- Heating consumption standard per sq m
- Standards for the consumption of utilities in Moscow
- Heating rates per 1 square meter
- How much are the standards for the consumption of utilities in Moscow in 2019
- Utilities Consumption Standards
- Calculation of heating in an apartment building from 01/01/2019
- How to reduce current heating costs
- General calculations
- Boiler
- Pipes
- Expansion tank
- Radiators
- Accurate heat load calculations
- Calculation for walls and windows
- Ventilation calculation
- Circulation pump
- Calculation of heat losses
- 1 Parameter importance
- Inspection with a thermal imager
- Antifreeze parameters and types of coolants
- Calculation of the power of the heating system by the volume of housing
- A few important notes
- the temperature regime of the heating surfaces should not cause external low-temperature corrosion.
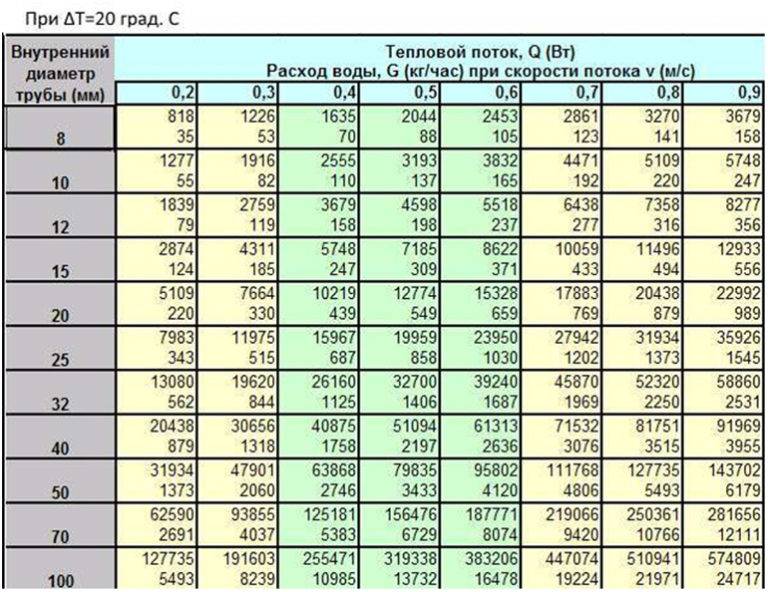
Heating consumption standard per sq m

hot water supply
1
2
3
1.
Multi-apartment residential buildings equipped with centralized heating, cold and hot water supply, sanitation with showers and bathtubs
Length 1650-1700 mm
8,12
2,62
Length 1500-1550 mm
8,01
2,56
Length 1200 mm
7,9
2,51
2.
Multi-apartment residential buildings equipped with centralized heating, cold and hot water supply, sewerage with a shower without baths
7,13
2,13
3.Multi-apartment residential buildings equipped with centralized heating, cold and hot water supply, sanitation without showers and bathtubs
5,34
1,27
4.
Standards for the consumption of utilities in Moscow
| No. p / p | Name of company | Tariffs including VAT (rubles/cub. m) | |
| cold water | drainage | ||
| 1 | JSC Mosvodokanal | 35,40 | 25,12 |
Note. Tariffs for cold water and sanitation for the population of the city of Moscow do not include commission fees charged by credit institutions and payment system operators for the services of accepting these payments.
Heating rates per 1 square meter
It should be remembered that it is not necessary to make a calculation for the entire apartment, because each room has its own heating system and requires an individual approach. In this case, the necessary calculations are made using the formula: C * 100 / P \u003d K, where K is the power of one section of your radiator battery, according to its characteristics; C is the area of the room.
How much are the standards for the consumption of utilities in Moscow in 2019
No. 41 "On the transition to a new system of payment for housing and utilities and the procedure for providing citizens of housing subsidies", the indicator for heat supply is valid:
- heat energy consumption for heating an apartment - 0.016 Gcal/sq. m;
- water heating - 0.294 Gcal / person.
Residential buildings equipped with sewerage, plumbing, baths with hot central water supply:
- water disposal - 11.68 m³ per 1 person per month;
- hot water - 4,745.
- cold water - 6.935;
Housing equipped with sewerage, plumbing, bathtubs with gas heaters:
- water disposal - 9.86;
- cold water - 9.86.
Houses with water supply with gas heaters near the baths, sewerage:
- 9.49 m³ per person per month.
- 9,49;
Residential buildings of a hotel type, equipped with water supply, hot water supply, gas:
- cold water - 4.386;
- hot - 2, 924.
- water disposal - 7.31;
Utilities Consumption Standards
Payment for electricity, water supply, sewerage and gas is made according to the established norms if an individual metering device is not installed.
- From July 1 to December 31, 2015 - 1.2.
- From January 1 to June 30, 2019 - 1.4.
- From July 1 to December 31, 2019 - 1.5.
- Since 2019 - 1.6.
- From January 1 to June 30, 2015 - 1.1.
Thus, if you do not have a collective heat meter installed in your house, and you pay, for example, 1 thousand rubles per month for heating, then from January 1, 2015 the amount will increase to 1,100 rubles, and from 2019 - up to 1,600 rubles.
