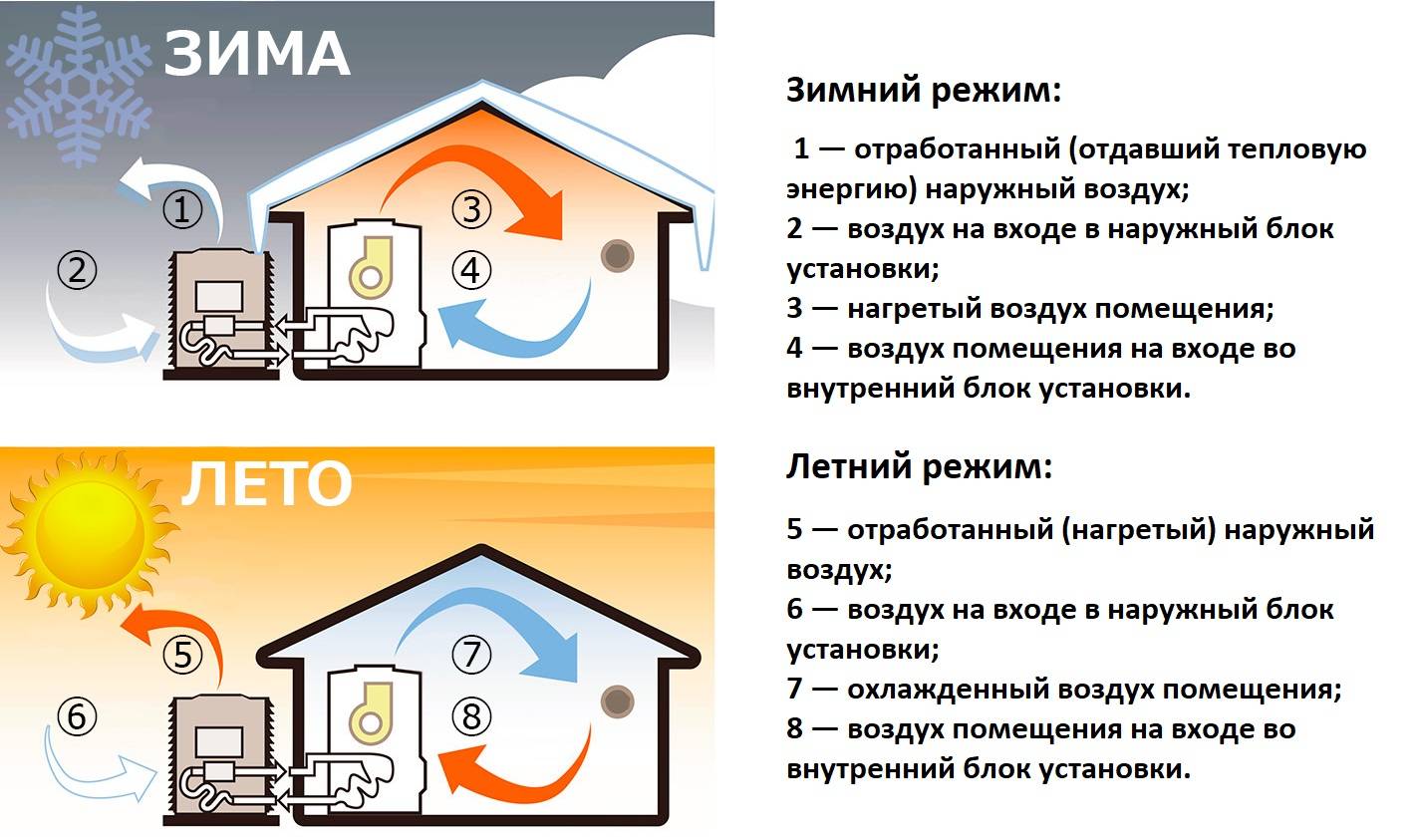
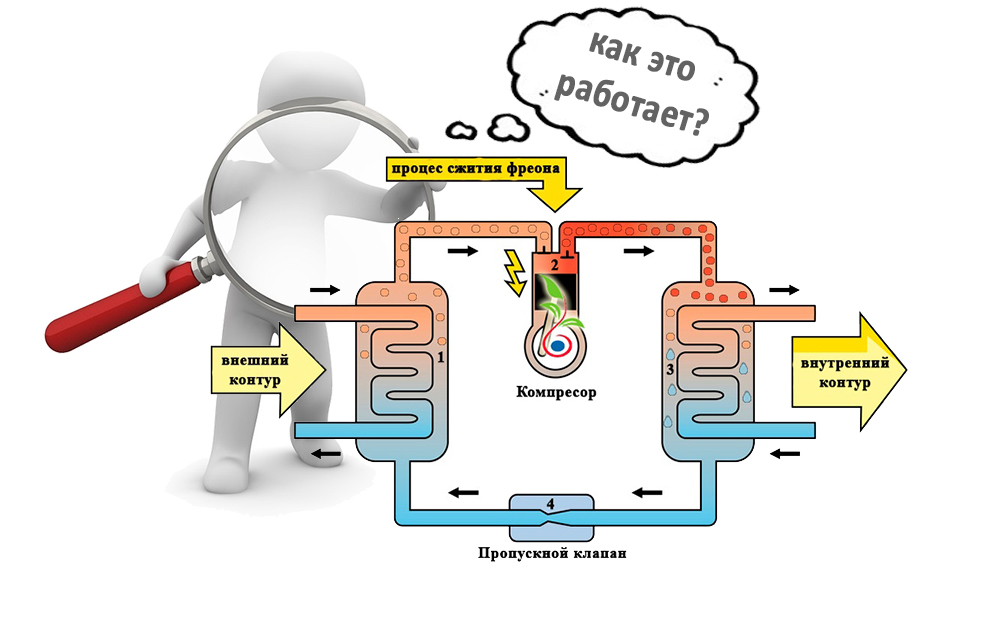
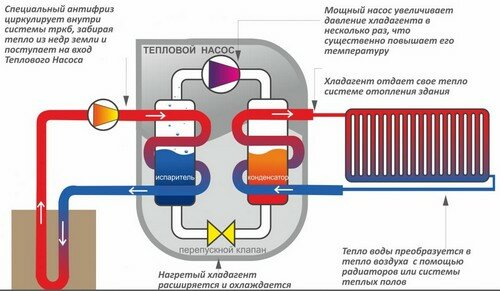
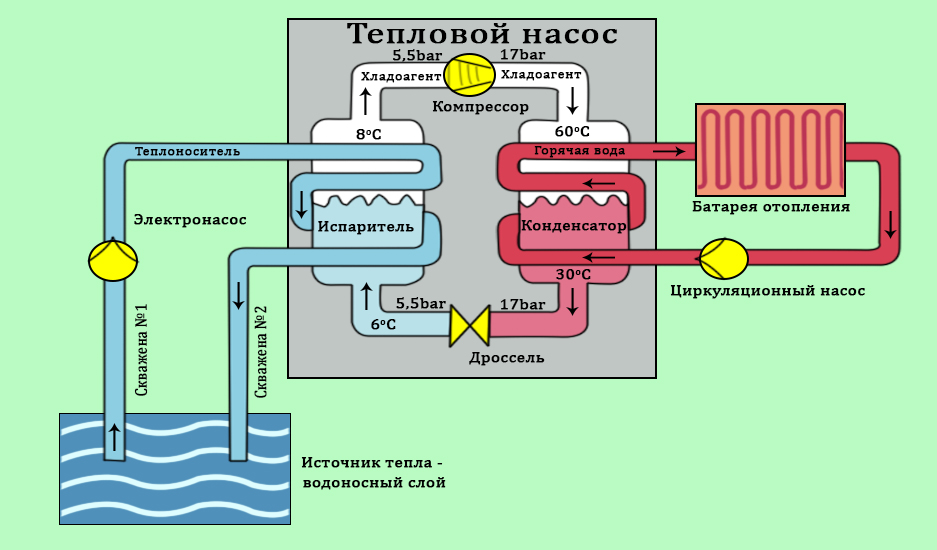
- Features of piping
- Advantages and disadvantages of heat pumps
- How is the power of the equipment calculated?
