- Recommendations for the selection and operation of coolants - which one is better to choose
- Antifreeze as a coolant
- Heating with antifreeze or water
- What are the problems when using antifreeze liquid in heating systems?
- Problem #1
- Problem #2
- Problem #3
- Properties and features of the use of antifreezes in heating systems
- Antifreeze based on ethylene glycol
- Propylene Glycol Antifreeze
- Is it possible to pour antifreeze into the heating system
- What type of radiators is suitable for a heating system with antifreeze
- Methods for filling the system with coolant
- Types and properties of heat-carrying liquids
- We choose "anti-freeze" for heating
Recommendations for the selection and operation of coolants - which one is better to choose
None of the heat carrier manufacturers will refute the fact that in the case of a stable operation of the heating system in winter, it is water that is the best option for which coolant to choose for heating. It is better if it is a special distilled liquid with modifying additives, as mentioned earlier. Those of the homeowners who consider the purchase of store-bought water a waste of money, usually carry out its own preparation, softening it, and equipping the system with the necessary filters.

If it was decided to use non-freezing coolants, it is important to have information about the conditions that exclude the possibility of their use:
- If the house has an open system.
- When using natural circulation in the circuits: such a coolant concentrate for heating, the system simply “will not pull”.
- It is unacceptable to have pipes or other elements in contact with the coolant that have a galvanized surface.
- All connecting assemblies equipped with tow or oil paint seals must be repacked, as glycolic substances will destroy them very quickly. As a result, antifreeze will begin to flow out, creating a real threat to people in the room. As a new sealing material, you can use the old tow, treating it with a special sealing paste "Unipak"
- It is forbidden to use non-freezing liquids in those systems that are not equipped with devices for accurately maintaining the temperature of the coolant. The heating level, which is dangerous for glycol antifreezes, begins already at + 70-75 degrees: these processes are irreversible and fraught with the most unpleasant consequences.
- Usually, after pouring antifreeze into the system, it is required to increase the power of pumping equipment, install a larger expansion tank, and increase the number of battery sections. Sometimes it is required to change pipes to wider ones.
- Incorrectness was noticed in the operation of automatic air vents after pouring antifreeze: they are recommended to be replaced with Mayevsky taps.
- Before pouring antifreeze, the system must be thoroughly cleaned and flushed. This is done with the help of special compounds.
- To change the concentration level of antifreeze, only distilled water is allowed. Even from the use of purified and softened water in this case, it is better to refrain.
- The correct concentration of antifreeze coolant for heating systems is of utmost importance. It is better not to expect that the winter will not be very severe by diluting the antifreeze excessively. It is recommended to stick to the threshold of -30 degrees even in the traditionally warm regions. In addition to protection against abnormal frosts, this will create optimal conditions for inhibitors and surfactants, the effectiveness of which is noticeably reduced if the water content is excessive.
- After filling with a new coolant, it is forbidden to immediately turn on the maximum mode of the system. It is best to increase power smoothly so that the antifreeze has time to adapt to new conditions and circuit elements.
- As studies show, at present, propylene glycol composition is considered the most reliable non-freezing coolant. Ethylene glycol is too dangerous, and glycerin is so controversial that it is rarely used. So it's better to overpay, but sleep well at night.
Antifreeze as a coolant
Higher characteristics for the efficient operation of the heating system have such a type of coolant as antifreeze. By pouring antifreeze into the heating system circuit, it is possible to reduce the risk of freezing of the heating system in the cold season to a minimum. Antifreeze is designed for lower temperatures than water, and they are not able to change its physical state.Antifreeze has many advantages, since it does not cause scale deposits and does not contribute to corrosive wear of the interior of the heating system elements.
Even if the antifreeze solidifies at very low temperatures, it will not expand like water, and this will not cause any damage to the heating system components. In the event of freezing, the antifreeze will turn into a gel-like composition, and the volume will remain the same. If, after freezing, the temperature of the coolant in the heating system rises, it will turn from a gel-like state into a liquid, and this will not cause any negative consequences for the heating circuit.