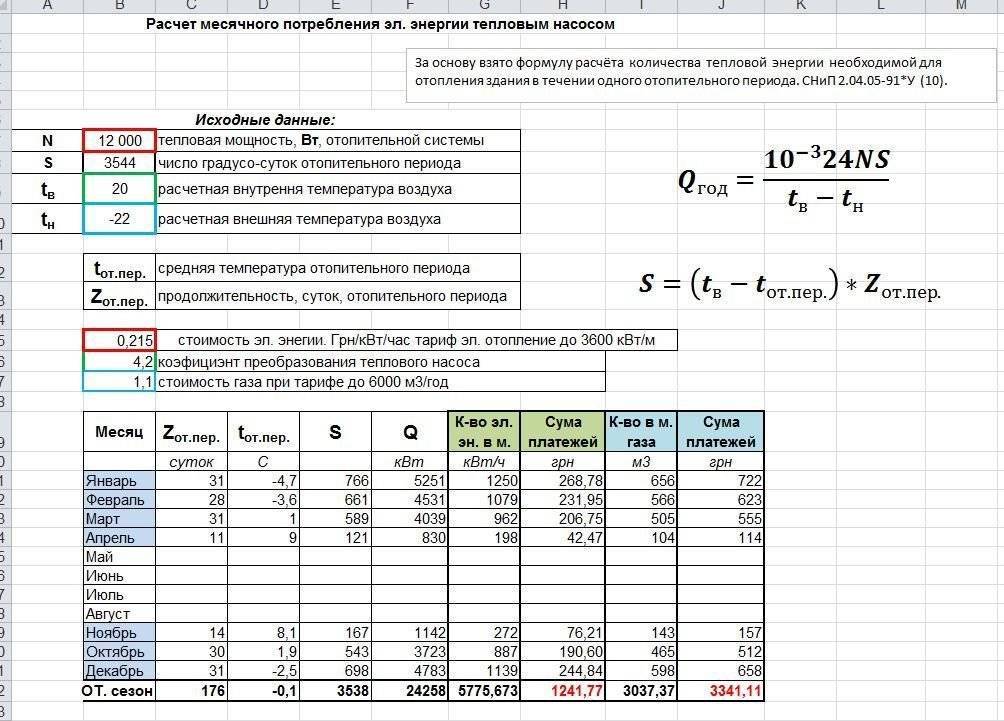
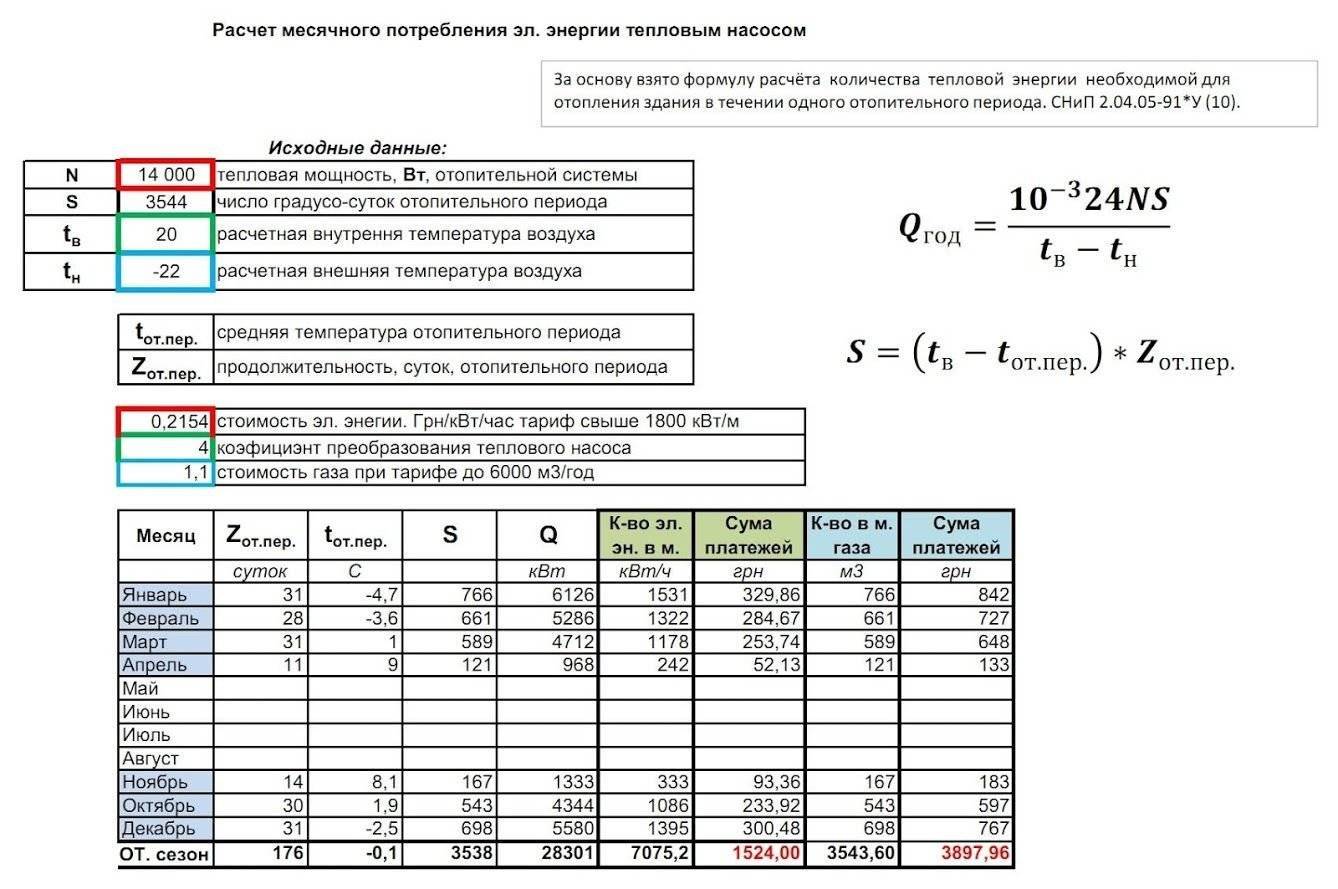
Calculation of heating in an apartment building from 01/01/2019
Methods and calculation examples presented below provide an explanation of the calculation of the amount of payment for heating for residential premises (apartments) located in multi-apartment buildings with centralized systems for supplying heat energy.