- Assembling a pump from an old refrigerator
- How to heat a house with air?
- Making a water-to-water heat pump with your own hands
- The principle of operation of an air-to-air heat pump
- What is the difference between an air-to-air heat pump and an air conditioner
- The main varieties, their principles of work
- ground water
- water-water
- Air to water
- Air
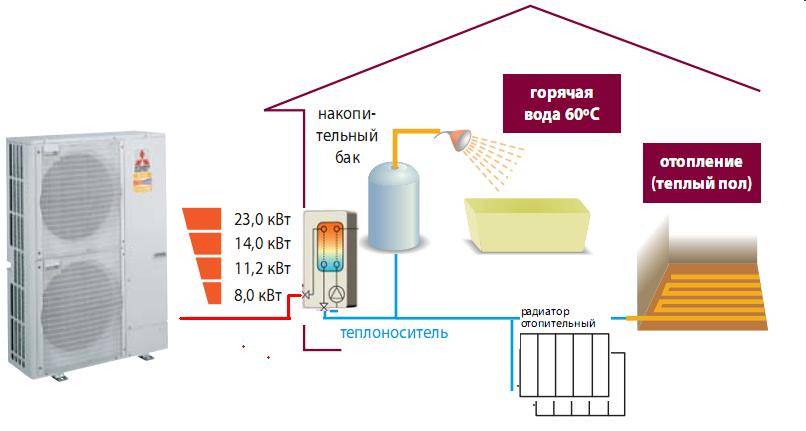
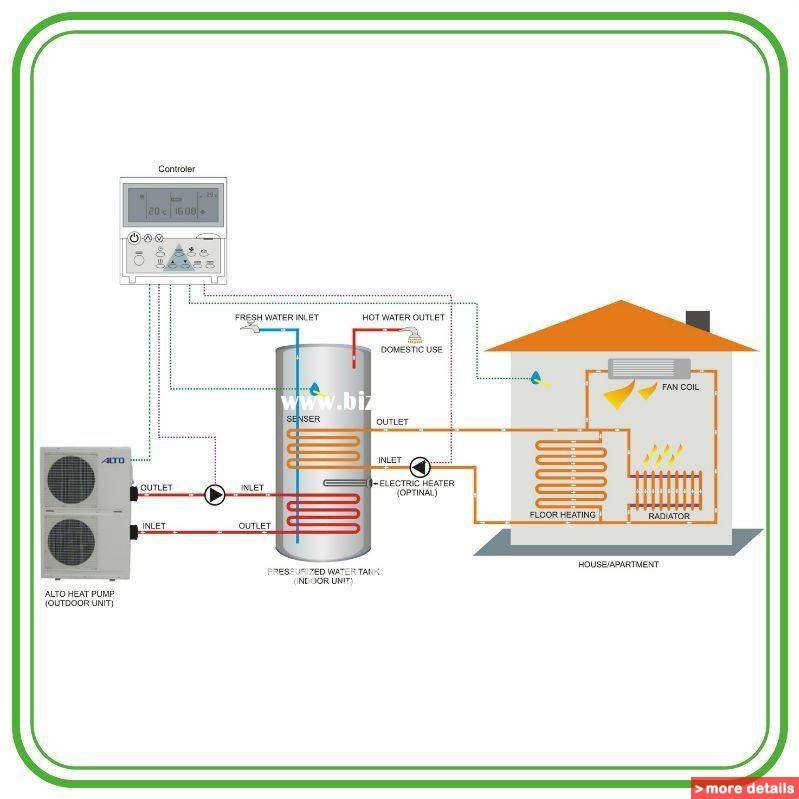
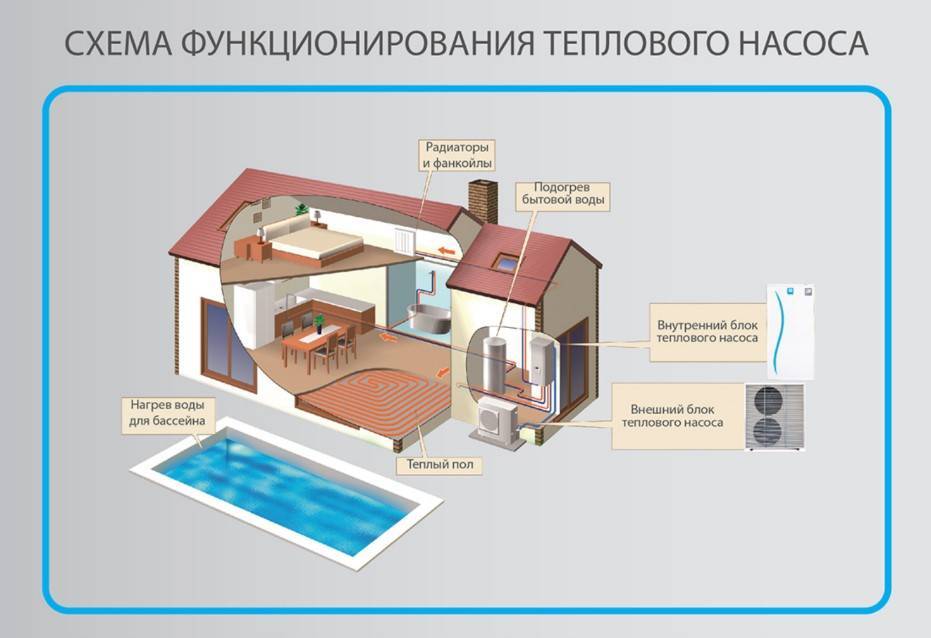
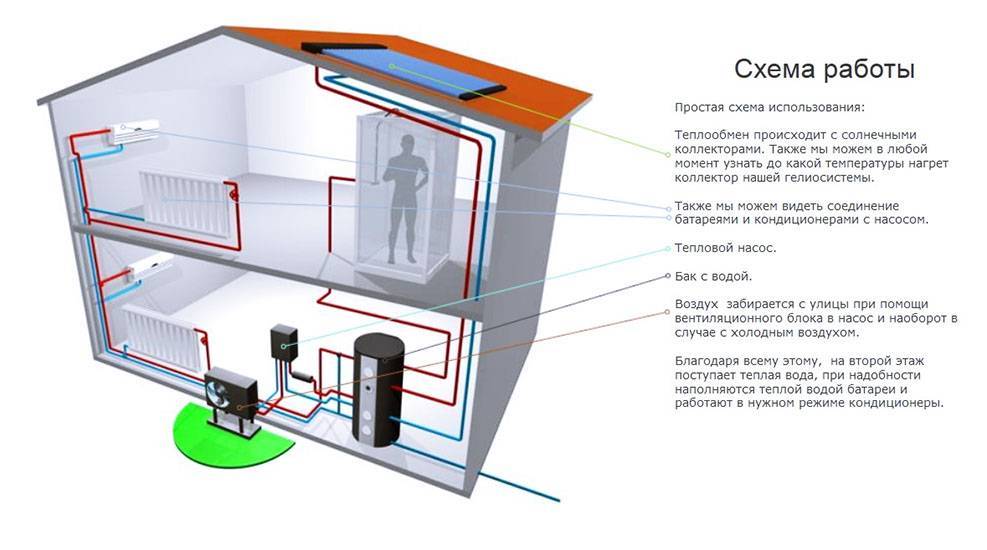
- Heating system with heat pumps
- Set of elements for the formation of air heating
- Where is the air heating system used?
