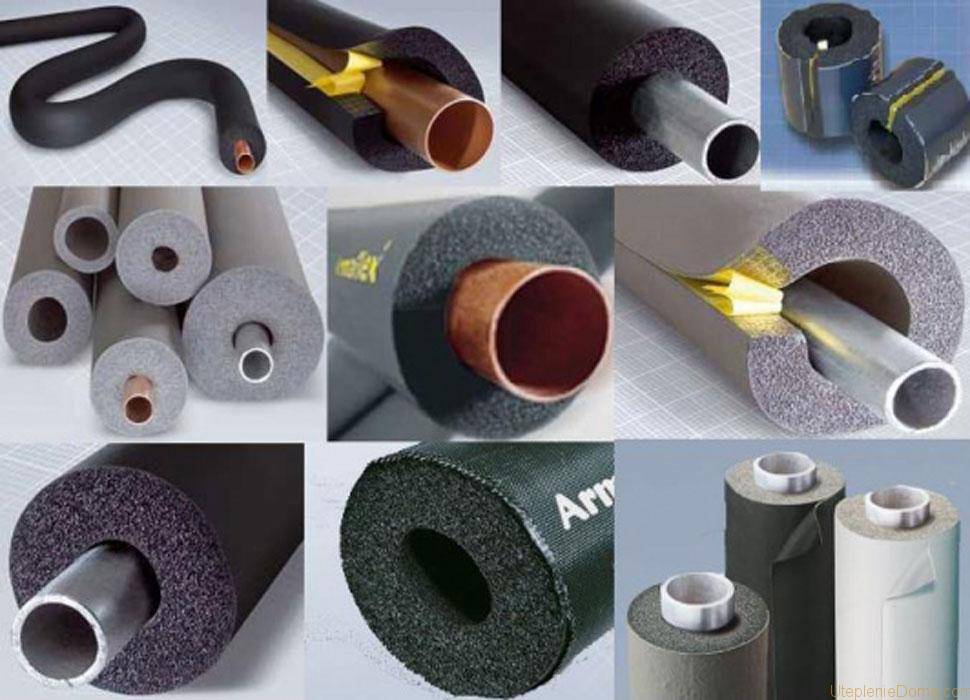
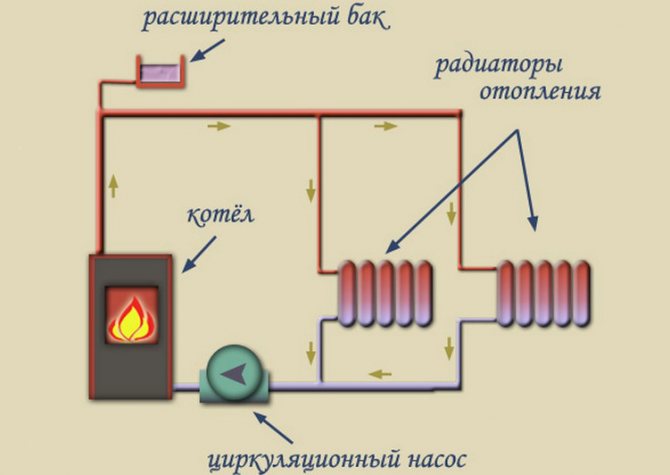
- Modern heaters and their application
- glass wool
- mineral types
- polyurethane foam
- Foamed polyethylene
- Liquid types
- Phased insulation technology
- Asbestos cement chimneys
- Steel chimneys
- brick chimney
- Ways to reduce heat loss
- Sheet and roll types
- Insulating materials
- Expanded polystyrene heat insulator for pipes
- What thickness of insulation is needed?
- Calculator of the thickness of the pipe insulation with mineral wool, taking into account the shrinkage of the material
- Types of thermal insulation materials
- Mineral wool
- glass wool
- polyurethane foam
- Foamed polyethylene
- Other heaters
- Polypropylene pipes
- pros
- Minuses
Modern heaters and their application
The most widely used in the insulation of pipelines for a heating system today are the following materials.
glass wool
The first is glass wool. This material is made of fiberglass and has good performance characteristics. Withstands temperatures up to 400-450°C, easy to use.
The disadvantage is high hygroscopicity and the ability to release fine glass dust into space, which makes glass wool useful only if it is additionally isolated. It is practically not used indoors.
