- Antifreeze based on ethylene glycol and propylene glycol
- Methods for filling the system with coolant
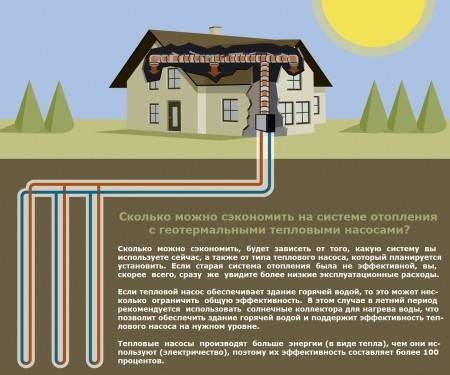
- Heat pumps
- Biofuel boilers
- Antifreeze as a coolant
- Immersion of a horizontal heat exchanger in a reservoir
- Advantages and disadvantages of water-coolant
- Coolant base
- Water use
- Antifreeze for heating
- Instructions for use
- Comparison of costs of different heating systems
- Solving the problem of heating
- natural circulation
- forced circulation
Antifreeze based on ethylene glycol and propylene glycol
The two most common substances used in heating antifreeze are ethylene glycol and propylene glycol. The first one, ethylene glycol, has become widespread due to its low cost. Only it is aggressive towards the materials used as seals and is not compatible with pipes and heat exchangers with a zinc inner coating. And this is only part of its features.
Ethylene glycol is a toxic substance, belongs to the 3rd hazard class. It is desirable to use it in closed heating systems and is not recommended for residential buildings. For the same reason, the use of ethylene glycol in conjunction with double-circuit heating boilers should not be allowed.There is a risk that a coolant with a toxic substance will enter the DHW circuit through the heat exchanger.
Manufacturers of boilers and heat exchangers often categorically prohibit or strongly discourage the use of antifreeze, urging the use of clean water. They do this because they cannot predict which composition will be used in the end, and, accordingly, select or develop equipment taking into account the physicochemical properties of the coolant. The selection of materials for seals and heat exchangers is oriented towards the use of distilled water, not assuming the use of other liquids. The more aggressive.
However, antifreeze has been on the market for a long time, which some manufacturers recommend using or at least do not prevent it. Propylene glycol appeared later than ethylene glycol, and immediately proved its superiority in many ways, except for cost. Propylene glycol is an environmentally friendly substance used in the food industry. It is non-corrosive to materials and has good qualities for creating non-freezing liquids.

Methods for filling the system with coolant
The question of filling, as a rule, appears only in the case of a closed system, since open circuits are filled without problems through an expansion tank. A coolant is simply poured into it, which, under the action of gravity, spreads over all contours
It is important that all air vents are open.
There are several methods for filling a closed heating system with a coolant: by gravity, with a submersible pump, or using special pressure testing equipment. Let's take a closer look at each of the methods.
By gravity.This method of pumping coolant for a heating system, although it does not require equipment, takes a lot of time. It takes a long time to squeeze out the air and just as long to gain the desired pressure. By the way, it is pumped up with a car pump. So the equipment is still required.
We need to find the highest point. Usually, this is one of the gas vents (it must be removed). When filling, open the valve to drain the coolant (lowest point). When water runs through it, the system is full:
- When the system is full (water ran out of the drain tap), take a rubber hose about 1.5 meters long and attach it to the system inlet.
- Select the inlet so that the pressure gauge is visible. Install a non-return valve and a ball valve at this point.
- Attach an easily removable adapter for connecting a car pump to the free end of the hose.
- After removing the adapter, pour the coolant into the hose (keep it up).
- After filling the hose, use the adapter to connect the pump, open the ball valve and pump fluid into the system with the pump. You have to be careful not to let air in.
- When almost all the water contained in the hose has been pumped in, the valve closes and the operation is repeated.
- On small systems, to get 1.5 bar, you will have to repeat it 5-7 times, with large ones you will have to fiddle longer.