- Selection and calculations of a heat pump
- Conclusions based on the results of use
Features of piping
In addition to the correct installation of the circulation pump itself, it is necessary to correctly position a number of other elements and fulfill the technological requirements. Namely:
- during the coolant flow, but a strainer is installed in front of the pump;
- shut-off valve installed on both sides;
- High power models require vibration damping liners (optional for low power pumps);
- If there are two or more circulation pumps, each pressure connection is equipped with a check valve and a similar redundant device;
- No pressure and pressure loading and twisting at the ends of the pipeline.
There are two ways to install devices for efficient circulation in the system:
- separate division;
- directly into the heating system.
The second option is the most preferred. There are two approaches to implementation. First, the circulation pump is simply inserted into the supply line.
The second is to use a U-piece attached in two places to the main pipe. In the middle of this version, a circulation pump is installed. This implementation is characterized by the presence of a bypass.
In the event of frequent power outages by the central system, this design ensures that the system remains operational. Although less efficient.
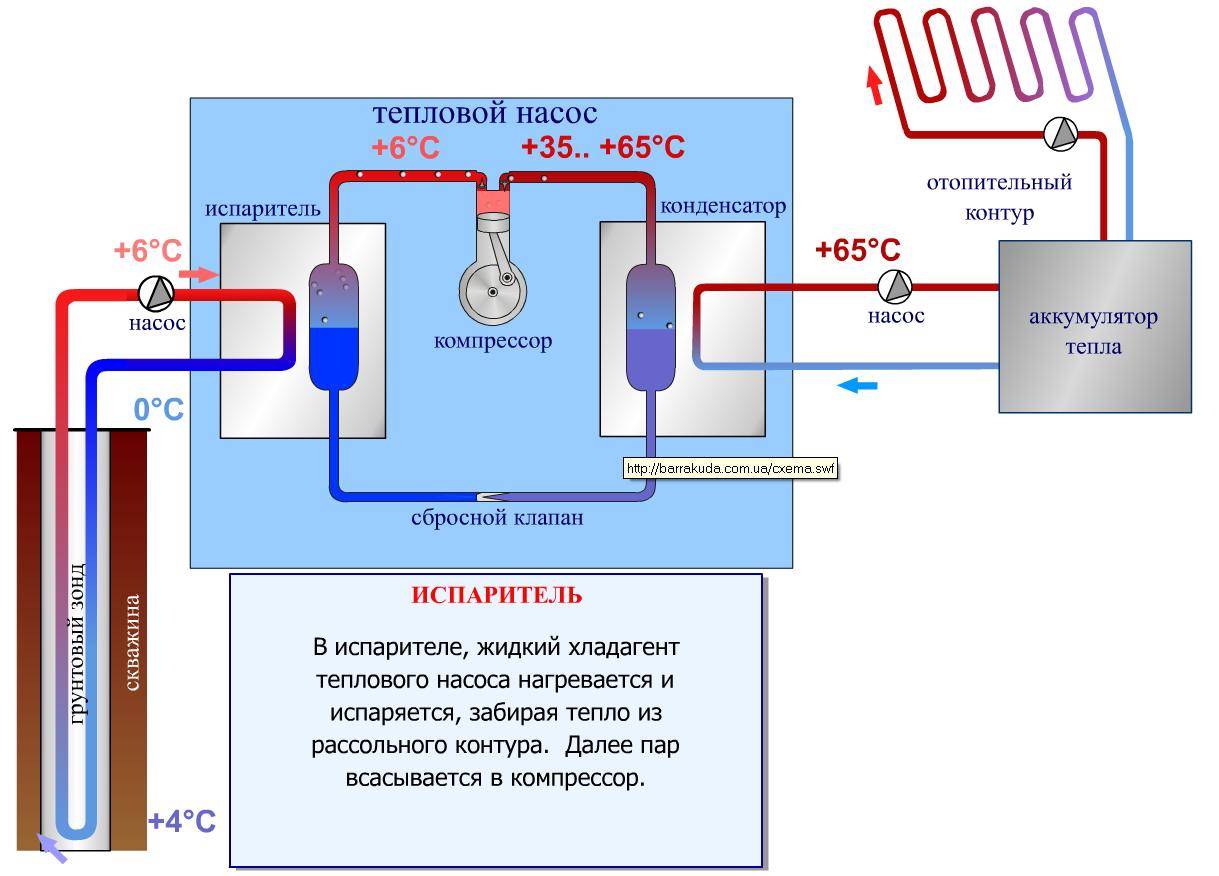
Advantages and disadvantages of heat pumps
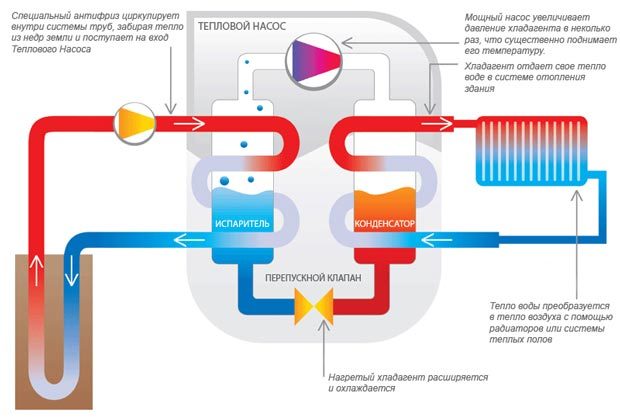
The principle of operation of heat pumps, in simple terms, is based on the collection of low-grade thermal energy and its further transfer to heating and climate systems, as well as to water treatment systems, but at a higher temperature. A simple example can be given in the form of a gas cylinder - when it is filled with gas, the compressor heats up due to its compression. And if you release gas from the cylinder, then the cylinder will cool - try to sharply release gas from a refillable lighter to understand the essence of this phenomenon.
Thus, heat pumps, as it were, take away thermal energy from the surrounding space - it is in the ground, in water and even in the air. Even if the air has a negative temperature, there is still heat in it.It is also found in any water bodies that do not freeze to the very bottom, as well as in deep layers of soil that are also not amenable to deep freezing - unless, of course, it is permafrost.
Heat pumps have a rather complicated device, as you can see by trying to disassemble a refrigerator or air conditioners. These household units familiar to us are somewhat similar to the above-mentioned pumps, only they work in the opposite direction - they take heat from the premises and send it outside. If you put your hand on the rear radiator of the refrigerator, we will note that it is warm. And this heat is nothing but the energy taken from fruits, vegetables, milk, soups, sausages and other products that are in the chamber.
Air conditioners and split systems work in a similar way - the heat generated by outdoor units is thermal energy collected bit by bit in cooled rooms.
The principle of operation of a heat pump is the opposite of that of a refrigerator. It collects heat from the air, water or soil in the same grains, after which it redirects it to consumers - these are heating systems, heat accumulators, underfloor heating systems, and water heaters. It would seem that nothing prevents us from heating the coolant or water with an ordinary heating element - it's easier that way. But let's compare the productivity of heat pumps and conventional heating elements:
When choosing a heat pump, the most important thing is the availability of a specific natural energy source.
- Conventional heating element - for the production of 1 kW of heat, it consumes 1 kW of electricity (excluding errors;
- Heat pump - it consumes only 200 W of electricity to produce 1 kW of heat.
No, there is no efficiency equal to 500% here - the laws of physics are unshakable.It's just the laws of thermodynamics at work here. The pump, as it were, accumulates energy from space, "thickens" it and sends it to consumers. Similarly, we can collect raindrops through a large watering can, getting a solid stream of water at the exit.
We have already given many analogies that allow us to understand the essence of heat pumps without abstruse formulas with variables and constants. Let's now look at their advantages:
- Energy savings - if the standard electric heating of a 100 sq. m. will lead to costs of 20-30 thousand rubles per month (depending on the air temperature outside), then the heating system with a heat pump will reduce costs to an acceptable 3-5 thousand rubles - you must admit, this is already quite a solid savings. And this is without tricks, without deception and without marketing tricks;
- Caring for the environment - coal, nuclear and hydroelectric power plants harm nature. Therefore, reduced electricity consumption reduces the amount of harmful emissions;
- A wide range of uses - the resulting energy can be used to heat a home and prepare hot water.