How to reduce current heating costs
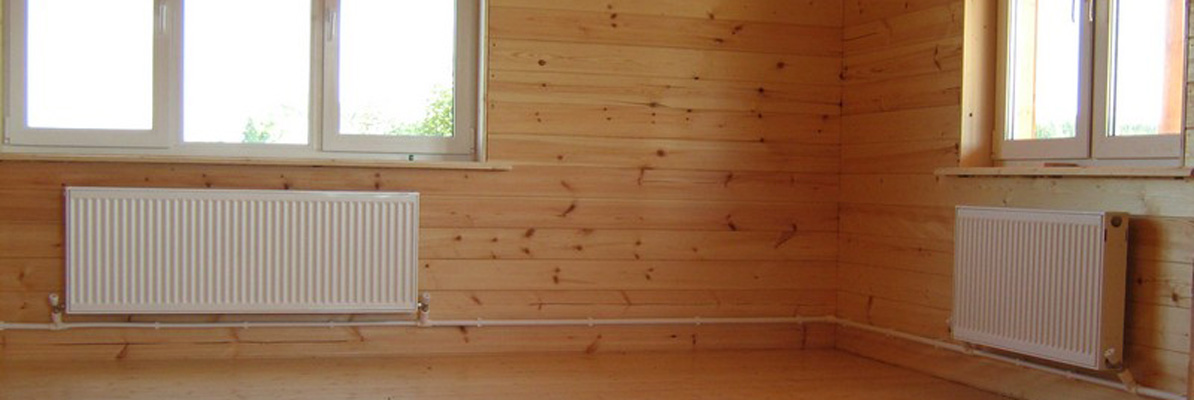
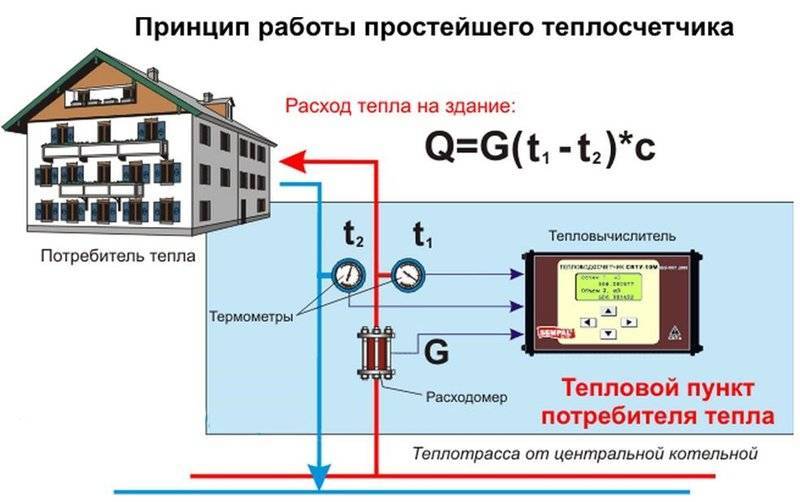
Scheme of central heating of an apartment building
Given the ever-increasing tariffs for housing and communal services for heat supply, the issue of reducing these costs becomes only more relevant every year. The problem of reducing costs lies in the specifics of the operation of a centralized system.
How to reduce the payment for heating and at the same time ensure the proper level of heating of the premises? First of all, you need to learn that the usual effective ways to reduce heat losses do not work for district heating. Those. if the facade of the house was insulated, the window structures were replaced with new ones - the amount of payment will remain the same.
