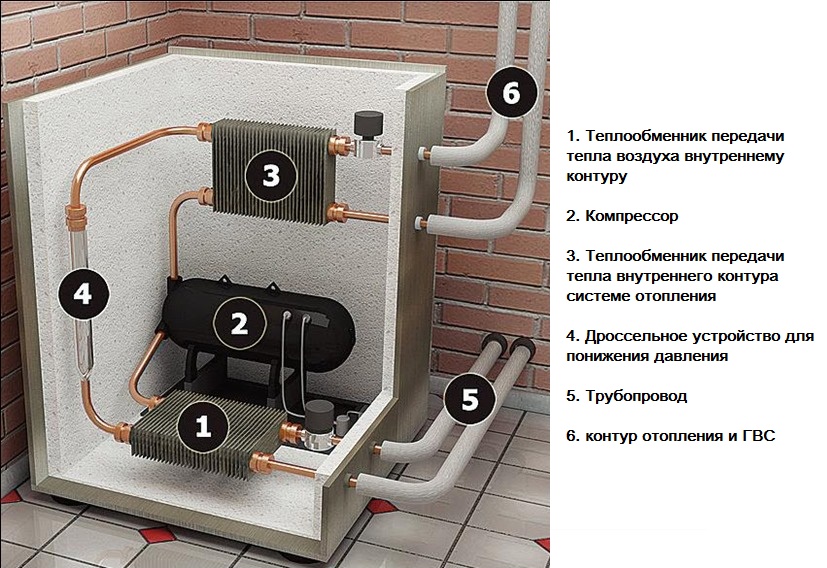
- Nuances of scheduled maintenance of air source heat pumps
- Owners of air source heat pumps told FORUMHOUSE how much this type of heating costs them in winter and whether they regretted their choice
- Homemade from an old refrigerator
- What is a heat pump for heating a private house? How does it work?
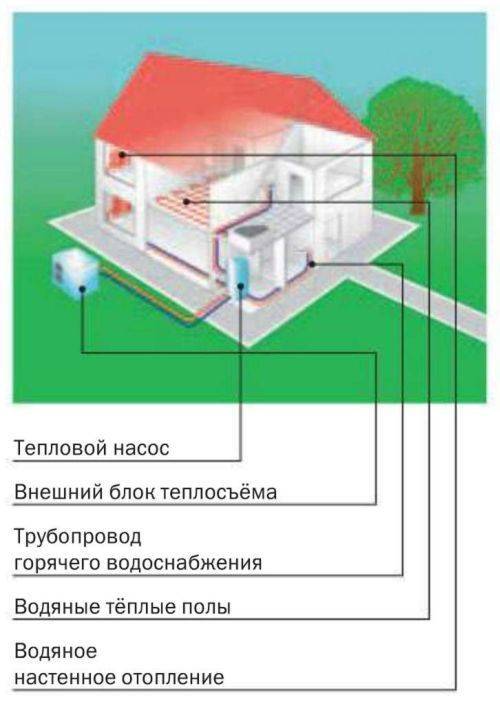
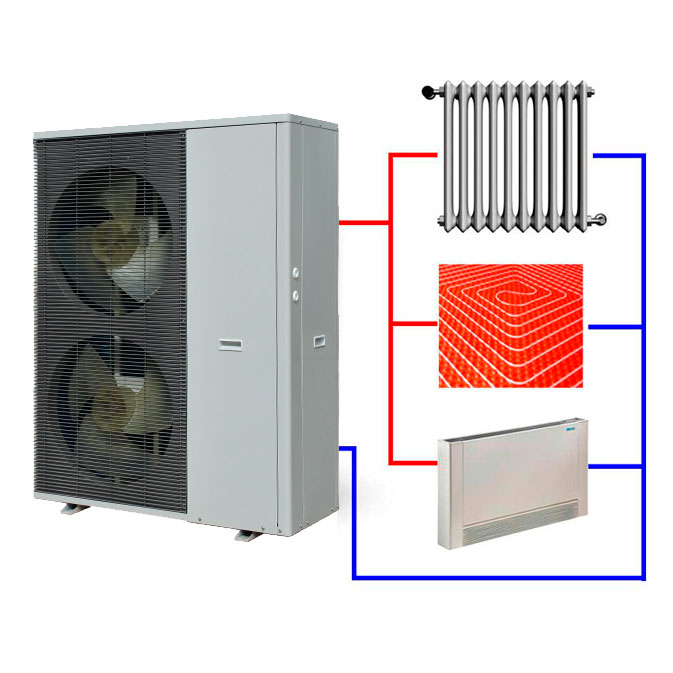
- Heat pump external circuit options
- Source of thermal energy - well
- Heat source - soil on the site
- Outer loop in water
- The principle and scheme of operation of a heat pump, types
- Principle
- Scheme of work
- Types of heat pumps
- Ground or earth ("ground-air", "ground-water")
- Water pump ("water-air", "water-water")
- Air (air-to-water, air-to-air)
- What is a heat pump and how does it work?
- Heat pump from air conditioner
- Air-to-water heat pump - the real facts
- Principle of operation
- Air-to-water heat pump
- Installation and operation of the AIR-WATER heat pump
- From tubes with a rarefied medium
- Conclusions and useful video on the topic
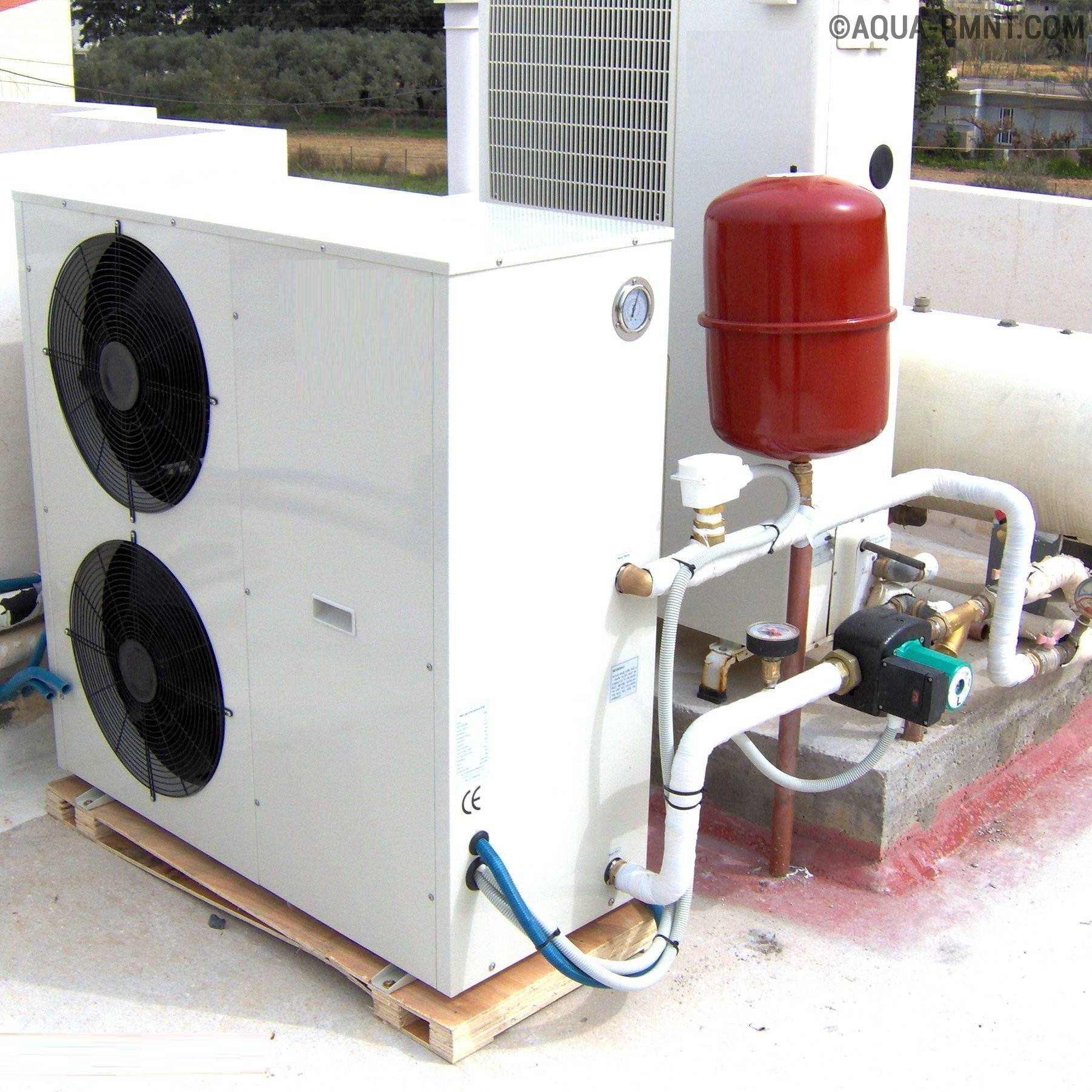
Nuances of scheduled maintenance of air source heat pumps
In order for the heat pump to serve its entire term, it is necessary from time to time to perform simple manipulations for its maintenance. The action plan includes:
- Timely cleaning of the outdoor unit of the pump.This mainly concerns the base of the fan and the heat exchanger.
- Scheduled leak test of the refrigerant circulation system.
- Changing the oil in the compressor unit and lubricating the moving parts of the fan.
- Checking power cables.
You do not need to spend a lot of effort to perform these actions, but they will allow you to keep the heat pump in perfect condition for a long time.