Such additives help to remove various deposits and scale from the elements of the heating system, as well as eliminate pockets of corrosion. When choosing antifreeze, you need to remember that such a coolant is not universal. The additives that it contains are only suitable for certain materials.
Existing coolants for heating systems-antifreezes can be divided into two categories based on their freezing point. Some are designed for temperatures up to -6 degrees, while others are up to -35 degrees.
Properties of various types of antifreeze
The composition of such a coolant as antifreeze is designed for a full five years of operation, or for 10 heating seasons. The calculation of the coolant in the heating system must be accurate.
Antifreeze also has its drawbacks:
- The heat capacity of antifreeze is 15% lower than that of water, which means that they will give off heat more slowly;
- They have a rather high viscosity, which means that a sufficiently powerful circulation pump will need to be installed in the system.
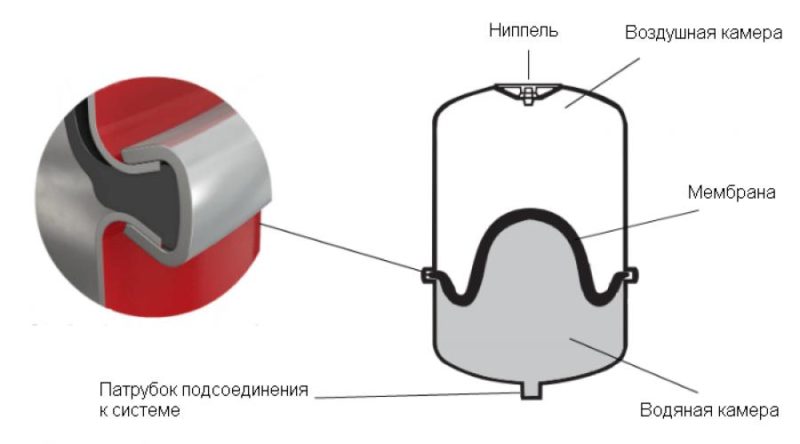
- When heated, antifreeze increases in volume more than water, which means that the heating system must include a closed-type expansion tank, and radiators must have a larger capacity than those used to organize a heating system in which water is the coolant.
- The speed of the coolant in the heating system - that is, the fluidity of antifreeze, is 50% higher than that of water, which means that all connectors of the heating system must be very carefully sealed.
- Antifreeze, which includes ethylene glycol, is toxic to humans, so it can only be used for single-circuit boilers.
In the case of using this type of coolant as antifreeze in the heating system, certain conditions must be taken into account:
- The system must be supplemented with a circulation pump with powerful parameters. If the circulation of the coolant in the heating system and the heating circuit is long, then the circulation pump must be outdoor installation.
- The volume of the expansion tank must be at least twice as large as the tank used for a coolant such as water.
- It is necessary to install volumetric radiators and pipes with a large diameter in the heating system.
- Do not use automatic air vents. For a heating system in which antifreeze is the coolant, only manual type taps can be used. A more popular manual type crane is the Mayevsky crane.
- If antifreeze is diluted, then only with distilled water. Melt, rain or well water will not work in any way.
- Before filling the heating system with coolant - antifreeze, it must be thoroughly rinsed with water, not forgetting about the boiler. Manufacturers of antifreezes recommend changing them in the heating system at least once every three years.
- If the boiler is cold, then it is not recommended to immediately set high standards for the temperature of the coolant to the heating system. It should rise gradually, the coolant needs some time to heat up.
If in winter a double-circuit boiler operating on antifreeze is turned off for a long period, then it is necessary to drain water from the hot water supply circuit. If it freezes, the water can expand and damage pipes or other parts of the heating system.
Heating with antifreeze or water
After reading this section, you are likely to refuse antifreeze in the heating system. The main plus of antifreeze is the safety of the system at low temperatures, completely crossed out by its minuses.