The only way to reduce heating costs is to install individual meters thermal energy accounting. However, you may encounter the following problems:
- A large number of thermal risers in the apartment. Currently, the average cost of installing a heating meter ranges from 18 to 25 thousand rubles. In order to calculate the cost of heating for an individual device, they must be installed on each riser;
- Difficulty in obtaining permission to install a meter. To do this, it is necessary to obtain technical conditions and, on their basis, select the optimal model of the device;
- In order to make timely payment for heat supply according to an individual meter, it is necessary to periodically send them for verification. To do this, dismantling and subsequent installation of the device that has passed verification is carried out. This also entails additional costs.
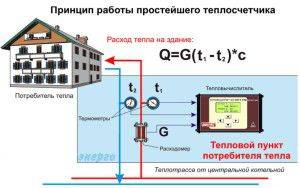
The principle of operation of a common house meter
But despite these factors, the installation of a heat meter will ultimately lead to a significant reduction in payment for heat supply services. If the house has a scheme with several heat risers passing through each apartment, you can install a common house meter. In this case, the cost reduction will not be so significant.
When calculating payment for heating according to a common house meter, it is not the amount of heat received that is taken into account, but the difference between it and in the return pipe of the system. This is the most acceptable and open way to form the final cost of the service. In addition, by choosing the optimal model of the device, you can further improve the heating system of the house according to the following indicators:
- The ability to control the amount of heat energy consumed in the building depending on external factors - the temperature in the street;
- A transparent way to calculate payment for heating. However, in this case, the total amount is distributed among all apartments in the house depending on their area, and not on the amount of thermal energy that came to each room.
In addition, only representatives of the management company can deal with the maintenance and configuration of the common house meter. However, residents have the right to demand all the necessary reporting for reconciliation of completed and accrued utility bills for heat supply.
Apart from installation of a metering device heat must be installed modern mixing unit for regulation of the degree of heating of the coolant included in the heating system of the house.
General calculations
It is necessary to determine the total heating capacity so that the power of the heating boiler is sufficient for high-quality heating of all rooms. Exceeding the permissible volume can lead to increased wear of the heater, as well as significant energy consumption.
Boiler
The calculation of the power of the heating unit allows you to determine the boiler capacity indicator. To do this, it is enough to take as a basis the ratio at which 1 kW of thermal energy is sufficient to efficiently heat 10 m2 of living space. This ratio is valid in the presence of ceilings, the height of which is not more than 3 meters.
As soon as the boiler power indicator becomes known, it is enough to find a suitable unit in a specialized store. Each manufacturer indicates the volume of equipment in the passport data.
Therefore, if the correct power calculation is performed, there will be no problems with determining the required volume.
Pipes
To determine sufficient volume of water in pipes, it is necessary to calculate the cross section of the pipeline according to the formula - S = π × R2, where:
- S - cross section;
- π is a constant constant equal to 3.14;
- R is the inner radius of the pipes.
Expansion tank
It is possible to determine what capacity the expansion tank should have, having data on the coefficient of thermal expansion of the coolant. For water, this indicator is 0.034 when heated to 85 °C.
When performing the calculation, it is enough to use the formula: V-tank \u003d (V syst × K) / D, where:
- V-tank - the required volume of the expansion tank;
- V-syst - the total volume of liquid in the remaining elements of the heating system;
- K is the expansion coefficient;
- D - the efficiency of the expansion tank (indicated in the technical documentation).
Radiators
Currently, there is a wide variety of individual types of radiators for heating systems. In addition to functional differences, they all have different heights.
To calculate the volume of working fluid in radiators, you must first calculate their number. Then multiply this amount by the volume of one section.
You can find out the volume of one radiator using the data from the technical data sheet of the product. In the absence of such information, you can navigate according to the average parameters:
- cast iron - 1.5 liters per section;
- bimetallic - 0.2-0.3 l per section;
- aluminum - 0.4 l per section.
The following example will help you understand how to correctly calculate the value. Let's say there are 5 radiators made of aluminum. Each heating element contains 6 sections. We make the calculation: 5 × 6 × 0.4 \u003d 12 liters.
Accurate heat load calculations
The value of thermal conductivity and heat transfer resistance for building materials
But still, this calculation of the optimal heat load on heating does not give the required calculation accuracy. It does not take into account the most important parameter - the characteristics of the building. The main one is the heat transfer resistance of the material for the manufacture of individual elements of the house - walls, windows, ceiling and floor. They determine the degree of conservation of thermal energy received from the heat carrier of the heating system.
What is heat transfer resistance (R)? This is the reciprocal of thermal conductivity (λ) - the ability of the material structure to transfer thermal energy. Those. the higher the thermal conductivity value, the higher the heat loss. This value cannot be used to calculate the annual heating load, since it does not take into account the thickness of the material (d). Therefore, experts use the heat transfer resistance parameter, which is calculated by the following formula:
Calculation for walls and windows
Heat transfer resistance of residential building walls
There are normalized values of the heat transfer resistance of walls, which directly depend on the region where the house is located.
