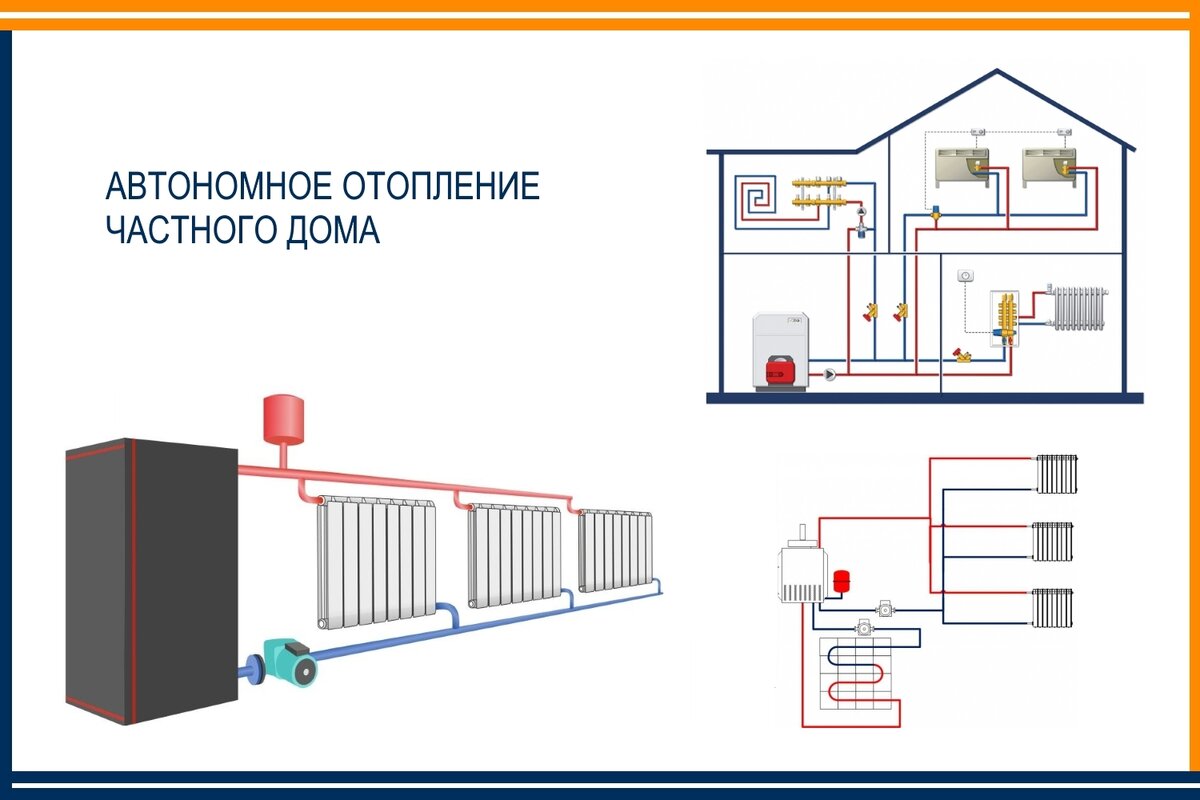
- 3 Main types
- What is the difference between solid fuel boilers
- Types of aggregates
- Soil-water system
- Water-to-water pump
- Universal air-to-water option
- Heat pumps - classification
- Geothermal pump - principles of design and operation
- Using water as a heat source
- Air is the most accessible source of heat
- How heat pumps work
- Electric heater installation
- Characteristics and principle of operation
- Air-to-water heat pump for home
- How do air-to-water heat pumps work?
- Advantages and disadvantages
- Installation capacity calculation
- Advantages and disadvantages of technology
- Environmental friendliness and safety ↑
- What is a heat pump and how does it work?
3 Main types
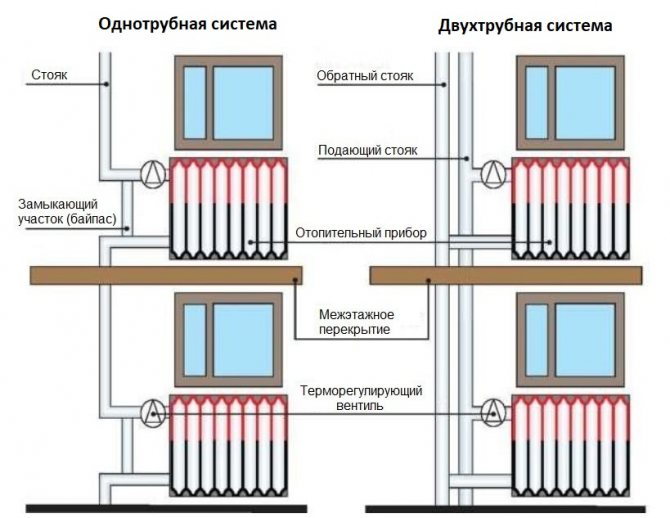
Before agreeing to install an open garage heating circuit with a circulation pump, you need to consider other options for fluid circulation. As you know, it can move through the principles of thermodynamics - in a natural way or gravitational.
Systems operating by means of natural circulation are quite suitable for rooms with an area of up to 60 square meters. The maximum loop length for this equipment is 30 meters.
It is also important to consider the following factors:
- 1. The height of the building.
- 2. Floors.
Natural circulation schemes are not suitable for use in low-temperature conditions, since the lack of sufficient heating of the coolant will not allow reaching the optimum pressure. The areas of application of such a system are as follows:
- 1. Connection to a warm floor. A circulation pump is connected to the water circuit.
- 2. Work with the boiler. The heating device is fixed on top of the system - just below the expansion tank.
What is the difference between solid fuel boilers
In addition to the fact that these heat sources produce heat energy by burning various types of solid fuels, they have a number of other differences from other heat generators. These differences are precisely the result of burning wood, they must be taken for granted and always taken into account when connecting the boiler to a water heating system. Features are as follows:
- High inertia. At the moment, there are no ways to abruptly extinguish a burning solid fuel in a combustion chamber.
- Formation of condensate in the firebox. The peculiarity manifests itself when a heat carrier with a low temperature (below 50 °C) enters the boiler tank.
Note. The phenomenon of inertia is absent only in one type of solid fuel units - pellet boilers. They have a burner, where wood pellets are dosed, after the supply is stopped, the flame goes out almost immediately.
The danger of inertia lies in the possible overheating of the water jacket of the heater, as a result of which the coolant boils in it. Steam is formed, which creates high pressure, tearing the body of the unit and part of the supply pipeline. As a result, there is a lot of water in the furnace room, a lot of steam and a solid fuel boiler unsuitable for further operation.
A similar situation may arise when the heat generator is connected incorrectly. After all, in fact, the normal mode of operation of wood-burning boilers is the maximum, it is at this time that the unit reaches its passport efficiency. When the thermostat responds to the heat carrier reaching a temperature of 85 ° C and closes the air damper, combustion and smoldering in the furnace still continues. The temperature of the water rises by another 2-4°C, or even more, before its growth stops.
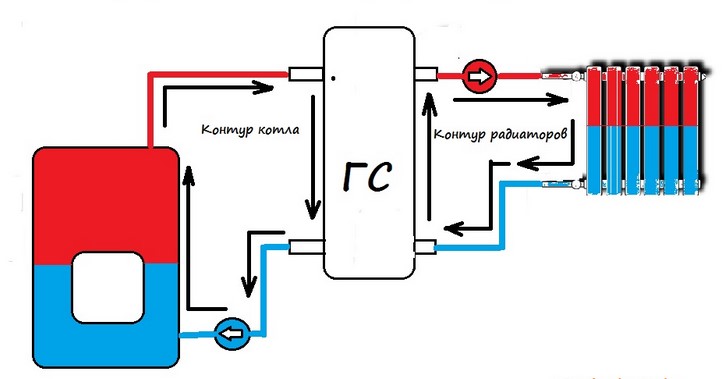
In order to avoid excess pressure and a subsequent accident, an important element is always involved in the piping of a solid fuel boiler - a safety group, more about it will be discussed below.
Another unpleasant feature of the operation of the unit on wood is the appearance of condensate on the inner walls of the firebox due to the passage of an unheated coolant through the water jacket. This condensate is not God's dew at all, since it is an aggressive liquid, from which the steel walls of the combustion chamber quickly corrode. Then, having mixed with the ash, the condensate turns into a sticky substance, it is not so easy to tear it off the surface. The problem is solved by installing a mixing unit in the piping circuit of a solid fuel boiler.
Such a deposit serves as a heat insulator and reduces the efficiency of a solid fuel boiler.
