- The use of heat accumulators
- We summarize: What are the advantages and disadvantages of using buffer tanks?
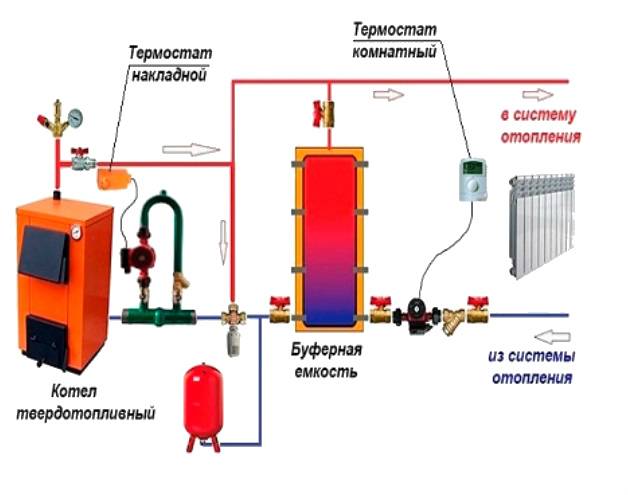
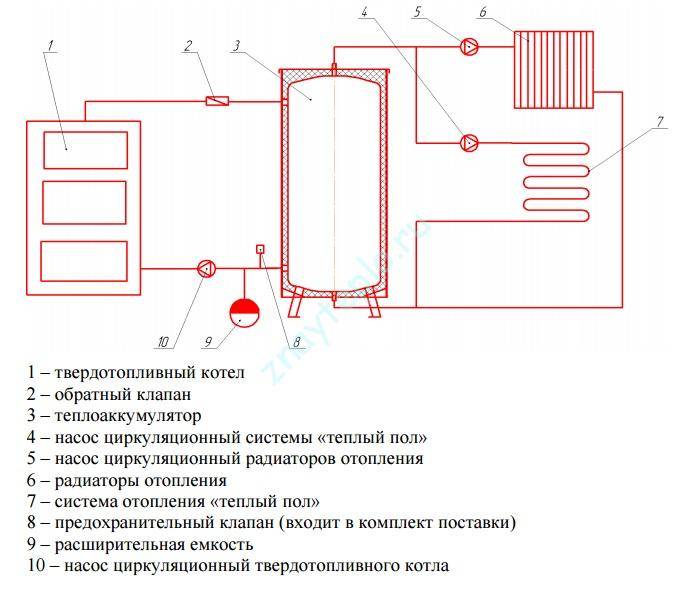
- The principle of operation of the system with a solid fuel boiler
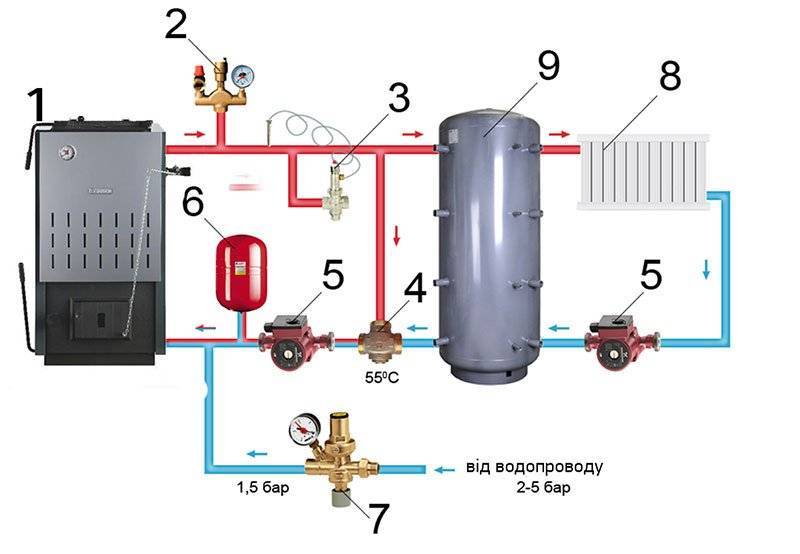
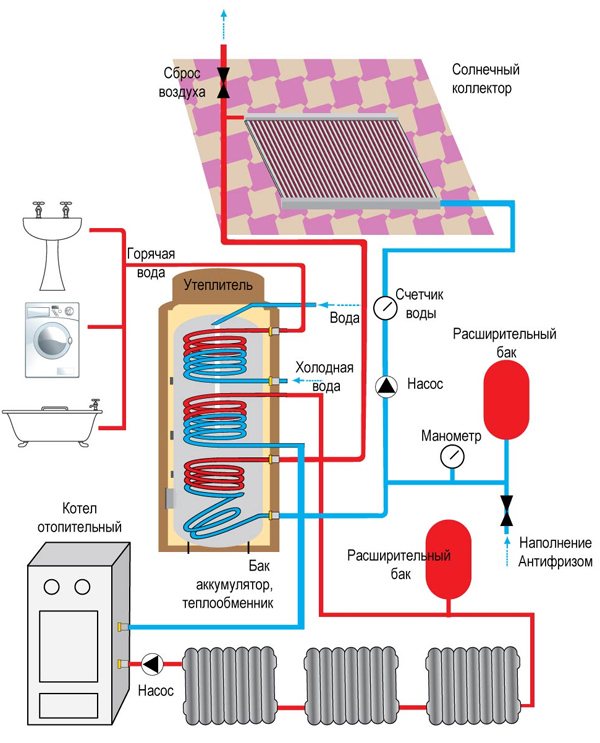