Low heat capacity of antifreeze. Increasing the size of radiators by 20-23% The heat capacity of antifreeze is significantly lower than the heat capacity of water. By diluting water with 35% antifreeze, we lose approximately 200 W from 1 kW of thermal energy. This means that it is required to increase the dimensions of pipes, radiators and boiler by 20%. In terms of a country house of 300 m2, we lose about 60 thousand rubles by increasing the size of the system.
The service life of antifreeze is from 5 to 10 years Over the years, antifreeze oxidizes and safely destroys brass joints. After 5 - 10 years, ethylene glycol and propylene glycol must be drained, disposed of and replaced with a new one. You will have to not only buy new antifreeze, but also pay for the disposal of the old one.Unfortunately, in our country there is no ethylene glycol recycling service in small volumes, so it will be difficult to find someone to hand over this chemistry to. I will not consider the idea of draining antifreeze to a neighbor on the site.
The use of sectional radiators in systems with antifreeze is unacceptable. Rubber intersection gaskets quickly oxidize, and radiators leak. We use only steel panels. The use of galvanized pipes is also unacceptable. Antifreeze safely washes out the zinc, and the pipe remains bare.
Why is antifreeze useless for a country house? Antifreeze will successfully cope with the task - the heating system will not freeze in the winter in your absence, but what to do with the water supply system? Water supply pipes at negative temperatures will freeze faster and with worse consequences, because. are laid not only in the floor, but also in the walls. You will have to remove the tiles, beat the screed and change the pipes in the bathrooms, showers, kitchen, replace the entire piping of the boiler room for water supply. Of course, pumping antifreeze into the water supply system will not work, as well as laying all pipes with heating cables.
Conclusion: Antifreezes are suitable either for heating small country houses for temporary residence, or large warehouses, workshops and enterprises. In the heating system of a full-fledged country house, antifreeze is useless.
Antifreeze for the heating system of a country house is needed if: you do not plan to live in the house in winter; in the house there are 1-2 bathrooms with a tee water supply system (without a collector), which can be drained before the onset of cold weather.
It is impossible to leave a full-fledged country house in winter without emergency heating. In winter, it is necessary to maintain a constant standby heating + 10-12 ° С.
So your engineering systems will be truly protected without antifreeze.
If you liked my article and you are looking for reliable design specialists - call or write to me by mail.
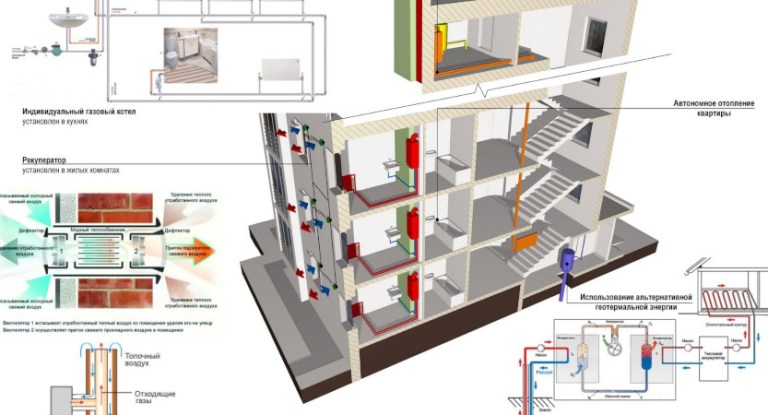
Sometimes the heating system stops functioning at the very height of the heating season. The reasons can be different, from a power outage to a breakdown of any element of the system. If water is used as a heat carrier, then the absence of its heating for a certain amount of time (including depends on the insulation of the house) leads to defrosting of the heating system. Defrosting, as a rule, leads to sad consequences, such as burst pipes, radiators, etc. However, this can be avoided if antifreeze is used as the coolant.

Heat carrier Thermagent Eko, 10 kg.