It is too early for owners of heat generators with cast-iron heat exchangers that are not afraid of corrosion to breathe a sigh of relief. They can expect another misfortune - the possibility of destruction of cast iron from temperature shock. Imagine that in a private house the electricity was turned off for 20-30 minutes and the circulation pump, which drives water through a solid fuel boiler, stopped.During this time, the water in the radiators has time to cool down, and in the heat exchanger - to heat up (due to the same inertia).
Electricity appears, the pump turns on and sends the cooled coolant from the closed heating system to the heated boiler. From a sharp temperature drop, a temperature shock occurs at the heat exchanger, the cast-iron section cracks, water runs to the floor. It is very difficult to repair, it is not always possible to replace the section. So even in this scenario, the mixing unit will prevent an accident, which will be discussed later.
Emergencies and their consequences are not described in order to scare users of solid fuel boilers or encourage them to purchase unnecessary elements of piping circuits. The description is based on practical experience, which must always be taken into account. With the correct connection of the thermal unit, the likelihood of such consequences is extremely low, almost the same as for heat generators using other types of fuel.
Types of aggregates
A visual representation of the design options for heat pumps is their classification according to the type of coolant on the external and internal contours of the structure. The device can receive energy from:
- soil;
- water (reservoir or source);
- air.
Inside the house, the resulting heat energy can be used in the heating system, as well as for heating water or for air conditioning. Therefore, there are several types of heat pumps depending on the combination of these elements and functions.
Soil-water system
Receiving heat from the ground is considered one of the most effective for this type of alternative heating, since already about five meters from the surface, the ground temperature remains fairly constant, little affected by changes in weather conditions.

The geothermal heat pump uses special heat-conducting probes
As a coolant on the external circuit, a special liquid is used, which is commonly called brine. This is an environmentally friendly composition.
The outer contour of the ground-to-water heat pump is made of plastic pipes. You can place them in the ground horizontally or vertically. In the first case, work may be required on a large area, from 25 to 50 square meters. m for each kilowatt of pump power. The areas allocated for the installation of a horizontal collector cannot be used for agricultural purposes. Only laying out a lawn or planting annual flowering plants is allowed here.
For the construction of a vertical collector, a series of wells with a depth of 50-150 meters will be required. Since the ground temperature is higher and more stable at this depth, such a ground source heat pump is considered to be more efficient. In this case, special deep probes are used to transfer heat.
Water-to-water pump
An equally effective choice can be a water-to-water heat pump, since at great depths the water temperature remains quite high and constant. The following can be used as a source of low-potential thermal energy:
- open reservoirs (lakes, rivers);
- groundwater (wells, wells);
- wastewater from industrial technological cycles (reverse water supply).
There are no fundamental differences in the design of ground-to-water or water-to-water heat pumps. The construction of a heat pump using the energy of an open reservoir will require the lowest costs: pipes with a heat carrier must be supplied with a load and immersed in water. When using the potential of groundwater, a more complex design will be needed. It may be necessary to build an additional well to discharge the water that passes through the heat exchanger.