With this method, you can connect the hose from the water supply, you can pour the prepared water into the barrel, raise it above the entry point and so pour it into the system. Antifreeze is also poured in, but when working with ethylene glycol, you will need a respirator, protective rubber gloves and clothing. If a substance gets on a fabric or other material, it also becomes toxic and must be destroyed.
With a submersible pump.To create a working pressure, the coolant for the heating system can be pumped with a low-power submersible pump:
- The pump must be connected to the lowest point (not the system drain point) through a ball valve and a non-return valve, a ball valve must be installed at the system drain point.
- Pour the coolant into a container, lower the pump, turn it on. During operation, constantly add coolant - the pump should not drive air.
- During the process, monitor the manometer. As soon as its arrow has moved from zero, the system is full. Up to this point, the manual air vents on the radiators can be open - air will escape through them. As soon as the system is full, they must be closed.
- Next, you need to increase the pressure, continuing to pump the coolant for the heating system with a pump. When it reaches the required mark, stop the pump, close the ball valve
- Open all air vents (on radiators too). Air escapes, pressure drops.
- Turn on the pump again, pump in a little coolant until the pressure reaches the design value. Release the air again.
- So repeat until their air vents stop air coming out.
Then you can start the circulation pump, bleed the air again. If at the same time the pressure remains within the normal range, the coolant for the heating system is pumped. You can put it to work.
Pressure pump. The system is filled in the same way as in the case described above. In this case, a special pump is used. It is usually manual, with a container into which the coolant for the heating system is poured. From this container, liquid is pumped through a hose into the system.
When filling the system, the lever goes more or less easily, when the pressure rises, it is already harder to work. There is a pressure gauge on both the pump and the system. You can follow where it is more convenient.
Further, the sequence is the same as described above: pumped up to the required pressure, bled air, repeated again. So until there is no air left in the system. After - you also need to start the circulation pump for about five minutes, bleed the air. Also repeat several times.
Heat pumps
The most versatile alternative heating for a private house is the installation of heat pumps. They work according to the well-known principle of a refrigerator, taking heat from a colder body and giving it away in the heating system.
It consists of a seemingly complex scheme of three devices: an evaporator, a heat exchanger and a compressor. There are a lot of options for the implementation of heat pumps, but the most popular are:
- Air to air
- Air to water
- water-water
- ground water
Air to air
The cheapest implementation option is air-to-air. In fact, it resembles a classic split system, however, electricity is spent only on pumping heat from the street into the house, and not on heating the air masses. This helps to save money, while perfectly heating the house throughout the year.
The efficiency of the systems is very high. For 1 kW of electricity, you can get up to 6-7 kW of heat. Modern inverters work great even at temperatures of -25 degrees and below.
Air to water
"Air-to-water" is one of the most common implementations of a heat pump, in which a large-area coil installed in an open area plays the role of a heat exchanger. Additionally, it can be blown by a fan, forcing the water inside to cool.
Such installations are characterized by more democratic cost and simple installation. But they are able to work with high efficiency only at temperatures from +7 to +15 degrees. When the bar drops to a negative mark, efficiency drops.
ground water
The most versatile implementation of a heat pump is ground-to-water. It does not depend on the climatic zone, since a layer of soil that does not freeze throughout the year is everywhere.
In this scheme, the pipes are immersed in the ground to a depth where the temperature is kept at the level of 7-10 degrees throughout the year. Collectors can be located vertically and horizontally. In the first case, several very deep wells will have to be drilled, in the second case, a coil will be laid at a certain depth.
The disadvantage is obvious: complex installation work that will require high financial investments. Before deciding on such a step, you should calculate the economic benefits. In areas with short warm winters, it is worth considering other options for alternative heating of private houses. Another limitation is the need for a large free area - up to several tens of square meters. m.
water-water
The implementation of a water-to-water heat pump is practically no different from the previous one, however, the collector pipes are laid in groundwater that does not freeze throughout the year, or in a nearby reservoir. It is cheaper due to the following advantages:
- Maximum well drilling depth - 15 m
- You can get by with 1-2 submersible pumps
Biofuel boilers
If there is no desire and opportunity to equip a complex system consisting of pipes in the ground, solar modules on the roof, you can replace the classic boiler with a model that runs on biofuel. They need:
- Biogas
- straw pellets
- Peat granules
- Wood chips, etc.