mineral types
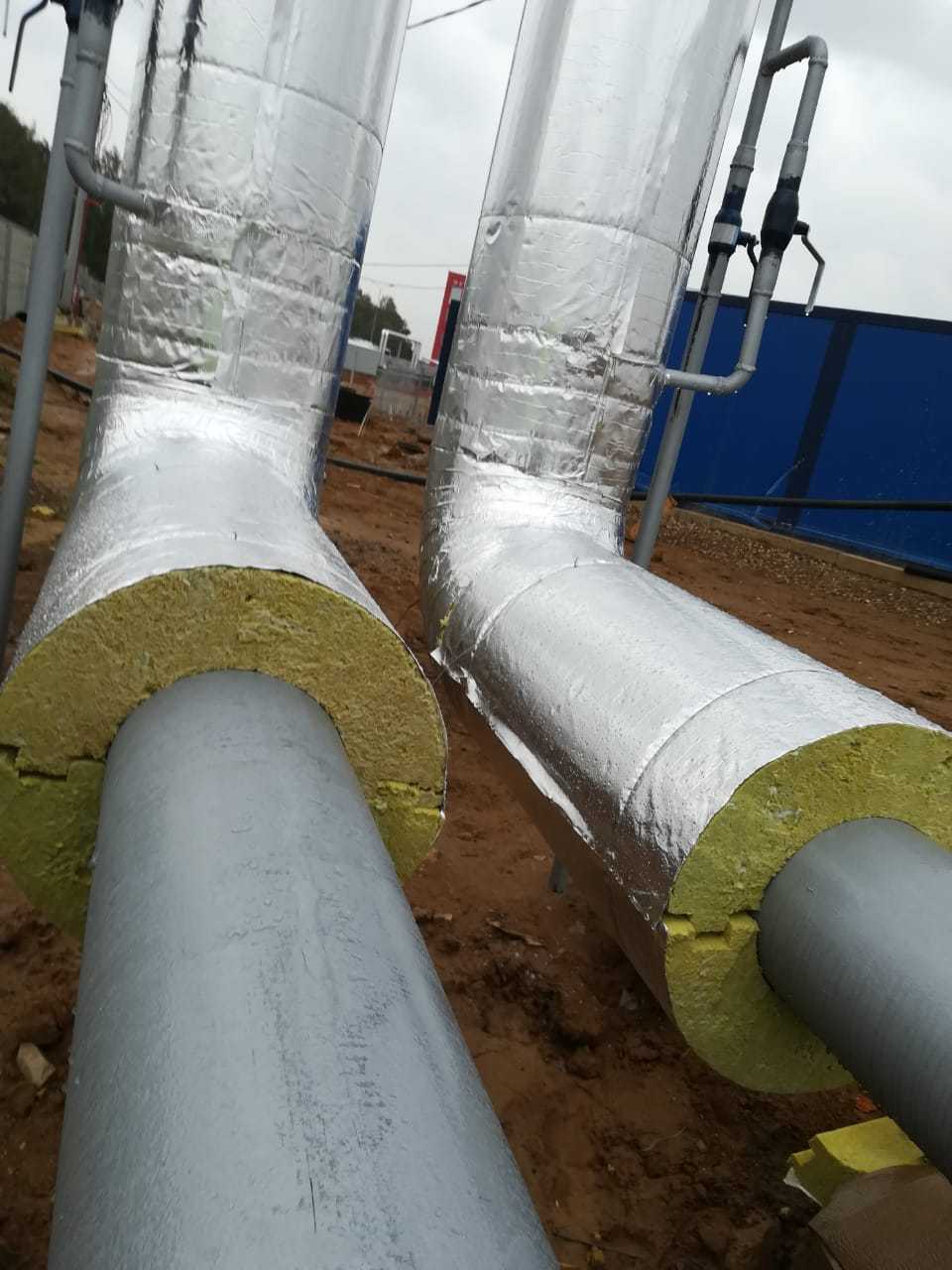
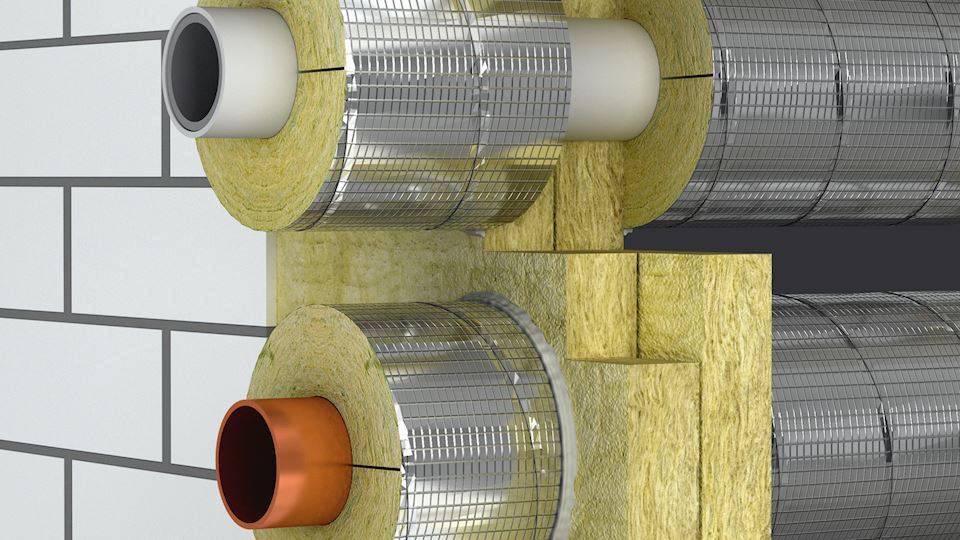
The second popular material is basalt or mineral wool.This is an improved version of insulation based on basalt mineral fibers. Environmentally, mineral wool is more preferable for use, it can withstand temperatures up to 1000 ° C, therefore it can be used for thermal insulation of chimneys. It absorbs less moisture, but its fibers still require protection from the external environment.
