- Why do you need a drainage device on the site?
- Pipeline laying technology
- Foundation wall drainage
- Drainage filters
- About geotextile
- When additional filters are not needed
- Options for laying a drainage pipe 110 with geotextile under the road, under the foundation, in a ditch of various depths
- Options for installing water flow around the house: the right way
- Peculiarities
- Gravel-free SoftRock drainage system
- Features of the SoftRock drainage system
- Features of laying the SoftRock system
- Geotextile for drainage - the main properties of the material
- Drainage field price
- Blind area: meaning and installation
- How to make a trench
- Prerequisites for organizing drainage
Why do you need a drainage device on the site?
Every second suburban area suffers from excess moisture in the soil, which negatively affects coatings, lawns and generally spoils the appearance of the territory. Usually the problem of waterlogging is caused by close-lying clays and loams with a low filtration coefficient. Such soils very slowly pass rain and melt water through themselves, leading to its accumulation and stagnation in the upper vegetation layer. Therefore, it is necessary to drain the area with a high level of groundwater.
The drainage device allows you to remove excess moisture from the soil and creates an optimal water balance in the area.Thus, the surface drainage of the territory creates comfortable conditions for the development of plants and lawn grass, while not overdrying the soil.
Any house, like an aquiclude on the path of surface runoff, collects water around it, especially if it is built at a low point in the site. And the installation of an annular drainage in front of the blind area prevents frost swelling and removes excess moisture from the house.
In addition, a properly designed and installed drainage system collects both surface water and maintains the overall water table at the required depth.

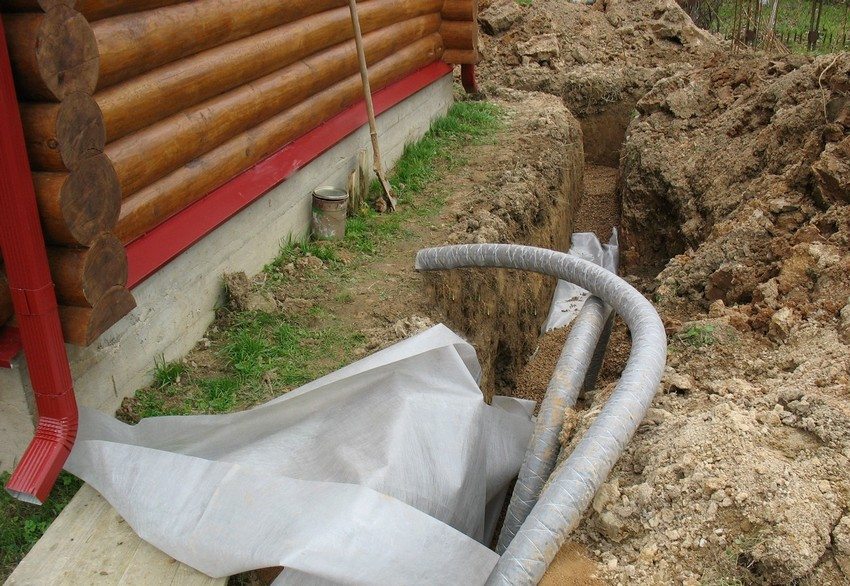
Fig.1 An example of a site where drainage work is required.
Pipeline laying technology
When arranging drainage, the relief of the site is of fundamental importance. The system must be built in such a way that there are no problems with the outflow of fluid into the ditches. If there are no results of geodetic studies, you should independently draw up a diagram, marking on it the places where rainwater drains.
When creating a circuit, you need to be careful, because. errors will cause drainage to be ineffective. According to the finished drawing, they outline how to lay and tilt the drainage pipe and where to install the water collectors. After checking the data, markup is carried out on the ground and work begins.
Image gallery
Photo from
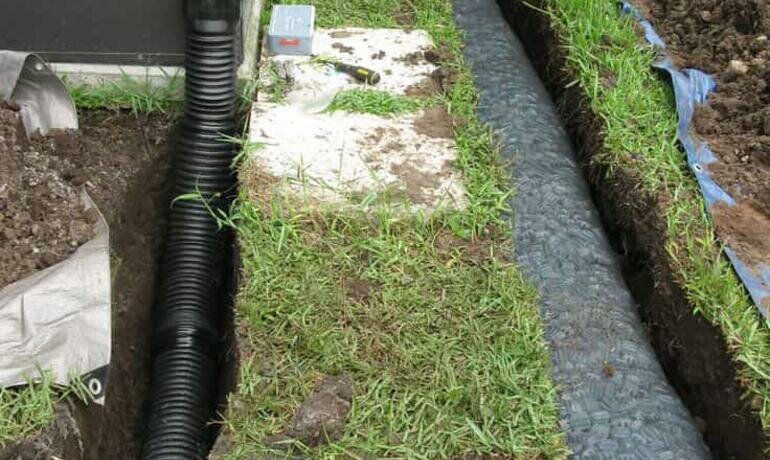
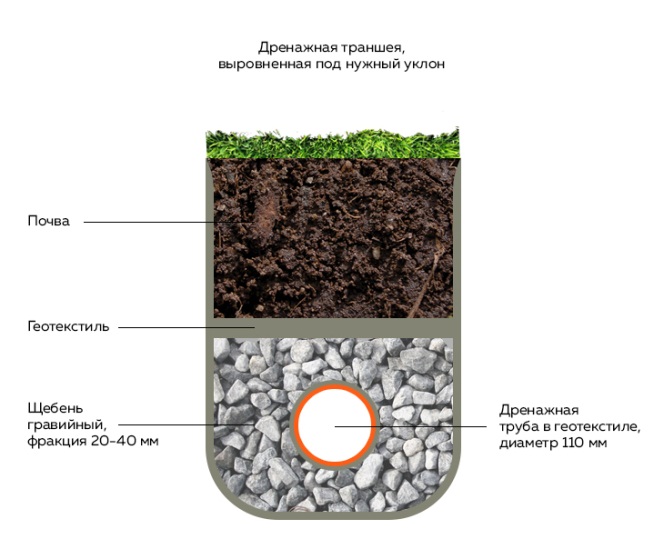
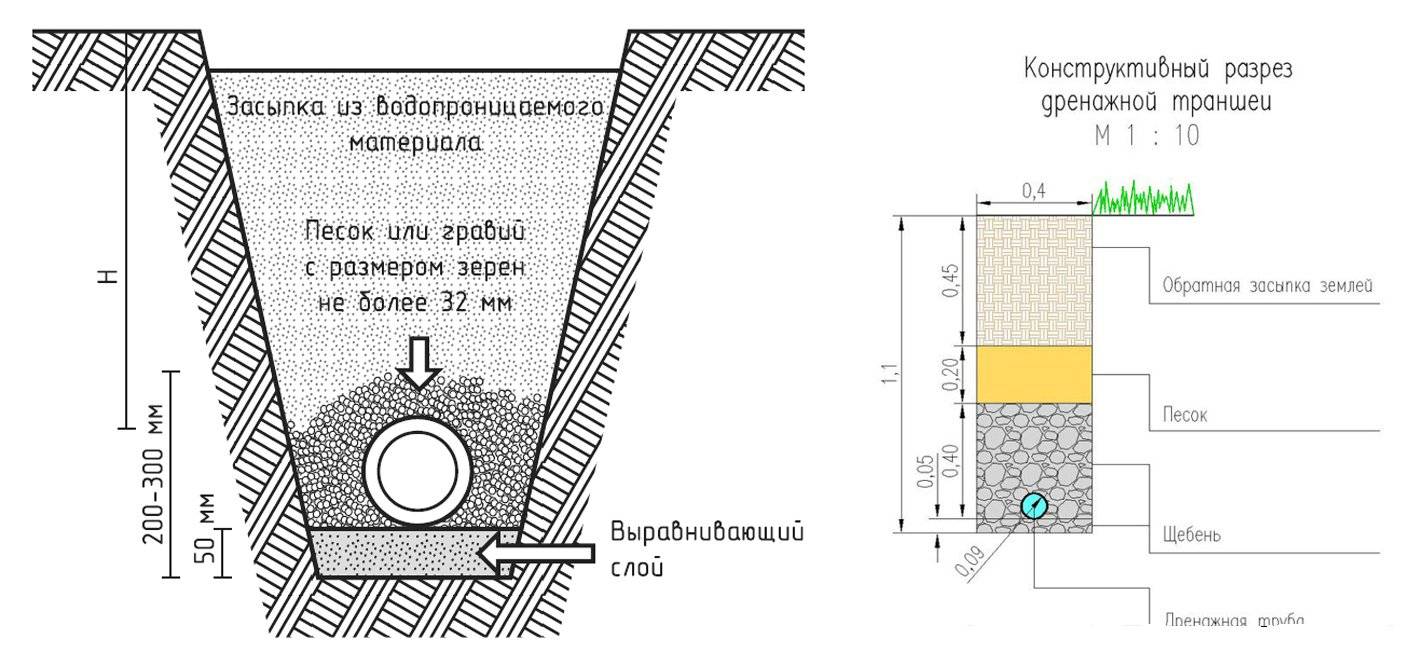
The width of the ditch is calculated based on the diameter of the selected pipe. 40 cm should be added to this figure. The shape of the finished trench can be rectangular or trapezoidal. It depends only on the wishes of the owner of the site and the tools used for earthworks.
