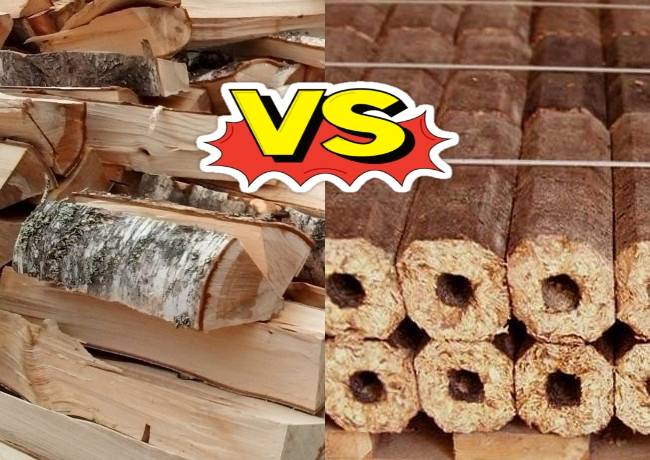
- What are fuel briquettes
- eurofirewood
- Firewood
- Advantages
- Flaws
- The question is the price
- Comparison of calorific value, price and convenience of wood briquettes and firewood
- What are fuel briquettes
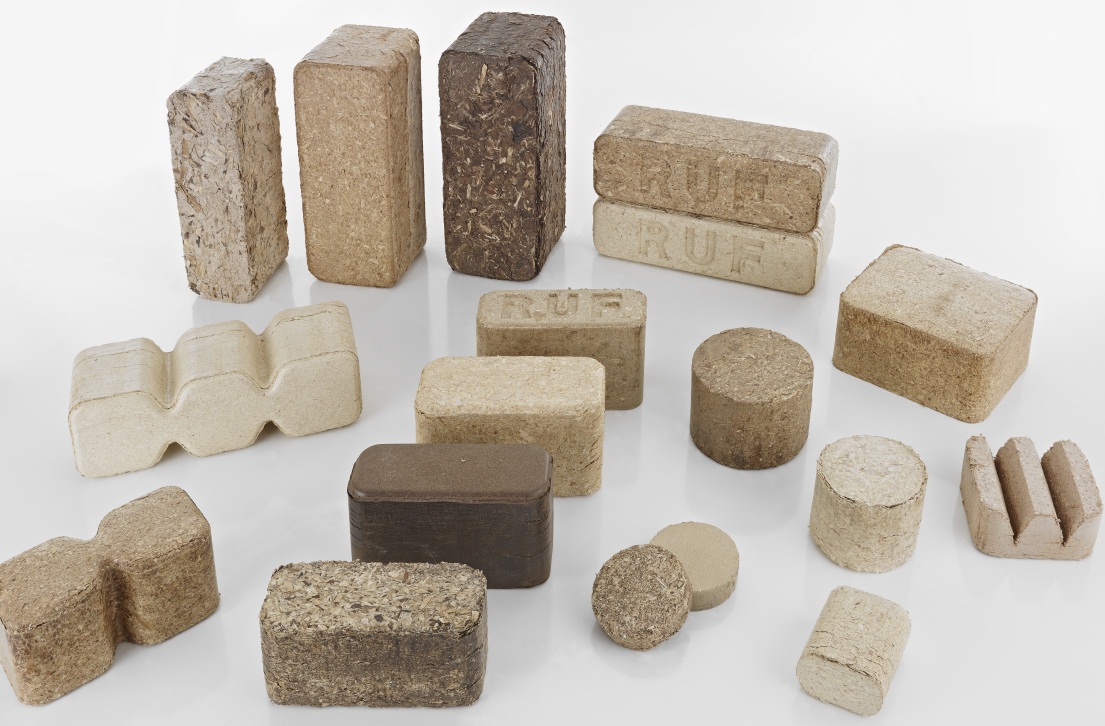
- Differences in form
- Differences in material
- Table comments
- Pros and cons of fuel briquettes
- Economic component
- Advantages of fuel briquettes
- Advantages and disadvantages
- General information
- The result of comparing the firebox with briquettes and firewood
- So in the end it’s cheaper - firewood or briquettes
What are fuel briquettes
Fuel briquettes are a relatively new type solid fuel. They are made by pressing fine-grained raw materials of natural origin. As such raw materials, sawdust, wheat, rice or buckwheat husks, sunflower husks can be used. Besides, pressing fuel briquettes from leaves, straw, reeds, tree bark, needles. Pellets are also made from reeds.
In the process of pressing, strong pressure is exerted on the raw materials from which wood fuel briquettes are made, as a result of which a special substance, lignin, is released. It acts as a connecting component. Thus, no additional chemicals are used in the production of wood pellets, which makes such fuel environmentally friendly.

For production of fuel briquettes different types of raw materials can be used
The release of lignin is possible only in cases where significant pressure is exerted on the raw materials from which wood briquettes are made. It is quite difficult to fulfill this condition when making fuel briquettes with your own hands on home-made equipment, therefore, in such cases, binders are added to the raw mixture. Clay, wallpaper glue, soaked paper or cardboard can be used as the latter.
Pressed briquettes for the furnace can differ not only in the material of manufacture and the degree of density of the internal structure, but also in their geometric parameters, in particular, in shape and size.
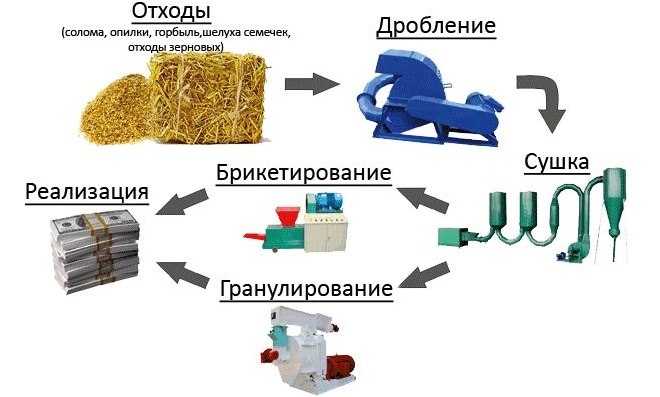
Scheme of the technological process for the production of briquettes
eurofirewood