Basalt insulation is produced in the form of rolls or rectangular sheets of different thicknesses, and for pipe insulation there are tubular or semi-tubular forms.
Additionally, most insulation based on basalt fiber is covered on one or both sides with aluminum foil. Thermally insulated pipes with a finished steel casing over the basalt layer are also commercially available.
polyurethane foam
The newest heaters on the basis of the made foam polyurethane are applied. This material has the best thermal insulation properties and low cost. It can be given any shape, which allows you to expand the scope. Tubular variants and shapes in the form of semi-cylindrical elements of different diameters and thicknesses are common. To connect with each other along the elements, locks such as carpentry spike joints are made.
Polyurethane foam does not withstand high temperatures and begins to melt at 300 ° C, but this does not prevent its use for heat supply. Special substances are added to modern foamed polyurethane, giving it the ability to not support combustion.
Foamed polyethylene
Polyethylene foam insulation is also popular. They are similar in properties to polyurethane foam elements, but more plastic and flexible. They are produced in the form of soft pipes of different diameters and wall thicknesses.They are used to insulate water pipes of small diameter (up to 50 mm), as well as sewer pipes.
The insulation is put on the pipe in advance, before installation, or a split seam is used, which is subsequently sealed. An example of such heaters is the products of the Termoizol company.
Liquid types
Finally, liquid heaters, which come in two types - foaming and ultra-thin. The principle of operation of the first material resembles mounting foam widely used in construction, applied directly to the pipeline or into the cavity between the pipe and a special casing.
The second material is a ready-made liquid mass, which is applied to the installed pipeline in a small layer, like paint. The advantages of such heaters include low weight and volume, ease of use and the absence of cold bridges.
Phased insulation technology
Due to the fact that chimneys come in different types and designs, we will describe how to properly insulate a chimney pipe made of brick, asbestos cement and steel.
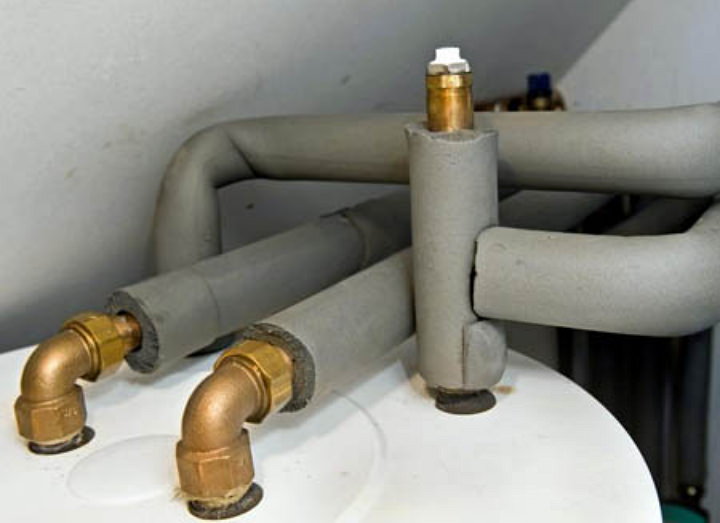
Asbestos cement chimneys
Asbestos-cement pipe
To understand how to insulate a chimney from an asbestos pipe, we will analyze the entire procedure in stages, following the recommendations of professional builders:
First you need to thoroughly clean the place of work from dust and dirt;
The next step is to make a special folding casing for the insulation (made of galvanized iron)
When determining its parameters, it should be taken into account that at least 6 cm must remain between the pipe and the iron for insulation;
Pay attention to the fact that a casing assembled from several parts is put on the asbestos pipe, and each of them should not exceed 1.5 m;
First of all, fix the lower part of the casing and carefully fill it with a sealant. Then, the second part is put on and the procedure is repeated. This design must run along the entire length of the asbestos pipe.
This design must run along the entire length of the asbestos pipe.
Thermal insulation scheme from a home master
This is what an asbestos chimney with a casing looks like
Often, many of the owners of cottages do without a casing. The pipe is simply wrapped with a roll of mineral wool and pulled together with staples. In order for this method of insulation to become truly reliable, several layers should be wound.
Steel chimneys
So, we sort of figured out the asbestos pipes, now let's see how to insulate the metal chimney pipe. In general, many manufacturers of building materials produce ready-made chimneys made of stainless steel. The design is quite simple and consists of only two pipes of different diameters.
How to insulate a metal chimney? To do this, take a pipe of a smaller diameter and insert it into a pipe of a larger diameter. Then, the remaining space between the pipes is filled with any of the above types of insulation. If you are interested in modern materials, then you can recommend basalt chimney insulation, which in its structure resembles mineral wool, but is much more practical and durable.
