- Types of heating boilers
- Types of radiators
- Cast iron radiators
- Steel radiators
- Aluminum radiators
- Bimetal radiators
- Heating radiator piping options
- Binding with one-way connection
- Binding with diagonal connection
- Strapping with saddle connection
- One-way bottom top connection
- Other options
- Location of radiators
- Conclusion
- Heating wiring options
- How to install an aluminum battery with your own hands?
- Preparatory work
- Radiator Assembly
- Choosing a place and method of installing a radiator
- Coolant circulation methods
- Radiator connection diagrams
- Radiators with bottom connection
- Radiators with side connection
- Option number 1. Diagonal connection
- Option number 2. Unilateral
- Option number 3. Bottom or saddle connection
- Cast iron battery
- How to place batteries
Types of heating boilers
The central element of the heating system is the boiler - a heating device in which the coolant reaches the desired temperature. The scheme for connecting heating in a private house largely depends on which boiler is used in it.
By appointment, boilers are divided into double-circuit and single-circuit.The first option is equipment designed for both heating and water heating. A single-circuit boiler heats only the heat carrier for heating. According to the method of installation, they are divided into floor and wall.
Boilers also differ in the type of fuel with which the coolant is heated. There are boilers of the following types:
- gas;
- electrical;
- solid fuel;
- liquid fuel;
- combined.
For the operation of solid fuel boilers, coal, firewood, less often peat and other options for solid combustible materials are used. Diesel or used oils are used as liquid fuel for boilers of the corresponding type.

Solid fuel water boiler in a private house
Most country cottages are heated by gas boilers. In non-gasified areas, heating with electricity is often used. Solid fuel and liquid fuel boilers are completely independent of communication networks. The first option is more attractive because it requires traditional firewood and coal, rather than dangerous combustible liquids.
The most prudent homeowners install combined boilers in their homes designed to work on different types of fuel. For example, you can install an electric boiler, supplemented by a combustion chamber for solid fuels, so that in the event of a power failure, you can switch to wood heating.
Double-circuit boilers that provide housing with heat and warm water are mainly gas devices. They are versatile as they save homeowners the hassle of buying and installing a separate water heater.

Scheme of dual-circuit heating in the house
Types of radiators
On sale today there are the most diverse models in terms of materials, power and design. They are mounted by mounting on walls, installed on the floor or built into the floors. The coolant is prepared water or antifreeze, the main property of which is a large heat capacity.
Cast iron radiators
Cast iron is a sufficiently corrosion-resistant alloy, which also has a high thermal inertia. On the one hand, it causes unnecessary energy consumption and a long time for heating the material itself, but on the other hand, it contributes to a more uniform heat transfer. When the heating is turned off, cast-iron batteries warm the room for a long time.
Despite the appearance of aluminum and bimetallic radiators, cast iron radiators can often be found in residential buildings. Until now, batteries in Soviet apartments, installed 40 or more years ago, are still coping with their task.
New models of cast iron radiators are modern stylish designs that amaze with their multicolor and sophisticated design. They can make any interior interesting, but they are quite expensive.
Flaw cast iron radiators - a lot of weight. Not every wall can withstand such a load. Therefore, often heating systems with "cast iron" provide for mounting batteries to the floor or installing them on legs.
Steel radiators
They are made in the form of panel heaters from stamped steel sheets, inside of which channels for the coolant are provided. The thickness of the metal used for radiators is 1.2-2 mm. The surface of the panels can be smooth or ribbed.
Dimensions depending on the model of the steel radiator are different:
- height - 200-900 mm;
- length - 300-4000 mm;
- depth - 60-170 mm.
The power of the devices depends not only on the size, but also on the number of convection rows and radiating plate elements.
Advantages of steel radiators:
- rapid heating;
- minimum volume of coolant;
- Efficiency up to 75%;
- possibility of adjustment;
- there are no connections where leakage could occur;
- nice design;
- economic price.
Bench-shaped steel battery
Among the disadvantages:
- instability to water hammer;
- restrictions on working pressure 13 atm., on the temperature of the coolant 110 ° C;
- susceptibility to corrosion.
To prevent rapid rusting, antifreeze is poured into the system. If water is used, it should not be drained for more than 2 weeks a year.
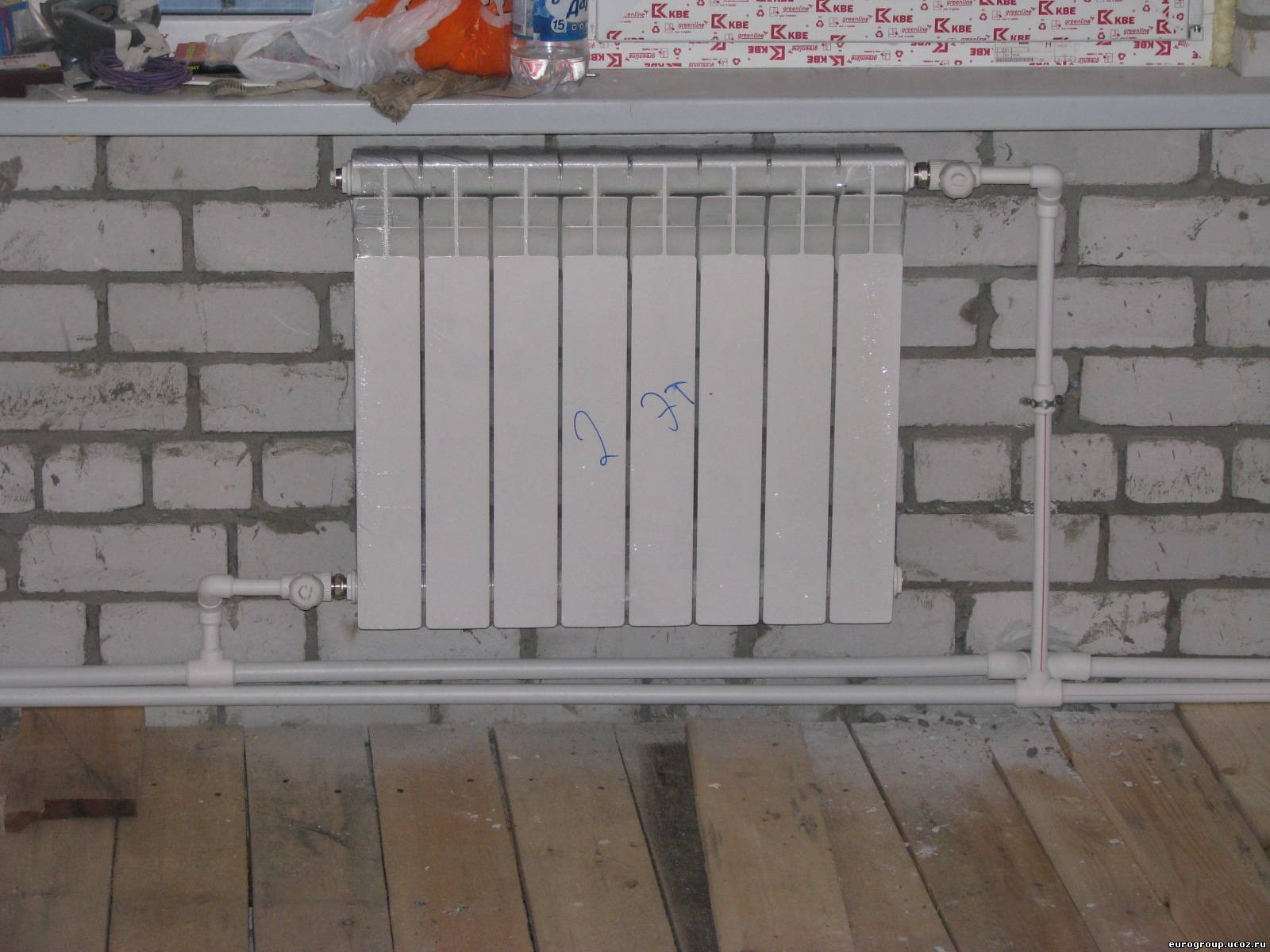
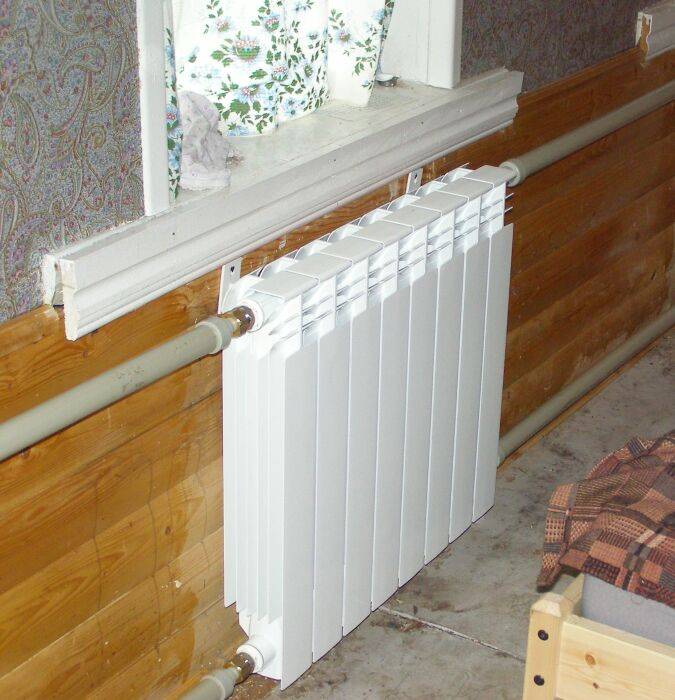
Aluminum radiators
Devices are made of aluminum alloys with other substances - copper, magnesium, silicon. Radiators consist of sections, the number of which can be reduced or increased at your discretion. Center distance in different models - 350 or 500 mm, depth - 80-100 mm. Heat transfer is ensured by transferring heat from tubes filled with coolant to radiant plates and then to the air circulating between them.