The composition of the briquette is subjected to strong pressing and drying. Burning fuel briquettes does not harm human health, as they do not contain chemicals. There are three main forms of fuel briquettes: ruf, pini-kay and nestro.
They differ from each other only in the maximum density, which directly depends on the shape, but there are no fundamental differences in the composition and calorific value of the material. Advantages of fuel briquettes:
- Low humidity and high density of the material, which provides high heat transfer and long burning time (up to 4 hours).
- Compared to firewood, they are more compact in storage due to their regular geometric shape.
- They do not spark or shoot when burned, emitting a minimum amount of smoke.
Flaws:
- Briquettes warm up for a long time due to the high density of the material and leave a fairly large amount of ash.
- In the room where the stove is heated with briquettes, there is a pungent specific smell of burning.
- Fuel briquettes have a very low moisture resistance, crumble under improper storage conditions.
- Very unstable to mechanical damage, which leads to the impossibility of their further operation.
- The absence of an aesthetic component when lighting a fireplace. Fuel briquettes are able to burn with a barely smoldering flame.
Firewood

Firewood is the most environmentally friendly and natural type of fuel. In addition, they have been used for space heating since ancient times. Firewood has a high heat capacity, thanks to which it heats up the stove quickly and is able to maintain heat for a long time.
However, specific combustion parameters (including, for example, heat transfer or the height of the flame columns) largely depend on the type of wood used for firewood. For example, poplar burns quickly and gives little heat; linden flares up very poorly, but gives a lot of heat; birch burns well, but it is very poorly stored and after a couple of years it can crumble into dust.
In general, regardless of the variety, firewood is characterized as follows:
- A source of hot fire with clearly visible flames and smoke. They are suitable for use both in stoves - as fuel for heating systems - and in fireplaces, where their burning has a more decorative than practical function;
- Little sensitive to wetness. Of course, wet firewood burns poorly and is not stored very well, as various pests begin to attack them, however, they can be placed under sheds or even in the open air (but only in extreme cases);
- They have different sizes and geometries. Therefore, folding them is not very convenient. To simplify the storage of firewood, woodpile is used - special devices that protect the trunks from rolling and getting wet;
- The quality of combustion depends on the type of wood. Worst of all, willow and poplar are suitable for heating - they burn out quickly and give very little heat. Best of all - birch and oak, but the first is poorly stored, and the second is too valuable a species of wood to use for firewood.
But, regardless of the type of wood, on average, it takes 1-2 hours to burn a log. Of course, for some breeds this period may be shorter, for others it may be longer. But in the vast majority of varieties, firewood burns out in 1-2 hours.
Advantages
- Relatively low price, which can be practically zero at all with hand-made harvesting;
- Do not require special storage conditions. Although, of course, it is better to keep them in a dry, ventilated place, protected from moisture. But you can even store it in the open air - but then they can partially or significantly lose their qualities or crumble under the influence of pests;
- Suitable for burning in fireplaces, as they create a beautiful flame;
- Easily survive shocks, shocks and other mechanical damage.
Flaws
- The quality of combustion depends on the type of wood, storage conditions, drying time and many other external factors;
- They smoke a lot, so they need a well-cleaned chimney;
- They can have different diameters, shapes, sizes and other geometric parameters, as a result of which it is better to use woodpile for storage - they will not allow the firewood to roll.
A good hood (ventilation, chimney) is necessary in any case. When burned, wood emits carbon dioxide, which has a harmful effect on the human body. And cumulative.
The question is the price
Fuel briquettes, like firewood, differ in their cost, which is determined by their quality.Today, companies offer briquettes of two types:
- Eurowood of the highest quality, which are characterized by a high density of 1400 kg / m3. Of the advantages of these briquettes, it is worth noting a longer burning time, the ability to release more heat and leave less ash. In finished form, they are products of a dense structure without cracks.
- Eurofirewood of ordinary quality, which have a density of 1000 kg / m3. Unlike top quality briquettes, these eurofirewood have a layered structure and are more susceptible to damage. During combustion, they release less thermal energy, burn faster and form more sediment.
The unequal prices for fuel briquettes can be explained by the manufacturer's costs for equipment. If the pressing of briquettes is carried out more carefully, then a better end product can be obtained, but at the same time it accelerates the wear of the equipment. All this is taken into account by manufacturers and is included in the final price of the goods.
It is quite logical that high quality eurofirewood will cost more than ordinary briquettes. But at the same time, briquettes of the highest quality will be more economical for the buyer compared to ordinary birch firewood. What can we say about ordinary quality briquettes.
Even if someone thinks that the cost of such fuel is too high compared to firewood, you can always find a way to save money - make them yourself. First you will have to stock up on raw materials for fuel briquettes - twigs and knots that you will surely find on your site. To them you need to add a little clay and pour water.You need to add water little by little so that bars can be formed from this mixture.
Next, you will need forms - without them, you will not be able to make briquette fuel correctly. They need to be filled with the prepared mixture, placed under a press and allowed to lie in the sun for a couple of days. But don't expect homemade oven briquettes to be of the same quality as store-bought ones. However, you can save money this way. Another positive aspect of this solution is that you will be able to clear your site of debris.
Comparison of calorific value, price and convenience of wood briquettes and firewood