Thermal insulation of a steel chimney
In principle, it is much easier to insulate an iron pipe than the same asbestos one, so there should not be any problems here.
brick chimney
Brick chimney
Insulation of a brick chimney - perhaps the most complex view of all presented in this article.Now we will give several options, of which everyone will choose for himself how to insulate a brick chimney:
Plastering method. To do this, you will need to fix a reinforced mesh on the chimney. Then prepare a solution of lime, slag and a small portion of cement. Spread the resulting solution over the entire surface of the chimney and level it (all work is done in one layer, which must be at least 3 cm).
When the solution dries, it will be possible to add a few more layers, and immediately cover up the cracks that have formed. To give an attractive appearance, in the future the pipe can be whitewashed or painted.
Scheme of thermal insulation of a brick chimney
Mineral wool insulation. To do this, you will need to take a roll of basalt wool and cut it into pieces that correspond to the size of the chimney area. Then, the insulation is glued to the pipe with adhesive tape. The last step of the work is to lay the insulation (for example, Rocklight) with a second layer of bricks or asbestos-cement slabs.
The process of thermal insulation of the chimney with mineral wool
Good luck!
Ways to reduce heat loss
There are several ways to store heat while transferring it. As a rule, all of them are used in combination in order to maximize the effectiveness of measures. First of all, this is a reduction in the surface area of heat radiation. It is known from the laws of geometry that the optimal shape for pipes is a cylinder. It has the smallest outer surface area in relation to the cross section. That is why heat pipes have a circular cross section, although other shapes might be convenient for installation.
The second way is to isolate the surface of the pipeline from the external environment. With this method, there is no active transfer of energy to air molecules from a heated surface. Ideal insulation with this method would be to create a vacuum layer around the pipe, which is widely used in thermoses and Dewar vessels.
Finally, the reflection of infrared radiation coming from the pipe in the opposite direction can help. The effect is achieved by the use of reflective coatings made of metal - usually aluminum - foil.
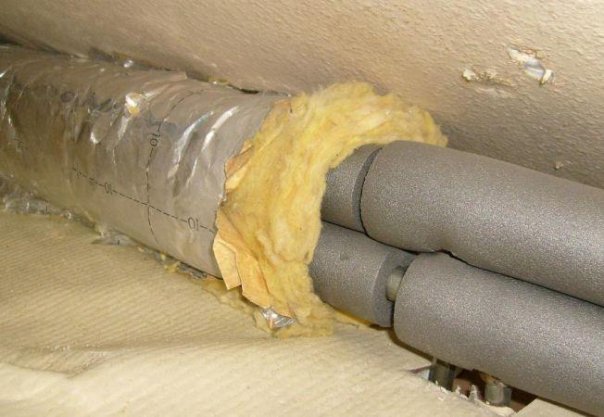
Sheet and roll types
Cheap, but not very easy-to-use insulation, which also requires additional waterproofing. Another disadvantage is a large amount of allergenic dust, so it is undesirable to use it indoors. It is better to leave fiberglass for insulation outdoors, and be sure to wear gloves, a respirator and goggles when working. Today, mineral wool brands such as Isover and Ursa have proven themselves well. Their characteristics are approximately the same: thermal conductivity 0.034-0.036 W/m∙°C, operating temperature up to +270 °C, water absorption at full immersion reaches 40%.
2. Foamed polyethylene (Izolon, Penofol).
In our case, NPE can only be considered as a hydro and vapor barrier protection for other types of insulation. Shells made of foamed polyethylene have completely different characteristics - one of the first representatives of insulation for heating pipes that appeared on our market. They withstand temperatures up to +100 °C (as, for example, Energoflex) and have a much greater thickness. We will describe them in detail in the next section of this review.

