- The principle of operation of the drainage system
- Scheme of a classical drainage system
- Drainage types
- Wall drainage device technology
- Installation requirements
- Materials and tools
- Work order
- Types and types of drainage
- Do-it-yourself foundation drainage
- The need for drainage for the foundation and its function
- Types of drainage
- Work technology
- Columnar (pile) foundation
- Rules for the organization of the drainage system
- Varieties and arrangement of drainage systems
- Surface (open) drain for collecting rainfall
- deep drainage
- Drainage system: features
- Definition
- Purpose
- Components of a drying system
- Purpose
- Calculation of system and materials
- What is drainage for?
- The main advantages of a monolithic foundation:
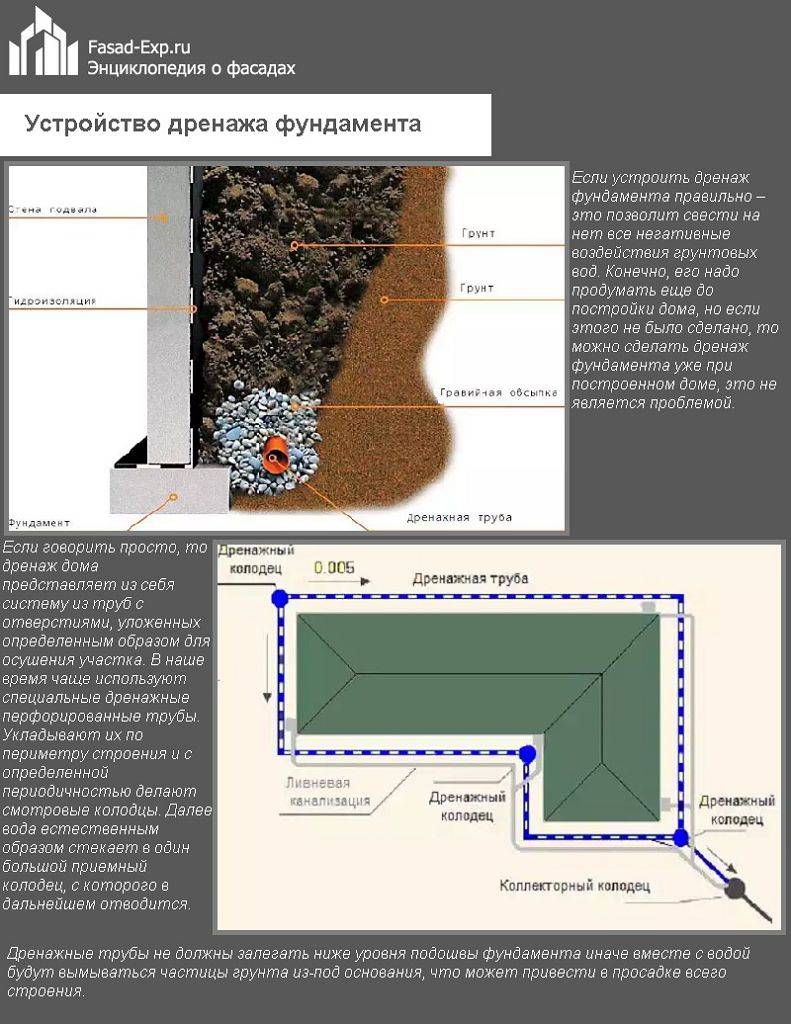
The principle of operation of the drainage system
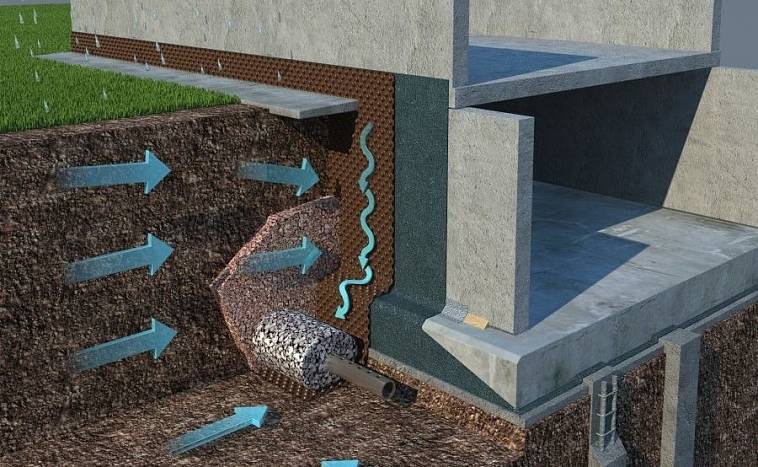
The action of the drainage is fully consistent with its main purpose - the removal of excess moisture to a safe distance. It would be a mistake to assume that one pipe laid around the perimeter of the house can cope with this problem.
In fact, this is a whole engineering and construction complex that fights against an excess of moisture, protecting foundations and basements, but without overdrying the surrounding area.
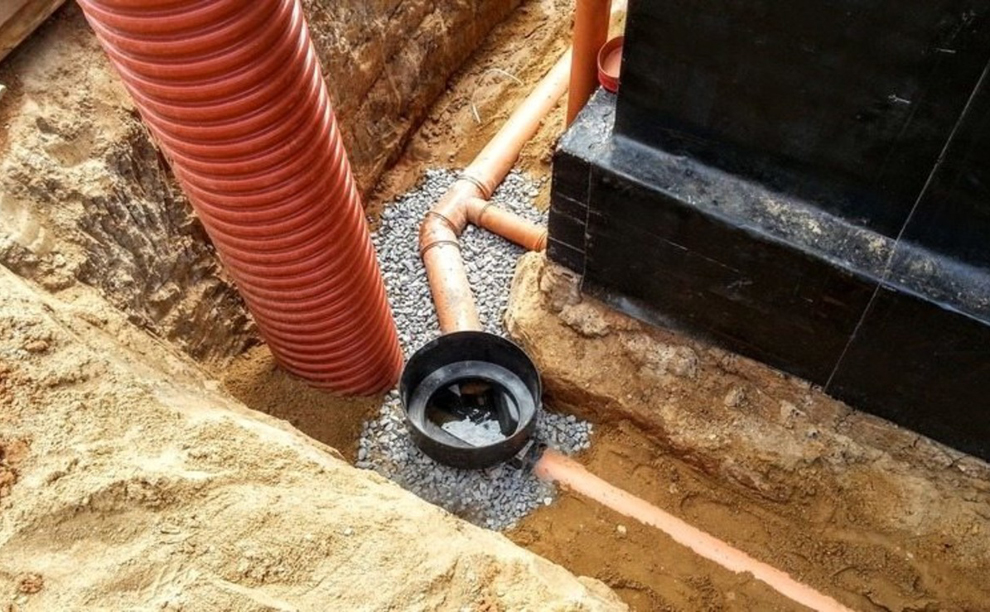
The wall type of drainage is appropriate in conditions of clay soil and loam, when melt, rain and groundwater cannot independently leave the area located around the building.A complex design of pipes, wells and outlets removes excess water quite effectively, despite the budgetary cost.
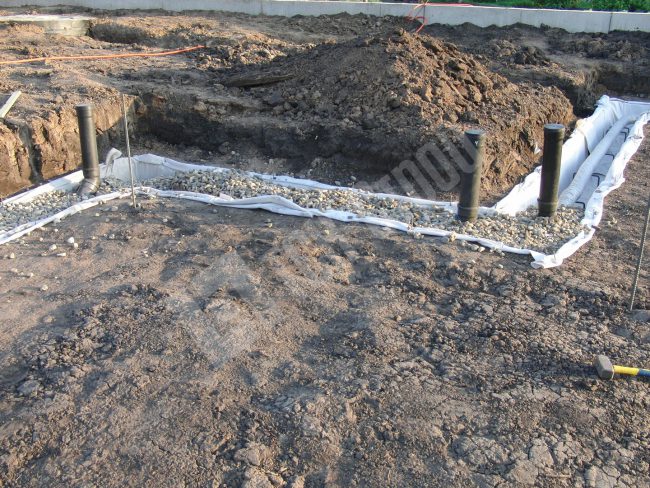
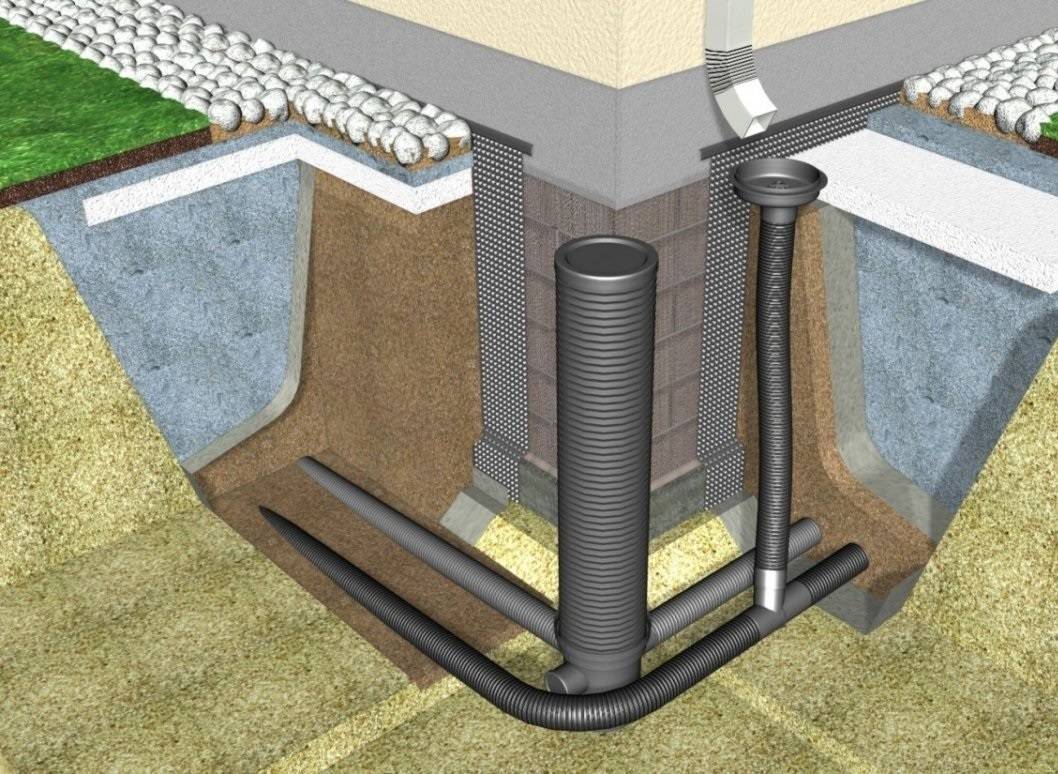
One of the simplest designs of wall drainage: installation of drains along the perimeter of the building, revision wells in the corners (sometimes two are enough), drainage outside the garden plot (+)
One of the popular schemes involves the connection of two systems - drainage and storm water - in the area of \u200b\u200bthe storage well, which is usually located at the lowest point of the territory adjacent to the house.