Note! Manufacturers add special additives to the coolant that prevent the formation of corrosion and scale. However, it should be noted that the action of additives, as a rule, lasts for a maximum of 5-6 years, after which their effectiveness is greatly reduced and the coolant, while maintaining anti-freezing properties, will no longer protect the system from corrosion and scale. After 5-6 years, it is recommended to fill in a new coolant, while first flushing the system with water.

Hot Stream-65, 47 kg. Up to -65°C.
What are the problems when using antifreeze liquid in heating systems?
Problem #1
- boiler power;
- increase the pressure of the circulation pump by 60%;
- increase the volume of the expansion tank by 50%;
- 50% increase in heat output of radiators.
Problem #2
Ethylene glycol-based antifreezes have one feature - they “do not like” overheating of the system.For example, if at any point in the system the temperature exceeds the critical temperature for a given brand of mixture, ethylene glycol and additives will decompose, resulting in the formation of solid precipitates and acids. When precipitation falls on the heating components of the boiler, soot appears, as a result of which heat transfer decreases, the appearance of new precipitation is stimulated, and the likelihood of overheating increases.

The acids formed during the decomposition of ethylene glycol react with the metals of the system, as a result of which the development of corrosion processes is possible. The decomposition of additives can cause a decrease in the protective characteristics of the composition in relation to seals, which can cause leakage at the joints. If the system is zinc coated, the use of antifreeze is unacceptable. When overheated, increased foaming appears, which means that airing the system is guaranteed. Therefore, in order to exclude all these phenomena, it is necessary to strictly control the heating process. As boiler manufacturers do not know the physical properties of the heat transfer fluids used (other than water), they exclude their use.
Problem #3
Antifreezes have increased fluidity. Consequently, an increase in the number of connecting places and elements entails an increase in the likelihood of leakage. And basically, such a problem appears when the system has cooled down, when the heating is turned off. When cooled, the volume of metal compounds decreases, microchannels appear, through which the composition oozes.
Therefore, it is important that all system connections are available. Given the toxicity of antifreezes, they cannot be used to heat water in hot water systems
Otherwise, the mixture may enter the hot water outlets, which will pose a danger to residents.

Properties and features of the use of antifreezes in heating systems
For private heating systems, two types of antifreezes can be found on sale: aqueous solutions of ethylene glycol and propylene glycol. Glycols, unlike water, gradually pass into the solid phase with decreasing temperature: the range from the temperature of the beginning of crystallization to complete solidification is 10-15 ° C. In this range, the liquid gradually thickens, turns into a gel-like “sludge”, but does not increase in volume. Glycols are sold in two "formats":
- Concentrate with crystallization start temperature -65 °С. It is assumed that the buyer himself will dilute it with softened water to the required parameters. Only ethylene glycol antifreezes are sold in the form of a concentrate.
- Ready-to-use solutions with a freezing point of -30 °C.
To save the concentrate, the homeowner can further dilute it to obtain a freezing point of -20 or -15 °C. Do not dilute anti-freeze by more than 50% - this reduces its protective properties.
All antifreeze fluids contain additive additives. Their purpose:
- protection of metal elements of the system from corrosion;
- dissolution of scale and precipitation;
- protection against destruction of rubber seals;
- foam protection.
Each brand of antifreeze has its own set of additives; there is no universal composition. Therefore, when choosing an anti-freeze, you should familiarize yourself with the types of additives and their purpose.
Antifreeze in the home heating system is very susceptible to overheating: when the critical temperature (each brand has its own) is exceeded, ethylene glycol and additives decompose, forming acids and solid precipitates. Soot appears on the heating elements of the boilers, the sealing elements are destroyed, and intense corrosion begins. When the additives are overheated and destroyed, foaming begins, and it leads to airing the system. For these reasons, boiler manufacturers strongly recommend not to use antifreeze, especially ethylene glycol, in the system.
Also, you can not use galvanized pipes: anti-freeze corrodes the zinc coating, white flakes form - an insoluble precipitate.

Destruction of a gas boiler burner caused by antifreeze
Filling the heating system with antifreeze occurs through the expansion tank. Every 4-5 years the coolant should be changed.
