- Pros and cons
- Calorific value of solid materials
- Features of different types of wood
- The influence of age on the properties of coal
- Characteristics of pellets and briquettes
- Production process technology
- Raw material selection
- GOST 24260-80 Raw wood for pyrolysis and charcoal burning. Specifications
- Drying wood
- Pyrolysis
- Calcination
- Characteristics and properties of wood
- Briquettes.
- Heat recovery factor
- Harmful impurities in wood
- What is the moisture content of wood, what does it affect?
- Brown coal
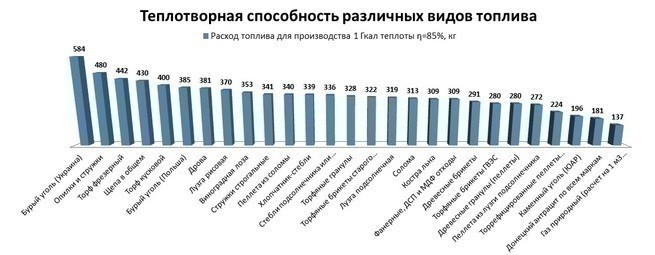
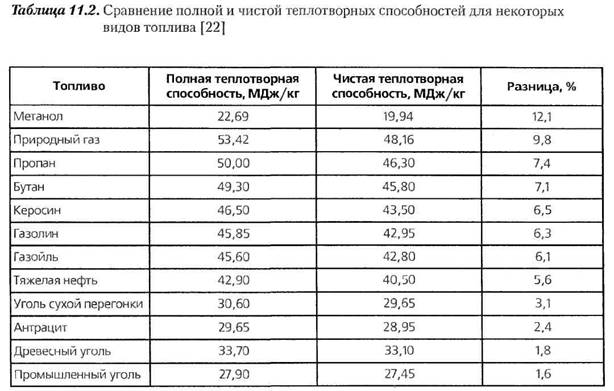
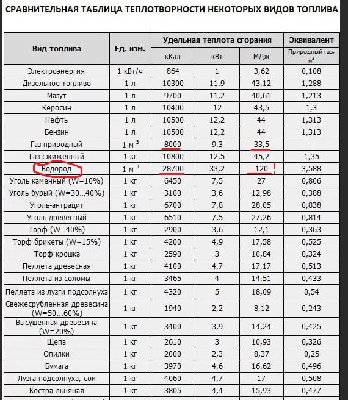
- Calorific value tables
- Firewood
- How to prepare firewood
- How to saw and chop wood
- wood properties
- Home heating in the mirror of numbers
- Comparative characteristics of various types of fuel
- Natural gas
- Coal or firewood
- Diesel fuel
- Electricity
- Creating optimal conditions for combustion
Pros and cons
Actually, we have already mentioned all the advantages and disadvantages of liquid fuel boilers, but just in case, we repeat them:
Pros:
- High degree of automation, the ability to create maximum thermal comfort.
- Complete autonomy from other energy sources (in addition to electricity, but the needs for it are small, you can get by with a generator)
Minuses:
- High operating costs.
- The need to have a capacious fuel storage, to prevent freezing of it and pipelines.
- Fan burners are quite noisy, their work is clearly audible through the wall.
- ZHTSW should be located in a separate room with good ventilation, preferably not connected with living quarters in any way - the "aroma" of diesel fuel is indestructible.

A modern oil-fired boiler room is a clean room, you will not see puddles of “solarium” on the floor in it. But the specific smell of fuel still seeps through
So, who will install ZHTS in his house? Firstly, those who do not have and are not expected to lay a gas pipeline in the near future. Secondly, a person is not poor, who prefers to pay more money, but to get comfortable living conditions. Thirdly, the one in whose house there are no electrical capacities sufficient for organizing alternative heating, and he is not satisfied with heating with firewood.
In conclusion, let's say that liquid fuel boilers are a rather complicated technique that requires professional maintenance. Therefore, installation, connection and service work must be carried out by qualified personnel.
Calorific value of solid materials
This category includes wood, peat, coke, oil shale, briquettes and pulverized fuels. The main constituent of solid fuels is carbon.
Features of different types of wood
The maximum efficiency from the use of firewood is achieved under the condition that two conditions are met - the dryness of the wood and the slow burning process.

Pieces of wood are sawn or chopped into segments up to 25-30 cm long so that the firewood is conveniently loaded into the firebox
Oak, birch, ash bars are considered ideal for wood-burning stove heating.Good performance is characterized by hawthorn, hazel. But in conifers, the calorific value is low, but the burning rate is high.
How different breeds burn:
- Beech, birch, ash, hazel are difficult to melt, but they can burn raw due to their low moisture content.
- Alder and aspen do not form soot and "know how" to remove it from the chimney.
- Birch requires a sufficient amount of air in the furnace, otherwise it will smoke and settle with resin on the walls of the pipe.
- Pine contains more resin than spruce, so it sparkles and burns hotter.
- Pear and apple tree splits more easily than others and burns perfectly.
- The cedar gradually turns into a smoldering coal.
- Cherry and elm smoke, and sycamore is difficult to split.
- Linden and poplar burn quickly.
