The principle of operation of the air-to-water pump
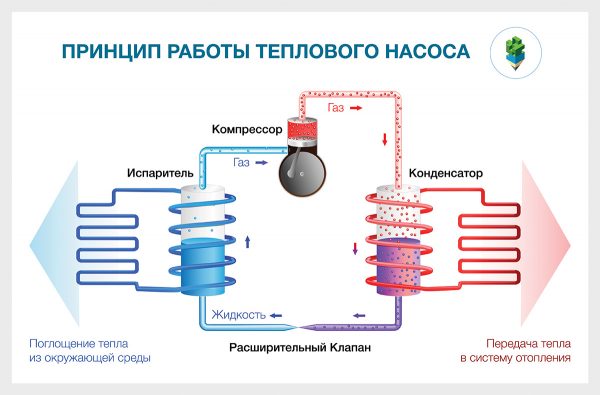 As already mentioned, the main source of thermal energy for installations of this type is atmospheric air. The fundamental basis of the operation of air pumps is the physical property of liquids to absorb and release heat during the phase transition from a liquid state to a gaseous state, and vice versa. As a result of the change of state, the temperature is released. The system works on the principle of a refrigerator in reverse.
As already mentioned, the main source of thermal energy for installations of this type is atmospheric air. The fundamental basis of the operation of air pumps is the physical property of liquids to absorb and release heat during the phase transition from a liquid state to a gaseous state, and vice versa. As a result of the change of state, the temperature is released. The system works on the principle of a refrigerator in reverse.
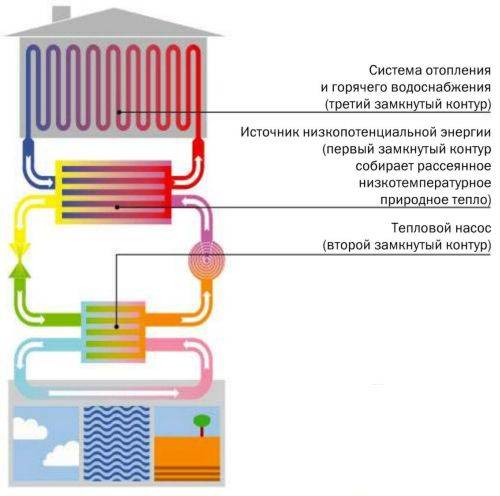
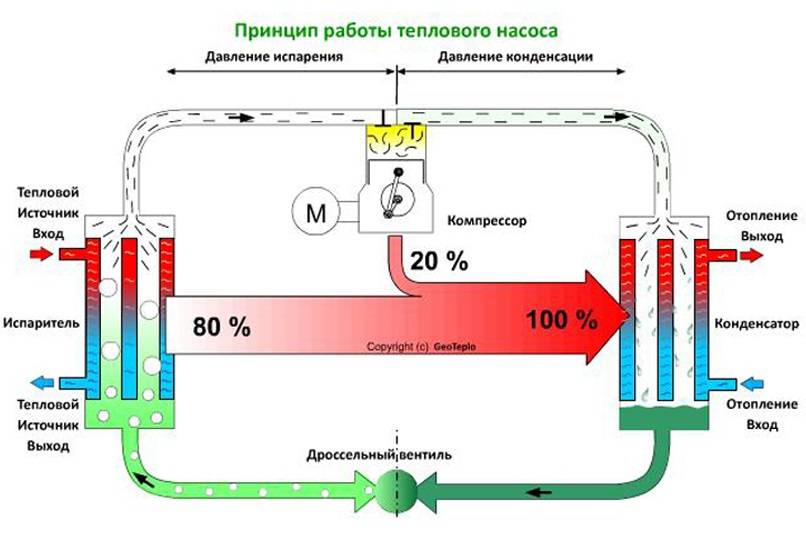
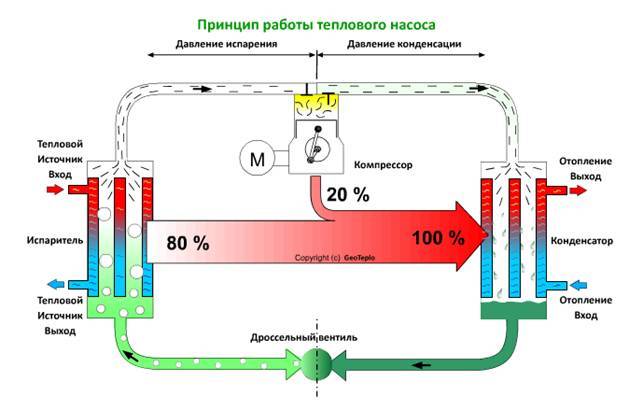
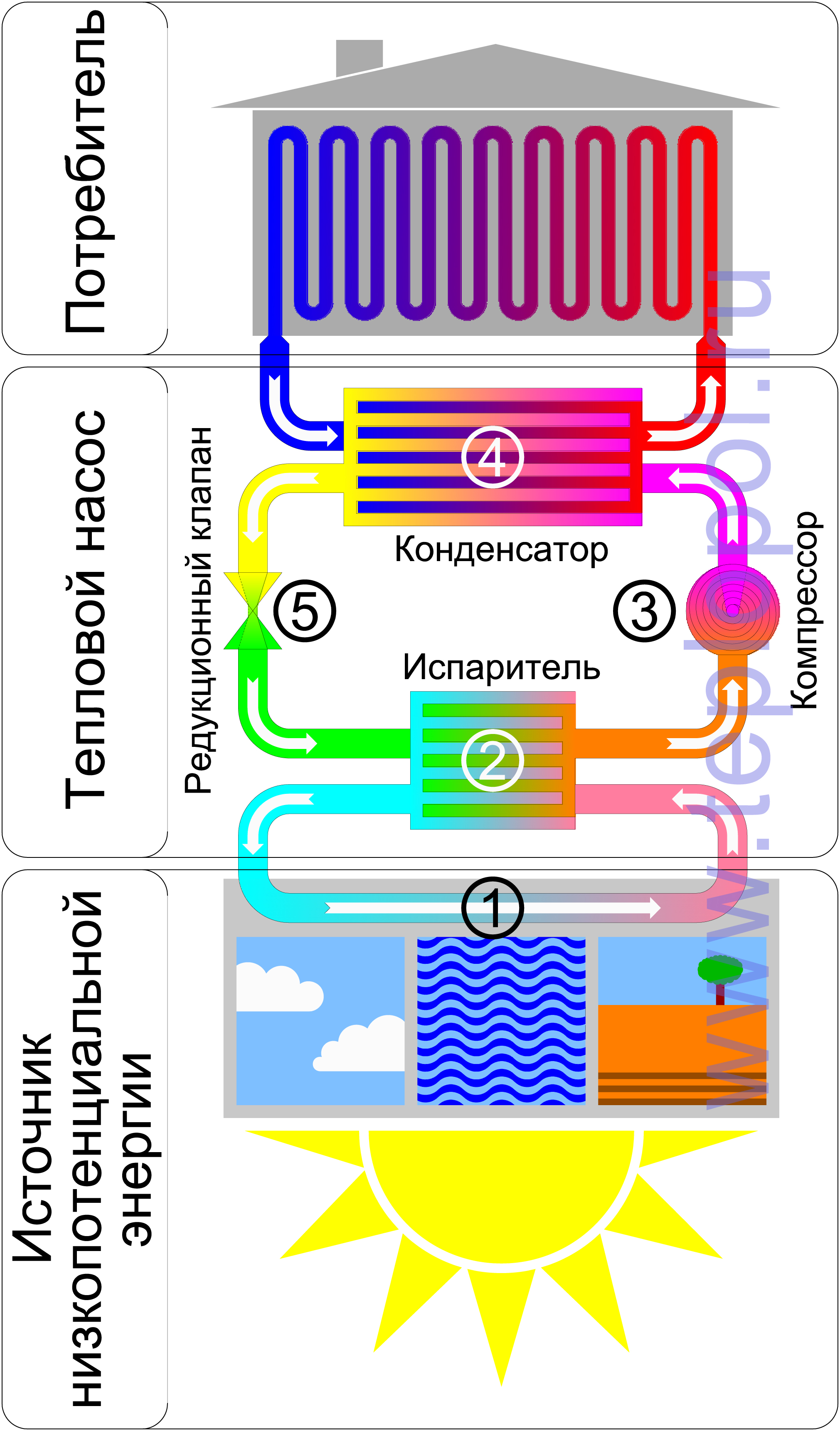
To effectively use these properties of the liquid, a low-boiling refrigerant (freon, freon) circulates in a closed circuit, the design of which includes:
- compressor with electric drive;
- fan blown evaporator;
- throttle (expansion) valve;
- plate heat exchanger;
- copper or metal-plastic circulation tubes connecting the main elements of the circuit.