Owners of air source heat pumps told FORUMHOUSE how much this type of heating costs them in winter and whether they regretted their choice
The constant rise in energy prices makes the owners of suburban real estate think about how to reduce heating costs. One option is to build an insulated house with minimal heat loss. The second step is to install a low-temperature heating system. The third is to heat the coolant with an air-to-water heat pump. At first glance, it seems that this is an unreasonably expensive solution, and the air source heat pump will work inefficiently in winter. Let's check if this is true using the example of FORUMHOUSE users who installed heat pumps in their house.
- Heating in winter with an air-to-water heat pump - myth or reality
- How much heat does an air-to-water heat pump produce at sub-zero temperatures?
- Conclusions and recommendations
This is interesting: Do-it-yourself solar battery - how make a custom panel
Homemade from an old refrigerator
It is quite difficult to assemble an air-to-air heat pump from individual compressors and condensers with your own hands without specialized engineering knowledge. But for a small room or a greenhouse, you can use an old refrigerator.
The simplest air heat pump can be made from a refrigerator by extending an air duct into it from the street and hanging a fan on the rear grille of the heat exchanger
To do this, you need to make two holes in the front door of the refrigerator. Through the first, street air will enter the freezer, and through the second lower one, it will be brought back to the street.
At the same time, during the passage through the inner chamber, it will give off part of the heat it contains to freon.
It is also possible to simply build the refrigeration machine into the wall with the door open to the outside, and the heat exchanger at the back into the room. But it should be borne in mind that the power of such a heater will be small, and it consumes a lot of electricity.
The air in the room is heated by a heat exchanger at the back of the refrigerator. However, such a heat pump is only able to operate at outdoor temperatures not lower than plus five Celsius.
This appliance is designed for indoor use only.
In a large cottage, the air heating system will have to be supplemented with air ducts that distribute warm air evenly throughout all rooms.
The installation of an air-to-air heat pump is extremely simple. It is necessary to install the external and internal units, and then connect them to each other with a circuit with a coolant.
The first part of the system is installed outdoors: directly on the facade, roof or next to the building. The second in the house can be placed on the ceiling or wall.
It is recommended to mount the outdoor unit a few meters from the entrance to the cottage and away from the windows, do not forget about the noise produced by the fan.
And the internal one is installed so that the flow of warm air from it is evenly distributed throughout the room.
If it is planned to heat a house with several rooms on different floors with an air-to-air heat pump, then you will have to equip a system of ventilation ducts with forced injection.
In this case, it is better to order a project from a competent engineer, otherwise the power of the heat pump may not be enough for all the premises.
The electricity meter and protective device must be able to withstand the peak loads generated by the heat pump. With a sharp cold snap outside the window, the compressor begins to consume electricity many times more than usual.
It is best to lay a separate supply line from the switchboard for such an air heater.
Particular attention should be paid to the installation of pipes for freon. Even the smallest chips inside can damage compressor equipment
Here you can not do without copper soldering skills. Refilling refrigerant should generally be entrusted to a professional in order to avoid problems with its leaks later.
What is a heat pump for heating a private house? How does it work?
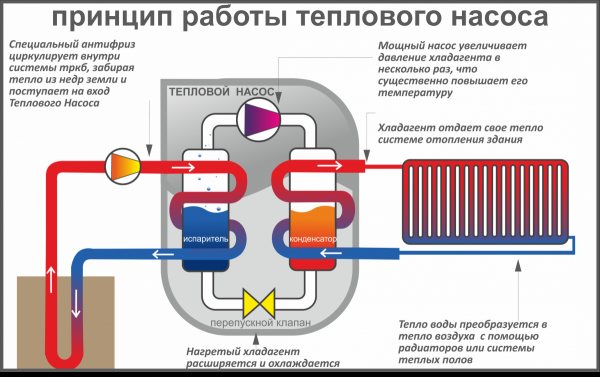
A special device that is able to extract heat from the environment is called a heat pump.
Such devices are used as the main or additional method of space heating. Some devices also work for passive cooling of the building - while the pump is used for both summer cooling and winter heating.
The energy of the environment is used as fuel. Such a heater extracts heat from air, water, groundwater, and so on, so this device is classified as a renewable energy source.
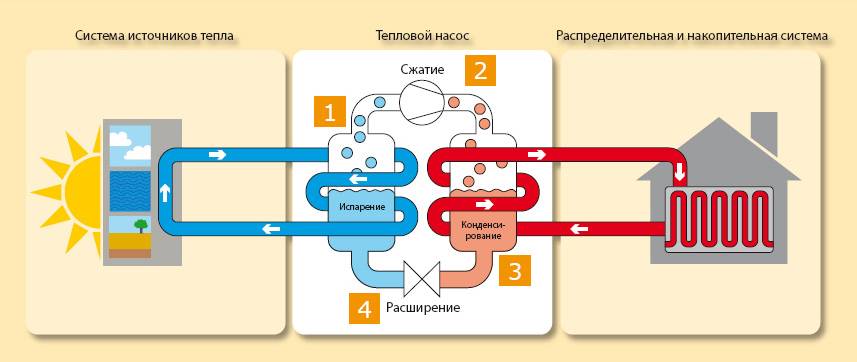
Important! These pumps require an electrical connection to operate.All thermal devices include an evaporator, a compressor, a condenser and an expansion valve. Depending on the heat source, water, air and other devices are distinguished.
The principle of operation is very similar to the principle of the refrigerator (only the refrigerator throws out hot air, and the pump absorbs heat)
Depending on the heat source, water, air and other devices are distinguished. The principle of operation is very similar to the principle of the refrigerator (only the refrigerator throws out hot air, and the pump absorbs heat)
All thermal devices include an evaporator, a compressor, a condenser and an expansion valve. Depending on the heat source, water, air and other devices are distinguished. The principle of operation is very similar to that of a refrigerator (only the refrigerator throws out hot air, and the pump absorbs heat).
Most devices operate both at positive and negative temperatures, however, the efficiency of the device directly depends on external conditions (i.e., the higher the ambient temperature, the more powerful the device will be). In general, the device works as follows:
- The heat pump comes into contact with the surrounding conditions. Typically, the device extracts heat from the ground, air or water (depending on the type of device).
- A special evaporator is installed inside the device, which is filled with refrigerant.
- Upon contact with the environment, the refrigerant boils and evaporates.
- After that, the refrigerant in the form of vapor enters the compressor.
- There it shrinks - due to this, its temperature rises seriously.
- After that, the heated gas enters the heating system, which leads to the heating of the main coolant, which is used for space heating.
- The refrigerant cools down little by little. In the end, it turns back into a liquid.
- Then the liquid refrigerant enters a special valve, which seriously lowers its temperature.
- At the end, the refrigerant enters the evaporator again, after which the heating cycle is repeated.
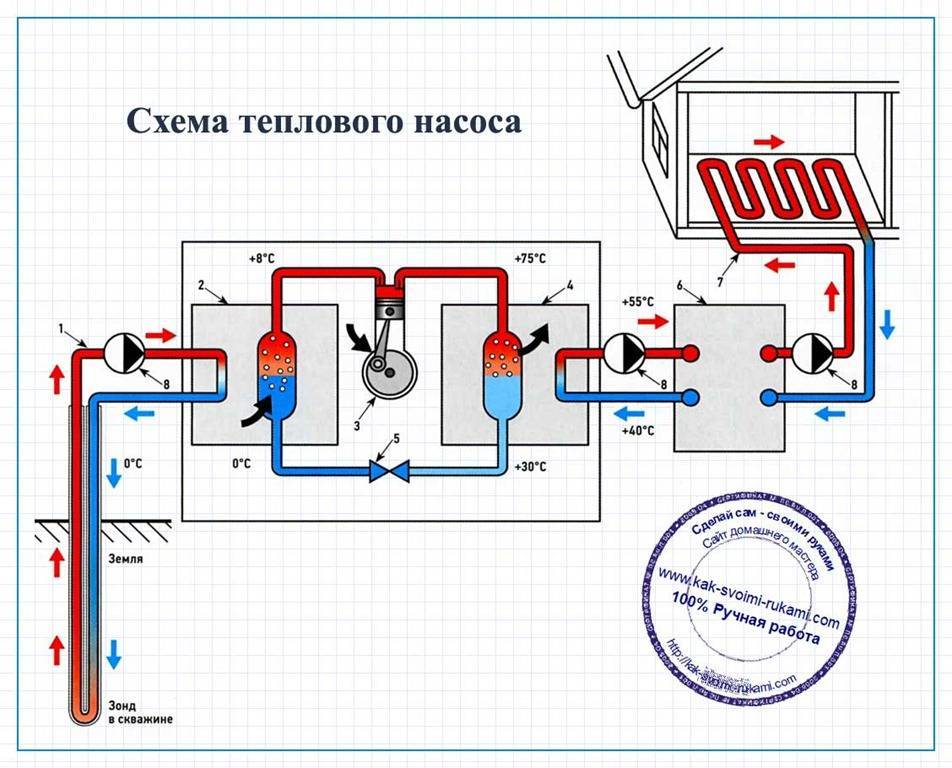
Photo 1. The principle of operation of a ground-to-water heat pump. Blue indicates cold, red indicates hot.
Advantages:
- Environmental friendliness. Such devices are renewable energy sources that do not pollute the atmosphere with their emissions (whereas natural gas produces harmful greenhouse gases, and electricity is often used to burn coal, which also pollutes the air).
- Good alternative to gas. A heat pump is ideal for space heating in cases where the use of gas is difficult for one reason or another (for example, when the house is far from all major utilities). The pump also compares favorably with gas heating in that the installation of such a device does not require state permission (but when drilling a deep well, you still have to get it).
