- The concept of hydraulic calculation
- Pump
- Calculation formula
- Room sizes and building heights
- 1 Parameter importance
- Thermal loads
- Thermal calculation of heating: general procedure
- Hydraulic calculation
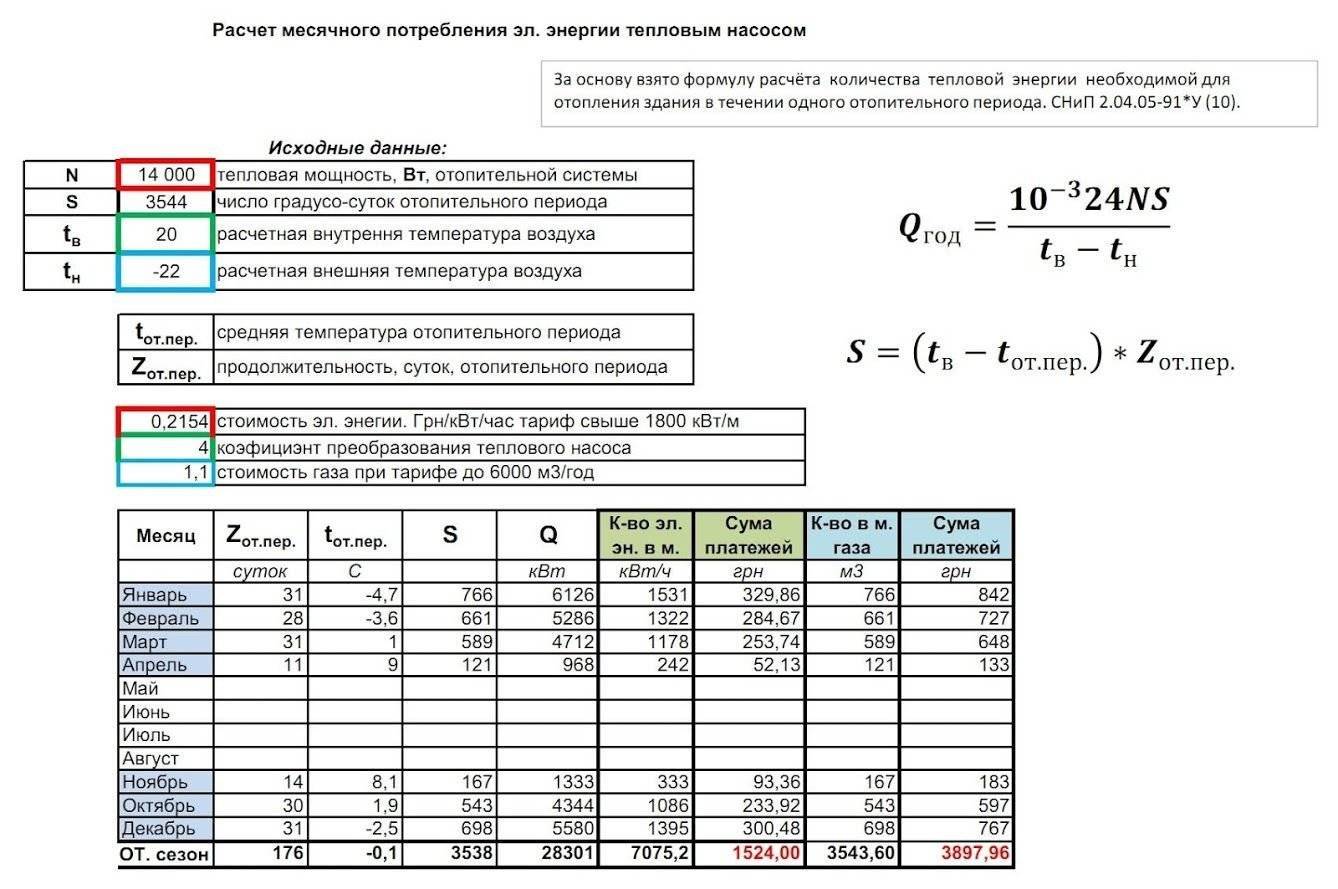
- We consider the heat consumption by quadrature
- Calculation of operating costs of the heating circuit ↑
- Costs of operating an electric boiler ↑
- Liquid fuel boiler, expenses ↑
- Annual payment for firewood ↑
- Calculation of heating costs with a gas boiler
- Possible mechanisms to stimulate the revision of contractual thermal loads of consumers (subscribers)
The concept of hydraulic calculation
The determining factor in the technological development of heating systems has become the usual savings on energy. The desire to save money makes us take a more careful approach to the design, choice of materials, methods of installation and operation of heating for a home.