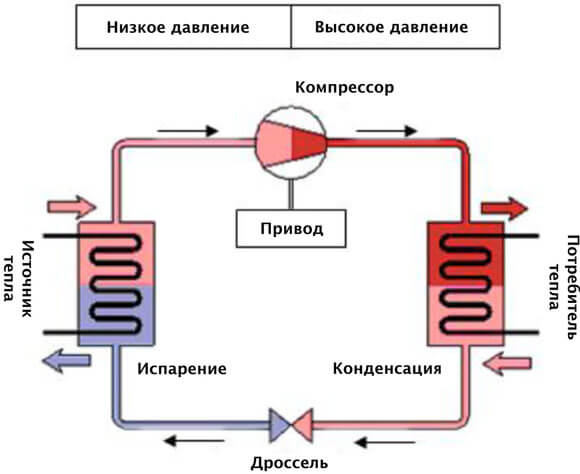
The movement of the refrigerant along the circuit is carried out due to the pressure developed by the compressor.To reduce heat losses, the pipes are covered with a heat-insulating layer of artificial rubber or polyethylene foam with a protective metallized coating. As a refrigerant, freon or freon is used, which can boil at a negative temperature and does not freeze up to -40 ° C.
The whole process of work consists of the following successive cycles:
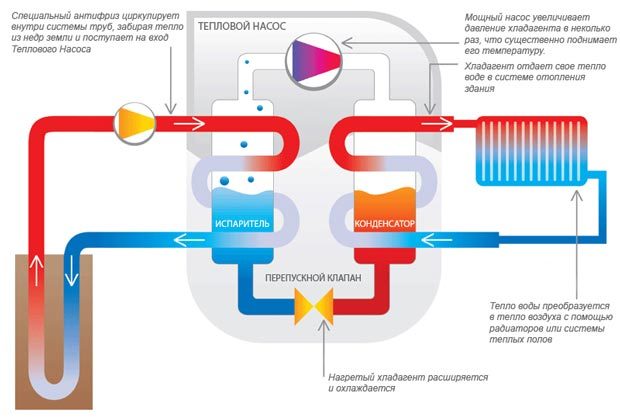
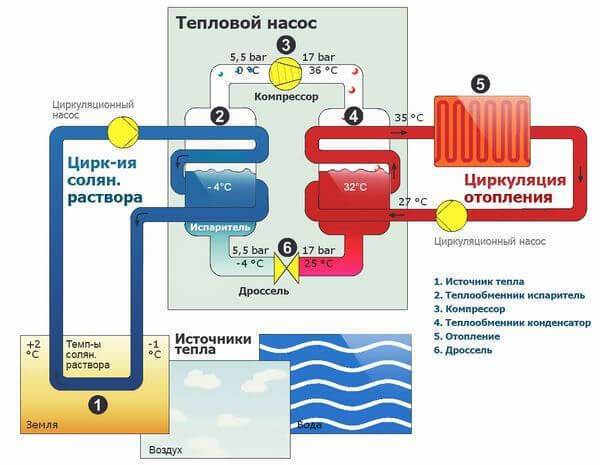
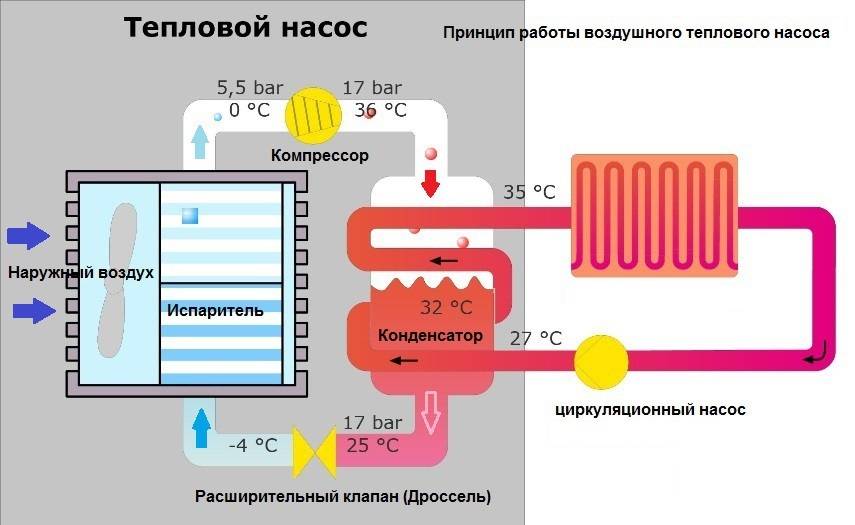
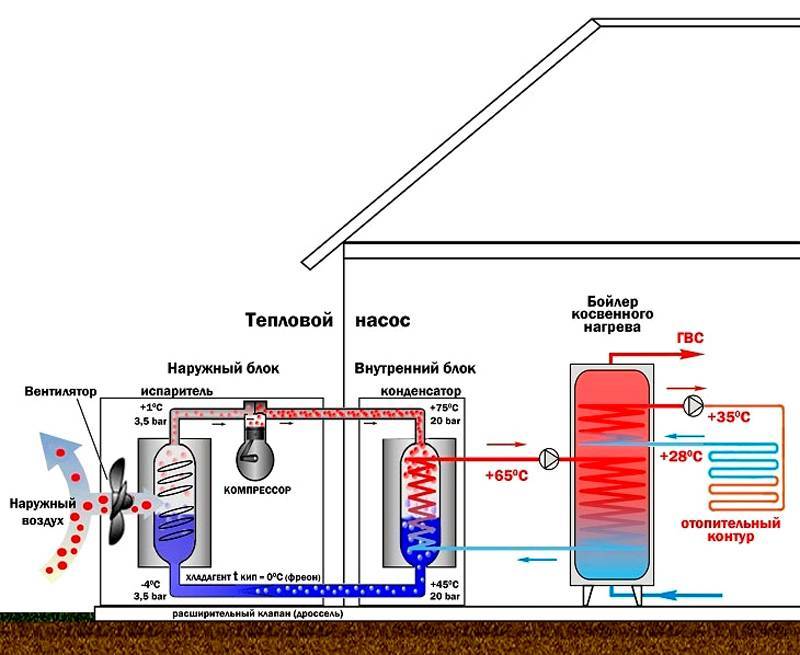
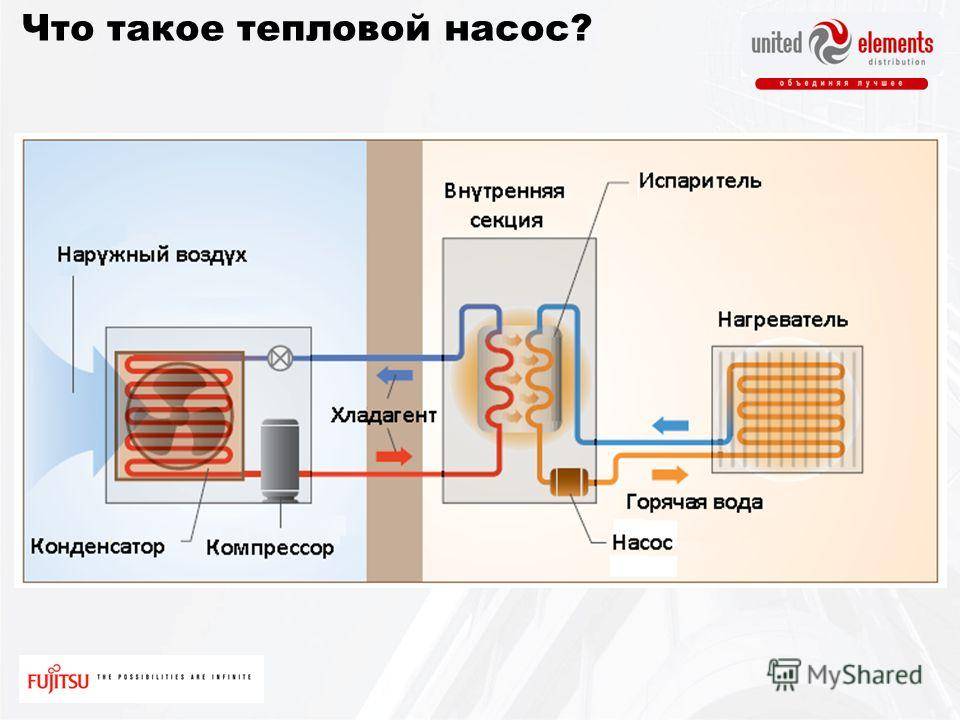