- Inexpensive additional heat source. The pump is ideal as a cheap auxiliary power source (the best option is to use gas in winter and a pump in spring and autumn).
Flaws:
- Thermal restrictions in case of using water pumps.All thermal devices function well at positive temperatures, while in the case of operation at negative temperatures, many pumps stop working. This is mainly due to the fact that the water freezes, which makes it impossible to use it as a heat source.
- There may be problems with devices that use water as heat. If water is used for heating, then a stable source will need to be found. Most often, a well must be drilled for this, due to which the installation costs of the device may increase.
Attention! Pumps usually cost 5-10 times more than a gas boiler, therefore, the use of such devices in order to save money in some cases may be impractical (for the pump to pay off, you will need to wait several years)
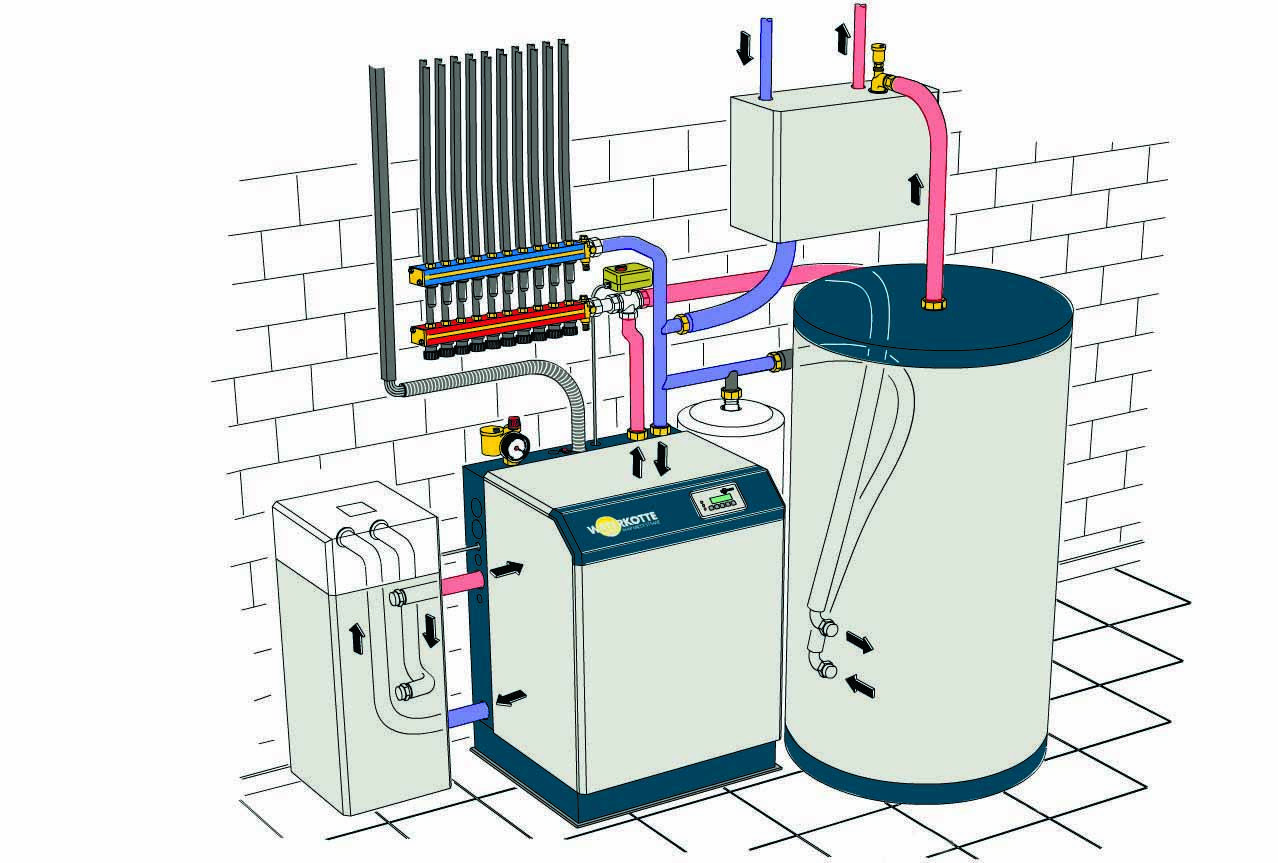
Heat pump external circuit options
The external circuit may be a heat exchanger pipeline that takes heat from a well, soil or reservoir. Each of these options has its own characteristics, advantages and disadvantages, both during installation and during operation. Therefore, we will consider them in more detail.
Source of thermal energy - well
In order to use such a heat source, it is necessary to drill a well (one deep or several shallow ones) or use an existing one. It is believed that 50-60 W of thermal energy can be obtained from one linear meter of a well. Therefore, for 1 kW of heat pump power, about 20 m of well will be required.
External circuit of the heat pump in the well
Advantage: the well does not take up much space on the site and is characterized by high heat transfer.
Disadvantage: a well, especially a deep one, must be drilled with the help of special mechanisms or machines.
Heat source - soil on the site
In this case, the outer circuit pipe must be laid to a depth exceeding the maximum freezing depth in the area. In this case, there can be two options for laying: remove all the soil in a certain area and lay the pipe in the form of zigzags, and then fill everything with soil, or you can lay the pipe in trenches dug for this.

Heat pump "ground-water"
For 1 kW of heat pump power, depending on the laying depth, density and water content of the soil, 35-50 m of the circuit may be needed. The minimum distance between the pipes of the circuit is 0.8 m.
Disadvantages of this type of external contour:
- for its placement, a sufficiently large area is required, on which subsequently it will not be possible to plant trees or shrubs, but only a lawn, flowers or annual plants;
- a large amount of earthworks.
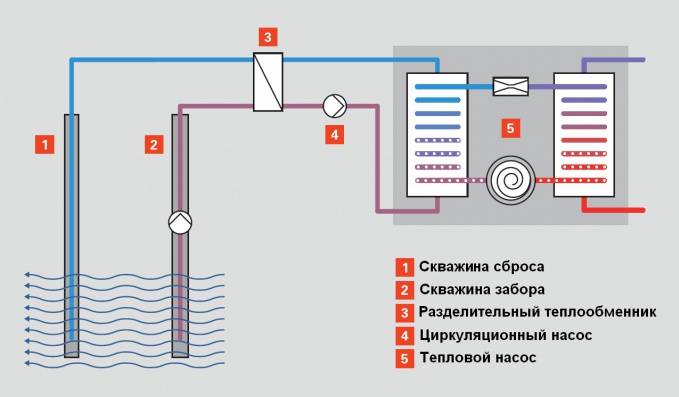
Outer loop in water
Another option for the external contour is that the pipe is laid on the bottom of the nearest reservoir, if it is near the house. At the same time, the reservoir should be deep enough so as not to freeze to the bottom in winter. From one linear meter of such an external circuit, a maximum of about 30 W of thermal energy can be obtained (at least 30 m of pipe per 1 kW of heat pump power). To ensure that the pipeline laid on the bottom does not float up, a load is placed on it - about 5 kg per linear meter.
External circuit of the heat pump in the reservoir
Advantage: no need to drill a well or carry out earthworks over a large area.
The main disadvantage of such an external circuit is that there is not always a suitable reservoir near the house.