Anti-advertising of firewood on the packaging of fuel briquettes - is it true?
We select portions of fuel briquettes and birch firewood equal in weight.
We kindle both firewood and briquettes with the help of newspapers and birch bark.
Wood briquettes are a modern fuel option. It is made from wood waste - compressed wood chips and sawdust. Wood briquettes are an environmentally friendly type of fuel that does not contain any “chemical” additives. Bonding of particles occurs at a large pressure due to lignin is a polymer found in the wood itself. Fuel briquettes are conveniently packed in plastic or in cardboard boxes; they take up little space during transportation and storage. Humidity of fuel briquettes at the correct storage is no more than 8-9%.
When burning briquettes, little ash is formed, they burn longer than firewood, and they emit more heat. At least that's what the ad says. Are there any disadvantages of fuel briquettes? Like everything good and convenient, there is only one drawback - the high price.
Related link: Fire safety of homemade stoves and chimneys
What are fuel briquettes
Briquettes differ in shape and material of manufacture.
Differences in form
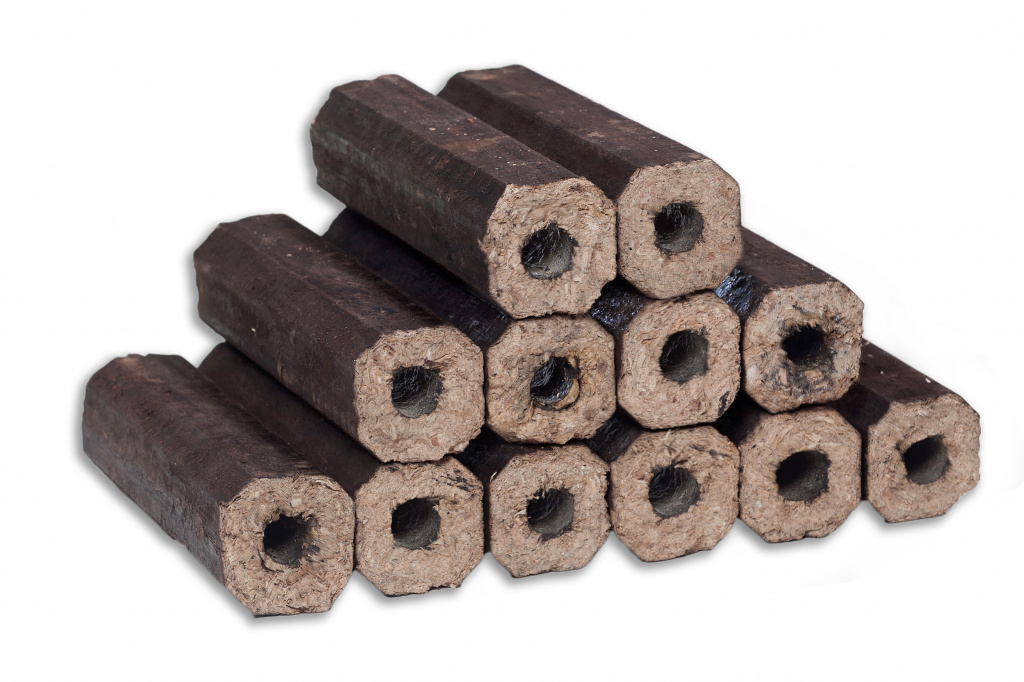
There are three main forms of fuel briquettes: pini-cay, ruf and nestro. Their difference is only in the maximum density that can be achieved in each of the forms. In terms of chemical composition or mass calorific value, there are no differences between European firewood.
Fuel briquettes pini-kay
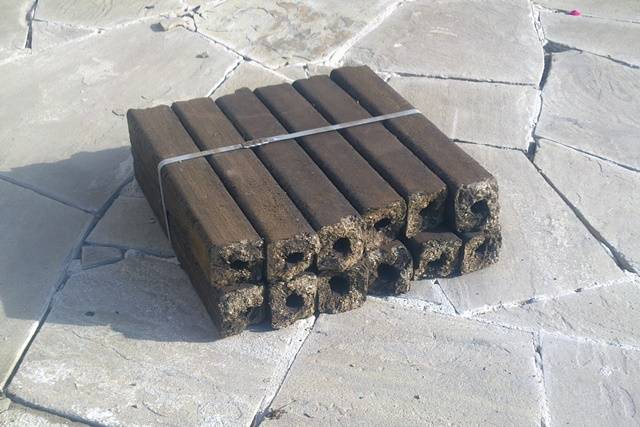