The TCT values of different breeds are highly dependent on the density of specific breeds. 1 cubic meter of firewood is equivalent to approximately 200 liters of liquid fuel and 200 m3 of natural gas. Wood and firewood are in the low energy efficiency category.
The influence of age on the properties of coal
Coal is a natural material of plant origin. It is mined from sedimentary rocks. This fuel contains carbon and other chemical elements.
In addition to the type, the calorific value of coal is also influenced by the age of the material. Brown belongs to the young category, followed by stone, and anthracite is considered the oldest.

Moisture is also determined by the age of the fuel: the younger the coal, the greater the moisture content in it. Which also affects the properties of this type of fuel
The process of burning coal is accompanied by the release of substances that pollute the environment, while the grate of the boiler is covered with slag. Another unfavorable factor for the atmosphere is the presence of sulfur in the composition of the fuel.This element in contact with air is transformed into sulfuric acid.
Manufacturers manage to reduce the sulfur content in coal as much as possible. As a result, TST differs even within the same species. Affects the performance and geography of production. As a solid fuel, not only pure coal, but also briquetted slag can be used.
The highest fuel capacity is observed in coking coal. Stone, wood, brown coal, anthracite also have good characteristics.
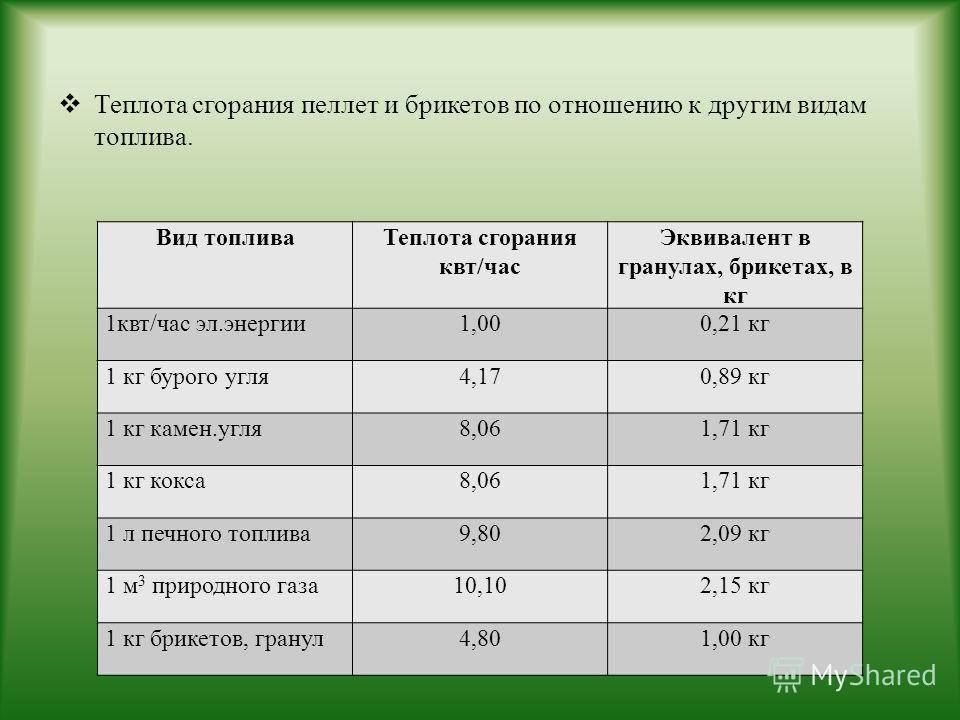
Characteristics of pellets and briquettes
This solid fuel is manufactured industrially from various wood and vegetable waste.
Shredded shavings, bark, cardboard, straw are dried and turned into granules with the help of special equipment. In order for the mass to acquire a certain degree of viscosity, a polymer, lignin, is added to it.

Pellets are distinguished by an acceptable cost, which is influenced by high demand and features of the manufacturing process. This material can only be used in boilers designed for this type of fuel.
Briquettes differ only in shape, they can be loaded into furnaces, boilers. Both types of fuel are divided into types according to raw materials: from round timber, peat, sunflower, straw.
Pellets and briquettes have significant advantages over other types of fuel:
- complete environmental friendliness;
- the ability to store in almost any conditions;
- resistance to mechanical stress and fungus;
- uniform and long burning;
- optimal size of pellets for loading into the heating device.
Eco-friendly fuel is a good alternative to traditional heat sources, which are not renewable and adversely affect the environment.But pellets and briquettes are characterized by an increased fire hazard, which should be taken into account when organizing a storage place.
If desired, you can arrange production of fuel briquettes personally, in more detail - in this article.
Production process technology
In ancient times, people used charcoal technology to make coal fuel. They placed firewood in special pits and covered them with earth, leaving small holes. After the industrial revolution, the procedure for burning charcoal began to be carried out using automated equipment capable of controlling the reactions of carbonization of substances and heating the material to the combustion temperature.
In industrial conditions, this material is produced in small quantities. Before you can produce charcoal, you need to choose the right raw materials, purchase specialized equipment and determine the manufacturing technology. The industry uses 3 main methods for the production of charcoal:
- drying;
- pyrolysis;
- calcination.