Aluminum battery as part of the design of the apartment
Advantages of aluminum radiators:
- rapid heating;
- high heat transfer;
- low weight;
- durability.
The disadvantages include:
- the possibility of corrosion as a result of stray currents or the use of untreated water;
- the accumulation of hydrogen gas in the system, which is a product of the reaction of water and aluminum.
The service life of radiators is 10-15 years and directly depends on the thickness of the metal.It is recommended to use products with a weight of one section of at least 1.3 kg, since thin walls are quickly destroyed, corrosion centers and leaks appear.
Bimetal radiators
The design of these heaters consists of a steel manifold and an aluminum shell. Externally, bimetallic radiators may look like sectional aluminum or steel. But unlike them, they react less to pressure surges in the system, do not react with the formation of explosive hydrogen.
A section of a quality instrument weighs at least 1.8 kg. This metal thickness is sufficient to withstand hydraulic loads up to 30-40 atmospheres. You should not buy lighter devices that are manufactured with violations of technology and do not guarantee long operation.
The most valuable qualities of bimetallic radiators:
- ease;
- long service life;
- high heat transfer;
- resistance to heavy loads.
Batteries made of two metals have low thermal inertia - they heat up quickly and cool down just as quickly. Their price is higher than others, but it is fully justified by strength and durability.
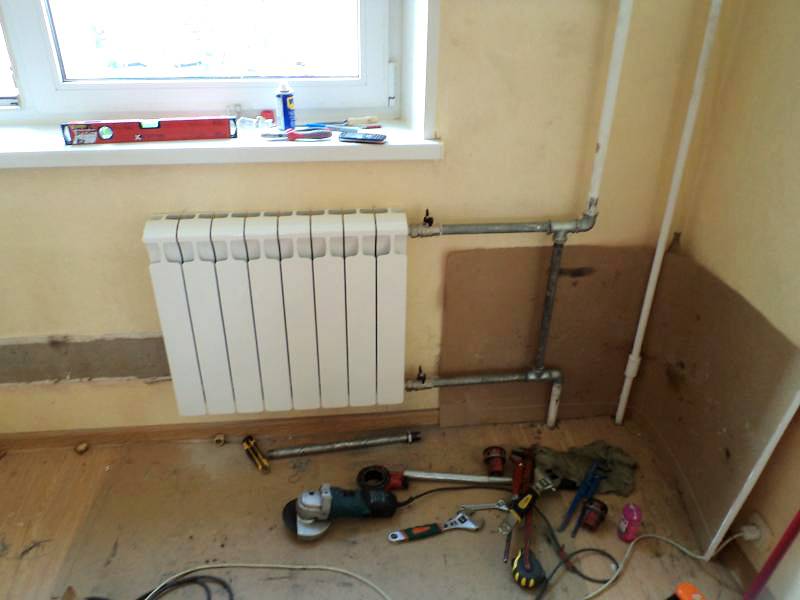
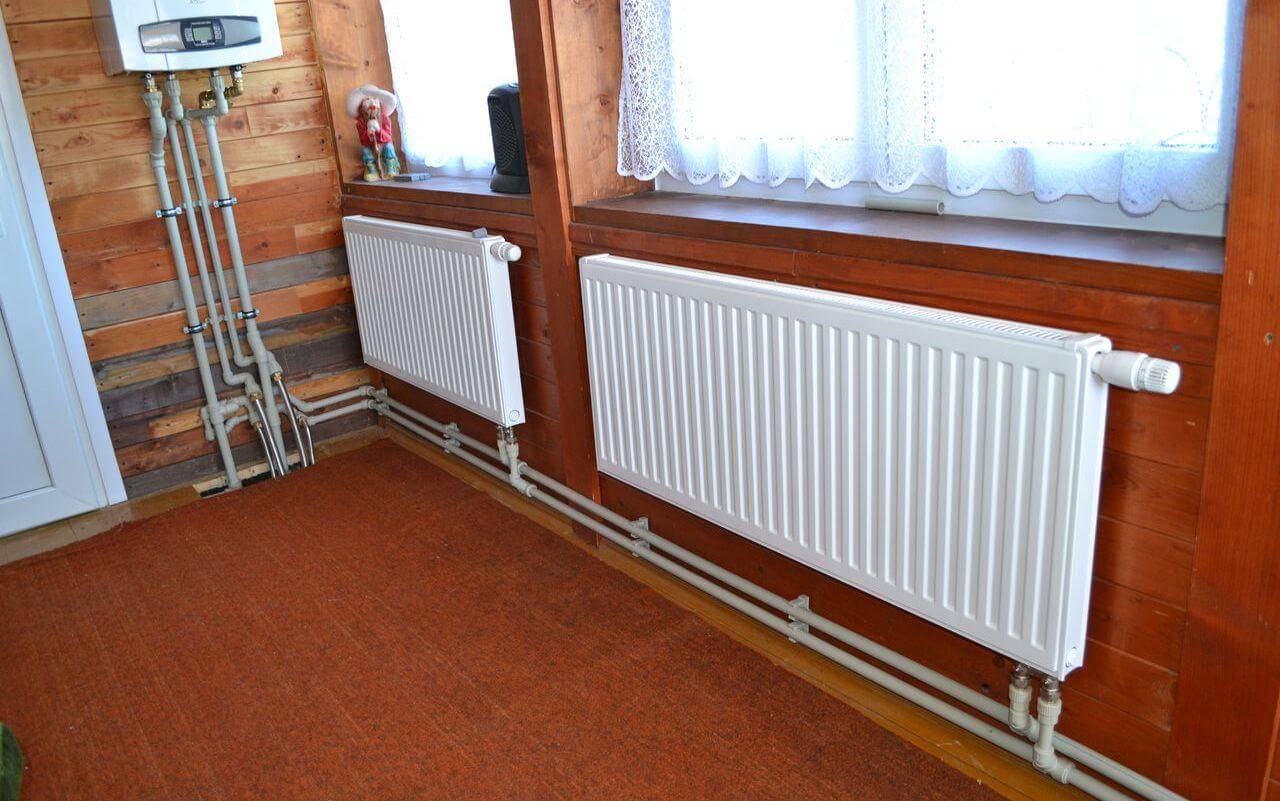
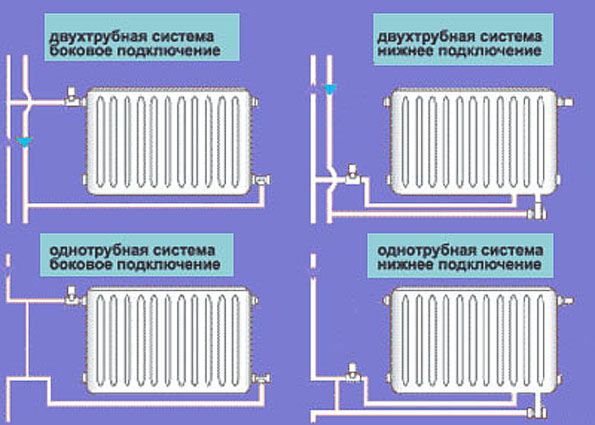
Heating radiator piping options
Installation of heating radiators involves their connection to pipelines. There are three main connection methods:
- saddle;
- unilateral;
- diagonal.