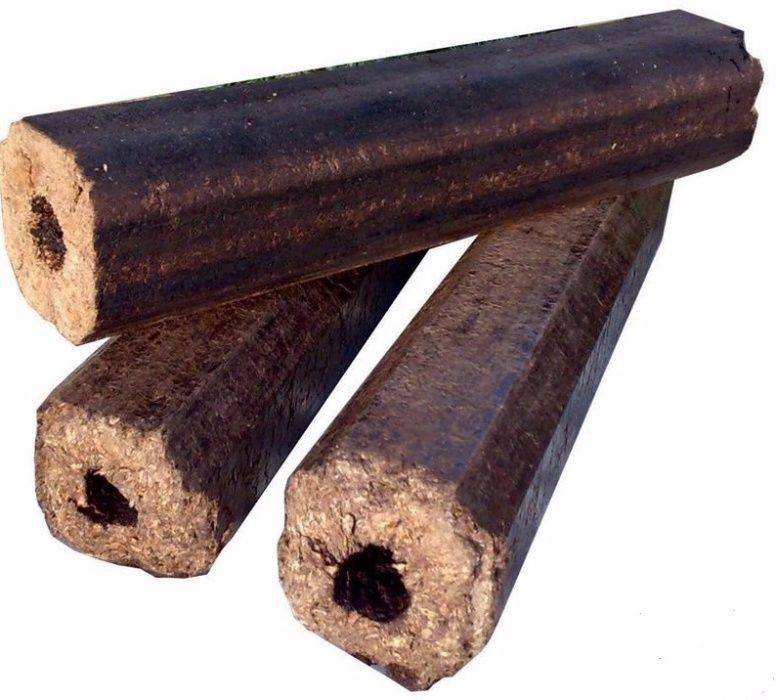
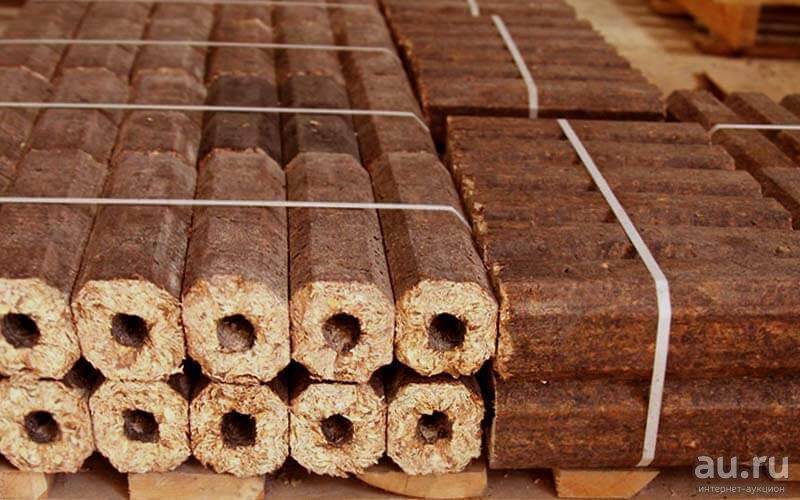
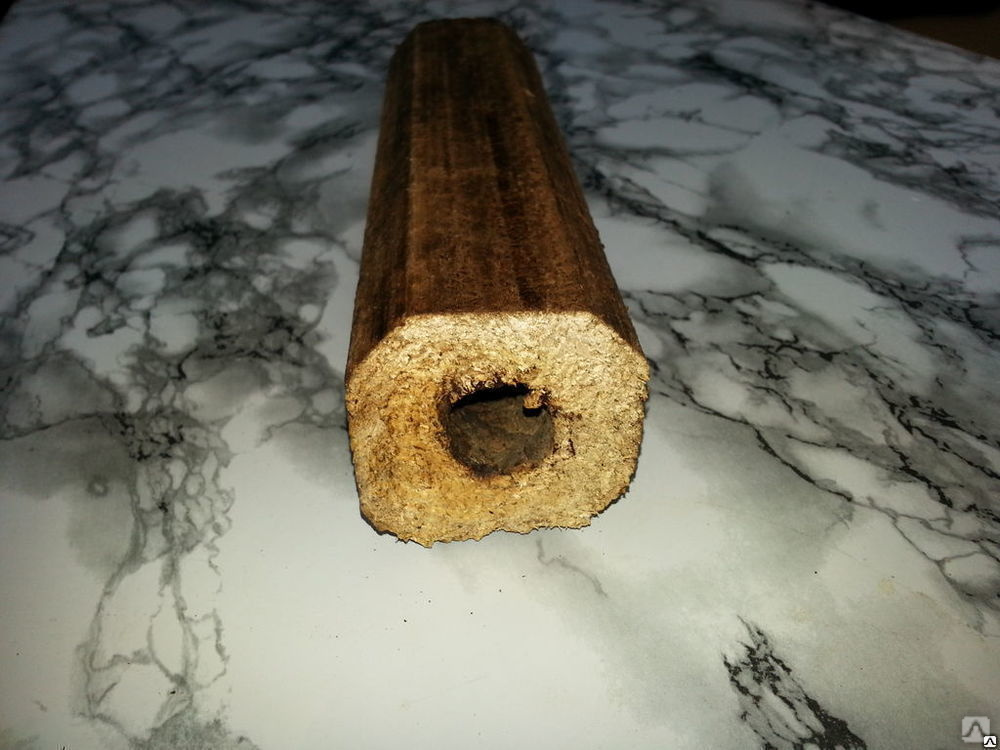
The highest density is from 1.08 to 1.40g/cm3. Section shape - square or hexagon. There is a through hole in the center, which provides better air movement and combustion of the briquette.
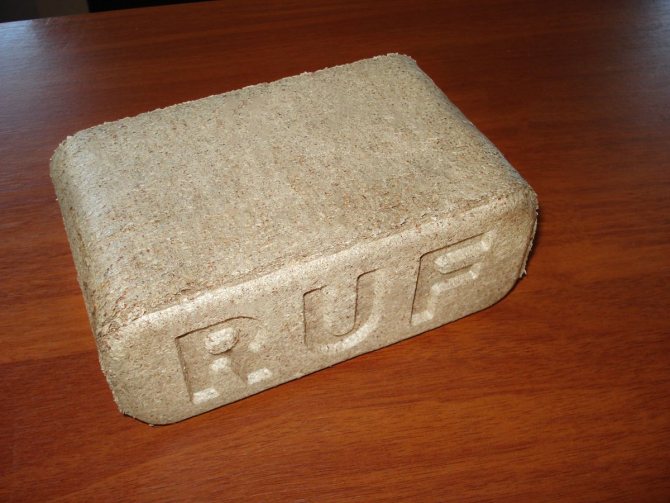
Fuel briquettes RUF
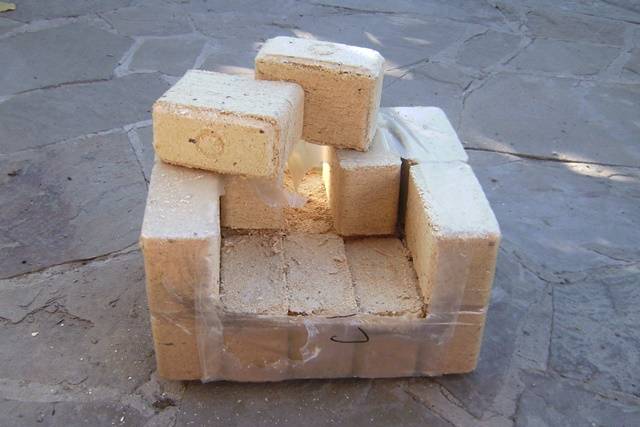