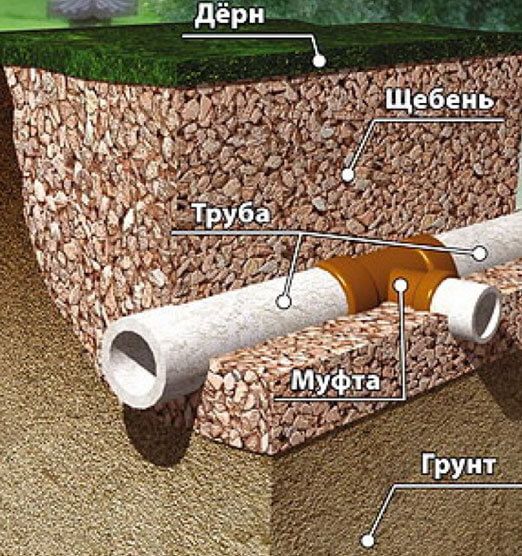
It is important that the bottom is smooth, free of protrusions, bricks, stones or other objects that can damage or deform the pipeline. Down stacked sand or gravel fine fraction, and on top of large gravel
The total height of the layer is at least 20 cm
Drainage pipes are laid on top of the finished pillow at a slope of 3 degrees and connected to each other. Special fasteners for PVC pipes are best suited. If asbestos-cement or ceramic pipes are selected, they are connected by inserting into sockets and treating with sealant
Ideally, the pipeline should be protected from silting with geotextile fabric. If this is not possible, it is covered with a 20-centimeter layer of rubble, and on top - with sand and soil. To the side where the water flows, the sand should be facing
Stage 1 - basic earthworks