Therefore, if you decide to create a unique and, first of all, economical heating system for your apartment or house, then we recommend that you familiarize yourself with the calculation and design rules.
Before defining the hydraulic calculation of the system, it is necessary to clearly and clearly understand that the individual heating system of an apartment and a house is conventionally located an order of magnitude higher than the central heating system of a large building.
A personal heating system is based on a fundamentally different approach to the concepts of heat and energy.

The essence of the hydraulic calculation lies in the fact that the flow rate of the coolant is not set in advance with a significant approximation to the real parameters, but is determined by linking the diameters of the pipeline with the pressure parameters in all the rings of the system
It suffices to make a trivial comparison of these systems in terms of the following parameters.
- The central heating system (boiler-house-apartment) is based on standard types of energy carrier - coal, gas. In a stand-alone system, almost any substance that has a high specific heat of combustion, or a combination of several liquid, solid, granular materials can be used.
- DSP is built on the usual elements: metal pipes, "clumsy" batteries, valves. An individual heating system allows you to combine a variety of elements: multi-section radiators with good heat dissipation, high-tech thermostats, different types of pipes (PVC and copper), taps, plugs, fittings, and of course your own more economical boilers, circulation pumps.
- If you enter the apartment of a typical panel house built 20-40 years ago, we see that the heating system is reduced to the presence of a 7-section battery under the window in each room of the apartment plus a vertical pipe through the whole house (riser), with which you can “communicate” with upstairs/downstairs neighbors. Whether it's an autonomous heating system (ACO) - allows you to build a system of any complexity, taking into account the individual wishes of the residents of the apartment.
- Unlike DSP, a separate heating system takes into account a fairly impressive list of parameters that affect transmission, energy consumption and heat loss. Ambient temperature conditions, the required temperature range in the rooms, the area and volume of the room, the number of windows and doors, the purpose of the rooms, etc.
Thus, the hydraulic calculation of the heating system (HRSO) is a conditional set of calculated characteristics of the heating system, which provides comprehensive information about such parameters as pipe diameter, number of radiators and valves.

This type of radiators was installed in most panel houses in the post-Soviet space. Savings on materials and the lack of a design idea “on the face”
GRSO allows you to choose the right water ring pump (heating boiler) for transporting hot water to the final elements of the heating system (radiators) and, in the end, to have the most balanced system, which directly affects financial investments in home heating.

Another type of heating radiator for DSP. This is a more versatile product that can have any number of ribs. So you can increase or decrease the heat exchange area
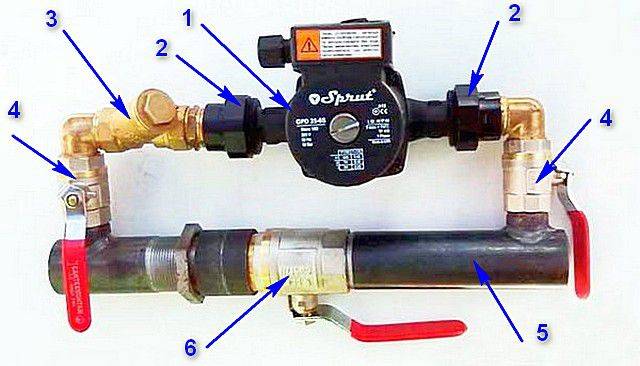
Pump
How to choose the optimal head and pump performance?