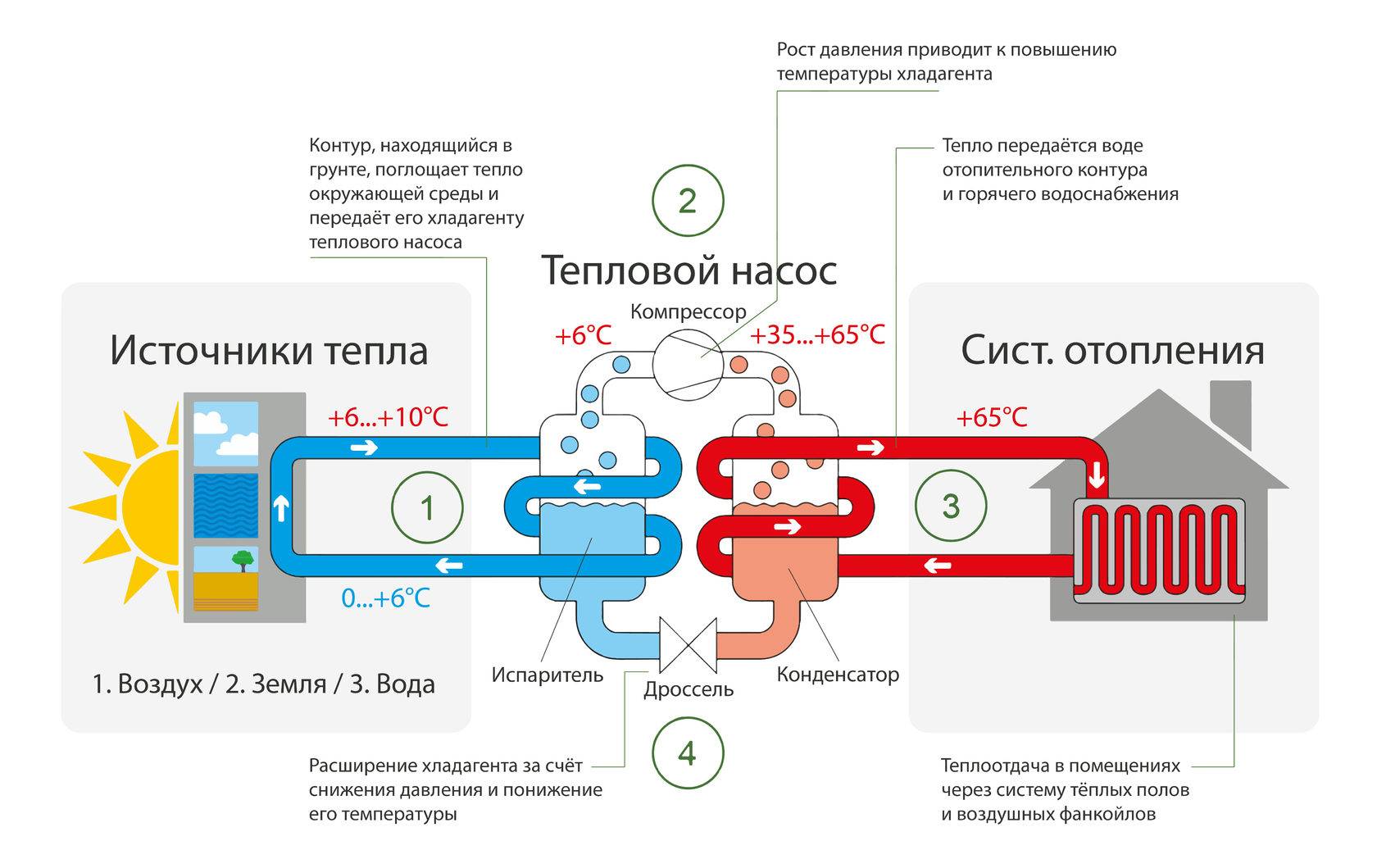
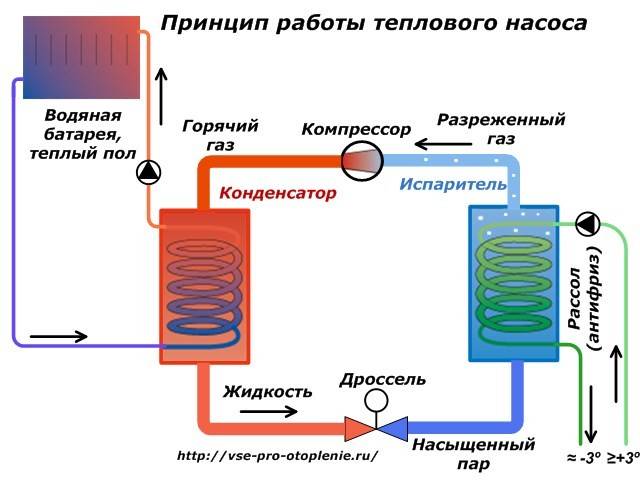
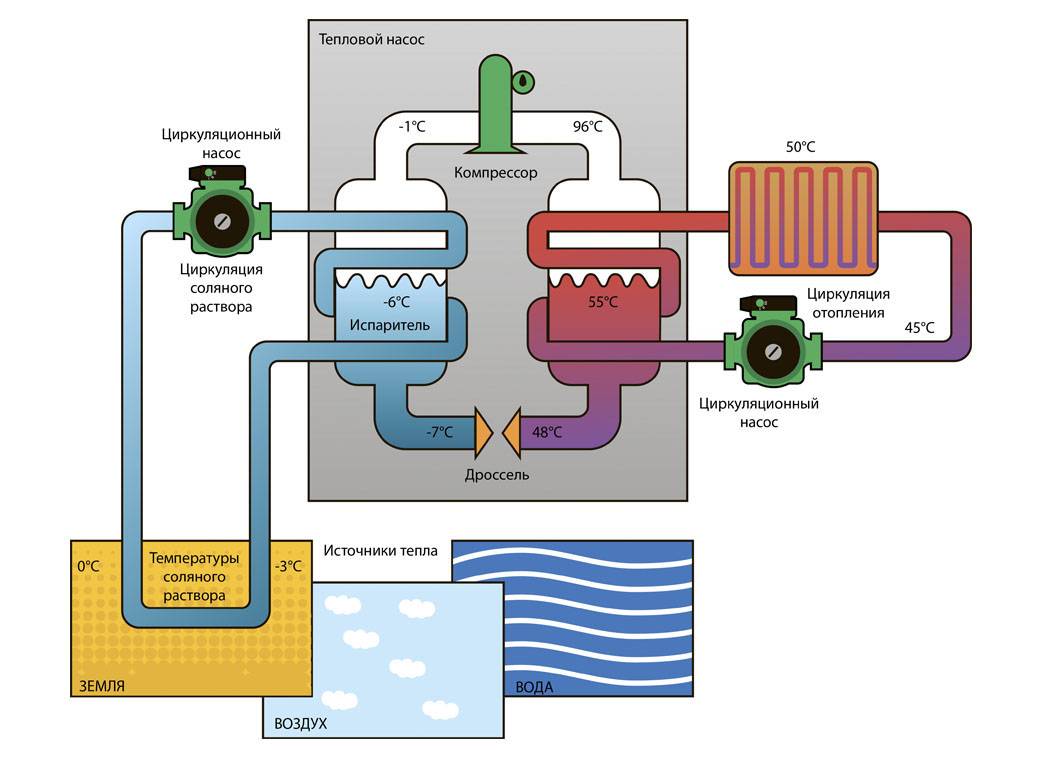
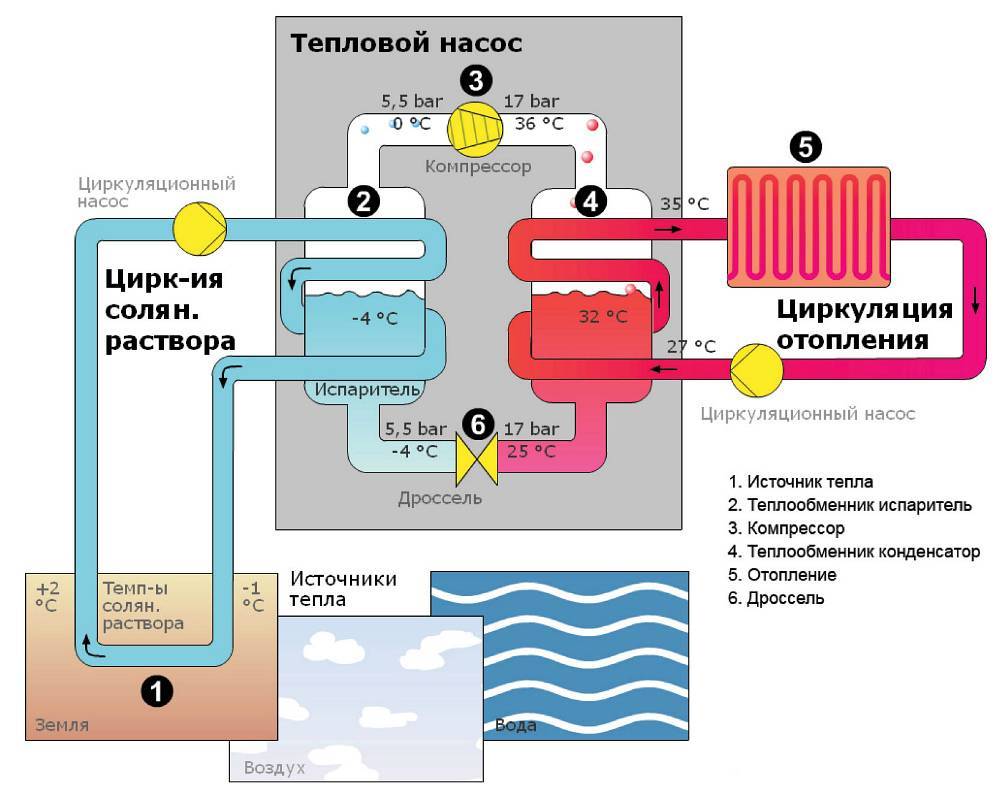
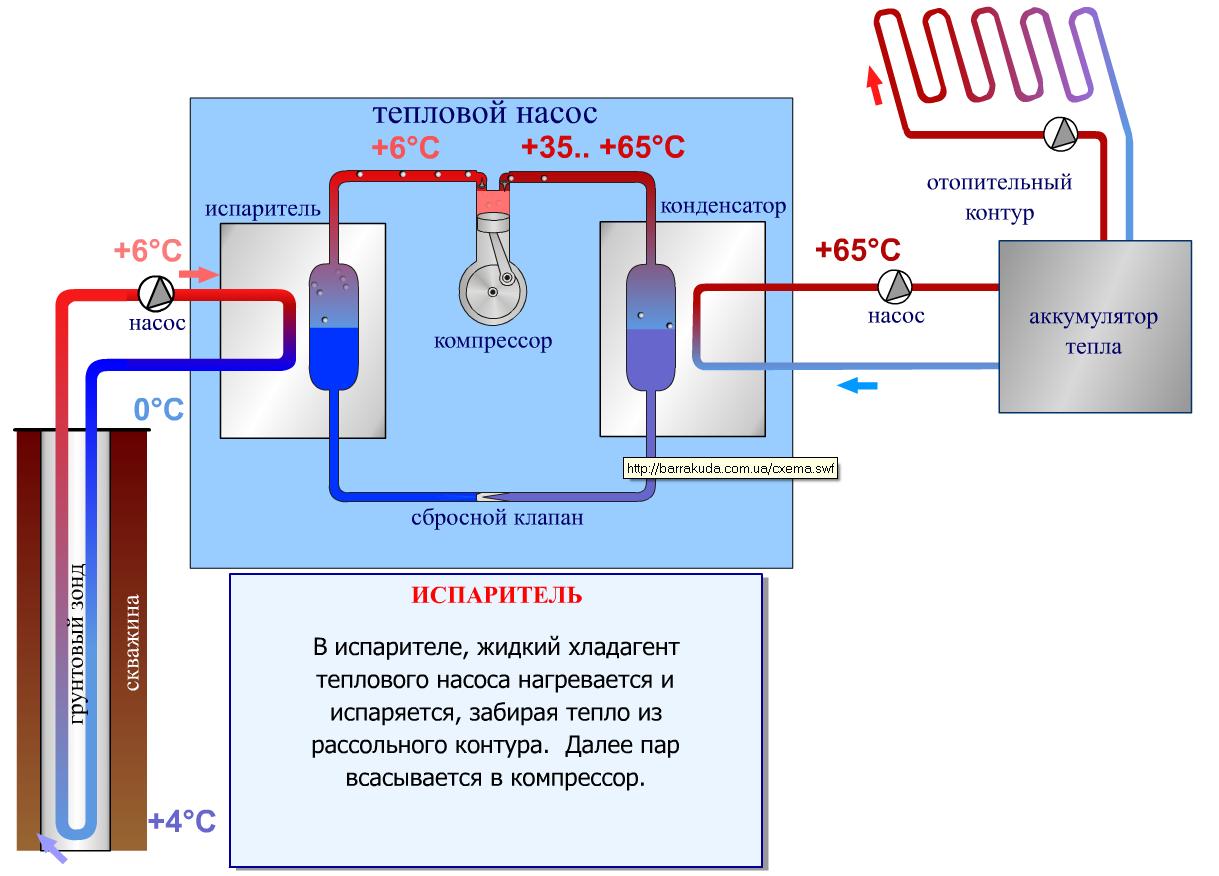
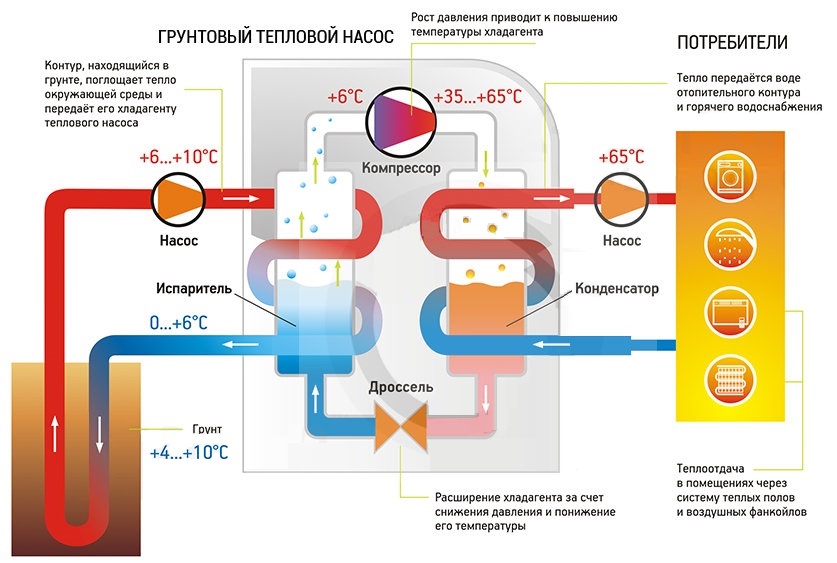
- The evaporator radiator contains a liquid refrigerant that is cooler than the outside air. During active radiator blowing, thermal energy from low-potential air is transferred to freon, which boils and passes into a gaseous state. At the same time, its temperature rises.
- The heated gas enters the compressor, where it heats up even more during the compression process.
- In a compressed and heated state, the refrigerant vapor is fed into a plate heat exchanger, where the heat carrier of the heating system circulates through the second circuit. Since the temperature of the coolant is much lower than that of the heated gas, freon actively condenses on the heat exchanger plates, giving off heat to the heating system.
- The cooled vapor-liquid mixture enters the throttle valve, which allows only the cooled low-pressure liquid refrigerant to pass to the evaporator. Then the whole cycle is repeated.
To increase the heat transfer efficiency of the tube, spiral fins are wound on the evaporator. The calculation of the heating system, the choice of circulation pumps and other equipment should take into account hydraulic resistance and coefficient heat transfer plate heat exchanger installation.