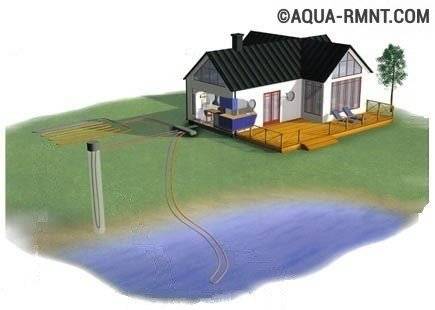
Using a water-to-water heat pump in open water can be very beneficial
Universal air-to-water option
In terms of efficiency, the air-to-water heat pump is inferior to other models, since in the cold season its power is significantly reduced. However, its installation does not require complex excavation work or the construction of deep wells. It is only necessary to select and install suitable equipment, for example, directly on the roof of the house.
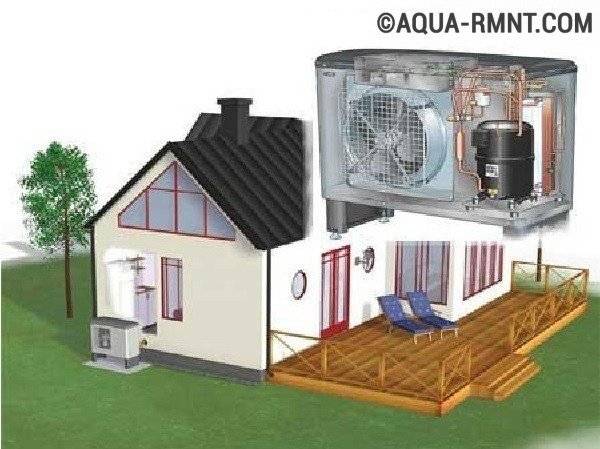
The air-to-water heat pump can be installed without extensive installation work
The undoubted advantage of this design is the ability to reuse the heat that leaves the rooms heated by the heat pump with exhaust air or water, as well as in the form of smoke, gas, etc. To compensate for the lack of power of the air heat pump in winter, alternative heating options should be provided.
The least costly option would be an air-to-air heat pump that does not require the complex work of a traditional hot water heating system.
Heat pumps - classification
The operation of a heat pump for heating a house is possible in a wide temperature range - from -30 to +35 degrees Celsius. The most common devices are absorption (they transfer heat through its source) and compression (the circulation of the working fluid occurs due to electricity). The most economical absorption devices, however, they are more expensive and have a complex design.
Classification of pumps by type of heat source:
- Geothermal. They take heat from water or earth.
- Air. They take heat from the air.
- secondary heat. They take the so-called production heat - generated in production, during heating, and other industrial processes.
The heat carrier can be:
- Water from an artificial or natural reservoir, groundwater.
- Priming.
- Air masses.
- Combinations of the above media.
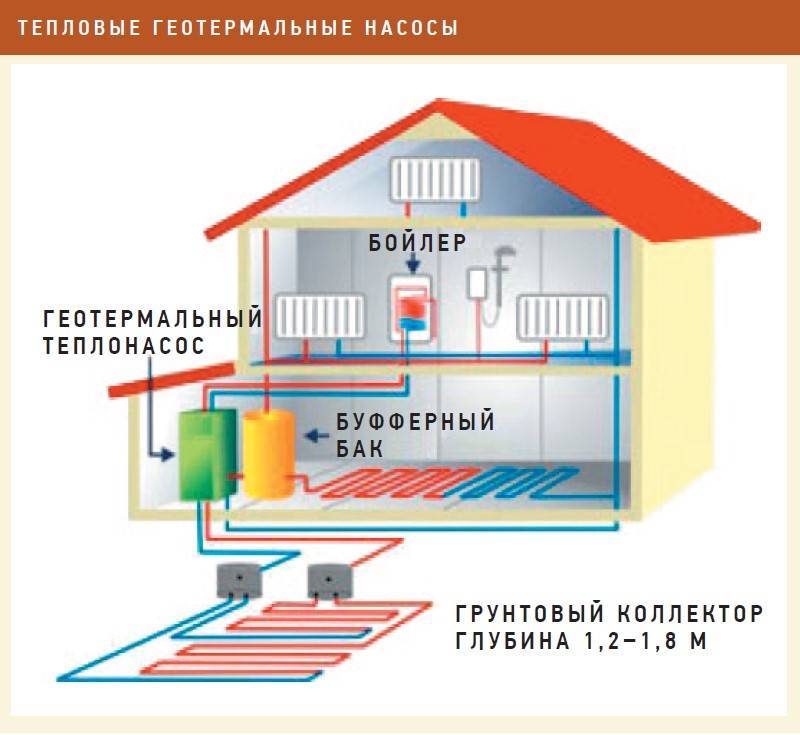
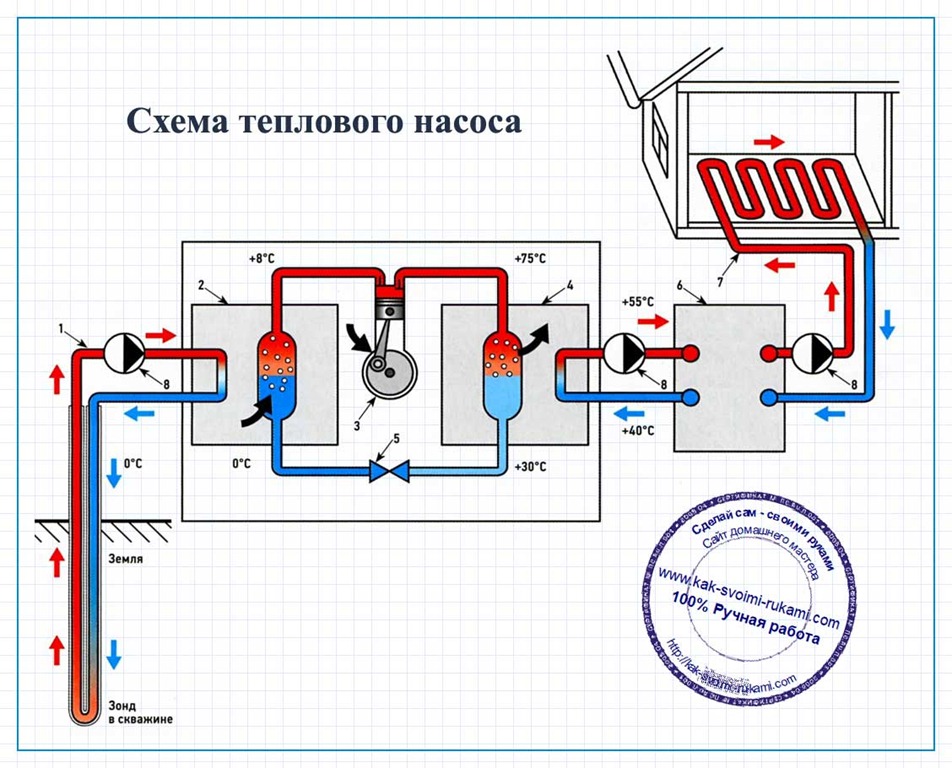
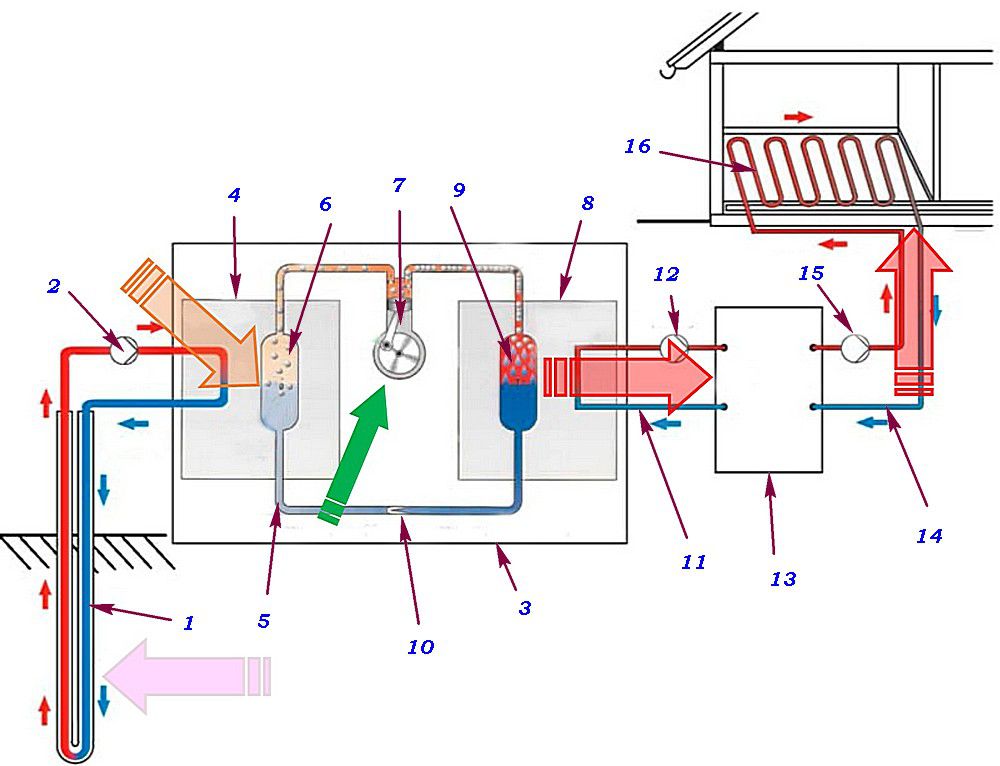
Geothermal pump - principles of design and operation
A geothermal pump for heating a house uses the heat of the soil, which it selects with vertical probes or a horizontal collector. Probes are placed at a depth of up to 70 meters, the probe is located at a small distance from the surface. This type of device is most efficient, since the heat source has a fairly high constant temperature throughout the year. Therefore, it is necessary to spend less energy on heat transportation.
Geothermal heat pump
Such equipment is expensive to install. The high cost of drilling wells. In addition, the area allotted for the collector should be several times larger than the area of the heated house or cottage.
It is important to remember: the land where the collector is located cannot be used for planting vegetables or fruit trees - the roots of the plants will be supercooled
Using water as a heat source
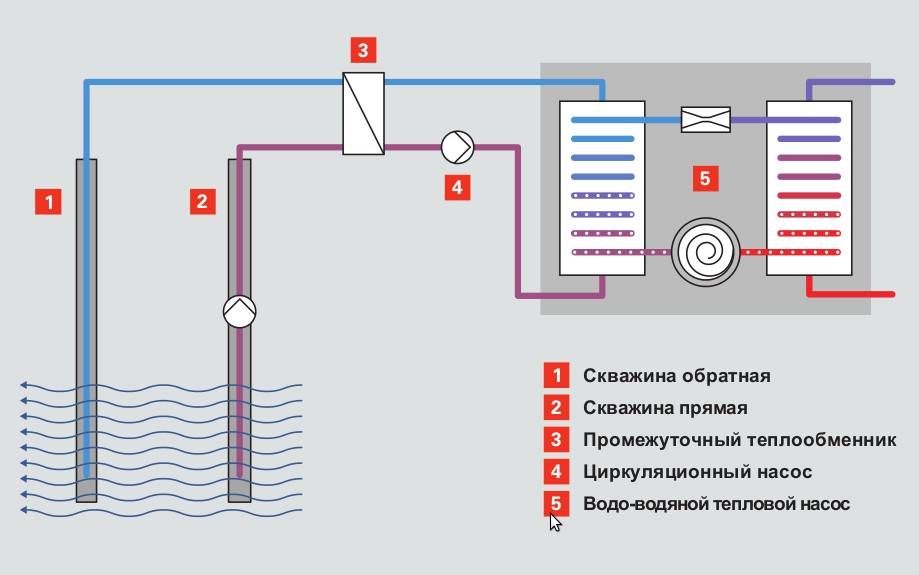
A pond is a source of a large amount of heat. For the pump, you can use non-freezing reservoirs from 3 meters deep or groundwater at a high level. The system can be implemented as follows: the heat exchanger pipe, weighed down with a load at the rate of 5 kg per 1 linear meter, is laid on the bottom of the reservoir. The length of the pipe depends on the footage of the house. For a room of 100 sq.m. the optimal length of the pipe is 300 meters.
In the case of using groundwater, it is necessary to drill two wells located one after the other in the direction of groundwater. A pump is placed in the first well, supplying water to the heat exchanger. Chilled water enters the second well. This is the so-called open heat collection scheme. Its main disadvantage is that the groundwater level is unstable and can change significantly.