It's easy with pressure. Its minimum value of 2 meters (0.2 kgf / cm2) is sufficient for a contour of any reasonable length.
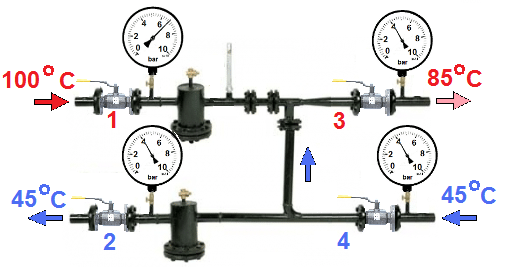
The difference between the mixture (top right) and the return (bottom) is not recorded by any pressure gauge.
Productivity can be calculated according to the simplest scheme: the entire volume of the circuit must turn around three times per hour.So, for the amount of coolant we have given above of 400 liters, a reasonable minimum performance of the circulation pump of the heating system at a working pressure should be 0.4 * 3 = 1.2 m3 / h.
For individual sections of the circuit, supplied with their own pump, its performance can be calculated using the formula G=Q/(1.163*Dt).
In it:
- G is the cherished value of productivity in cubic meters per hour.
- Q is the thermal power of the heating system section in kilowatts.
- 1.163 is a constant, the average heat capacity of water.
- Dt is the temperature difference between the supply and return pipelines in degrees Celsius.
So, for a circuit with a thermal power of 5 kilowatts at a 20-degree delta between supply and return, a pump with a capacity of at least 5 / (1.163 * 20) \u003d 0.214 m3 / hour is needed.

Pump parameters are usually indicated in its labeling.
Calculation formula
Thermal energy consumption standards
Thermal loads are calculated taking into account the power of the heating unit and the heat losses of the building. Therefore, in order to determine the capacity of the designed boiler, necessary heat loss of the building multiply by a multiplier of 1.2. This is a kind of margin equal to 20%.
Why is this ratio needed? With it, you can:
- Predict the drop in gas pressure in the pipeline. After all, in winter there are more consumers, and everyone tries to take more fuel than the rest.
- Vary the temperature inside the house.
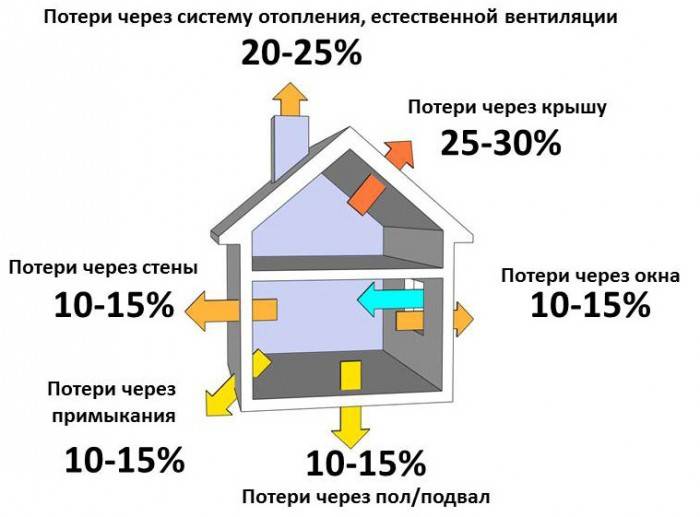
We add that heat losses cannot be distributed evenly throughout the building structure. The difference in indicators can be quite large. Here are some examples:
- Up to 40% of the heat leaves the building through the outer walls.
- Through floors - up to 10%.
- The same applies to the roof.
- Through the ventilation system - up to 20%.
- Through doors and windows - 10%.