In contrast to the enlarged calculation of the heating load, you first need to calculate the heat transfer resistance for external walls, windows, the floor of the first floor and the attic. Let's take as a basis the following characteristics of the house:
- Wall area - 280 m². It includes windows - 40 m²;
- The wall material is solid brick (λ=0.56). The thickness of the outer walls is 0.36 m. Based on this, we calculate the TV transmission resistance - R \u003d 0.36 / 0.56 \u003d 0.64 m² * C / W;
- To improve the thermal insulation properties, an external insulation was installed - polystyrene foam 100 mm thick.For him λ=0.036. Accordingly R \u003d 0.1 / 0.036 \u003d 2.72 m² * C / W;
- The overall R value for exterior walls is 0.64 + 2.72 = 3.36 which is a very good indicator of the thermal insulation of the house;
- Heat transfer resistance of windows - 0.75 m² * C / W (double-glazed window with argon filling).
In fact, heat losses through the walls will be:
(1/3.36)*240+(1/0.75)*40= 124 W at 1°C temperature difference
We take the temperature indicators the same as for the enlarged calculation of the heating load + 22 ° С indoors and -15 ° С outdoors. Further calculation must be done according to the following formula:
Ventilation calculation
Then you need to calculate the losses through ventilation. The total air volume in the building is 480 m³. At the same time, its density is approximately equal to 1.24 kg / m³. Those. its mass is 595 kg. On average, the air is renewed five times per day (24 hours). In this case, to calculate the maximum hourly load for heating, you need to calculate the heat losses for ventilation:
(480*40*5)/24= 4000 kJ or 1.11 kWh
Summing up all the obtained indicators, you can find the total heat loss of the house:
In this way, the exact maximum heating load is determined. The resulting value directly depends on the temperature outside. Therefore, to calculate the annual load on the heating system, it is necessary to take into account changes in weather conditions. If the average temperature during the heating season is -7°C, then the total heating load will be equal to:
(124*(22+7)+((480*(22+7)*5)/24))/3600)*24*150(heating season days)=15843 kW
By changing the temperature values, you can make an accurate calculation of the heat load for any heating system.
To the results obtained, it is necessary to add the value of heat losses through the roof and floor.This can be done with a correction factor of 1.2 - 6.07 * 1.2 \u003d 7.3 kW / h.
The resulting value indicates the actual cost of the energy carrier during the operation of the system. There are several ways to regulate the heating load of heating. The most effective of them is to reduce the temperature in rooms where there is no constant presence of residents. This can be done using temperature controllers and installed temperature sensors. But at the same time, a two-pipe heating system must be installed in the building.
To calculate the exact value of heat loss, you can use the specialized program Valtec. The video shows an example of working with it.
Anatoly Konevetsky, Crimea, Yalta
Anatoly Konevetsky, Crimea, Yalta
Dear Olga! Sorry for contacting you again. Something according to your formulas gives me an unthinkable thermal load: Cyr \u003d 0.01 * (2 * 9.8 * 21.6 * (1-0.83) + 12.25) \u003d 0.84 Qot \u003d 1.626 * 25600 * 0.37 * ((22-(-6)) * 1.84 * 0.000001 \u003d 0.793 Gcal / hour According to the enlarged formula above, it turns out only 0.149 Gcal / hour.I can’t understand what’s wrong? Please explain!
Anatoly Konevetsky, Crimea, Yalta
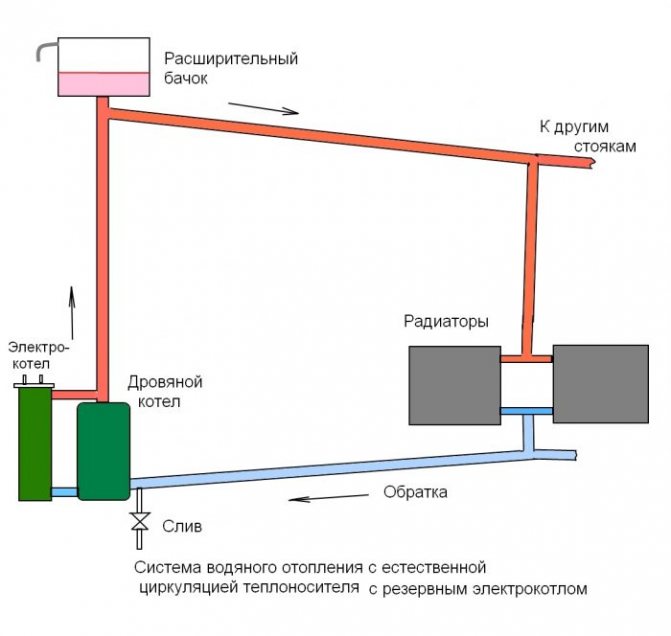
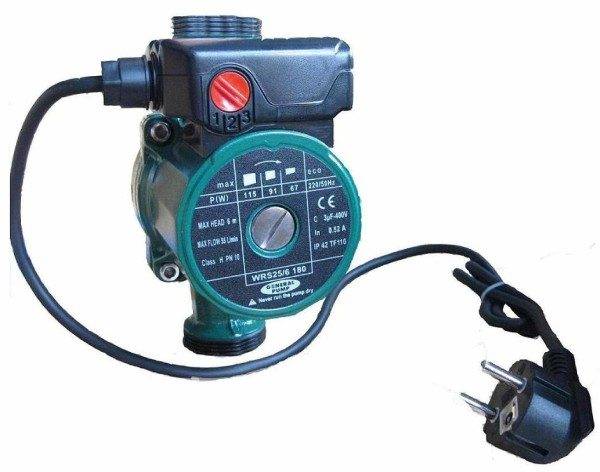
Circulation pump
Two parameters are important for us: the pressure created by the pump and its performance.