Antifreeze based on ethylene glycol
Ethylene glycol antifreezes are more common due to their comparative cheapness. However, ethylene glycol is a very toxic substance, even in diluted form, so it is strictly forbidden to use non-freezing liquids based on it in open heating systems, where the poison evaporates from the expansion tank into the surrounding area, and in two-circuit systems, where ethylene glycol can enter the hot water taps.
Important! Antifreezes on ethylene glycol are painted red, so their entry into the DHW system can be easily detected
Propylene Glycol Antifreeze
This is a new and more expensive generation of antifreeze. They are completely harmless, and food propylene glycol is even used in confectionery products under the guise of food additive E1520.Propylene glycol antifreezes are less aggressive to metal and sealing elements. Due to their harmlessness, they are recommended for use in two-circuit systems.
Important! Propylene glycol antifreeze is green
Green and red antifreeze liquids
Is it possible to pour antifreeze into the heating system
Automotive antifreeze antifreeze is made on the basis of ethylene glycol, but it is not intended for heating systems. Its additives are designed for the operating conditions of automobile engines, and act destructively on the elements of the heating system.
It is necessary to switch from water to antifreeze for home heating systems due to the threat of long-term power outages, which is important for areas remote from large cities. An alternative is to have backup power sources in the house, as well as the use of solid fuel boilers (burning wood, coal, pellets). But if the transition to non-freezing is inevitable, then it is better to entrust the design and installation of such a system to professionals so as not to damage expensive equipment.
What type of radiators is suitable for a heating system with antifreeze
The question in this section, which coolant to choose for aluminum, cast iron or steel radiators, is not worth it. This refers to antifreeze, not water. Because this issue does not affect the material from which the radiators are made. Modern antifreeze liquids do not adversely affect cast iron, steel, or aluminum. The only thing, and this has already been mentioned above, is that antifreeze cannot be poured into the system if it contains parts and assemblies made of galvanized steel.
The question is posed from a different angle.Namely, which heating radiators are suitable for antifreeze in terms of internal dimensions. After all, the whole point is that a viscous liquid creates pressure inside the system, which negatively affects the operation of the boiler and the circulation pump. So here are some recommendations:
- radiators with a large volume of internal space are installed;
- the expansion tank should be 10-15% larger;
- pump power is 10-20% higher;
- it is also better to increase the boiler in terms of power, because the total volume of the coolant also increases.
Methods for filling the system with coolant
The question of filling, as a rule, appears only in the case of a closed system, since open circuits are filled without problems through an expansion tank. A coolant is simply poured into it, which, under the action of gravity, spreads over all contours
It is important that all air vents are open.
There are several methods for filling a closed heating system with a coolant: by gravity, with a submersible pump, or using special pressure testing equipment. Let's take a closer look at each of the methods.
By gravity. This method of pumping coolant for a heating system, although it does not require equipment, takes a lot of time. It takes a long time to squeeze out the air and just as long to gain the desired pressure. By the way, it is pumped up with a car pump. So the equipment is still required.
We need to find the highest point. Usually, this is one of the gas vents (it must be removed). When filling, open the valve to drain the coolant (lowest point). When water runs through it, the system is full:
- When the system is full (water ran out of the drain tap), take a rubber hose about 1.5 meters long and attach it to the system inlet.
- Select the inlet so that the pressure gauge is visible. Install a non-return valve and a ball valve at this point.
- Attach an easily removable adapter for connecting a car pump to the free end of the hose.
- After removing the adapter, pour the coolant into the hose (keep it up).
- After filling the hose, use the adapter to connect the pump, open the ball valve and pump fluid into the system with the pump. You have to be careful not to let air in.
- When almost all the water contained in the hose has been pumped in, the valve closes and the operation is repeated.
- On small systems, to get 1.5 bar, you will have to repeat it 5-7 times, with large ones you will have to fiddle longer.