In practice, the option is often used when the drainage pipeline is cut into the manholes of the storm sewer. However, this is possible only under one condition - if the total volume of effluents does not exceed the norms calculated for the installed equipment.
If the drain zone is located above the water level in the reservoir, pumping equipment has to be installed. A popular option is a submersible drainage pump, matched by power.
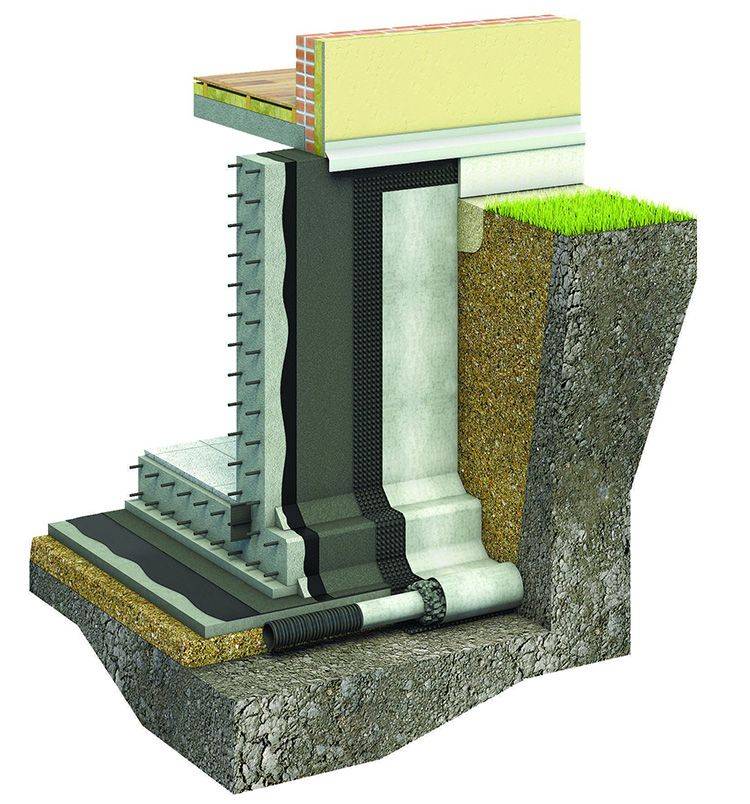
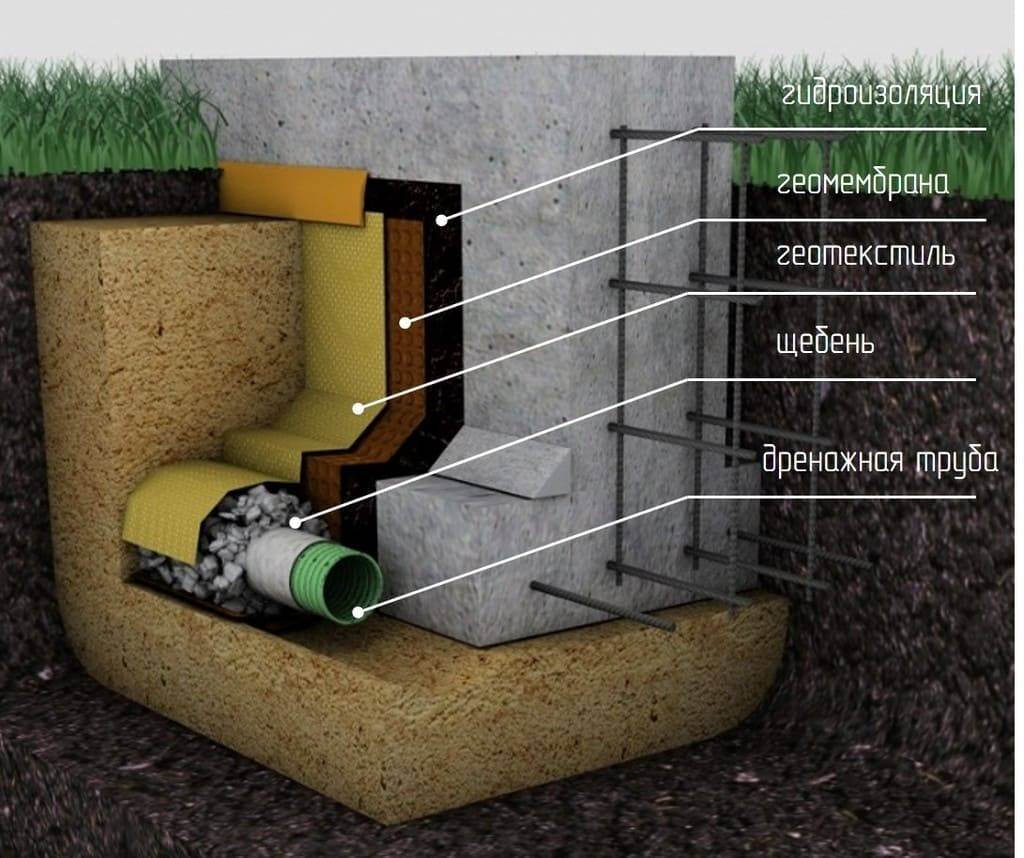
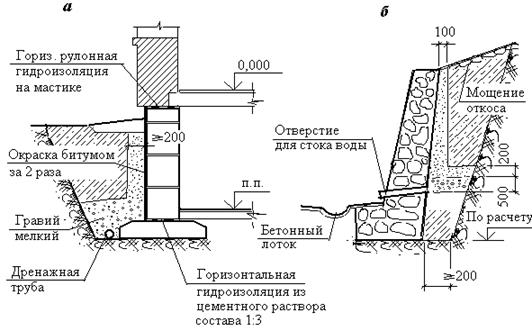
There are two options for arranging drainage around the foundation: traditional and more reliable. Traditional - this is the installation of pipes with gravel backfill, a filter and a clay lock. Its performance has been proven for decades.
The clay lock, which is one of the important elements of the system, is compacted in layers to increase water resistance. It cuts off groundwater from the foundation, thus creating an impenetrable water barrier (+)
More reliable modern drainage is distinguished by the design of the foundation. A geomembrane is fixed along its entire width, the characteristics of which are not inferior to a clay castle.
Installation of a geomembrane is more economical in terms of device: no need to dig a deep ditch, look for the right grade of clay, transport a heavy load to a construction site, remove excess soil (+)
The installation process is much simpler, if only because you do not need to do calculations and calculate the angle of inclination of the clay "plug". Now almost all wall drainage schemes include the use of a geomembrane, because it is reliable, practical, fast and efficient.
Scheme of a classical drainage system
Do-it-yourself classic drainage system scheme is a system along the perimeter of the building foundation. Drains are mounted at an angle of approximately seven degrees. The entire foundation around is surrounded by this system, starting from the highest mark and ending with the lowest. At the end, a drainage tank is installed in which the pump is mounted.
When constructing this system, it is necessary to use pipes with a stiffness index of SN6 or more.
Tank wells are installed around the perimeter of the entire system. At each bend of 90 degrees, wells must be installed to collect sludge. Otherwise, your system will regularly silt up.
Drainage types
There are no uniform standards for the design and construction of drainage structures for private construction. In each case, the decision is made on the basis of the accompanying conditions.
There are the following types of drainage systems:
- Perfect. It is a completely closed structure, where the functions of collecting liquid are completely delimited and isolated from each other. All drains (sewage, storm, ground) are laid separately, as well as retaining and collection tanks. Communications are laid underground, only inspection hatches are located on the surface.