Fuel briquettes from sawdust ruf, in the form of a brick. They have a small size and the lowest density - 0.75-0.8 g / cm3.
Briquettes Nestro
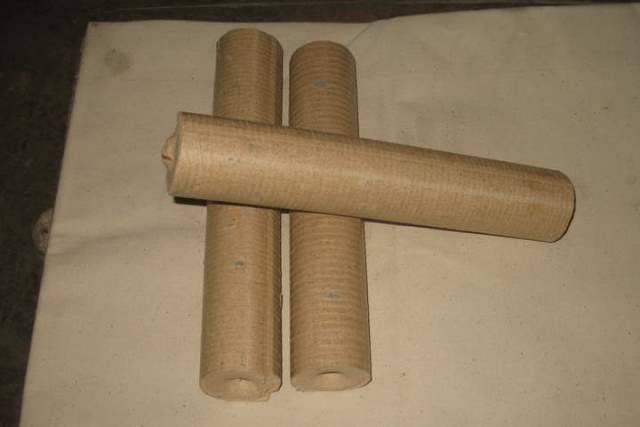

At fuel briquettes Nestro cylinder shape and average density 1 - 1.15 g / cm3.
Peat briquettes
Peat fuel briquettes have a special shape, unlike the others. And because of the high ash content and the presence of other harmful impurities in the composition, they are not recommended for use at home. Such briquettes are suitable for industrial ovens or boilerscapable of running on low quality fuel.
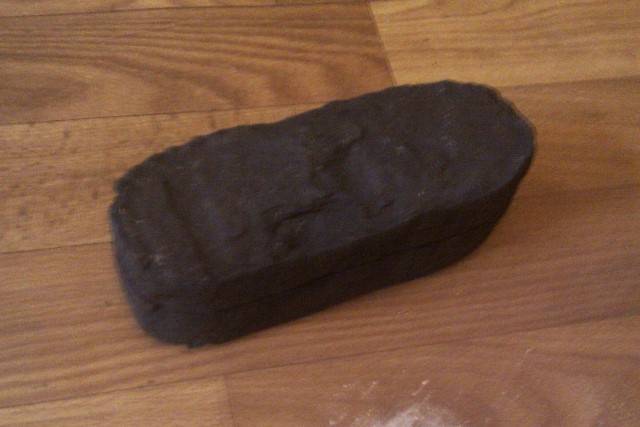

Fuel briquette from peat
Differences in material
Eurowood is made from sawdust, seed husks, rice and buckwheat, straw, tyrsa, peat and other materials. The material affects the calorie content of the fuel briquette, ash content, the amount of soot emitted, the quality and completeness of combustion.
Below in the table is a comparison of the characteristics of briquettes from different materials - seed husks, rice, straw, tyrsa and sawdust. Such an analysis shows not only that briquettes made of different materials differ from each other. But also the fact that even briquettes from the same material differ in quality and properties.
All data are taken from real test reports of fuel briquettes.
Calorie content, humidity, ash content and density of fuel briquettes from different materials.
Table comments
Seed. The highest calorific value of seed husk briquettes is 5151kcal/kg. This is due to their low ash content (2.9-3.6%) and the presence of oil in the briquette, which burns and is of energy value. On the other hand, due to oil, such briquettes more intensively pollute the chimney with soot, and it has to be cleaned more often.
Wood. Wood sawdust briquettes are in second place in terms of calorific value - 5043kcal/kg at 4% humidity and 4341kcal/kg at 10.3% humidity. The ash content of wood briquettes is the same as that of a whole tree - 0.5-2.5%.
Straw. Straw briquettes are not much inferior to seed husks or sawdust and have a good potential for use. They have a slightly lower calorie content - 4740 kcal / kg and 4097 kcal / kg, and a relatively high ash content - 4.8-7.3%.
Tyrsa. Tyrsa is a perennial herb. Such briquettes have a fairly low ash content - 0.7% and good heat transfer of 4400 kcal / kg.
Rice. Rice husk briquettes have the highest ash content - 20% and low calorific value - 3458 kcal / kg. This is even less than that of wood, at 20% humidity.
Pros and cons of fuel briquettes
Now consider eurofirewood. Fuel briquettes are made from woodworking and furniture waste. Chips or sawdust are usually crushed. The resulting wood flour is then pressed under a large pressure and outlet “bricks”, “cylinders”, “tablets” are obtained, glued together with lignin - a natural polymer.

Fuel briquettes are also made from agro-industrial waste - sunflower husks and straw. From peat and coal.

Advantages of wood fuel briquettes:
- High specific heat of combustion - 4500 - 5000 kcal (5.2 - 5.8 kWh per 1 kg)
- A small percentage of humidity - 8 - 10%.
- Low ash content - 1%.
Coal fuel briquettes give more specific heat of combustionthan Eurowood, but they have a higher ash content.
Practice shows that fuel briquettes with a higher density (about 1000 kg/m3) and lower humidity burn longer and better than firewood.
vita01User
I will share my experience. There is no gas. The allocated electric power is not enough. I do not want to be heated by diesel fuel or coal. He heated a solid fuel boiler with dry firewood and briquettes. It is more convenient for me to heat with fuel briquettes, and not to harvest firewood for future use. Dry them. Briquettes take up three times less storage space than firewood. They burn longer. One bookmark is enough for a day. I want to properly insulate the house and then, I think, the briquettes will be enough for 2 days.
But, briquettes are different. The quality is highly dependent on the manufacturer and raw materials. Negligent manufacturers use waste from plywood production with phenol-formaldehyde glue. Waste from sawmills - bark, slab. This affects the quality of eurofirewood and their calorific value.
XUWHUKUser
I bought myself a sample of briquettes in the form of "bricks". Didn't like it. They burn for a long time. There is little heat from them. The boiler does not reach maximum power. Before them I tried fuel briquettes in the form of "cylinders" with a hole in the middle. They burn much better. And give a lot more heat. But they cost more. By the way, even those briquettes in the form of "bricks" still burned better than firewood. Maybe I just got raw briquettes?
Unlike firewood, fuel briquettes are not bought with a margin of 2-3 years in advance. The fresher the product, i.e. just arrived from production, the better. During long-term storage, even eurofirewood packed in a protective film gains excess moisture, which worsens their calorific value.

According to Andreyraduga, when buying fuel briquettes, pay attention not to the name, but to what they are made of. The user, for the fireplace, bought different briquettes
For example, brown "cylinders" with a hole in the middle, although the most expensive, burned out very quickly. “Bricks”, made not from shavings (this can be seen by eye), but from wood flour and tightly pressed, burn for a long time and hot and give a little ash.
Ham59User
He heated a house with an area of 210 sq. m birch firewood, but there is a lot of tar about them. I bought fuel briquettes "bricks". For a month, one pallet with euro firewood left + bought 20 packs. Total spent 6100 rubles. If it is 10 - -15 ° C outside, then one pallet of eurowood is enough for heating. Well, once a week, I burn 2-3 aspen logs to clean the boiler and chimney. Used briquettes from coniferous breeds. Fraction - almost sawdust. They burn very quickly. Unsuitable. Birch briquettes in Perm cost 55 rubles. for 1 pack of 12 pcs. There are 96 packs on a pallet. Total - 5280 rubles. Coniferous briquettes - 86 rubles. for 1 pack. The pallet costs 8256 rubles. Not beneficial. For comparison: when heating with electricity, 2 heating elements of 3 kW, it took 10,000 - 12,000 rubles per month.
Economic component
When making a choice between ordinary firewood and fuel briquettes, one should also take into account the cost of both types of solid fuel. Euro firewood, which today is produced by many domestic manufacturers, on average costs 2-3 times more than ordinary firewood.Meanwhile, inexpensive ordinary firewood is quite rarely homogeneous in quality.
Most often, the total mass of firewood contains only 20-30% of well-dried logs, while up to 50% of the total mass of purchased firewood can be logs with increased humidity, and 20-30% - stale firewood of not very high quality. If we talk about fuel briquettes, then the moisture content of such fuel, for the manufacture of which well-dried sawdust is used, does not exceed 9%.
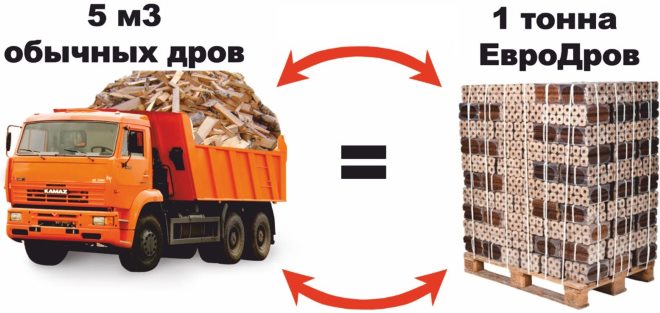
Briquettes clearly outperform firewood in terms of transportation
- The burning time of fuel briquettes, which is about two hours, is almost twice the period during which ordinary firewood burns.
- The heat transfer of firewood, which is especially noticeable when located in the immediate vicinity of the heating boiler, is much higher than the similar parameter of fuel briquettes.
- The amount of ash remaining after the combustion of fuel briquettes is about ¼ less than the amount of combustion products remaining after burning ordinary firewood.
Thus, pellets are better used as fuel. for long burning boilers, and ordinary firewood is more suitable for kindling fireplaces. In any case, when making a choice in favor of one or another type of solid fuel, one should be guided by all of the above facts, and also take into account the type of heating equipment.
Advantages of fuel briquettes
Fuel briquettes are distinguished by the ability of high heat transfer. Their calorific value is 4600-4900 kcal/kg. For comparison, dry birch firewood has a calorific value of about 2200 kcal/kg. And birch wood of all types of wood has the highest heat transfer rates.Therefore, as we see, fuel briquettes give 2 times more heat than firewood. In addition, throughout the combustion, they maintain a constant temperature.
Long burning time
Briquettes are also characterized by a rather high density, which is 1000-1200 kg/m3. Oak is considered the most dense wood applicable for heating. Its density is 690 kg/cu.m. Again we see a big difference in favor of fuel briquettes.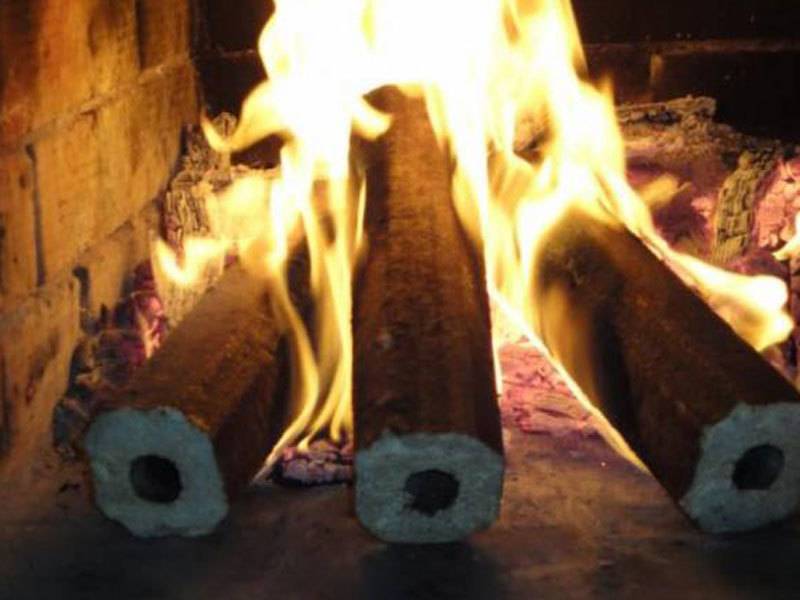 Good density just contributes to the long-term burning of fuel briquettes. They are able to give a steady flame from laying to complete combustion within 2.5-3 hours. With the supported smoldering mode, one portion of high-quality briquettes is enough for 5-7 hours. This means that you will need to add them to the stove 2-3 times less than if you fired wood.
Good density just contributes to the long-term burning of fuel briquettes. They are able to give a steady flame from laying to complete combustion within 2.5-3 hours. With the supported smoldering mode, one portion of high-quality briquettes is enough for 5-7 hours. This means that you will need to add them to the stove 2-3 times less than if you fired wood.
Low humidity
Humidity of fuel briquettes is no more than 4-8%, while the minimum moisture content of wood is 20%. The briquettes have such a low moisture content due to the drying process, which is an essential step in the production.
Due to their low humidity, briquettes reach a high temperature during combustion, which contributes to their high heat transfer.
Minimum ash content
Compared to wood and coal, the ash content of briquettes is much less. After burning, they leave only 1% ash. Burning coal leaves up to 40% ash. Moreover, the ashes of the briquettes can still be used as fertilizer, and the ashes of coal will still have to be disposed of.
The advantage of heating with briquettes is that the cost of cleaning and maintaining the fireplace or stove is much reduced.
Environmental friendliness
Choice of fuel briquettes for heating in the house is a great option for people who care about their health.Briquettes practically do not emit smoke and other harmful volatile substances, so you can fire the stove without charcoal even with a low chimney draft.
Unlike coal, the combustion of briquettes does not form dust that settles in the room. Also, since briquettes are fuel produced from waste, there is less damage to the environment.
Ease of storage

