- Do-it-yourself open tank
- Water/Water Glycol Volume Expansion Coefficient vs. Temperature
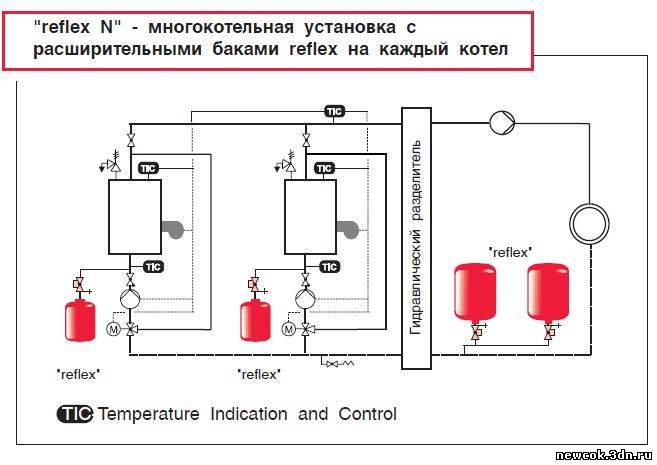
- Principle of operation and scope
- Expansion tank of open type for heating systems
- Operating principle
- Design
- Volume
- Appearance
- Volume calculation
- Where to put the expansion tank in a closed heating system?
- Hydraulic tank connection diagrams
- Where is the expansion tank installed?
- About additional containers
- Tips
- Where is the expansion tank installed?
- Pressure in a closed heating system
- Complete set and principle of operation of the system
Do-it-yourself open tank
open tank
Another thing is the expansion tank for heating an open house. Previously, when only the opening of the system was assembled in private homes, there was even no question of buying a tank. As a rule, an expansion tank in the heating system, the scheme of which consists of five main elements, was made right at the installation site. It is not known whether it was possible, in general, to buy it at that time. Today it is easier, as you can do it in a specialized store. Now in the predominant majority of housing is heated by sealed systems, although there are still many houses where there are opening circuits.And as you know, tanks tend to rot and it may be necessary to replace it.
A store-bought heating expansion tank device may not meet the requirements of your circuit. There is a possibility that it won't fit. You may have to make it yourself. For this you will need:
- tape measure, pencil;
- Bulgarian;
- welding machine and skills to work with it.
Remember safety, wear gloves and work with welding only in a special mask. Having everything you need, you can do everything in a couple of hours. Let's start with what metal to choose. Since the first tank is rotten, then you need to make sure that this does not happen to the second. Therefore it is better to use stainless steel. It is not necessary to take a thick one, but also too thin. Such metal is more expensive than usual. In principle, you can do with what is.
Now let's take a step-by-step look at how to make a tank with your own hands:
action first.
Metal sheet marking. Already at this stage, you should know the dimensions, since the volume of the tank also depends on them. A heating system without an expansion tank of the required size will not work correctly. Measure the old one or count it yourself, the main thing is that it has enough space for the expansion of water;
Cutting blanks. The design of the heating expansion tank consists of five rectangles. This is if it is without a lid. If you want to make a roof, then cut out another piece and divide it in a convenient proportion. One part will be welded to the body, and the second will be able to open. To do this, it must be welded onto the curtains to the second, immovable, part;
third act.
Welding blanks in one design.Make a hole in the bottom and weld a pipe there through which the coolant from the system will enter. The branch pipe must be connected to the entire circuit;
action four.
Expansion tank insulation. Not always, but often enough, the tank is in the attic, since the peak point is located there. The attic is an unheated room, respectively, it is cold there in winter. The water in the tank may freeze. To prevent this from happening, cover it with basalt wool, or some other heat-resistant insulation.
As you can see, there is nothing difficult in making a tank with your own hands. The simplest design is described above. At the same time, in addition to the branch pipe through which the tank is connected to the heating system, the following holes can be additionally provided in the scheme of the expansion tank for heating:
- through which the system is fed;
- through which the excess coolant is drained into the sewer.
Scheme of a tank with make-up and drain
If you decide to make a tank with your own hands with a drain pipe, then place it so that it is above the maximum fill line of the tank. The withdrawal of water through the drain is called an emergency release, and the main task of this pipe is to prevent the coolant from overflowing through the top. Make-up can be inserted anywhere:
- so that the water is above the level of the nozzle;
- so that the water is below the level of the nozzle.
Each of the methods is correct, the only difference is that the incoming water from the pipe, which is above the water level, will murmur. This is more good than bad. Since make-up is carried out if there is not enough coolant in the circuit. Why is it missing there?
- evaporation;
- emergency release;
- depressurization.
If you hear that water from the water supply enters the expansion tank, then you already understand that there is a possibility of some kind of malfunction in the circuit.
As a result, to the question: “Do I need an expansion tank in the heating system?” - you can definitely answer that it is necessary and mandatory. It should also be noted that different tanks are suitable for each circuit, so the correct selection and correct setting of the expansion tank in the heating system is extremely important.