Stage 2 - preparing trenches for laying pipes
Stage 3 - laying drainage pipes
Stage 4 - backfilling the pipeline
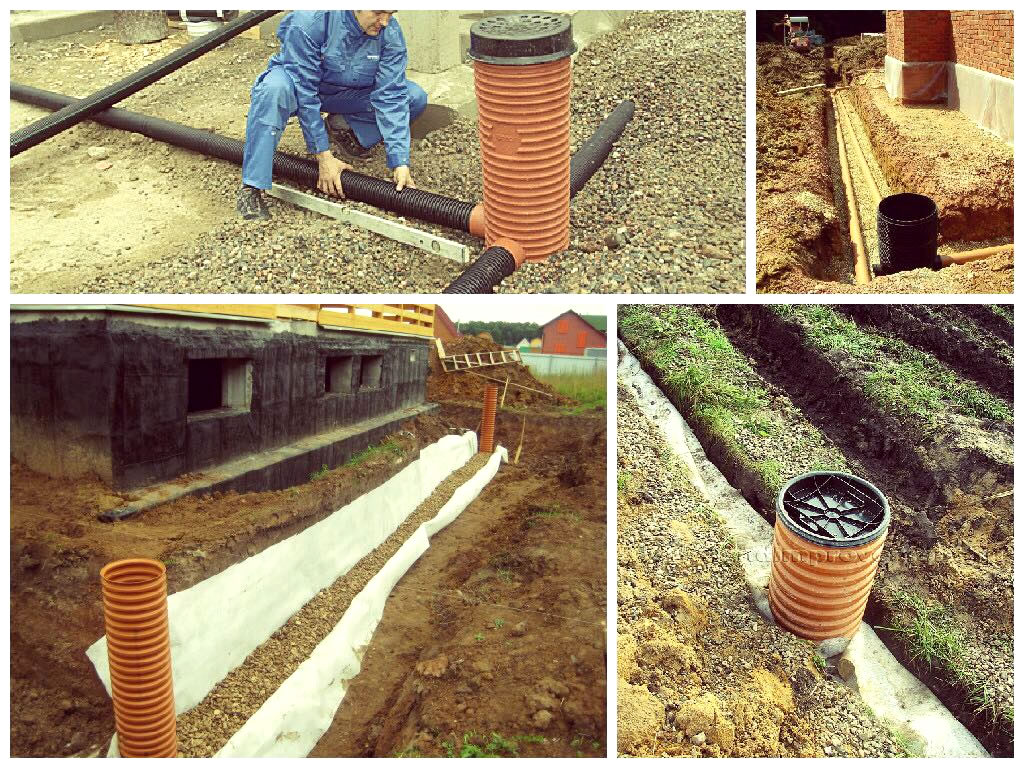
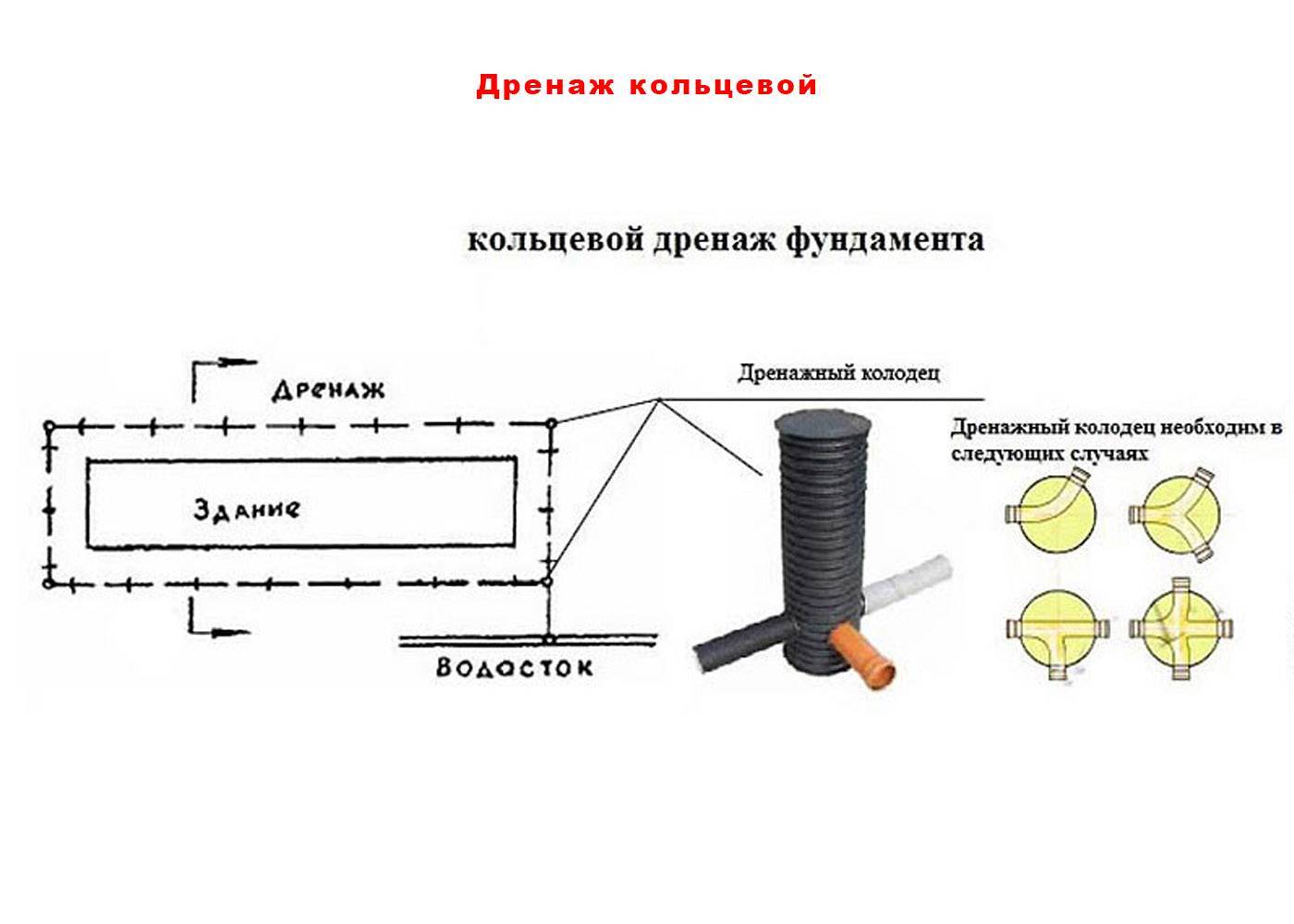
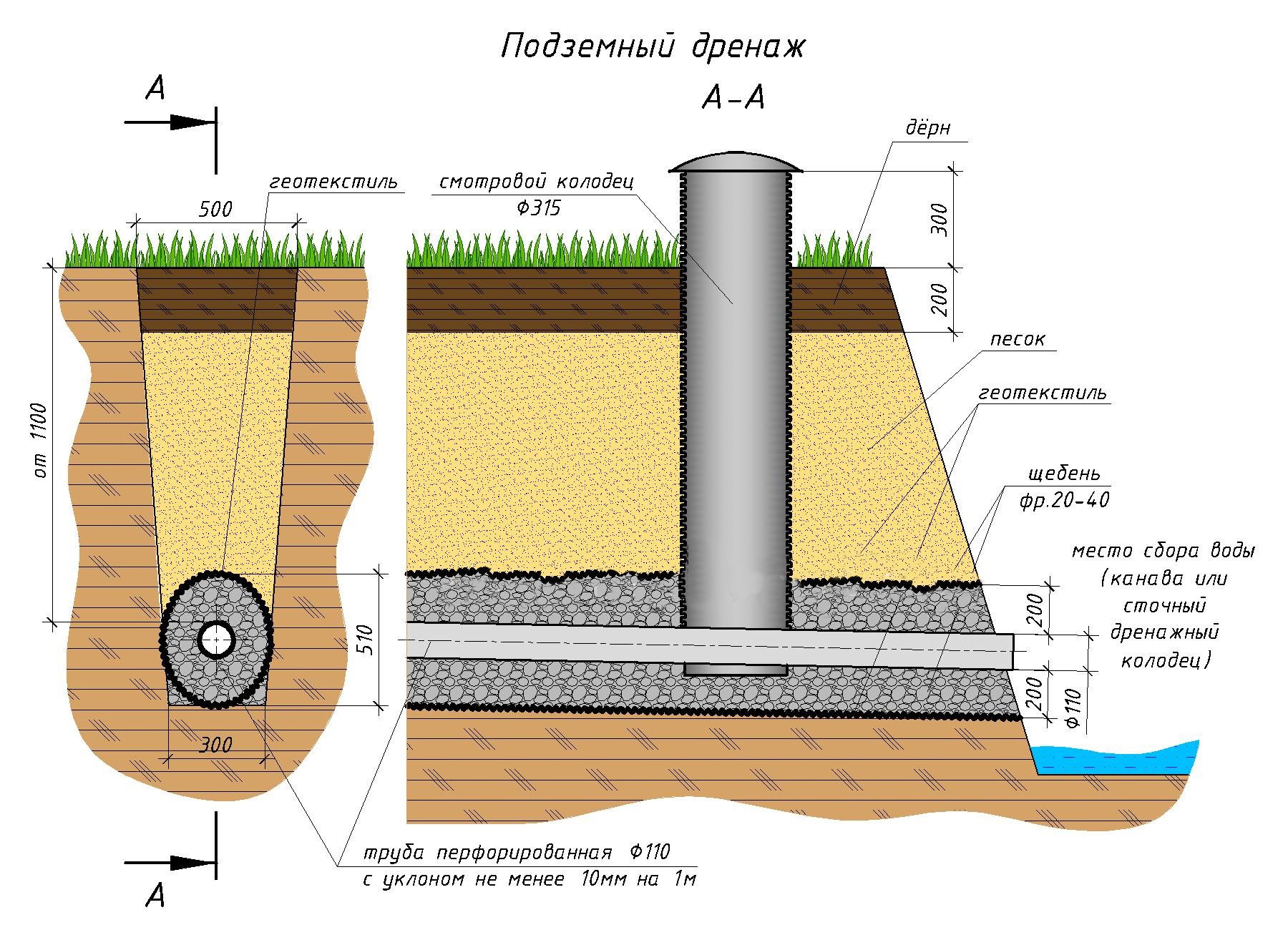
The pipeline leads to a drainage well. If it is long and located on a flat area, manholes are equipped at each segment of 50 m. They are also needed in places where the pipeline turns and bends, where the slope changes.
A drainage well can also be built with your own hands. It consists of a bottom, a shaft with a neck and a hatch. The dimensions of the well should be large enough so that a person can descend into it and clean it of silt. If it is not possible to equip an overall well, then it should be equipped in such a way that it is possible to wash the walls with a hose and scoop out the dirt.