The received production is packed up in bags, briquetted and marked. GOST 7657-84 describes how charcoal is made in production. It describes the flow charts and provides precise information on the amount of temperature required to heat the raw material.
Charcoal can be produced at home, forming a handicraft industry. Most often, a personal plot is chosen as a place for the manufacture of this raw material. Before making charcoal, you need to equip the premises in accordance with safety rules, choose a manufacturing technology and evaluate the prospects for the development of a business project.
Raw material selection
According to GOST 24260-80 “Raw materials for pyrolysis and charcoal burning”, the production of charcoal requires wood from hardwood trees. This group includes birch, ash, beech, maple, elm and oak. Coniferous trees are also used in the manufacture: spruce, pine, fir, larch and cedar. Soft-leaved woods are used to a lesser extent: pear, apple, plum and poplar.
GOST 24260-80 Raw wood for pyrolysis and charcoal burning. Specifications
1 file 457.67 KB Raw materials must have the following dimensions: thickness - up to 18 cm, length - up to 125 cm. There should not be a large amount of sap rot on the wood (up to 3% of the total area of the blanks). Its presence reduces the hardness of the material and increases its ash content. Large amounts of water are not allowed. This substance leads to the appearance of cracks on the surface of the workpieces.
Drying wood
During the drying process, the raw materials are placed in a charcoal block. Wood is affected by flue gas. As a result of heat treatment, the temperature of the blanks rises to 160 °C. The amount of water contained in the wood affects the duration of the process. As a result of drying, a material with a moisture level of 4-5% is obtained.

Pyrolysis
Pyrolysis is a chemical reaction of decomposition, which consists in heating a substance with a lack of oxygen. During combustion, dry distillation of wood occurs. The blanks are heated up to 300 °C. During pyrolysis, H2O is removed from the raw material, which leads to carbonization of the material. With further heat treatment, the wood is converted into fuel, the percentage of carbon is 75%.
Calcination
After completion of pyrolysis, the product is subjected to calcination. This procedure is necessary to separate resins and unnecessary gases. The calcination takes place at a temperature of 550 °C. After that, the substance is cooled to 80 °C. Refrigeration is necessary to prevent spontaneous combustion of the product in contact with oxygen.
Characteristics and properties of wood
Currently, there is a trend of transition from installations based on the process of gas combustion to solid fuel domestic heating systems.
Not everyone knows that the creation of a comfortable microclimate in the house directly depends on the quality of the selected fuel. As a traditional material used in such heating boilers, we single out wood.
In harsh climatic conditions, characterized by long and cold winters, it is quite difficult to heat a dwelling with wood for the entire heating season. With a sharp drop in air temperature, the owner of the boiler is forced to use it on the verge of maximum capabilities.
When choosing wood as a solid fuel, serious problems and inconveniences arise. First of all, we note that the combustion temperature of coal is much higher than that of wood. Among the shortcomings is the high rate of combustion of firewood, which creates serious difficulties in the operation of the heating boiler. Its owner is forced to constantly monitor the availability of firewood in the furnace; a sufficiently large amount of them will be required for the heating season.

Briquettes.
Briquettes are a solid fuel formed in the process of compressing waste from the woodworking process (chips, chips, wood dust), as well as household waste (straw, husks), peat.
Solid fuel: briquettes
Fuel briquettes are convenient for storage, harmful binders are not used in the manufacture, therefore this type of fuel is environmentally friendly. When burning, they do not spark, do not emit fumes, they burn evenly and smoothly, which ensures a sufficiently long combustion process in the boiler chamber. In addition to solid fuel boilers, they are used in home fireplaces and for cooking (on the grill, for example).
There are 3 main types of briquettes:
- RUF briquettes. Formed "bricks" of a rectangular shape.
- NESTRO briquettes. Cylindrical, can also be with holes inside (rings).
- Pini&Kay briquettes. Faceted briquettes (4,6,8 facets).
Heat recovery factor
The heat recovery coefficient is the ratio of the amount of heat received by the waste heat boiler to the heat of the fuel burned in the furnace.
The heat recovery coefficient of modern gas boilers with a closed combustion chamber, with a gas and air supply regulated by a processor, exceeds 99%.
The heat recovery coefficient of all atmospheric boilers does not exceed 90% due to the fact that during the combustion process in atmospheric boilers, part of the warm air that is taken from the room is not used, is heated in the furnace by the energy released by the fuel to a temperature exceeding 100 ° and is thrown into the chimney .
The heat recovery coefficient of solid fuel boilers does not exceed 80% due to the high temperature in the reactor (furnace) and the complexity of its regulation.
Thus, the utilization factor of the calorific value of gaseous fuel in modern boilers with a closed combustion chamber reaches 98%, and is calculated from the gross calorific value (if a condensing type boiler is used).Liquid fuel is used by no more than 77%, and solid fuel by only 68%.
Harmful impurities in wood
During the chemical combustion reaction, the wood does not burn completely. After combustion, ash remains - that is, the unburned part of the wood, and during the combustion process, moisture evaporates from the wood.
Ash has less effect on the quality of combustion and the calorific value of firewood. Its amount in any wood is the same and is about 1 percent.