Air is the most accessible source of heat
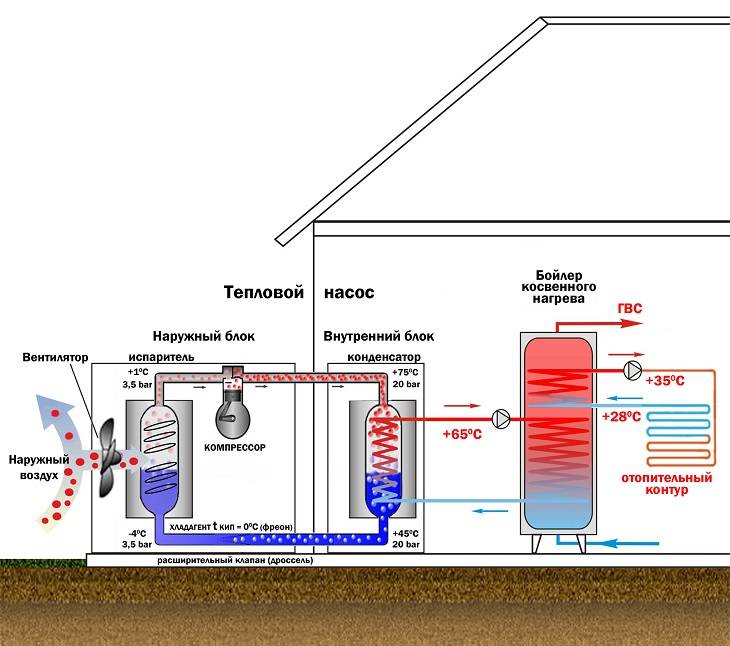
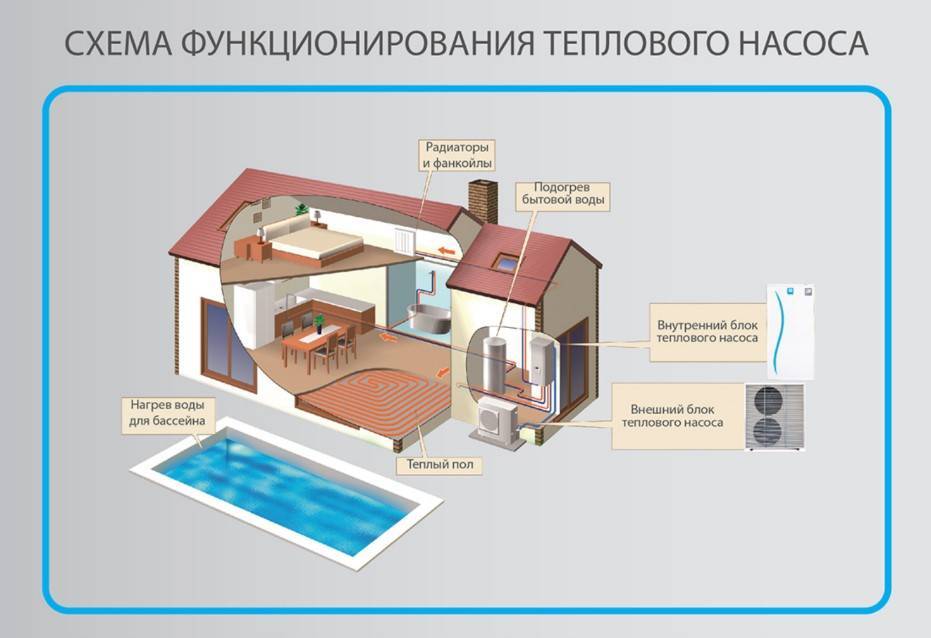
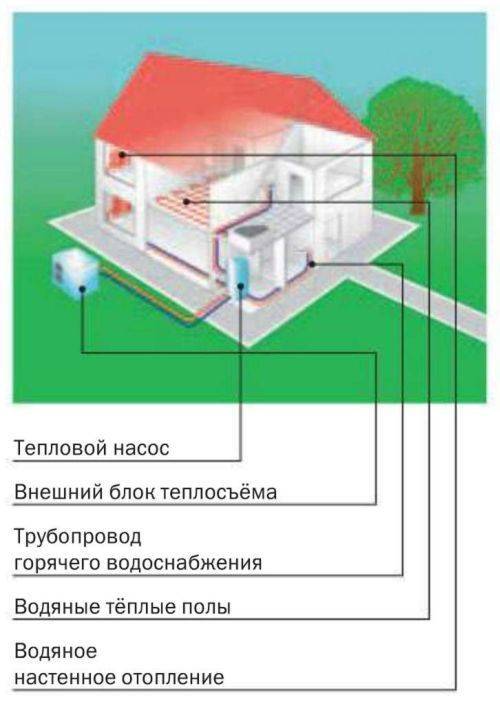
In the case of using air as a heat source, the heat exchanger is a radiator forcedly blown by a fan. If a heat pump works for heating a house using an air-to-water system, the user benefits from:
- Possibility to heat the whole house. Water, acting as a heat carrier, is diluted through heating devices.
- With minimal electricity consumption - the ability to provide residents with hot water. This is possible due to the presence of an additional heat-insulated heat exchanger with storage capacity.
- Pumps of a similar type can be used to heat water in swimming pools.
Scheme of heating a house with an air source heat pump.
If the pump operates on an air-to-air system, no heat carrier is used to heat the space. Heating is produced by the received thermal energy. An