There are also disadvantages:
- The high cost of heat pumps - this disadvantage imposes a restriction on their use;
- The need for regular maintenance - you have to pay for it;
- Difficulty in installation - this applies to the greatest extent to heat pumps with closed circuits;
- Lack of acceptance by people - few of us would agree to invest in this equipment in order to reduce the burden on the environment.But some people who live far from gas mains and are forced to heat their homes with alternative heat sources agree to spend money on buying a heat pump and reduce their monthly electricity bills;
- Dependence on the mains - if the supply of electricity stops, the equipment will immediately freeze. The situation will be saved by installing a heat accumulator or a backup power source.
As you can see, some of the disadvantages are quite serious.
Gasoline and diesel power generators can serve as backup power sources for heat pumps.
How is the power of the equipment calculated?
A small amount of heat is present in the airspace even when the temperature has dropped to -20 degrees Celsius
It is important that it is suitable for home heating with an autonomous design. To calculate the required parameters, special software is usually used
You can use online systems that have fields for specifying numerical values. They can specify the area of \u200b\u200bthe room and the height of the ceilings. Sometimes it is allowed to set the temperature range characteristic of the region.
The heat pump is able to function even in severe frosts, but it will work with less efficiency. Favorable for the system is the temperature range from -10 to +10 degrees Celsius. In order not to make a mistake when choosing a pump, it is worth considering the following factors:
- refrigerant volume;
- the total surface area of the coils in the outdoor and indoor units;
- the planned volume of heat transfer.
Since the system has a relatively simple design, even a master with little experience in handling equipment can install it. But it is advisable to entrust the calculations to specialists. At the very least, they should be consulted. Experts will help determine the required coefficients, calculate the air-to-air heat pump, taking into account all factors. In central Russia, a 5 kilowatt unit is enough for a house of 100 square meters.
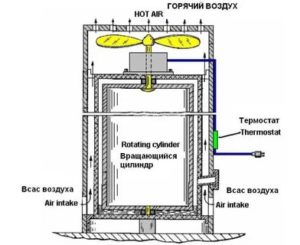
Assembling a pump from an old refrigerator
There are two ways to make a heat pump from an old refrigerator.
In the first case, the refrigerator must be located inside the room, and outside it is required to lay 2 air ducts and cut into the front door. The upper air enters the freezer, the air is cooled, and it leaves the refrigerator through the lower air duct. The room is heated by a heat exchanger, which is located on the rear wall.
According to the second method, making a heat pump with your own hands is also quite simple. To do this, you need an old refrigerator, it only needs to be built in outside the heated room.
Such a heater can operate at outdoor temperatures down to minus 5 ºС.
How to heat a house with air?
They tried to use the heat of the surrounding air for space heating for a long time, but this idea was most effectively put into practice, thanks to the discoveries of scientists in the field of thermodynamics and the study of the properties of liquids and gases. It was thanks to these discoveries that the heat pump was invented, and in particular its variety - the air-to-air system.
During the operation of the device, electrical energy is used, which is necessary for the operation of the compressor, control and protection devices, as well as other devices.The presence of devices depends on the model of the device.
In air-to-air heat pumps, in addition to controls and automation installed on other types of devices, a reversibility valve is installed that allows the device to operate the pump in heating or air conditioning mode at the request of the owner.
When deciding to heat a house with this device, it is necessary to determine the criteria that should be followed when choosing a particular device.
When choosing a device, consider:
- Heating power of the unit.
This value shows how much heat energy this device produces per unit of time.
- Cooling capacity of the unit.
This value shows in what volume of premises the device is able to provide air conditioning.
- Consumed electric power of the unit.
This value determines how much electrical energy the device uses per unit of time.
In addition, due to the fact that the air-to-air heat pump consists of outdoor and indoor units, these parts of the device are subject to separate requirements that characterize their characteristics, such as:
- For outdoor unit:
- Overall dimensions and weight of the system element - determine the method and place of installation.
- Noise level is a characteristic that also determines the place and method of installation.
- Ambient temperature - sets the parameters of the operation of a particular model and the ability to work in different regions of the country.
- The maximum length of the connecting pipelines determines the installation location of this unit.
- Permissible difference between the height marks of the outdoor and indoor units.
- Possibility of connecting several units to a common system.
- For indoor unit:
- Overall dimensions and weight of the block.
- Fan speed.
- Block noise level.
- Installation performance.
- Electrical characteristics (power, voltage).
- Type and material of thermal insulation.
- Characteristics of installed air filters.
Having studied the selection criteria and decided to install a heat pump as a heat source, you can start choosing a specific model.
Making a water-to-water heat pump with your own hands
The described unit is an expensive design, and, unfortunately, not everyone is able to afford such an acquisition, and even more so - to pay a one-time fee, and even taking into account installation work.
Like many other systems, a water pump for heating can be made independently. Moreover, you can save a lot by using some used components, which will be easy to buy.
The construction of a heat pump is a very laborious procedure, and you should start by checking that the electrical wiring is suitable for the expected loads. This is especially true in older buildings.
Let's start!
- The first step is to purchase a compressor. A device from an air conditioner is quite suitable, and buying it in specialized stores or companies is not difficult. It will be mounted on the wall using an L-300 size bracket.
- As a condenser, a tank with a volume of about 120 liters, made of stainless steel, is suitable for us. A coil is mounted in a container cut in half, which can be made from a copper pipe of small diameters. You can also use a pipe from the refrigerator.Make sure that the wall thickness of the coil is at least 1 mm, in order to avoid excessive fragility.
- To obtain a home-made pump coil from a copper pipe, we wind it on a cylinder, maintaining the required distance between the turns. To fix a given shape, you can use an aluminum perforated corner, in the grooves of which it will be possible to fix the coil turns. In addition, this will help establish a uniform helix pitch.
- When the coil is ready and mounted inside the tank, the two halves of the latter are welded back together.
- A homemade evaporator for a heat pump can be made from a plastic bottle, about 70 liters in size. A coil made of a pipe with a diameter of 20 mm should be installed inside.
- Everything is ready, you can assemble the system together, weld pipes, and then pump freon.
- In no case should you try to complete the last stage yourself, without having the necessary skills or appropriate education. This can not only damage the device, but is also traumatic.
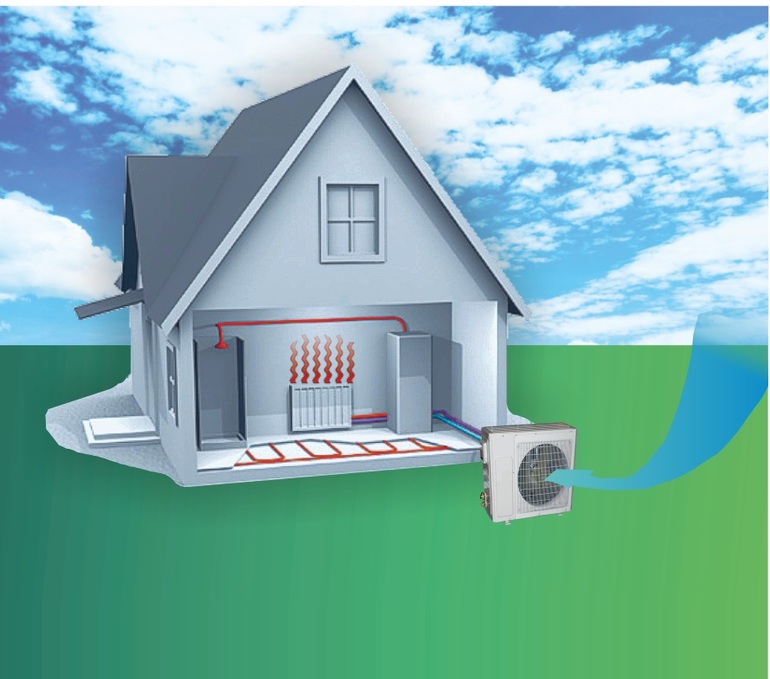
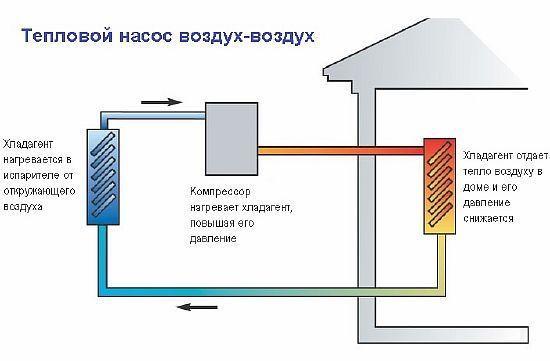
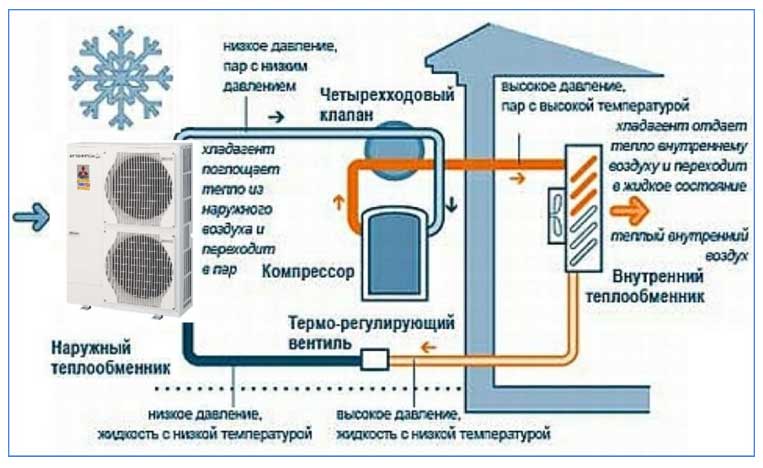
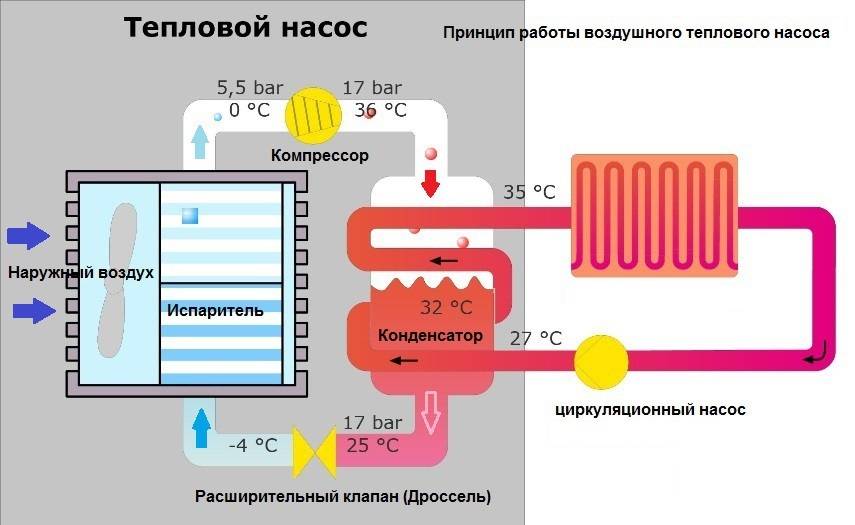
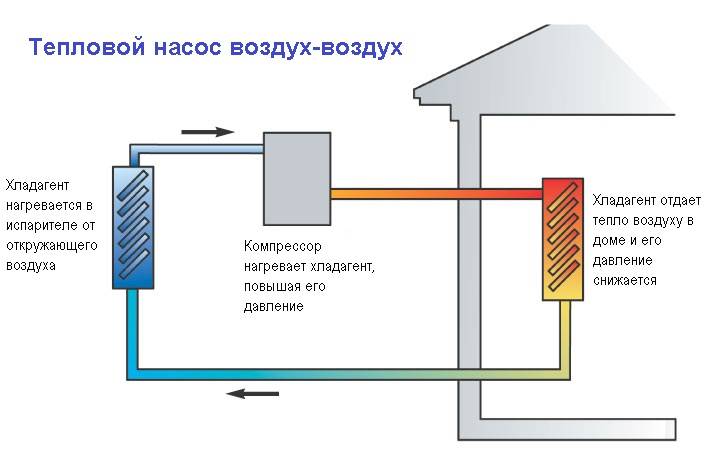
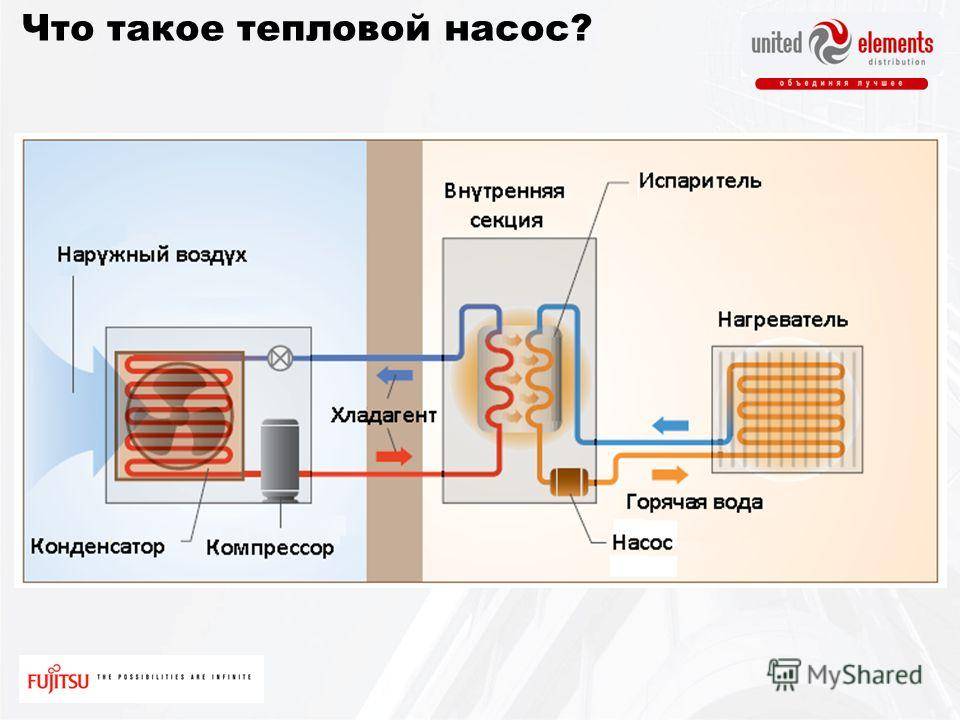
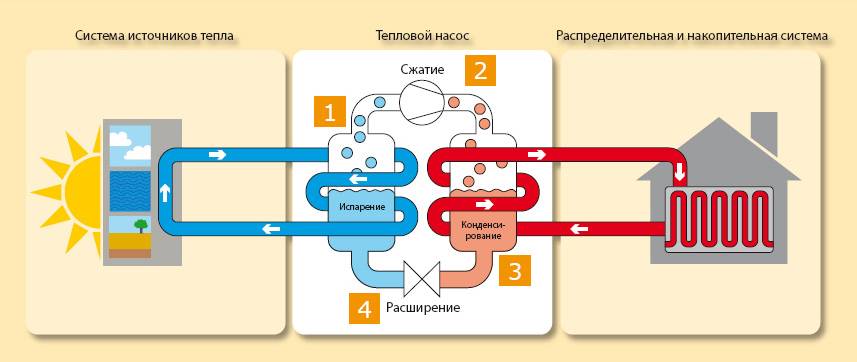
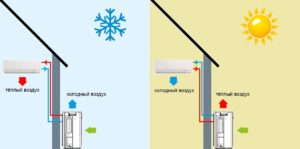
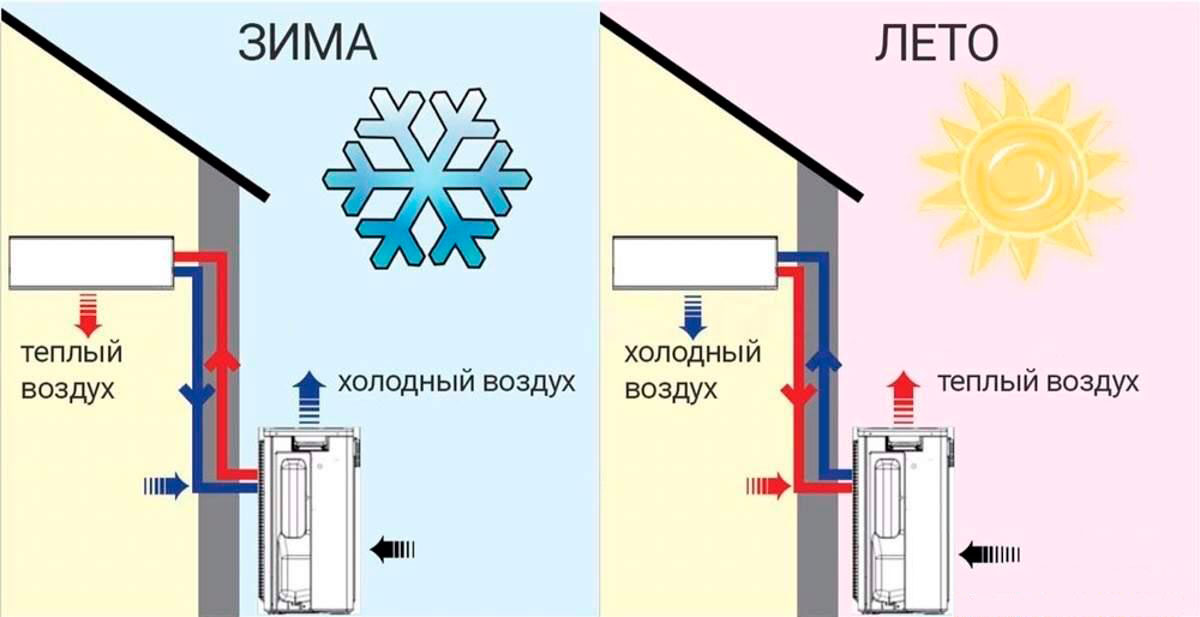
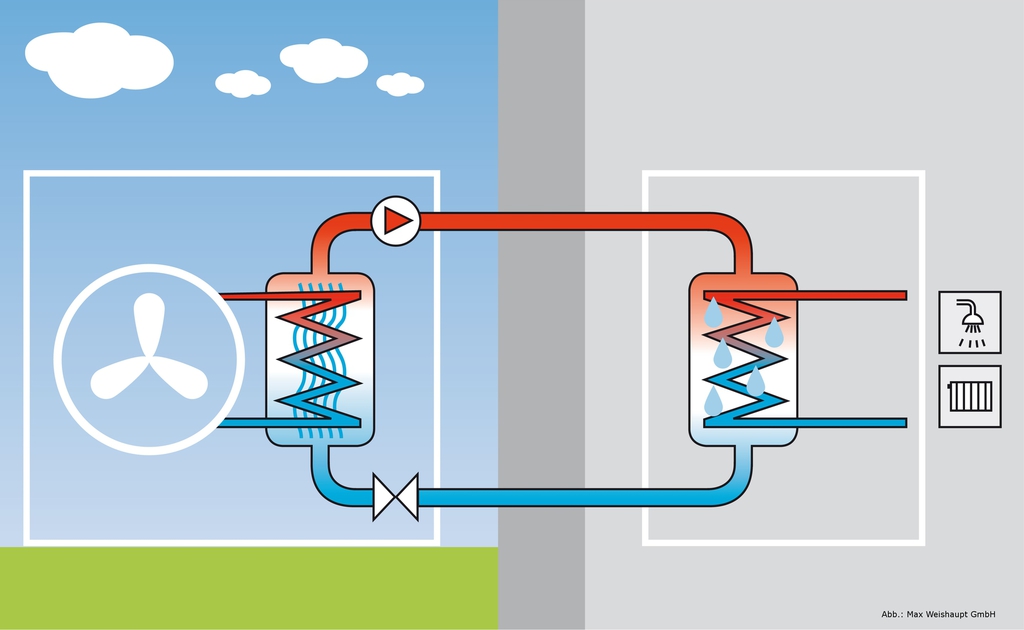
The principle of operation of an air-to-air heat pump
The general principle of operation of the HP is in many respects similar to that used in the air conditioner, in the “space heating” mode, with the only difference. The heat pump is “sharpened” for heating, and the air conditioner for cooling rooms. During operation, low-potential air energy is used. As a result, electricity consumption has been reduced by more than 3 times. The principle of operation of an air-to-air heat pump unit, without going into technical details, is as follows:
- Air, even at negative temperatures, retains a certain amount of thermal energy. This happens until the temperature readings reach absolute zero.Most HP models are able to extract heat when the temperature reaches -15°C. Several well-known manufacturers have released stations that remain operational at -25 ° C and even -32 ° C.
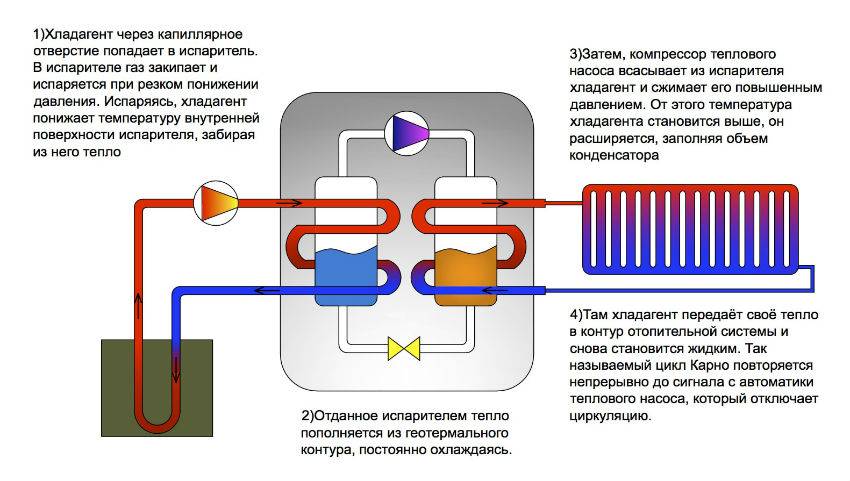
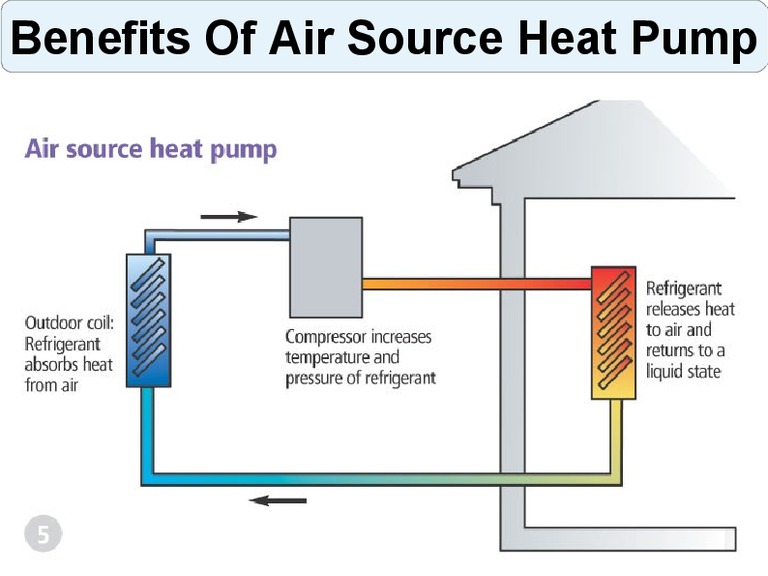
- The intake of low-grade heat occurs due to the evaporation of freon circulating through the internal circuit of the HP. For this, an evaporator is used - a unit in which optimal conditions are created for converting the refrigerant from a liquid to a gaseous state. At the same time, according to physical laws, a large amount of heat is absorbed.