Polymer wells are very popular. They are purchased ready-made. The advantages of such tanks are tightness, strength (due to the corrugated surface, stiffeners), chemical and biological stability.
Concrete, plastic, brick can be used as materials for the manufacture of wells.
The strongest and most durable structures - from reinforced concrete well rings. They have a large diameter, they are easy to maintain. Minus - difficulties with installation due to the large mass. As a rule, you have to attract assistants or use special equipment.
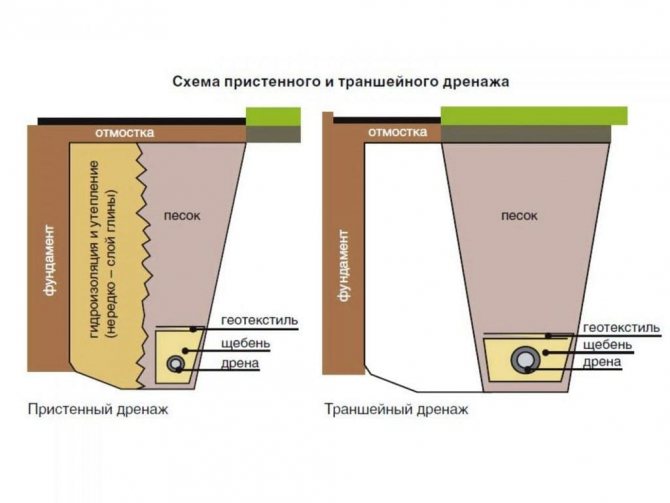
Foundation wall drainage
Wall drainage of the foundation is designed to divert water from the foundation of the house, which will protect the foundation from destruction. Drainage device systems run around the house along the perimeter. There are two withdrawal methods groundwater from home:
- Open,
- Closed.
An open method allows you to collect and divert rainwater. But it is not very suitable for the removal of groundwater. Especially if trays or sawn halves of large pipes are laid at the bottom of such a ditch encircling the house. Foundation drainage requires deep ditches, below the level to which the foundation is buried. And leaving such ditches open is not entirely safe.
Therefore, the drainage for the foundation is performed closed.
Foundation drainage scheme: simple and clear
Scheme foundation drainage should take account of:
- The distance of the pipe from the foundation. It should be no more than the thickness of the foundation.
- The depth of the pipe. Hence, the depth of the trench. The drainage system should be located below the level of the foundation. In addition, the depth of the pipes should take into account the depth of soil freezing. Pipes are laid below this mark by 50 cm.
- Presence (absence) of a drain pipeline;
- Location of manholes.
And since the process of digging a ditch for drainage is laborious, it is advisable to perform the foundation drainage at the same time as the foundation itself, or immediately after it.The drainage pipe is laid with a slight slope (2-5 cm of slope per meter of pipe is enough) so that the water accumulated in it flows out in a given direction. The wall drainage system of the foundation should be located below the foundation itself, regardless of whether the type is chosen: tape, slab or pile.