Video overview of the system device and its operation
Inverter heat pumps
The presence of an inverter as part of the installation allows for a smooth start-up of the equipment and automatic regulation of modes depending on the outdoor temperature. This maximizes the efficiency of the heat pump by:
- achievement of efficiency at the level of 95-98%;
- reducing energy consumption by 20-25%;
- minimization of loads on the electrical network;
- increase the service life of the plant.
As a result, the indoor temperature is stably maintained at the same level, regardless of weather changes. At the same time, the presence of an inverter complete with an automated control unit will provide not only heating in winter, but also the supply of cooled air in summer in hot weather.
At the same time, it should be taken into account that the presence of additional equipment always entails an increase in its cost and an increase in the payback period.
Division by type of working fluid
Modern heat pumps can use gaseous body or chemical liquid ammonia solution as a heat transporter. The suitability of a particular scheme is evaluated by several factors, system features.
- Freon installations have a heat pump cycle based on gas compression and expansion processes. They are somehow built on the compressor scheme. The equipment has attractive performance indicators, but it also has disadvantages. Although the weighted average consumption of the system at the time of the operating cycle is stable, the wiring is heavily loaded. In addition, heat pumps with a gaseous heat transporter will not be useful in regions where there is no centralized electricity network or a power source of sufficient load capacity.
- Evaporative type plants using ammonia solution have a duty cycle based on the evaporation process of the substance at low boiling points. Liquefaction after the passage of an external heat exchanger occurs under the action of an energy source. This is a heat burner. Almost any fuel can be used for it: solid, gasoline, diesel, gas, kerosene, in some cases - methyl alcohol. Therefore, evaporative heat pumps are attractive in places where there is no electricity. In addition, the cheapness of fuel of a certain type in the region may prompt the choice of such equipment.
The nature of the working fluid used in the system can say a lot about the performance of the installation and power output. So, freon compressor heat pumps are capable of a sharp jerk, quickly warming up the room. Ammonia evaporation models are not capable of such feats. Their preferred mode of use is stable, continuous operation at rated heat output.
Types of heat pumps
Heat pumps are divided into several types. The first type (type) in the classification according to the method of transfer of thermal energy:
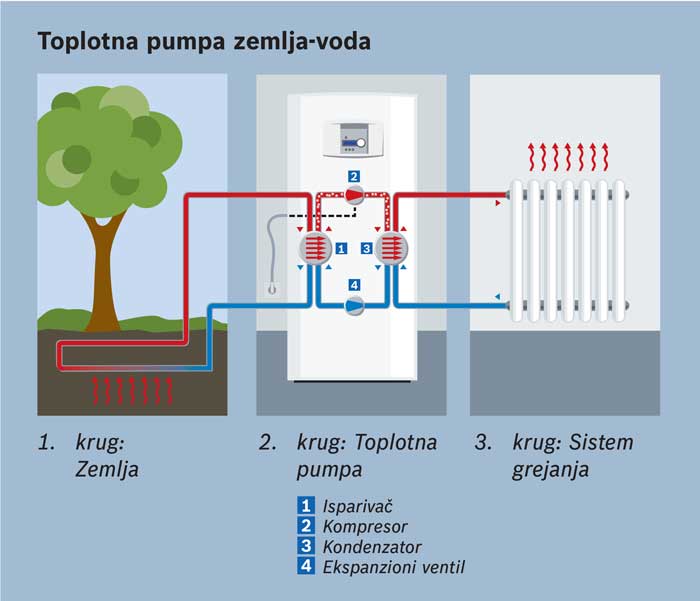
Compression. The main installation elements are compressors, condensers, expanders and evaporators. This type of pump is very high quality and efficient, which makes it very popular in the market.
Absorption. The latest generation of heat pumps. They use an absorbent freon in their work. Thanks to this, the quality of work is increased several times.
Can be distinguished types of heat pumps according to heat sources, namely:
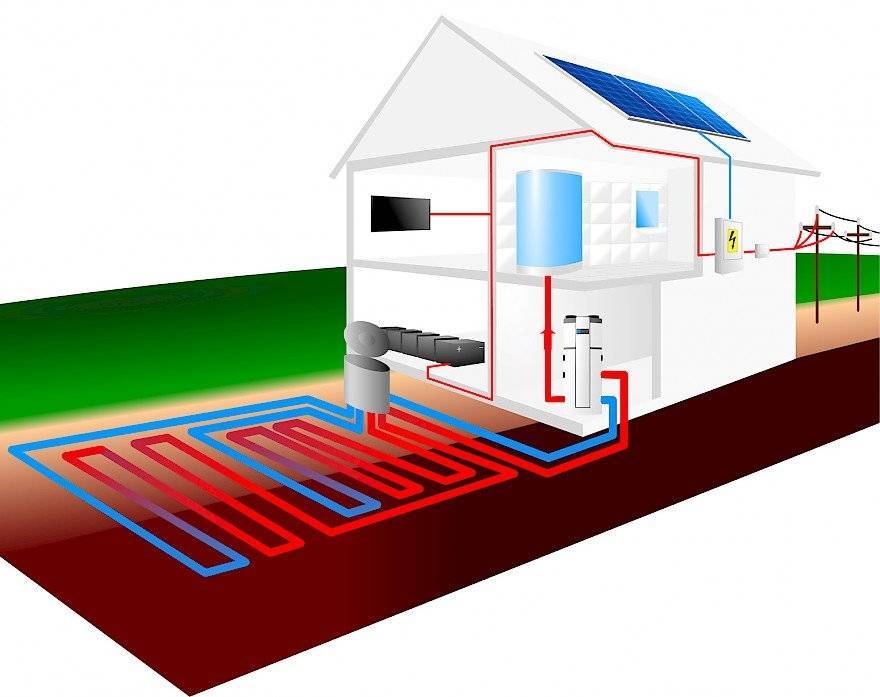
- Heat energy is created by the soil (pictured);
- water;
- Air currents
- Re-warmth. They are obtained from water runoff, dirty air or sewage.

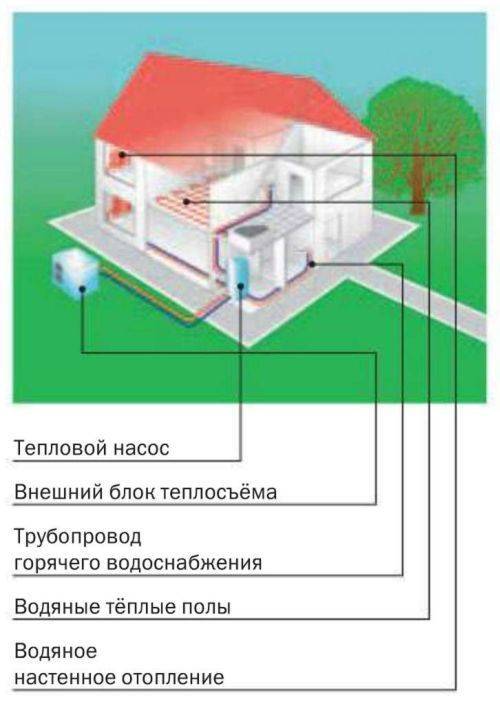
By types of input-output circuits:
- air-to-air. The pump takes cold air, lowers its temperature, receives the required heat, which transfers it to where heating is required.
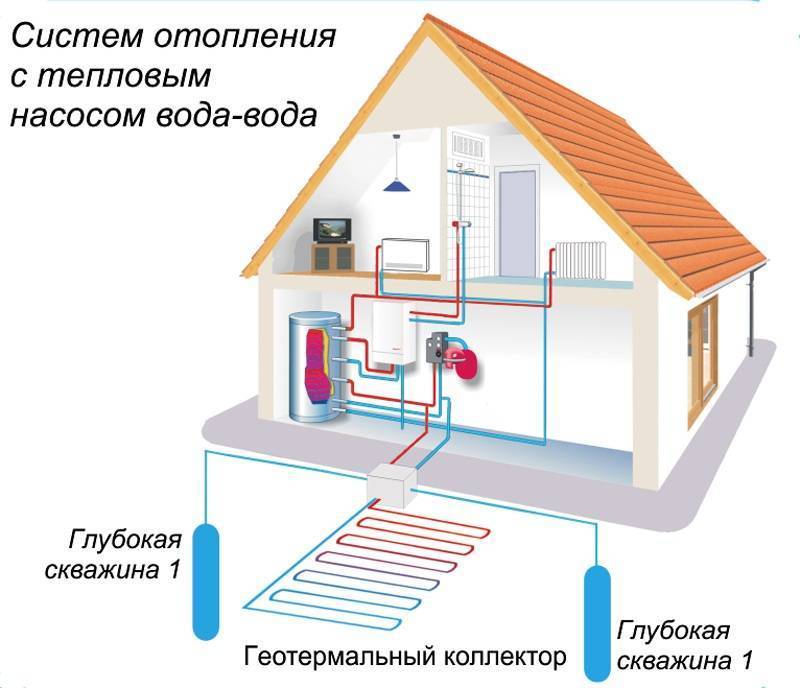
- water-to-water. The pump takes the heat from the ground water, which gives it to the water to heat the room.