In the photo - a pump in the heating circuit.
With pressure, everything is not simple, but very simple: a circuit of any length that is reasonable for a private house will require a pressure of no more than the minimum 2 meters for budget devices.
Reference: a difference of 2 meters makes the heating system of a 40-apartment building circulate.
The simplest way to choose the performance is to multiply the volume of coolant in the system by 3: the circuit must turn around three times per hour.So, in a system with a volume of 540 liters, a pump with a capacity of 1.5 m3 / h (rounded) is enough.
A more accurate calculation is performed using the formula G=Q/(1.163*Dt), in which:
- G - productivity in cubic meters per hour.
- Q is the power of the boiler or section of the circuit where circulation is to be provided, in kilowatts.
- 1.163 is a coefficient tied to the average heat capacity of water.
- Dt is the temperature delta between the supply and return of the circuit.
Hint: for a standalone system, the standard settings are 70/50 C.
With the notorious boiler heat output of 36 kW and a temperature delta of 20 C, the pump performance should be 36 / (1.163 * 20) \u003d 1.55 m3 / h.

Sometimes performance is indicated in liters per minute. It's easy to count.
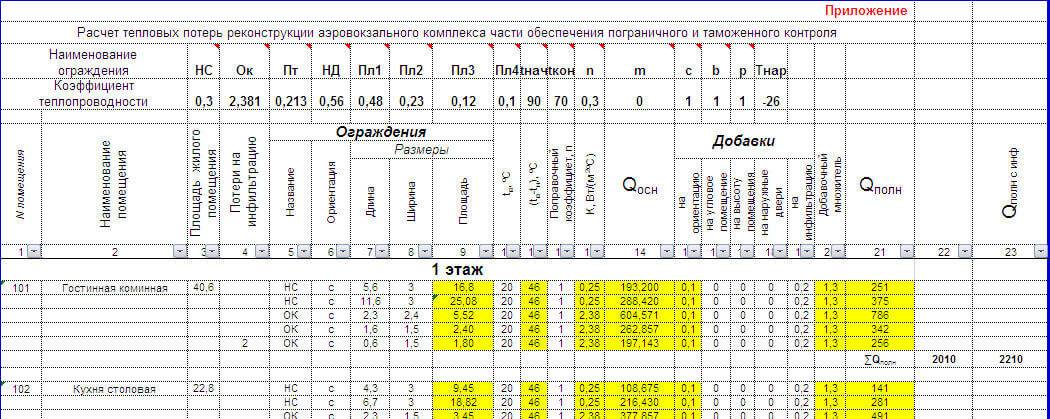
Calculation of heat losses
The first stage of the calculation is to calculate the heat loss of the room. The ceiling, the floor, the number of windows, the material from which the walls are made, the presence of an interior or front door - all these are sources of heat loss.
Consider the example of a corner room with a volume of 24.3 cubic meters. m.:
- room area - 18 sq. m. (6 m x 3 m)
- 1st floor
- ceiling height 2.75 m,
- external walls - 2 pcs. from a bar (thickness 18 cm), sheathed from the inside with gypsum board and pasted over with wallpaper,
- window - 2 pcs., 1.6 m x 1.1 m each
- floor - wooden insulated, below - subfloor.
Surface area calculations:
- external walls minus windows: S1 = (6 + 3) x 2.7 - 2 × 1.1 × 1.6 = 20.78 sq. m.
- windows: S2 \u003d 2 × 1.1 × 1.6 \u003d 3.52 sq. m.
- floor: S3 = 6×3=18 sq. m.
- ceiling: S4 = 6×3= 18 sq. m.
Now, having all the calculations of heat-releasing areas, we estimate the heat loss of each:
- Q1 \u003d S1 x 62 \u003d 20.78 × 62 \u003d 1289 W
- Q2= S2 x 135 = 3x135 = 405W
- Q3=S3 x 35 = 18×35 = 630W
- Q4 = S4 x 27 = 18x27 = 486W
- Q5=Q+ Q2+Q3+Q4=2810W
1 Parameter importance
Using the heat load indicator, you can find out the amount of heat energy needed to heat a particular room, as well as the building as a whole. The main variable here is the power of all heating equipment that is planned to be used in the system. In addition, it is required to take into account the heat loss of the house.
The ideal situation seems to be in which the capacity of the heating circuit allows not only to eliminate all losses of heat energy from the building, but also to provide comfortable living conditions. In order to correctly calculate the specific heat load, it is necessary to take into account all the factors that affect this parameter:
- Characteristics of each structural element of the building. The ventilation system significantly affects the loss of heat energy.
- Building dimensions. It is necessary to take into account both the volume of all rooms and the area of windows of structures and external walls.
- climate zone. The indicator of the maximum hourly load depends on the temperature fluctuations of the ambient air.