- How does a heating system with a heat accumulator work?
- Heat accumulator: purpose and principle of operation
- 3 Accessories
- Do-it-yourself heat accumulator: diagrams and description of the process
- Warming of the heat accumulator
- What is a heat accumulator and what is it for?
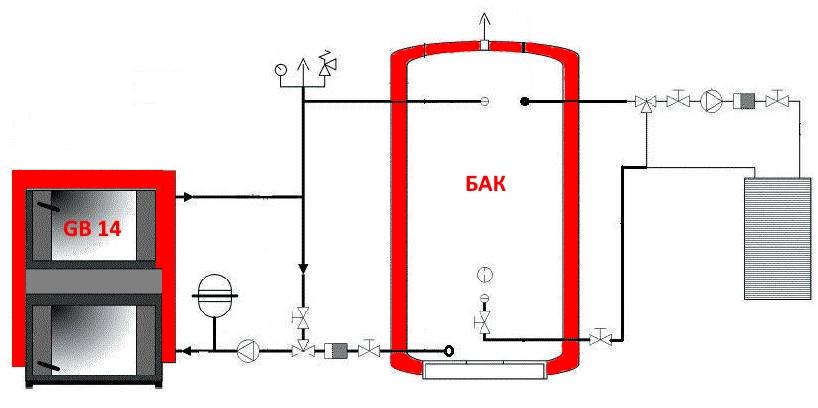
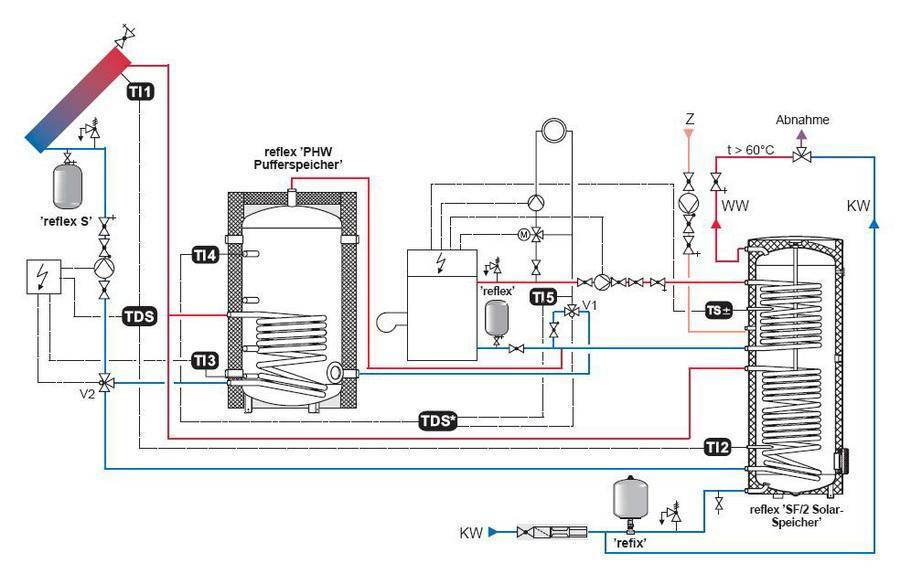