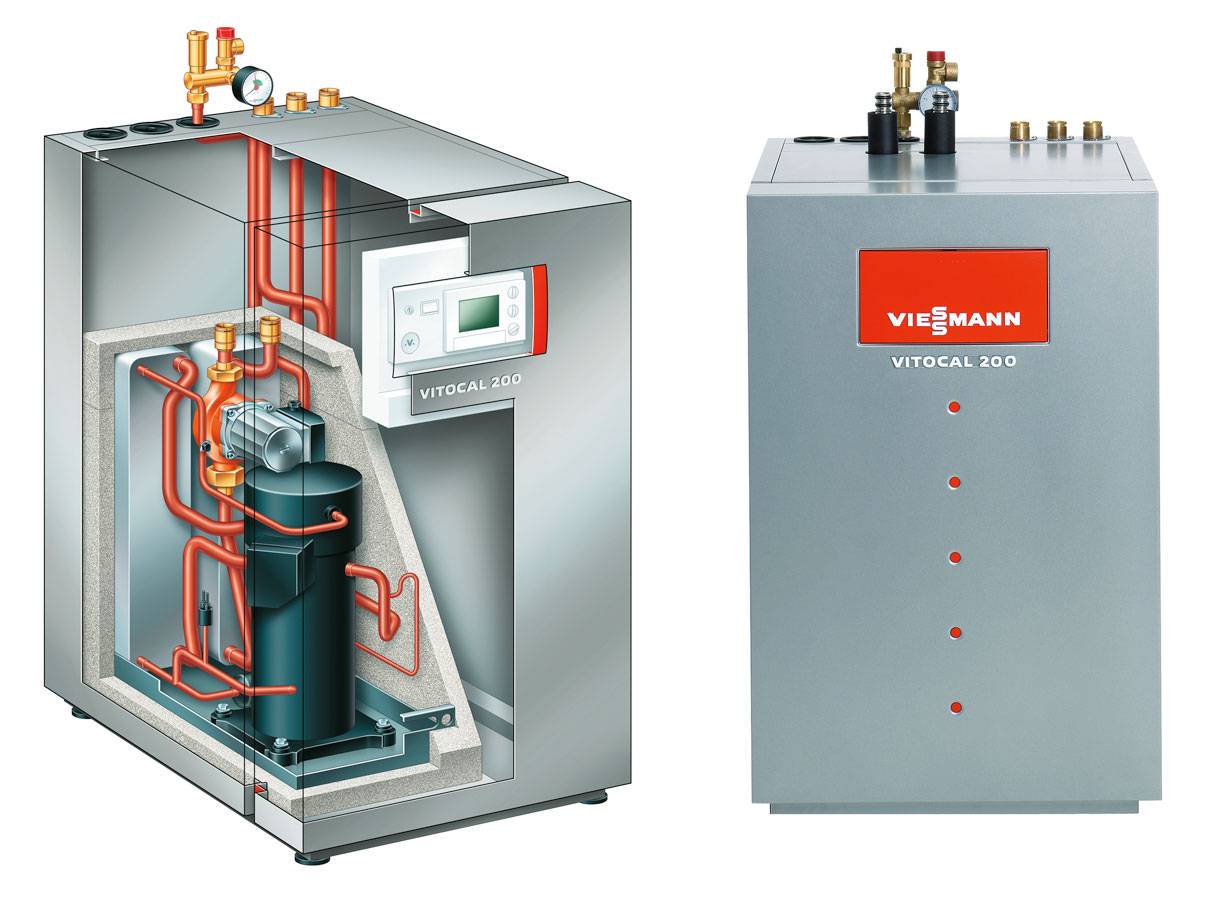
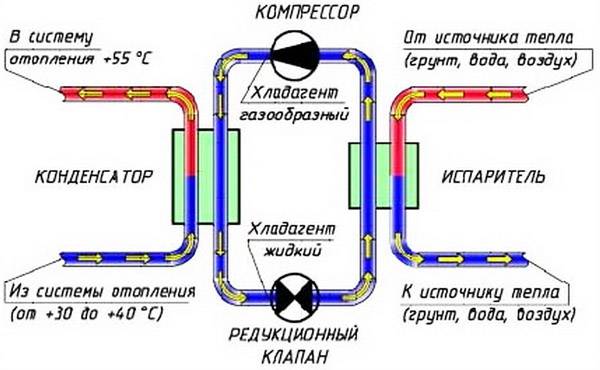
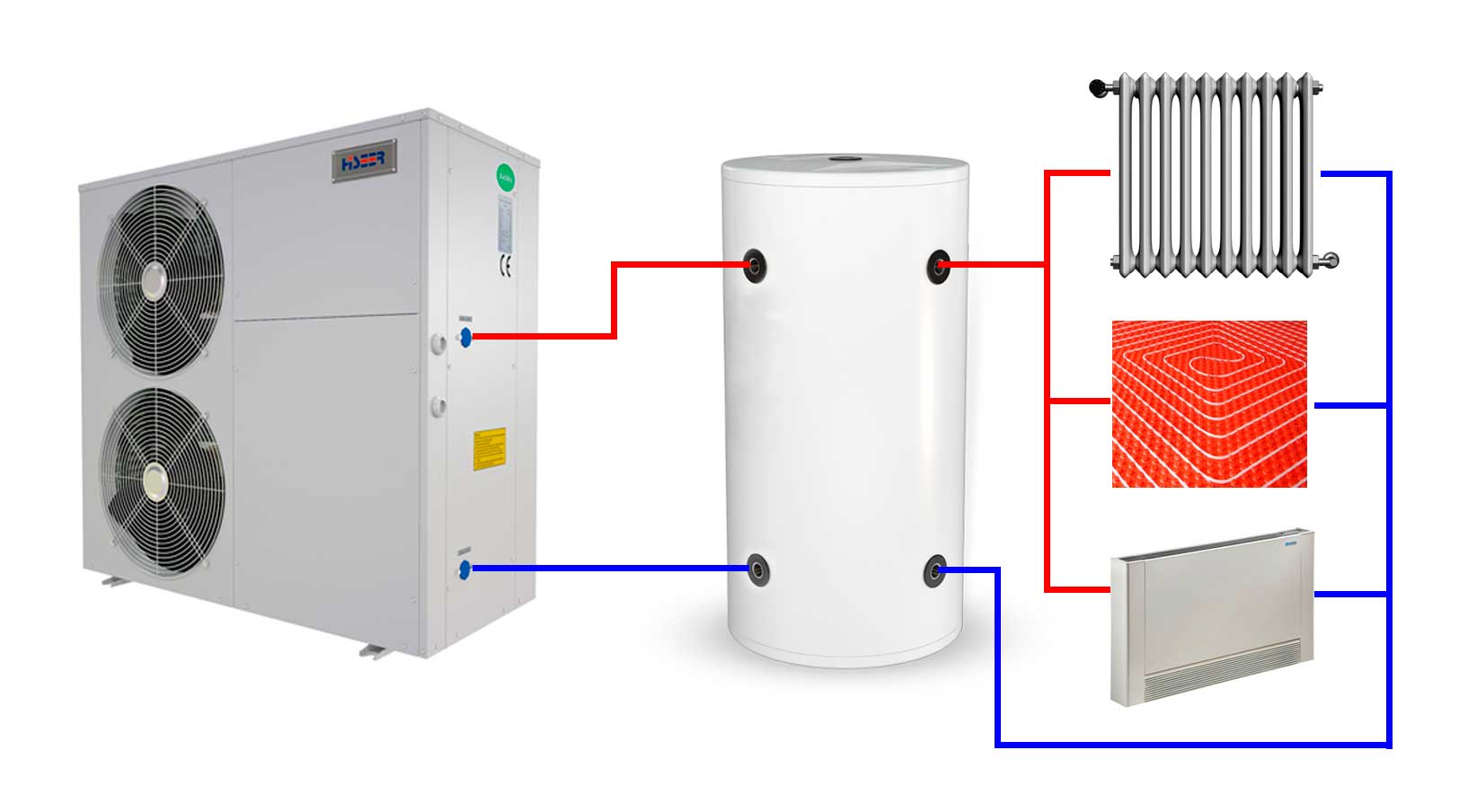
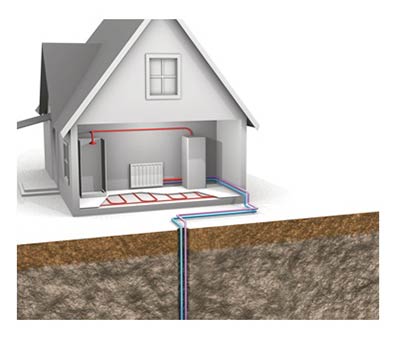
The principle and scheme of operation of a heat pump, types
Principle
The design of any heat pump provides for 2 parts: external (absorbs heat from external sources) and internal (transfers the withdrawn heat directly to the heating system of the room). External renewable sources of thermal energy are, for example, the heat of the earth, air or ground water. This design allows you to significantly reduce the cost of heating or cooling for a private house, because approximately 75% of the energy is generated thanks to free sources.
Scheme of work
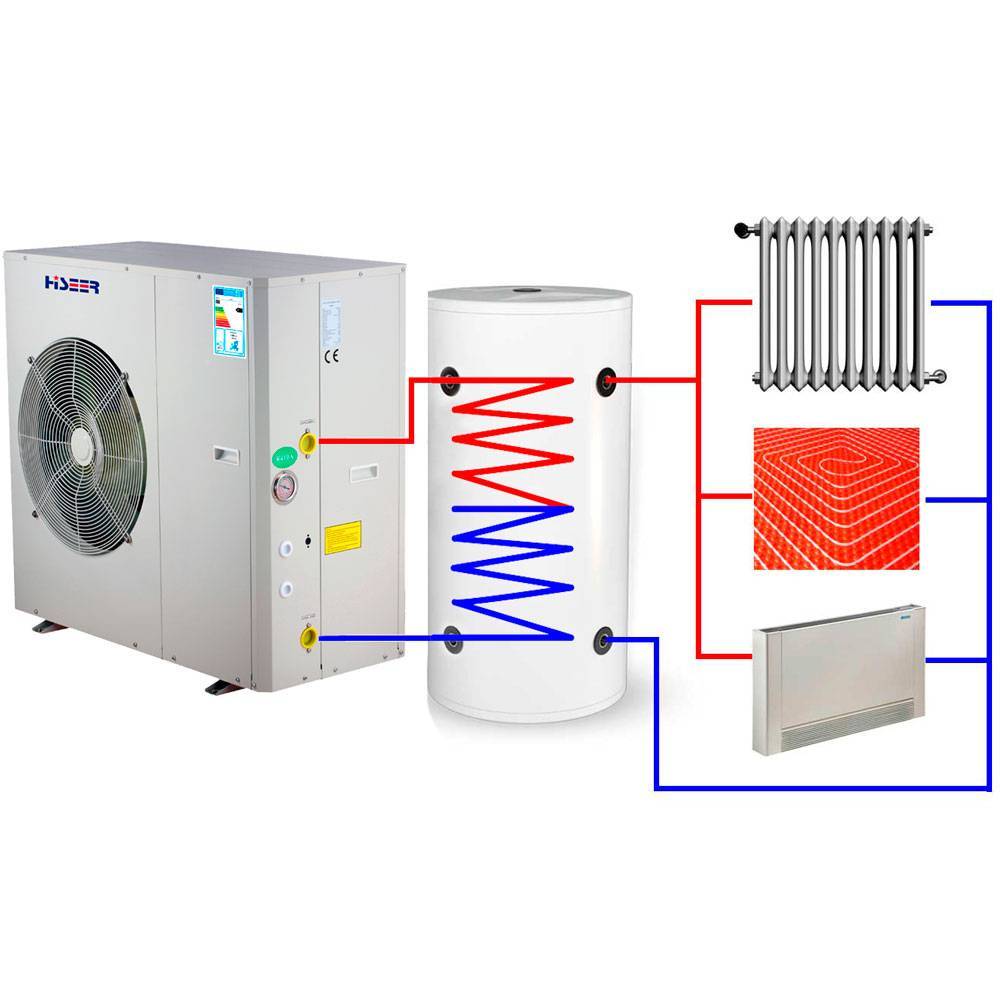
The composition of the heating installation includes: evaporator; capacitor; a discharge valve that lowers the pressure in the system; pressure booster compressor. Each of these nodes is connected to each other by a closed circuit of the pipeline, inside which the refrigerant is located. The refrigerant in the first cycles is in a liquid state, in the next - in a gaseous state. This substance has a low boiling point, therefore, with the option of earth-type equipment, it is able to transform into gas, reaching the level of soil temperature. Next, the gas enters the compressor, where there is a strong compression, which leads to rapid heating. After that, hot steam enters the inside of the heat pump, and is already used here directly for space heating or for heating water. The refrigerant then cools down, condenses and re-liquids. Through the expansion valve, the liquid substance flows into the underground part to repeat the heating cycle.