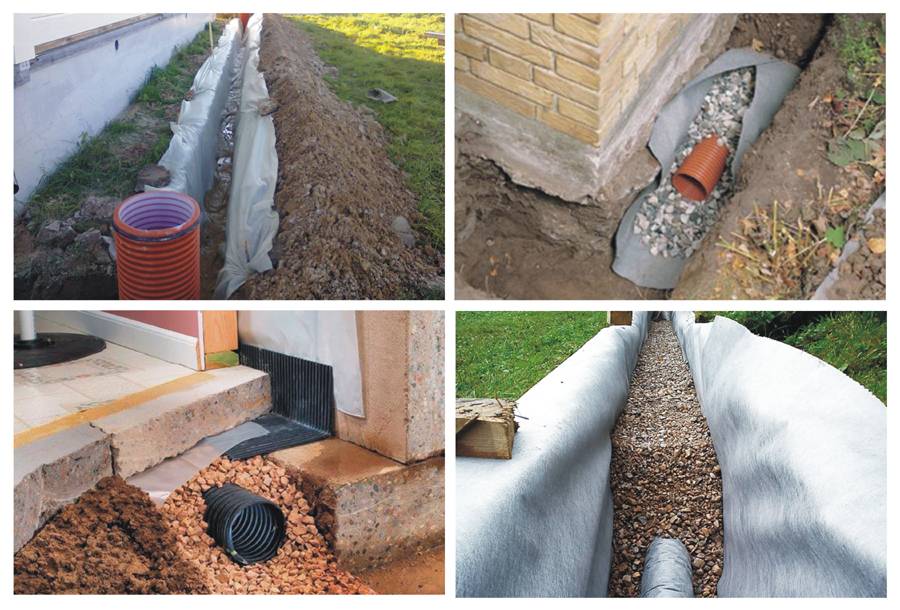
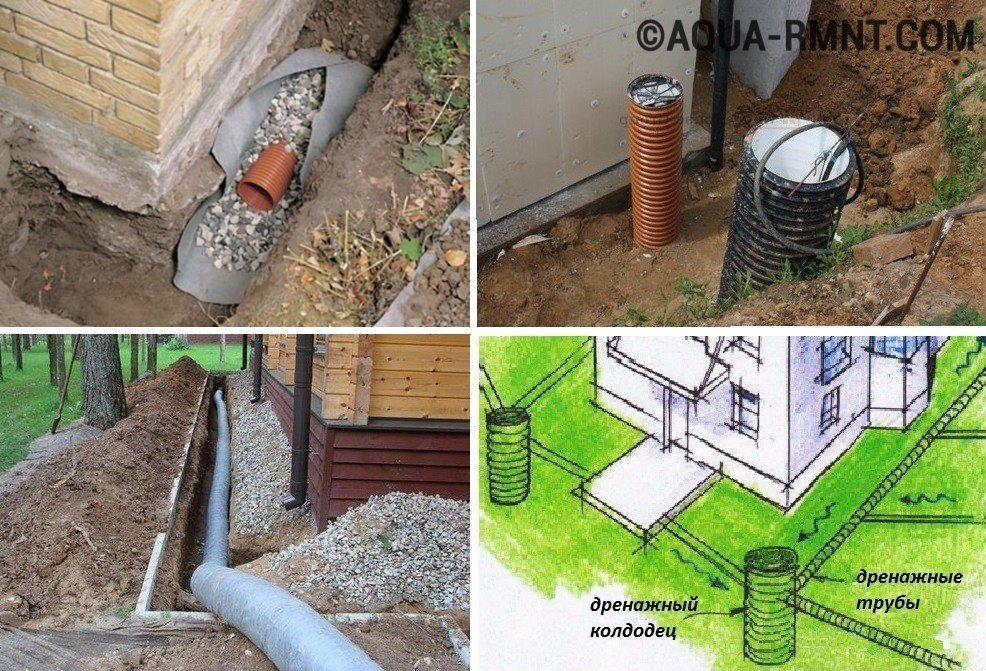
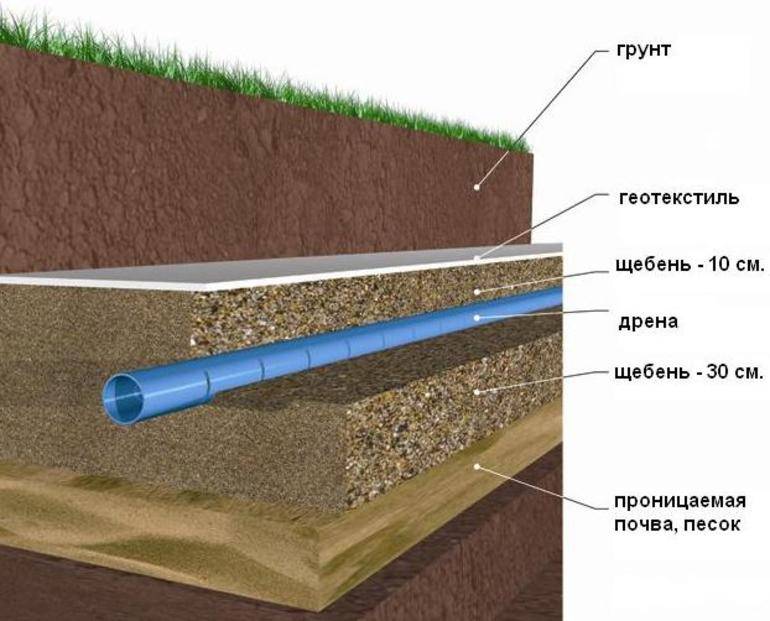
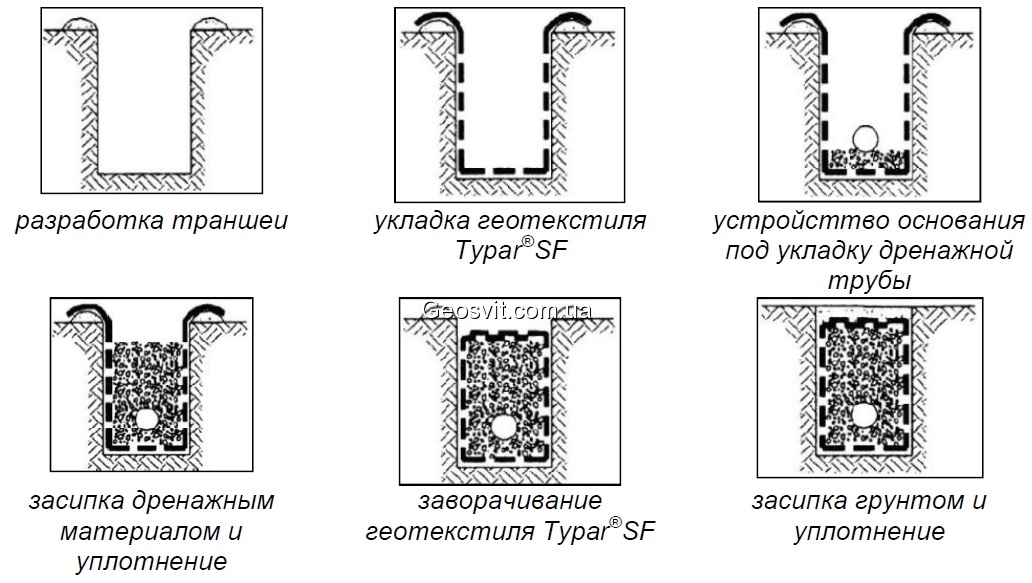
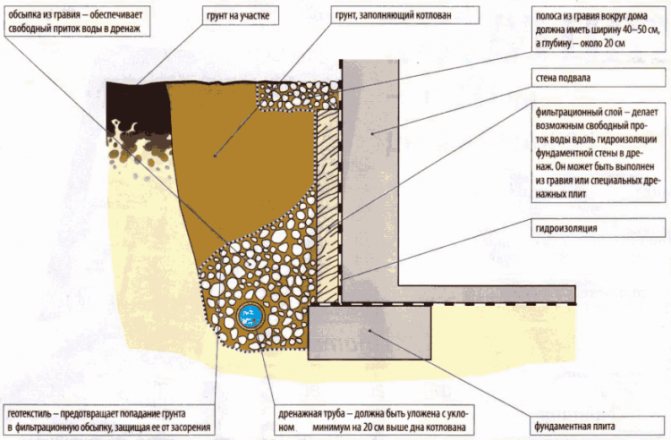
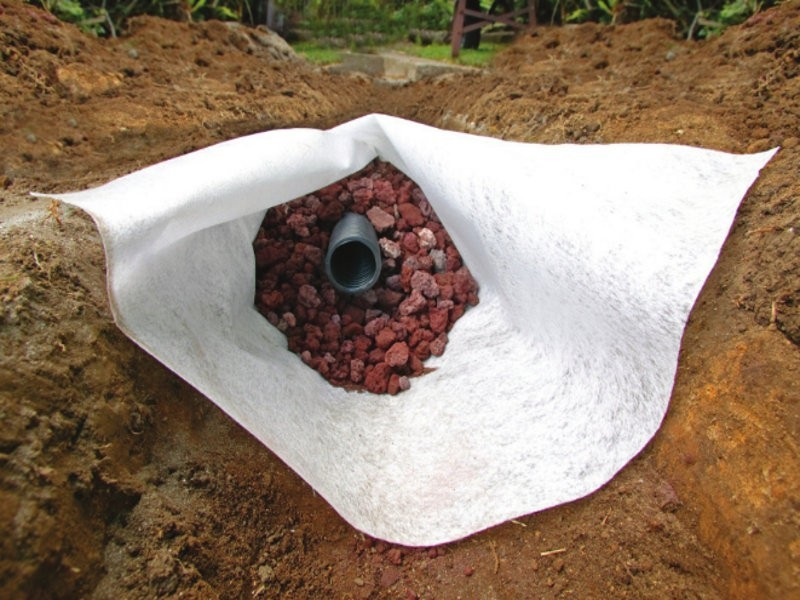
Geotextile is laid in the trench. This porous material acts as a filter. It is needed so that sand and fine fractions contained in the soil do not get into the pipe. Gravel 15-20 mm in size is poured on top of textiles. Smaller ones will block the holes in the pipe. A pipe is laid on the gravel. And from above it is covered with rubble, which is covered with the edges of geotextiles.
The degree of its perforation depends on the humidity. The construction market offers pipes
- with full perforation, when the holes are located along the entire perimeter of the pipe at an angle of 60 degrees and in a checkerboard pattern, along the length of the holes are located at a distance of 10-20 cm.
- With partial perforation, which provides for the presence of 3 holes only on the upper half of the pipe, also at an angle of 60o and at a distance of 10-20 cm.
Important note. In no case should the drainage pipe serve as a storm sewer; rain drains from the roof of the house should not be connected to it. The reason lies in the perforation of the drainage pipe
The reason lies in the perforation of the drainage pipe.
Geotextile. This porous material acts as a filter for drainage.
In the process of overflowing the drainage system, drain water enters the soil from the pipe, which leads to an increased moisture content in it.
But drainage deaf pipes can be laid next to the perforated, or above them, the second tier. This will prevent you from digging extra ditches.
At the corners of the house, manholes should be provided, which include pipes. Now drainage manholes plastics are purchased on the construction market along with pipes and geofabric.
Drainage filters
The main problem of drainage systems is possible silting. Deposits of soil particles that have penetrated the pipes can create plugs and completely stop the functioning of the drainage system. Properly performed installation allows the drainage system to work smoothly for decades at no additional cost and with a small amount of preventive maintenance.