But the moisture in the wood can cause a lot of problems when burning them. So, immediately after felling, wood can contain up to 50 percent moisture. Accordingly, when burning such firewood, the lion's share of the energy released with the flame can simply be spent on the evaporation of the wood moisture itself, without doing any useful work.
calorific value calculation
The moisture present in wood dramatically reduces the calorific value of any firewood. Burning firewood not only does not fulfill its function, but also becomes unable to maintain the required temperature during combustion. At the same time, the organic matter in the firewood does not burn out completely; when such firewood burns, a suspended amount of smoke is released, which pollutes both the chimney and the furnace space.
What is the moisture content of wood, what does it affect?
The physical quantity that describes the relative amount of water contained in wood is called moisture content. The moisture content of the wood is measured as a percentage.
When measuring, two types of humidity can be taken into account:
- Absolute humidity is the amount of moisture present in wood relative to a completely dried wood. Such measurements are usually carried out for construction purposes.
- Relative humidity is the amount of moisture that wood currently contains relative to its own weight. Such calculations are made for wood used as fuel.
So, if it is written that wood has a relative humidity of 60%, then its absolute humidity will be expressed as 150%.
To calculate the calorific value of firewood at a known moisture content, you can use the following formula:
Analyzing this formula, it can be established that firewood harvested from coniferous wood with a relative humidity index of 12 percent will release 3940 kilocalories when burning 1 kilogram, and firewood harvested from hardwood with comparable humidity will already release 3852 kilocalories.
To understand what a relative humidity of 12 percent is, let's explain that such humidity is acquired by firewood, which is dried for a long time on the street.
Brown coal
Brown coal is the youngest hard rock, which was formed about 50 million years ago from peat or lignite. At its core, it is "immature" coal.
This mineral got its name because of the color - shades vary from brown-red to black. Brown coal is considered to be a fuel with a low degree of coalification (metamorphism). It contains from 50% carbon, but also a lot of volatile substances, mineral impurities and moisture, so it burns much easier and gives more smoke and a burning smell.
Depending on the humidity, brown coal is divided into grades 1B (moisture more than 40%), 2B (30-40%) and 3B (up to 30%). The yield of volatile substances in brown coals is up to 50%.

With prolonged contact with air, brown coal tends to lose structure and crack. Among all types of coal, it is considered the most low-quality fuel, since it emits much less heat: the calorific value is only 4000 - 5500 kcal / kg.