Water/Water Glycol Volume Expansion Coefficient vs. Temperature
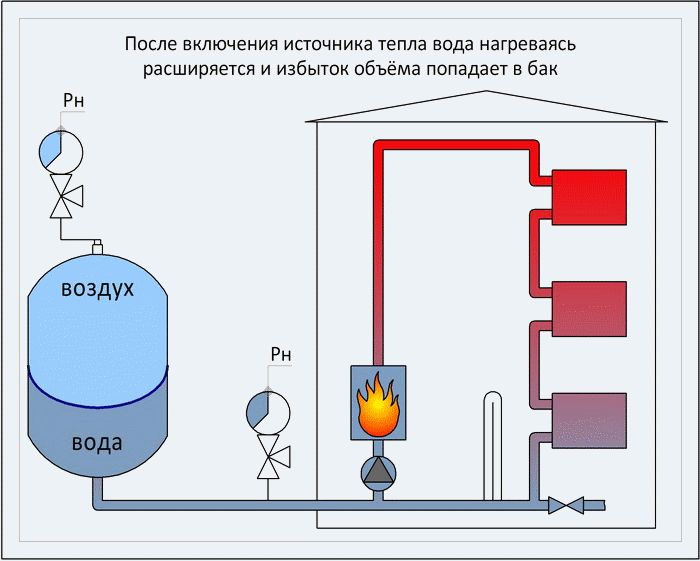
As is known from the laws of physics, all liquids expand when heated (as, indeed, any body). This fact must be taken into account when calculating the volume of the expansion tank.
Water increases in volume when heated to 95C by 4%. This statement is accurate enough, so it can be used in calculations without fear.
If a water-glycol mixture is used as a heat carrier, the picture changes somewhat, depending on the content of ethylene glycol.

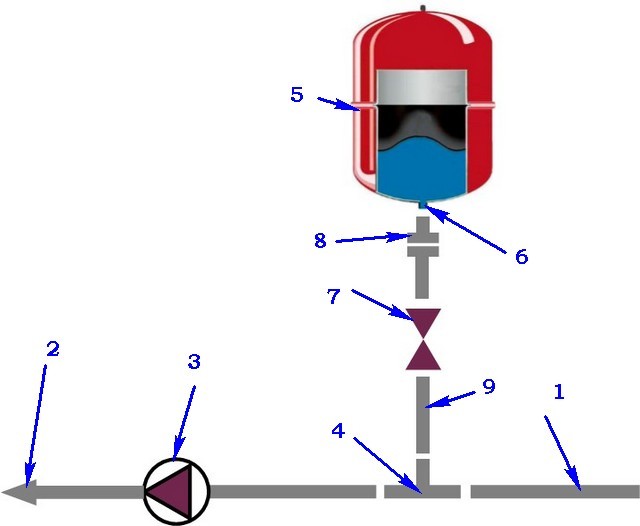
Expansion tank in the heating system
In this case, the expansion coefficient of the working fluid is determined as follows:
- 4% x 1.1 \u003d 4.4% - with an ethylene glycol content of 10% of the total volume of the coolant;
- 4% x 1.2 = 4.8% - if the volume of ethylene glycol in the mixture is 20%, etc.
The above values will vary depending on the temperature to which the coolant is heated. For example, at 80 degrees, the expansion coefficient of water will be 0.0290. If 10 percent of its volume is replaced with ethylene glycol, the coefficient will be equal to 0.0320. A mixture of glycol in half with water (50%) is characterized by an expansion coefficient of 0.0436.
Principle of operation and scope
A compensator is used in all networks - hermetic, open.
The principle of operation is simple:
- when heated, the volume of water is increased;
- excess volume increases pressure;
- the pipeline of the circuit is designed with a certain throughput, excess pressure can cause water hammer, break the line;
- the tank accumulates excess water, preventing an increase in pressure;
- after the liquid cools, the volume is reduced, the pressure drops;
- the compensator restores the normal level of pressure, giving the accumulated volume of water.
This is how all tanks work, regardless of their purpose and design.
The container has two functions:
- Hydraulic accumulator. Excess hot water can be used to distribute hot water without turning on the pump due to the pressure stored in the tank.
- compensator. With sudden on / off water, the damper reduces the pressure on the system nodes.