- The next unit located in the air-to-air heat supply system is the compressor. It is here that the refrigerant in the gaseous state is supplied. Pressure is built up in the chamber, which leads to a sharp and significant heating of freon. Through the nozzle, the refrigerant is injected into the condenser. The heat pump compressor has a scroll design, which makes it easier to start at low temperatures.
- In the indoor unit, located directly in the room, there is a condenser that simultaneously performs the function of a heat exchanger. Gaseous heated freon purposefully condenses on the walls of the module, while giving off thermal energy. HP distributes the received heat in a manner similar to a split system.
Channel distribution of heated air is allowed. This solution is especially practical when heating large multi-apartment buildings, warehouses and industrial premises.
The principle of operation of an air-to-air heat pump and its efficiency are directly related to the ambient temperature. The colder "outside the window", the lower the performance of the station.The operation of the air-to-air heat pump at a temperature of minus -25°C (in most models) stops completely. To compensate for the lack of heat, a backup boiler is installed. The simultaneous use of an electric heating element is optimal.
Air-to-air heat pumps consist of two outdoor and indoor units. The design is in many ways reminiscent of a split system and is installed in a similar way. The indoor unit is mounted on a wall or ceiling. The settings are set using the remote control.
What is the difference between an air-to-air heat pump and an air conditioner
An air-to-air heat pump works like an air conditioner, but has significant differences in terms of design and performance
Although there is an external similarity, in fact, the differences, if you pay attention to the technical characteristics, are significant:
- Productivity - air-to-air heat pump for home heating, works as efficiently as possible to heat the room. Some models are capable of cooling the air. During air conditioning, the energy efficiency is significantly inferior to conventional air conditioners.
- Economical - even inverter air conditioners consume more electricity during operation than is required for heating with an air-to-air heat pump. When switching to heating mode, the cost of electricity increases even more.
For HP, the energy efficiency coefficient is determined according to the COP. The average indicators of stations are 3-5 units. The cost of electricity in this case is 1 kW for every 3-5 kW of heat received. - Scope of application - air conditioners are used for ventilation and additional heating of the premises, provided that the ambient temperature is not less than +5°C.Air-to-air heat pumps are used as the main source of heating throughout the year in mid-latitudes. With a certain modification, they can be used to cool rooms.
World experience in the use of air-to-air heat pumps has convincingly proved that the use of renewable energy sources is not only possible, but also cost-effective, despite the need for initial investment.
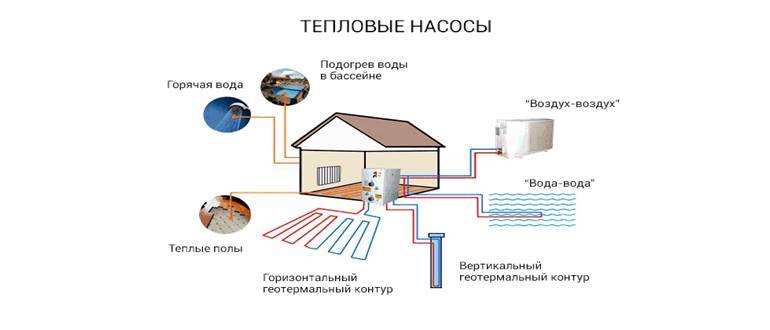
The main varieties, their principles of work
All heat pumps differ from each other in terms of energy source. The main classes of devices are ground-to-water, water-to-water, air-to-water, and air-to-air.

The first word indicates the source of heat, and the second - what it turns into in the device.
For example, in the case of a ground-water device, heat is extracted from the ground, and then it is converted into hot water, which is used as a heater in the heating system. Below we will consider the types of heat pumps for heating in more detail.
ground water
Ground-water installations extract heat directly from the ground using special turbines or collectors. In this case, the earth is used as a source, which heats the freon. It heats the water in the condenser tank. In this case, the freon is cooled and fed back to the pump inlet, and the heated water is used as a heat carrier in the main heating system.
The liquid heating cycle continues as long as the pump receives electricity from the network. The most costly, from an economic point of view, is the ground-water method, since for the installation of turbines and collectors, it will be necessary to drill deep wells or change the location of the soil on a large plot of land.
water-water
In terms of their technical characteristics, water-to-water pumps are very similar to ground-to-water devices, with the only difference being that in this case, water is not used as the primary heat source. As a source, both groundwater and various reservoirs can be used.
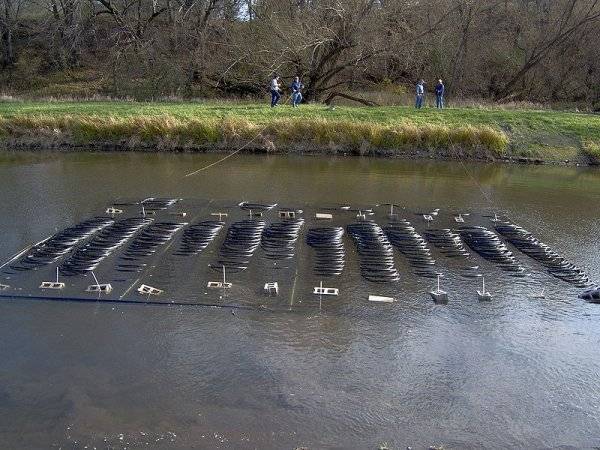

Photo 2. Installation of a structure for a water-to-water heat pump: special pipes are immersed in a reservoir.
Water-to-water devices are much cheaper than ground-to-water pumps, since they do not require deep wells to be installed.
Reference. To operate a water pump, it is enough to immerse several pipes in the nearest body of water, so no wells need to be drilled for its operation.
You will also be interested in:
Air to water
Air-to-water units receive heat directly from the environment. Such devices do not need a large external collector to collect heat, and ordinary street air is used to heat freon. After heating, freon gives off heat to water, after which hot water enters the heating system through pipes. Devices of this type are quite cheap, since an expensive collector is not needed to operate the pump.
Air
An air-to-air unit also receives heat directly from the environment, and it also does not require an external collector for its operation. After the contact of warm air, the freon is heated, then the freon heats the air in the pump. Then this air is thrown into the room, which leads to a local increase in temperature. Devices of this type are also quite cheap, since they do not require the installation of an expensive collector.
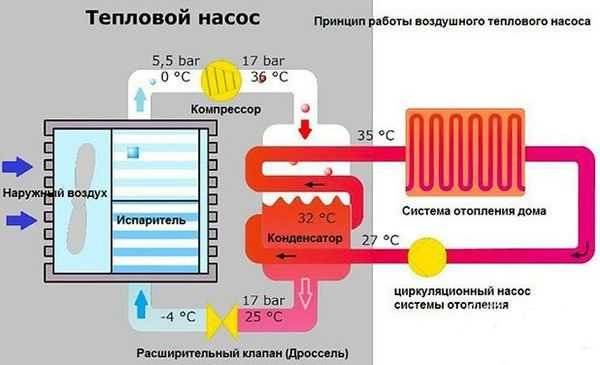
Photo 3. The principle of operation of an air-to-air heat pump.A coolant with a temperature of 35 degrees enters the heating radiators.