Brown coal occurs at shallow depths (up to 1 km), so it is much easier and cheaper to mine. However, in Russia, as a fuel, it is used much less frequently than coal. Due to the low cost, brown coal is still preferred by some small and private boiler houses and thermal power plants.
In Russia, the largest deposits of brown coal are located in the Kansk-Achinsk basin (Krasnoyarsk Territory). In general, the site has reserves of almost 640 billion tons (about 140 billion tons are suitable for open pit mining).
It is rich in brown coal reserves and the only coal deposit in Altai is Soltonskoye. Its predicted reserves are 250 million tons.
About 2 trillion tons of brown coal is hidden in the Lena coal basin, located on the territory of Yakutia and the Krasnoyarsk Territory. In addition, this type of mineral often occurs together with coal - for example, it is also obtained at the deposits of the Minusinsk and Kuznetsk coal basins.
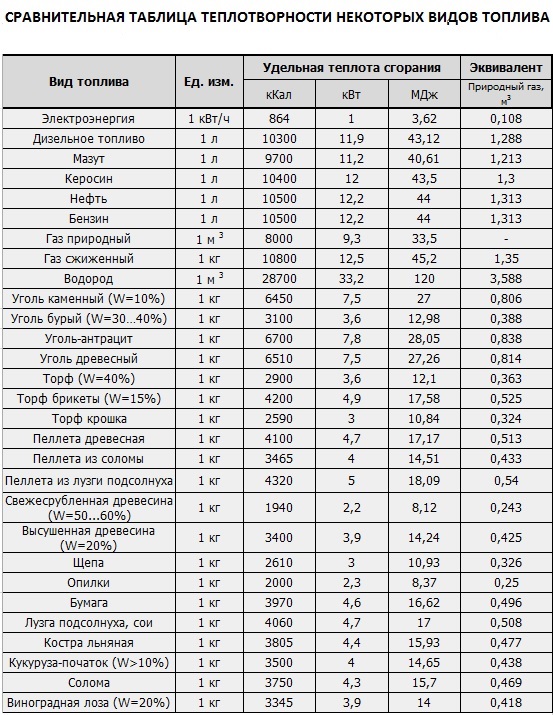
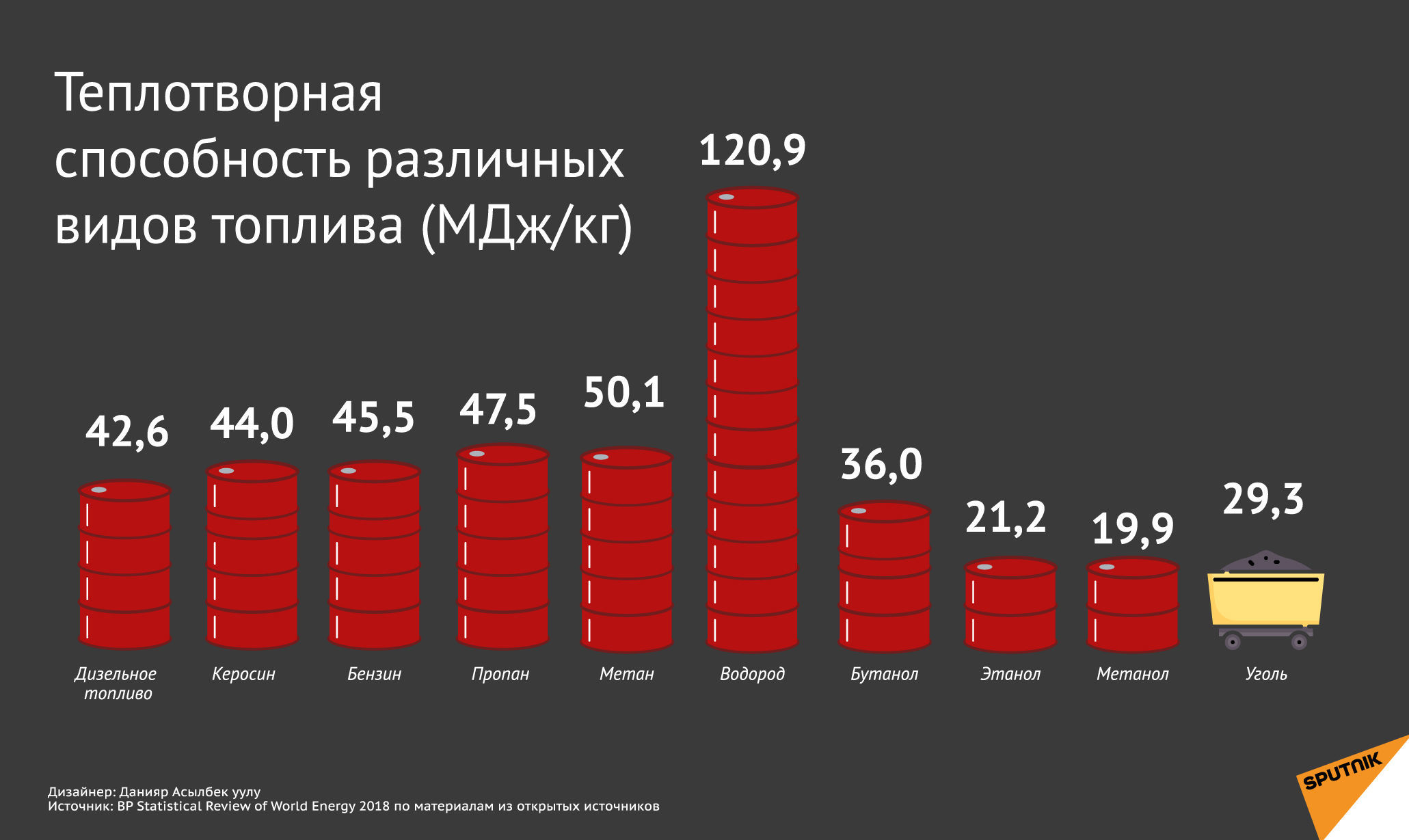
Calorific value tables
| Fuel | HHV MJ/kg | HHV Btu/lb | HHV kJ/mol | LHV MJ/kg |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen | 141,80 | 61 000 | 286 | 119,96 |
| Methane | 55,50 | 23 900 | 889 | 50.00 |
| Ethane | 51,90 | 22 400 | 1,560 | 47,62 |
| Propane | 50,35 | 21 700 | 2,220 | 46,35 |
| Butane | 49,50 | 20 900 | 2 877 | 45,75 |
| Pentane | 48,60 | 21 876 | 3 507 | 45,35 |
| Paraffin candle | 46.00 | 19 900 | 41,50 | |
| Kerosene | 46,20 | 19 862 | 43.00 | |
| Diesel | 44,80 | 19 300 | 43,4 | |
| Coal (anthracite) | 32,50 | 14 000 | ||
| Coal (lignite - USA) | 15.00 | 6 500 | ||
| Wood ( ) | 21,70 | 8 700 | ||
| wood fuel | 21.20 | 9 142 | 17.0 | |
| Peat (dry) | 15.00 | 6 500 | ||
| Peat (wet) | 6.00 | 2,500 |
| Fuel | MJ/kg | Btu/lb | kJ/mol |
|---|---|---|---|
| methanol | 22,7 | 9 800 | 726,0 |
| ethanol | 29,7 | 12 800 | 1300,0 |
| 1-propanol | 33,6 | 14 500 | 2,020,0 |
| Acetylene | 49,9 | 21 500 | 1300,0 |
| Benzene | 41,8 | 18 000 | 3 270,0 |
| Ammonia | 22,5 | 9 690 | 382,6 |
| Hydrazine | 19,4 | 8 370 | 622,0 |
| Hexamine | 30,0 | 12 900 | 4 200,0 |
| Carbon | 32,8 | 14 100 | 393,5 |
| Fuel | MJ/kg | MJ / l | Btu/lb | kJ/mol |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alkanes | ||||
| Methane | 50,009 | 6.9 | 21 504 | 802.34 |
| Ethane | 47,794 | — | 20 551 | 1 437,2 |
| Propane | 46 357 | 25,3 | 19 934 | 2 044,2 |
| Butane | 45,752 | — | 19 673 | 2 659,3 |
| Pentane | 45,357 | 28,39 | 21 706 | 3 272,6 |
| Hexane | 44,752 | 29.30 | 19 504 | 3 856,7 |
| Heptane | 44,566 | 30,48 | 19 163 | 4 465,8 |
| Octane | 44,427 | — | 19 104 | 5 074,9 |
| Nonan | 44,311 | 31,82 | 19 054 | 5 683,3 |
| Decane | 44,240 | 33.29 | 19 023 | 6 294,5 |
| Undecan | 44,194 | 32,70 | 19 003 | 6 908,0 |
| Dodecan | 44,147 | 33,11 | 18 983 | 7 519,6 |
| Isoparaffins | ||||
| Isobutane | 45,613 | — | 19 614 | 2 651,0 |