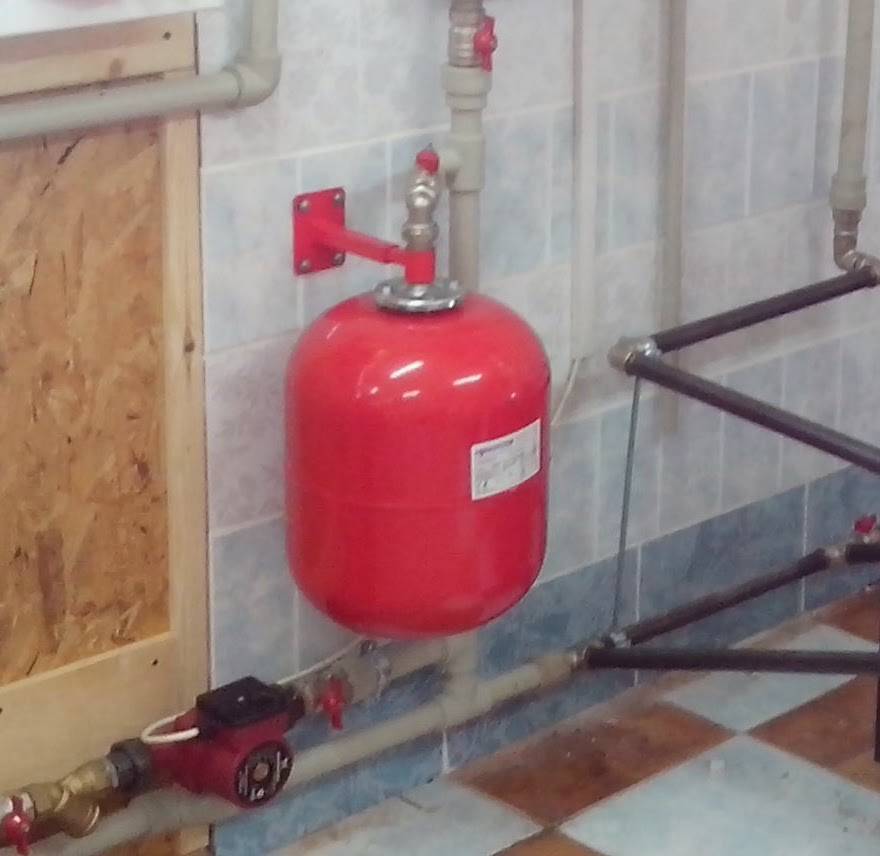
Expansion tank of open type for heating systems
Large heating structures use expensive closed tanks.
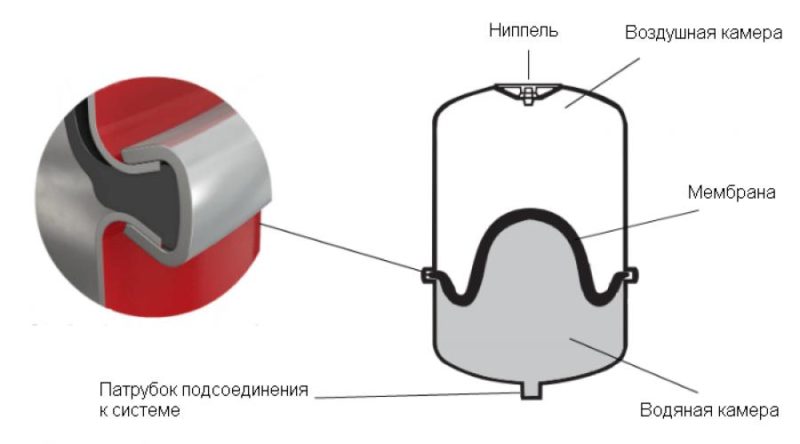
They are characterized by the tightness of the body with an internal rubber partition (membrane) due to which the pressure is adjusted when the coolant expands.
For the full operation of home systems, an open-type expansion tank is a suitable alternative that does not require special knowledge or professional training for the operation and further repair of equipment.
An open tank performs some functions for the smooth operation of the heating mechanism:
- “takes” excess heated coolant and “returns” the cooled liquid back to the system to adjust the pressure;
- removes air, which, due to the slope of the pipes with a couple of degrees, rises to the expansion open tank, located at the top of the heating system;
- The open design feature allows the vaporized volume of liquid to be added directly through the top cap of the reservoir.
Operating principle
The workflow is divided into four simple steps:
- fullness of the tank by two-thirds in normal condition;
- an increase in the incoming liquid into the tank and an increase in the filling level when the coolant is heated;
- liquid leaving the tank when the temperature drops;
- stabilization of the coolant level in the tank to its original position.
Design
The shape of the expansion tank exists in three versions: cylindrical, round or rectangular. An inspection cover is located on the top of the case.
Photo 1. The device of an expansion tank of an open type for heating systems. Components are listed.
The body itself is made of sheet steel, but with a home-made version, other materials are possible, for example, plastic or stainless steel.
Reference. The tank is covered with an anti-corrosion layer to prevent premature destruction (first of all, this applies to iron containers).