So, we figured out the design of the building and made one very important conclusion that heat losses that need to be compensated depend on the architecture of the house itself and its location. But much is also determined by the materials of the walls, roof and floor, as well as the presence or absence of thermal insulation. This is an important factor
This is an important factor.
For example, let's determine the coefficients that reduce heat loss, depending on window structures:
- Ordinary wooden windows with ordinary glass. To calculate the thermal energy in this case, a coefficient equal to 1.27 is used. That is, through this type of glazing, thermal energy leaks, equal to 27% of the total.
- If plastic windows with double-glazed windows are installed, then a coefficient of 1.0 is used.
- If plastic windows are installed from a six-chamber profile and with a three-chamber double-glazed window, then a coefficient of 0.85 is taken.
We go further, dealing with the windows. There is a certain relationship between the area of \u200b\u200bthe room and the area of \u200b\u200bwindow glazing. The larger the second position, the higher the heat loss of the building. And here there is a certain ratio:
- If the window area in relation to the floor area has only a 10% indicator, then a coefficient of 0.8 is used to calculate the heat output of the heating system.
- If the ratio is in the range of 10-19%, then a coefficient of 0.9 is applied.
- At 20% - 1.0.
- At 30% -2.
- At 40% - 1.4.
- At 50% - 1.5.
And that's just the windows. And there is also the effect of the materials that were used in the construction of the house on thermal loads.Let's arrange them in a table where wall materials will be located with a decrease in heat losses, which means that their coefficient will also decrease:
Type of building material
As you can see, the difference from the materials used is significant. Therefore, even at the stage of designing a house, it is necessary to determine exactly what material it will be built from. Of course, many developers build a house based on the budget allocated for construction. But with such layouts, it is worth reconsidering it. Experts assure that it is better to invest initially in order to later reap the benefits of savings from the operation of the house. Moreover, the heating system in winter is one of the main items of expenditure.
Room sizes and building heights
Heating system diagram
So, we continue to understand the coefficients that affect the formula for calculating heat. How does room size affect heat loads?
- If the ceiling height in your house does not exceed 2.5 meters, then a coefficient of 1.0 is taken into account in the calculation.
- At a height of 3 m, 1.05 is already taken. A slight difference, but it significantly affects heat loss if the total area of \u200b\u200bthe house is large enough.
- At 3.5 m - 1.1.
- At 4.5 m -2.
But such an indicator as the number of storeys of a building affects the heat loss of a room in different ways. Here it is necessary to take into account not only the number of floors, but also the location of the room, that is, on which floor it is located. For example, if this is a room on the ground floor, and the house itself has three or four floors, then a coefficient of 0.82 is used for the calculation.
When moving the room to the upper floors, the rate of heat loss also increases. In addition, you will have to take into account the attic - is it insulated or not.
As you can see, in order to accurately calculate the heat loss of a building, it is necessary to determine various factors. And all of them must be taken into account. By the way, we have not considered all the factors that reduce or increase heat losses. But the calculation formula itself will mainly depend on the area of \u200b\u200bthe heated house and on the indicator, which is called the specific value of heat losses. By the way, in this formula it is standard and equal to 100 W / m². All other components of the formula are coefficients.
1 Parameter importance
Using the heat load indicator, you can find out the amount of heat energy needed to heat a particular room, as well as the building as a whole. The main variable here is the power of all heating equipment that is planned to be used in the system. In addition, it is required to take into account the heat loss of the house.
The ideal situation seems to be in which the capacity of the heating circuit allows not only to eliminate all losses of heat energy from the building, but also to provide comfortable living conditions. In order to correctly calculate the specific heat load, it is necessary to take into account all the factors that affect this parameter:
- Characteristics of each structural element of the building. The ventilation system significantly affects the loss of heat energy.
- Building dimensions. It is necessary to take into account both the volume of all rooms and the area of windows of structures and external walls.
- climate zone. The indicator of the maximum hourly load depends on the temperature fluctuations of the ambient air.