Such installations are recommended to be installed together with the alternative sources considered earlier. In situations where one of the heaters does not work, it will be possible to use the second.
Main advantages
When deciding on the installation and subsequent operation of alternative sources of thermal energy, it is necessary to answer the question: how quickly will they pay off? Undoubtedly, the considered systems have advantages, among which:
- The cost of the energy produced is less than when using traditional sources
- High efficiency
However, one should be aware of the high initial material costs, which can reach tens of thousands of dollars. The installation of such installations cannot be called simple, therefore, the work is entrusted exclusively to a professional team that is able to provide a guarantee for the result.
Summing up
Demand is acquiring alternative heating for a private house, which becomes more profitable against the backdrop of rising prices for traditional sources of thermal energy. However, before starting to re-equip the current heating system, it is necessary to calculate everything by considering each of the proposed options.
It is also not recommended to abandon the traditional boiler.It must be left and in certain situations, when alternative heating does not fulfill its functions, it will remain possible to warm your home and not freeze.
Antifreeze as a coolant
Higher characteristics for the efficient operation of the heating system have such a type of coolant as antifreeze. By pouring antifreeze into the heating system circuit, it is possible to reduce the risk of freezing of the heating system in the cold season to a minimum. Antifreeze is designed for lower temperatures than water, and they are not able to change its physical state. Antifreeze has many advantages, since it does not cause scale deposits and does not contribute to corrosive wear of the interior of the heating system elements.
Even if the antifreeze solidifies at very low temperatures, it will not expand like water, and this will not cause any damage to the heating system components. In the event of freezing, the antifreeze will turn into a gel-like composition, and the volume will remain the same. If, after freezing, the temperature of the coolant in the heating system rises, it will turn from a gel-like state into a liquid, and this will not cause any negative consequences for the heating circuit.
Many manufacturers add various additives to antifreeze that can increase the life of the heating system.
Such additives help to remove various deposits and scale from the elements of the heating system, as well as eliminate pockets of corrosion. When choosing antifreeze, you need to remember that such a coolant is not universal. The additives that it contains are only suitable for certain materials.
Existing coolants for heating systems-antifreezes can be divided into two categories based on their freezing point. Some are designed for temperatures up to -6 degrees, while others are up to -35 degrees.
Properties of various types of antifreeze
The composition of such a coolant as antifreeze is designed for a full five years of operation, or for 10 heating seasons. The calculation of the coolant in the heating system must be accurate.
Antifreeze also has its drawbacks:
- The heat capacity of antifreeze is 15% lower than that of water, which means that they will give off heat more slowly;
- They have a rather high viscosity, which means that a sufficiently powerful circulation pump will need to be installed in the system.
- When heated, antifreeze increases in volume more than water, which means that the heating system must include a closed-type expansion tank, and radiators must have a larger capacity than those used to organize a heating system in which water is the coolant.
- The speed of the coolant in the heating system - that is, the fluidity of antifreeze, is 50% higher than that of water, which means that all connectors of the heating system must be very carefully sealed.
- Antifreeze, which includes ethylene glycol, is toxic to humans, so it can only be used for single-circuit boilers.
In the case of using this type of coolant as antifreeze in the heating system, certain conditions must be taken into account:
- The system must be supplemented with a circulation pump with powerful parameters.If the circulation of the coolant in the heating system and the heating circuit is long, then the circulation pump must be outdoor installation.
- The volume of the expansion tank must be at least twice as large as the tank used for a coolant such as water.
- It is necessary to install volumetric radiators and pipes with a large diameter in the heating system.