The principle of cooling of such an installation is similar to the principle of heating, but not radiators, but fan coil units are used. The compressor does not work in this case.Cold air from the well directly enters the air conditioning system.
Types of heat pumps
What are the types of heat pumps? Equipment is distinguished by an external source of heat energy that is used in the system. Among household options, there are 3 types.
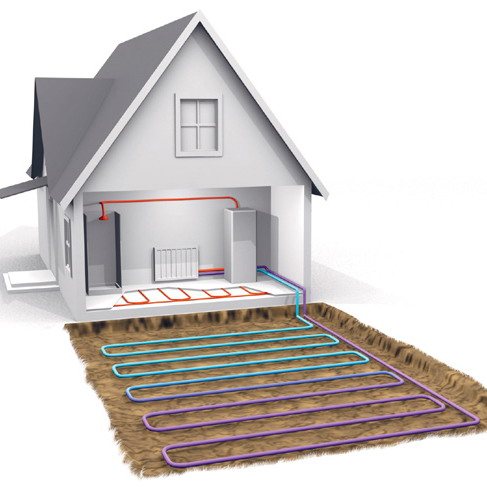
Ground or earth ("ground-air", "ground-water")
The use of an earthen heat pump as a source of heat energy will ensure eco-cleanliness and safety. The cost of such equipment is high, but its functionality is huge. No frequent service is required, and a long service life is ensured.
Ground source heat pumps can be of two types: with vertical or horizontal installation of pipelines. The vertical laying method is more costly as deep well drilling is required in the range of 50-200 meters. With a horizontal arrangement, the pipes are laid to a depth of about a meter. In order to ensure the collection of the required amount of heat energy, the total area of pipelines should exceed the area of heated premises by 1.5-2 times.
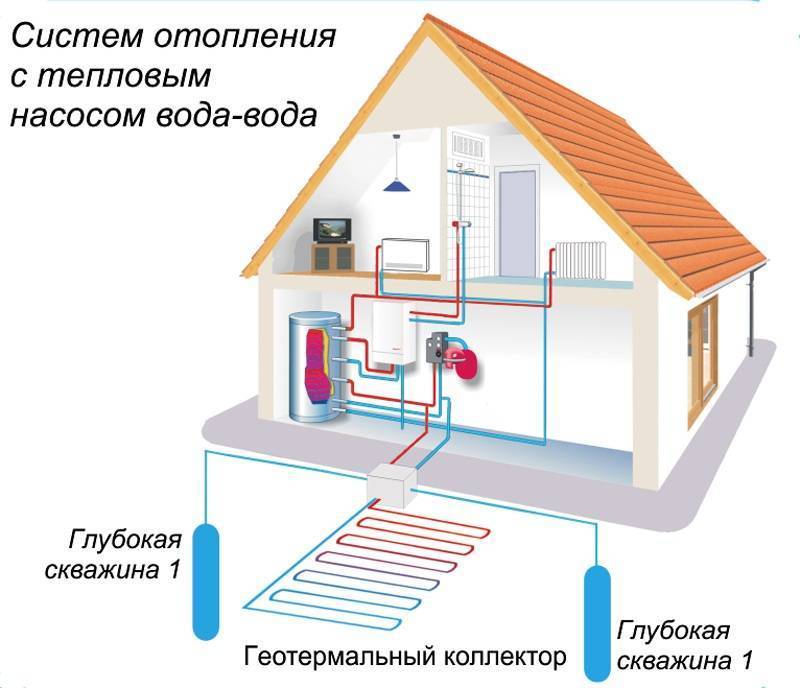
Water pump ("water-air", "water-water")
For southern regions with a warm climate, water installations are suitable. In sun-warmed water bodies, the water temperature at a certain depth is relatively stable. It is preferable to lay the hoses in the bottom soil itself, where the temperature is higher. A weight is used to fix underwater pipelines.
Air (air-to-water, air-to-air)
In an air-type unit, the source of energy is air from the external environment, which enters the evaporator heat exchanger, where the liquid refrigerant is located.The temperature of the refrigerant is always lower than the temperature of the air entering the system, so the substance instantly boils and becomes a hot vapor.
In addition to classic models, combined installation options are in demand. Such heat pumps are supplemented with a gas or electric heater. In case of bad climatic conditions, the performance of the heating device decreases and the device switches to an alternative heating option. Such an addition is especially relevant for air-to-water or air-to-air equipment, since it is these types that tend to reduce efficiency.
For regions with long cold winters, it is most reliable to use geothermal (ground) heat pumps. Air heat pumps are suitable for areas with a mild southern climate. Also, when installing equipment that uses earth energy, the characteristics of the soil should be taken into account. The productivity of the heat pump will be much higher in clay soil than in sandy soil. In addition, the depth of the pipelines is important, the pipes must be laid deeper than the ground freezing level during cold periods.
What is a heat pump and how does it work?
The term heat pump refers to a set of specific equipment. The main function of this equipment is the collection of thermal energy and its transportation to the consumer. The source of such energy can be any body or medium with a temperature of +1º and more degrees.
There are more than enough sources of low-temperature heat in our environment.These are industrial waste from enterprises, thermal and nuclear power plants, sewage, etc. For the operation of heat pumps in the field of home heating, three independently recovering natural sources are needed - air, water, earth.
Heat pumps “draw” energy from processes that regularly occur in the environment. The flow of processes never stops, therefore the sources are recognized as inexhaustible according to human criteria.
The three listed potential energy suppliers are directly related to the energy of the sun, which, by heating, sets the air and wind in motion and transfers thermal energy to the earth. It is the choice of source that is the main criterion according to which heat pump systems are classified.
The principle of operation of heat pumps is based on the ability of bodies or media to transfer thermal energy to another body or environment. Recipients and suppliers of energy in heat pump systems usually work in pairs.
So there are the following types of heat pumps:
- Air is water.
- Earth is water.
- Water is air.
- Water is water.
- Earth is air.
- Water - water
- Air is air.
In this case, the first word defines the type of medium from which the system takes low-temperature heat. The second indicates the type of carrier to which this thermal energy is transferred. So, in heat pumps water is water, heat is taken from the aquatic environment and liquid is used as a heat carrier.
Heat pumps by design type are vapor compression plants. They extract heat from natural sources, process and transport it to consumers (+)
Modern heat pumps use three main sources of heat energy. These are soil, water and air.The simplest of these options is an air source heat pump. The popularity of such systems is associated with their rather simple design and ease of installation.
However, despite such popularity, these varieties have a rather low productivity. In addition, the efficiency is unstable and dependent on seasonal temperature fluctuations.
With a decrease in temperature, their performance drops significantly. Such variants of heat pumps can be considered as an addition to the existing main source of thermal energy.
Equipment options that use ground heat are considered more efficient. The soil receives and accumulates thermal energy not only from the Sun, it is constantly heated by the energy of the earth's core.
That is, the soil is a kind of heat accumulator, the power of which is practically unlimited. Moreover, the temperature of the soil, especially at a certain depth, is constant and fluctuates within insignificant limits.
Scope of energy generated by heat pumps:
The constancy of the source temperature is an important factor in the stable and efficient operation of this type of power equipment. Systems in which the aquatic environment is the main source of thermal energy have similar characteristics. The collector of such pumps is located either in the well, where it is in the aquifer, or in the reservoir.
The average annual temperature of sources such as soil and water varies from +7º to + 12º C. This temperature is quite enough to ensure the efficient operation of the system.
The most efficient are heat pumps that extract heat energy from sources with stable temperature indicators, i.e. from water and soil
Heat pump from air conditioner
Modern split systems, especially inverter type, successfully perform the functions of the same air-to-air heat pump. Their problem is that the efficiency of work falls along with the outside temperature, even the so-called winter set does not save.
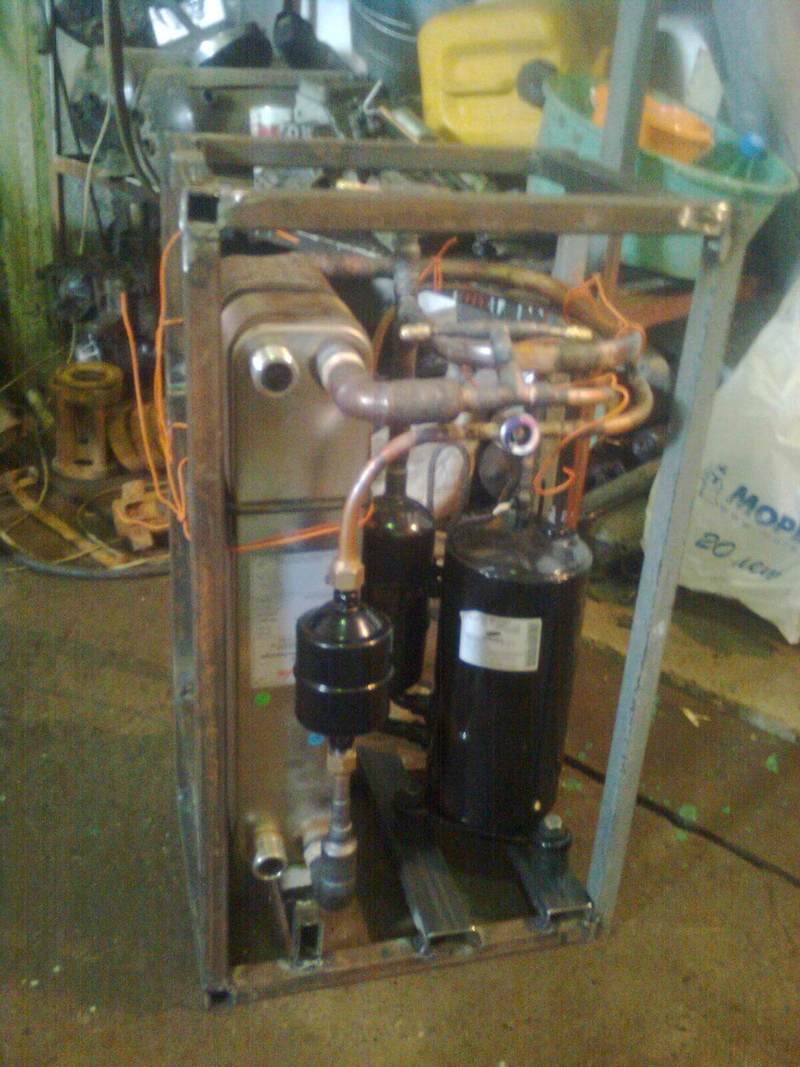

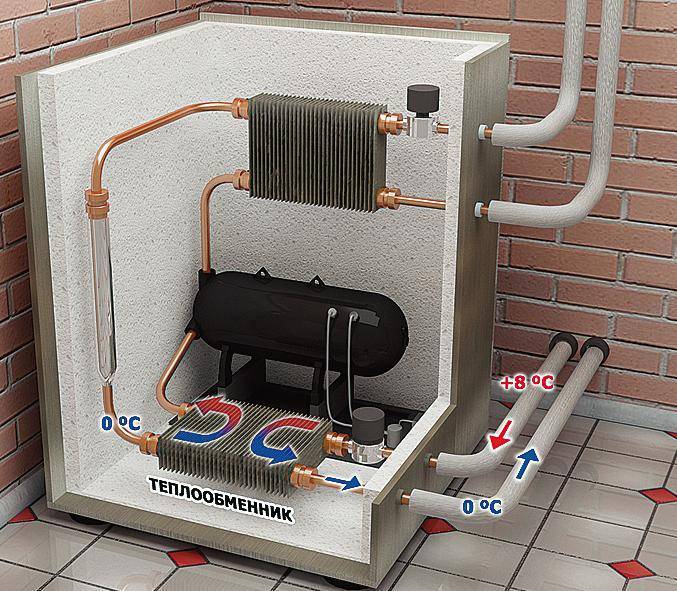
Home craftsmen approached the issue differently: they assembled a home-made heat pump from an air conditioner, which takes the heat of running water from a well. In fact, only a compressor is used from the air conditioner, sometimes an indoor unit that plays the role of a fan coil unit.
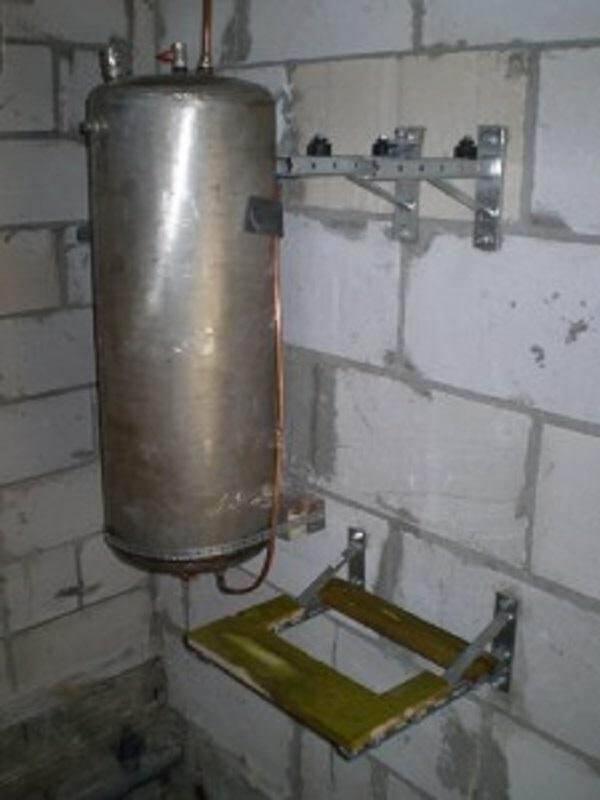

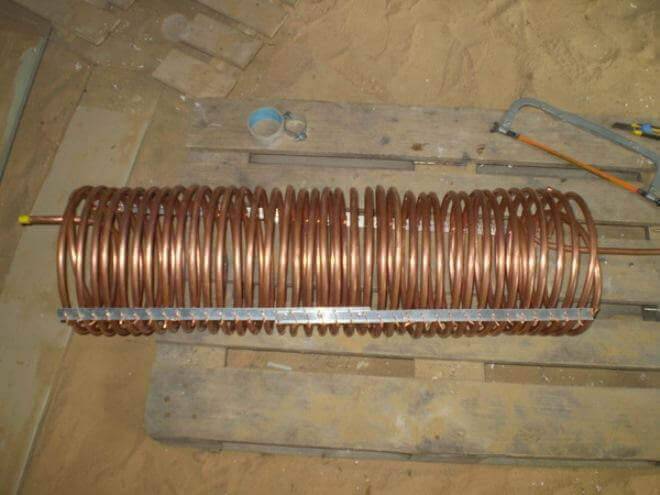
By and large, the compressor can be purchased separately. It will need to make a heat exchanger for heating water (condenser). A copper tube with a wall thickness of 1–1.2 mm and a length of 35 m is wound to form a coil onto a pipe with a diameter of 350–400 mm or a cylinder. After that, the turns are fixed with a perforated corner, and then the whole structure is placed in a steel container with water pipes.

The compressor from the split system is connected to the lower input to the condenser, and the control valve is connected to the upper one. The evaporator is made in the same way; an ordinary plastic barrel will do for it. By the way, instead of homemade capacitive heat exchangers, you can use factory plate heat exchangers, but this will not be cheap.

The assembly of the pump itself is not too complicated, but here it is important to be able to properly and efficiently solder the copper tube connections. Also, to refuel the system with freon, you will need the services of a master, you won’t specifically buy additional equipment
Next is the stage of setting up and starting up the heat pump, which does not always go well. You may have to tinker a lot to achieve the result.

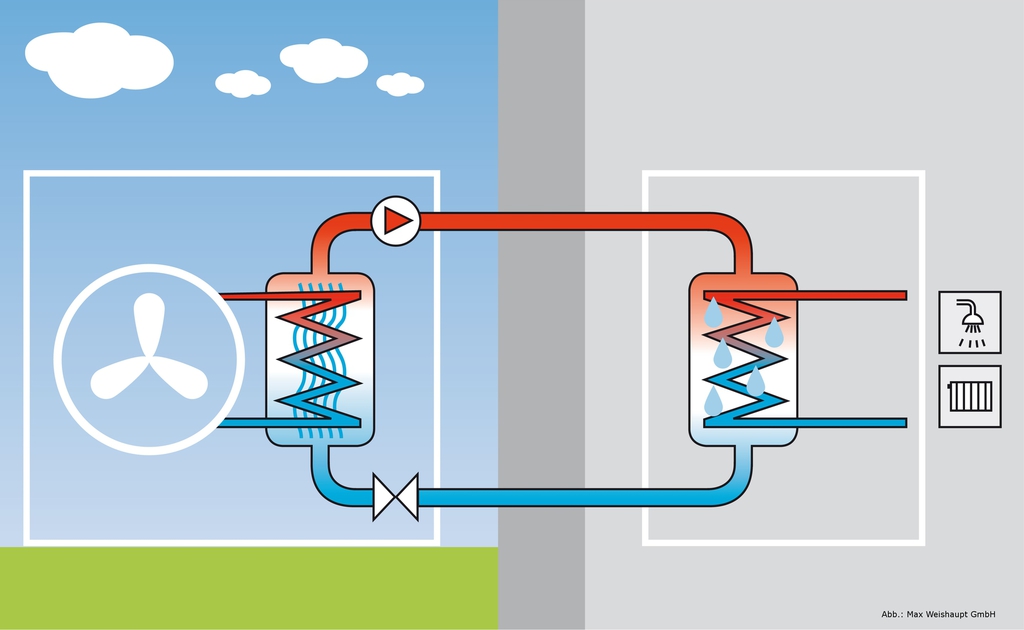
Air-to-water heat pump - the real facts
This type of thermal equipment causes a lot of controversy. Users are divided into two camps. Some believe that, for heating a house, nothing better has been invented. Others believe that, due to the high cost of heat pumps (HP) and harsh climatic conditions in many regions of the Russian Federation, the initial investment will not be recouped. It is more profitable to put money in the bank, and, on the interest received, to heat the house with electricity. As always, the truth is in the middle. Looking ahead, we will say that, in the article, we will only talk about air-to-water heat pumps. First, a little theory.