Inspection with a thermal imager
Increasingly, in order to increase the efficiency of the heating system, they resort to thermal imaging surveys of the building.
These works are carried out at night. For a more accurate result, you must observe the temperature difference between the room and the street: it must be at least 15 o. Fluorescent and incandescent lamps are switched off. It is advisable to remove carpets and furniture to the maximum, they knock down the device, giving some error.
The survey is carried out slowly, the data are recorded carefully. The scheme is simple.
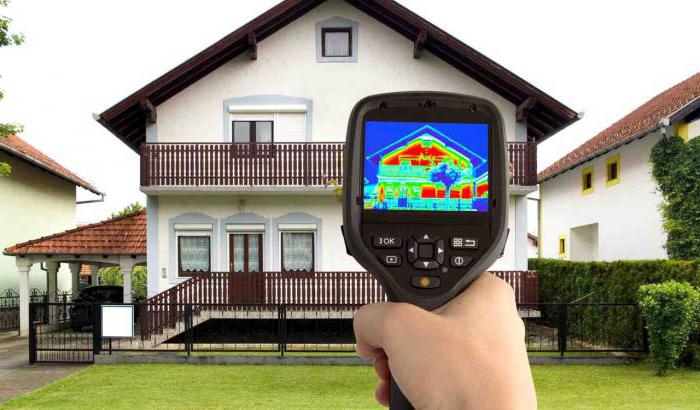

The first stage of work takes place indoors
The device is moved gradually from doors to windows, paying special attention to corners and other joints.
The second stage is the examination of the external walls of the building with a thermal imager. The joints are still carefully examined, especially the connection with the roof.
The third stage is data processing. First, the device does this, then the readings are transferred to a computer, where the corresponding programs complete the processing and give the result.
If the survey was conducted by a licensed organization, then it will issue a report with mandatory recommendations based on the results of the work. If the work was carried out personally, then you need to rely on your knowledge and, possibly, the help of the Internet.

20 photos of cats taken at the right moment Cats are amazing creatures, and perhaps everyone knows about it. They are also incredibly photogenic and always know how to be at the right time in the rules.

Never do this in a church! If you're not sure if you're doing the right thing in church or not, then you're probably not doing the right thing. Here is a list of the terrible ones.

Contrary to all stereotypes: a girl with a rare genetic disorder conquers the fashion world This girl's name is Melanie Gaidos, and she broke into the fashion world quickly, shocking, inspiring and destroying stupid stereotypes.

How to look younger: the best haircuts for those over 30, 40, 50, 60 Girls in their 20s don't worry about the shape and length of their hair. It seems that youth was created for experiments on appearance and bold curls. However, already
11 Weird Signs That You're Good in Bed Do you also want to believe that you're giving your romantic partner pleasure in bed? At least you don't want to blush and apologize.
What does the shape of your nose say about your personality? Many experts believe that by looking at the nose, you can tell a lot about a person's personality.
Therefore, at the first meeting, pay attention to the nose of an unfamiliar
Antifreeze parameters and types of coolants
The basis for the production of antifreeze is ethylene glycol or propylene glycol. In their pure form, these substances are very aggressive environments, but additional additives make antifreeze suitable for use in heating systems. The degree of anti-corrosion, the service life and, accordingly, the final cost depend on the additives introduced.
The main task of additives is to protect against corrosion. Having a low thermal conductivity, the rust layer becomes a heat insulator. Its particles contribute to clogging of channels, disable circulation pumps, lead to leaks and damage in the heating system.
Moreover, the narrowing of the inner diameter of the pipeline entails hydrodynamic resistance, due to which the coolant velocity decreases, and energy costs increase.
Antifreeze has a wide temperature range (from -70°C to +110°C), but by changing the proportions of water and concentrate, you can get a liquid with a different freezing point. This allows you to use intermittent heating mode and turn on space heating only when needed. As a rule, antifreeze is offered in two types: with a freezing point of no more than -30 ° C and no more than -65 ° C.
In industrial refrigeration and air conditioning systems, as well as in technical systems with no special environmental requirements, antifreeze based on ethylene glycol with anti-corrosion additives is used. This is due to the toxicity of the solutions.For their use, expansion tanks of a closed type are required; use in double-circuit boilers is not allowed.
Other possibilities of application were received by a solution based on propylene glycol. This is an environmentally friendly and safe composition, which is used in the food, perfume industry and residential buildings. Wherever it is required to prevent the possibility of toxic substances entering the soil and groundwater.
The next type is triethylene glycol, which is used at high temperatures (up to 180 ° C), but its parameters have not been widely used.
Calculation of the power of the heating system by the volume of housing
Imagine the following method for calculating the power of a heating system - it is also quite simple and understandable, but at the same time it has a higher accuracy of the final result. In this case, the basis for the calculations is not the area of \u200b\u200bthe room, but its volume. In addition, the calculation takes into account the number of windows and doors in the building, the average level of frost outside. Let's imagine a small example of the application of this method - there is a house with a total area of 80 m2, the rooms in which have a height of 3 m. The building is located in the Moscow region. In total there are 6 windows and 2 doors facing the outside. The calculation of the power of the thermal system will look like this. How to make autonomous heating in an apartment building, you can read in our article".