With this method, you can connect the hose from the water supply, you can pour the prepared water into the barrel, raise it above the entry point and so pour it into the system. Antifreeze is also poured in, but when working with ethylene glycol, you will need a respirator, protective rubber gloves and clothing. If a substance gets on a fabric or other material, it also becomes toxic and must be destroyed.
With a submersible pump. To create a working pressure, the coolant for the heating system can be pumped with a low-power submersible pump:
- The pump must be connected to the lowest point (not the system drain point) through a ball valve and a non-return valve, a ball valve must be installed at the system drain point.
- Pour the coolant into a container, lower the pump, turn it on. During operation, constantly add coolant - the pump should not drive air.
- During the process, monitor the manometer.As soon as its arrow has moved from zero, the system is full. Up to this point, the manual air vents on the radiators can be open - air will escape through them. As soon as the system is full, they must be closed.
- Next, you need to increase the pressure, continuing to pump the coolant for the heating system with a pump. When it reaches the required mark, stop the pump, close the ball valve
- Open all air vents (on radiators too). Air escapes, pressure drops.
- Turn on the pump again, pump in a little coolant until the pressure reaches the design value. Release the air again.
- So repeat until their air vents stop air coming out.
Then you can start the circulation pump, bleed the air again. If at the same time the pressure remains within the normal range, the coolant for the heating system is pumped. You can put it to work.
Pressure pump. The system is filled in the same way as in the case described above. In this case, a special pump is used. It is usually manual, with a container into which the coolant for the heating system is poured. From this container, liquid is pumped through a hose into the system.
When filling the system, the lever goes more or less easily, when the pressure rises, it is already harder to work. There is a pressure gauge on both the pump and the system. You can follow where it is more convenient.
Further, the sequence is the same as described above: pumped up to the required pressure, bled air, repeated again. So until there is no air left in the system. After - you also need to start the circulation pump for about five minutes, bleed the air. Also repeat several times.
Types and properties of heat-carrying liquids
The working fluid of any water system - the heat carrier - is a liquid that takes a certain amount of boiler energy and transfers it through pipes to heating devices - batteries or underfloor heating circuits. Conclusion: the efficiency of heating depends on the physical properties of the liquid medium - heat capacity, density, fluidity, and so on.
In 95% of private houses, ordinary or prepared water with a heat capacity of 4.18 kJ/kg•°C (in other units - 1.16 W/kg•°C, 1 kcal/kg•°C) is used, freezing at a temperature of about zero degrees. The advantages of a traditional heat carrier for heating are availability and low price, the main disadvantage is an increase in volume during freezing.

Crystallization of water is accompanied by expansion; cast-iron radiators and metal-plastic pipelines are equally destroyed by ice pressure
The ice that forms in the cold literally splits pipes, boiler heat exchangers and radiators. To prevent the destruction of expensive equipment due to defrosting, 3 types of antifreezes made on the basis of polyhydric alcohols are poured into the system:
- Glycerin solution is the oldest type of non-freezing coolant. Pure glycerin is a transparent liquid of increased viscosity, the density of the substance is 1261 kg / m³.
- An aqueous solution of ethylene glycol - dihydric alcohol with a density of 1113 kg / m³. The initial liquid is colorless, inferior in viscosity to glycerin. The substance is toxic, the lethal dose of dissolved glycol when taken orally is about 100 ml.
- The same, based on propylene glycol - a transparent liquid with a density of 1036 kg / m³.
- Compositions based on a natural mineral - bischofite. We will analyze the characteristics and features of this chemical separately (below in the text).