Connection options
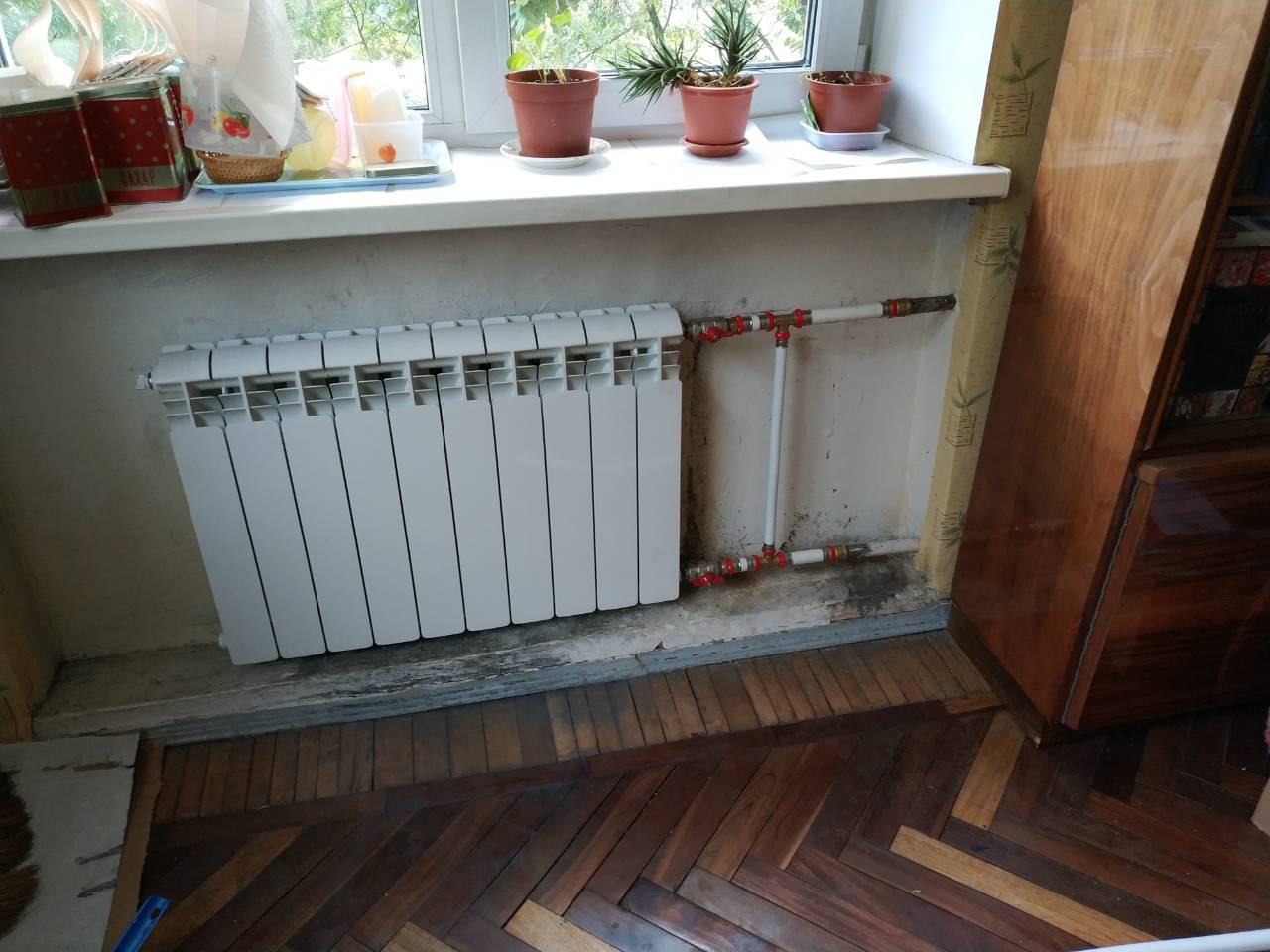
If you install radiators with a bottom connection, you have no choice. Each manufacturer strictly ties the supply and return, and its recommendations must be strictly followed, because otherwise you simply won’t get heat. There are more options with lateral connection (read more about them here).