- Do not use automatic air vents. For a heating system in which antifreeze is the coolant, only manual type taps can be used. A more popular manual type crane is the Mayevsky crane.
- If antifreeze is diluted, then only with distilled water. Melt, rain or well water will not work in any way.
- Before filling the heating system with coolant - antifreeze, it must be thoroughly rinsed with water, not forgetting about the boiler. Manufacturers of antifreezes recommend changing them in the heating system at least once every three years.
- If the boiler is cold, then it is not recommended to immediately set high standards for the temperature of the coolant to the heating system. It should rise gradually, the coolant needs some time to heat up.
If in winter a double-circuit boiler operating on antifreeze is turned off for a long period, then it is necessary to drain water from the hot water supply circuit. If it freezes, the water can expand and damage pipes or other parts of the heating system.
Immersion of a horizontal heat exchanger in a reservoir
This method requires a special location of the household - at a distance of about 100 m from the reservoir, which has sufficient depth.In addition, the indicated reservoir should not freeze to the very bottom, where the external contour of the system will be located. And for this, the area of \u200b\u200bthe reservoir cannot be less than 200 square meters. m.
This option for placing a heat exchanger is considered the least expensive, but such an arrangement of home ownership is still not common. In addition, difficulties may arise if the reservoir belongs to public facilities.
The obvious advantage of this method is the absence of mandatory labor-intensive earthworks, although you still have to tinker with the underwater location of the collector. And you will also need a special permit to carry out such work.
However, a geothermal plant that uses water energy is still the most economical.
Advantages and disadvantages of water-coolant
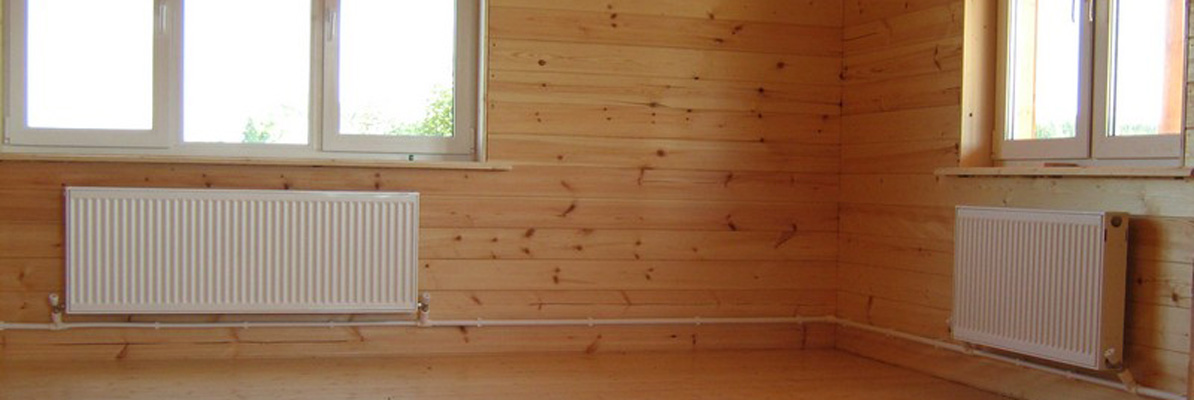
Water is the most common coolant option, the popularity of which is explained by the following advantages:
- Cheapness - financially, water is affordable for everyone: you can regularly change the coolant and safely release fluid from the system for maintenance work, because refilling will not entail high costs.
- High thermal performance - water has an increased heat capacity at maximum density. So, 1 liter of liquid transfers 20 kcal of heat energy through heating devices - according to this indicator, water has no equal.
- Maximum safety - water does not bear the slightest harm to either the environment or humans.
There are coolant water and cons:
- Freezing - at critical negative temperatures without a regular influx of heat, water quickly turns into a crystalline form, which can cause deformation of the heating system.
- Corrosiveness - water is a powerful oxidizing agent, therefore it is dangerous for equipment made of some ferrous and non-ferrous metals.