| Isopentane | 45,241 | 27,87 | 19 454 | 3 264,1 |
| 2-methylpentane | 44,682 | 29,18 | 19 213 | 6 850,7 |
| 2,3-dimethylbutane | 44,659 | 29,56 | 19 203 | 3 848,7 |
| 2,3-dimethylpentane | 44,496 | 30,92 | 19 133 | 4 458,5 |
| 2,2,4-trimethylpentane | 44,310 | 30,49 | 19 053 | 5 061,5 |
| Naften | ||||
| Cyclopentane | 44,636 | 33,52 | 19 193 | 3,129,0 |
| Methylcyclopentane | 44,636? | 33,43? | 19 193? | 3756,6? |
| Cyclohexane | 43,450 | 33,85 | 18 684 | 3 656,8 |
| Methylcyclohexane | 43,380 | 33,40 | 18 653 | 4 259,5 |
| Monoolefins | ||||
| Ethylene | 47,195 | — | — | — |
| Propylene | 45,799 | — | — | — |
| 1-butene | 45,334 | — | — | — |
| cis- 2-butene | 45,194 | — | — | — |
| trance- 2-butene | 45,124 | — | — | — |
| Isobutene | 45,055 | — | — | — |
| 1-pentene | 45,031 | — | — | — |
| 2-methyl-1-pentene | 44,799 | — | — | — |
| 1-hexene | 44 426 | — | — | — |
| Diolefins | ||||
| 1,3-butadiene | 44,613 | — | — | — |
| Isoprene | 44,078 | — | — | — |
| Nitrous oxide | ||||
| Nitromethane | 10,513 | — | — | — |
| Nitropropane | 20,693 | — | — | — |
| Acetylenes | ||||
| Acetylene | 48,241 | — | — | — |
| Methylacetylene | 46,194 | — | — | — |
| 1-Butyn | 45 590 | — | — | — |
| 1-Pentyne | 45,217 | — | — | — |
| Aromatics | ||||
| Benzene | 40,170 | — | — | — |
| Toluene | 40,589 | — | — | — |
| about- xylene | 40,961 | — | — | — |
| m- xylene | 40,961 | — | — | — |
| P- xylene | 40,798 | — | — | — |
| Ethylbenzene | 40,938 | — | — | — |
| 1,2,4-trimethylbenzene | 40,984 | — | — | — |
| n- propylbenzene | 41,193 | — | — | — |
| Cumene | 41,217 | — | — | — |
| Alcohols | ||||
| methanol | 19,930 | 15,78 | 8 570 | 638,55 |
| ethanol | 26,70 | 22,77 | 12 412 | 1329,8 |
| 1-propanol | 30,680 | 24,65 | 13 192 | 1843,9 |
| Isopropanol | 30,447 | 23,93 | 13 092 | 1829,9 |
| n- butanol | 33,075 | 26,79 | 14 222 | 2 501,6 |
| Isobutanol | 32,959 | 26,43 | 14 172 | 2442,9 |
| tert- butanol | 32,587 | 25,45 | 14 012 | 2 415,3 |
| n- pentanol | 34,727 | 28,28 | 14 933 | 3061,2 |
| Isoamyl alcohol | 31,416? | 35,64? | 13 509? | 2769,3? |
| Ethers | ||||
| Methoxymethane | 28,703 | — | 12 342 | 1 322,3 |
| Ethoxyethane | 33 867 | 24,16 | 14 563 | 2 510,2 |
| Propoxypropane | 36,355 | 26,76 | 15,633 | 3 568,0 |
| Butoxybutane | 37,798 | 28,88 | 16 253 | 4 922,4 |
| Aldehydes and ketones | ||||
| Formaldehyde | 17,259 | — | — | 570,78 |
| Acetaldehyde | 24,156 | — | — | — |
| propionaldehyde | 28,889 | — | — | — |
| Butyraldehyde | 31,610 | — | — | — |
| Acetone | 28,548 | 22,62 | — | — |
| Other types | ||||
| Carbon (graphite) | 32,808 | — | — | — |
| Hydrogen | 120 971 | 1,8 | 52 017 | 244 |
| carbon monoxide | 10.112 | — | 4 348 | 283,24 |
| Ammonia | 18,646 | — | 8 018 | 317,56 |
| Sulfur ( hard ) | 9,163 | — | 3 940 | 293,82 |
- Recording
- There is no difference between lower and higher calorific values when carbon, carbon monoxide, and sulfur are burned, because no water is formed when these substances are burned.