Binding with one-way connection
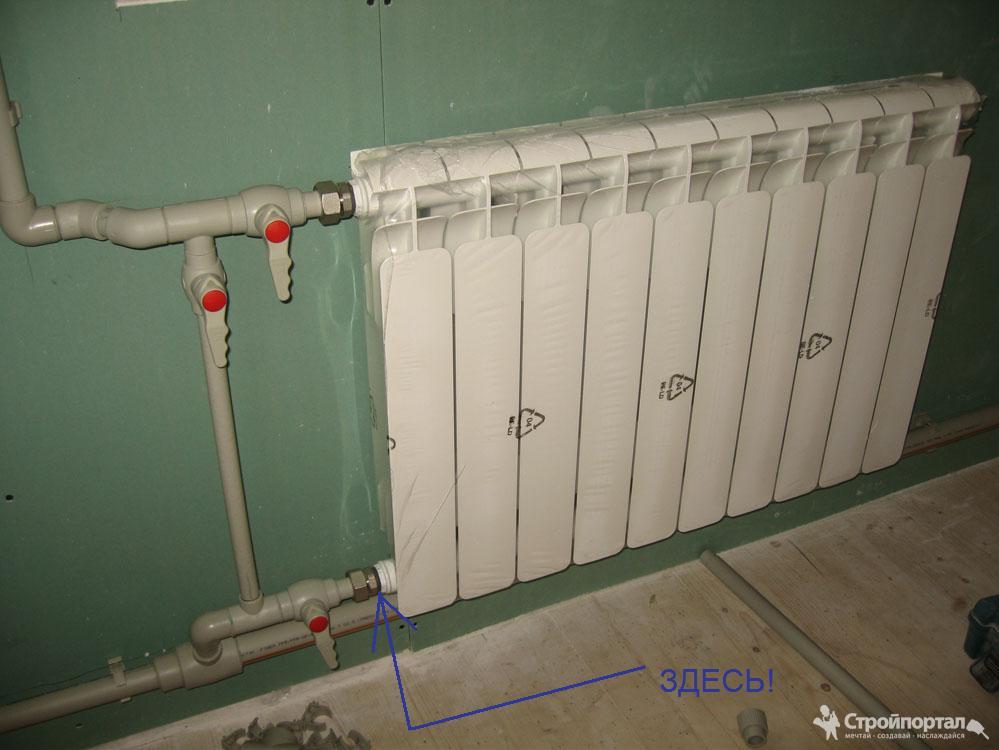
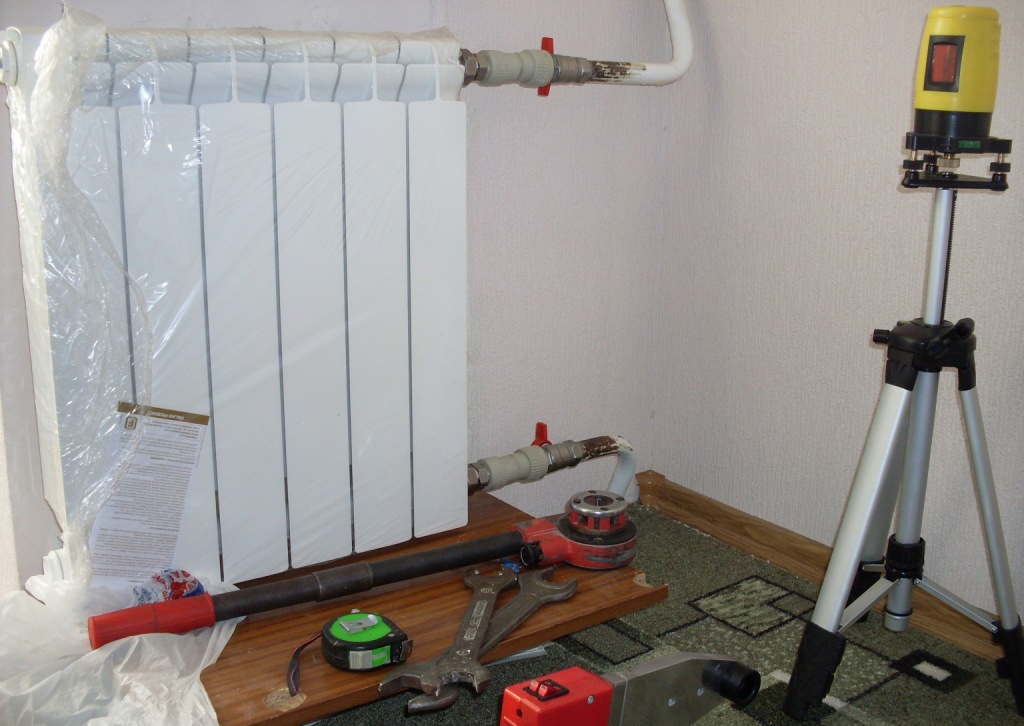
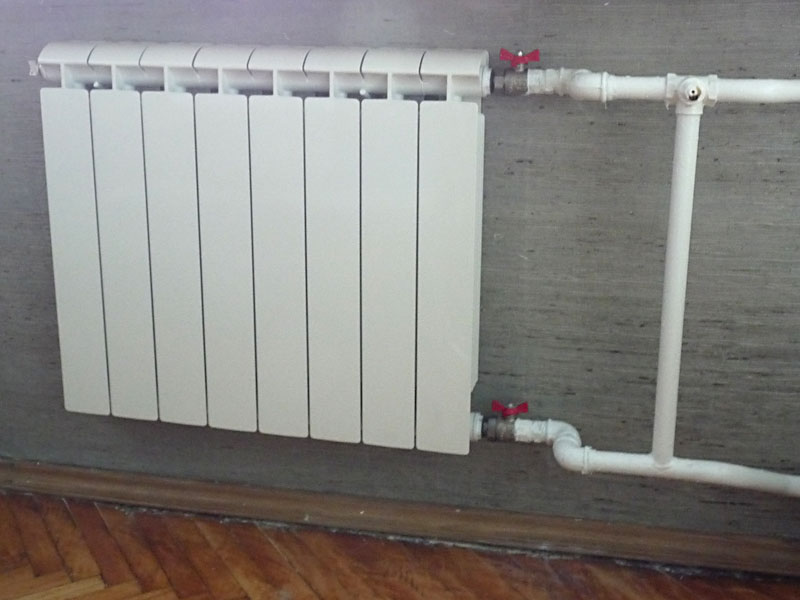
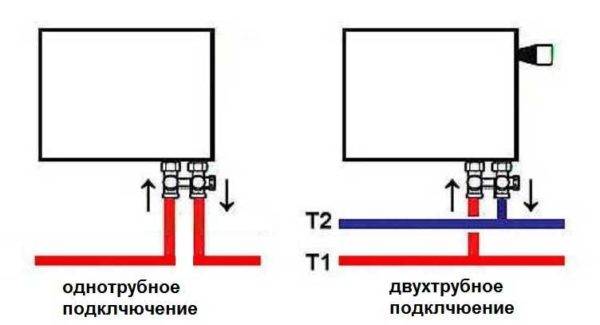
One-way connection is most often used in apartments. It can be two-pipe or one-pipe (the most common option). Metal pipes are still used in apartments, so we will consider the option of tying the radiator with steel pipes on the spurs. In addition to pipes of a suitable diameter, two ball valves, two tees and two spurs are needed - parts with external threads at both ends.
Side connection with bypass (one-pipe system)
All this is connected as shown in the photo. With a single-pipe system, a bypass is required - it allows you to turn off the radiator without stopping or lowering the system. You can’t put a tap on the bypass - you will block the movement of the coolant along the riser with it, which is unlikely to please the neighbors and, most likely, you will fall under a fine.
All threaded connections are sealed with fum-tape or linen winding, on top of which packing paste is applied. When screwing the tap into the radiator manifold, a lot of winding is not required. Too much of it can lead to the appearance of microcracks and subsequent destruction. This is true for almost all types of heating appliances, except for cast iron. When installing all the rest, please, without fanaticism.
Option with welding
If you have the skills / ability to use welding, you can weld the bypass. This is what the piping of radiators in apartments usually looks like.
With a two-pipe system, a bypass is not needed. The supply is connected to the upper entrance, the return is connected to the lower one, taps, of course, are needed.
One-way piping with a two-pipe system
With lower wiring (pipes are laid along the floor), this type of connection is made very rarely - it turns out inconvenient and ugly, it is much better to use a diagonal connection in this case.
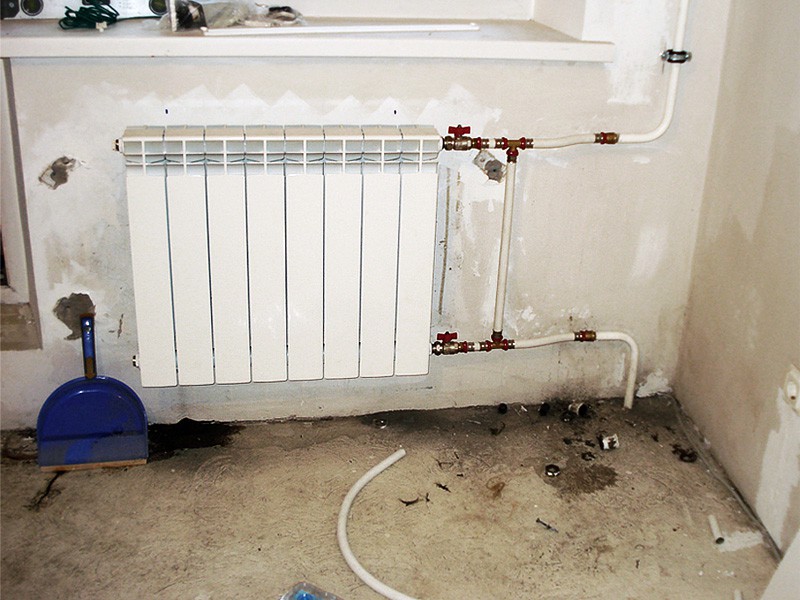
Binding with diagonal connection
Installing heating radiators with a diagonal connection is the best option in terms of heat transfer. She is the highest in this case. With a lower wiring, this type of connection is implemented easily (example in the photo) - supply from one side at the top, return from the other at the bottom.