- Aggressive composition - untreated water contains a lot of salts, iron, hydrogen sulfide and other compounds that are layered with deposits and clog heating equipment.
Coolant base
In modern systems, the role of a coolant is played by water or antifreeze - special frost-resistant liquids. They are selected according to certain criteria:
- the coolant must be harmless to heating equipment;
- choose safe antifreezes that will not harm residents during a leak or repair;
- long period of use;
- high heat capacity.
In this video, we will consider the danger of non-freezing in the heating system:
3 id="use-water">Use water
The fluidity and high heat capacity of water make it an ideal heat carrier for heating a private house. In a closed-type system, you can pour liquid directly from the tap. Salts and alkalis in its composition can settle in the pipes of the equipment, but this happens only once. Water circulates through pipes for several years, and new liquid is poured very rarely.
Requirements for water quality increase if an open heating system is installed in the house. Water in such equipment constantly evaporates, so it needs to be replenished. Accordingly, the amount of sediment on the pipes is constantly growing. Liquid with a high iron content is especially dangerous for open equipment. For such systems, purified, filtered or distilled water is used.
Antifreeze for heating
Instead of water, antifreezes based on polyhydric alcohols are used. Manufacturers are trying to include new substances in their composition. Three types of antifreeze liquids are now known:
- based on propylene glycol;
- with ethylene glycol;
- containing glycerin.
Ethylene glycol liquid is very toxic: you can get poisoned even from its contact with the skin or evaporation. Such antifreeze is most often purchased because of its low cost. It has an increased fluidity, is able to foam and is very active chemically. When there is a possibility of fluid leakage, the poisonous vapors of ethylene glycol quickly spread throughout the room, so it is better to purchase more expensive antifreeze with propylene glycol.
Glycol liquid does not pose a risk to human health, but at too high a temperature, its fluidity slows down. If the temperature reaches seventy degrees, propylene glycol can freeze. Such antifreeze is chemically neutral and practically does not interact with other substances.
Glycerin antifreeze is not toxic, but reacts poorly to overheating and can leave deposits on equipment parts. But due to the content of glycerin, the coolant does not freeze. The main characteristics of this fluid are the average between propylene and ethylene antifreeze. The cost is also average.
Instructions for use
If your system was previously running on water, switching to antifreeze will not be easy. Theoretically, radiators with a boiler can be emptied and filled with a cold-resistant coolant, but in practice the following will happen:
- due to the lower heat capacity, the return of batteries and the efficiency of heating rooms will decrease;
- due to viscosity, the load on the pump will increase, the coolant flow will drop, less heat will come to the radiators;
- antifreeze expands more than water, so the capacity of the old tank will not be enough, pressure will rise in the network;
- to improve the situation, you will have to add the temperature on the boiler, which will lead to excessive fuel consumption and an increase in pressure.

Leaking joints must be repacked, sealing the threads with dry flax or thread with sealant
In order for the heating to function normally on a chemical coolant, it is necessary to calculate in advance or redo the existing system according to the new requirements:
- The capacity of the expansion tank is selected at the rate of 15% of the total volume of liquid (it was 10% on water);
- The performance of the pump is assumed to be 10% higher, and the generated pressure is assumed to be 50%. Let us explain with an example: if there used to be a unit with a working pressure of 0.4 Bar (4 meters of water column), then take a 0.6 Bar pump for antifreeze.
- In order to operate the boiler in the optimal mode and not raise the temperature of the coolant, it is advisable to add 1-3 (depending on power) sections to each battery.
- Pack all joints with dry flax or use high-quality pastes - sealants such as LOCTITE, ABRO or Germesil.
- When buying shut-off and control valves, consult with the seller about the resistance of rubber seals to glycol mixtures.
- Pressurize the system again by filling pipes and heating equipment with water.
- When starting the boiler unit at a negative temperature, set the minimum power. Cold antifreeze must be warmed up slowly.