The type of filter layer largely depends on the soil of the drained area.

Most often, several types of filtration are used.
The filter can be:
- crushed stone, gravel, brick and concrete battle;
- fabric materials (for example, geotextiles);
- membranes made of polymeric and natural materials.
About geotextile
A non-woven material that performs the most important function of a fine filter in drainage systems. It is able to hold even the smallest particles of sand. Today you can buy pipes already wrapped with geotextile - they can be laid immediately on any base, without fear of traffic jams.

Finished products may have a geotextile coating
You can apply geotextiles without wrapping them directly around the pipes. The material is laid on a sand cushion, then crushed stone is poured, a pipe is laid, then again a layer of crushed stone and then another layer of geotextile.
When additional filters are not needed
As a general guideline, soils can be characterized as follows:
- Sandy soil itself is filtering. It is only necessary to wrap the drainage pipes with geotextile, protecting them from the smallest grains of sand, and also to make additional backfilling with crushed stone.
- For crushed stone soil, the best solution would be to use rigid perforated pipes plus additional gravel or crushed stone.
- In clayey soils, sometimes it is enough to lay pipes without a filtering fabric layer - crushed stone backfill or a coconut filter is enough.
For an ideal drainage system made once and for all, it is better to use all available filtration methods in combination
Options for laying a drainage pipe 110 with geotextile under the road, under the foundation, in a ditch of various depths
When choosing the principle of moisture removal on the farm, you need to know how the drainage pipe is laid. Waters are divided into 2 types: external and underground, respectively, surface and deep drainage are distinguished.
Surface drainage is one of the most affordable ways to remove moisture. Allows you to effectively remove water from seasonal precipitation or snowmelt. Such a system can be point or linear.
Point drainage is the installation of storm water inlets in an area with a large accumulation of moisture. For example, at the drain, in lowland areas (everyone knows sewage wells on the road), where water taps are installed on the territory. Such systems are equipped with gratings, which catch large debris and partially prevent the appearance of odor on the surface.
A linear water collection system is characterized by the presence of trays, gutters, channels that lead to water collection points. As a rule, a special grill is also installed on top. A linear drainage system is advisable to use in such cases:
- If the slope of the soil surface is more than 3 degrees. In addition to draining water, it prevents the washing out of fertile soil.
- If the main constituent of the soil is clay, which does not pass water enough.
- If it is an area with a high level of precipitation.
With deep drainage, a pipe is installed for draining groundwater.
Options for installing water flow around the house: the right way
There are several options for removing moisture. They are conditionally divided into open and closed.
Laying corrugated drainage pipes
- Installation in the soil of the trench. This is a closed drain. Crushed stone, broken brick are placed on top and sprinkled with a layer of sand. For more efficient work, they dig a system of trenches in the shape of a herringbone. The main point of its proper operation is the condition that the central trench be sloping towards the catchment point. On clay soil, it is no more than 10m, on loamy soil - 20m and sandy - 50m.
- Open way. With this option, ditches are dug in the soil, through which water flows into a well or other collection point. Its difference from the previous system is that crushed stone and sand are not poured from above. The main disadvantage of such water collection is an unattractive appearance.
- Water drainage system where a corrugated pipe is used. This is a deep type of drainage, suitable for waters lying close to the ground surface. A corrugated plastic pipe is installed in the ditch. To drain the liquid, a ceramic or asbestos-cement pipe with special holes is also used. For the device of a modern drainage system, a perforated pipe or a complete system is used.
- Special drainage trays.They are made of concrete or plastic, covered with a grate from above. The sides of such trays coincide with the level of the soil. The slope at which effective drainage is ensured should be at least 2-3 percent. The disadvantage of such a system is an unattractive appearance.
The laying of the drainage pipe should only be carried out by a knowledgeable person.
Peculiarities
Before installing drainage pipes for draining groundwater, consider the features of some types.
- Corrugated - suitable for installation of storm sewers and drainage of water passing at shallow depths. They are made of polymeric materials. They have 2 layers: the top one is highly resistant to damage, and the bottom one has good sliding performance.
- Perforated stainless pipe - suitable for maintaining the necessary balance of moisture in the soil. The main indicators of water intake are the location and area of the holes on their body. If only wastewater is needed, the holes are located within 120-180 degrees. To control the level of humidity, a line with holes in the region of 240-360 degrees is mounted. They are single layer and double layer. To prevent debris from entering, a pipe with geotextile is produced.
- Ceramic products - produced back in Soviet times and used for agriculture.
- Concrete pipes - are used only in utilities. These are large diameter drain pipes. Installing such systems in a private courtyard is not economically viable.
- Asbestos-cement products are a rather fragile material, which also has significant weight. Due to the emergence of new types of pipelines, the demand for them has fallen.
- Perforated profile pipe - used for mounting a horizontal drainage frame.
For laying a modern drainage system, PVC pipes are used.
Storage of perforated pipes
Gravel-free SoftRock drainage system
One of the integral elements of the drainage system is a pillow made of rubble or gravel. However, there are special systems that allow you to do without this, it would seem, a necessary component. Such systems include SoftRock.
Features of the SoftRock drainage system
The new, high-tech SoftRock drainage systems include a flexible, perforated drainage pipe lined with an EPS thermal insulation layer encased in a tightly woven fiberglass mesh and a durable geotextile top layer. It is the presence of a heat-insulating layer that makes it possible to avoid laying a crushed stone pillow.
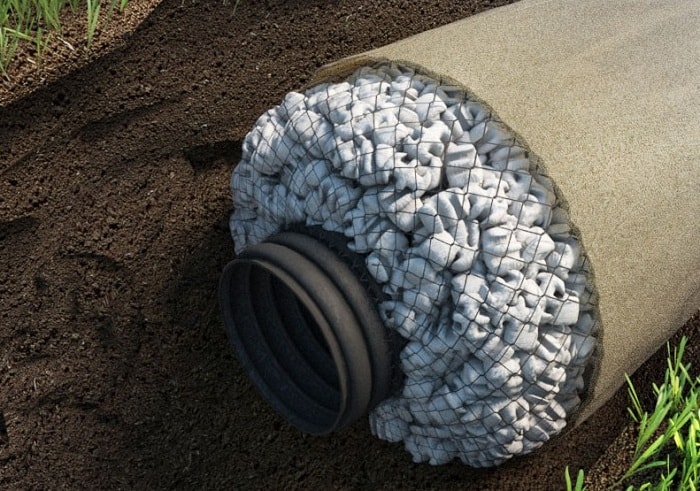

SoftRock systems have the following advantages:
- consistently high quality of all structural elements;
- flexibility and light weight allow you to carry out installation work on your own;
- the SoftRock drainage system can be located anywhere on the site, including the garden and recreation area;
- the system can be mounted at any ambient temperature;
- the use of SoftRock completely eliminates the swamping of the site and the stagnation of rainwater;
- a wide range of operating temperatures;
- high mechanical strength;
- no need to clutter the site with rubble and other building materials.
Significant disadvantages include the high cost of the elements of the system.
Features of laying the SoftRock system
Installation of the drainage system can be carried out independently, without the involvement of specialists and the use of special equipment. Great help with carrying out installation work can provide detailed instructions included in the package.