- Choosing a heat accumulator
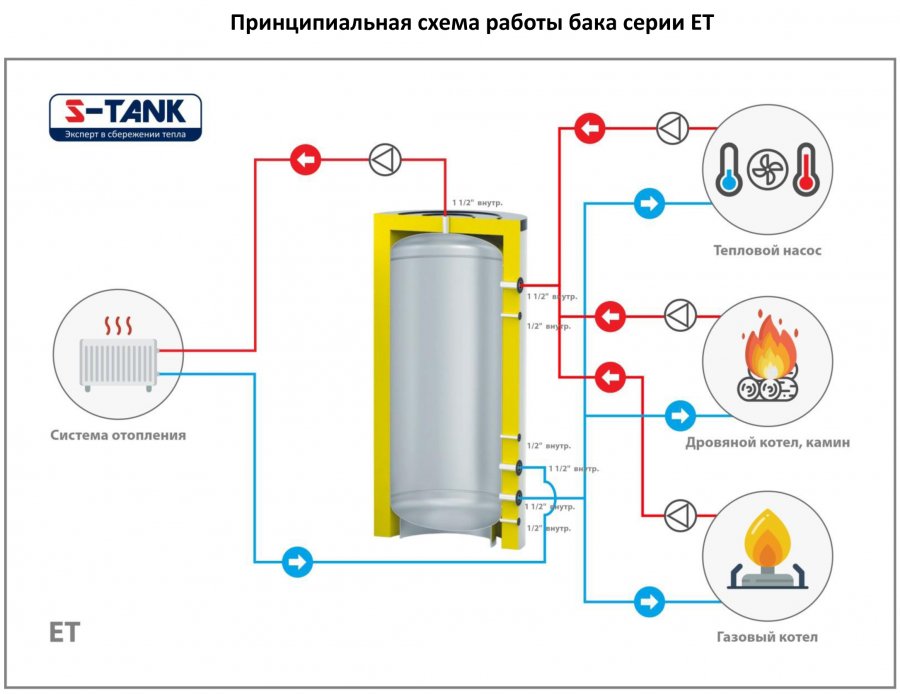
- Heat accumulator piping schemes
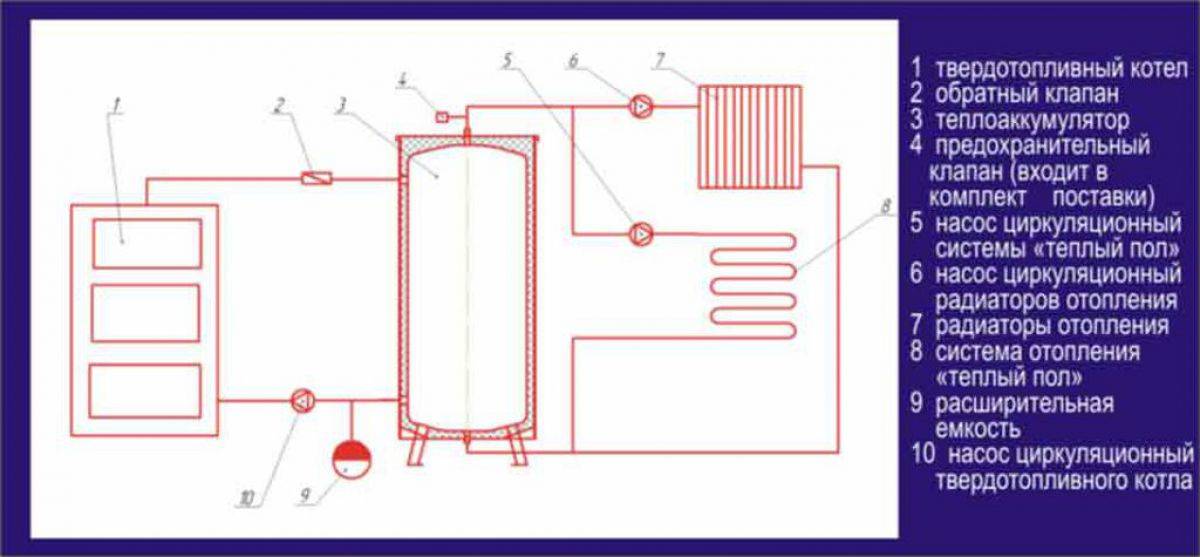
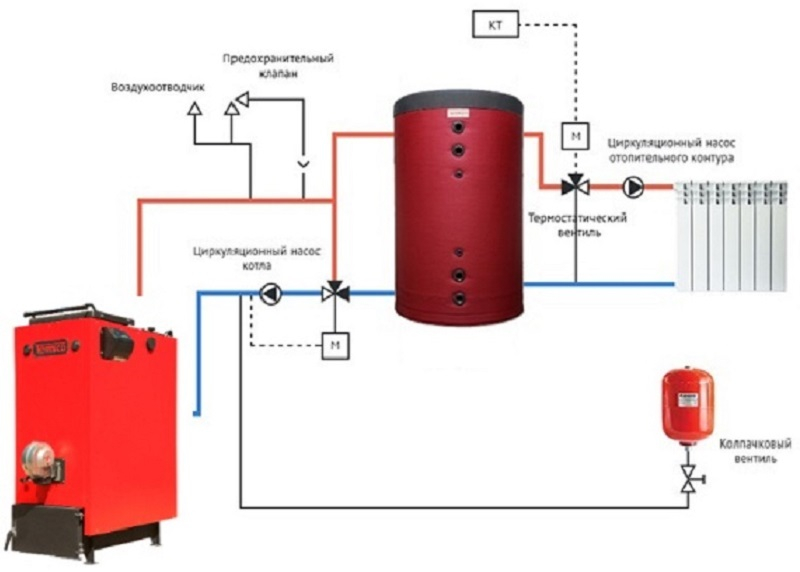
- Scheme with a solid fuel boiler and a heat accumulator
- Key functions of heat storage
The use of heat accumulators
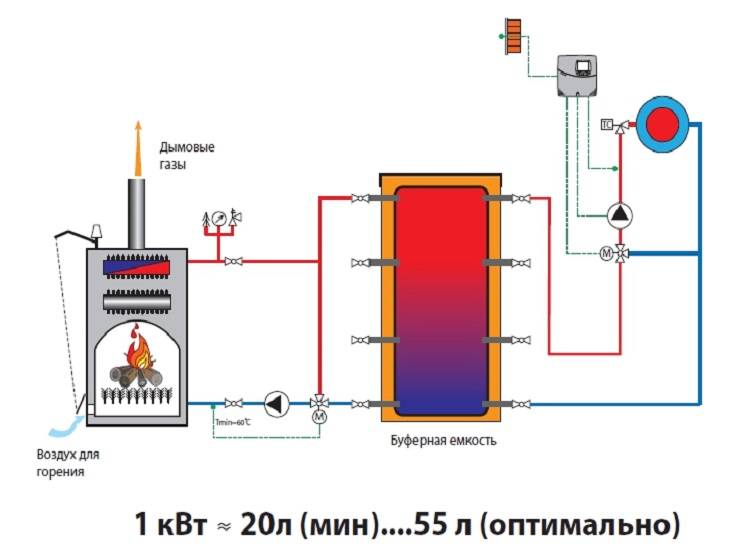
There are several methods for calculating the volume of a tank. Practical experience shows that, on average, 25 liters of water are additionally needed for each kilowatt of heating equipment. The efficiency of solid fuel boilers, which includes a heating system with a heat accumulator, increases to 84%. Due to the leveling of combustion peaks, up to 30% of energy resources are saved.