A single pipe system with vertical risers (in apartments) does not look so good, but people put up with it because of the higher efficiency.
Coolant supply from above
Please note that with a one-pipe system, a bypass is again required. Coolant supply from below
Coolant supply from below
Strapping with saddle connection
With lower wiring or hidden pipes, installing heating radiators in this way is the most convenient and most inconspicuous.
With saddle connection and bottom single-pipe wiring, there are two options - with and without bypass. Without a bypass, the taps are still installed, if necessary, you can remove the radiator, and install a temporary jumper between the taps - a drive (a piece of pipe of the desired length with threads at the ends).
Saddle connection with one-pipe system
With vertical wiring (risers in high-rise buildings), this type of connection can be seen infrequently - too large heat losses (12-15%).
One-way bottom top connection
Used mainly in multi-storey buildings. In cottages on 2 or 3 floors with one-pipe heating, it is also sometimes used. The difference between the lower and upper connections is that in the first case, hot water is supplied to the lower inlet and is discharged under pressure through the upper inlet, and in the second case, the opposite happens. In both cases, the plant and the coolant outlet are located on the same side.It is worth noting that of all the existing options, a one-way bottom connection is the most inefficient.
Which radiator connection system to choose
Other options
Theoretically, it is also possible to use a diagonal connection with infeed from below or a double-sided connection with infeed from above. These two options will also work if done correctly. However, the functioning of the system will be greatly hampered by the intersection of flows. Therefore, it is better not to experiment and take a diagonal top connection or a two-sided bottom connection as a basis.
Location of radiators
For high-quality heating of the cottage it is necessary not only to correctly choose the heating scheme, but also to correctly position the batteries in the premises. The installation of heating batteries in a private house is carried out on the basis of calculations made by specialists. Number of radiators and sections for each radiator is determined taking into account various factors:
- volume of premises;
- the level of heat loss of the building;
- radiator tie-in scheme;
- at what height the batteries will be installed, and much more.
How to calculate the number of heating radiators
Installation of heating radiators
Conclusion
The process of calculating, designing and installing a heating system can only be trusted by qualified specialists. But every homeowner should know the simplest rules for connecting radiators. The effective principle of connecting and locating heating equipment is a guarantee that a favorable and comfortable microclimate will always reign in the house.
Heating wiring options

The most commonly used options are:
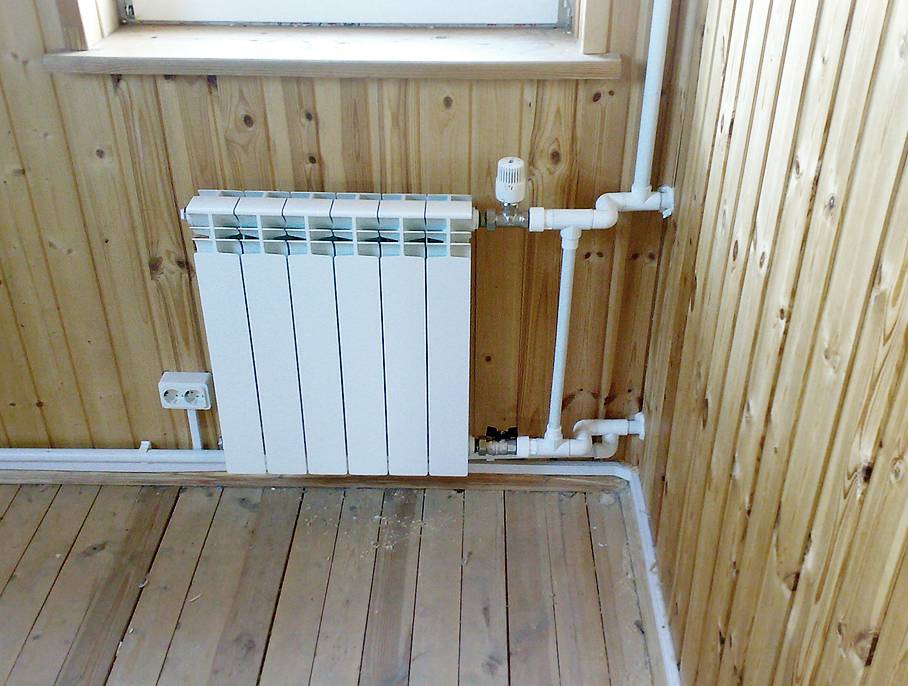
- Diagonal connection. Usually it is used for arranging multi-section heating structures.A distinctive feature of the diagonal installation is the connection of pipelines: the supply pipe is connected on one side of the battery to the upper futorka, and the return pipe is connected to the lower futorku on the other side of the device. When connected in series, the heat transfer fluid circulates due to the pressure that exists in the heating system.
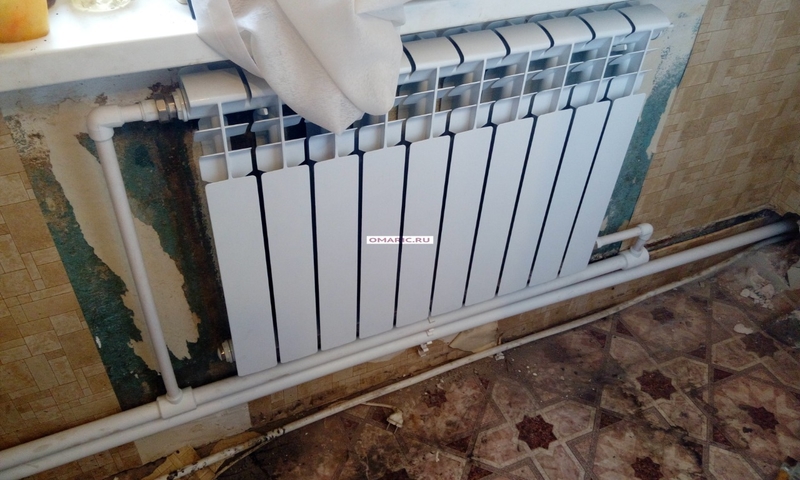
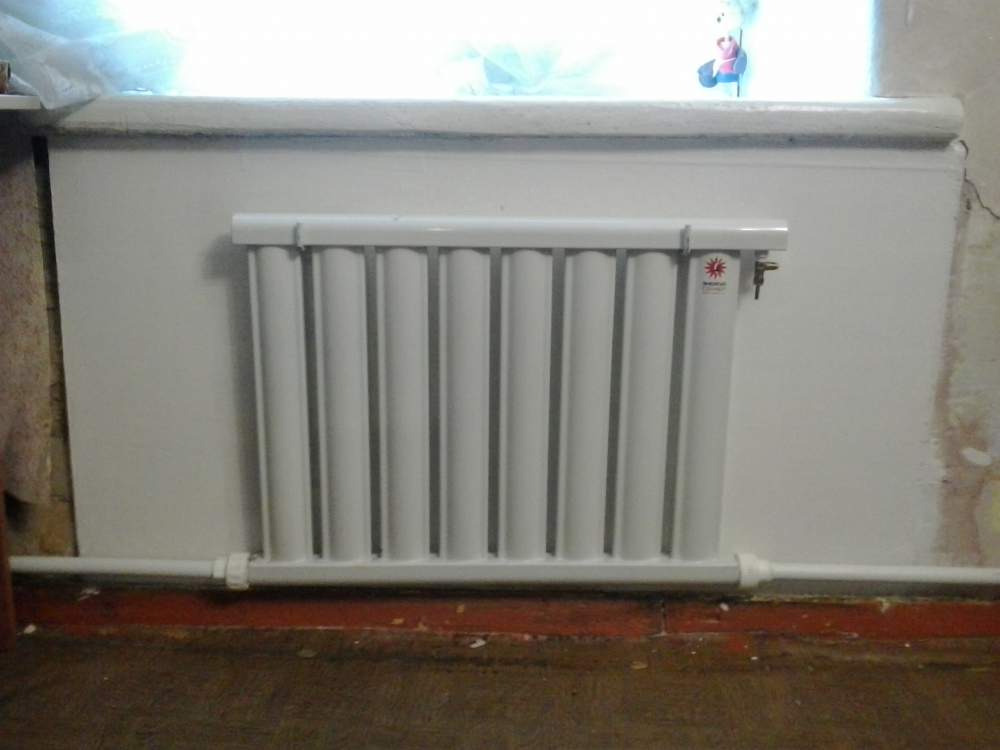
Mayevsky taps are used to remove air from the battery, placing them on a radiator. - Bottom connection. This type of wiring is used when pipelines are planned to be placed in the floor covering or under the baseboard. The bottom connection is considered the most aesthetic when creating an interior. The branch pipes of the return and supply pipes are located at the bottom of the radiator and directed vertically towards the floor. How it looks, clearly shows the photo.