- Btu/lb values are calculated from MJ/kg (1 MJ/kg = 430 Btu/lb).
Firewood
These are sawn or chipped pieces of wood, which, during combustion in furnaces, boilers and other devices, generate thermal energy.
For ease of loading into the furnace, wood material is cut into individual elements up to 30 cm long. To increase the efficiency of their use, firewood should be as dry as possible, and the combustion process should be relatively slow. In many respects, firewood from such hardwoods as oak and birch, hazel and ash, hawthorn is suitable for space heating. Due to the high resin content, increased burning rate and low calorific value, conifers are significantly inferior in this regard.
It should be understood that the density of wood affects the value of the calorific value.
| Firewood (natural drying) | Calorific value kWh/kg | Calorific value mega J/kg |
| hornbeam | 4,2 | 15 |
| beech | 4,2 | 15 |
| ash | 4,2 | 15 |
| Oak | 4,2 | 15 |
| birch | 4,2 | 15 |
| From larch | 4,3 | 15,5 |
| Pine | 4,3 | 15,5 |
| Spruce | 4,3 | 15,5 |
How to prepare firewood
Firewood harvesting usually begins at the end of autumn or at the beginning of winter, before permanent snow cover is established. Felled trunks are left on the plots for primary drying. After some time, usually in winter or early spring, firewood is taken out of the forest. This is due to the fact that during this period no agricultural work is carried out and the frozen ground allows you to load more weight on the vehicle.
But this is the traditional order. Now, due to the high level of development of technology, firewood can be harvested all year round. Entrepreneurial people can bring you already sawn and chopped firewood any day for a reasonable fee.
How to saw and chop wood
Saw the brought log into pieces that fit the size of your firebox. After the resulting decks are split into logs. Decks with a cross section of more than 200 centimeters are pricked with a cleaver, the rest with an ordinary ax.
The decks are pricked into logs so that the cross section of the resulting log is about 80 sq.cm. Such firewood will burn for quite a long time in a sauna stove and give off more heat. Smaller logs are used for kindling.
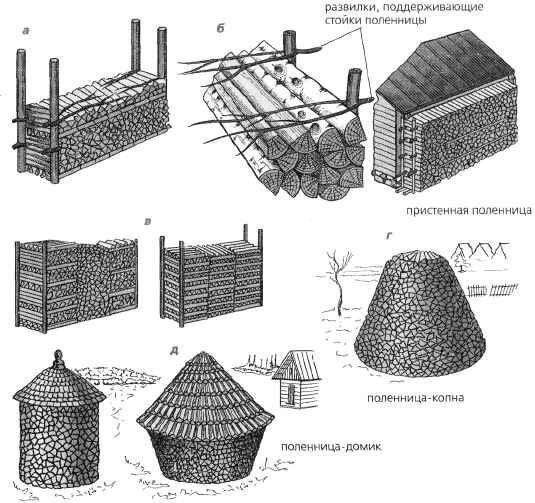
woodpile
Chopped logs are stacked in a woodpile. It is intended not only for the accumulation of fuel, but also for drying firewood. A good woodpile will be located in an open space, blown by the wind, but under a canopy that protects the firewood from precipitation.
The lower row of woodpile logs is laid on logs - long poles that prevent firewood from contacting wet soil.
Drying firewood to an acceptable moisture content takes about a year. In addition, wood in logs dries much faster than in logs. Chopped firewood reaches an acceptable moisture content already in three months of summer. When dried for a year, firewood in a woodpile will receive a moisture content of 15 percent, which is ideal for combustion.
wood properties
Different tree species have the following physical properties:
- Color - it is influenced by climate and wood species.
- Shine - depends on how the heart-shaped rays are developed.
- Texture - related to the structure of wood.
- Humidity - the ratio of moisture removed to the mass of wood in a dry state.
- Shrinkage and swelling - the first is obtained as a result of the evaporation of hygroscopic moisture, swelling - the absorption of water and an increase in volume.
- Density - approximately the same for all tree species.
- Thermal conductivity - the ability to conduct heat through the thickness of the surface, depends on the density.
- Sound conductivity - characterized by the speed of sound propagation, depends on the location of the fibers.
- Electrical conductivity is the resistance to the passage of electric current. It is influenced by the breed, temperature, humidity, the direction of the fibers.

Before using wooden raw materials for certain purposes, first of all, they get acquainted with the properties of wood, and only then it goes into production.