Casings and cylinders
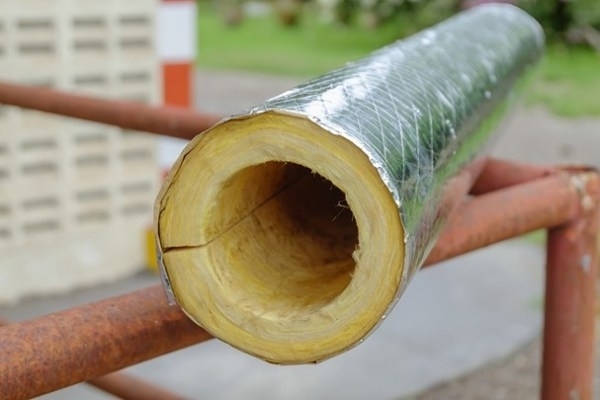
1. Basalt wool (Rockwool, Paroc).
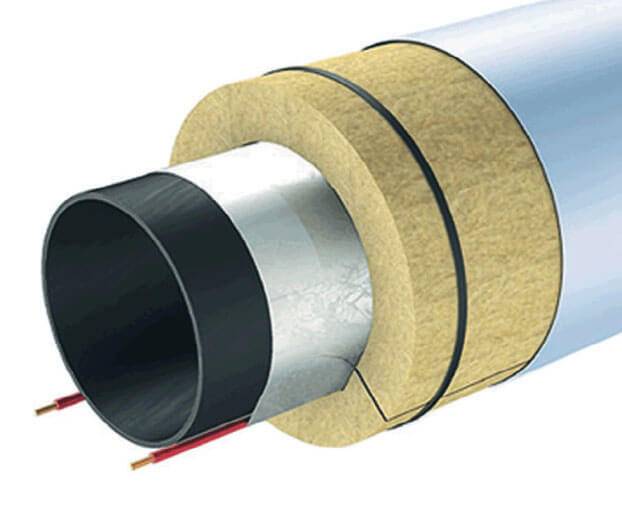
Thermal insulation meets all the requirements, although it loses somewhat in terms of water resistance. To protect against external moisture, mineral wool cylinders usually come with a foil coating, and the fibers themselves are treated with water-repellent impregnations. However, according to reviews, laminated polyethylene foam and casings made of plastic or galvanized corrugation protect such a shell much better. The maximum wall thickness of basalt insulation is 80 mm, the permissible temperature is +700 - ° C, which makes it suitable even for use in industrial facilities.
2. XPS and foam.
Rigid foamed polymers for insulating heating pipes are available in the form of split shells of different diameters. Due to their high resistance to most external factors, they are used to protect underground utilities and some internal networks. The only limitation is that in the open air such thermal insulation of pipelines is carried out only in the presence of an opaque sheath, since it is quickly destroyed by the action of sunlight.
In terms of technical characteristics, extruded polystyrene foam is preferable to polystyrene foam. Its thermal conductivity, like the price, is slightly higher, but the strength and water resistance are much better than those of the budget PSB-S. However, even such material is not suitable for pipes with temperatures above +120 ° C (for foam plastic, it is even +85 ° C). EPPS cylinders have a standard length of 1-2 m and a wall thickness of at least 10 mm. PSB casings are produced no thinner than 30 mm, since this insulation is quite fragile.
Plumbers: You'll pay up to 50% LESS for water with this faucet attachment
Combined shells with PET foil or thin galvanized sheet casing.Polymer heaters are resistant to all external factors, therefore, they have practically no restrictions in use. The normal temperature regime for them is +140 ° С. Release form: split cylinders 1 m long and at least 4 mm thick.
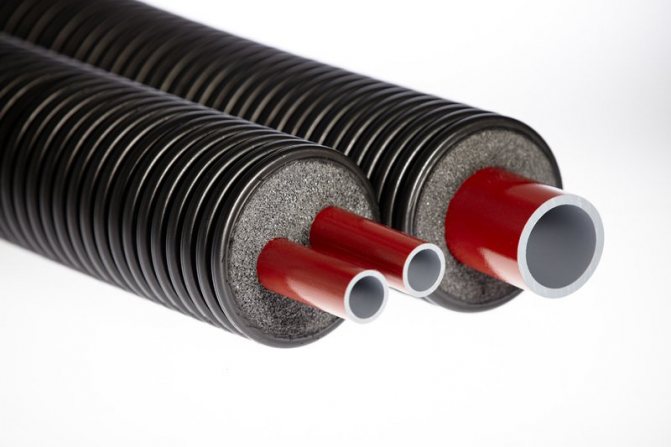
4. Thermal insulation made of polyethylene foam for pipes (Tilit, Energoflex).
The design of such heaters is extremely simple and allows you to mount them in a matter of minutes. An elastic cylinder made of foamed PET is put on the contour like a stocking or cut along the markings if the heating pipes are already connected. The joints are smeared with glue and sealed with a special tape of the Energoflex type. For shells with a length of 2 m or 10-meter coils with a maximum wall thickness of 2 cm, the main thing is to choose the right size of insulation. The inner diameter of the protection should be slightly larger than the outer diameter of the communications.
Energoflex tubes are very flexible, so they are used even on highly curved heating branches. In addition, they are moisture-resistant (that is, they continue to work as heaters when condensate appears) and are strong enough to withstand medium mechanical loads. The permissible temperature does not exceed +100 ° C - this is enough for most heating systems, but with an increase in heating, the polyethylene will simply begin to melt, losing its original volume.
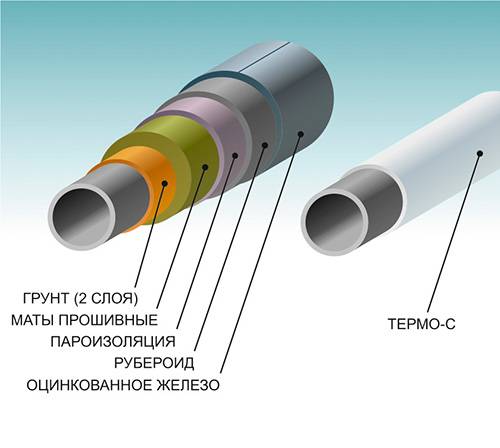
Insulating materials
Below is a list of the most commonly used materials for insulating DHW pipes, as well as a description of their main characteristics. For specific information on each type of insulation, visit the article directory on our website. All insulating materials can be divided into 5 main types:
- Cellular insulation is made up of small, individual cells that are either connected or sealed from each other to form a cellular structure. The basis for such heaters is glass, plastic or rubber, and then various foaming agents are used. The cell structure is further classified into 2 subtypes: as open cell (cells connected) or closed (sealed from each other). As a rule, materials containing more than 80% air are honeycomb insulation.