- water-to-air. From water to air. The use of probes and wells for water is typical, and heating takes place through an air heating system.
- air-to-water. From air to water. Pumps of this type use heat from the atmosphere to heat water.
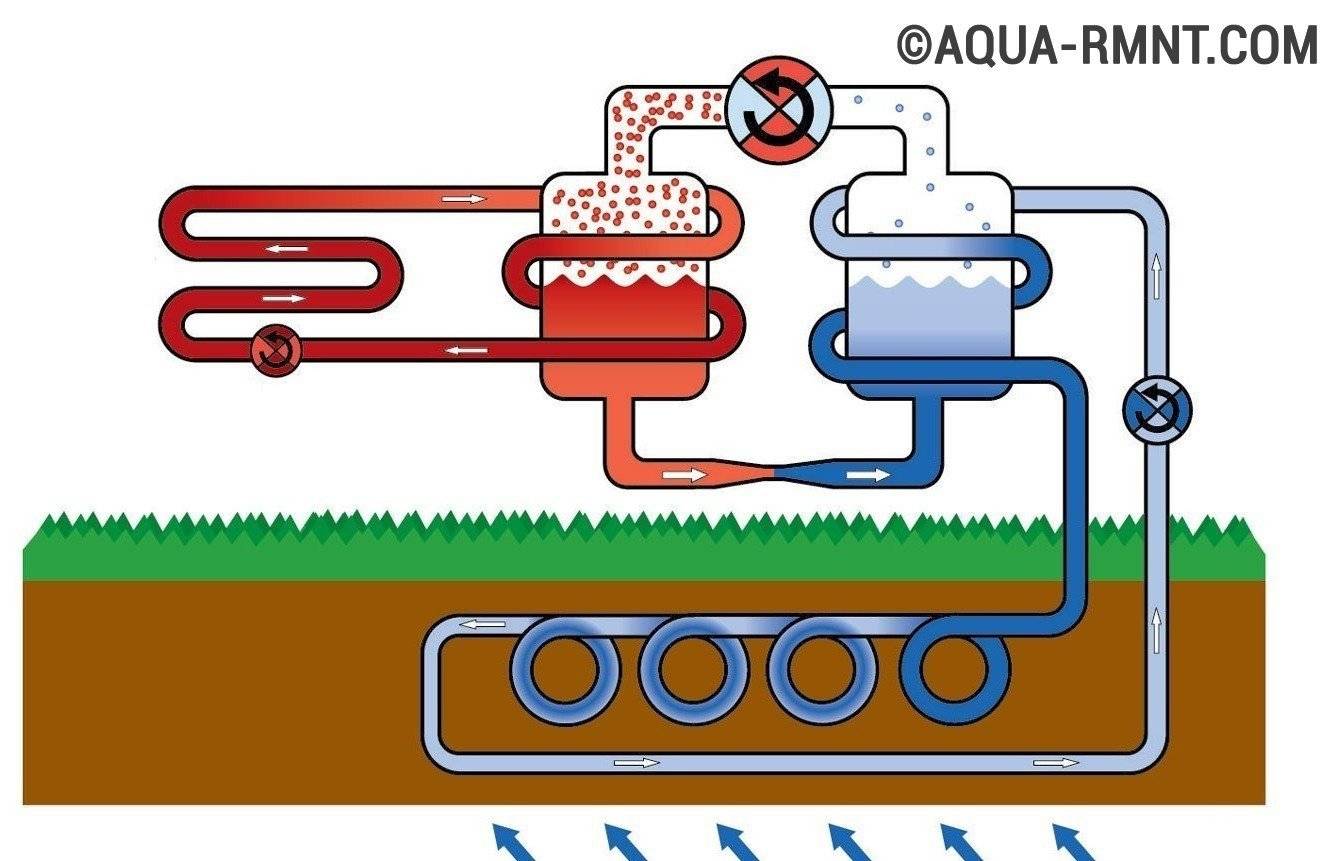
- soil-water. In this form, heat is taken from pipes with water laid in the ground. Heat is taken from the ground (soil).
- ice water. An interesting type of heat pump. To heat water for space heating, an ice production technique is used, in which colossal thermal energy is released. If you freeze up to 200 liters of water, you can get energy that can heat a medium size within 40-60 minutes.
Advantages and disadvantages of heat pumps
Principle heat pump operation, in simple terms, is based on the collection of low-grade thermal energy and its further transfer to heating and climate systems, as well as to water treatment systems, but at a higher temperature. A simple example can be given in the form of a gas cylinder – when it is filled with gas, the compressor heats up by compressing it. And if you release gas from the cylinder, then the cylinder will cool - try to sharply release gas from a refillable lighter to understand the essence of this phenomenon.
Thus, heat pumps, as it were, take away thermal energy from the surrounding space - it is in the ground, in water and even in the air. Even if the air has a negative temperature, there is still heat in it. It is also found in any water bodies that do not freeze to the very bottom, as well as in deep layers of soil that are also not amenable to deep freezing - unless, of course, it is permafrost.
Heat pumps have a rather complicated device, as you can see by trying to disassemble a refrigerator or air conditioners. These household units familiar to us are somewhat similar to the above-mentioned pumps, only they work in the opposite direction - they take heat from the premises and send it outside. If you put your hand on the rear radiator of the refrigerator, we will note that it is warm. And this heat is nothing but the energy taken from fruits, vegetables, milk, soups, sausages and other products that are in the chamber.
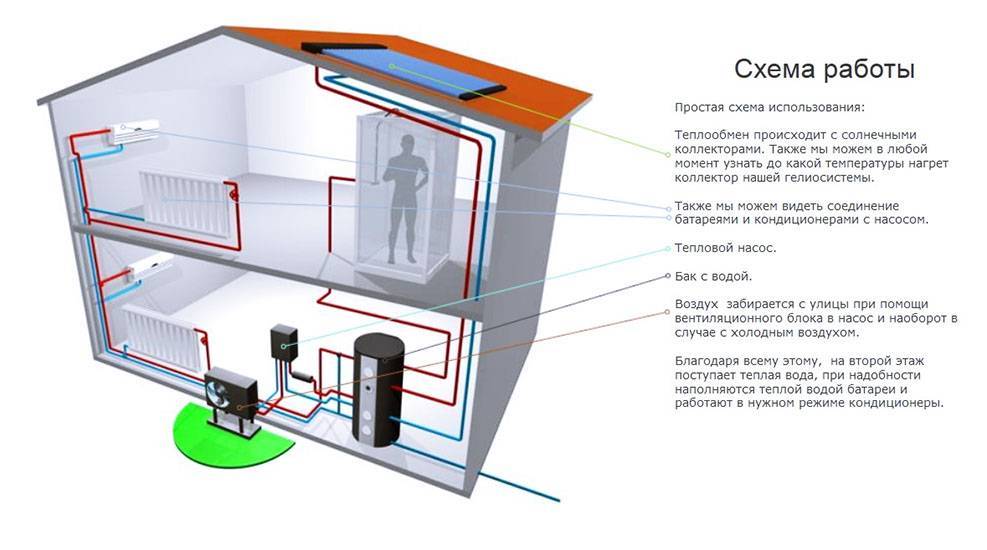
Air conditioners and split systems work in a similar way - the heat generated by outdoor units is thermal energy collected bit by bit in cooled rooms.