- Lateral one-way connection. This method is the most common, because it provides maximum heat transfer. Its essence lies in connecting the supply pipe to the upper futorka, and the return pipe to the lower one. The rules for installing heating batteries regulate that if the sections are not heated enough in multi-section devices, an extension of the coolant flow should be installed.
- Parallel connection. The connection is made through a pipeline connected to the supply riser. The spent coolant leaves the radiator through a pipeline that is connected to the return. The presence of a valve in front of the battery and after it allows you to remove and repair the device without turning off the heat supply. The disadvantage of the parallel method is the need to maintain high pressure in the system, otherwise the circulation of the liquid is disturbed.

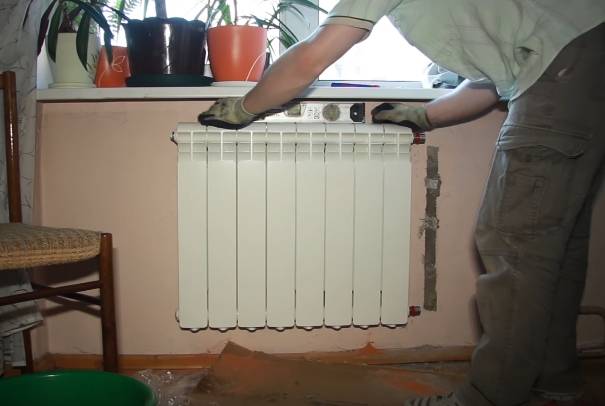
How to install an aluminum battery with your own hands?
This process takes place in stages.
Preparatory work
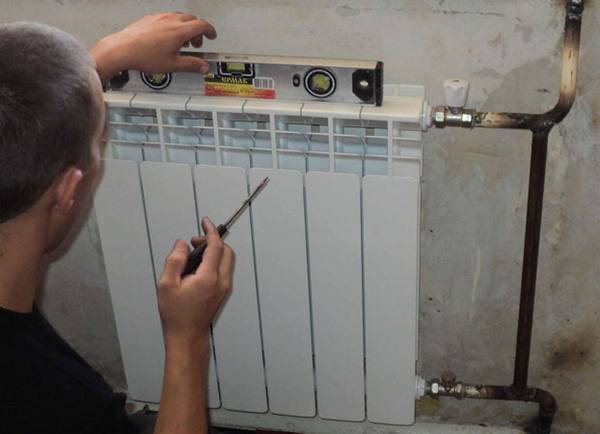
They begin with the fact that the location of the future installation of the radiator is determined and the brackets are fixed.
For a competent calculation of the installation of the battery, the following construction indicators of indents must be taken into account:
- from 10 cm or more - from the windowsill;
- 3–5 cm from the wall;
- about 12 cm from the floor level.
The bracket is fixed to the wall with dowels. The holes left by the drill are filled with cement.
If the battery is floor type, then it is placed on a special stand, and it is attached slightly to the wall, only to establish its stable balance.
Radiator Assembly
Before starting the battery directly, it is necessary to install it step by step:
- screw in the plugs and radiator plugs;
- docking with shutoff valves;
- collection of thermostats;
- nipples stability control;
- fixing air valves.
Attention! For further correct operation of the valves, it is necessary to install their outlet heads so that they are facing upwards. After completing all the steps, the radiator is fixed to the brackets
After completing all the steps, the radiator is fixed to the brackets.
Hooks are located between sections. Detailed assembly instructions an aluminum space heating source should come with it.
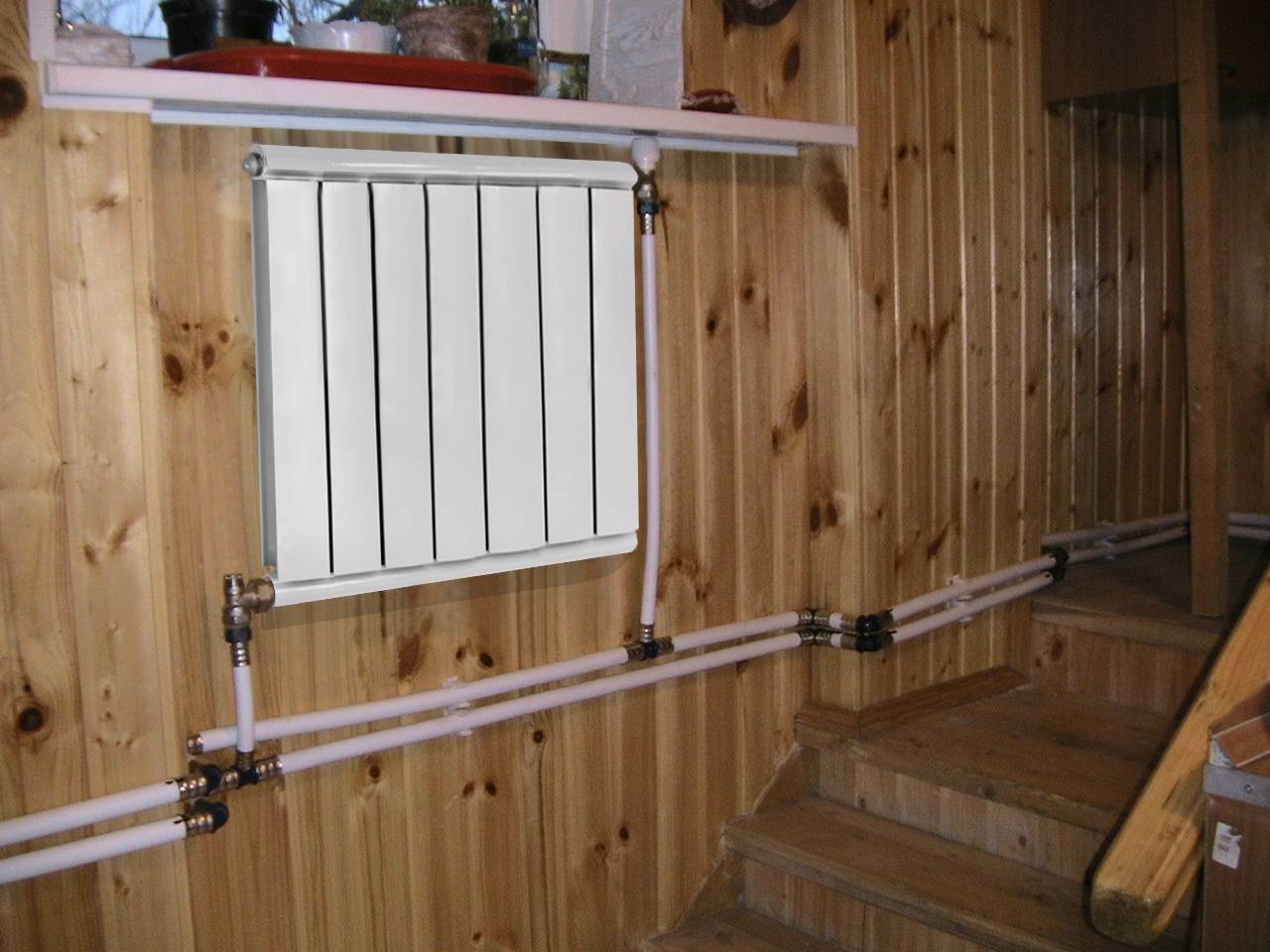
Choosing a place and method of installing a radiator
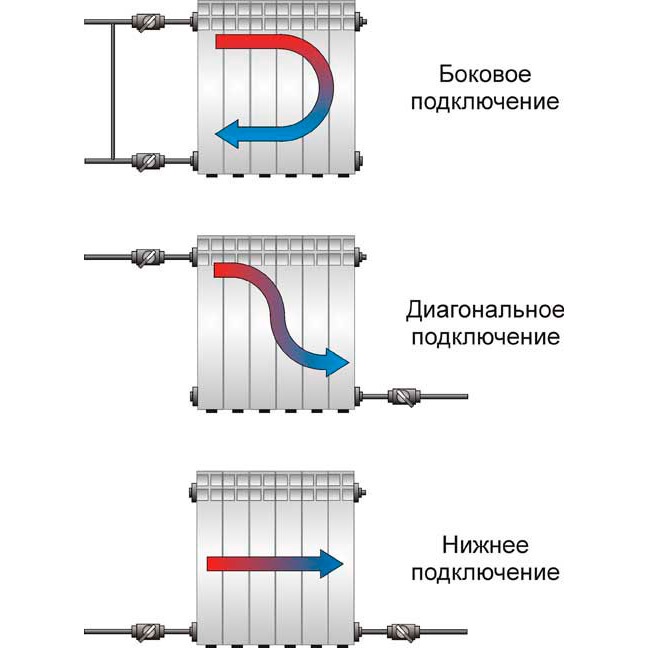
The options for connecting heating radiators depend on the general heating scheme in the house, the design features of the heaters and the method of laying pipes. The following are common ways to connect radiators heating:
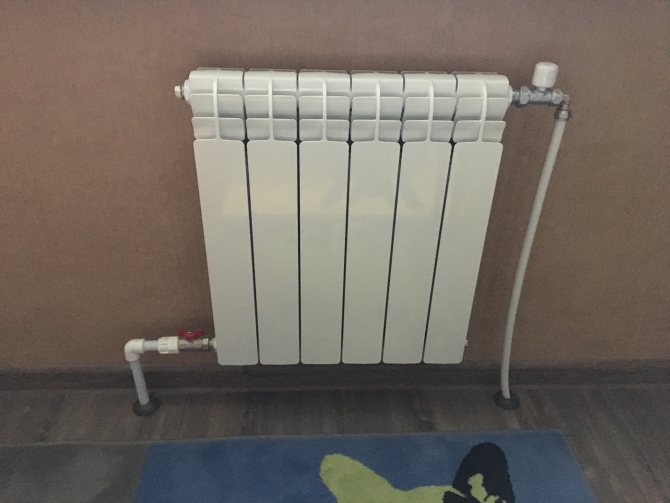
- Lateral (unilateral). The inlet and outlet pipes are connected on the same side, while the supply is located at the top. The standard method for multi-storey buildings, when the supply is from the riser pipe. In terms of efficiency, this method is not inferior to the diagonal one.
- Lower. In this way, bimetallic radiators with a bottom connection or a steel radiator with a bottom connection are connected. The supply and return pipes are connected from below on the left or right side of the device and connected through the lower radiator connection unit with union nuts and shut-off valves. The union nut is screwed onto the lower radiator pipe. The advantage of this method is the location of the main pipes hidden in the floor, and heating radiators with a bottom connection harmoniously fit into the interior and can be installed in narrow niches.