- Fibrous insulation - consists of fibers of various materials of small diameter, among which a large amount of air is trapped. The fibers may be organic or inorganic, typically held together by a binding agent. Typical inorganic fibers include glass, stone wool, cinder wool and alumina. Fibrous insulation is divided into wool or textile. Textile consists of woven and non-woven fibers and threads. Fibers and threads are either natural or synthetic. Basically, these are composite plates or rolls, which are not convenient for wrapping pipes, but are very effective insulating, complete with reflective films.
- Flake insulation is made up of small, irregular-leaf-like particles that separate the surrounding air space and are easily molded into specific shapes. These flakes can be bonded together with an adhesive backing or sprinkled
into the necessary forms or covers without fasteners. Vermiculite, or expanded mica, is a flaky insulation. - Granular insulation consists of small round-shaped fractions of various diameters, which contain voids or are completely filled.These materials are sometimes confused with open cell insulation because the final bonded product has a similar appearance to foam insulation. Calcium silicate and molded perlite insulators are considered granular insulation materials.
- The reflective insulation reduces the long wavelength radiation that comes from the pipes, thereby reducing the radian heat transfer from the surface. Some reflective insulation systems consist of several parallel thin sheets or alternate layers to minimize convective heat transfer. Foamed polyethylene with a thin aluminum film (penofol foil) is the main and very striking example of reflective insulation.
In conclusion, consider one new insulation compound that is rapidly gaining momentum and increasing its sales in the field of building materials. Thermal insulation coatings or paints are widely used for use on pipes, channels and tanks. Currently, these paints have not been thoroughly tested, it is too early to judge the final effect. The information available comes only from manufacturers, without any laboratory research or opinions of independent experts.
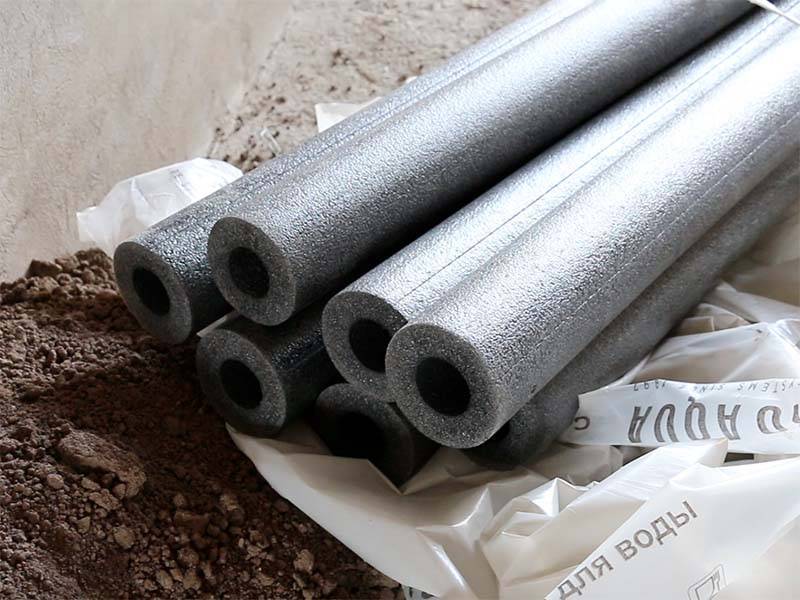
Expanded polystyrene heat insulator for pipes
Styrofoam shells are a popular insulator for insulating sewer pipes. Two percent of its composition is small, from 1 to 5 mm, polystyrene granules, the remaining 98% is air. After processing the material with a blowing agent, the granules acquire lightness, elasticity, are attracted to each other and stick together.
By pressing, followed by high-temperature steam treatment, the material is given the desired shape.
In fact, this is a simple foam, but in the form of a shell, designed for repeated use. The difference between the thermal conductivity coefficient of polystyrene foam insulation (0.03-0.05) and mineral wool is small. The shell, which has the shape of hemispheres, copes with the task of retaining heat quite effectively.
 The foam shell can consist of 2 or 3 elements. On their sides there are locks with a device for fixing. The shell is selected according to the diameter of the pipe and, putting it on, snaps into place
The foam shell can consist of 2 or 3 elements. On their sides there are locks with a device for fixing. The shell is selected according to the diameter of the pipe and, putting it on, snaps into place
Since the foam is not very resistant to mechanical stress, manufacturers supply the shells with an outer coating of aluminum foil, fiberglass and other materials.
High heat-insulating properties are provided by thin-walled microcells that do not transmit heat. The service life of the heat-insulating shell is quite large - about 50 years.
There are 2 types of this material - ordinary and extruded polystyrene foam. The characteristics of the latter are higher, but the cost also differs upwards.
Despite a lot of positive qualities, polystyrene foam also has disadvantages. It does not tolerate ultraviolet radiation, therefore, when laying pipes in open places, additional protection from the sun is required. This material is dense, but fragile, and when burned, it can cause poisoning, because. the smoke they give off is poisonous.