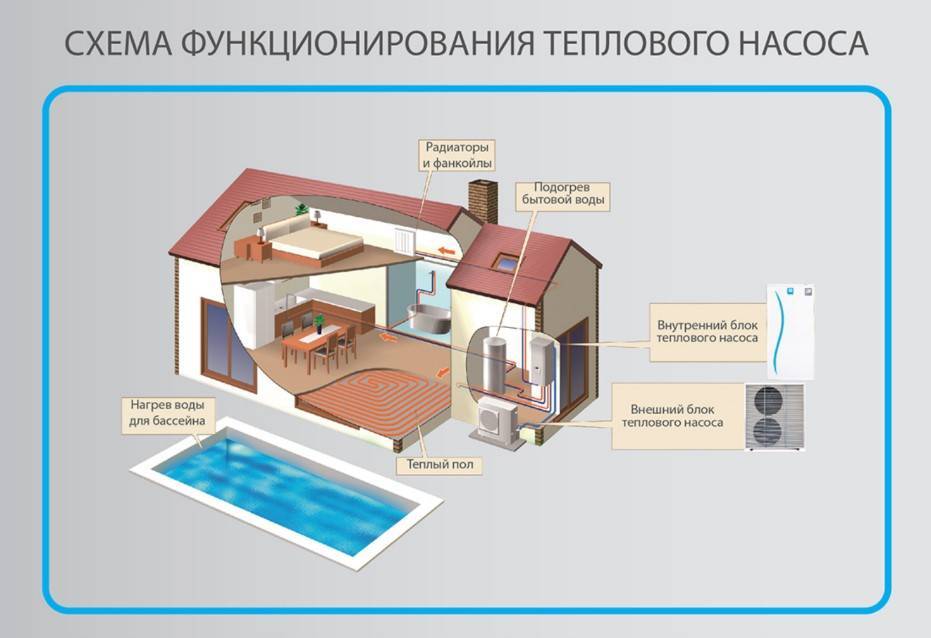
The principle of operation of a heat pump is the opposite of that of a refrigerator. It collects heat from the air, water or soil in the same grains, after which it redirects it to consumers - these are heating systems, heat accumulators, underfloor heating systems, and water heaters. It would seem that nothing prevents us from heating the coolant or water with an ordinary heating element - it's easier that way. But let's compare the productivity of heat pumps and conventional heating elements:
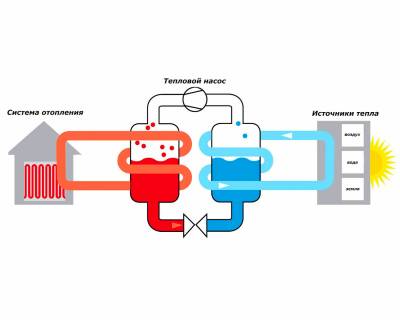
When choosing a heat pump, the most important thing is the availability of a specific natural energy source.
- Conventional heating element - for the production of 1 kW of heat, it consumes 1 kW of electricity (excluding errors;
- Heat pump - it consumes only 200 W of electricity to produce 1 kW of heat.
No, there is no efficiency equal to 500% here - the laws of physics are unshakable. It's just the laws of thermodynamics at work here. The pump, as it were, accumulates energy from space, "thickens" it and sends it to consumers. Similarly, we can collect raindrops through a large watering can, getting a solid stream of water at the exit.
We have already given many analogies that allow us to understand the essence of heat pumps without abstruse formulas with variables and constants. Let's now look at their advantages:
- Energy savings - if the standard electric heating of a 100 sq. m. will lead to costs of 20-30 thousand rubles per month (depending on the air temperature outside), then the heating system with a heat pump will reduce costs to an acceptable 3-5 thousand rubles - you must admit, this is already quite a solid savings. And this is without tricks, without deception and without marketing tricks;
- Caring for the environment - coal, nuclear and hydroelectric power plants harm nature. Therefore, reduced electricity consumption reduces the amount of harmful emissions;
- A wide range of uses - the resulting energy can be used to heat a home and prepare hot water.
There are also disadvantages:
- The high cost of heat pumps - this disadvantage imposes a restriction on their use;
- The need for regular maintenance - you have to pay for it;
- Difficulty in installation - this applies to the greatest extent to heat pumps with closed circuits;
- Lack of acceptance by people - few of us would agree to invest in this equipment in order to reduce the burden on the environment. But some people who live far from gas mains and are forced to heat their homes with alternative heat sources agree to spend money on buying a heat pump and reduce their monthly electricity bills;
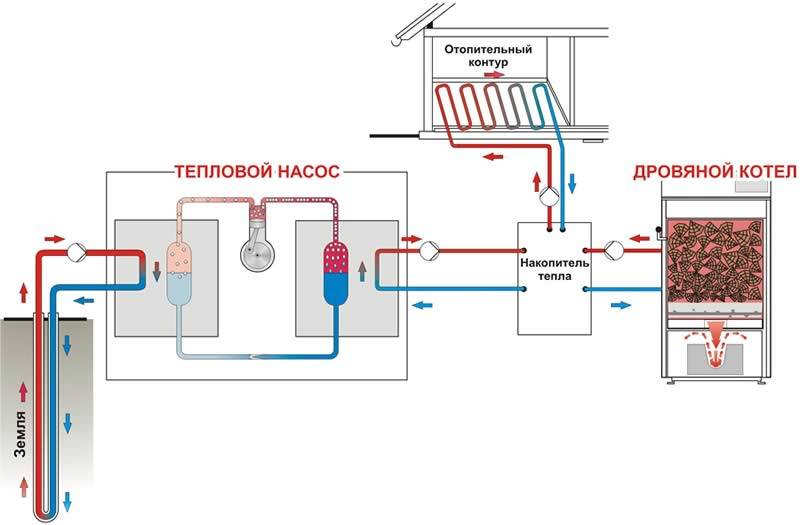
- Dependence on the mains - if the supply of electricity stops, the equipment will immediately freeze. The situation will be saved by installing a heat accumulator or a backup power source.
As you can see, some of the disadvantages are quite serious.
Gasoline and diesel power generators can serve as backup power sources for heat pumps.
Tips & Tricks
A heat pump is a technically complex and rather expensive equipment, so its choice should be approached with great responsibility. In order not to be unfounded, here are some very specific recommendations.
1. Never start choosing a heat pump without first making calculations and creating a project. The absence of a project can cause fatal errors, which can only be corrected with the help of huge additional financial investments.
2. The design, installation and maintenance of the heat pump and heating system should only be entrusted to professionals. How to make sure that professionals work in this company? First of all, by the availability of all the necessary documentation, a portfolio of implemented objects, certificates from equipment suppliers.It is highly desirable that the entire range of necessary services be provided by one company, which in this case will be fully responsible for the implementation of the project.
3. We advise you to give preference to a European-made heat pump. Do not be confused by the fact that it is more expensive than Chinese or Russian equipment. When included in the estimate of the cost of installation, commissioning and debugging of the entire heating system, the difference in the price of the pumps will be almost imperceptible. But on the other hand, having a “European” at your disposal, you will be sure of its reliability, since the high price of the pump is only the result of using modern technologies and high-quality materials to create it.
Main varieties
All circulation pumps for heating systems are divided into two design types: devices with a "dry" rotor and circulation pumps with a "wet" rotor.
In circulation pumps of the first type, which is already clear from their name, the rotor does not come into contact with the liquid working medium - the coolant. The impeller of such pumps is separated from the rotor and stator by sealing steel rings, pressed against each other by means of a special spring that compensates for the wear of these elements. The tightness of this sealing assembly during the operation of the pump is ensured by a thin layer of water between the steel rings, which is formed due to the difference between the pressures in the heating system and in the external environment.
Circulation pumps for heating with a "dry" rotor are distinguished by fairly high efficiency (89%) and productivity, but hydraulic machines of this type also have disadvantages, including strong noise at work and complexity in operation, maintenance and repair.As a rule, industrial heating systems are equipped with pumps of this type; they are rarely used in domestic heating systems.
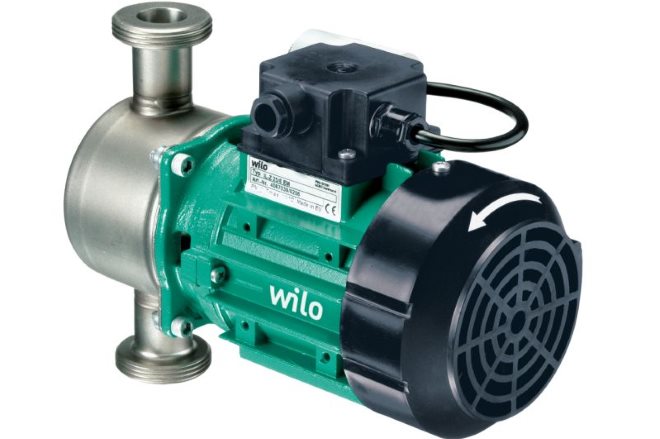

Single-stage circulation pump with a "dry" rotor
A circulation pump for heating systems equipped with a “wet” type rotor is a device whose impeller and rotor are in constant contact with the coolant. The working medium in which the rotor and impeller rotates acts as a lubricant and coolant. The stator and rotor of pumps of this type are isolated from each other using a special glass made of stainless steel. Such a glass, inside of which a rotor and an impeller rotating in the coolant medium, protects the energized stator winding from the ingress of working fluid onto it.