Before pumping frost-resistant liquid, fill in water and test pipelines with a pressure exceeding the working one by 25%
The concentrated coolant must be diluted with water, ideally with distillate. Do not aim for an excessive margin of frost resistance - the more water you add, the better the heating will work. Recommendations for the preparation of the coolant:
- Under heating elements, electric and gas double-circuit heat generators, prepare the mixture at minus 20 degrees. A more concentrated solution may foam from contact with the heater, soot will appear on the surface of the heating element.
- In other cases, mix components for freezing point according to the table below. The proportions are indicated per 100 liters of coolant.
- In the absence of a distillate, first conduct an experiment - dilute the concentrate in a jar with plain water. If you see a precipitate of white flakes - a decomposition product of inhibitors and additives, this water cannot be used.
- A similar check is done before mixing antifreezes from two different manufacturers. It is unacceptable to dilute ethylene glycol with propylene.
- Prepare the coolant immediately before pouring.
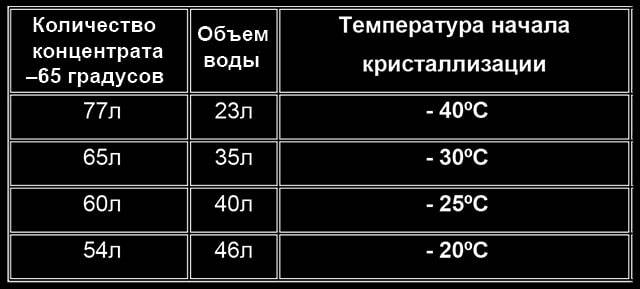
The ratio of concentrate and water is given per 100 liters. To find out the amount of ingredients for a volume of 150 liters, multiply the figures given by a factor of 1.5
The maximum service life of any non-freezing substance in pipes and heating radiators is 5 years. At the end of the specified period, the liquid is drained, the system is flushed twice and filled with fresh antifreeze.
Comparison of costs of different heating systems
Often the choice of a particular heating system is based on the starting cost of the equipment and its subsequent installation. Based on this indicator, we obtain the following data:
-
Electricity. Initial investment up to 20,000 rubles.
-
solid fuel. The purchase of equipment will require from 15 to 25 thousand rubles.
-
Oil boilers. Installation will cost 40-50 thousand.
-
Gas heating with own storage. The price is 100-120 thousand rubles.
-
Centralized gas pipeline. Due to the high cost of communication and connection, the cost exceeds 300,000 rubles.
Solving the problem of heating
The principle of operation of water heating is not complicated. The design consists of a heating device, pipes and heating devices, which are closed in a single system.
The heating boiler creates the required temperature of the coolant, which is used as water or antifreeze. The heated coolant moves through the pipeline to the radiators, which are installed in heated rooms. The latter transfer the received heat to the atmosphere of the room, thereby warming it up. The coolant, which gave off heat, moving through the pipes, returns to the boiler, where it is heated again. Then the cycle repeats.
Depending on the method of moving the coolant, the heating system can be with natural or forced circulation.