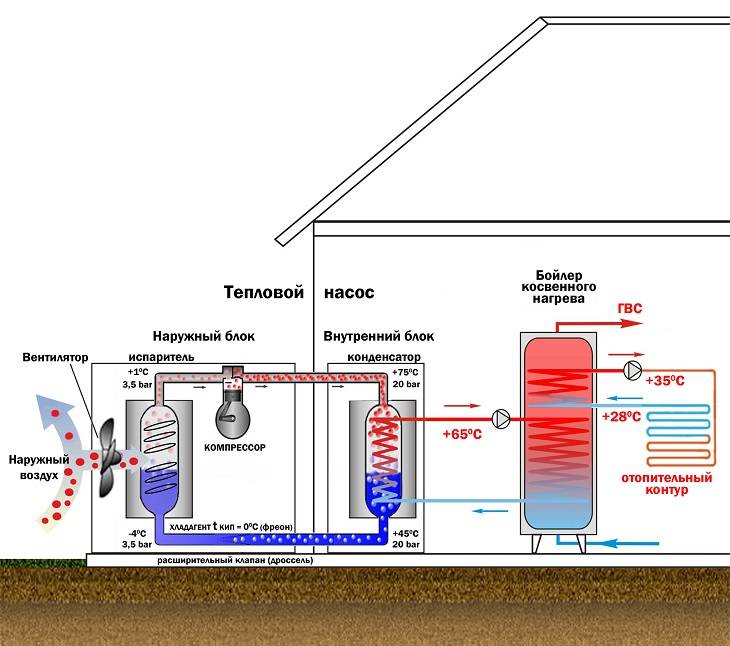
Heating system with heat pumps
Air-to-air heating is used in everyday life in local areas or throughout the house. When re-equipping a boiler room, gas, electric boilers will become an additional source of heat, which will be useful in case of significant drops in outside temperature - in this case, the efficiency of the HP drops and backup heating will help to cope with the load on the system.
It is most convenient to use a heat pump as a local equipment of local importance, you do not have to buy and install bulky units, heat is supplied through a flexible system with heat control, and a breakdown of one device will not disable the entire system.
The local scheme also has disadvantages:
- Difficulties with a clear direction of the flow of heated air. Directivity cannot be achieved without a duct system, and it is not always rational to pull additional pipelines.
- The efficiency of one powerful heating boiler is higher than the combined performance of all heat pumps, many outdoor units will overload the facade.
- The maximum length of the route between the outdoor and indoor units is limited. The parameters are prescribed in the data sheet of the devices and can become an obstacle to the construction of a local heating network for an office inside a small building.

If a centralized supply is arranged using an air-to-air heat pump, then one powerful unit is purchased, a central air duct is laid with outlets to each heated room.It is necessary to punch holes in the walls for air ducts, in addition, warm streams supplied from the ceiling raise dust - but these are the only drawbacks of the network.
More pluses:
- control of temperature indicators of heating in all rooms of the house;
- availability of integration of additional equipment - filters, humidifiers;
- with a decrease in thermal efficiency, the network is supplemented with a recuperation device, which minimizes heat leakage;
- One powerful device is much more profitable to maintain.
In order not to face the problem of freezing of outdoor units, it is recommended to establish an air preparation system based on a soil heat exchanger - this will simplify the operation of the air-to-air heat pump when the temperature drops.
Set of elements for the formation of air heating
To assemble the system, an outdoor unit, an indoor unit and a refrigerant transport circuit are required. A fan will also come in handy, which will force air into the channels. Air ducts and ventilation equipment are useful only when forming a centralized network; blocks and a circuit are enough for local heating.

The indoor unit is installed indoors, the outdoor unit is taken out of the building. Installation of the outdoor unit is allowed at a certain distance from the indoor unit - the size of the removal is indicated in the data sheet. As for the indoor module, it is hung in such a way as to supply heat to the local area, taking into account the efficiency of the flow distribution.
Where is the air heating system used?
The area of use depends on the type of network. Direct-flow circuits with constant air renewal in the room are used in industrial workshops where there is a risk of accumulation of explosive or flammable particles.Local heating is more profitable to use in offices, private buildings.
The system is beneficial for homeowners, provided that interruptions occur with other coolants. For example, the installation of gas heating starts from $7,000 (450,000 rubles) plus obtaining permits, regular checks, and an air-to-air heat pump costs from $1,000 (65,000 rubles) and can work for heating and cooling from the first day of operation. A centralized network will not require permits, it is enough to correctly calculate the length of pipelines and the power of the unit - experts will charge from $ 150 (10,000 rubles) for drafting a project.
Selection and calculations of a heat pump
An air-to-air heat pump will only be effective if it is properly selected. It is necessary to calculate in advance its power, depending on the quadrature of the house. And only then look at the prices of different manufacturers.
In the calculations, the energy efficiency coefficient COP is used (the ratio of HP power to consumed energy).
Under "greenhouse conditions" it often reaches 4-5 points, and the most modern models up to 7-8. However, when the outside temperature drops to -15–20°C, this figure drops sharply to only two.
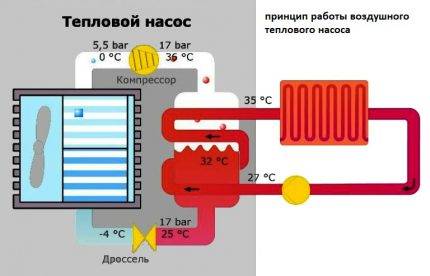 The heat pump delivers optimal heating performance at outdoor temperatures of -10 ... +10 degrees Celsius, so it takes up to ¾ of the heat energy from the street
The heat pump delivers optimal heating performance at outdoor temperatures of -10 ... +10 degrees Celsius, so it takes up to ¾ of the heat energy from the street
When calculating air heating, it is necessary to take into account:
- thermal insulation and insolation of premises;
- area of rooms;
- the number of people living in the cottage;
- general climatic conditions of the area where the house stands.
For most houses, for every ten square meters, about 0.7 kW of heat pump power is needed. But everything here is rather conditional.If the ceilings are higher than 2.7 m or the walls and windows are poorly insulated, then more heat will be required.
There are many manufacturers of air-to-air heat pumps in Asia and Europe.
Good reviews have systems from Daikin, Dimplex, Hitachi, Vaillant, Mitsubishi, Fujitsu, Carrier, Aertec, Panasonic and Toshiba. Almost all of their models are adapted to domestic operating conditions and have proven themselves well.
Even with voltage drops, they do not break, continuing to work properly after turning on the electricity.
The price of running air heat pumps varies from 90 to 450 thousand rubles. Here, much depends not only on the power of the unit, but also on additional functionality and the country of manufacture.
Individual models complement:
• air purification and disinfection filters; • backup heaters; • electric generators; • GSM modules for system management; • ionizers and ozonizers.
Practice shows that at frosts below -15 ° C, it becomes cool in rooms heated only by an air heat pump. And without an additional heater, the comfort in the rooms frankly does not smell.
However, in the southern regions, where such frosts are rare, HP is quite effective and more than justifies the money spent due to energy savings.
Conclusions based on the results of use
The entire turnkey ventilation and heating system cost about 280,000 rubles. Here it should be taken into account that the work was carried out on our own, and when purchasing equipment and materials, the talents of “knocking out” discounts were used to the maximum.
Many do not believe that in our latitudes it is possible to heat the air heated by electricity. From our own experience we can say that it is real. Such systems work and even save money.The average monthly amount for heating is 6000-8000 rubles. From the experience of neighbors with houses of the same area, we know that they pay both 20,000 and 25,000 rubles a month. It turns out that all our expenses for installing an air-to-air heat pump will fully pay off in about 2 years.