Thermal loads
Thermal load - the amount of heat to compensate for the heat loss of the building (premises), taking into account the use of heating devices in peak temperature conditions.
Power, a set of capacities of heating devices involved in heating the building, providing a comfortable temperature for living, doing business. The capacity of the heat sources should be sufficient to maintain the temperature on the coldest days of the heating season.
The heat load is measured in W, Cal / h, - 1W \u003d 859.845 Cal / h. Calculation is a complex process. It is difficult to perform independently, without knowledge, skills.
The internal thermal regime depends on the design of the building load. Errors have a negative impact on heat consumers connected to the system. Probably everyone on cold, winter evenings, wrapped in a warm blanket, complained about the heating network with cold batteries - the result of a discrepancy with the actual thermal conditions.
The heat load is formed taking into account the number of heating devices (radiator batteries) to maintain heat, with the following parameters:
- heat loss of the building, which consists of the indicators of thermal conductivity of the building materials of the box, the roof of the house;
- during ventilation (forced, natural);
- hot water supply facility;
- additional heat costs (sauna, bath, household needs).
With the same requirements for the building, in different climatic zones, the load will be different. Influenced by: location relative to sea level, the presence of natural barriers to cold winds, and other geological factors.
Thermal calculation of heating: general procedure
The classical thermal calculation of a heating system is a summary technical document that includes the required step-by-step standard calculation methods.
But before studying these calculations of the main parameters, you need to decide on the concept of the heating system itself.
The heating system is characterized by forced supply and involuntary removal of heat in the room.
The main tasks of calculating and designing a heating system:
- most reliably determine heat losses;
- determine the amount and conditions for the use of the coolant;
- select the elements of generation, movement and heat transfer as accurately as possible.
When building a heating system, it is necessary to initially collect various data about the room / building where the heating system will be used. After performing the calculation of the thermal parameters of the system, analyze the results of arithmetic operations.
Based on the data obtained, the components of the heating system are selected with subsequent purchase, installation and commissioning.

Heating is a multi-component system for ensuring the approved temperature regime in a room/building. It is a separate part of the communications complex of a modern residential building
It is noteworthy that the indicated method of thermal calculation makes it possible to accurately calculate a large number of quantities that specifically describe the future heating system.
As a result of the thermal calculation, the following information will be available:
- number of heat losses, boiler power;
- the number and type of thermal radiators for each room separately;
- hydraulic characteristics of the pipeline;
- volume, speed of the heat carrier, power of the heat pump.
Thermal calculation is not a theoretical outline, but quite accurate and reasonable results, which are recommended to be used in practice when selecting the components of a heating system.
Hydraulic calculation
So, we have decided on heat losses, the power of the heating unit has been selected, it remains only to determine the volume of the required coolant, and, accordingly, the dimensions, as well as the materials of the pipes, radiators and valves used.
First of all, we determine the volume of water inside the heating system. This will require three indicators:
- The total power of the heating system.
- Temperature difference at the outlet and inlet to the heating boiler.
- Heat capacity of water. This indicator is standard and equal to 4.19 kJ.
Hydraulic calculation of the heating system
The formula is as follows - the first indicator is divided by the last two. By the way, this type of calculation can be used for any section of the heating system.
Here it is important to break the line into parts so that in each the speed of the coolant is the same. Therefore, experts recommend making a breakdown from one shut-off valve to another, from one heating radiator to another. Now we turn to the calculation of the pressure loss of the coolant, which depend on the friction inside the pipe system
For this, only two quantities are used, which are multiplied together in the formula. These are the length of the main section and specific friction losses
Now we turn to the calculation of the pressure loss of the coolant, which depends on the friction inside the pipe system. For this, only two quantities are used, which are multiplied together in the formula. These are the length of the main section and specific friction losses.
But the pressure loss in the valves is calculated using a completely different formula. It takes into account indicators such as:
- Heat carrier density.