Antifreezes are sold in two forms: ready-made solutions designed for a certain sub-zero temperature (usually -30 ° C), or concentrates that the user dilutes with water himself. We list the properties of glycol antifreezes that affect the operation of heating networks:
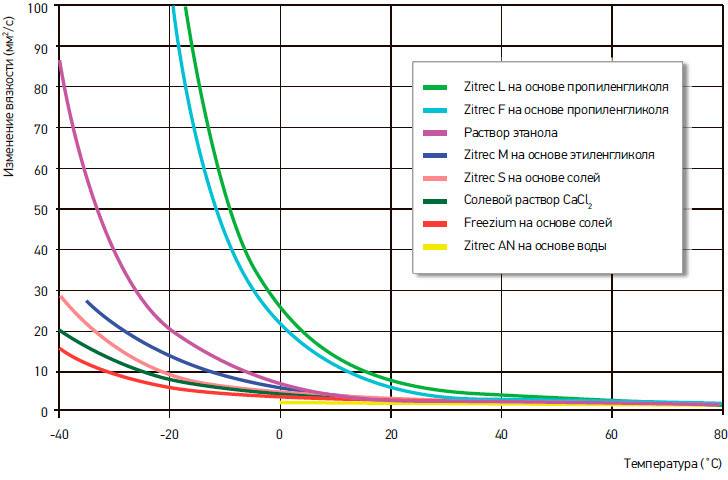
- Low crystallization temperature. Depending on the concentration of polyhydric alcohol in an aqueous solution, the liquid begins to freeze at a temperature of minus 10 ... 40 degrees. The concentrate crystallizes at 65°C below zero.
- High kinematic viscosity. Example: for water, this parameter is 0.01012 cm² / s, for propylene glycol - 0.054 cm² / s, the difference is 5 times.
- Increased fluidity and penetrating power.
- The heat capacity of non-freezing solutions lies in the range of 0.8 ... 0.9 kcal / kg ° C (depending on concentration). On average, this parameter is 15% lower than that of water.
- Aggressiveness to some metals, for example, zinc.
- From heating, the substance foams, when boiled, it quickly decomposes.

Propylene glycol antifreezes are usually dyed green, and the prefix "ECO" is added to the marking.
In order for antifreezes to meet operational requirements, manufacturers add additive packages to glycol solutions - corrosion inhibitors and other elements that maintain antifreeze stability and reduce foaming.
We choose "anti-freeze" for heating
Tip number one: buy and fill antifreeze only in extreme cases - for periodic heating of remote country houses, garages or buildings under construction. Try to use water - regular and distilled, this is the least troublesome option.
When choosing a frost-resistant coolant, observe the following recommendations:
- If your budget is limited, take ethylene glycol of any well-known brand - Teply Dom, Dixis, Spektrogen Teplo OZH, Bautherm, Termo Tactic or Termagent. The cost of the concentrate -65 °C from Dixis is only 1.3 cu. e. (90 rubles) per 1 kg.
- If there is a danger of antifreeze getting into domestic water (for example, through an indirect heating boiler, a double-circuit boiler), or you are very worried about the environment and safety, buy harmless propylene glycol. But keep in mind: the price of the chemical is higher, the ready-made Dixis solution (minus 30 degrees) will cost 100 rubles (1.45 USD) per kilogram.
- For large heating systems, we recommend using premium HNT coolant. The liquid is made on the basis of propylene glycol, but it has an extended service life of 15 years.
- Do not buy glycerin solutions at all. Causes: precipitation in the system, too high viscosity, tendency to foam, a large number of low-quality products made from technical glycerin.
- For electrode boilers, a special liquid is needed, for example, XNT-35. Be sure to consult with the manufacturer's representative before use.
- Do not confuse automotive antifreeze with heating chemicals. Yes, both formulations are based on glycol, but the additive packages are completely different. The engine coolant is not compatible with domestic hot water heating.
- For open and gravity heating systems, it is better to use water, in extreme cases - propylene glycol diluted by minus 20 ° C.
- If the heating wiring is made with galvanized pipes, it makes no sense to purchase glycol mixtures.The substance will deal with zinc, lose the package of additives and quickly degrade.
There is a lot of controversy on the topic of the harmfulness of ethylene glycol compounds, including on the pages of construction forums
Without denying the harmful effects of the chemical on human health, let us pay attention to the convincing fact
Homeowners whose closed systems are well installed have enjoyed inexpensive glycol for years without any problems. Let's listen to the expert's opinion on the video: