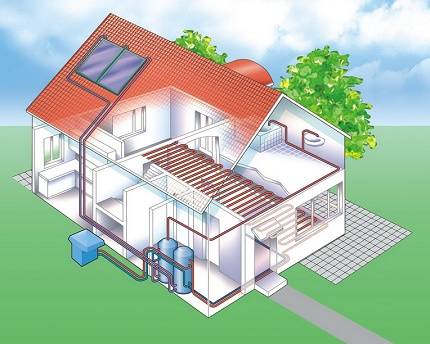
- Types of collector soil water
- Energy carriers for or against?
- Receiving well
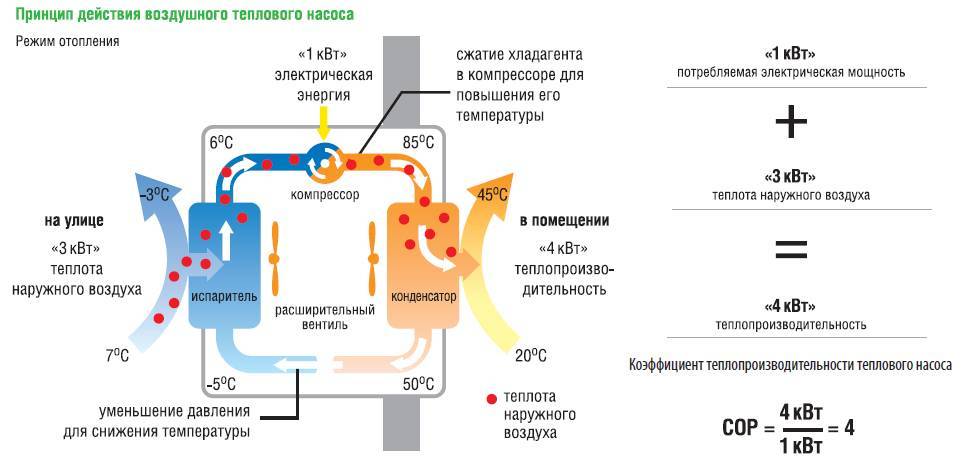
- Principle of operation
- Principle of operation
- Helpful Tips
- Homemade from an old refrigerator
- Efficiency and principle of operation of a heat pump
- Mounting technology
- How to make a project
- How to assemble a heat pump
- Installation of collector communications
- Equipment installation
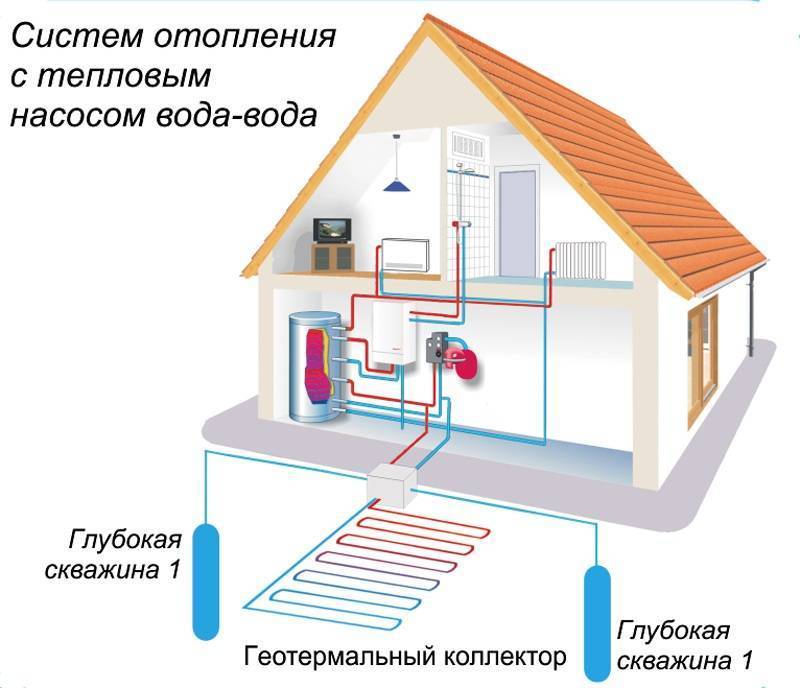
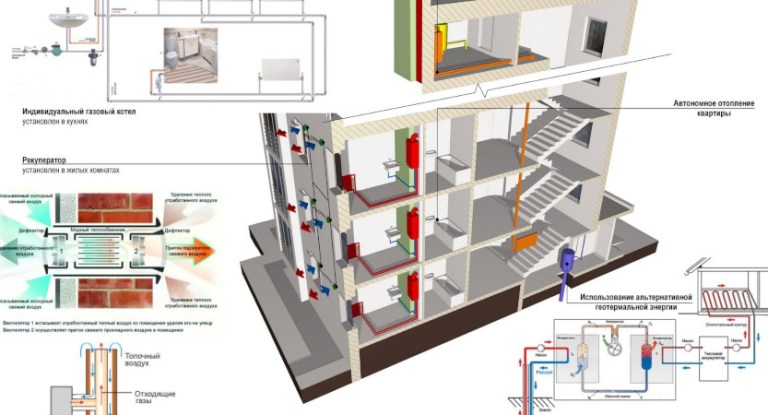
- What is a heat pump for heating a private house? How does it work?
- The principle of operation of heat pumps
- Geothermal heating at home: how it works
- Heat pumps: ground - water
- Type of water-to-water pump
- Air-to-water pumps
- Features of the thermal air-water system
- Specifics of application and work
- How the system works
- Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Types of collector soil water
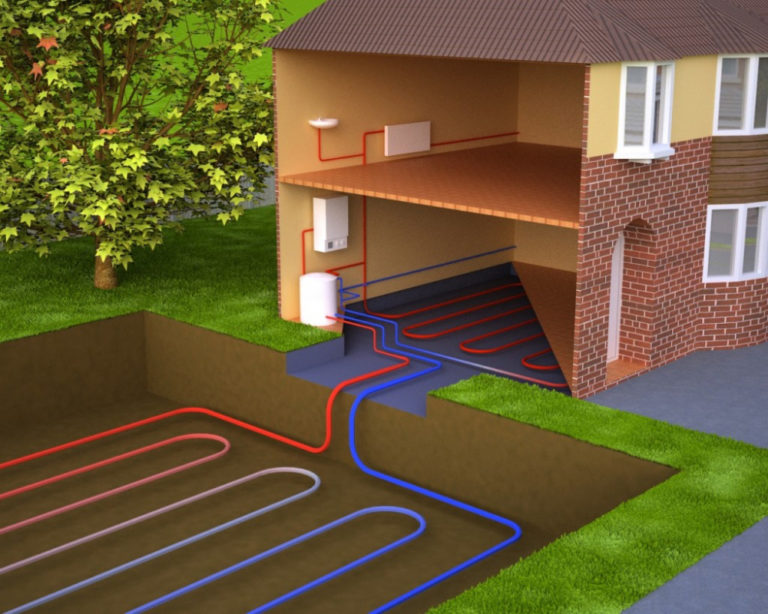
The collector of a ground source heat pump can be of two types (Fig. 2):
- Vertical;
- Horizontal.
 Rice. 2 Types of collectors for soil pumps: vertical and horizontal
Rice. 2 Types of collectors for soil pumps: vertical and horizontal
A vertical collector is a long pipeline lowered into a well, the length of which is from 40 to 150 m. This type of heat exchanger is better than horizontal ones in that the temperature is higher at such a depth. If the well is very deep, then the heat exchanger is also equipped with a protective casing, and if the depth is relatively small, then this is not necessary.But a significant disadvantage of this method of reservoir placement is the high cost of such a well.
Of course, experts recommend drilling a well deeper. But if the technique or soil does not allow, then several wells can be made. For example, you can make one well with a depth of 80 m, or you can make 4 wells of 20 m each. The main thing is that the total result is sufficient for heating the house. There may be rocky soil, which is quite difficult to work with, it is possible to drill wells no more than 15-20 meters in it.
Horizontal collector (Fig. 3) - this type of soil collector for a soil-water pump looks like a pipeline that is laid out in a horizontal position to a certain depth, under a layer of earth. This manifold is easy to install.
 Rice. 3 External circuit of the ground-water pump
Rice. 3 External circuit of the ground-water pump
The area on which the collector of an earthen heat pump is installed is quite large, in contrast to the vertical version, which requires a small piece of land. As a rule, a horizontal heat exchanger occupies from 25 to 50 m2, and maybe more, depending on the heated area. The negative factor of this option is that the area with this collector can only be used for lawn.
Depending on various circumstances, the heat exchanger can be laid in a zigzag, loops, snake, etc.
It is very important what is the thermal conductivity of the soil in which the heat exchanger is installed. It depends on the quality of the soil, for example, if the soil is wet, then the thermal conductivity is greater, and if the soil is sandy, then the thermal conductivity is small.
If there are many loops in the heat exchanger, then a circulation pump must be included in the configuration.
Energy carriers for or against?
However, that's not all.The rise in prices for energy carriers and the high costs of their delivery lead to a rapid increase in the cost of heat and electricity. And this forces consumers to look for new ways to save. Even from school textbooks, we remember that heat transfer flows from heated bodies to cooler ones, but not vice versa. Our centuries-old experience does not remember the reverse procedure, and science proves this. However, cunning modern engineering techniques make it possible to transfer heat in the opposite direction - from a less heated body to a hotter one.
 Scheme of heat transfer in a heat pump
Scheme of heat transfer in a heat pump
For us, there is nothing surprising, for example, in the operation of the refrigerator. Where the heat from the freezer, the temperature in which is often negative, is released into the environment. If this heat is used to heat buildings, and the refrigeration chamber is replaced by a proven, constantly functioning natural heat source, then this will be the so-called heat pump.
A simple heat pump (air-to-air) with which you can heat a living space is an air conditioner that is familiar to everyone, with a heating function. You can successfully use it, because today there are air conditioners that can work even at significant sub-zero temperatures - up to -15 gr. and below. However, if we want to get the most efficiency and comfort when heating the whole house in such an economical way (and a heat pump is three times more economical than conventional heaters, or even more), then more advanced systems must be used.
On a note: many are wondering - how is it, because there is a law of conservation of energy.Why such a disproportionate ratio of heat transfer to electricity consumption? The whole secret is that in a heat pump, electricity is spent only on the electromagnetic winding of the compressor (which, of course, heats up, but this heat is not used to heat the room), and heat energy is generated, "sucked" from the external environment, thanks to the special processes of the heat pump ( the word pump itself indicates this). To understand this, you need to know more than a school course in physics. But let's try to walk through the basics below.
Receiving well
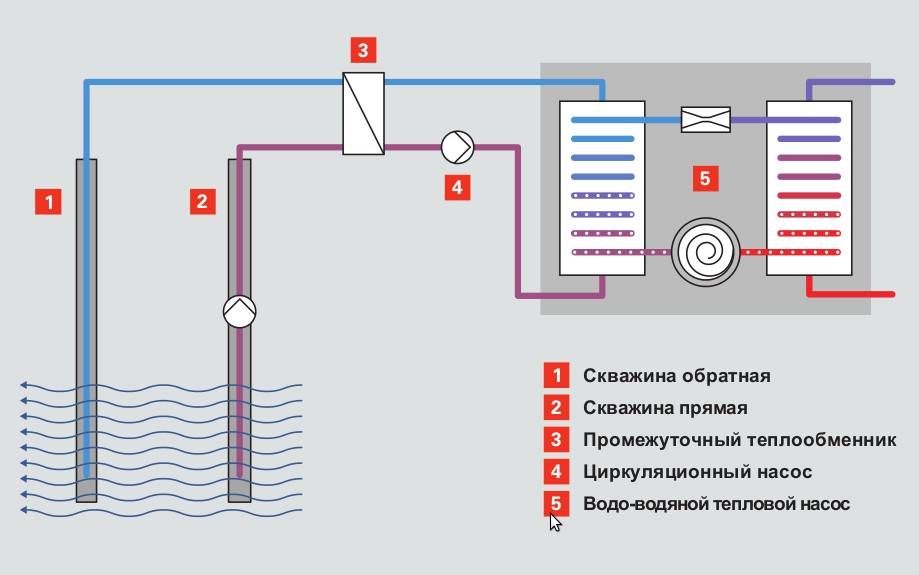
The biggest problem when installing an open circuit heat pump is when the water is discharged from above into the well. So wrong. The pipe should go almost to the very bottom of the well and rise from it by 0.5-1 meter. Everything below should be seething. When water is discharged from above, the well can quickly become silted up and stop receiving water. Overflow occurs. If this happens with a good minus on the street, then the skating rink is provided for you. Therefore, if there is a river or some kind of reservoir nearby, a storm drain or a drainage trench, then it is better to connect the receiving well to them with an overflow pipe, in case of overflow. If there is nothing nearby, then you will have to drill not one, but two or more wells for reception. No one knows the answer to the question of how long a receiving well will last. It can take many years, or it can clog after one heating season. Therefore, the biggest disadvantage of an open circuit is unpredictability.

Another important point. The receiving well should be located downstream from the debit well, at a distance of at least 6 meters. This is another ambiguity. How to determine in which direction an underground river flows. The answer to this question will be given only by experiment.If the water does not sink in the debit well after the heat pump is started, everything is fine, you guessed it. If it starts to fall in temperature, then the wells need to be swapped, and the submersible pump must be moved. The pipelines of the debit and drain wells are best made from HDPE pipes, as a cheaper material. The reliability and durability of such pipes is also enough.
The ideal option is when the wells are located across the underground flow. Then it is enough to make a detachable connection of the pipeline in the well of the well, throw power into both wells with a detachable waterproof plug, and you can reverse the wells once a year, changing the debit and receiving places.
Principle of operation
For those who are not quite versed in the topic, it is worth explaining what an air-to-water heat pump is. In fact, this is a "refrigerator in reverse" - a device that cools the air outside of itself and heats the water that is in the tank. This water can then be used for domestic hot water or home heating.

The heat pump uses a closed cycle, it consumes only electricity. Its efficiency is measured as the ratio of the consumed electrical energy to the heat received. The efficiency of heat pumps is also measured in COP (Coefficient of performance). COP 2 corresponds to an efficiency of 200% and means that for 1 kW of electricity it will provide 2 kW of heat.
Principle of operation
The operation of the heat pump is due to the heat extracted from the water. Lakes, rates, rivers, wells, wells become a source of water. The depth of the reservoir in central Russia should be at least 2 meters so that the lower layers do not freeze. According to the location of the heat exchanger, heat deposits are divided into:
- horizontal (pipes are laid in rings on the bottom);
- vertical (the heat exchanger is located vertically in the well).
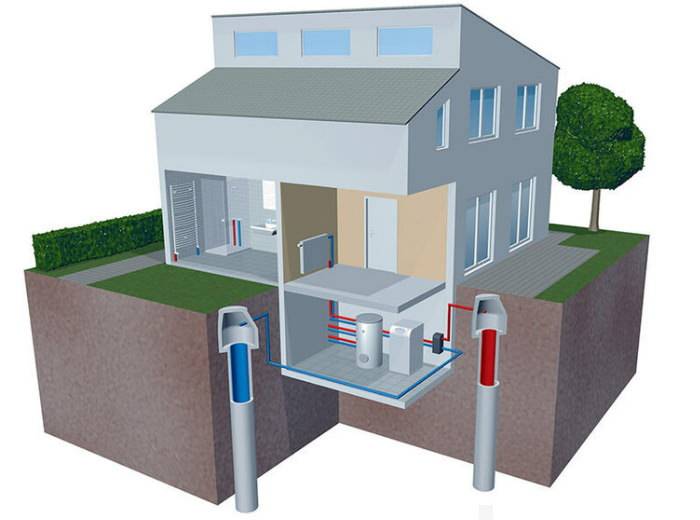
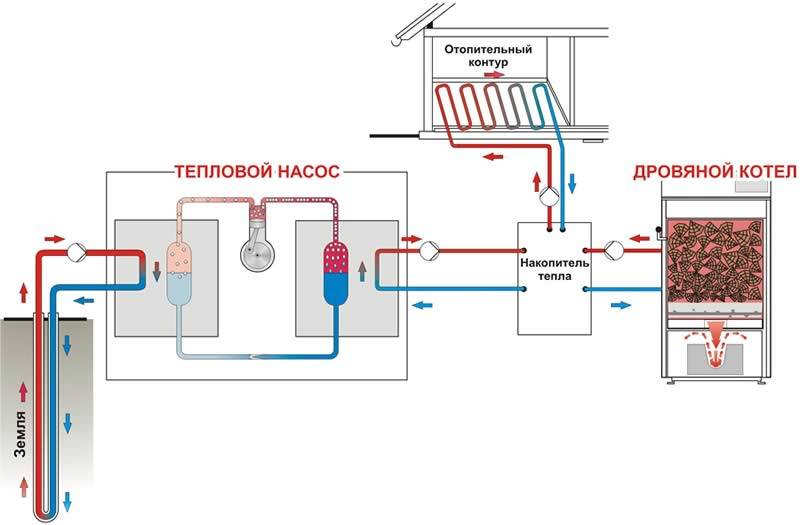
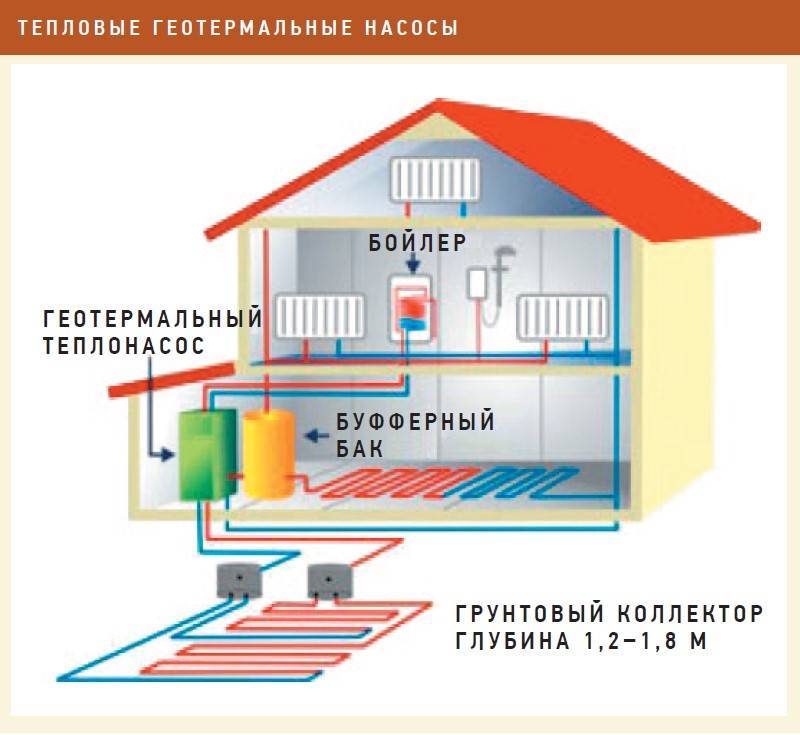
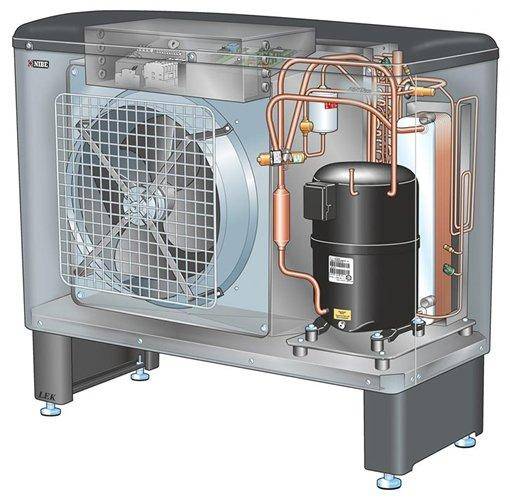
Since frost-free reservoirs are not located near every house, most often pipes are laid in wells. A standard water-to-water heat pump has several main parts:
- heating pipes;
- water supply and discharge pipes;
- evaporator (coil in which freon evaporates);
- compressor;
- condenser (coil in which freon is liquefied).
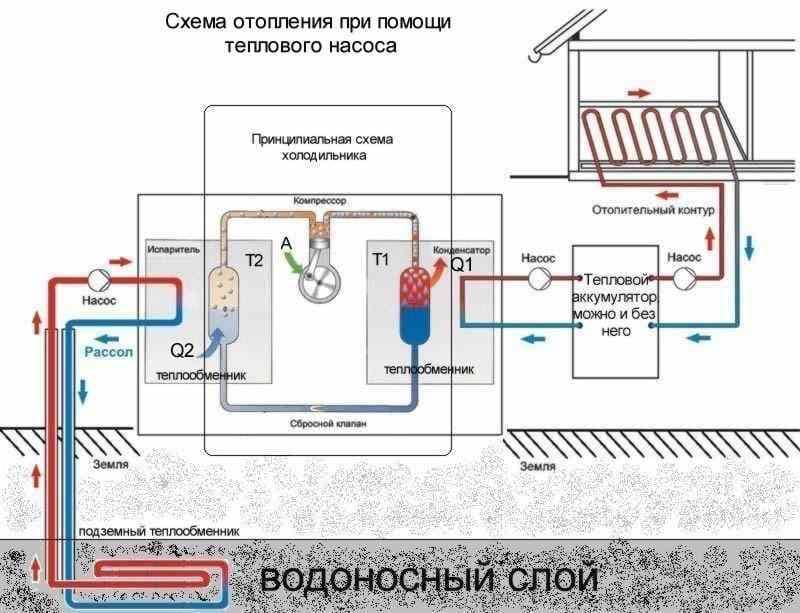
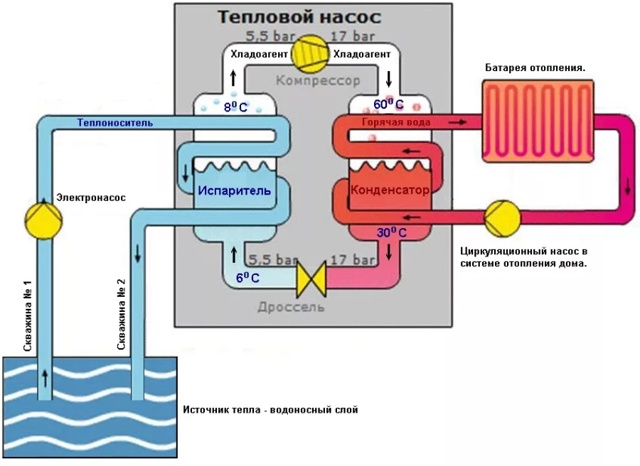
Depending on the time of year, the temperature of groundwater is 4-10 °C, it varies in small ranges. This ensures stable and productive operation of the heat pump. Two wells are drilled at a distance of 8-10 m from each other. Groundwater enters the pipe from the first well and rises up to the evaporator, heating it. At the same time, liquefied freon is fed into the evaporator. As a result of the pressure drop in the evaporator, the heat from the walls passes to the refrigerant. The refrigerant (freon) becomes gaseous.
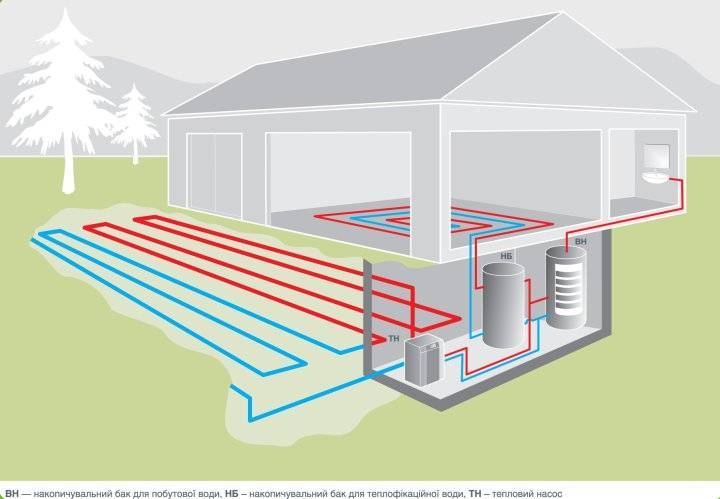
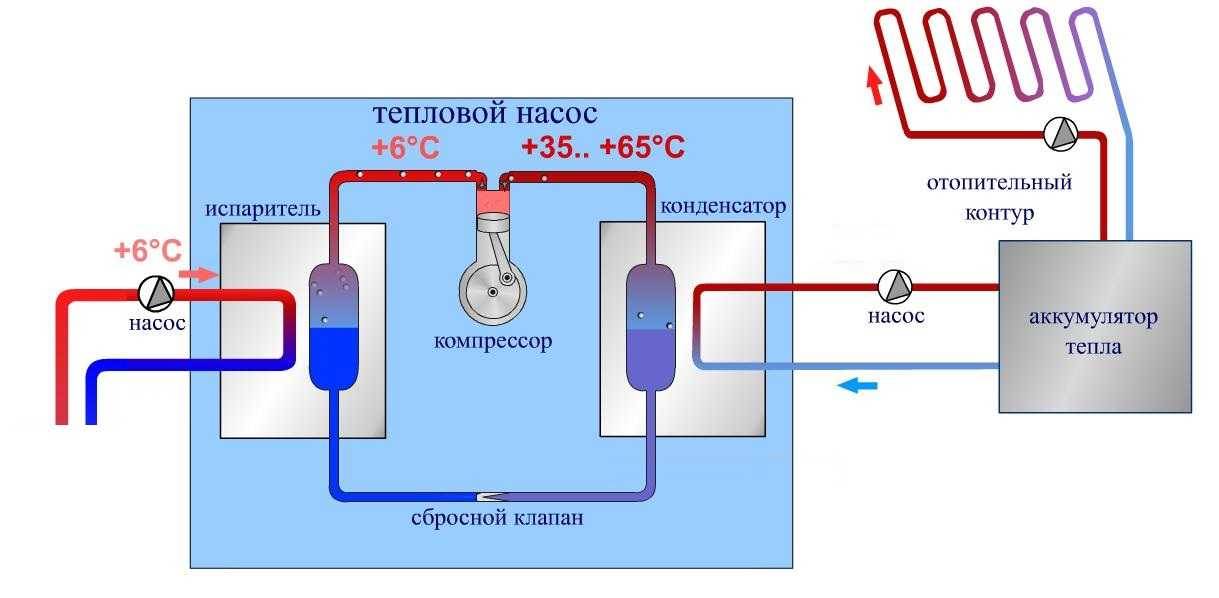
Freon then enters the compressor and is compressed. Then it enters the condenser, turns into a liquid, and the heat released as a result of this process passes to the coolant (most often it is water). The coolant, in turn, heats the radiator pipes. This is how the house is heated. Ground water is discharged into the second well. A complete picture of the principles of operation is given by the heat pump diagram. Since the temperature of groundwater is more stable than the temperature of the lower layers of reservoirs, it is much more efficient to use wells. But here we must also take into account the cost of drilling wells. A heat pump with a water-to-water boiler is installed, heating the room and heating water for domestic needs.The electrical energy spent on the operation of the pump is 4-5 times less than the energy it generates.
House heating scheme using a Water-Water heat pump
This is interesting: Solar collector for heating a private house - homemade battery
Helpful Tips
At all stages of building a house, starting from the design stage, it must be remembered that HP is an inertial system. It can be compared to a massive Russian stove, which was usually heated once a day during cooking. Then the accumulated heat heated the dwelling until the next morning.
Walls made of heavy logs have a fairly high degree of thermal inertia. Simply put, they slowly cool down when the night gets colder. Good thermal inertia for thick stone walls, as well as for heavy concrete or brick.
Polyfoam and foam concrete have good thermal insulation properties. But due to the low specific gravity, they have a low thermal inertia. A heat pump in a building with walls made of such materials, with a sharp drop in outdoor temperature, will not always be able to “pump” enough heat from the outside into the “warm floor” heating system.
You also need to take into account other factors:
- To reduce heat loss or not to freeze pipes at all in the line between the house and the wells or the collector, it is necessary to lay them to a depth below the freezing level. In Crimea, 0.75 meters is enough, and at the latitude of Moscow, at least 1.5.
- The biggest heat loss is usually through windows. Therefore, triple glazing is not a luxury at all, but an economically sound building solution. The ideal option is to use glasses that can reflect infrared rays.
- In the case of using the option of 2 wells for water intake and discharge, the distance between them must be at least 20 meters.
- It is better to try a home-made TN first in a utility room or garage. The installation of underfloor heating in a residential area will require additional costs.
Homemade from an old refrigerator
It is quite difficult to assemble an air-to-air heat pump from individual compressors and condensers with your own hands without specialized engineering knowledge. But for a small room or a greenhouse, you can use an old refrigerator.
The simplest air heat pump can be made from a refrigerator by extending an air duct into it from the street and hanging a fan on the rear grille of the heat exchanger
To do this, you need to make two holes in the front door of the refrigerator. Through the first, street air will enter the freezer, and through the second lower one, it will be brought back to the street.
At the same time, during the passage through the inner chamber, it will give off part of the heat it contains to freon.
It is also possible to simply build the refrigeration machine into the wall with the door open to the outside, and the heat exchanger at the back into the room. But it should be borne in mind that the power of such a heater will be small, and it consumes a lot of electricity.
The air in the room is heated by a heat exchanger at the back of the refrigerator. However, such a heat pump is only able to operate at outdoor temperatures not lower than plus five Celsius.
This appliance is designed for indoor use only.
In a large cottage, the air heating system will have to be supplemented with air ducts that distribute warm air evenly throughout all rooms.
The installation of an air-to-air heat pump is extremely simple.It is necessary to install the external and internal units, and then connect them to each other with a circuit with a coolant.
The first part of the system is installed outdoors: directly on the facade, roof or next to the building. The second in the house can be placed on the ceiling or wall.
It is recommended to mount the outdoor unit a few meters from the entrance to the cottage and away from the windows, do not forget about the noise produced by the fan.
And the internal one is installed so that the flow of warm air from it is evenly distributed throughout the room.
If it is planned to heat a house with several rooms on different floors with an air-to-air heat pump, then you will have to equip a system of ventilation ducts with forced injection.
In this case, it is better to order a project from a competent engineer, otherwise the power of the heat pump may not be enough for all the premises.
The electricity meter and protective device must be able to withstand the peak loads generated by the heat pump. With a sharp cold snap outside the window, the compressor begins to consume electricity many times more than usual.
It is best to lay a separate supply line from the switchboard for such an air heater.
Particular attention should be paid to the installation of pipes for freon. Even the smallest chips inside can damage compressor equipment
Here you can not do without copper soldering skills. Refilling refrigerant should generally be entrusted to a professional in order to avoid problems with its leaks later.
Efficiency and principle of operation of a heat pump
The efficiency of a heat pump for heating will always be greater than 1. For geothermal systems, the heat conversion factor is more correct.If it is equal to 4, then this means that at a power of 1 kW, the heat pump at the output provides 4 kW of energy, of which 3 kW was provided by the earth.
The principle underlying the operation of a heat pump for heating a house was developed at the beginning of the 19th century. engineer Sadi Carnot and was called the Carnot cycle. Based on this operation of a conventional household refrigerator, in which the products are cooled due to the fact that the dissipated heat is removed through the radiator to the outside. But to apply for heating houses, when everything happens exactly the opposite, i.e. the operation of the heat pump is based on the principle of the reverse Carnot cycle, it has recently become.

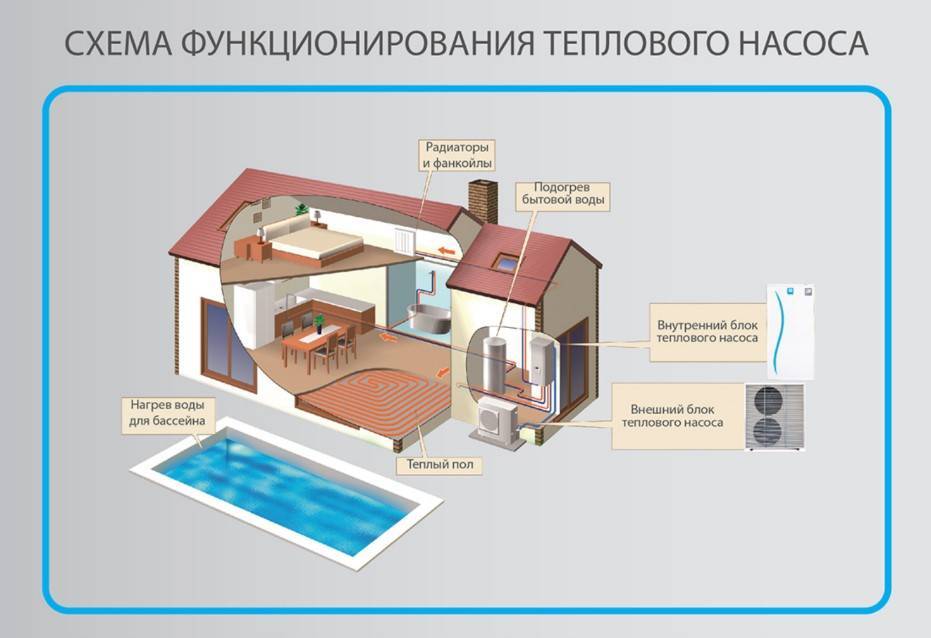
A heat pump for home heating is a device in which low-temperature heat is converted into high-temperature heat, which is used for heating. The source of heat is earth, water and air (the first of them is the most widespread, since it is effective (although the level of thermal insulation of the house matters, the method used to heat the house, etc.) and has an optimal ratio of price and consumer qualities).
The operation of a heat pump designed for heating a house requires electricity, but at a cost of 1 kW of electricity, the return is 4–6 kW of thermal energy.
In addition to heating the house in summer, the heat pump can work as an air conditioner, for which it is enough that the system is capable of reverse operation. Heat pumps are classified into several types:
- "earth - water";
- "earth - air";
- "water - water";
- "water - air"
- "air - water";
- "air-air".
The following is a detailed description of how different types of heat pumps work for heating a house.
Mounting technology
The assembly of this type of equipment is carried out in several stages:
- a project is being drawn up;
- collector communications are assembled;
- a heat pump is installed in the system;
- equipment is installed inside the house;
- coolant is being filled.
Next, we will consider how to install a turnkey heat pump with your own hands step by step.
How to make a project
Before proceeding with the assembly of communications of this type, of course, all the necessary calculations should be made. The work of the external part of the system must be fully coordinated with the work of the internal. Calculations are made depending on the selected type of equipment. For horizontal collectors, they are performed as follows:
- The amount of antifreeze needed is determined. In this case, the formula Vs = Qo 3600 / (1.05 3.7 t) is used, where Qo is the thermal power of the source, t is the temperature difference between the supply and return lines. The Qo parameter is calculated as the difference between the pump power and the electric power used to heat the refrigerant.
- The required collector length is determined. The calculation formula in this case looks like this: L = Qo / q, where q is the specific heat removal. The value of the latter indicator depends on the type of soil on the site. For clay, for example, it is 20 W per rm, for sand - 10 W, etc.
- The area required for laying the collector is determined. In this case, the calculation is carried out according to the formula A = L da, where da is the pipe laying step.
The power of the heat pump is determined approximately at the rate of 70 W of heat per 1 m2 with a ceiling height of 2.7 m. The collector pipes are usually laid at a distance of 0.8 m from each other or a little more.
How to assemble a heat pump
This type of equipment is quite expensive. The design of a heat pump is relatively simple. Therefore, you can try to make it yourself. This procedure is performed like this:
- A compressor is purchased (equipment from an air conditioner is suitable).
- Capacitor housing is made. To do this, a 100-liter stainless steel tank is cut in half.
- A coil is being made. A gas or oxygen cylinder is wrapped with a copper tube from the refrigerator. The latter can be fixed with aluminum perforated corners.
- The coil is installed in the body, after which the latter is sealed.
- An evaporator is made from a plastic container of 80 liters. A coil from a ¾ inch pipe is mounted in it.
- Water pipes are connected to the evaporator to deliver and drain water.
- The system is filled with refrigerant. This operation should be entrusted to a specialist. With inept actions, you can not only ruin the assembled equipment, but also get injured.
Installation of collector communications
The technology for installing the external circuit of the heating system also depends on its type. For a vertical collector, wells are drilled with a depth of 20-100 m. Under a horizontal one, trenches are broken through with a depth of 1.5 m. At the next stage, pipes are laid. Trees should not grow near the horizontal collector, as their roots can damage the mains. For the assembly of the latter, low-pressure polyethylene pipes can be used.
Equipment installation
This operation is performed in the usual way. That is, heating radiators are installed in the premises, lines are laid and they are connected to the boiler.An expansion tank, a filter and a circulation pump on the bypass are mounted on the return pipe. You can also assemble and connect a "warm floor" system to the heat pump. At the final stage, the selected type of coolant is poured into the external and internal circuits.
As you can see, you can mount the heat pump and collector yourself. Technologically, the procedure is not particularly complicated. However, unlike other types of similar equipment, the assembly of such a system, even of a horizontal type, is a physically rather laborious operation. Drilling wells for vertical drilling on your own without special equipment is practically impossible. Therefore, it may be worth hiring specialists to perform calculations and work on assembling the system. Today, there are companies on the market that install equipment such as a heat pump on a turnkey basis.
What is a heat pump for heating a private house? How does it work?
A special device that is able to extract heat from the environment is called a heat pump.
Such devices are used as the main or additional method of space heating. Some devices also work for passive cooling of the building - while the pump is used for both summer cooling and winter heating.
The energy of the environment is used as fuel. Such a heater extracts heat from air, water, groundwater, and so on, so this device is classified as a renewable energy source.
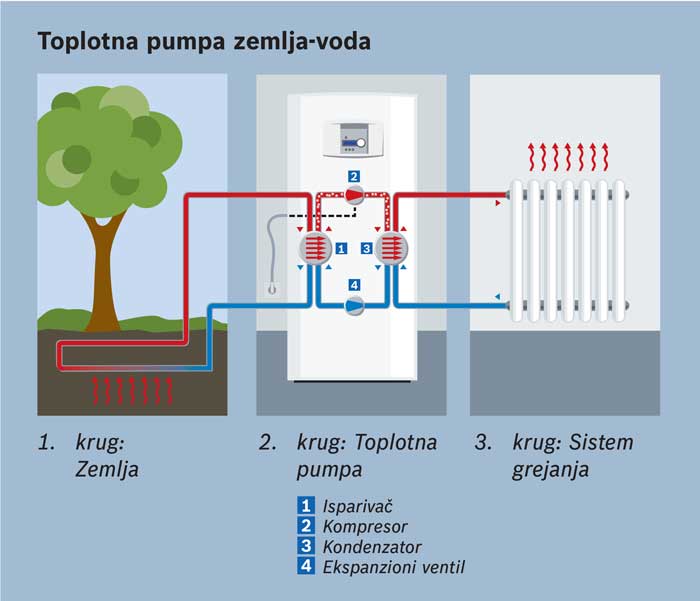
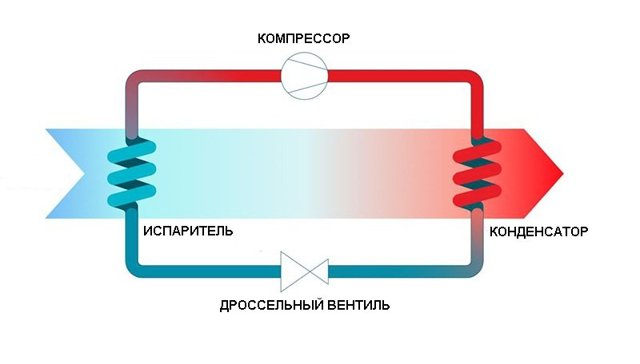
Important! These pumps require an electrical connection to operate. All thermal devices include an evaporator, a compressor, a condenser and an expansion valve.Depending on the heat source, water, air and other devices are distinguished.
The principle of operation is very similar to the principle of the refrigerator (only the refrigerator throws out hot air, and the pump absorbs heat)
Depending on the heat source, water, air and other devices are distinguished. The principle of operation is very similar to the principle of the refrigerator (only the refrigerator throws out hot air, and the pump absorbs heat)
All thermal devices include an evaporator, a compressor, a condenser and an expansion valve. Depending on the heat source, water, air and other devices are distinguished. The principle of operation is very similar to that of a refrigerator (only the refrigerator throws out hot air, and the pump absorbs heat).
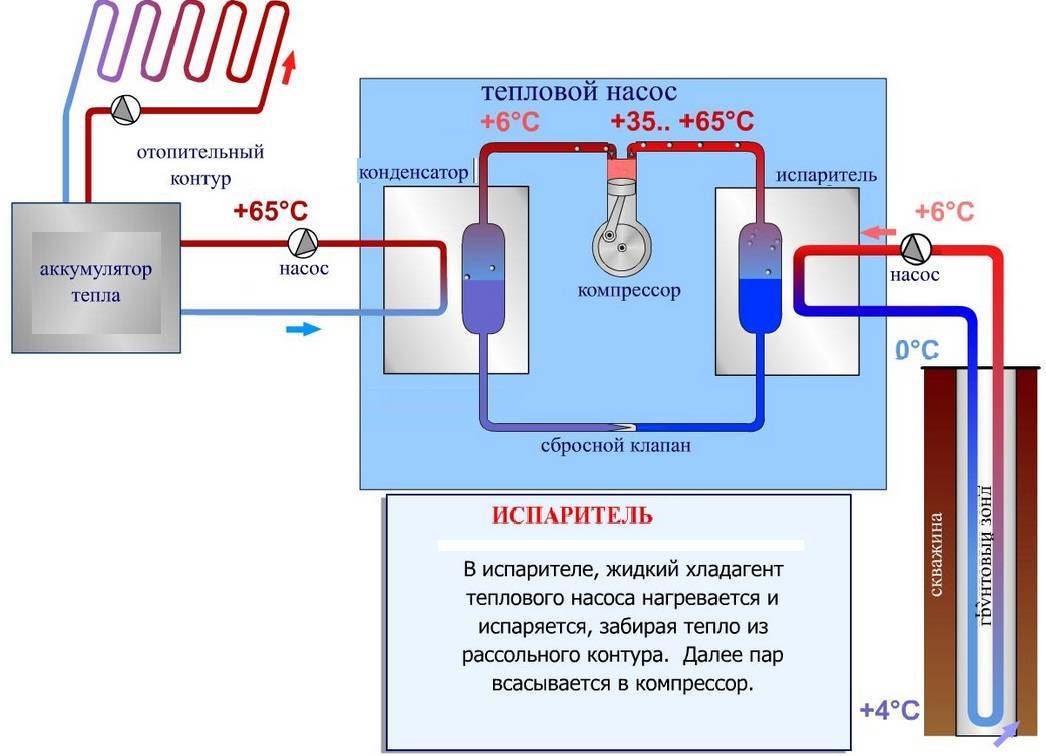
Most devices operate both at positive and negative temperatures, however, the efficiency of the device directly depends on external conditions (i.e., the higher the ambient temperature, the more powerful the device will be). In general, the device works as follows:
- The heat pump comes into contact with the surrounding conditions. Typically, the device extracts heat from the ground, air or water (depending on the type of device).
- A special evaporator is installed inside the device, which is filled with refrigerant.
- Upon contact with the environment, the refrigerant boils and evaporates.
- After that, the refrigerant in the form of vapor enters the compressor.
- There it shrinks - due to this, its temperature rises seriously.
- After that, the heated gas enters the heating system, which leads to the heating of the main coolant, which is used for space heating.
- The refrigerant cools down little by little. In the end, it turns back into a liquid.
- Then the liquid refrigerant enters a special valve, which seriously lowers its temperature.
- At the end, the refrigerant enters the evaporator again, after which the heating cycle is repeated.
Photo 1. The principle of operation of a ground-to-water heat pump. Blue indicates cold, red indicates hot.
Advantages:
- Environmental friendliness. Such devices are renewable energy sources that do not pollute the atmosphere with their emissions (whereas natural gas produces harmful greenhouse gases, and electricity is often used to burn coal, which also pollutes the air).
- Good alternative to gas. A heat pump is ideal for space heating in cases where the use of gas is difficult for one reason or another (for example, when the house is far from all major utilities). The pump also compares favorably with gas heating in that the installation of such a device does not require state permission (but when drilling a deep well, you still have to get it).
- Inexpensive additional heat source. The pump is ideal as a cheap auxiliary power source (the best option is to use gas in winter and a pump in spring and autumn).
Flaws:
- Thermal restrictions in case of using water pumps. All thermal devices function well at positive temperatures, while in the case of operation at negative temperatures, many pumps stop working. This is mainly due to the fact that the water freezes, which makes it impossible to use it as a heat source.
- There may be problems with devices that use water as heat. If water is used for heating, then a stable source will need to be found. Most often, a well must be drilled for this, due to which the installation costs of the device may increase.
Attention! Pumps usually cost 5-10 times more than a gas boiler, therefore, the use of such devices in order to save money in some cases may be impractical (for the pump to pay off, you will need to wait several years)
The principle of operation of heat pumps
It should be noted that almost any medium has thermal energy. Why not use the available heat to heat your home? A heat pump will help with this.
The principle of operation of a heat pump is as follows: heat is transferred to the coolant from an energy source with low potential. In practice, everything happens as follows.
The coolant passes through pipes that are buried, for example, in the ground. Then the coolant enters the heat exchanger, where the collected thermal energy is transferred to the second circuit. The refrigerant, which is located in the external circuit, heats up and turns into a gas. After that, the gaseous refrigerant passes into the compressor, where it is compressed. This causes the refrigerant to heat up even more. Hot gas goes to the condenser, and there the heat passes to the coolant, which already heats the house itself.
Geothermal heating at home: how it works
Refrigeration systems are arranged according to the same principle. This means that refrigeration units can be used to cool indoor air.
Types of heat pumps
There are several types of heat pumps. But most often, devices are classified by the nature of the coolant on the external circuit.
Devices can draw energy from
- water,
- soil,
- air.
The resulting energy in the house can be used for space heating, for heating water. Therefore, there are several types of heat pumps.
Heat pumps: ground - water
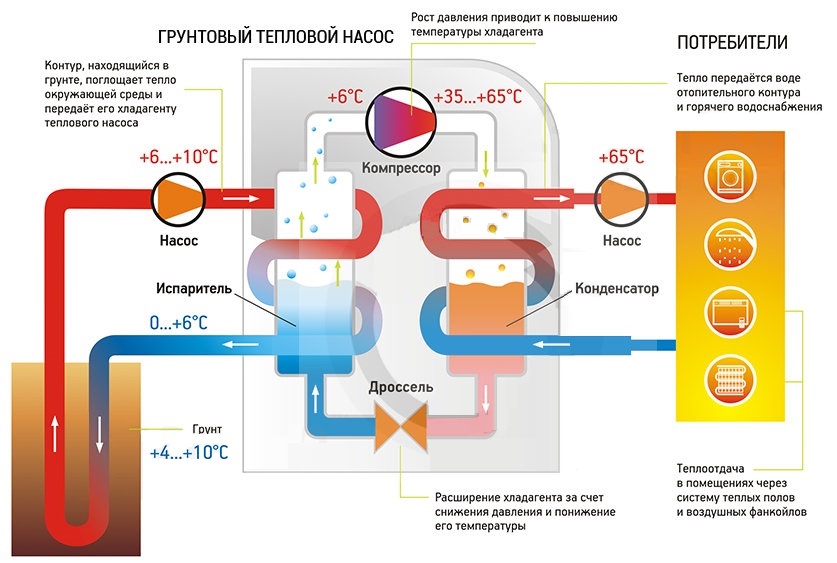
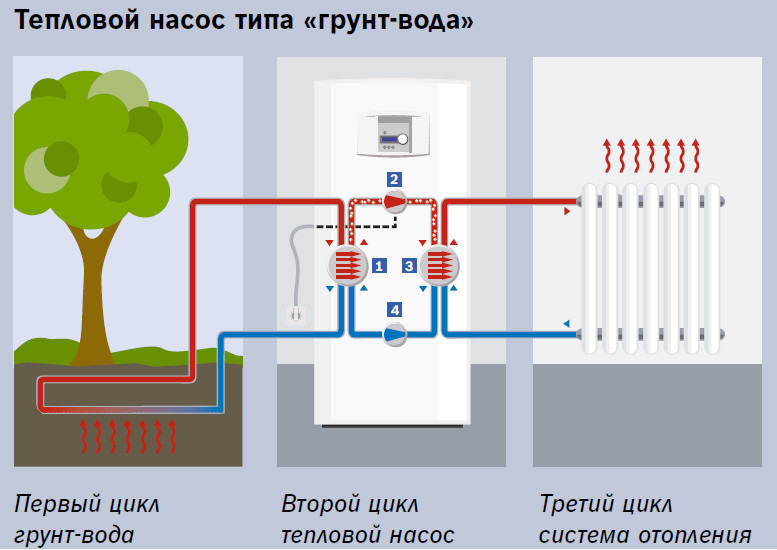
The best option for alternative heating is to obtain thermal energy from the ground. So, already at a depth of six meters, the earth has a constant and unchanging temperature. A special liquid is used as a heat carrier in the pipes. The outer contour of the system is made of plastic pipes. Pipes in the ground can be placed vertically or horizontally. If the pipes are placed horizontally, then a large area must be allocated. Where pipes are installed horizontally, it is impossible to use the land for agricultural purposes. You can only arrange lawns or plant annuals.
To arrange pipes vertically in the ground, it is necessary to make several wells up to 150 meters deep. This will be an efficient geothermal pump, since the temperature is high at a great depth near the earth. Deep probes are used for heat transfer.
Type of water-to-water pump
In addition, heat can be obtained from water, which is located deep underground. Ponds, groundwater or wastewater can be used.
It should be noted that there are no fundamental differences between the two systems. The smallest costs are required when a system for obtaining heat from a reservoir is created. Pipes must be filled with coolant and immersed in water.A more complex design is needed in order to create a system for generating heat from groundwater.
Air-to-water pumps
It is possible to collect heat from the air, but in regions with very cold winters, such a system is not effective. At the same time, the installation of the system is very simple. You only need to select and install the desired device.