- His speed in the system.
- The total indicator of all coefficients that are present in this element.
In order for all three indicators, which are derived by formulas, to approach standard values, it is necessary to choose the right pipe diameters. For comparison, we will give an example of several types of pipes, so that it is clear how their diameter affects heat transfer.
- Metal-plastic pipe with a diameter of 16 mm. Its thermal power varies in the range of 2.8-4.5 kW. The difference in the indicator depends on the temperature of the coolant. But keep in mind that this is a range where the minimum and maximum values are set.
- The same pipe with a diameter of 32 mm. In this case, the power varies between 13-21 kW.
- Polypropylene pipe. Diameter 20 mm - power range 4-7 kW.
- The same pipe with a diameter of 32 mm - 10-18 kW.
And the last is the definition of a circulation pump. In order for the coolant to be evenly distributed throughout the heating system, it is necessary that its speed be at least 0.25 m /sec and no more 1.5 m/s In this case, the pressure should not be higher than 20 MPa. If the coolant velocity is higher than the maximum proposed value, then the pipe system will work with noise. If the speed is less, then airing of the circuit may occur.
We consider the heat consumption by quadrature
For an approximate estimate of the heating load, the simplest thermal calculation is usually used: the area of \u200b\u200bthe building is taken according to the external measurement and multiplied by 100 W. Accordingly, the heat consumption of a country house of 100 m² will be 10,000 W or 10 kW. The result allows you to choose a boiler with a safety factor of 1.2-1.3, in in this case, the power of the unit is taken equal to 12.5 kW.
We propose to perform more accurate calculations, taking into account the location of rooms, the number of windows and the building region.So, with a ceiling height of up to 3 m, it is recommended to use the following formula:

The calculation is carried out for each room separately, then the results are summarized and multiplied by the regional coefficient. Explanation of formula designations:
- Q is the desired load value, W;
- Spom - the square of the room, m²;
- q - indicator of specific thermal characteristics, related to the area of the room, W / m²;
- k is a coefficient that takes into account the climate in the area of residence.
In an approximate calculation for the total quadrature, the indicator q \u003d 100 W / m². This approach does not take into account the location of the rooms and the different number of light openings. The corridor inside the cottage will lose much less heat than the corner bedroom with windows of the same area. We propose to take the value of the specific thermal characteristic q as follows:
- for rooms with one outer wall and a window (or door) q = 100 W/m²;
- corner rooms with one light opening - 120 W / m²;
- the same, with two windows - 130 W / m².
How to choose the right q value is clearly shown on the building plan. For our example, the calculation looks like this:
Q \u003d (15.75 x 130 + 21 x 120 + 5 x 100 + 7 x 100 + 6 x 100 + 15.75 x 130 + 21 x 120) x 1 \u003d 10935 W ≈ 11 kW.
As you can see, the refined calculations gave a different result - in fact, 1 kW of thermal energy will be spent on heating a particular house of 100 m² more. The figure takes into account the heat consumption for heating outdoor air that enters the dwelling through openings and walls (infiltration).
Calculation of operating costs of the heating circuit ↑
Operating costs are the main cost component.House owners face the need to cover it every year, and they spend only once on the construction of communications. It often happens that in an effort to reduce the cost of organizing heating, the owner then pays many times more than his prudent neighbors, who made the calculation of heat consumption for heating before designing the heating system and before purchasing the boiler.
Costs of operating an electric boiler ↑
Electric heating installations are preferred due to ease of installation, lack of requirements for chimneys, ease of maintenance, and the presence of built-in security and control systems.

Electric boiler - silent, convenient equipment
Z,11 rub. × 50400 = 156744 (rubles per year will need to be paid to electricity suppliers)
The organization of a heating network with an electric boiler will cost less than all schemes, but electricity is the most expensive energy resource. In addition, not in all settlements there is a possibility of its connection. Of course, you can buy a generator if you do not plan to connect to centralized sources of electricity in the next decade, but the cost of building a heating circuit will be significantly increased. And the calculation will need to include fuel for the generator.