Step 1. The volume of the building is determined. This can be the sum of each individual room or the total figure. In this case, the volume is calculated as follows - 80 * 3 \u003d 240 m3.
Step 2The number of windows and the number of doors facing the street are counted. Let's take the data from the example - 6 and 2, respectively.
Step 3. A coefficient is determined, depending on the area in which the house stands and how severe frosts are there.
Table. Values of regional coefficients for calculating the heating power by volume.
| winter type | Coefficient value | Regions for which this coefficient is applicable |
|---|---|---|
| Warm winter. Colds are absent or very weak | 0.7 to 0.9 | Krasnodar Territory, Black Sea coast |
| moderate winter | 1,2 | Central Russia, Northwest |
| Severe winter with fairly severe cold | 1,5 | Siberia |
| Extremely cold winter | 2,0 | Chukotka, Yakutia, regions of the Far North |
Calculation of the power of the heating system by the volume of housing
Since in the example we are talking about a house built in the Moscow region, the regional coefficient will have a value of 1.2.
Step 4. For detached private cottages, the value of the volume of the building determined in the first operation is multiplied by 60. We make the calculation - 240 * 60 = 14,400.
Step 5. Then the result of the calculation of the previous step is multiplied by the regional coefficient: 14,400 * 1.2 = 17,280.
Step 6. The number of windows in the house is multiplied by 100, the number of doors facing the outside by 200. The results are summed up. The calculations in the example look like this - 6*100 + 2*200 = 1000.
Step 7. The numbers obtained from the fifth and sixth steps are summed up: 17,280 + 1000 = 18,280 watts. This is the power of the heating system required to maintain the optimum temperature in the building under the conditions indicated above.
It should be understood that the calculation of the heating system by volume is also not absolutely accurate - the calculations do not pay attention to the material of the walls and floor of the building and their thermal insulation properties. Also, no allowance is made for natural ventilation inherent in any home.
A few important notes
As noted above, there are circulation pumps with a "dry" and "wet" rotor, as well as with an automatic or manual speed control system. Experts recommend using pumps whose rotor is completely submerged in water, not only because of the reduced noise level, but also because such models cope with the load more successfully. The pump is installed in such a way that the rotor shaft is horizontal. Read more about installation here.
High-quality models are made using durable steel, as well as a ceramic shaft and bearings. The service life of such a device is at least 20 years. You should not choose a pump with a cast-iron casing for a hot water supply system, since in such conditions it will quickly collapse. Preference should be given to stainless steel, brass or bronze.
If noise appears in the system during pump operation, this does not always indicate a breakdown. Often the cause of this phenomenon is the air remaining in the system after starting. Before starting the system, the air must be bled through special valves. After the system has been running for a few minutes, you need to repeat this procedure, and then adjust the pump.
If the start is made using a pump with manual adjustment, you must first set the device to the maximum operating speed, in adjustable models, when starting the heating system, you should simply turn off the lock.
the temperature regime of the heating surfaces should not cause external low-temperature corrosion.
Fulfillment of these requirements is ensured by various methods.
organization of coolant flows (recirculation and jumper), as well as
regulation of the supply of thermal energy by boiler units to the heating network
only by changing the temperature of the water at the outlet of the boiler unit.
Consider these methods of regulation on a specific hot water scheme
boiler room. Water from the return pipeline of the heating network comes with a small
pressure to the network pumps (NS). The suction line of the network pumps is supplied
also water used in the thermal circuit for the source's own needs
heat, and make-up water from the water treatment unit, compensating for leaks in
thermal network.
To avoid low-temperature corrosion, before entering the return mains
water into the hot water boiler unit, its temperature is increased by supplying
WW recirculation line with the HP pump of the estimated amount already heated in
water boiler unit. Minimum water temperature t`to at the entrance to
steel hot water boilers when operating on gas and low-sulfur fuel oil is accepted
not lower than 70 ° C, and when working on sulfur and high-sulphur fuel oil -
not lower than 90 and 110оС, respectively.
After heating in the boiler unit, the water is divided into three streams:
own needs Gs.n. heat source, for recirculation Grc
and into the heating network GWith. Recirculation of water is required in almost all
all modes (with the exception of the maximum winter mode during the operation of boiler houses
units running on gas and low-sulphur fuel oil according to the increased temperature schedule
t`With=150; t"With = 70оС), since the reverse network
water has a temperature below the normalized minimum values t`to.
In all operating modes, except for the maximum winter, to ensure
required (according to the temperature curve) supply water temperature
heating network t`With required amount of return network water GP
m through the temperature controller (RT) through the jumper is supplied, bypassing the boiler
unit, to be mixed with the water coming out of it Gto.
Water temperature and G flow ratesp m, lines
recycling Grc, network water GWith, feeding hearth Gsign
and hot water for own needs source Gs.n. necessary
determine for the following outdoor temperatures:
1. minimum winter;
2. the average of the coldest month;
3. average for the heating period;
4. at the temperature break point
graphic arts;
5. summer.