Work sequence:
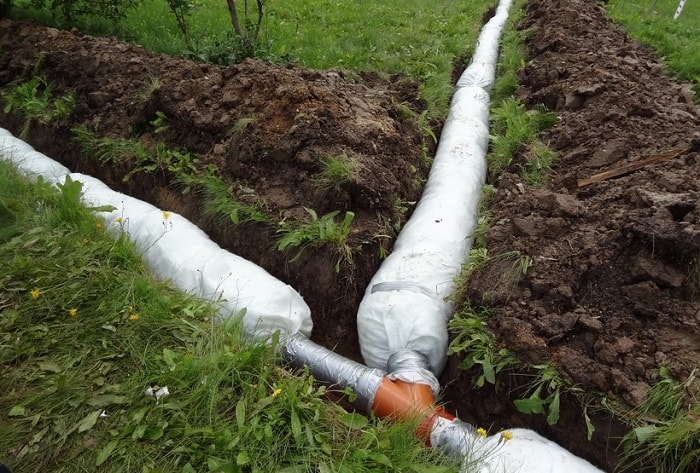
- First of all, according to the layout of the main pipelines, trenches with a width of 500 mm or more are dug, the depth of which should be at least 450 mm.
- A slope is formed in the trenches, the value of which is 25 mm / mp.
- SoftRock elements are laid in trenches and connected using special couplings.
- A coating of geotextile or special cardboard is laid on top of the pipes. Most often, this operation is not necessary, since the pipes are already enclosed in a protective sheath of geotextile.
- The remaining space is covered with soil and covered with a layer of turf.
Subject to all installation requirements, the SoftRock drainage system will provide reliable protection of the underground part of the foundations and will allow for effective removal of excess moisture from the site.
Geotextile for drainage - the main properties of the material
In drainage systems, geofabric plays a very important role - its strength, which is determined by parameters such as stiffness and porosity, determines the speed and quality of water filtration that must be removed from the site. The main task of the coating is to keep the drainage pipe and materials from debris, and hence from blockages, to prevent it from flooding and stagnant water.
The fabric cloth is made of polypropylene fibers, can have different density, high strength and is not subject to decomposition under the influence of biochemical processes.The principle of operation of this material is very simple: it is a layer that is used to separate two other layers from each other, some of its types are able to pass water, others are not.

On sandy soils, geotextile can be used as an additional filter element.
The most important property of a geotextile is its unique ability to clean water from impurities soil and at the same time keep the filtering perforated walls of the product clean
In this case, when choosing a fabric, it is necessary to pay attention to such a parameter as the filtration coefficient, which is present in the description of the sample.
For drainage systems, the optimal indicator is 125–140 m / day. Moreover, it is also necessary to take into account the composition of the fabric. The use of a cloth with impurities of cotton fibers is unacceptable, since over time they can be washed out, and, consequently, the filtering characteristics of the material will decrease due to an increase in the diameter of micropores. Monofilament is the only suitable option for use in filter drainage systems.
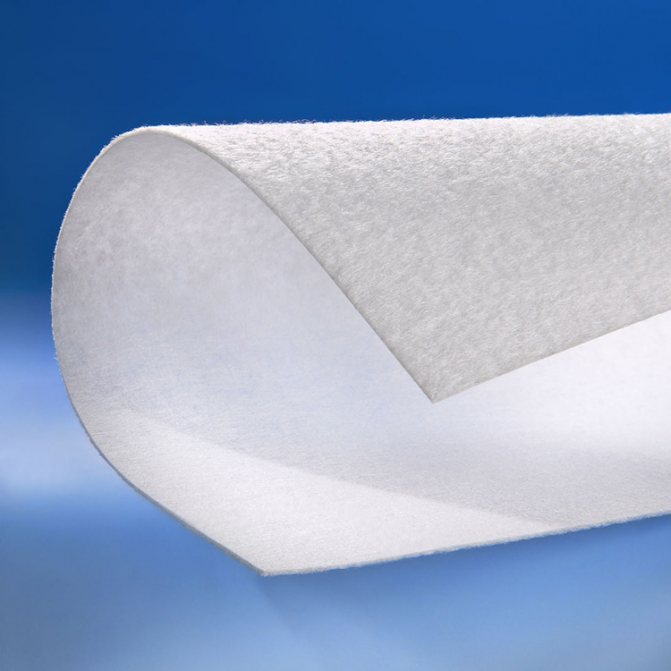

Non-woven geotextile, needle-punched, made of monofilament
For the device of drainage systems, a game-punched geofabric is most often used. The holes in it are made randomly using a special machine. The material has excellent water permeability, but it is quite durable. For information, we present tables of types of geotextiles depending on the density and scope. And if you still have questions about how to choose the right geofabric, watch this video.
Drainage field price
Building a drainage field with your own hands is physically difficult due to the significant amount of earthwork.Usually, a team with special equipment is hired to dig a pit, but small after-cleaners can be made by hand.
When determining the price of a drainage field, the following should be taken into account:
- All types of earthworks associated with digging a hole to a depth below the freezing level.
- The cost of bulk materials for creating a filter layer - crushed stone, sand, as well as the cost of their delivery.
- The price of pipes, fittings, distribution wells and other elements of the drainage field. These products must be of high quality, as it is difficult to control their condition and repair.
- Prices for the installation of a drainage pipeline.
- Removal of the remaining land and landscaping.
When determining the cost of an aftertreatment for sewerage, you can use the information given in the tables below.
The cost of arranging a drainage field in Ukraine:
| The type of work | Features of work | Price |
| Digging a pit and trenches up to 1.5 m deep by hand | For small size recleaner, depends on soil type, pit depth, movement from pit and other factors | 200-500 UAH/m3 |
| Finishing the bottom of the pit and trench | Formation of a gravel-sand filter with a thickness of 30-50 cm | 100-130 UAH/m3 |
| Laying drainage and sewer pipes | Depends on pipe material and line assembly technology | 70-140 UAH/rm |
| Geotextile laying | Laying fabric on drains | 40-60 UAH/rm |
| Installation of distribution and closing well | Installation of factory-made products in a regular place, depends on the design of the tank | 300 UAH |
| Backfilling the soil, improving the area above the pipes | Backfilling of pits and trenches | 180-300 UAH/m3 |
The cost of arranging a drainage field in Russia:
| The type of work | Features of work | Price |
| Digging a pit and trenches up to 1.5 m deep by hand | For small size recleaner, depends on soil type, pit depth, movement from pit and other factors | 500-1100 rub/m3 |
| Finishing the bottom of the pit and trench | Formation of a gravel-sand filter with a thickness of 30-50 cm | 300-360 rub/m3 |
| Laying drainage and sewer pipes | Depends on pipe material and line assembly technology | 250-340 rub./rm |
| Geotextile laying | Laying fabric on drains | 100-130 rub./rm |
| Installation of distribution and closing well | Installation of factory-made products in a regular place, depends on the design of the tank | 700-900 rub. |
| Backfilling the soil, improving the area above the pipes | Backfilling of pits and trenches | 400-460 rub/m3 |
The cost of a drainage field is greatly influenced by the prices of perforated pipes. They must be of high quality, and such products are not cheap. The table below shows the cost of drains from different companies.