A heat pump is a “machine” that takes heat from a low-grade source and transfers it to the house.
Heat sources for a heat pump:
- air;
- water;
- Earth.
Schematic diagram of the heat pump.
Important point: The heat pump does not produce heat. It pumps heat from the external environment to the consumer, but for the heat pump to function, electricity is required. The efficiency of the heat pump is expressed in the ratio of the pumped heat energy to the energy consumed from the electrical network. This value is called the coefficient of heat transformation COP (coefficient of performance). If the technical characteristics of the heat pump state that COP = 3, then this means that the HP pumps three times more heat than it “takes” electricity.
It seems that here it is - the solution to all problems - relatively speaking, having spent 1 kW of electricity in one hour, we will receive 3 kilowatt-hours of heat for the heating system during this time. In fact, becausewe are talking about air source heat pumps with an outdoor unit installed outside the house, the transformation ratio for the heating season will vary depending on the outside temperature. In severe frosts (-25 - -30 ° C and below), the COP of the air vent drops to one.
This stops suburban residents from installing air-to-water heat pumps - equipment in which the pumped heat is used to heat the heat transfer fluid. People believe that for our conditions - not the southern regions of the country, geothermal heat pumps with a ground heat exchanger buried in the ground - a system of pipes laid horizontally or vertically are best suited.
Is this true?
I often come across the myth that an air-to-water heat pump is inefficient in cold weather, but a geothermal HP is just that. Compare the heat transformation coefficient of the equipment in the spring. The geothermal circuit is depleted after winter. Well, if the temperature there is about 0 degrees. But the air is already warm enough. The need for heat decreases, but does not disappear in the summer, because. hot water is needed all year round. Geothermal heat pumps are great for regions with harsh winters and long heating periods. For the Southern Federal District and the Moscow Region, the air-to-water HP shows an average annual COP comparable to that of a geothermal.
Temperatures of -20 - -25 ° C and below in the Moscow region are rare and last only a few days. On average, winters in Moscow Region are characterized by -7 - -12 ° C and frequent thaws with temperatures rising to -3 - 0 degrees.Therefore, for most of the heating season, an air heat pump will operate with a COP close to three units.
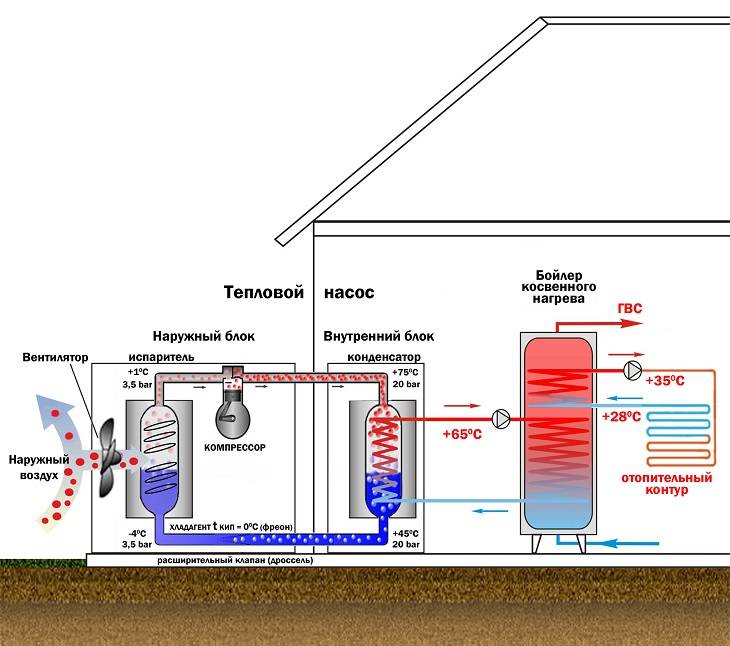
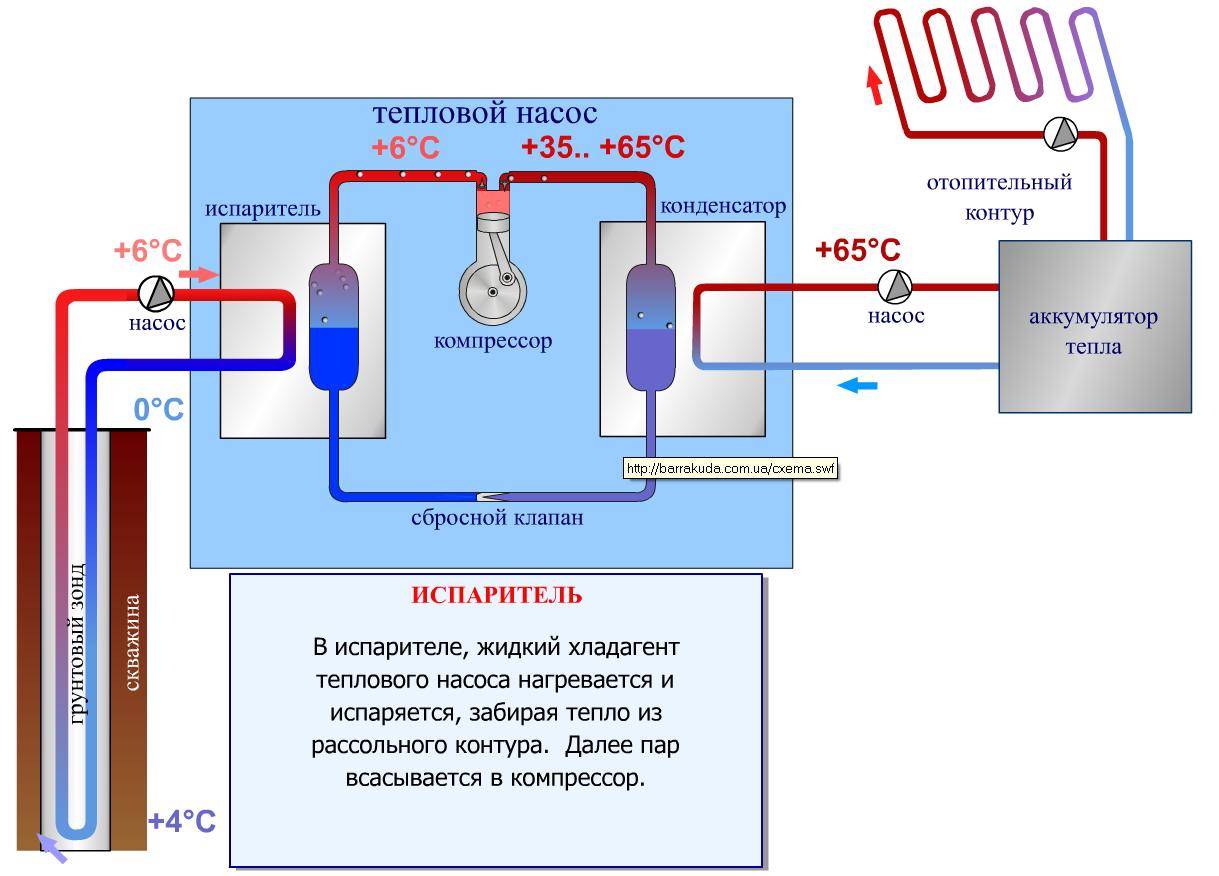
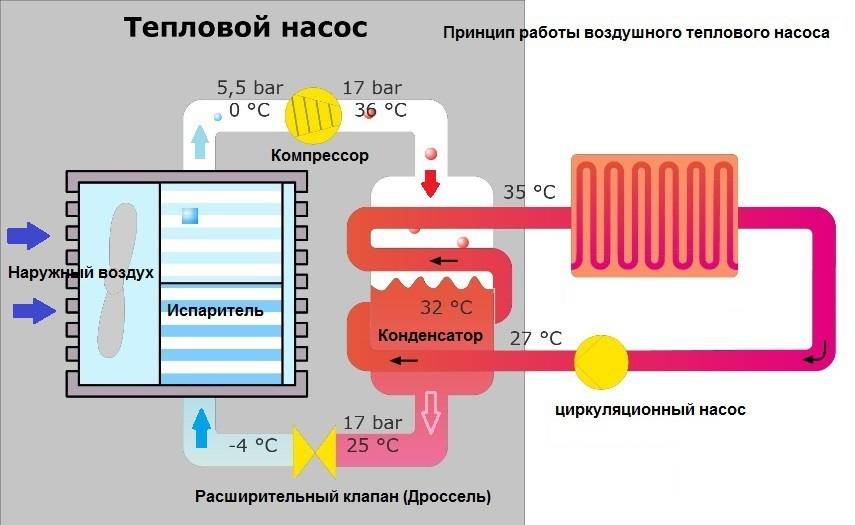
Principle of operation
All the space around us is energy - you just need to know how to use it. For a heat pump, the ambient temperature must be greater than 1C°. Here it should be said that even the earth in winter under snow or at some depth retains heat. The work of a geothermal or any other heat pump is based on the transportation of heat from its source using a heat carrier to the heating circuit of the house.