- Imperfect. As a rule, this is a system of ditches up to 70 cm deep and up to 50 cm wide, led into a common reservoir. The trenches receive rainwater and groundwater. To protect against destruction, the walls and bottom of the ditches are reinforced with stones, slate or geotextiles. From above, trenches can be covered with decorative gratings or equipped with bridges.
Based on the type of drainage, its price also varies. Perfect designs are more convenient and practical, but the price of their construction is many times higher.
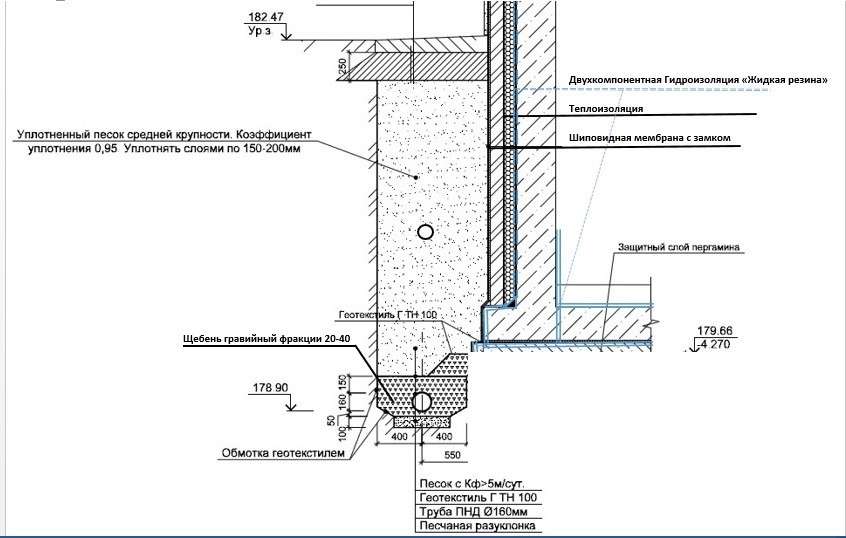
Wall drainage device technology
This system is most common in private housing construction. It is required for almost all objects, since it allows you to avoid trouble during heavy rainfall and in the spring, when the topsoil is abundantly moistened. In addition to the above joint venture, when laying it is also necessary to be guided by SNiP 3.07.03-85 * and SNiP 3.05.05-84.
Wall drainage can be done in two ways, the choice between which depends on the type of foundation:
- linear (according to the joint venture, the effective drainage depth is up to 4-5 m) along the perimeter of the blind area for tape bases;
- layered at the level of the sand cushion under the foundation slabs (according to the norms, they should also include a linear type).
The technology for the most common linear editing is discussed below.
Installation requirements
When designing a drainage system, it is necessary to take into account the requirements for its location:
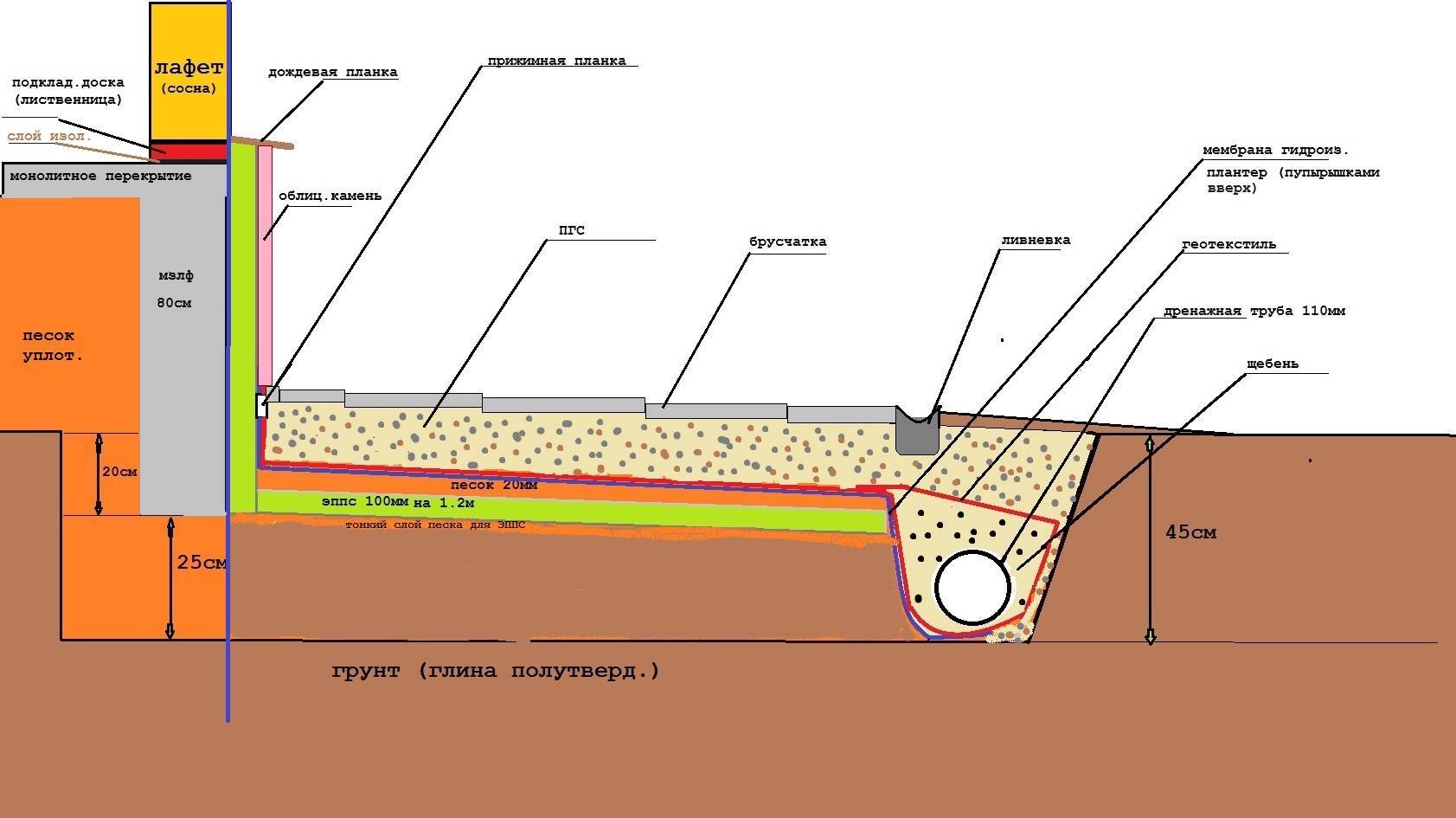
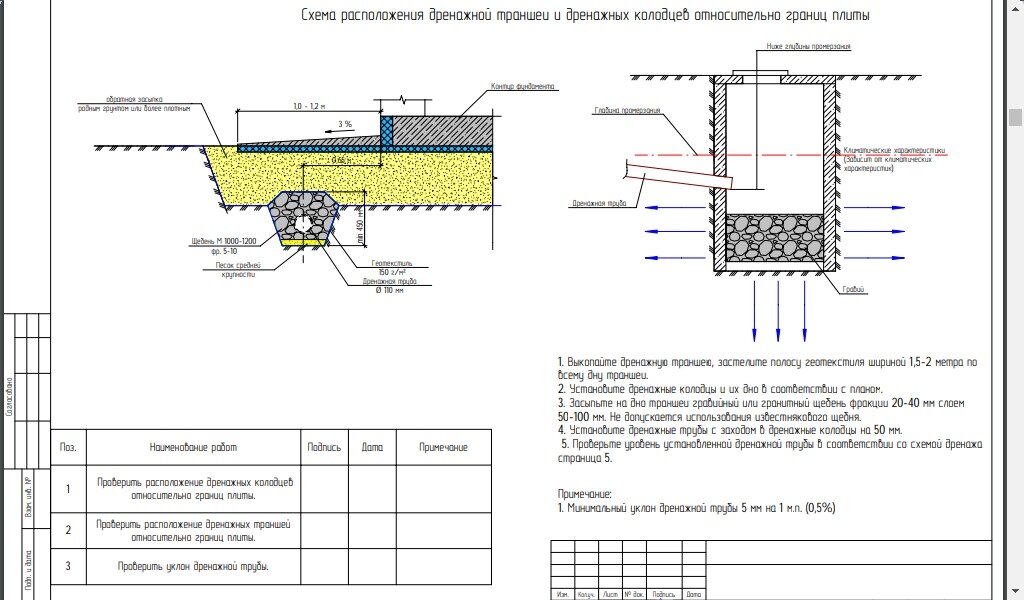
- wall drainage laying depth - 30-50 cm below the base of the foundation;
- slope towards the watershed - 0.02 (for every meter 2 centimeters);
- the maximum distance from the outer edge of the foundation tape is 1 m.
Before laying pipes, determine the upper and lower points of the system.First, they are determined with the collection point (lower), from which water will be drained from the drainage. After determining this point, the top mark is calculated taking into account the length of the pipes and their required slope.
Materials and tools
To do the job you will need the following tools:
- bayonet and shovel;
- pick;
- electric or pneumatic perforator;
- building level and tape measure;
- wheelbarrow or trolley for transporting soil;
- manual rammer or vibrating plate.
To equip the drainage system, you will also need materials:
- pipes;
- crushed stone or gravel;
- sand;
- geotextile;
- polypropylene rope.
Pipes for carrying out drainage measures according to regulatory documents can be made of asbestos cement, ceramics or plastic. Crushed stone should be selected with a fraction (grain) size of 20-40 mm. Sand is used the same as for backfilling (medium-grained or coarse-grained).
Work order
The arrangement of drainage is carried out in stages:
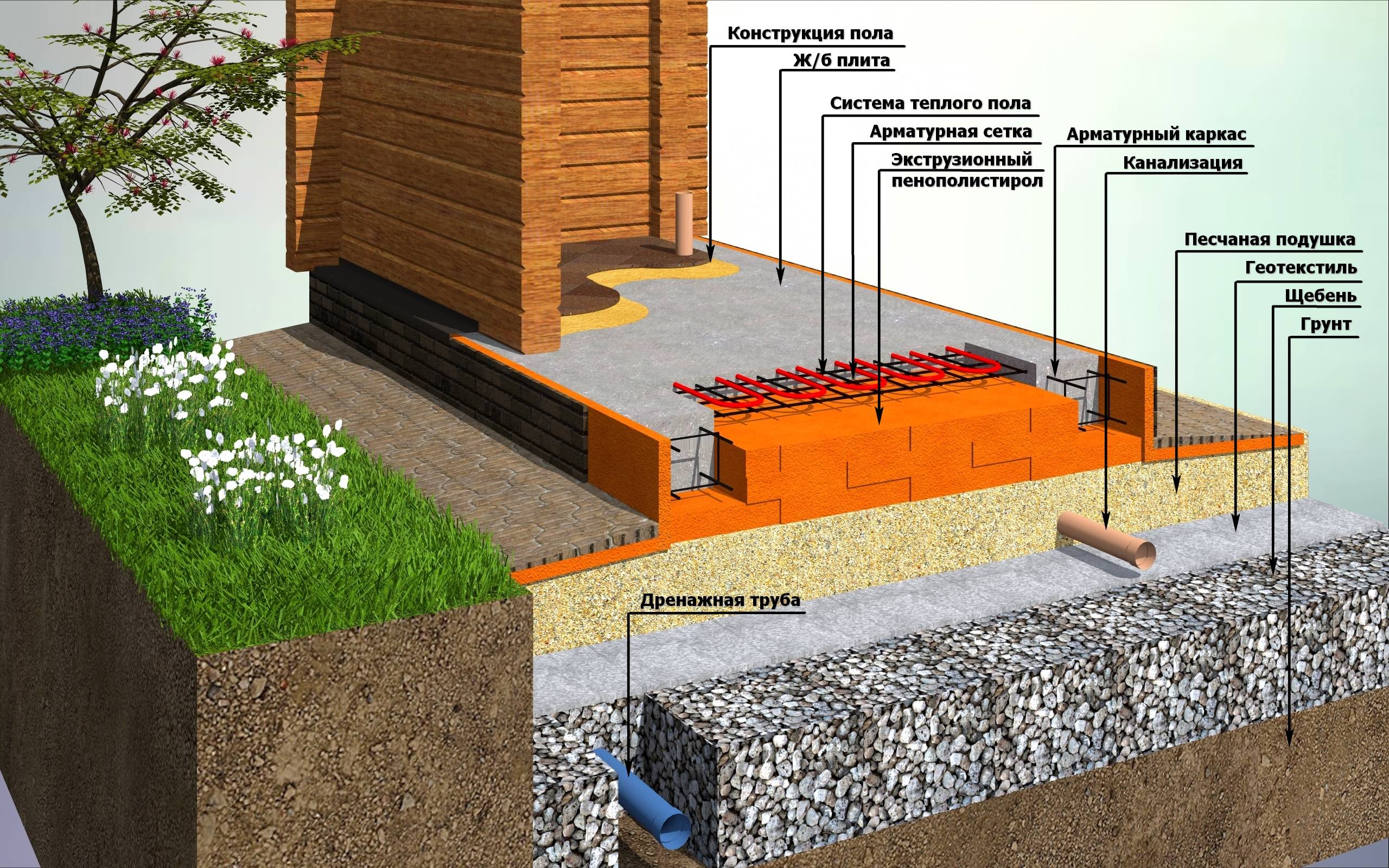
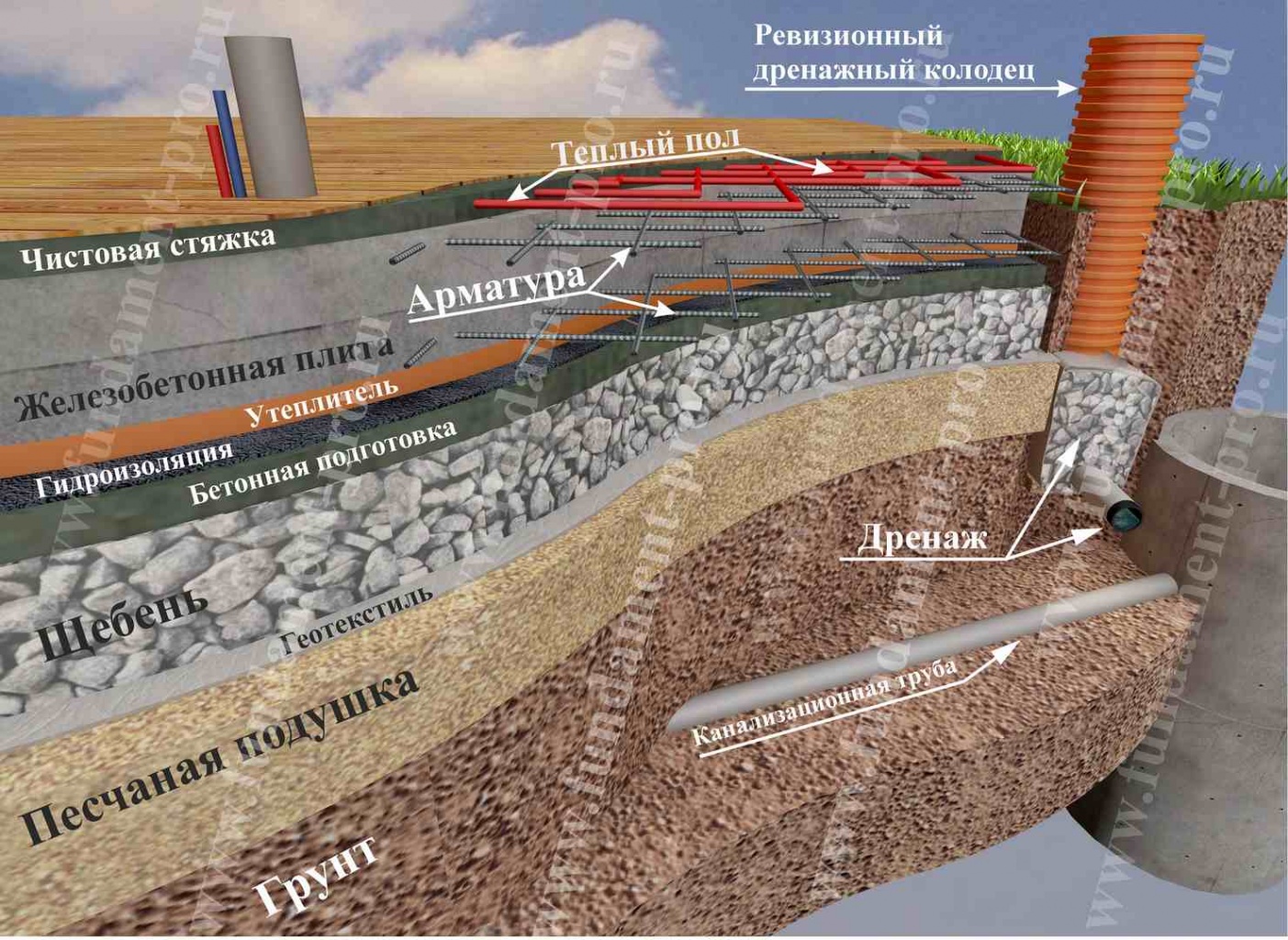
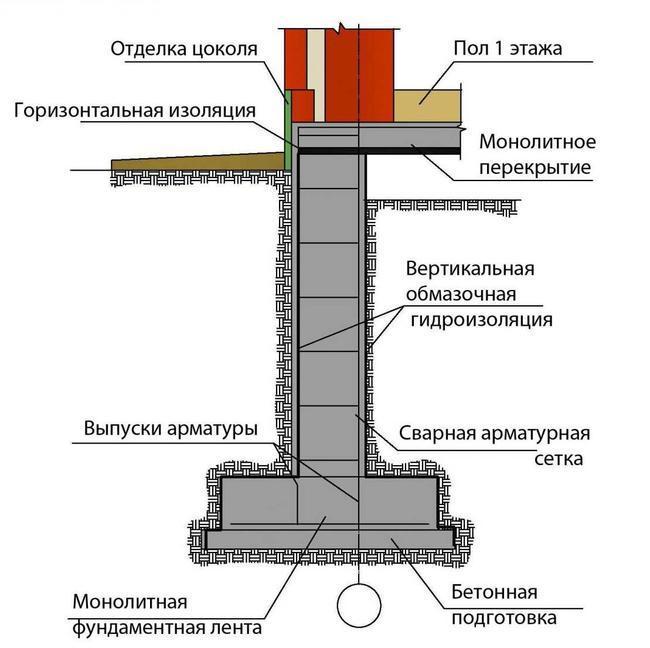
- Basement wall waterproofing. Most often, bitumen-based mastic is used. It is applied in several layers, if necessary, reinforced with fiberglass. For foundations with a laying depth of up to 3 m, waterproofing with a total thickness of 2 mm is sufficient; for deeper laying, the total thickness of the bitumen layers is increased to 4 mm.
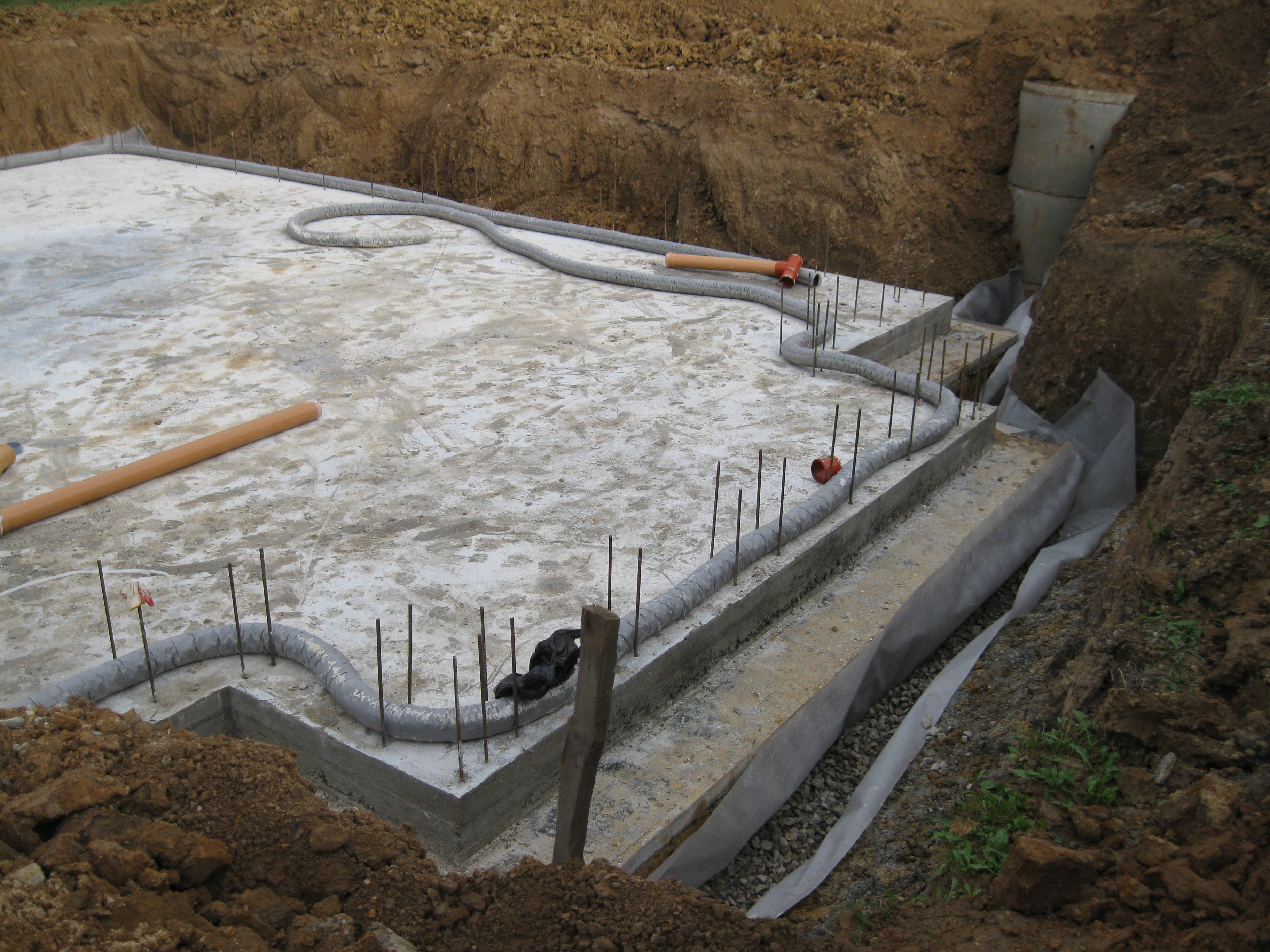
- Excavation of a trench for pipes, taking into account the requirements for the location.
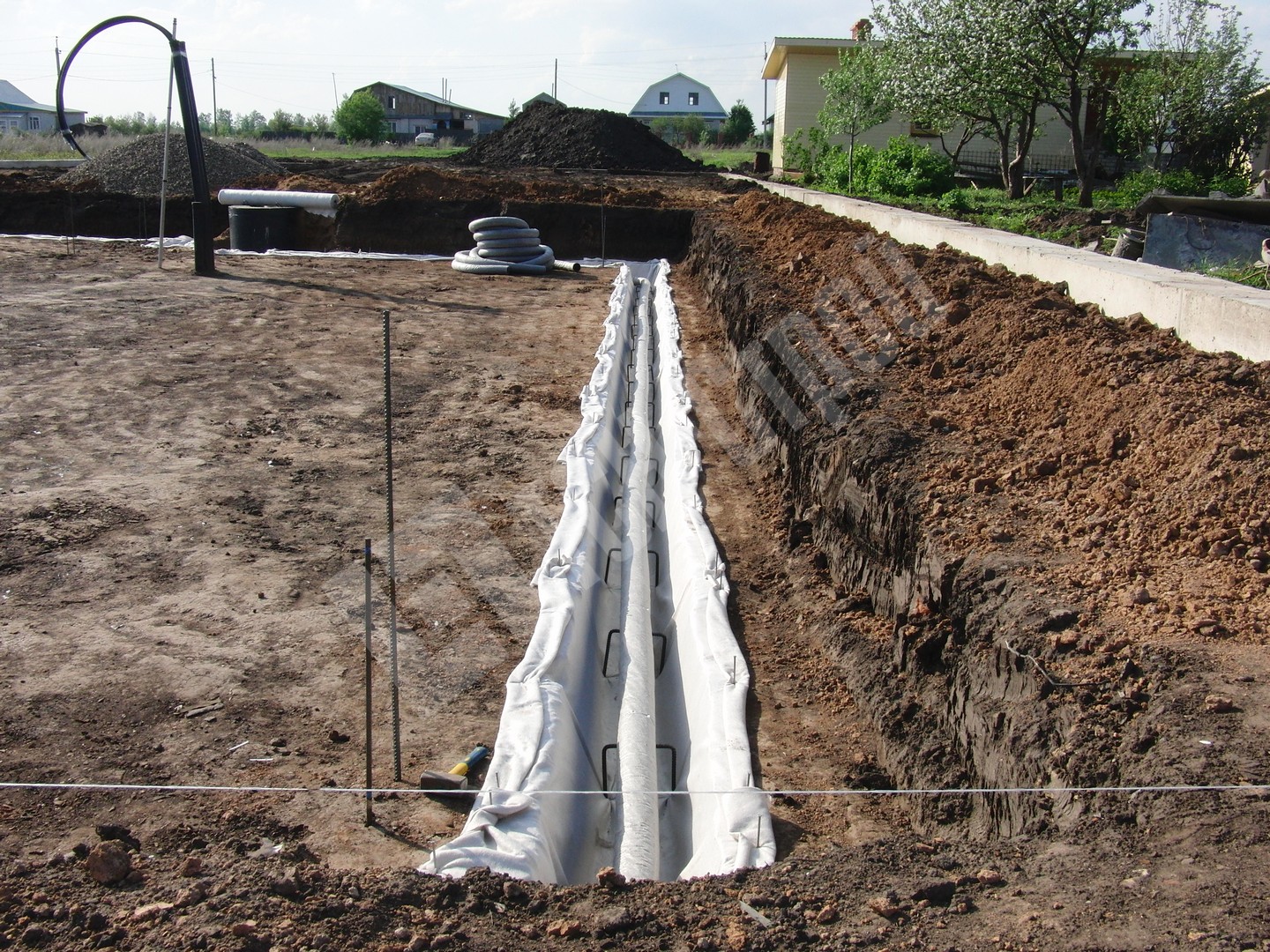
- At the bottom of the trench, a sand cushion is laid, on top of which geotextiles are spread. The width of the web should be such that it is possible to wrap the pipe without gaps.
- A layer of crushed stone 10 cm thick (or gravel) is laid on the geotextile, pipes are laid on top of the crushed stone with the necessary slope for the gravity-fed operation of the system.
- The pipes are connected. At each turn, a vertical pipe section (manhole) with a lid is provided. This is required for checking and flushing pipes.
- Crushed stone or gravel is poured over the pipes, the layer thickness is 15-20 cm. The bulk material is wrapped in geotextile with an overlap.
- Perform backfilling with sand with layer-by-layer tamping. Compaction can be carried out with a vibrating plate or a manual rammer with moisture.
Some Tips
For proper work, it is necessary to take into account:
- drainage holes in pipes must be smaller than the minimum particle size of crushed stone or gravel;
- after wrapping with geotextile, it is additionally fixed with a polypropylene rope, pieces of rope must be laid under the geotextile in advance;
- with a large number of turns, the norms are allowed to provide manholes through one;
- with independent construction, you can not perform hydraulic calculations, and choose the diameter of the drainage pipes in the range of 110-200 mm;
- draining water from a drainage well (collector) can be performed into a storm sewer or into an open area after filtering through a layer of crushed stone (gravel).
With a careful approach to drainage at the construction stage, it will not cause problems during operation and will last for decades.
Types and types of drainage
Modern drainage is of two types:
- Perfect plumbing. It is performed on the aquifer. Water ingress in this type of drainage occurs from the side and from above. Therefore, it is necessary to sprinkle this type from the sides and from above.
- Imperfect drainage. It is performed above the level of the aquiclude.Water ingress occurs from the side, from below and from above. Sprinkling of this type of foundation must be done from all sides.
There are also several types of foundation drainage for a stand-alone building:
- Ring drainage of the foundation.
- Wall drainage.
- Plast drainage.
An annular drainage system is used to prevent water from entering the basements of separately erected buildings built on sand. Since water freely penetrates through the sand, only an annular drainage can save the foundation.
Things to consider when choosing this type of drainage:
- the type of this drainage is a ring, which has an internal cavity isolated from water;
- if the flow of water occurs from a specific one side, then it is possible to perform drainage in an open circle;
- this type is mounted below the level of your floor or basement, which must be protected from moisture;
- this system should be laid at a distance of about 7 meters from the outer wall. If the distance is less than 5 meters, then you need to take care of the weakening, removal or settlement of the soil of your building.
Wall drainage is used to prevent flooding of the basement of a building or basement erected on loamy or clay soil. Water through this type of soil penetrates very poorly.
What you need to know when using this type of drainage:
- it is quite often used as a prevention against flooding;
- this drainage system is used for mixed groundwater;
- lay a drainage system outside of your building. The required distance from the wall of the house to the drainage system is equal to the width of the foundation of your building;
- this system must be laid not lower than the level of the sole of your foundation;
- if the foundation is too deep, drainage can be done a little higher.
Formation drainage is used in combination with wall or ring drainage.
Things to consider when choosing a reservoir system:
- it is advisable to use it with a large volume of groundwater on any type of soil;
- used for prevention in loamy and clay soil;
- for the interaction of this system with an external drainage system, it is necessary to lay special. pipe through the entire foundation of the building.
The main feature of the annular drainage from the wall is that it is installed directly near the foundation of the building, and the annular drainage is at a distance of up to about 3 meters from the foundation. In other cases, they are basically the same.
Do-it-yourself foundation drainage
Closely located groundwater or a large accumulation of moisture in the soil have a negative impact on any buildings, especially on the foundation. Therefore, to eliminate excessive moisture, it is necessary to carry out measures related to the installation of a drainage system. Draining the foundation is not so difficult if you know features of its installation and work technology.
The need for drainage for the foundation and its function
Even the deep occurrence of groundwater in some cases requires the arrangement of drainage, in each case a large number of factors are considered. In some situations, drainage around the foundation is necessary anyway. Here is some of them:
With a large depth of the basement, when it is below the groundwater level, or less than half a meter from the basement floor to them,
If the basement is equipped in loamy or clay soil, the level of groundwater passage in this case is not taken into account,
With a depth of underground premises of more than 1-1.5 meters in conditions of loamy or clayey soil,
If the place where the building is located is a zone of capillary moisture.
Based on the foregoing, it can be concluded that drainage is necessary when groundwater is located in critical proximity to the building, or passes high enough, giving the impression of a swampy area with no vegetation. There is no need to equip such a system when the soil is dry, and even during the rainy season the groundwater level does not rise to critical levels.
The main functions of the drainage system include:
If the right choice of the type of drainage is made, and the design is made in compliance with the project, then the pipes and wells included in the drainage system will significantly reduce the likelihood of cracks and cracks in the foundation, improving its strength characteristics.
Types of drainage
Depending on the installation depth of the drainage system, wall drainage of the foundation is distinguished:
Each of these types of drainage can be both an annular type and a reservoir type.
The ring type scheme is a closed loop encircling the building along the perimeter. With a deep laying system, such a structure can also be laid in a radial way over the entire plane of the structure.
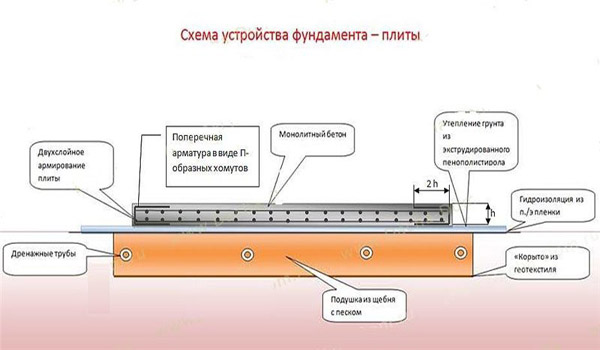
It is most expedient to build reservoir drainage in the case of the Foundation of the building of the "Swedish plate" type. It is laid at a level lower than the plane of the foundation. The peculiarity of the technology of its laying is that drainage pipes are laid on a sand and gravel cushion, on top of which they are covered with a foundation slab.
Work technology
Do-it-yourself foundation drainage is quite simple, for this you need to follow certain rules for its construction, depending on the type of foundation of the building.
Columnar (pile) foundation
The drainage of the pile foundation is done in this way:
- A 20 cm layer of sand, crushed stone is laid in a ditch dug along the perimeter of the building, and a drainage pipe is placed on top,
- A layer of crushed stone of 30 cm is again poured from above, and geotextiles are laid,
- Everything is covered with earth.
Rules for the organization of the drainage system
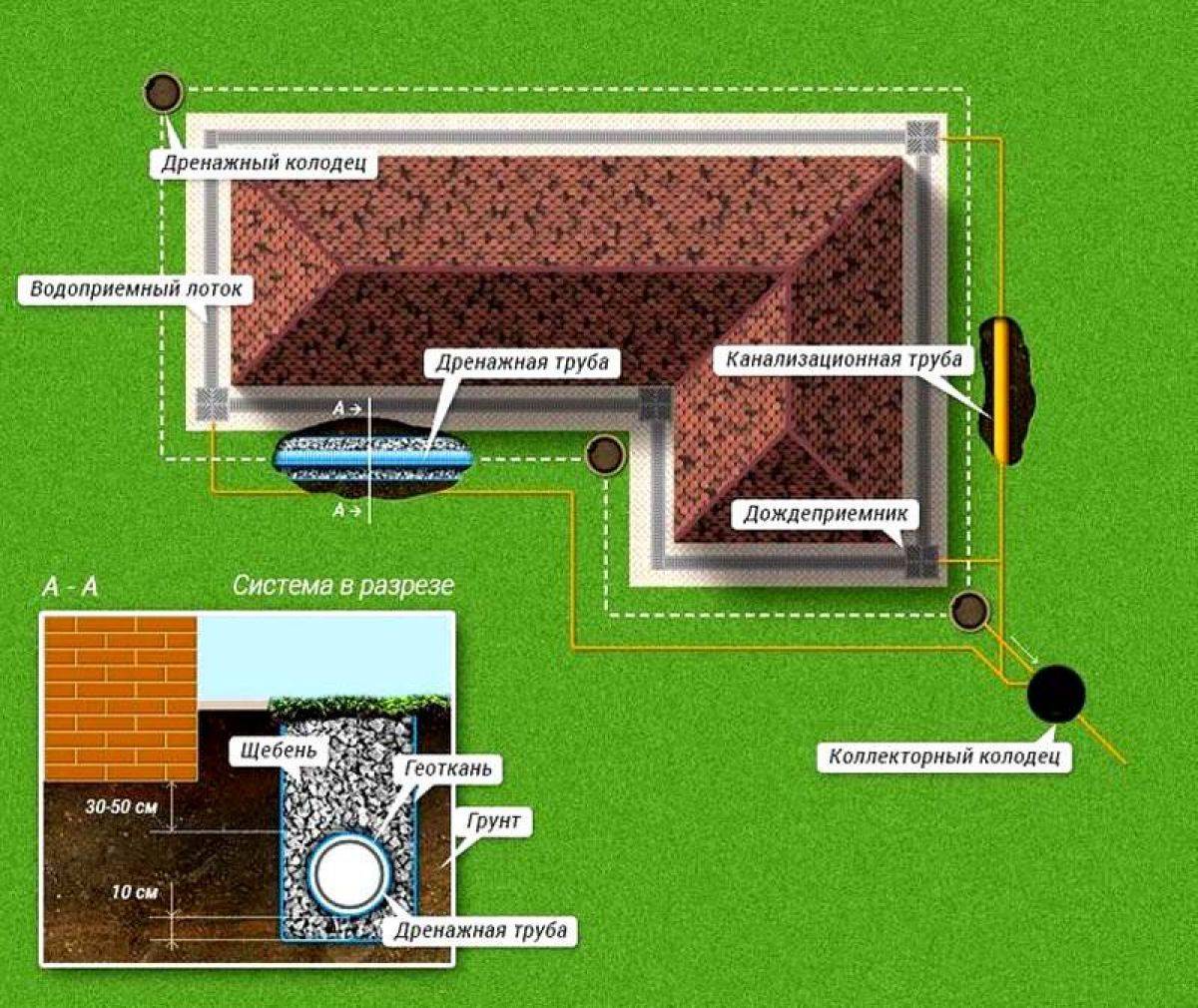
After completing all the work, it is necessary to make wells into which excess water will flow. There are some rules for installing them:
Installation of the drainage system is done at a distance of 1.5 - 3 meters from the foundation. The slope should be towards the main receiving well, its beginning should be from the far corner well.
To make your foundation protected from moisture and precipitation, groundwater, you should use the most suitable drainage system, choosing its type depending on the base and soil characteristics.
High-quality drainage, made according to the rules, can reliably protect the house from flooding, prevent the formation of excess moisture, mold and mildew on the walls of the basement or basement, and also extend the life of the entire house.
Varieties and arrangement of drainage systems
To solve the problem of excessive soil moisture on the site, two types of drainage systems can be used - surface and deep. The decision which one to use to drain your site directly depends on the reasons that lead to the flooding of the territory.
Surface (open) drain for collecting rainfall
Surface-type drainage is a system of storm water inlets designed to collect and remove rain and melt water outside the site, preventing it from soaking into the ground. Such a drainage system works excellently on clay soils and can complement traditional storm sewers. Water is drained into filtration wells or outside the site. In addition, the lion's share of precipitation simply evaporates.

Point drainage is very often combined with a linear drainage system.
Depending on the design of the drain surface drainage is divided into two types:
- point,
- linear.
When arranging point drainage, wastewater is collected using storm dampers, drains, storm water inlets and ladders. Their installation sites are door wells, roof gutter drain points, areas under water taps and other areas that need local water collection. Point collectors are connected to underground pipes, through which effluent enters the storm sewer collector.

The trays of the linear drainage system are closed with gratings that prevent them from clogging.
Linear drainage can be near-wall or remote from structures. It is a system of grated trays for collecting precipitation that did not fall into the point storm water inlets. This method of drying is rational to use in such cases:
- if there is a danger of washing off the upper, fertile soil layer. Most often, such a nuisance occurs in areas whose slope relative to the horizon is more than 3 degrees;
- when the site is located in a lowland.Because of this, water flowing during rain and snowmelt poses a threat to buildings and green spaces;
- to remove sediment from sidewalks and paths. In this case, pedestrian zones are arranged on a slight elevation, with a slope towards the drainage channel.
Linear also includes road drainage, which is made in the form of a ditch parallel to the roadbed for the movement of cars.
deep drainage
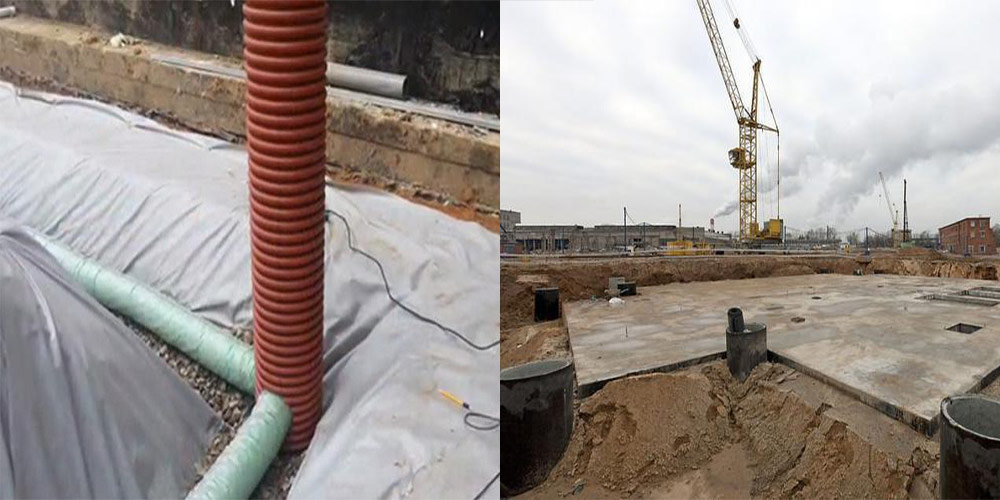
Arrangement of a deep drainage system is necessary where groundwater approaches the surface of the site closer than 2.5 meters. During its construction, a large amount of earthwork is required, therefore it is best to construct such drainage at the same time as digging foundation pits for the foundation of the house and outbuildings.

Prefabricated Drainage Pipes and Recommended Ground Types
For the construction of deep drainage, perforated pipes (drains) are used, which are laid in the soil layer at an angle. The presence of holes allows drains to collect excess moisture and transport it to a storage collector, filtration well or drainage tunnel.
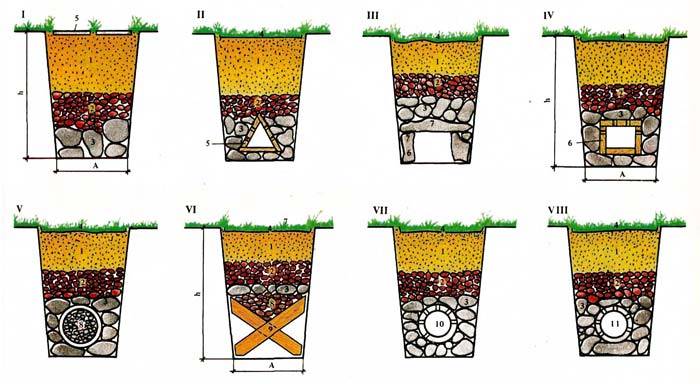
Design features of deep drainage systems
Another common type of deep drainage is a reservoir or backfill system. It is made in the form of an underground channel, half filled with a filter pad made of crushed stone or crushed brick. To prevent the absorption of the collected moisture, the bottom of the formation drains is sealed with a layer of clay, on top of which a rolled waterproofing is laid.
Drainage system: features
Definition
The word "drainage" comes from the word "drano", which means "pipe".Drainage system is an engineering and technical design, which is intended for the elimination of surface, atmospheric, ground water. It implies the presence of pipes and manholes connected to each other. Drainage is located around the perimeter of the territory. The task of the system is to protect the site from excessive moisture. How it works? Look: the water accumulated in the soil enters the pipes, through them - into the manholes, and from them - into the ditch.
Purpose
The main task of drainage is to protect the object from the destructive action of water. Drying reduces the risk of:
- structural collapse;
- flooding of the site and basement;
- swamping of the territory;
- the occurrence of fungus and mold in the structure.
That is, the service life, comfort, aesthetics and safety of the object depend on the drainage.
You cannot do without a drainage system if:
- groundwater is close to the basis of the object;
- the house is located on clay soil;
- there is a very deep basement - below the groundwater level;
- the design is placed in the zone of capillary moistening;
- the adjacent area has a slight slope;
- the area is characterized by heavy rainfall;
- the territory is swampy and there is no vegetation on it;
- nearby are reservoirs that tend to overflow;
- the calculation of the water supply and drainage was performed incorrectly.
“If the house or any other structure is located on a dry site, and the water level does not reach a critical level during the rainy and flood season, the drainage system can be abandoned,” experts say.
But many people do not agree with this opinion.Why? Well, at least, because the climate is changing due to global warming - this is no secret to anyone, and, alas, no one knows exactly what it will be, for example, in 20 years.
Therefore, it is better to play it safe and immediately make a drainage system around the house. “What’s stopping her from doing it later?” - you ask. Then, as you know, soup with a cat. What I mean? If some visionary had told our ancestors that in the future people would rent housing, since the cost of building a house would become fabulous, they would roll with laughter. Maybe in 20 years it will not be possible to build drainage from high quality materials. However, this is a personal matter for everyone. My job is to warn.
Components of a drying system
 Drainage pipes in geotextile
Drainage pipes in geotextile
The drainage structure consists of:
- pipes made of polymer and composite materials that have filtering properties;
- wells located in the places of turns of drains, that is, pipes;
- drainage pumps, which are intended for pumping water, which is why they are mounted directly in the manholes (as an option).
Purpose
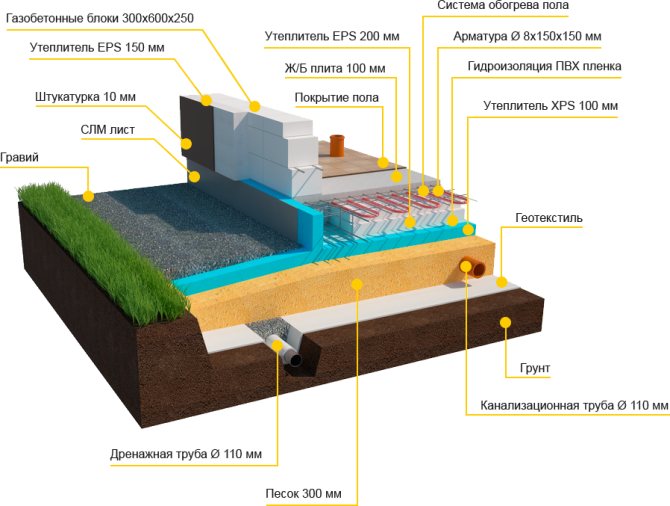
Drainage around the house is designed to collect excess moisture from the surface of the site and the soil, as well as to divert it outside the territory. The drainage system of the foundation is recommended to be made in the following cases:
- groundwater comes out close to the surface;
- the presence of nearby water bodies that contribute to waterlogging of the site;
- the soil is composed of loam, capable of absorbing a large amount of moisture;
- abundant rainfall.
Water can quickly destroy the foundation of any building. Even reinforced concrete cannot withstand its harmful effects.Negative processes are activated in the cold season, when moisture freezes in the pores and cracks of the base of the house and breaks the building material from the inside.
In addition, high humidity in the basement contributes to the appearance of mold and fungus on the elements of the building, corrosion of metal fittings. Such consequences significantly reduce the life of the foundation, and hence the entire building as a whole. To prevent this from happening, it is necessary to protect the building with a drainage system.
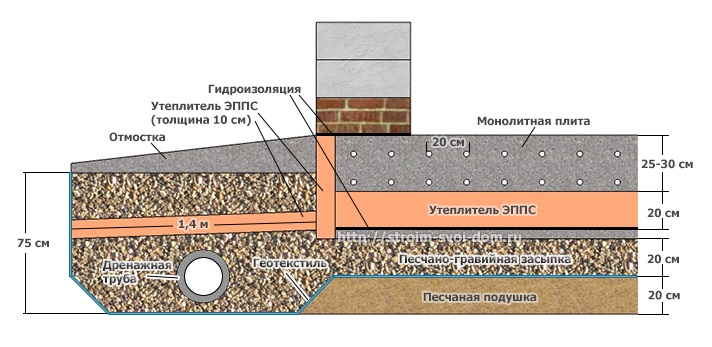
Calculation of system and materials
Proper drainage of the foundation begins with the calculations of the drainage system and materials.
- The depth of laying the pipe in the trenches should be more (deeper) than the value of laying the foundation cushion by 0.3 ... 0.5 meters. This reserve is sufficient to remove excess ground fluid from the supporting structure.
- The slope of the pipeline must be at least 2 cm per 1 pm of drainage for the natural removal of water from the structures to the destination.
To organize drainage on the perimeter, you need to find the highest and lowest point.
- In the high place there is a well for collecting water;
- A receiving well is installed in the low one, from which it is diverted to the collector well for further transportation.
To count the amount of materials, follow a few rules:
- Draw a diagram of the house with the designation of the sides. On the plan, apply the proposed drainage water supply line, taking into account the distance from the wall (up to 0.5 m for a wall outlet, 1.5 ... 3.0 m for an annular outlet).
- For each meter, add 2 cm per slope. If the length of the section is 10 meters, we get 20 cm of slope from the top to the bottom.
- Mark the position of the manholes.They should be located in the corners of the house or at every second turn, but at a distance in a straight line no more than 40 m from each other.
- According to the data obtained, calculate the required number of pipes and wells.
- For turns, provide couplings, for pipe joints - separate special components.
What is drainage for?
Drainage of the site adjacent to the foundation will help eliminate or reduce the negative impact of groundwater, floods, and seasonal precipitation.
As a result of frost heaving in winter, soil movements occur and parts of the foundation are pushed to the surface. This is facilitated by the freezing of the top layer of the earth saturated with moisture. Timely removal of moisture with the help of a drainage system eliminates the main reason - excessive moisture in the soil adjacent to the structure.
The soil is saturated with water in rainy autumn and when snow melts, even at low GWL. The highest quality foundation waterproofing does not 100% protect the structure from moisture. The walls of basements and basements are covered with stains of fungus and mold. In winter frosts, the moisture that has turned into ice increases in volume, breaking the pores of concrete. Cracks appear and propagate with each freeze-thaw cycle.
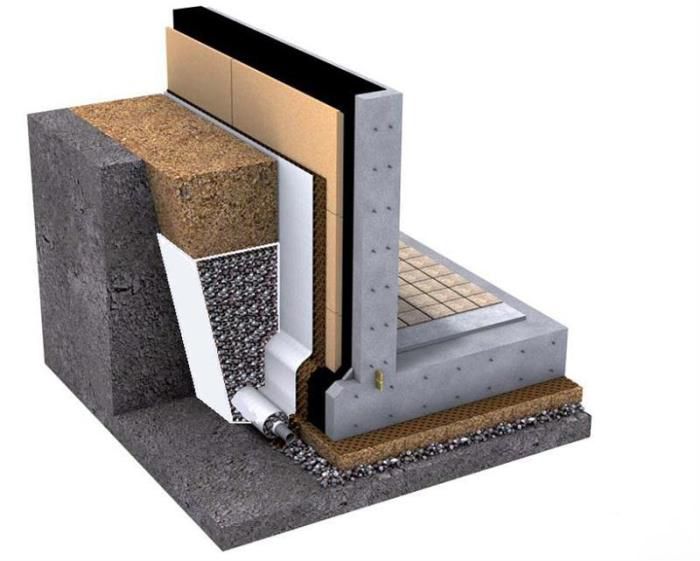
Fundamental drainage scheme
Lack of drainage negatively affects the bearing capacity of soils. Prolonged rains and flood waters erode dense layers of soil, making them loose and unstable. This leads to deformations of the foundation, threatens to destroy the entire house.
Waterlogging of clayey, loamy, peaty and silty soils, sapropels is especially dangerous. On such soils, at any groundwater level, it is recommended to arrange drainage around the foundation without fail.This will help to avoid dampness of the basement walls, freezing of structures, frost heaving, and extend the life of the base.
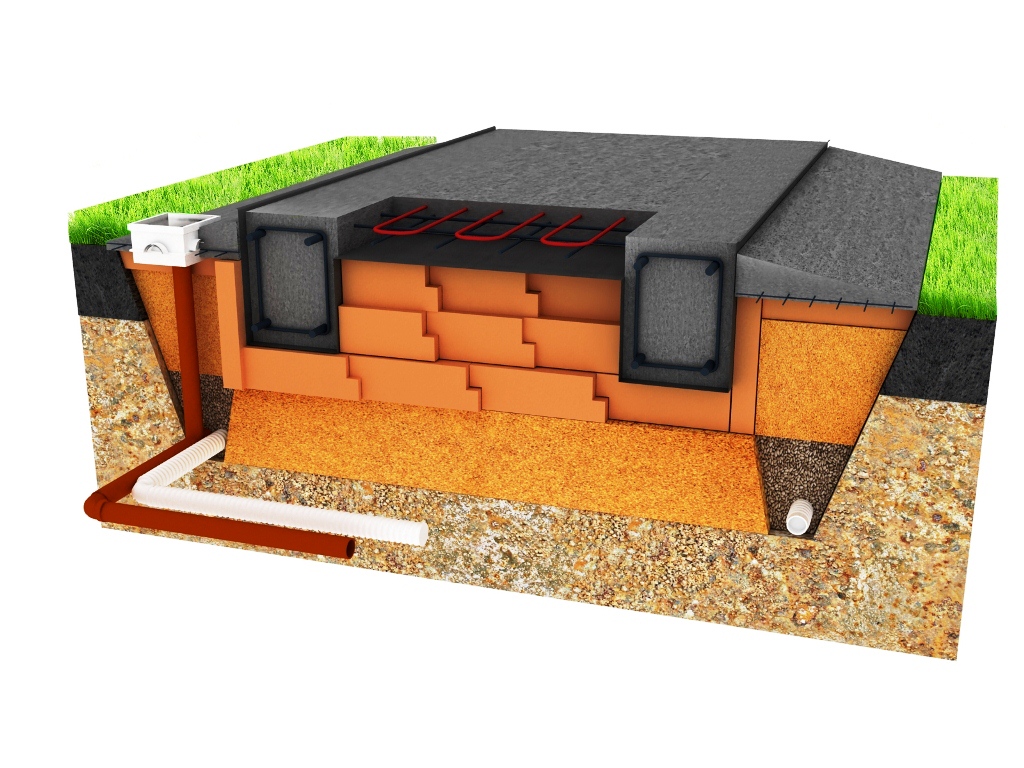
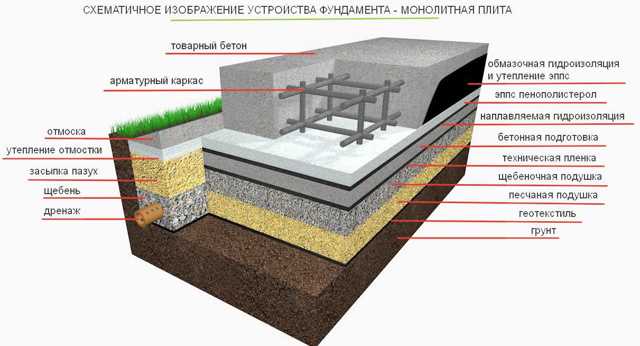
The main advantages of a monolithic foundation:
- excellent ability to withstand horizontal and vertical loads;
- high resistance to moisture;
- reliability, strength and rigidity, adaptability to various types of soil;
- the ability to withstand any movement of the soil, earthquakes, increased loads;
- durability;
- Internally, the location of the walls in the building can be anything. First you can build a foundation, then do the layout of the room;
- lack of rodents and insects;
- there is no need to install an expensive floor insulation and waterproofing system.
For the construction of the foundation, many materials are needed - sand, steel reinforcement, cement, additives, crushed stone. Such a composition guarantees strength, accelerates the hardening of concrete.
Given the design features of this foundation and the complexity of its arrangement, only qualified specialists with extensive experience should be used for its implementation. In addition, special construction equipment is required.