Installation work is so simple that it does not require special qualifications. Putting insulation segments on the sewer pipe, they overlap, shifting them along the length relative to each other by 200-300 mm.In order to avoid the appearance of cold bridges, the thermal insulation elements are joined together using a quarter or tenon-groove system.
After the connection is made, both parts are strongly compressed. The contact points are glued with adhesive tape. Sometimes the joints are coated with glue, but then the insulation loses such an advantage as the possibility of reuse, because. when dismantling it will have to be cut.
A protective coating is put on the shell, which comes with it, or simply wrapped with plastic wrap, if it is not there.
The shells are used both on elevated routes and for laying highways underground. This insulation can be put on a pipe with a minimum diameter of 1.7 cm and a maximum diameter of 122 cm. Already with a diameter of 200 mm, the cylinder consists of 4 elements, and large products may have 8 of them.
Trenches with sewer pipes are first covered with sand to a height of about 0.2 m, then with earth. In regions with very cold winters, thermal insulation in the form of an expanded polystyrene shell is supplemented with an insulating cable, placing it under the shell.
What thickness of insulation is needed?
Surely the interested reader will have a question - what should be the thickness of the insulation layer in order to guarantee the protection of the water pipe from freezing.
Answering this is not so easy. There is a calculation algorithm that takes into account the mass of the initial values, and includes several formulas that are difficult even for visual perception. This technique is set out in the Code of Rules SP 41-103-2000. If anyone wants to find this document and try to make an independent calculation - you are welcome.
But there is an easier way.The fact is that specialists have already taken on the brunt of the calculations - in the same document (SP 41-103-2000), which is easy to find by any search engine, the application contains many tables with ready-made values for the thickness of the insulation. The only problem is that it is physically impossible to present these tables here in our publication. They are compiled for each type of insulation separately, and - with a gradation also by location - soil, open air or room. In addition, the type of pipeline and the temperature of the pumped liquid are taken into account.
But if you spend 10 ÷ 15 minutes studying the tables, then there will certainly be an option in them that is as close as possible to the conditions that interest the reader.
It would seem that this is all, but it is necessary to dwell on one more important nuance. It applies only to cases of warming the water supply with mineral wool. When it came to this thermal insulation material, in a series of shortcomings of mineral wool, its tendency to gradual caking, shrinkage was indicated.
And this means that if you initially set only the estimated thickness of the insulation, then after some time the thickness of the insulation layer may become insufficient for full thermal insulation of the pipe.
When it came to this thermal insulation material, in a series of shortcomings of mineral wool, its tendency to gradual caking and shrinkage was indicated. And this means that if you initially set only the estimated thickness of the insulation, then after some time the thickness of the insulation layer may become insufficient for full thermal insulation of the pipe.
Therefore, when performing insulation, it is advisable to pre-lay a certain margin of thickness. The question is what?
This one is easy to calculate.There is a formula, which, I think, does not make sense to demonstrate here, since the online calculator offered to your attention is based on it.
The two initial values for calculation are the outer diameter of the insulated pipe and the recommended value of the thermal insulation thickness found from the tables.
One more parameter remains unclear - the so-called "densification factor". We take it from the table below, focusing on the selected thermal insulation material and the diameter of the pipe to be insulated.
| Mineral wool insulation, insulated pipe diameter | Compaction factor Kc. |
|---|---|
| Mineral wool mats | 1.2 |
| Thermal insulation mats "TEHMAT" | 1,35 ÷ 1,2 |
| Mats and sheets made of super-thin basalt fiber (depending on the conditional diameter of the pipe, mm): | |
| → Doo | 3 |
| ̶ the same, with an average density of 50-60 kg/m³ | 1,5 |
| → DN ≥ 800, at an average density of 23 kg/m³ | 2 |
| ̶ the same, with an average density of 50-60 kg/m³ | 1,5 |
| Mats made of glass staple fiber on a synthetic binder, brand: | |
| → M-45, 35, 25 | 1.6 |
| → M-15 | 2.6 |
| Mats made of glass spatula fiber "URSA", brand: | |
| → M-11: | |
| ̶ for pipes with DN up to 40 mm | 4,0 |
| ̶ for pipes with DN from 50 mm and above | 3,6 |
| → M-15, M-17 | 2.6 |
| → M-25: | |
| ̶ for pipes with DN up to 100 mm | 1,8 |
| ̶ for pipes with DN from 100 to 250 mm | 1,6 |
| ̶ for pipes with DN more than 250 mm | 1,5 |
| Mineral wool boards on a synthetic binder brand: | |
| → 35, 50 | 1.5 |
| → 75 | 1.2 |
| → 100 | 1.1 |
| → 125 | 1.05 |
| Glass staple fiber board grades: | |
| → P-30 | 1.1 |
| → P-15, P-17 and P-20 | 1.2 |
Now, armed with all the initial values, you can use the calculator.