example of the implementation of such a scheme is a conventional air conditioner set to heating mode. Today, all devices that use air as a heat source are inverter-based. They convert alternating current to direct current, providing flexible control of the compressor and its operation without stopping. And this increases the resource of the device.
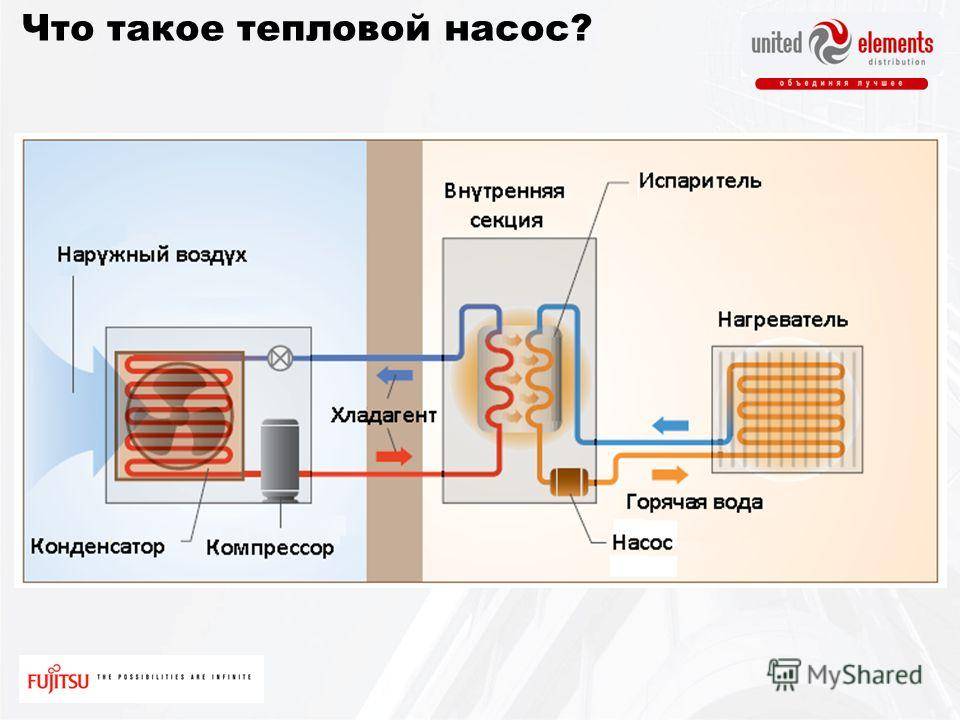
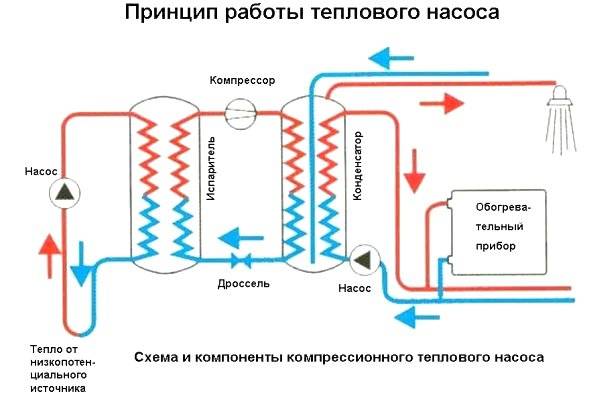
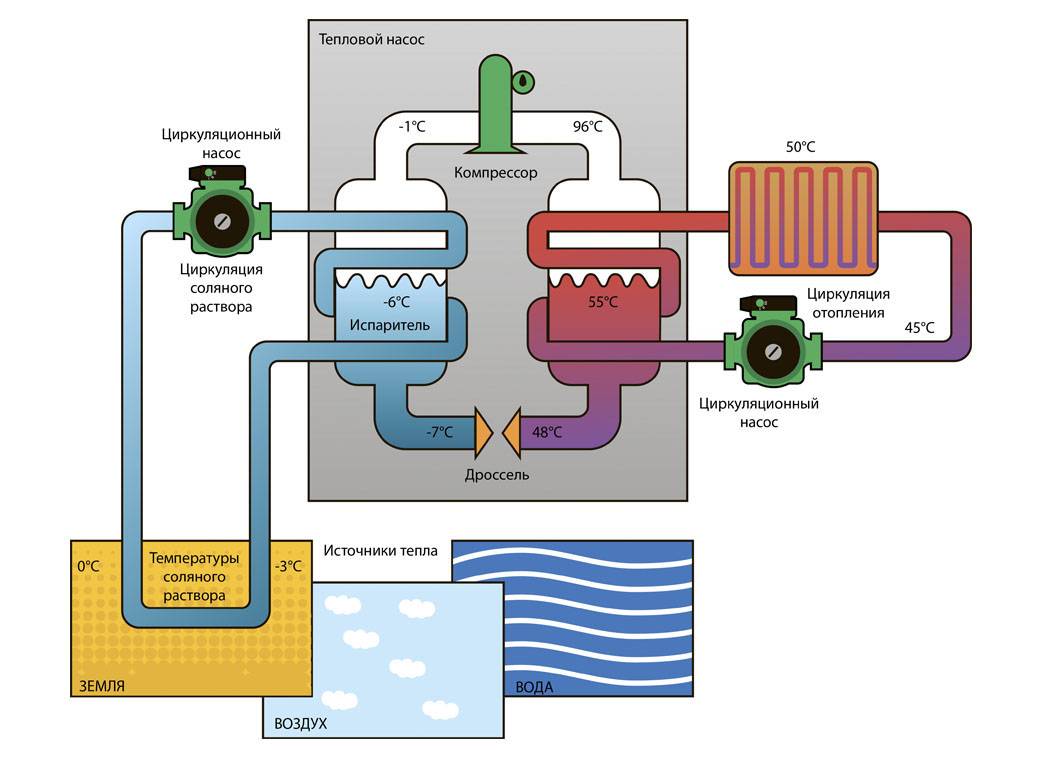
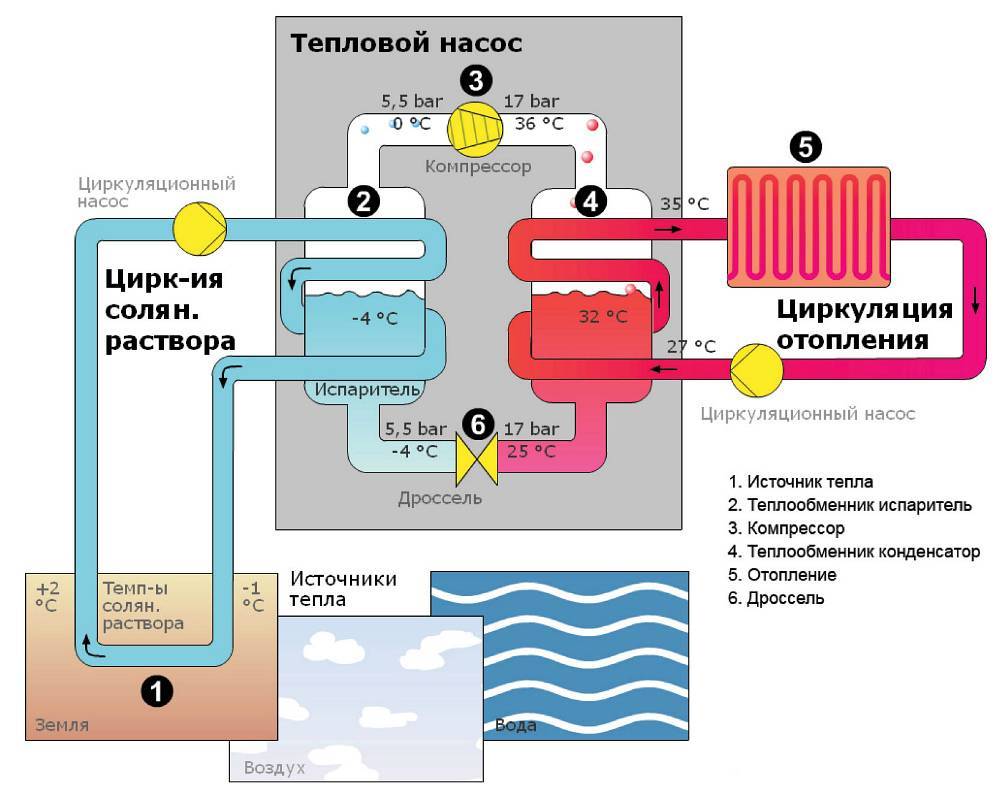
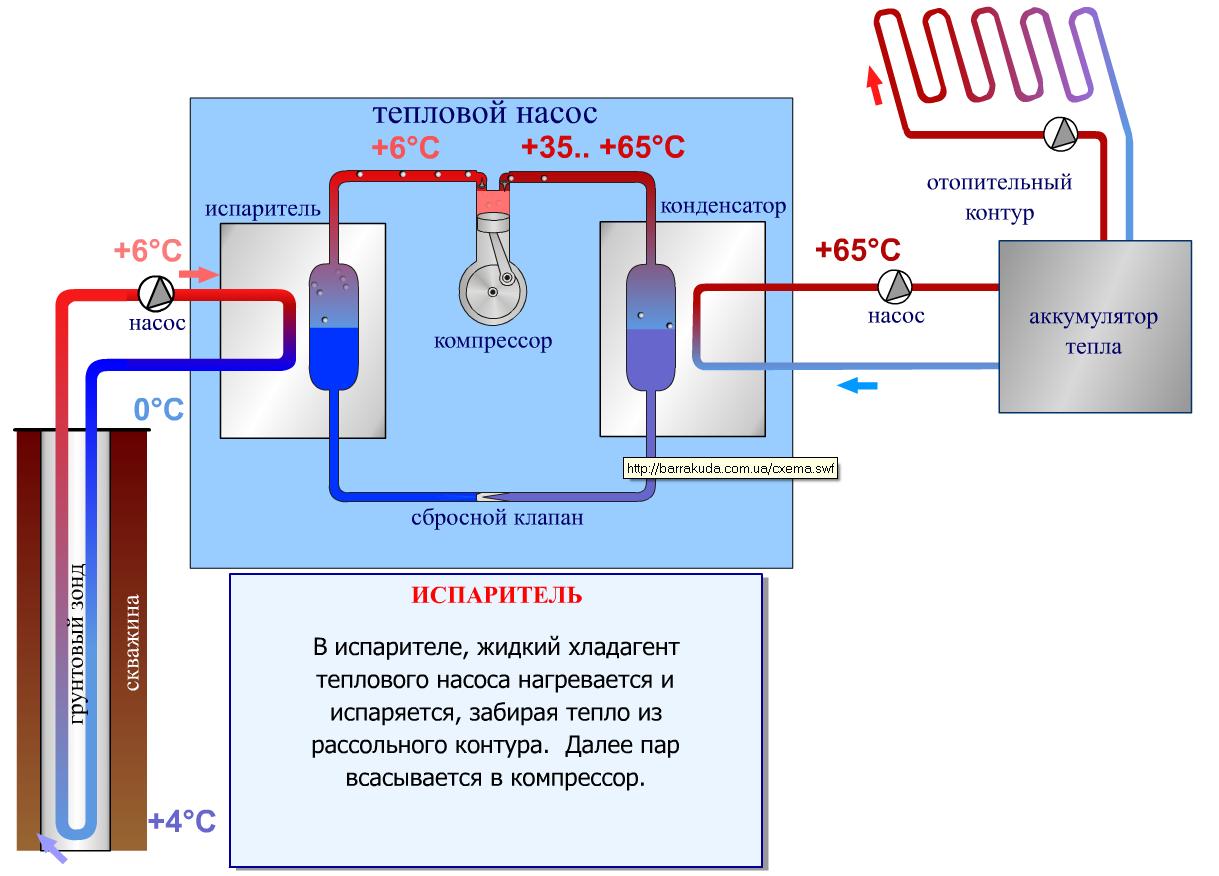
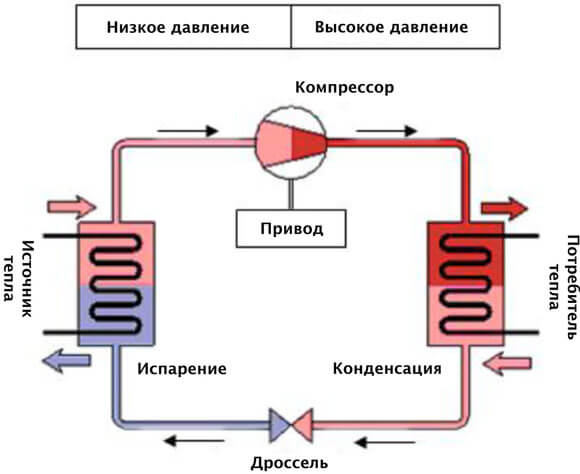
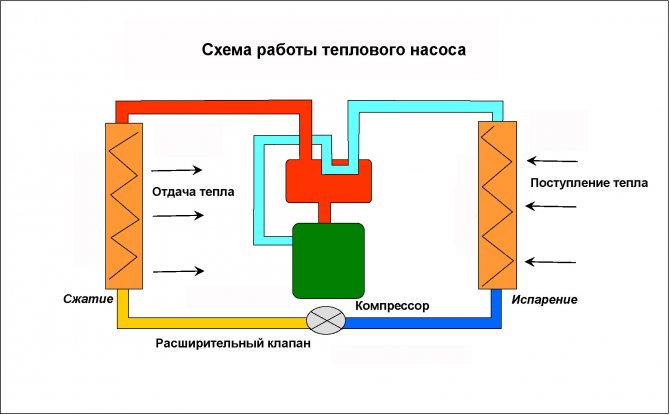
How heat pumps work
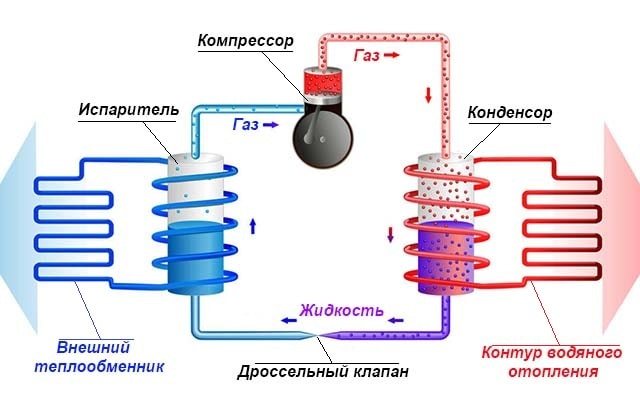
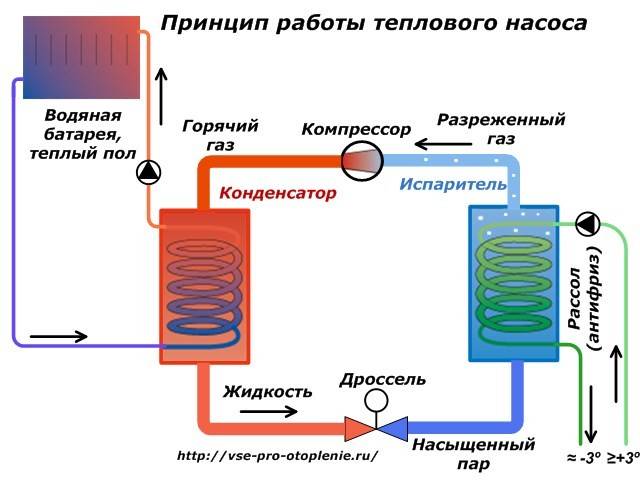
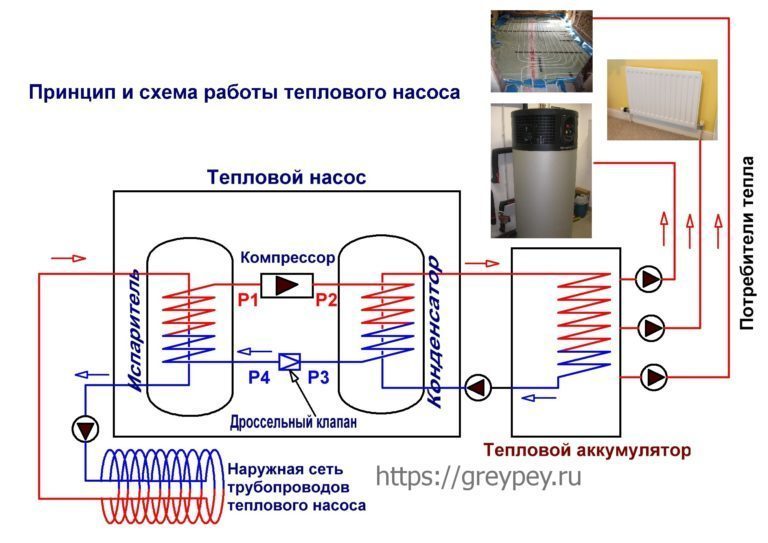
In any HP there is a working medium called a refrigerant. Usually freon acts in this capacity, less often - ammonia. The device itself consists of only three components:
- evaporator;
- compressor;
- capacitor.
The evaporator and condenser are two reservoirs that look like long curved tubes - coils. The condenser is connected at one end to the compressor outlet, and the evaporator to the inlet. The ends of the coils are joined and a pressure reducing valve is installed at the junction between them. The evaporator is in contact - directly or indirectly - with the source medium, while the condenser is in contact with the heating or DHW system.
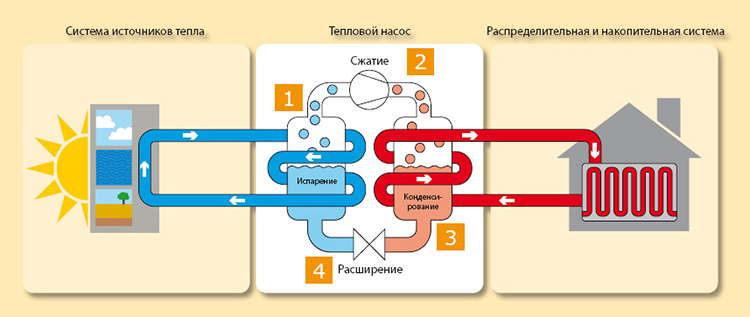
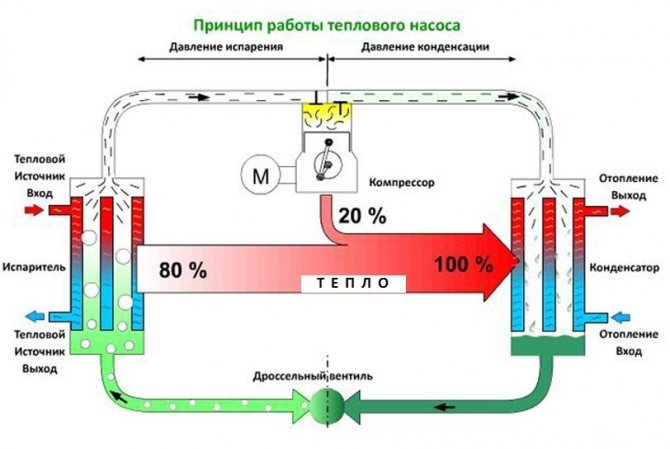
How a heat pump works
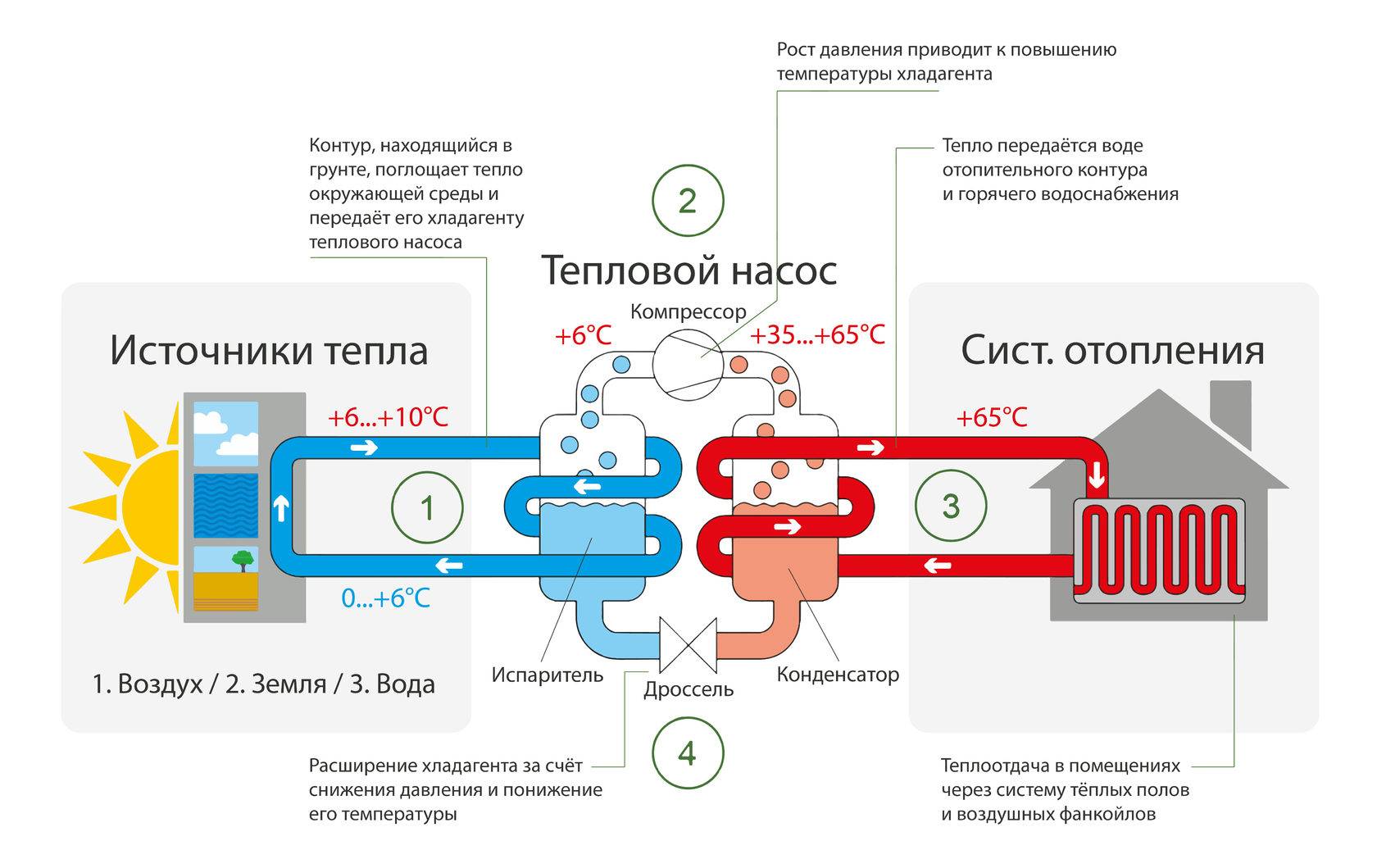
The operation of the HP is based on the interdependence of the volume, pressure and temperature of the gas. Here is what happens inside the aggregate:
- Ammonia, freon or other refrigerant, moving through the evaporator, heats up from the source medium, for example, to a temperature of +5 degrees.