- Diagonal. The coolant enters through the upper inlet, and the return is connected from the opposite side to the lower outlet. The optimal type of connection, providing uniform heating of the entire area of the battery. In this way, correctly connect the heating battery, the length of which exceeds 1 meter. Heat loss does not exceed 2%.
- Saddle. The supply and return are connected to the bottom holes located on opposite sides. It is mainly used in single-pipe systems when no other method is possible. Heat losses as a result of poor circulation of the coolant in the upper part of the device reach 15%.
WATCH VIDEO
When choosing a place for installation, several factors are taken into account that ensure the correct operation of heating devices.Installation is carried out in the places least protected from the penetration of cold air, under window openings. It is recommended to install a battery under each window. The minimum distance from the wall is 3-5 cm, from the floor and window sill - 10-15 cm. With smaller gaps, convection worsens and battery power drops.
Typical mistakes when choosing an installation location:
- Space for installation of control valves is not taken into account.
- A small distance to the floor and window sill prevents proper air circulation, as a result of which heat transfer decreases and the room does not warm up to the set temperature.
- Instead of several batteries located under each window and creating a thermal curtain, one long radiator is chosen.
- Installation of decorative grilles, panels that prevent the normal spread of heat.
Coolant circulation methods
The circulation of the coolant through the pipelines occurs natural or forced way. The natural (gravitational) method does not involve the use of additional equipment. The coolant moves due to a change in the characteristics of the liquid as a result of heating. The hot coolant entering the battery, cooling down, acquires a greater density and mass, after which it falls down, and a hotter coolant enters in its place. Cold water from the return flows by gravity into the boiler and displaces the already heated liquid. For normal operation, the pipeline is installed at a slope of at least 0.5 cm per linear meter.
Scheme of coolant circulation in the system using pumping equipment
For forced supply of coolant, the installation of one or more circulation pumps is mandatory.The pump is installed on the return pipe in front of the boiler. The operation of heating in this case depends on the electrical supply, however, it has significant advantages:
- The use of pipes of small diameter is allowed.
- The main is installed in any position, vertically or horizontally.
- Less coolant required.
Radiator connection diagrams
How well the radiators will heat up depends on how the coolant is supplied to them. There are more and less effective options.
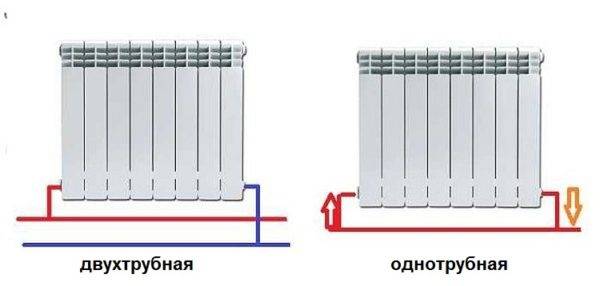
Radiators with bottom connection
All heating radiators have two types of connection - side and bottom. There can be no discrepancies with the lower connection. There are only two pipes - inlet and outlet. Accordingly, on the one hand, a coolant is supplied to the radiator, on the other hand it is removed.
Bottom connection of heating radiators with one-pipe and two-pipe heating systems
Specifically, where to connect the supply, and where the return is written in the installation instructions, which must be available.