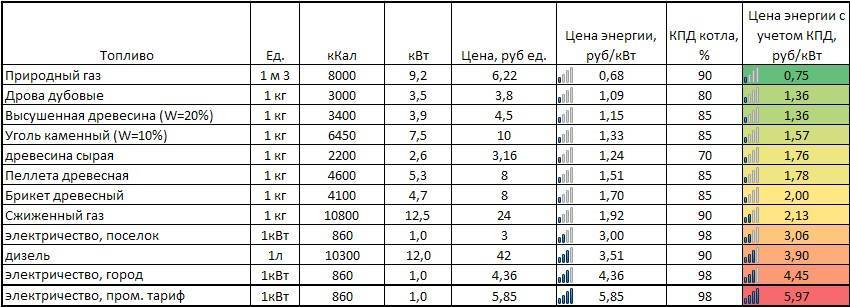
Home heating in the mirror of numbers
Pellet boilers are characterized by a fairly high efficiency precisely due to the possibility of the most complete combustion of wood pellets. In fact, these are processed and granulated woodworking waste: sawdust, bark, branches.
Cheap fuel, environmental friendliness, practicality and efficiency - these are the main advantages of pellet boiler equipment.
Boilers working on pellets are spared from the most serious drawback of other solid fuel boilers, they allow you to fully automate the operation of the boiler room, that is, to supply fuel, control the combustion process and remove combustion products without human intervention. The use of traditional firewood and coal does not provide such an opportunity.
Modern pellet boilers provide a fairly long period of operation in automatic mode, the duration of which is limited only by the volume of the tank from which the fuel is supplied. Cleaning of the working surfaces of the boilers is carried out no more than once a month and does not require the involvement of specialists, which reduces the cost of maintaining the installation.
The presented table compares different types of fuel according to various indicators.
Comparative characteristics of various types of fuel
| Type of fuel | Humidity, % | Ash content, % | Sulfur, % | Heat of combustion, mJ/kg | Specific weight, kg/m3 | Amount of CO2 in flue gases | Unit efficiency, % | Environmental damage | Heat cost, rub/Gcal |
| Natural gas | 3-5 | — | 0,1-0,3 | 35-38 | 0,8 | 95 | Missing | 199 | |
| PELLETS | 8-10 | 0,4-0,8 | 0-0,3 | 19-21 | 550-700 | 90 | Missing | 523 | |
| Firewood | 8-60 | 2 | 0-0,3 | 16-18 | 300-350 | 60 | Missing | 652 | |
| Coal | 10-40 | 25-35 | 1-3 | 15-17 | 1200-1500 | 60 | 70 | High | 960 |
| Electricity | — | — | — | 4,86 | — | — | 100 | Missing | 988 |
| fuel oil | 1-5 | 1,5 | 1,2 | 42 | 940-970 | 78 | 80 | High | 1093 |
| Diesel fuel | 0,1-1 | 1 | 0,2 | 42,5 | 820-890 | 78 | 90 | High | 1420 |
| * Information as of 2011 |
Natural gas
Economically, gas heating is the most profitable. However, if there is no gas main in direct access, and it is necessary to heat the house, a pellet boiler will be the best option. To install such a boiler, unlike a gas boiler, no approvals and connection costs are required.
In the simplest case, a room is required that is equipped in accordance with the fire safety requirements for solid fuel boilers. In terms of environmental impact, pellet boilers practically do not harm the environment, the level of CO in the combustion products of wood pellets is the same as that of natural gas.
Coal or firewood
Traditional types of fuel are able to compete with pellets, their price is relatively low, and there are no problems with the purchase. However, in addition to the difficulties with delivery and storage, these types of fuel require constant, daily efforts to maintain the boiler: loading with fuel, cleaning and removing ash, which must be put somewhere else in such quantities. That small part of the fuel that remains after the combustion of pellets in the form of ash contains a minimum of harmful compounds and can be used as fertilizer in the beds.
Diesel fuel
When this fuel is burned, the area next to the house will get almost the entire periodic table. The cost of purchasing a boiler in this case is 2-3 times lower, but the monthly cost of diesel fuel is 7-8 times more. Delivering and storing diesel fuel in the quantities required for heating is even more difficult than coal. And it is basically impossible to get rid of the smell accompanying this type of fuel. By the way, the smell of burning wood pellets is quite pleasant and harmless.
Electricity
As a rule, even new settlements in our time are connected to the power grid fairly quickly. The stumbling block is usually the quota of energy consumption allocated to the site, determined by the state of external engineering networks and the pliability of the energy sales company. When using electric heating, you can be sure of only one thing: the price per kilowatt, and hence the cost of heating, regardless of the economic situation, will only grow. Which she has been doing for the last few years.
As a result, if you do not take into account natural gas, pellet plants are the most modern, comfortable, environmentally friendly and promising type of heating. Sufficiently high initial costs for the purchase of a boiler are more than paid off within the first two or three years, after which it begins to bring its owner a constant and significant savings, read profit.
Creating optimal conditions for combustion
Due to the high temperature, all internal elements of the furnace are made of special refractory bricks. Refractory clay is used for their laying. When creating special conditions, it is quite possible to obtain a temperature in the furnace exceeding 2000 degrees. Each type of coal has its own flash point.
After reaching this indicator, it is important to maintain the ignition temperature by continuously supplying an excess amount of oxygen to the furnace.
Among the disadvantages of this process, we highlight the loss of heat, because part of the energy released will go through the pipe. This leads to a decrease in the furnace temperature. In the course of experimental studies, scientists managed to establish the optimal excess amount of oxygen for various types of fuel. Thanks to the choice of excess air, complete combustion of the fuel can be expected. As a result, you can count on the minimum loss of thermal energy.