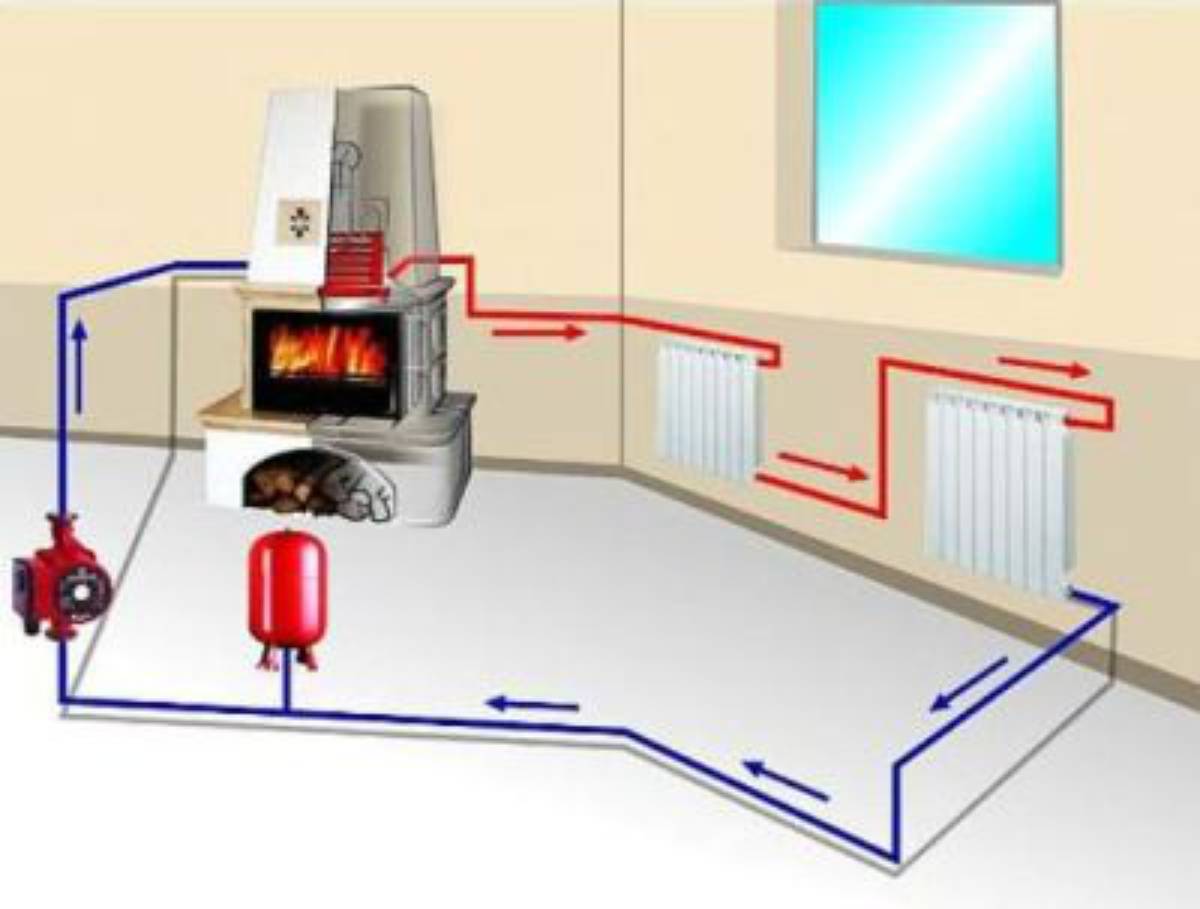 Coolant circulation system
Coolant circulation system
natural circulation
The operation of the heating system is based on the difference in the densities of the heated and cold liquids. The heated coolant has a smaller mass, so it moves up when moving through the pipes.When moving, the temperature decreases and the density of the substance decreases, so it tends to go down when returning to the boiler.
The operation of the heating system in this case does not depend on electricity, which makes it completely autonomous. In addition, the design of such heating is greatly simplified.
The disadvantage of such a heating system is the significant length of the pipeline, as well as the need to use pipes of large diameter. This circumstance increases the cost of the structure.
In addition, in this case, the creation of a pipe slope is required and there is no possibility of using modern heating devices.
forced circulation
When creating a heating system in a country house with forced circulation of the coolant, a pump that creates pressure is included in the circuit. Also, a similar design provides for the installation of an expansion tank, which is necessary to remove excess fluid in the system. The design of the tank can be open or closed. The use of the second option is preferable, since evaporation losses are excluded. If the heat carrier is a non-freezing solution, then the tank must necessarily have a closed design. A manometer is mounted to control the pressure.
In the case of using such a heating design, it becomes possible to use a smaller amount of coolants, reduce the length of the pipeline and reduce the diameter of the pipes. The temperature can be adjusted in each heater individually.
The circulation pump requires an electrical connection. Otherwise, the system will not work.