Fuel briquettes are convenient both to use and store. Unlike shapeless firewood, briquettes have a fairly regular and compact shape. Therefore, even if you try to put firewood as carefully as possible into a compact woodpile, they will still take up 2-3 times more space than briquettes.
No condensation on chimneys
Since firewood has a higher moisture content, during combustion it forms condensate on the walls of the chimney. Depending on the moisture content of the wood, there will be more or less condensation, respectively. What is bad about condensate in a chimney is that it narrows its working section over time. With heavy condensate, after one season you will notice a strong drop in draft in the chimney.
8% humidity of the briquettes practically does not form condensate, consequently, the chimney's working capacity is maintained longer.
Advantages and disadvantages
To understand how good fuel briquettes are, you should consider their positive and negative sides.

The pros are as follows:
- Since eurofirewood has the correct shape, it is very convenient to store them.
- Fuel briquettes are much more calorific than firewood. This results in savings on raw materials.
- Suitable for all ovens and gas boilers. Due to the long burning of compressed sawdust, the addition of new portions of raw materials occurs much less frequently.
- Burning is even and silent, small coals do not fly around. When using raw materials, the emission of smoke and the formation of tar, ash is insignificant. This leads to a reduction in labor costs for cleaning and cleaning chimneys.
- Depending on the method of manufacturing eurofirewood, their shelf life is from one to 5 years.
- The bars do not contain chemicals, therefore they are considered an environmentally friendly product.
- During one heating season, 1.5-2 times less briquette fuel is used compared to conventional firewood.
- Combustion of eurobriquettes occurs slowly and gently. This releases a lot of heat.
In addition to positive qualities, compressed products have some disadvantages:
- Avoid contact with water during storage.
- Some species are stored for no more than one year.
- The cost of raw materials is quite high.
General information
Let's first understand what fuel briquettes are and how they are made in order to understand the essence of this alternative fuel.
Fuel briquettes are known to most people under the name "euro firewood". Like ordinary firewood, briquettes are considered solid fuel and are used to kindle stoves and fireplaces. They are made from various natural materials, worn down to sawdust and pressed on a machine under high pressure to a given shape. Usually, either a rectangular shape or log imitation is used.
Currently, all fuel briquettes, eurofirewood, can be divided into three types that do not differ too much from each other:
- Eurobriquettes RUF (Ruf);
- Eurobriquettes Pini Kay;
- Eurobriquettes Nestro.