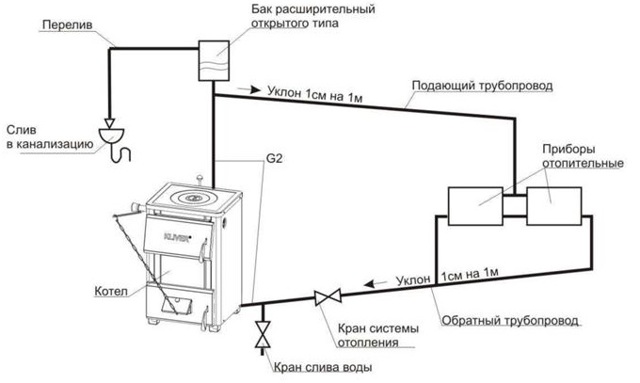
The open tank system includes several different nozzles:
- to connect an expansion pipe through which water fills the tank;
- at the junction of the overflow, for pouring out excess;
- when connecting a circulation pipe through which the coolant enters the heating system;
- for connecting a control pipe designed to eliminate air and adjust the fullness of the pipes;
- spare, necessary during repairs to discharge the coolant (water).
Volume
Correctly calculated volume of the tank affects the duration of operation of the joint system and the smooth functioning of individual elements.
A small tank will lead to a breakdown of the safety valve due to frequent operation, and a too large one will require additional finances when buying and heating an excess volume of water.
The presence of free space will also be an influential factor.
Appearance
An open tank is a metal tank in which the upper part is simply closed with a lid, with an additional hole for adding water. The body of the tank is round or rectangular. The latter option is more practical and reliable during installation and fastening, but the round one has the advantage of sealed seamless walls.
Important! A rectangular tank requires additional reinforcement of the walls with an impressive volume of water (home-made version). This makes the entire expansion mechanism heavier, which must be lifted to the highest point of the heating system, for example, to the attic.
Advantages:
- Standard form. In most cases, it is a rectangle that you can install and connect to the general mechanism yourself.
- Simple design without excessive control elements, which makes it easy to control the smooth operation of the tank.
- The minimum number of connecting elements, which gives the body strength and reliability in the process.
- Average market price, thanks to the above facts.
Flaws:
- Unattractive appearance, without the ability to hide thick-walled bulky pipes behind decorative panels.
- Low efficiency.
- The use of water as a heat carrier. With other antifreezes, evaporation occurs faster.
- The tank is not sealed.
- The need to constantly add water (once a week or once a month) due to evaporation, which, in turn, affects airing and the normal functioning of the heating system.
- The presence of air bubbles leads to internal corrosion of the system elements and a decrease in the service life and heat transfer, as well as the appearance of noise.
Volume calculation
The volume of the tank in a closed system should be 10% of the total volume of the heat conductor. That is, it is necessary to calculate the total volume of liquid in pipes, batteries and in the whole system. A tenth of this figure should be in the expansion tank. But such figures can only be used when the coolant is water. If antifreeze is used, the volume of the tank is increased by 50%.
 Calculating the required volume of the tank is not difficult, but when connecting equipment, it is better to give preference to large sizes.
Calculating the required volume of the tank is not difficult, but when connecting equipment, it is better to give preference to large sizes.
To be more precise, the calculation example described below:
- the total volume of the system is 28 liters;
- tank size - 2.8 liters;
- antifreeze tank size - 4.2 liters.
In any case, when buying and connecting such a container, it is better to give preference to large sizes. The supply of space will only positively affect the operation of the structure. If there is no experience in installation and calculation, then you can use online calculators, they are available on specialized sites.
Where to put the expansion tank in a closed heating system?
By the way, in private houses there are no open and closed systems, there are gravitational and pressure (pumping) systems. In the first, water moves due to the difference in specific gravity (natural circulation), and in the second, it is forcibly induced by the pump.
For reference. An open system works simultaneously for heating and hot water, it is used only in large centralized networks. That is why all individual systems are closed.
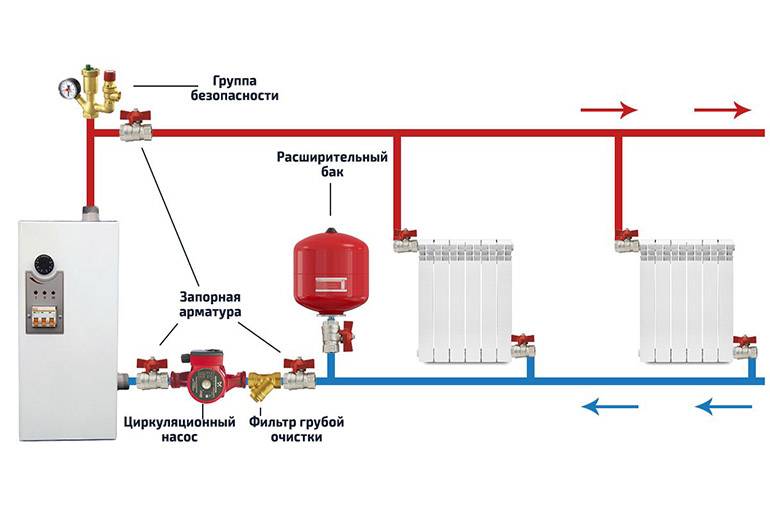
To properly install the expansion tank in the heating system, the following requirements must be met:
- the location of the tank is the furnace room, not far from the boiler;
- the device must be located in a place where it will be freely accessible for configuration and maintenance;
- in the case of mounting the tank to the wall on the bracket, it is recommended to maintain a height convenient for access to its air valve and shutoff valves;
- the supply pipe together with the taps must not load the expansion tank with its weight. That is, the eyeliner should be attached to the wall separately;
- the connection to the floor expansion tank for heating is not allowed to be laid along the floor across the passage;
- do not put the container close to the wall, leave enough clearance for inspection.