Calculator of the thickness of the pipe insulation with mineral wool, taking into account the shrinkage of the material
An interesting feature.When calculating, it can sometimes turn out that the end result is less than the tabular thickness of the insulation. In these cases, nothing needs to be changed - the value that is found according to the tables of the Code of Rules is taken as true.
Types of thermal insulation materials
Mineral wool
Mineral wool is especially well suited for the insulation of large diameter pipelines.
Due to their high efficiency, heat insulators consisting of mineral wool are very popular. Among their advantages are the following:
- a sufficient degree of heat resistance (up to 650 C), while the material, when heated, does not lose its original mechanical and thermal insulation characteristics;
- chemical resistance to solvents, alkalis, acids, oil solutions;
- slight water absorption - due to treatment with special impregnating compounds;
- mineral wool is considered a non-toxic building material.
Insulation for heating pipes based on mineral wool is ideal for thermal insulation of heating and hot water pipelines in public, industrial and residential buildings. It is often used for installation on pipes that are subjected to constant heating, for example, on stove chimneys.
There are several types of mineral wool heat insulators:
- stone wool - made from basalt rocks (you have already read about it above);
- glass wool (fiberglass) - the raw material is broken glass or staple fiber made from quartz sand. Glass insulation, unlike stone, is not so heat-resistant, so the areas where it can be used are somewhat narrower.
glass wool
Felt glass wool for pipes
Glass mineral insulation is produced with a thickness of 3-4 microns in rolls 1550-2000 mm long. Glass wool has a low density and can be used for pipelines whose heating temperature is not higher than 180 C.
The insulation is suitable for thermal insulation of ground communications. Among its positive properties:
- resistance to vibration;
- resistance to biological and chemical influences;
- long service life.
polyurethane foam
Polyurethane foam insulation
A polyurethane foam heat insulator is a rigid structure consisting of ribs and walls. Insulation is cast under production conditions using the "pipe in pipe" method. Another name for such an insulator is a heat-insulating shell. It is very durable and retains heat well inside the pipeline. It is especially worth noting that polyurethane foam insulation:
- has a neutral odor and is non-toxic;
- resistant to decay;
- safe for the human body;
- very durable, which prevents possible pipeline breakdowns associated with external mechanical loads;
- has good dielectric properties;
- chemically resistant to alkalis, acids, plasticizers, solvents;
- withstands various weather conditions, so it can be used to insulate heating pipes on the street.
But polymer insulation has one significant drawback - the high price.
Foamed polyethylene
Cylinders for polyethylene foam insulation
Environmentally friendly, harmless to humans, resistant to humidity and sudden temperature fluctuations, polyethylene foam is in great demand as a heat-insulating material. It is made in the form of a tube of a certain diameter, equipped with an incision.It can be used for insulation of heating pipes, as well as cold and hot water supply.
It retains its characteristics when interacting with various building materials (lime, concrete, etc.).
Other heaters
Several other types of heaters are also available:
- Styrofoam.
The insulation is made in the form of two connecting halves. The connection takes place using the tongue-and-groove method, which prevents the formation of so-called "cold bridges" in the heat-insulating layer.
- Styrofoam.
A low degree of moisture absorption and thermal conductivity, a long service life (50 years or more), good sound insulation and heat resistance, as well as resistance to ignition, make polystyrene an indispensable insulation used in industrial construction.
Expanded polystyrene, polystyrene, penoizol, foam glass - the best heaters for heating pipes
- Penoizol.
It is similar in its properties to polystyrene, differs only in that it is produced in liquid form. When applied to pipes, it does not leave “gaps” and ensures the tightness of the system after drying.
- Foam glass.
It is an absolutely safe insulation, as it consists of glass of a cellular structure. The insulation is non-shrinking, strong and durable, non-flammable, resistant to chemical environments and vapors, easily endures rodent invasions.
Insulation of heating pipes with foam glass is not difficult even for beginners, while you can be sure of its long service life.
Polypropylene pipes
These products appeared on the market not so long ago, but have already become one of the most popular materials. They are purchased for the construction of engineering communications - heating, water supply, gas supply, sewerage.Polypropylene pipes are used for irrigation and watering systems, where carriers are extremely active and aggressive.

pros
If we consider polypropylene as a material for pipes, then it has both advantages and disadvantages. It has sufficient density, but according to this indicator, PP is inferior to other plastics. The polymer "feels" well at a temperature of 90 °.
It is resistant to abrasion, light, does not have a high level of water absorption, and is chemically neutral. Polypropylene is characterized by increased resistance to water hammer, which is not characteristic of either metal or metal-plastic pipes. Excellent sound insulation is another plus of the products.
Minuses
The disadvantages of PP include poor flexibility, resistance to cracking only under optimal conditions. The latter property is unstable: the strength of the material is greatly reduced at low temperatures. Its durability depends on the operating conditions: on the pressure in the system and on the temperature of the coolant.
Some reagents are capable of destroying polypropylene in certain situations, so special stabilizers are added to the working fluid. For the installation of a polypropylene pipeline, a special tool is needed - a soldering iron, which is also called a welding machine. Independent soldering (welding) requires skills from the master.