Warehouse for RUF euro briquettes
The first option can be considered classic eurofirewood.They are created according to the technology described above from sawdust, which are compressed into pretty rectangles, like small bricks. Fuel briquettes for the stove in this design are inexpensive, so this type can be considered optimal in terms of price and quality.
The second option is not much different from the first, just here, at the last stages of production, the firing of eurobriquettes is added, which is necessary to create the possibility of increasing the shelf life of sawdust products. Roasting allows you to create some kind of shell, protection from moisture and other unpleasant influences, which ensures long-term preservation, and most importantly, the integrity of the briquette.
The third option is a kind of hybrid of the first and second species. These briquettes have a regular cylindrical shape, similar to poles, but they are not fired on the outside.
Like all fuel briquettes, Pini-kei products are created in a rectangular shape, similar to firewood. However, unlike ordinary firewood, they have a through hole in the center.

Warehouse of eurobriquettes Pini-Key
Another procedure with raw materials affects the price, which for Pini-Key euro briquettes is slightly higher than the RUF analogue. However, no matter what options you choose for a fireplace or stove, they will still cost inexpensively, cheaper than ordinary firewood.
How much do fuel briquettes cost, approximately a couple of thousand rubles per ton, which is quite comparable to the cost of several tons of ordinary wood, and we will consider what is better to choose next.
The result of comparing the firebox with briquettes and firewood
Fuel briquettes do burn longer than birch firewood, but the difference is not as great as the description of the briquettes claims. But at the same time, the intensity of heat release during the combustion of firewood is incomparably greater.The amount of ash after briquettes is actually less than after birch firewood, but not at times, as stated, but only by 25-33%.
Thus, in my subjective opinion, a 2-3-fold excess of the price of fuel briquettes over birch firewood in the current price conditions with constant operation does not justify itself economically. Since a large flame is not obtained when burning inexpensive fuel briquettes, their use in fireplaces and in fireplace stoves, which are also installed for aesthetic pleasure from contemplating fire, does not make much sense.
At the same time, fuel briquettes have a number of undeniable advantages: they are compactly packed, leave little debris and less ash. The long burning time allows less fuel to be added to the stove or fireplace. Although ordinary firewood is better for quickly warming up a cold house, fuel briquettes can be successfully used to maintain the desired temperature in the house.
Since I come to the dacha in the heating season in short trips, it’s easier for me to buy several packages of fuel briquettes in the supermarket than to buy a car of firewood for the season. In the cold season in my house with an area of 120 m 2, which is well insulated, it takes two packs of fuel briquettes (20 kg) to warm up on the first day, and to maintain the temperature on the following days - 1 pack per day with slight frosts and 1.5 -2 packs per day in severe frosts (subject to additional heating by several electric convectors).
Thus, each type of fuel has its advantages and disadvantages. Knowing about them, everyone can choose the best type of fuel for themselves, depending on the mode of operation of the house and personal preferences.
Weichai drill chop wood splitting tool for splitting cone splitting…
303.6 rub.Free shipping ★★ ★★ ★★ ★★ ★★ (4.60) | Orders (13)
Recently, it has become fashionable to use not only traditional fuel in the form of firewood for kindling stoves, but also other, alternative options. For example, natural materials pressed under high temperature are becoming increasingly popular: sawdust, peat, straw, etc. Created from biological waste, 100% natural and environmentally friendly, fuel briquettes allow you to effectively and inexpensively drink a house, a bathhouse.
In this article we will talk about how to make fuel briquettes with your own hands from improvised materials. To do this, you need to buy or make a suitable processing equipment waste products and learn how to properly produce eurofirewood. Making fuel briquettes with your own hands will allow you to solve several problems at once:
- get rid of waste;
- obtain efficient and technologically advanced fuel for home heating;
- save money on wood.
Homemade fuel briquettes can be of any shape
So in the end it’s cheaper - firewood or briquettes
The main thing in firewood is not weight and cost, but the cost of a unit of heat. You can burn 5kg and 10kg of different firewood, but get the same amount of heat. Let's carry out a simple calculation (figures as of the winter of 2013):
- 1 m3 of firewood weighs 500-600kg and costs 550 UAH;
- 1 m3 of briquettes weighs 1000 kg and costs 1800 UAH;
1 m3 of wood contains 40-50% less real fuel than the same volume of briquettes. Let's determine the cost of 1 ton of firewood.
1 ton of wood = 1.66m3. Its cost will be 550 * 1.66 = 913 hryvnia.
Now let's calculate the cost of 1W of heat emitted by firewood and briquettes
| Firewood | Briquettes | |
| Price for 1 ton | 913 UAH | 1800 UAH |
| The amount of heat | 2900 kcal-h/ | 5200 Wh |
| Price for 1W | 0.31 UAH | 0.35 UAH |
As a result, it can be seen that the difference is insignificant - 4 kopecks per 1 watt of thermal energy. It turns out that the effect of firewood and briquettes is almost the same, despite the significant difference in price at first glance.
It is important to take into account:
- Poor wood quality. Often, when buying firewood, you can stumble upon freshly sawn wood with a moisture content of 40-50%. The calorific value of such firewood is even less
- Firewood takes up more space, which means that their transportation will cost even more.



















