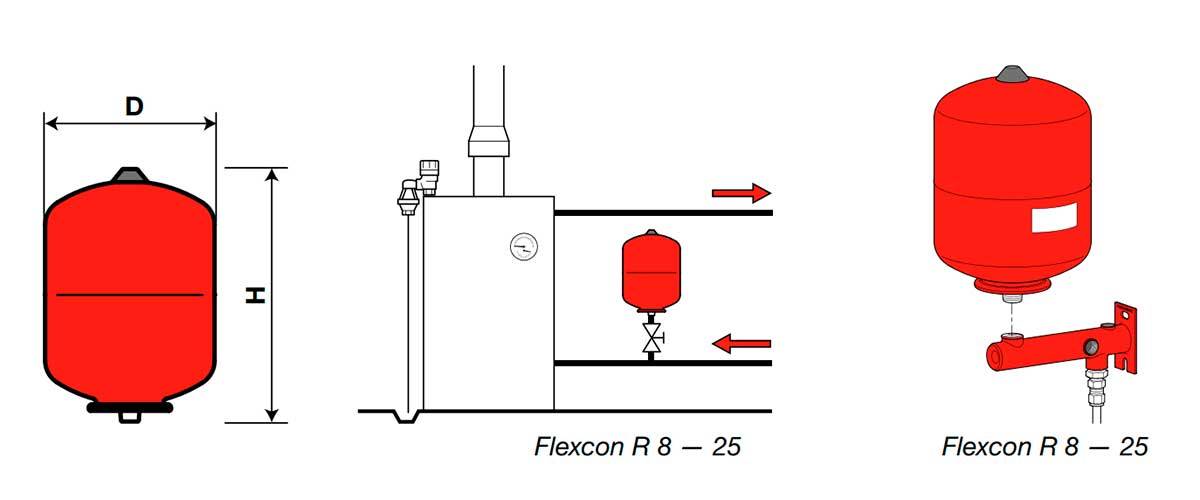
Tanks of small capacity may be suspended from the wall, provided that its bearing capacity is sufficient. As for the orientation of the tank in space, there is a lot of conflicting advice. Some recommend an installation method in which the pipe is connected to the tank from above, and the air chamber, respectively, is located below. Rationale - it is easier to remove air from under the membrane when filling, water will force it out.
In fact, in its original state, the rubber “pear”, pressed on one side by air pressure, leaves no room for it on the other side, as shown in the photo above. Installation experts just advise installing the expansion tank with the connecting pipe down, and only in this way. In some models, the fitting is initially located on the side wall, in its lower part, and it is impossible to put the vessel in a different way (see photo below).
It's easy to explain. The device will function in any position, albeit lying on its side. Another thing is that sooner or later cracks will appear in the membrane. When the membrane expansion tank is installed with the air chamber up and the pipe down, the air will penetrate through the cracks into the coolant very slowly and the tank will still last for some time. If he stands upside down, then the air, being lighter than water, will quickly flow into the chamber with the coolant and the tank will have to be urgently changed.
Note. Some manufacturers offer to install the expansion tank of the heating system, just hanging it "head" down on the bracket. This is not prohibited, everything will work, only in the event of a membrane malfunction, the unit will fail immediately.
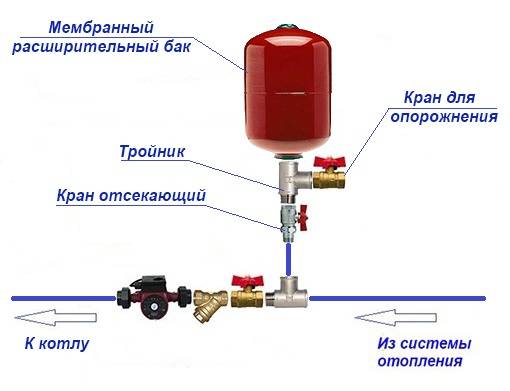
Hydraulic tank connection diagrams
For a hot water supply system, the installation of an expansion tank is carried out in the section of the circulation line, the suction line of the pump, closer to the water heater.
The tank is equipped with:
- pressure gauge, safety valve, air vent - safety group;
- shut-off valve with a device that prevents accidental shutdown.