A little more about the principle of operation of geothermal pumps
For heating it is very advantageous to use heat pumps. Houses with an area of more than 400 square meters pay off the costs of the system very quickly. But if your house is not very large, then you can make a heating system with your own hands.
First you need to buy a compressor. A device that is equipped with a conventional air conditioner is suitable. We mount it on the wall. You can make your own capacitor. It is necessary to make a coil from copper pipes. It is placed in a plastic case. The evaporator is also wall mounted. Soldering, refilling with freon and similar work should only be carried out by a professional. Inept actions will not lead to a good result. Moreover, you can get injured.
Before putting the heat pump into operation, it is necessary to check the condition of the electrification of the house. The power of the meter should be rated at 40 amperes.
Homemade geothermal heat pump
Note that a heat pump created by oneself does not always live up to expectations. The reason for this is the lack of correct thermal calculations. The system is underpowered and maintenance costs are rising
Therefore, it is important to carry out all calculations accurately.
Features of the thermal air-water system
The heat pump to which this article is devoted, unlike other modifications of such a device (in particular, water-to-water and ground-to-water), has a number of advantages:
- saves electricity;
- installation does not require large-scale land works, drilling of wells, obtaining special permits;
- If you connect the system to solar panels, you can ensure its complete autonomy.
A significant advantage of a thermal system that extracts wind energy and transfers it to water is one hundred percent environmental safety.
Before proceeding with the design of the pump, it is necessary to find out in which cases the system manifests itself as efficiently as possible, and when its use is impractical.
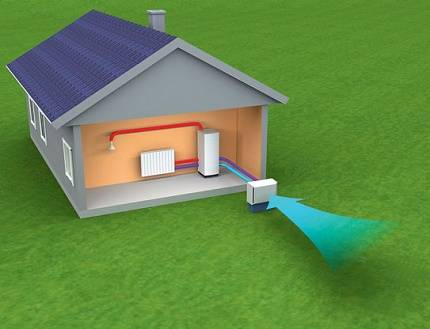
A heat pump system that extracts energy from the air mass can be used to heat all types of heat carriers used in the CIS: water, air, steam
Specifics of application and work
The heat pump works productively exclusively in the temperature range from -5 to +7 degrees. At an air temperature of +7, the system will generate more heat than necessary, and at an indicator below -5, it will not be enough for heating. This is due to the fact that the concentrated freon in the structure boils at a temperature of -55 degrees.
Theoretically, the system can generate heat even in 30-degree frost, but it will not be enough for heating, because the heat output directly depends on the difference between the boiling point of the refrigerant and the air temperature.
Therefore, residents of the Northern regions, where colds come earlier, this system will not work, and in the homes of the Southern regions, it can effectively serve for several cold months.
If standard batteries are installed in the room, the heat pump will work less efficiently. Best of all, the air-to-water device is combined with convectors and other radiators with a large area, as well as with "warm floor", "warm wall" water-type systems.
Also, the room itself should be well insulated from the outside, have built-in multi-chamber windows that provide better thermal insulation than ordinary wooden or plastic ones.
The heat pump interacts best with the "warm floor" water system, which does not require heating of the coolant above 40 - 45º C
A homemade heat pump can effectively heat houses up to 100 square meters. m and is guaranteed to produce a power of 5 kW. It should be understood that freon cannot be poured with sufficient quality into a structure created at home, so you should count on its boiling point to -22 degrees.
The home assembly device is ideal for supplying heat to a garage, greenhouse, utility room, small private pool, etc. The system is usually used as additional heating.
An electric boiler or other traditional equipment for the heating season will be required in any case. During severe frosts (-15-30 degrees), it is recommended to turn off the heat pump in order to avoid wasting electricity, because during this period its efficiency is no more than 10%.
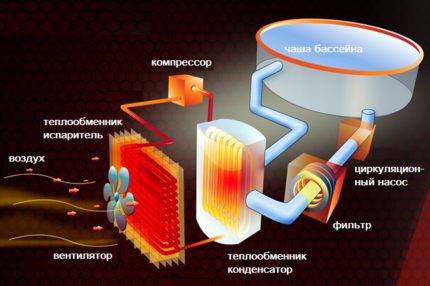 Heat pumps supply enough energy to heat water in indoor private pools (+)
Heat pumps supply enough energy to heat water in indoor private pools (+)
How the system works
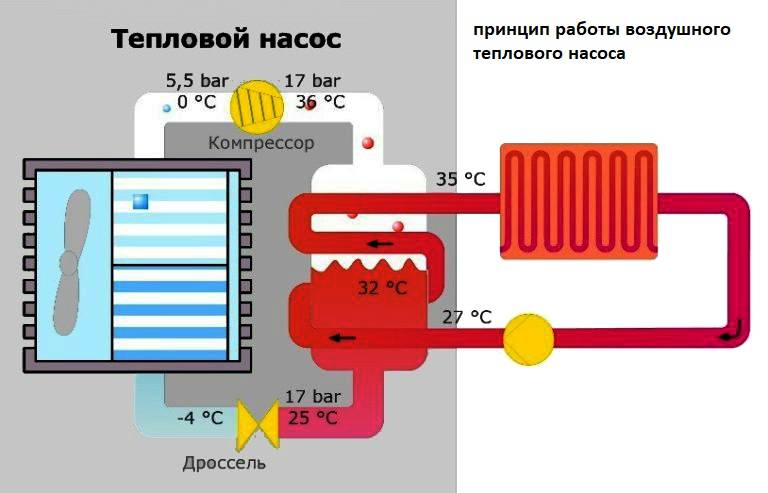
The working substance in the structure is air. Through the outdoor unit, which is installed on the street, oxygen enters the evaporator through pipes, where it interacts with the refrigerant.
Freon under the influence of temperature becomes gaseous (because it boils at -55 degrees) and in a heated form under pressure enters the compressor. The device compresses the gas, thereby increasing its temperature.
Hot freon enters the storage tank (condenser) circuit, where heat is transferred to water, which can later be used to organize heating and DHW. In the condenser, freon loses only part of its heat, and is still in a gaseous state.
Passing through the throttle, the refrigerant is sprayed, as a result of which its temperature decreases. Freon becomes liquid and in this form passes into the evaporator. The cycle is repeated.
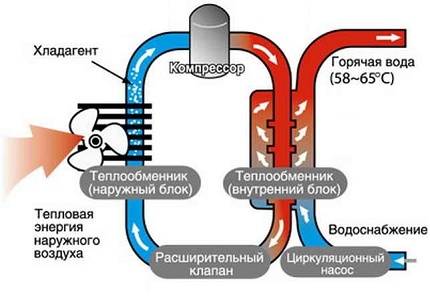
The figure schematically shows the implementation of the principle of an elementary heat pump, divided by a compressor and an expander into two circuits - high and low pressure
Those who wish to independently build a heat pump from waste materials and obsolete equipment, for example, from an old refrigerator, will be helped by the information presented in the article we recommend.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
The video will introduce the principle of operation and features of the device:
As a result, we can conclude that a water-to-water heat pump is considered an effective environmentally friendly equipment designed to heat houses up to 150 square meters. The arrangement of a larger area may already require quite complex engineering surveys.
If you have any questions while reading the information provided, please ask them in the block below. We are waiting for your comments, questions on the topic, stories and photos about the construction of a mini-hydroelectric power station with your own hands. We are interested in your opinion.