Radiators with side connection
With a lateral connection, there are much more options: here the supply and return pipelines can be connected to two pipes, respectively, there are four options.
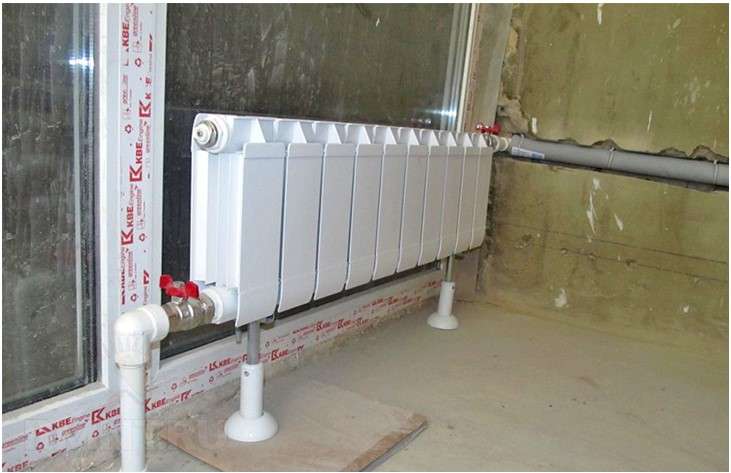
Option number 1. Diagonal connection
Such a connection of heating radiators is considered the most effective, it is taken as a standard, and this is how manufacturers test their heaters and the data in the passport for thermal power - for such an eyeliner. All other connection types are less efficient at dissipating heat.
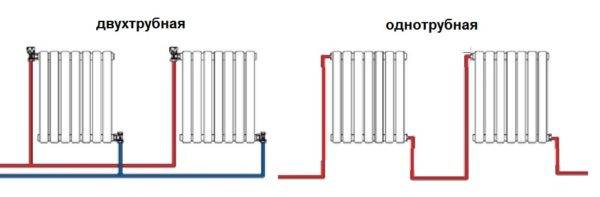
Diagonal connection diagram for heating radiators with a two-pipe and one-pipe system
This is because when the batteries are connected diagonally, the hot coolant is supplied to the upper inlet on one side, passes through the entire radiator and exits from the opposite, lower side.
Option number 2. Unilateral
As the name implies, pipelines are connected on one side - supply from above, return - from below. This option is convenient when the riser passes to the side of the heater, which is often the case in apartments, because this type of connection usually prevails. When the coolant is supplied from below, such a scheme is used infrequently - it is not very convenient to arrange pipes.

Lateral connection for two-pipe and one-pipe systems
With this connection of radiators, the heating efficiency is only slightly lower - by 2%. But this is only if there are few sections in the radiators - no more than 10. With a longer battery, its farthest edge will not heat up well or even remain cold. In panel radiators, to solve the problem, flow extensions are installed - tubes that bring the coolant a little further than the middle. The same devices can be installed in aluminum or bimetallic radiators, while improving heat transfer.
Option number 3. Bottom or saddle connection
Of all the options, the saddle connection of heating radiators is the most inefficient. Losses are approximately 12-14%. But this option is the most inconspicuous - the pipes are usually laid on the floor or under it, and this method is the most optimal in terms of aesthetics. And so that the losses do not affect the temperature in the room, you can take a radiator a little more powerful than required.
Saddle connection of heating radiators
In systems with natural circulation this type you should not make connections, but if there is a pump, it works well. In some cases, even worse than the side. Just at some speed of movement of the coolant, vortex flows arise, the entire surface heats up, and heat transfer increases. These phenomena have not yet been fully studied, therefore it is not yet possible to predict the behavior of the coolant.
Cast iron battery
In many apartments of old houses, it is the cast-iron battery that needs to be removed, so the first thing you have to do is contact the housing office or the house manager. This is necessary because you have to drain the water from the heating system, and this can only be done by an appropriate specialist.
After you have agreed to run the system on a certain day, you need to prepare the tool. You will need:
- pipe wrench number 3, in order to unscrew the lock nuts and futorki (special nuts that connect a larger diameter pipe to a smaller pipe);
- pipe cutter or grinder for cutting pipes;
- hacksaw for metal;
- a hammer;
- chisel;
- metal brush to remove rust;
- blowtorch or industrial hair dryer;
- basin for water;
- rag.
After all the tools are prepared, and the water is drained from the system, we proceed to dismantle.
- It should be remembered that if there is no water in the system, this does not mean that the battery is completely dry. For this we need a basin and rags. With their help, remove the remaining water from the radiator after dismantling.
- As a rule, old radiators are covered with more than one layer of oil paint. And not only the radiators themselves, but the entire fasteners. To remove the paint, use a blowtorch or hair dryer.We need to burn off the old paint on all joints.
- After that, with a metal brush, we finally clean the connections.
- Now, using a pipe wrench, unscrew all the nuts. It is this period of operation that is the dirtiest, since the remains of rusty water will pour out of the radiator. You should be ready for this.
- It may turn out that even after firing the old paint, unscrewing the nuts on the supply pipes will not work. Especially if the radiator has not been cleaned for 10 years or more. In this case, you will have to use a pipe cutter or a grinder and cut off the supply pipes immediately in front of the radiator.
- The cast-iron battery is held on the wall by special brackets. You need to lift it up and take it off. If the battery consists of 3-5 sections, you can carry out a similar procedure yourself. If there are more sections, you will need help: cast-iron radiators are very heavy.
How to place batteries
First of all, the recommendations relate to the installation site. Most often, heating devices are placed where heat loss is most significant. And first of all, these are windows. Even with modern energy-saving double-glazed windows, it is in these places that the most heat is lost. What can we say about the old wooden frames.
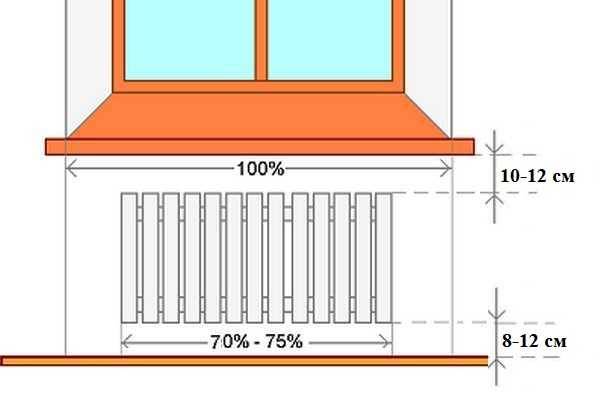
It is important to correctly place the radiator and not make a mistake in choosing its size: not only power is important
If there is no radiator under the window, then cold air descends along the wall and spreads across the floor. The situation is changed by installing a battery: warm air, rising up, prevents cold air from “draining” onto the floor. It must be remembered that in order for such protection to be effective, the radiator must occupy at least 70% of the width window. This norm is spelled out in SNiP.Therefore, when choosing radiators, keep in mind that a small radiator under the window will not provide the proper level of comfort. In this case, there will be zones on the sides where cold air will go down, there will be cold zones on the floor. At the same time, the window can often “sweat”, on the walls in the place where warm and cold air will collide, condensation will fall out, and dampness will appear.
For this reason, do not seek to find a model with the highest heat dissipation. This is justified only for regions with a very harsh climate. But in the north, even of the most powerful sections, there are large radiators. For central Russia, an average heat transfer is required, for the south, low radiators are generally needed (with a small center distance). This is the only way you can fulfill the key rule for installing batteries: block most of the window opening.

The battery installed near the doors will work effectively
In cold climates, it makes sense to arrange a thermal curtain near the front door. This is the second problem area, but it is characteristic it is more for private houses. This problem may occur in the apartments of the first floors. Here the rules are simple: you need to put the radiator as close to the door as possible. Choose a place depending on the layout, also taking into account the possibility of piping.