You can order the connection of the site to the centralized power grid. You will need to pay 300 - 350 thousand for this along with the project. It is worth thinking about what is cheaper.
Liquid fuel boiler, expenses ↑
Let's take the price of a liter of diesel fuel for about 30 rubles. The value of this variable depends on the supplier and on the volume of purchased liquid fuel. Different modifications of liquid fuel boilers have unequal efficiency.Averaging the indicators given by manufacturers, we will decide that 0.17 liters of diesel fuel will be needed to generate 1 kW per hour.
30 × 0.17 = 5.10 (rubles will be spent per hour)
5.10 × 50400 = 257040 (rubles will be spent annually on heating)

Boiler processing liquid fuel
Here we have identified the most costly heating scheme, which also requires strict adherence to regulatory installation rules: a mandatory chimney and ventilation device. However, if an oil-fired boiler has no alternative, then you will have to put up with the costs.
Annual payment for firewood ↑
The cost of solid fuel is affected by the type of wood, the packing density per cubic meter, the prices of logging companies and delivery. A densely packed cubic meter of solid fossil fuel weighs about 650 kg and costs about 1,500 rubles.
For one kg they pay about 2.31 rubles. In order to get 1 kW, you need to burn 0.4 kilos of firewood or spend 0.92 rubles.
0.92 × 50400 = 46368 rubles per year

Solid fuel boiler could cost more money than alternatives
For the processing of solid fuels, a chimney is required, and equipment must be cleaned of soot regularly.
Calculation of heating costs with a gas boiler
For main gas consumers Just multiply two numbers.
0.30 × 50400 = 15120 (rubles must be paid for the use of main gas during the heating season)

Gas boilers in the heating system
Conclusion: the operation of a gas boiler will be the cheapest. However, this scheme has several nuances:
- mandatory allocation for the boiler of a separate room with certain dimensions, which must be done at the design stage of the cottage;
- summing up all communications related to the operation of the heating system;
- ensuring ventilation of the furnace room;
- construction of chimneys;
- strict adherence to the technological rules of the installation.
If there is no possibility of connecting to a centralized gas supply system in the area, the owner of the house can use liquefied gas from special tanks - gas holders.
Possible mechanisms to stimulate the revision of contractual thermal loads of consumers (subscribers)
Reviewing the contractual loads of subscribers and understanding the true values in the demand for heat consumption is one of the key opportunities for optimizing existing and planned production capacities, which in the future will lead to:
ü reducing the rate of growth of tariffs for thermal energy for the end consumer;
ü reducing the connection fee by transferring the unused heat load of existing consumers, and, as a result, creating a favorable environment for the development of small and medium-sized businesses.
The work carried out by PJSC "TGC-1" to review the contractual loads of subscribers showed a lack of motivation on the part of consumers in reducing contractual loads, including in carrying out related measures to save energy and improve energy efficiency.
As mechanisms to encourage subscribers to review the heat load, the following can be proposed:
· establishment of a two-part tariff (rates for thermal energy and for capacity);
· introduction of mechanisms for paying for unused capacity (load) by the consumer (expanding the list of consumers for which the reservation procedure should apply and (or) changing the very concept of “reserve thermal power (load)).
With the introduction of two-part tariffs, it is possible to solve the following problems that are relevant for heat supply systems:
— optimization of costs for the maintenance of thermal infrastructure with the decommissioning of excess heat generating capacities;
— incentives for consumers to equalize the contractual and actual connected capacity with the release of capacity reserves to connect new consumers;
— equalization of TCO financial flows due to the “capacity” rate, evenly distributed throughout the year, etc.
It should be noted that in order to implement the mechanisms discussed above, it is necessary to refine the current legislation in the field of heat supply.