The efficiency of pumps of this type is rather low and is only 55%, but the technical capabilities of such a device are quite enough to ensure the circulation of the coolant in heating systems not too big houses. If we talk about the advantages of circulation pumps with a "wet" rotor, then they should include the minimum amount of noise emitted during the operation of such devices, high reliability, ease of operation, maintenance and repair.

Wet circulation pump
Selecting the type of heat pump
The main indicator of this heating system is power. First of all, the financial costs for the purchase of equipment and the choice of one or another source of low-temperature heat will depend on the power.The higher the power of the heat pump system, the greater the cost of components.
First of all, this refers to the compressor power, the depth of wells for geothermal probes, or the area to accommodate a horizontal collector. Correct thermodynamic calculations are a kind of guarantee that the system will work efficiently.

If there is a reservoir near your personal area, the most cost-effective and productive choice will be heat pump water-water
First you need to study the area that is planned for the installation of the pump. The ideal condition would be the presence of a reservoir in this area. Using the water-to-water option will significantly reduce the amount of excavation.
The use of the heat of the earth, on the contrary, involves a large number of works associated with excavation. Systems that use water as low-grade heat are considered the most efficient.

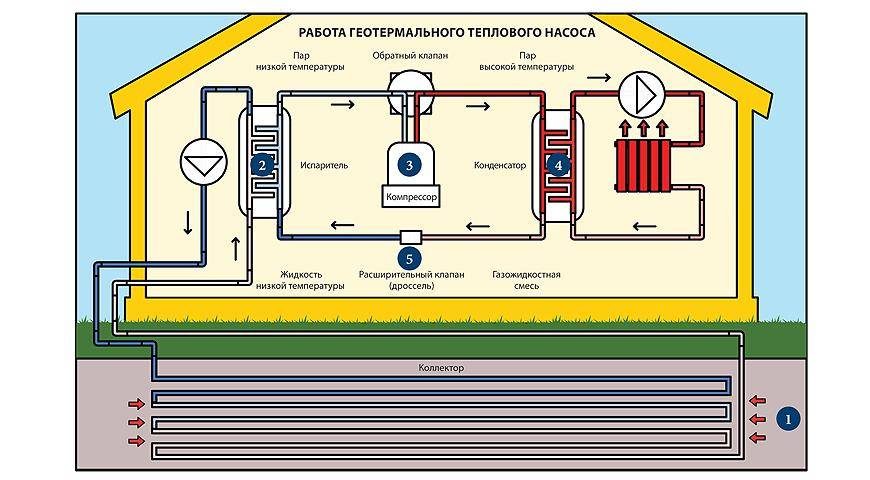
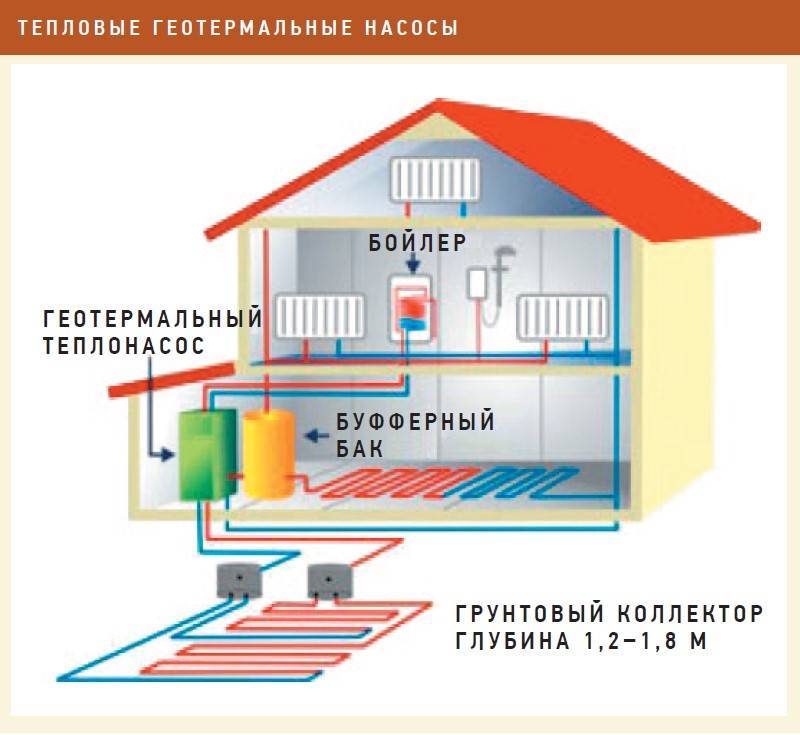
The device of a heat pump that extracts thermal energy from the ground involves an impressive amount of earthworks. The collector is laid below the level of seasonal freezing
There are two ways to use the thermal energy of the soil. The first involves drilling wells with a diameter of 100-168 mm. The depth of such wells, depending on the parameters of the system, can reach 100 m or more.
Special probes are placed in these wells. The second method uses a collector of pipes. Such a collector is placed underground in a horizontal plane. This option requires a fairly large area.
For laying the collector, areas with wet soil are considered ideal. Naturally, drilling wells will cost more than a horizontal reservoir.However, not every site has free space. For one kW of heat pump power, you need from 30 to 50m² area.
The construction for the intake of thermal energy by one deep well may turn out to be a little cheaper than digging a pit
But a significant plus lies in the significant savings in space, which is important for owners of small plots. In the case of the presence of a high-lying groundwater horizon on the site, heat exchangers can be arranged in two wells located at a distance of about 15 m from each other
In the case of the presence of a high-lying groundwater horizon on the site, heat exchangers can be arranged in two wells located at a distance of about 15 m from each other.
The extraction of thermal energy in such systems by pumping groundwater in a closed circuit, parts of which are located in wells. Such a system requires the installation of a filter and periodic cleaning of the heat exchanger.
The simplest and cheapest heat pump scheme is based on extracting thermal energy from the air. Once it became the basis for the construction of refrigerators, later air conditioners were developed according to its principles.
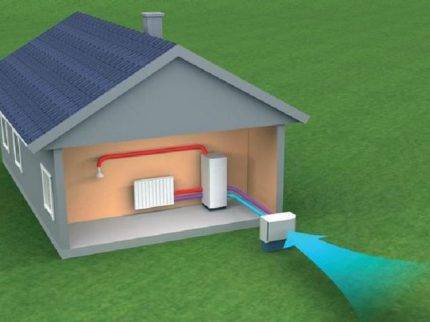
The simplest heat pump system obtains energy from the air mass. In summer it is involved in heating, in winter in air conditioning. The disadvantage of the system is that, in an independent version, a unit with insufficient power
Efficiency various types of this equipment not the same. Pumps that use air have the lowest performance. In addition, these indicators are directly dependent on weather conditions.
Ground varieties of heat pumps have stable performance. The efficiency coefficient of these systems varies within 2.8 -3.3.Water-to-water systems are the most efficient. This is primarily due to the stability of the source temperature.
It should be noted that the deeper the pump collector is located in the reservoir, the more stable the temperature will be. To obtain a system power of 10 kW, about 300 meters of pipeline are needed.
The main parameter characterizing the efficiency of a heat pump is its conversion factor. The higher the conversion factor, the more efficient the heat pump is considered.
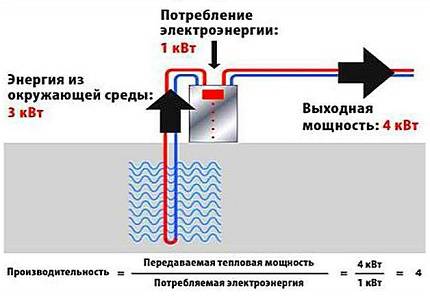
The conversion factor of a heat pump is expressed through the ratio of the heat flow and the electrical power spent on the operation of the compressor