- After passing the evaporator, the gas reaches the compressor, which pumps it into the condenser.
- The refrigerant pumped by the compressor is held in the condenser by a pressure reducing valve, so its pressure is higher here than in the evaporator.As you know, with increasing pressure, the temperature of any gas increases. This is exactly what happens to the refrigerant - it heats up to 60 - 70 degrees. Since the condenser is washed by the coolant circulating in the heating system, the latter is also heated.
- Through the pressure reducing valve, the refrigerant is discharged in small portions into the evaporator, where its pressure drops again. The gas expands and cools, and since part of the internal energy was lost by it as a result of heat transfer at the previous stage, its temperature drops below the initial +5 degrees. Following the evaporator, it heats up again, then it is pumped into the condenser by the compressor - and so on in a circle. Scientifically, this process is called the Carnot cycle.
The main feature of HP is that thermal energy is taken from the environment literally for nothing. True, for its production it is necessary to spend a certain amount of electricity (for the compressor and the circulation pump / fan).
But HP still remains very profitable: for each kWh of electricity spent, it is possible to obtain from 3 to 5 kWh of heat.
Electric heater installation
Installation of such a device is not particularly difficult. It is quite possible to do it with your own hands.
If we are dealing with a wall-mounted device, then to install it, it will be necessary to drill holes in the wall for dowels.
Drilling holes in the wall
The floor boiler is usually placed on stands. After that, it must be connected to the heating system using couplings and adapters.
Electric boiler connection diagram
Having finished this work, it is necessary to draw water into the system and turn on the device. If the pipes began to heat up, then everything was done correctly. You can watch a more detailed description of the installation process in the video that is on our website.
We hope that the above arguments have convinced you that electric heating can be a very appropriate and convenient option for heating a summer house. And you can verify this on your own experience by installing an electric boiler.
Characteristics and principle of operation
In a simplified form, the pump device is very similar to the design of an air conditioner, only on a larger scale. It does not require a fuel boiler. The essence of the work - the pump transfers heat from a source with a small charge of energy to a coolant, which is characterized by an elevated temperature.
In reality, a polypropylene system works like this:
- The heat carrier is transported to a pipe hidden in the soil or elsewhere, and its temperature becomes higher.
- The coolant is transferred to the heat exchanger and transports energy to the circuit.
- There is a refrigerant in the outer casing - this is a material with a minimum boiling point with low pressure. In the evaporator, the temperature of the refrigerant rises significantly and it is converted into a gas.

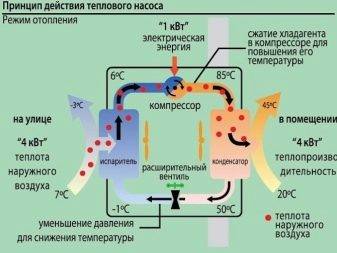
- The gas circulates in the compressor, and under the influence of increased pressure, it is compressed and heated.
- The combustible gas is transferred to the condenser, where the energy enters the heat carrier of the internal heating system.
- As a result, the refrigerant, whose temperature is reduced, enters again in a liquid state.

Refrigeration structures work according to a similar scheme, so some types of systems in the summer can be safely operated as air conditioners.
The design of volatile heating devices has 3 main components:
- Compressor. Designed to raise the temperature of vapors and pressure, which are formed due to the boiling of the refrigerant. Today, scroll compressors that can be operated in frost are popular. Elements of this type operate quietly, they are compact and light in weight.
- Evaporator. In it, the liquid refrigerant is converted into vapor, after which it is transported towards the compressor.
- Capacitor. It is used to transfer energy to the circuit of heating equipment.

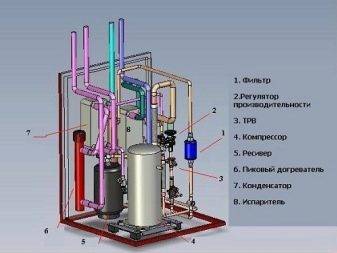
For the operation of the pump, you need to connect to the mains, but the performance and power of this equipment is much higher than that of an electric heater, and the electricity consumption is less. The heating coefficient depends on the type of equipment.
Air-to-water heat pump for home
A feature of air-to-water systems is the strong dependence of the temperatures of the coolant in the heating system on the temperature of the source - the outside air. The efficiency of such equipment is constantly changing both seasonally and in weather conditions. This shows a significant difference between aerothermal systems and geothermal complexes, whose operation is stable throughout the entire service life and does not depend on external conditions.
In addition, air-to-water heat pumps are capable of both heating and cooling indoor air, which makes them in demand in regions with relatively cold winters and hot summers. In general, the use of such systems is most effective in relatively warm areas, and for the northern regions, additional means of heating are required (usually electric heaters are used).
How do air-to-water heat pumps work?
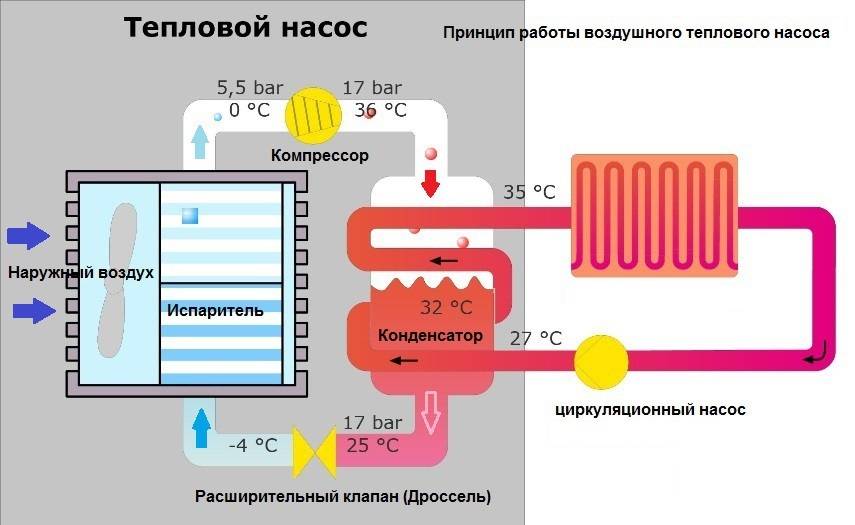
The air-to-water heat pump is based on the Carnot principle. In a more understandable language, the design of a freon refrigerator is used. The refrigerant (freon) circulates in a closed system, passing successively through the stages:
- evaporation accompanied by strong cooling
- heating from the heat of the incoming outside air
- strong compression, at which its temperature becomes high
- liquid condensation
- passage through the throttle with a sharp drop in pressure and evaporation
For normal circulation of the refrigerant, it is necessary to have two compartments - an evaporator and a condenser. In the first, the temperature is low (negative); thermal energy from the ambient air is used for heating. The second compartment is used to condense the refrigerant and transfer thermal energy to the heat carrier of the heating system.