Scheme of operation of the device by points:
- the heat carrier (water, soil, air) fills the pipeline under the soil and heats it;
- then the coolant is transported to the heat exchanger (evaporator) with subsequent heat transfer to the internal circuit;
- the external circuit contains the refrigerant, a liquid with a low boiling point under low pressure. For example, freon, water with alcohol, glycol mixture. Inside the evaporator, this substance is heated and becomes a gas;
- the gaseous refrigerant is sent to the compressor, compressed under high pressure and heated;
- hot gas enters the condenser and there its thermal energy is transferred to the house;
- the cycle ends with the conversion of the refrigerant into a liquid, and it, due to heat loss, returns back to the system.
The same principle is used for refrigerators, so home heat pumps can be used as air conditioners to cool a room. Simply put, a heat pump is a kind of refrigerator with the opposite effect: instead of cold, heat is generated.
Air-to-water heat pump
Installation and operation of the AIR-WATER heat pump
Air as a source of low-temperature thermal energy
Theoretically, air can be used as a source of low-temperature thermal energy, regardless of its temperature. In practice, air-to-water heat pumps are effective at an air temperature of at least -15 C. To date, there are already pumps on sale that operate at a temperature of -25 C, but so far their cost is too high, which makes this type of heat engineering equipment inaccessible to the general consumer.
In its most primitive form, an air-to-water heat pump can be thought of as an air conditioner used to cool the environment and dump "excess" heat into a heated room.
At the same time, an air-to-water heat pump does not require digging pits or drilling wells, laying pipelines along the bottom of reservoirs or installing vertical collectors necessary to enable water-to-water or ground-to-water heat pumps to operate. It is easy to operate and at the same time allows you to get inexpensive heat for heating your home.
As well as air conditioning systems, heat pumps of this type can be made according to 2 layout schemes:
- In the form of a split system consisting of 2 blocks connected by communications
- in the form of a monoblock
As a rule, a monoblock is a single device assembled in one housing and installed inside or outside the house. For indoor installation, it is necessary to provide a free channel for air intake. At the same time, outdoor installation is preferable: it allows you to move the compressor as a source of noise outside the room.
To date, many manufacturers produce air-to-water heat pumps in the form of monoblocks.It is convenient and practical, allows you to freely move the pump and install it without complicated installation and connection. The only drawback is the low power of pumps of this type: from 3 to 16 kW.
The split system is divided into two blocks, one of which includes a condenser and an automatic control system. It is installed indoors. The second (outdoor) unit includes a compressor. Its economic feasibility of installing air-to-water heat pumps
Air-to-water heat pumps are efficient at positive outside temperatures. They have found wide application in the southern regions of our country: in the Kuban, in the Stavropol Territory, etc. where severe frosts are rare, and in winter the temperature rarely drops below zero.
This does not mean at all that in other regions of our country, with more severe climatic conditions, heat pumps of this type cannot be used. Not at all. It's just that the efficiency of an air-to-water pump decreases as the air temperature drops, along with an increase in the cost of electricity needed to run the pump.
Therefore, the expediency of operating a heat pump at a negative air temperature, as well as the selection of equipment in accordance with the required power, should be carried out by qualified heating engineers.
To date, the best option is to use an air-to-water heat pump for heating and hot water supply at positive ambient temperatures and to turn on a boiler or other source of thermal energy when frost sets in.
Another condition for using a heat pump for heating a house is the high thermal efficiency of the building, the absence of heat losses in it associated with poor-quality thermal insulation and drafts.
From tubes with a rarefied medium
This method of heating the liquid can be used not only in summer, but also in winter, it is one of the most difficult. The installation location of the vacuum tube device should not be shady, directed to the south. Overheating is not allowed, the liquid circulation must be from top to bottom.
You will need the following tools:
- Wrench.
- Screwdrivers.
- Device for welding plastic pipes.
- Drill.
First, build a frame and put it in the intended installation location, the best option is the roof, then fix it, for example, with anchor bolts. Then connect the temperature sensor, air outlet. Connect the water conduit using materials that are resistant to freezing temperatures.
Let's proceed with the installation of the heating element, take a copper pipe and wrap it with aluminum sheet, insert it into a glass vacuum pipe. Put a fixing cup and a rubber boot on the bottom of the tube. Fix the metal end in a brass condenser (you can see sticky grease on the tube, do not wipe it off).

Close the fixing bowl, install the remaining elements in a similar way. Install the mounting block and run 220V electricity to it.Connect a temperature sensor to it, an air outlet, although they are moisture resistant, it is better to install a protective screen for them, then we connect the controller, with its help the system is controlled, that's the whole process of installing a solar boiler with your own hands. Program the system for the required parameters and start up.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
The principle of operation of the thermal air-to-air split system:
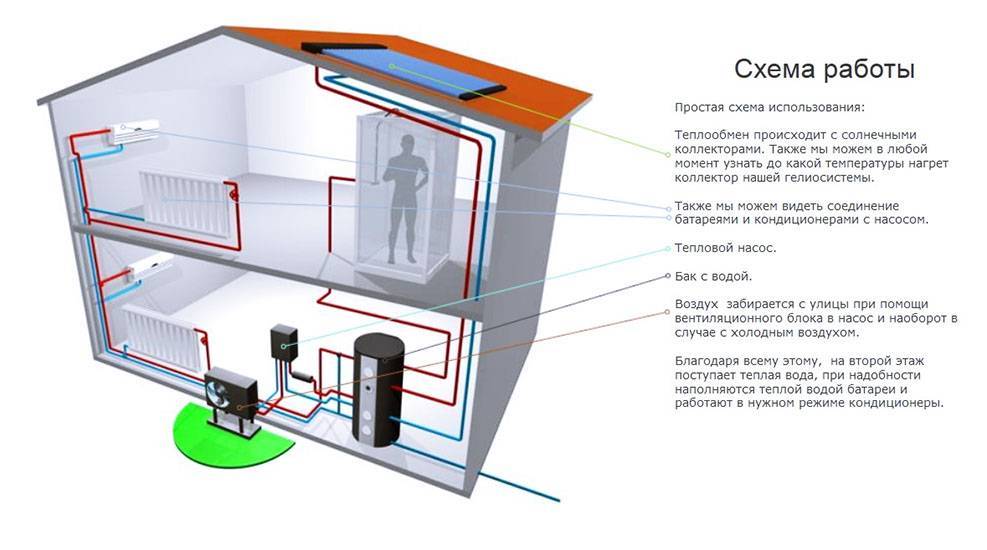
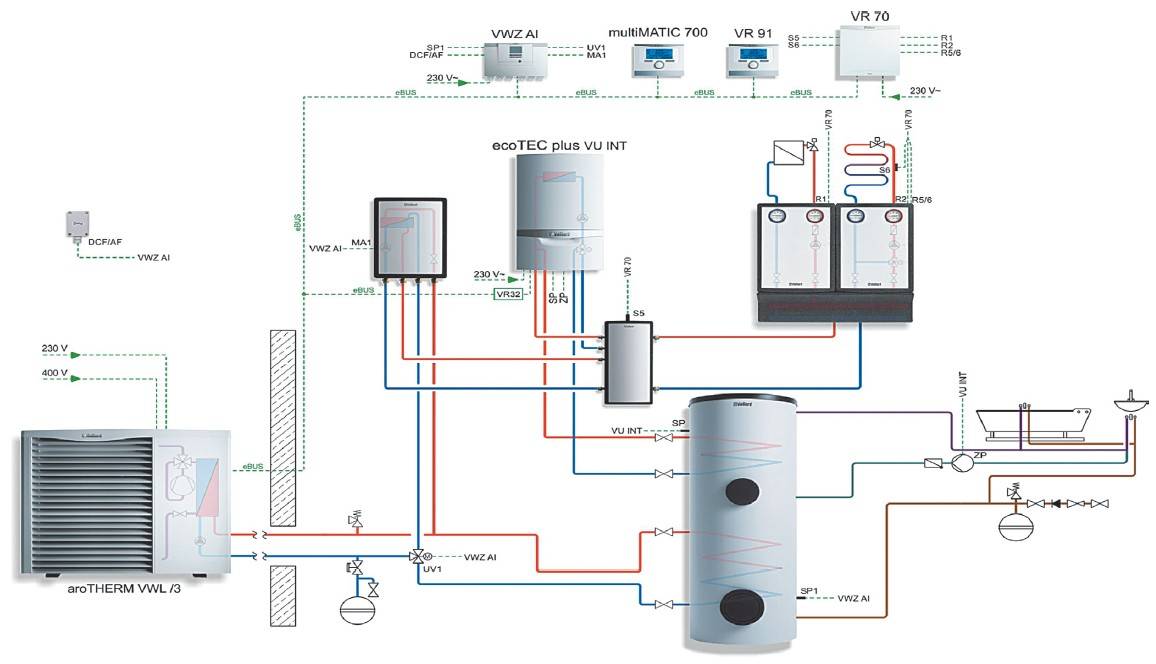
Air source heat pump in the heating system of a two-story house:
Inverter air conditioner or air heat pump - which is better?
Air-to-air heat pumps are highly efficient devices. They are easy to maintain, convenient to operate and economical.
There is a huge range of such systems on sale now, for any home you can choose a heating installation. It is only necessary to correctly calculate its power, then it will effectively serve for many years.
What do you think about the efficiency and feasibility of using air-to-air heat pumps? Share your opinion, leave feedback on the use of units and ask questions. The comment form is located below.