The price of plastic pipes for a drainage field in Ukraine:
| Manufacturer | Outer diameter, mm | Price for 1 linear meter, UAH | Number of layers |
| Wavin | 126 | 75-80 | 1 |
| 110-120 | 1 + geotextile filter | ||
| 115-130 | 1 + coconut fiber filter | ||
| 160 | 120-150 | 1 | |
| 160-190 | 1 + geotextile filter | ||
| 230-240 | 1 + coconut fiber filter | ||
| Perfocore | 110 | 60-75 | single layer in coils (SN 4) |
| 85-90 | single-layer in segments of 6 m (SN  | ||
| 160 | 95-110 | single layer in coils (SN 4) | |
| 140-170 | single-layer in segments of 6 m (SN  | ||
| 60-70 | 2 + filter | ||
| 55-60 | 2 |
Price of plastic pipes for drainage field in Russia:
| Manufacturer | Outer diameter, mm | Price for 1 linear meter, rub. | Number of layers |
| Wavin | 126 | 160-175 | 1 |
| 245-260 | 1 + geotextile filter | ||
| 335-339 | 1 + coconut fiber filter | ||
| 160 | 325-345 | 1 | |
| 425-460 | 1 + geotextile filter | ||
| 510-530 | 1 + coconut fiber filter | ||
| Perfocore | 110 | 140-160 | single layer in coils (SN 4) |
| 190-200 | single-layer in segments of 6 m (SN  | ||
| 160 | 200-210 | single layer in coils (SN 4) | |
| 300-350 | single-layer in segments of 6 m (SN  |
What is a drainage field - look at the video:
The drainage field for sewerage completely purifies water from sewage, so such systems are popular with owners of country mansions. The correct calculation of the dimensions of the afterpurifier and compliance with the technology of its construction will ensure a long service life of the structure and protect the territory from pollution. Despite the fact that the construction of such a soil filter is expensive, and a significant area of \u200b\u200bthe adjacent territory will have to be allocated for it, the use of a drainage field for sewage is much more profitable than other types of after-cleaners.
Related article: Drainage pipes for groundwater
Blind area: meaning and installation
An additional element to protect the building from excess moisture is the blind area. It complements the drainage. The blind area is the laying of waterproof material around the perimeter of the foundation, adjacent directly to the building.
The material should be placed strictly at an angle outward so that moisture can drain. Thus, getting on the blind area, water is immediately removed from the house. The contact of the foundation and walls with moisture will be minimal.
As a material suitable for the blind area, you can take asphalt, concrete, clay, stone, paving slabs. The first two are the most popular for the blind area and are used most often. This is due to the fact that they require less labor and capital investment. But such surfaces will not look very profitable either.Paving slabs, stone and clay require more time and effort, but all work will justify the excellent result and attractive appearance.
We talked about what drainage is, what types and types of it exist. They also gave advice on self-installation of various types of drainage. If you follow the technology, the process will go quickly and smoothly, and the result will definitely please. Modern and high-quality drainage will protect your home from the negative effects of excessive moisture, make it comfortable, and extend its life.
How to make a trench
Before you make a drainage ditch in the country or in the courtyard of a private house, you need to transfer its device to paper. The drawing will help calculate the required slope, pipe size, determine the type of ditch and its parameters. We recommend that you apply for instructions to the geological organization of your locality with a finished project. In addition to the basic parameters of trenches, you need to calculate soil freezing depth and average annual rainfall.
How to make a drainage ditch in a summer cottage with your own hands: instructions:
Such a drainage ditch device is universal, the technology can be used both in the country house and in a private house or cottage.
It is quite easy to equip drainage around your site to remove excess moisture.
It is important to choose the optimal format according to which the drainage ditch will be prepared along the fence, and determine the required set of materials and tools
Problems to be solved:
- In areas with heavy rainfall, soil erosion is a problem;
- With a high passage of groundwater in the area, the soil is waterlogged;
- With a natural slope of the site, all the water accumulates in the lower part and “pulls” the entire fertile soil layer with it;
- In hilly and mountainous areas, depending on the season, a huge amount of water falls on the site from the territory above the slope;
- Atmospheric precipitation from the road surface accumulates under the fence along the perimeter of the site and can wash away the base and supports of the fence.
In all these situations, the optimal solution is the arrangement of drainage ditches or a productive hidden drainage system around the perimeter of the site.
The main task of the drainage ditch is to collect surface precipitation and remove it from the site.
However, it is not used to transport excess water. , it is rather a localized drainage field, where excess water accumulates and gradually soaks into the ground, without bringing negative consequences to the buildings and the fertile soil layer of the site.
Prerequisites for organizing drainage
Drainage is an expensive system, even if you do not have to pay for the services of specialists, and the owner of the site is ready to do all the work on his own. Therefore, you should figure out how much it is generally needed.
The need for a system device cannot be determined “by eye”, because close to the surface they can groundwater, which becomes a real problem only during floods or heavy rains.
The drainage system is designed to collect and drain groundwater that accumulates in the upper layers due to low filtration qualities of the rocks.
-
Drainage pipe in gravel backfill
-
Corrugated Drain Pipe
-
Gravel backfill - a component of drainage
-
The use of geotextiles in the drainage system
-
Compliance with the slope when arranging drainage
-
Drainage depth
-
Designation of the drainage system on the site
-
Drainage and sewer pipe in one trench
Many areas are located in the lowlands. Waterlogged soil causes root rot, which creates many difficulties in caring for the garden and garden. Plants often infect fungal diseases, “eat” mold. Some crops do not take root in wet soil, and the crop rots in the bud.
Dense clay soils do not absorb water well. This leads to frequent flooding of the underground parts of buildings. Due to the high degree of mineralization, flood and atmospheric waters adversely affect buildings: they destroy building materials and provoke corrosion.
Even high-quality waterproofing is not able to 100% prevent basement flooding, erosion of foundations and plinths. As a result, buildings serve much less than they could.

Construction of closed drainage
Open drainage systems are designed for collecting and discharging rain, flood and melt water, closed drainage systems - to protect underground structures from groundwater.
Determine if you need drainage in the area, can be in several ways:
- Terrain relief. Sites located in lowlands and on steep slopes need a drainage system. Otherwise, fertile soils can be eroded or flooded during rains and floods.
- Puddles. The flat terrain is convenient for construction, but puddles can appear and remain for a long time. This is a clear sign that water is poorly absorbed into the soil. A drainage system should be installed throughout the site.
- Rotting of the root system of plants.If excess liquid remains in vegetable gardens, flower beds and lawns, the plants will rot and get sick.
- moisture loving plants. If one or more types of moisture-loving plants grow on the site, this clearly indicates waterlogging of the soil.
- Flooding of basements and cellars. An obvious "symptom" of the need for drainage is the flooding of foundations and underground building structures.
- Hydrogeological research and observations. If experts have determined that the site has a high GWL, or similar conclusions can be reached during excavation, care should be taken to drain the soil.
Proper styling drainage pipes in the area - the only way to inexpensively and effectively get rid of excess water.
If you contact a specialized company, the system will cost significantly more. It is better to understand the features of the arrangement of drainage and do everything yourself.
To build a drainage system with your own hands, you will need a perforated corrugation or a rigid plastic pipe with slot-like or round holes, which you can drill or cut with your own hands. Gravel backfill and geotextiles will be needed.