In the plumbing system, where there is water heating equipment, the device takes on the functions of an expansion tank.
Scheme of installation in the HW system: 1 - hydraulic tank; 2 - safety valve; 3 - pumping equipment; 4 – filtration element; 5 - check valve; 6 - shut-off valve
In the cold water system, the main rule when installing a hydraulic accumulator is installation at the beginning of the piping, closer to the pump.
The connection diagram must include:
- check and shutoff valve;
- security group.
Connection schemes can be very different. A connected hydraulic tank normalizes the operation of the equipment, reducing the number of pump starts per unit of time and thereby extending its service life.
Installation scheme in the cold water system with a well: 1 - tank; 2 - check valve; 3 - shut-off valve; 4 - relay for pressure control; 5 - control device for pumping equipment; 6 - security group
In a scheme with a booster pumping station, one of the pumps is constantly running. Such a system is installed for houses or buildings with high water consumption. The hydraulic tank here serves to neutralize pressure surges, and a container of the largest possible volume is installed to accumulate water.
Where is the expansion tank installed?
The installation location of the tank depends on the type of heating system and the purpose of the tank itself. The question is not what the expansion tank is for, but where it should compensate for the expansion of water. That is, in the heating network of a private house there may be not one such vessel, but several. Here is a list of functions that are assigned to tanks installed in different places:
- compensation of thermal expansion of water in open-type heating systems;
- the same for closed systems;
- serve as an addition to the regular expansion tank of the gas boiler;
- perceive the increasing volume of water in the hot water supply network.
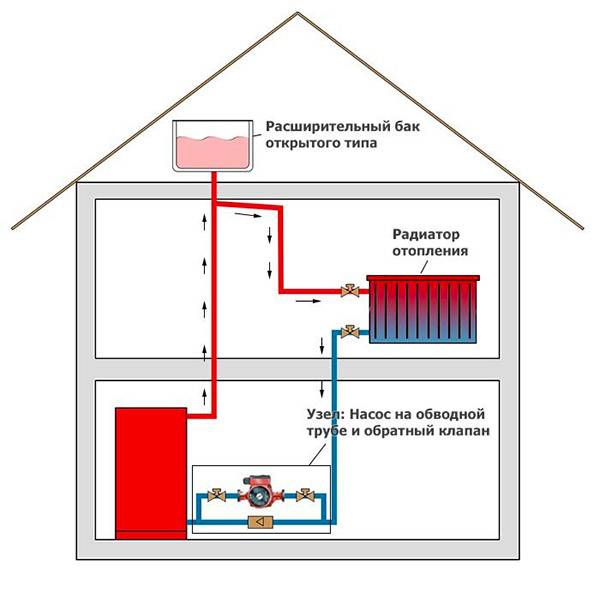
An open tank, where the coolant is in contact with atmospheric air, is the hallmark of an open heating system. In this case, the expansion tank is installed at the highest point in the heating network of a private house. Often such systems are made gravity flow with increased pipeline diameters and a large amount of coolant. The capacity of the tank should be appropriate and be about 10% of the total water volume. Where, if not in the attic, to put such an overall tank.
For reference. In old one-story houses, you can often see small expansion tanks for an open heating system installed in the kitchen next to a floor-standing gas boiler. This is also correct, the container under the ceiling is easier to control. True, it does not look too good in the interior. To put it mildly.

Alternative homemade tanks
Heating systems of a closed type are distinguished by the fact that a membrane expansion tank for water can be placed anywhere. But still, the best installation option is in the boiler room, next to the rest of the equipment. Another place where it is sometimes necessary to install a closed expansion tank for heating is the kitchen in a small house, since the heat source itself is located there.
About additional containers
Following new trends, many manufacturers complete their heat generators with built-in tanks that perceive the volume of coolant that increases when heated.These vessels cannot correspond to all existing heating schemes, sometimes their capacity is not enough. In order for the pressure of the coolant to be within the normal range during heating, an additional expansion tank for the wall-mounted boiler is installed in accordance with the calculation.
For example, you converted an open gravity system to a closed one without changing the lines. The new heating unit was selected according to the heat load. Whatever the capacity in it, it will not be enough for such an amount of water. Another example is heating with underfloor heating in all rooms of a two- or three-story house, plus a radiator network. Here, the volume of coolant will also come out impressive, a small tank will not cope with its increase and the pressure can rise greatly. That's why you need a second expansion tank for the boiler.
Note. The second tank to help the boiler is also a closed membrane tank, located in the furnace room.
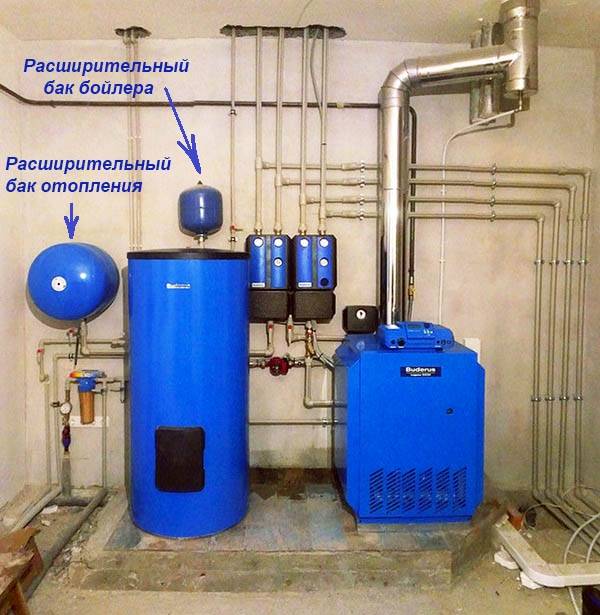

When the hot water supply at home is provided by an indirect heating boiler, the question also arises - what to do with the expanding water when heated. One option is to install a relief valve, as is done on electric water heaters. But the indirect heating boiler is much larger in size and through the valve it will lose too much hot water. Where is the best place to choose and install an expansion tank for a boiler.
For reference. In buffer tanks (heat accumulators) of some manufacturers, it is also possible to connect a compensating tank.Moreover, experts recommend putting it even on large-capacity electric boilers, which is shown in the video:
Tips

In conclusion, we note a rather important feature of the choice and adjustment of the safety valve. This element is included in the mandatory list of equipment for heating points.
The threshold value after which the valve must operate is considered to be 10% more than allowed for the weakest link in this regard. In order to be able to regulate this indicator when choosing safety valves, preference should be given to those that allow you to indicate the limit at which they operate.
Also, it is important to pay attention to the fact that there should be a forced opening mechanism. Its presence will allow periodic checking of the valve, since the spool can stick and it will not work with a significant increase in pressure.
Where is the expansion tank installed?

The choice of location for the expansion tank depends both on the type of heating circuit and on the functions of the tank itself. Position the reservoir so that it effectively compensates for the expansion of the liquid.
It is even possible to install several containers, this applies to private houses, to stabilize the network.
In addition to compensating for expansion due to temperature rise (both in closed and open heating circuits), expanders also supplement the regular expansion tanks of gas boilers and receive excess liquid in the network.
In open heating systems, where there is direct contact of the coolant with air, the tank is installed at the highest point of the heating circuit of the house. In this case, the volume of the container must be at least 10% of the liquid.Most often, such structures are gravity-flowing with a large volume of circulating fluid, so it is more convenient to place them in the attic.
If this is not possible, some mount tanks under the ceiling, not far from the floor-standing gas boiler. This is convenient, since easier access to the tank makes it possible to constantly monitor its functionality, but such a device also has a negative side, as it spoils the interior of the room.
As for closed-type systems, the place of the expansion tank does not play a role at all. Most often, tanks are installed in a boiler room, or other room where the rest of the heating elements are located. In small houses where space is limited, tanks are mounted directly in the kitchens, next to the boiler.
Pressure in a closed heating system
Three types of pumps are used in closed heating circuits. They are differentiated by the pressure of the water column:
- 4;
- 6;
- 8 meters
Accordingly, the pressure is distributed in proportions:
- 0,4.
- 0,6.
- 0.8 bar.
For a private household with an area of \u200b\u200babout two hundred square meters, a head of 4 meters is enough. If the area is three hundred square meters, then a pump of 0.6 bar will be required, and if the area is more than 500 square meters, then a pressure of 0.8 bar will be required. On all pumps there is a marking of technical indicators. The pressure is relatively low, there are also safety valves, an explosion in closed thermal circuits is impossible.
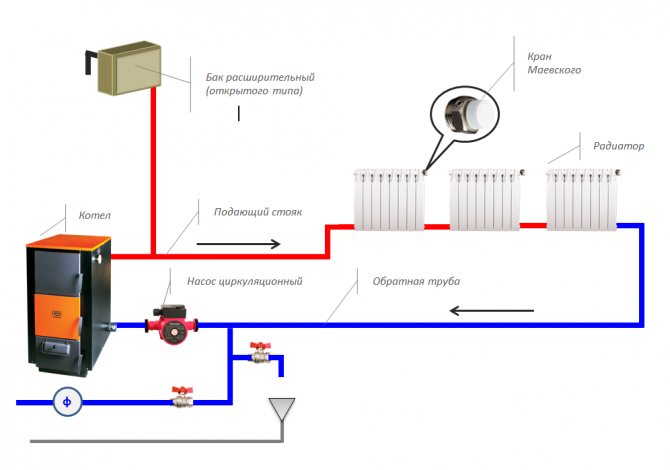
Complete set and principle of operation of the system
In a water heating system, a liquid acts as an intermediary in the transfer of thermal energy from a boiler plant to radiators. The circulation of the coolant can be carried out over long distances, providing heating for houses and premises of different sizes.This explains the widespread introduction of water heating.
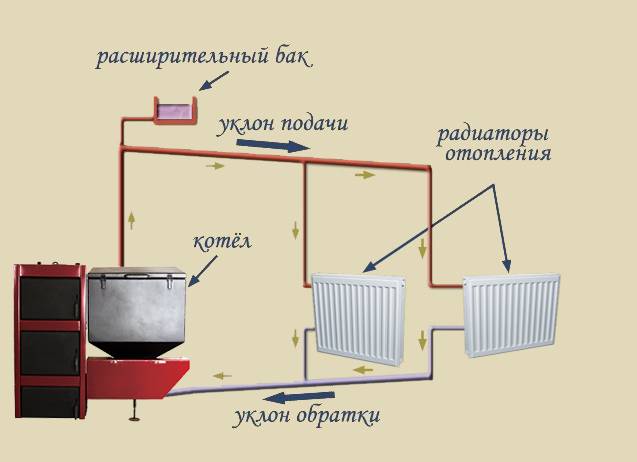
The operability of an open type heating system is possible without the use of a pump. The coolant circulation is based on the principles of thermodynamics. The movement of water through pipes occurs due to the difference in the density of hot and cold liquids, as well as due to the slope of the laid pipes.
An indispensable element of the system is an open expansion tank, into which excess heated coolant enters. Thanks to the tank, the liquid pressure is automatically stabilized. The container is installed above all system components.
The whole process of functioning of "open heat supply" is conditionally divided into two stages:
- Innings. The heated coolant moves from the boiler to the radiators.
- Return. Excess warm water enters the expansion tank, cools down and returns to the boiler.
In single-pipe systems, the function of supply and return is performed by one line, in two-pipe schemes, the supply and return pipes are independent of each other.
The density of warm water is lower than the density of cold water, so a hydrostatic head is formed in the system. Pressurized hot water moves to the radiators
The simplest and most affordable for self-assembly is considered a single-pipe system. The design of the system is elementary.
The basic equipment of one-pipe heat supply includes:
- boiler;
- radiators;
- expansion tank;
- pipes.
Some refuse to install radiators and place a pipe with a diameter of 8-10 cm around the perimeter of the house. However, experts note that the efficiency of the system and ease of use with this solution is reduced.
The scheme of a gravitational one-pipe system of an open type is non-volatile.The cost of acquiring pipes, fittings and equipment is relatively low. Can be used with different types of boilers
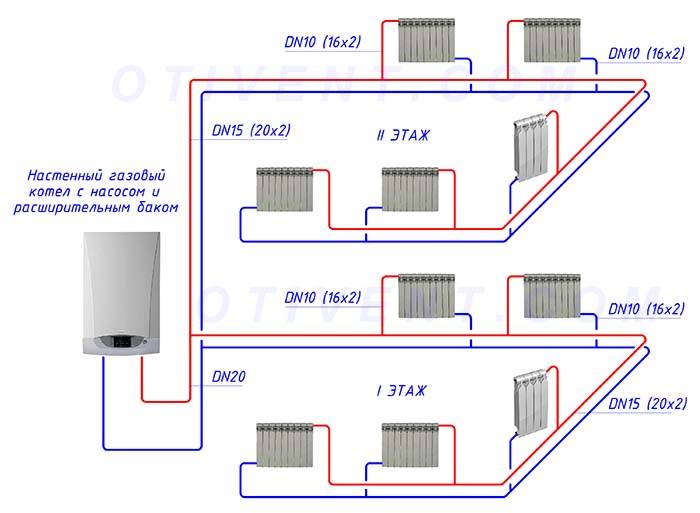
The two-pipe heating version is more complicated in the device and more expensive in execution. However, the cost and complexity of the construction is fully offset by the elimination of the standard disadvantages of single-pipe systems.
The coolant with the same temperature is supplied almost simultaneously to all devices, the cooled water is collected by the return line, and does not flow into the next battery.
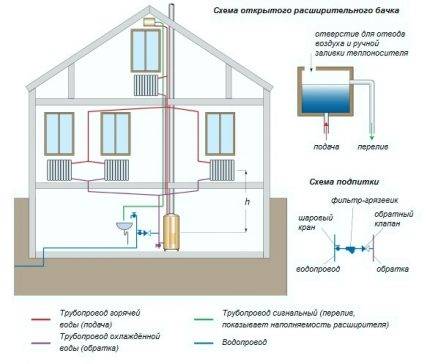 To service each device in a two-pipe heating circuit, a supply and return line are arranged, due to which the temperature of the system supplies a coolant of equal temperature to all points, and the cooled water is collected and sent to the boiler by a return line - independent of the supply line
To service each device in a two-pipe heating circuit, a supply and return line are arranged, due to which the temperature of the system supplies a coolant of equal temperature to all points, and the cooled water is collected and sent to the boiler by a return line - independent of the supply line