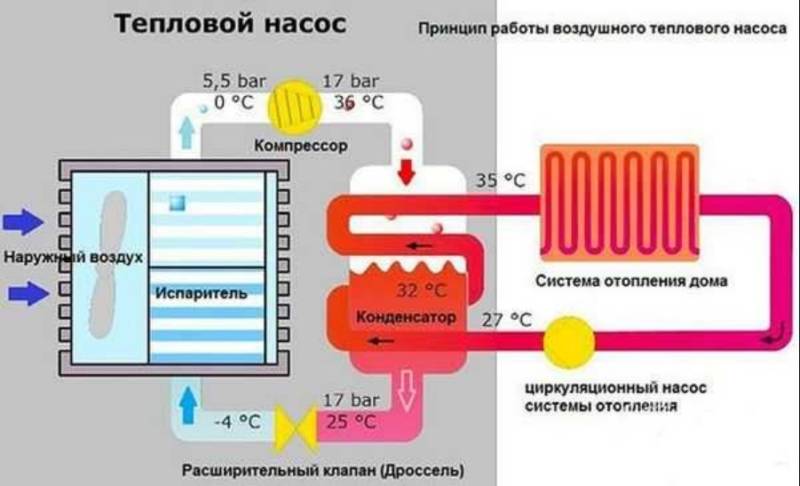
The role of the incoming air is to transfer heat to the evaporator, where the temperature is very low and needs to be increased for the upcoming compression. The thermal energy of the air is available even at negative temperatures and is stored until the temperature drops to absolute zero. Low-potential sources of thermal energy allow to obtain high efficiency of the system, but when the outdoor temperature drops to -20°C or -25°C, the system stops and requires the connection of an additional heating source.
Advantages and disadvantages
The advantages of air-to-water heat pumps are:
- easy installation, no excavation
- The source of thermal energy - air - is available everywhere, it is available and completely free.The system requires only power supply for the circulation equipment, compressor and fan
- the heat pump can be structurally combined with ventilation, which will significantly increase the efficiency of both systems
- the heating system is environmentally friendly and operationally safe
- the operation of the system is almost silent, it can be controlled by automation systems
The disadvantages of an air-to-water heat pump are:
- limited application. Household models of HP require connection of additional heating systems already at -7°C, industrial designs are able to keep temperatures down to -25°C, which is too low for most regions of Russia
- the dependence of the system efficiency on the outdoor temperature makes the system unstable and requires constant reconfiguration of the operating modes
- fans, compressors and other devices require a stable power supply
When planning the use of such a heating and hot water system, these features must be taken into account.
Installation capacity calculation
The procedure for calculating the power of the installation is reduced to determining the area of \u200b\u200bthe house to be heated, calculating the required amount of thermal energy and selecting equipment that corresponds to the values obtained. It makes no sense to present a detailed calculation methodology, since it is extremely complex and requires knowledge of many parameters, coefficients and other values. In addition, experience in performing such calculations is needed, otherwise the result will be completely erroneous.
To solve the problem, it is recommended to use an online calculator found on the net. Using it is easy, you just need to substitute your data in the windows and get an answer. If in doubt, the calculation can be duplicated on another resource in order to obtain balanced data.
Advantages and disadvantages of technology
The most important advantages of TN are:
- Profitability: for every kilowatt of electricity consumed, the HP produces from 3 to 5 kW of heat. That is, we are talking about almost gratuitous heating.
- Environmental friendliness and safety: the operation of HP is not associated with the formation and release into the atmosphere of any environmentally hazardous substances, and the absence of a flame makes this technology absolutely safe.
- Ease of operation: unlike gas and solid fuel boilers, HP does not need to be cleaned of soot and soot. You also do not have to build and maintain a chimney.
A significant drawback of this technology is the high cost of equipment and installation work.
Let's do a simple calculation. For a 120 sq. m will need a HP with a capacity of 120x0.1 = 12 kW (at the rate of 100 W per 1 sq. M). The Diplomat model from Thermia with this performance costs about 6.8 thousand euros. The DUO model of the same manufacturer will cost a little less, but its cost cannot be called democratic either: about 5.9 thousand euros.

Heat pump Thermia Diplomat
Even when compared with the most expensive type of traditional heating - electric (4 rubles per 1 kWh, 3 months - work at full load, 3 months - with half), the payback will take more than 4 years, and this is without taking into account the cost installation of the outer circuit.In reality, the HP does not always work with the calculated performance, respectively, and the payback period may be longer.
Environmental friendliness and safety ↑
For those who care about the environmental safety of their homes, a heat pump can be an ideal option for a comfortable heating system, the principle of operation of which does not provide for the emission of such harmful compounds as CO, CO2, SO2, PbO2, NOx into the atmosphere.
As for the possibility of an explosion or a fire, then, with normal insulation of electrical wires, it does not exist. Which, unfortunately, cannot be said about boilers for liquid fuel or natural gas. The heat pump system is designed in such a way that overheating of its parts sufficient to cause an explosion or ignition is impossible.
What is a heat pump and how does it work?
The term heat pump refers to a set of specific equipment. The main function of this equipment is the collection of thermal energy and its transportation to the consumer. The source of such energy can be any body or medium with a temperature of +1º and more degrees.
There are more than enough sources of low-temperature heat in our environment. These are industrial waste from enterprises, thermal and nuclear power plants, sewage, etc. For the operation of heat pumps in the field of home heating, three independently recovering natural sources are needed - air, water, earth.
Heat pumps “draw” energy from processes that regularly occur in the environment. The flow of processes never stops, therefore the sources are recognized as inexhaustible according to human criteria.
The three listed potential energy suppliers are directly related to the energy of the sun, which, by heating, sets the air and wind in motion and transfers thermal energy to the earth. It is the choice of source that is the main criterion according to which heat pump systems are classified.
The principle of operation of heat pumps is based on the ability of bodies or media to transfer thermal energy to another body or environment. Recipients and suppliers of energy in heat pump systems usually work in pairs.
So there are the following types of heat pumps:
- Air is water.
- Earth is water.
- Water is air.
- Water is water.
- Earth is air.
- Water - water
- Air is air.
In this case, the first word defines the type of medium from which the system takes low-temperature heat. The second indicates the type of carrier to which this thermal energy is transferred. So, in heat pumps water is water, heat is taken from the aquatic environment and liquid is used as a heat carrier.
Heat pumps by design type are vapor compression plants. They extract heat from natural sources, process and transport it to consumers (+)
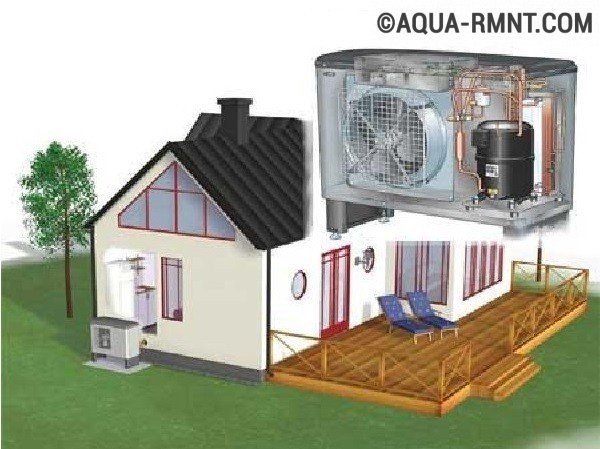
Modern heat pumps use three main sources of heat energy. These are soil, water and air. The simplest of these options is an air source heat pump. The popularity of such systems is associated with their rather simple design and ease of installation.
However, despite such popularity, these varieties have a rather low productivity. In addition, the efficiency is unstable and dependent on seasonal temperature fluctuations.
With a decrease in temperature, their performance drops significantly.Such variants of heat pumps can be considered as an addition to the existing main source of thermal energy.
Equipment options that use ground heat are considered more efficient. The soil receives and accumulates thermal energy not only from the Sun, it is constantly heated by the energy of the earth's core.
That is, the soil is a kind of heat accumulator, the power of which is practically unlimited. Moreover, the temperature of the soil, especially at a certain depth, is constant and fluctuates within insignificant limits.
Scope of energy generated by heat pumps:
The constancy of the source temperature is an important factor in the stable and efficient operation of this type of power equipment. Systems in which the aquatic environment is the main source of thermal energy have similar characteristics. The collector of such pumps is located either in the well, where it is in the aquifer, or in the reservoir.
The average annual temperature of sources such as soil and water varies from +7º to + 12º C. This temperature is quite enough to ensure the efficient operation of the system.
The most efficient are heat pumps that extract heat energy from sources with stable temperature indicators, i.e. from water and soil