When using tanks for supplying domestic hot water, there are no interruptions during peak hours. At night, when the needs are reduced to zero, the coolant in the tank accumulates heat and in the morning again provides all the needs in full.
Reliable thermal insulation of the device with foamed polyurethane (polyurethane foam) allows you to save the temperature. Additionally, it is possible to install heating elements, which helps to quickly “catch up” with the desired temperature in case of emergency.
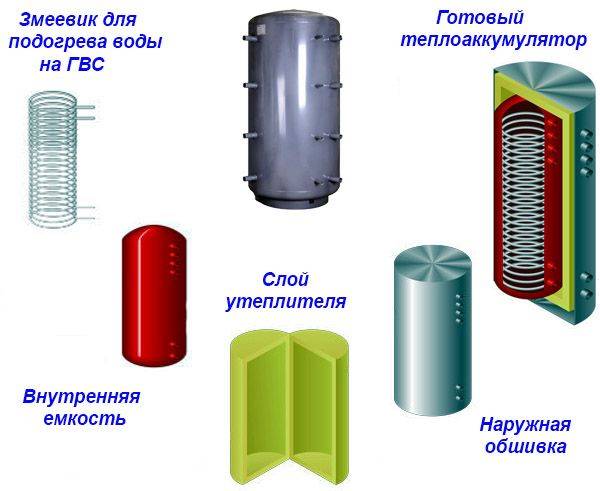
Sectional heat accumulator
Heat storage is recommended in cases of:
- high demand for hot water. In a cottage where more than 5 people live, and two bathrooms are installed, this is a real way to improve living conditions;
- when using solid fuel boilers. Accumulators smooth the operation of heating equipment during the hour of greatest load, take away excess heat, preventing boiling, and also increase the time between laying solid fuel;
- when using electric energy at separate tariffs for day and night;
- in cases where solar or wind batteries are installed to store electrical energy;
- when used in the heat supply system of circulation pumps.
This system is perfect for rooms heated by radiators or underfloor heating. Its advantages are that it is able to accumulate energy received from different sources. The combined energy supply system allows you to choose the most optimal option for obtaining heat in a given period of time.
We summarize: What are the advantages and disadvantages of using buffer tanks?
The obvious "pluses" of autonomous solid fuel heating systems with a heat accumulator include the following:
- The energy potential of solid fuel is used to the maximum extent possible. Accordingly, the efficiency of boiler equipment increases sharply.
- The operation of the system will require much less human intervention - from reducing the number of boiler loadings with fuel to expanding the possibilities of automating the control of the operating modes of various heating circuits.
- The solid fuel boiler itself receives reliable protection against overheating.
- The operation of the system becomes smoother and more predictable, providing a differentiated approach to heating different rooms.
- There are ample opportunities for upgrading the system, including the launch of additional sources of thermal energy, without dismantling the old ones.
- In most cases, the problem of hot water supply at home is also solved at the same time.
The disadvantages are very peculiar, and you also need to be aware of them:
- The heating system, equipped with a buffer tank, is characterized by a very large inertia. This means that a lot of time will be required from the moment of initial ignition of the boiler to reaching the nominal operating mode. It is unlikely that this will be justified in a country house, which in winter the owners visit only on weekends - in such situations, rapid heating is required.
- Heat accumulators are bulky and heavy (especially when filled with water) structures. They require enough space and a well-prepared solid foundation. And - close to the heating boiler. This is not possible in every boiler room. Plus, there are difficulties with delivery by unloading, and often also with bringing the container into the room (it may not go through the door). All this should be taken into account in advance.
- The disadvantages include the very high price of such devices, which sometimes even exceeds the cost of the boiler.This "minus", however, brightens up the expected savings effect from a more rational use of fuel.
- The heat accumulator will fully reveal its positive qualities only if the nameplate power of the solid fuel boiler (or the total power of other heat sources) is at least twice as high as the calculated value required for efficient heating of the house. Otherwise, the acquisition of buffer capacity is seen as unprofitable.
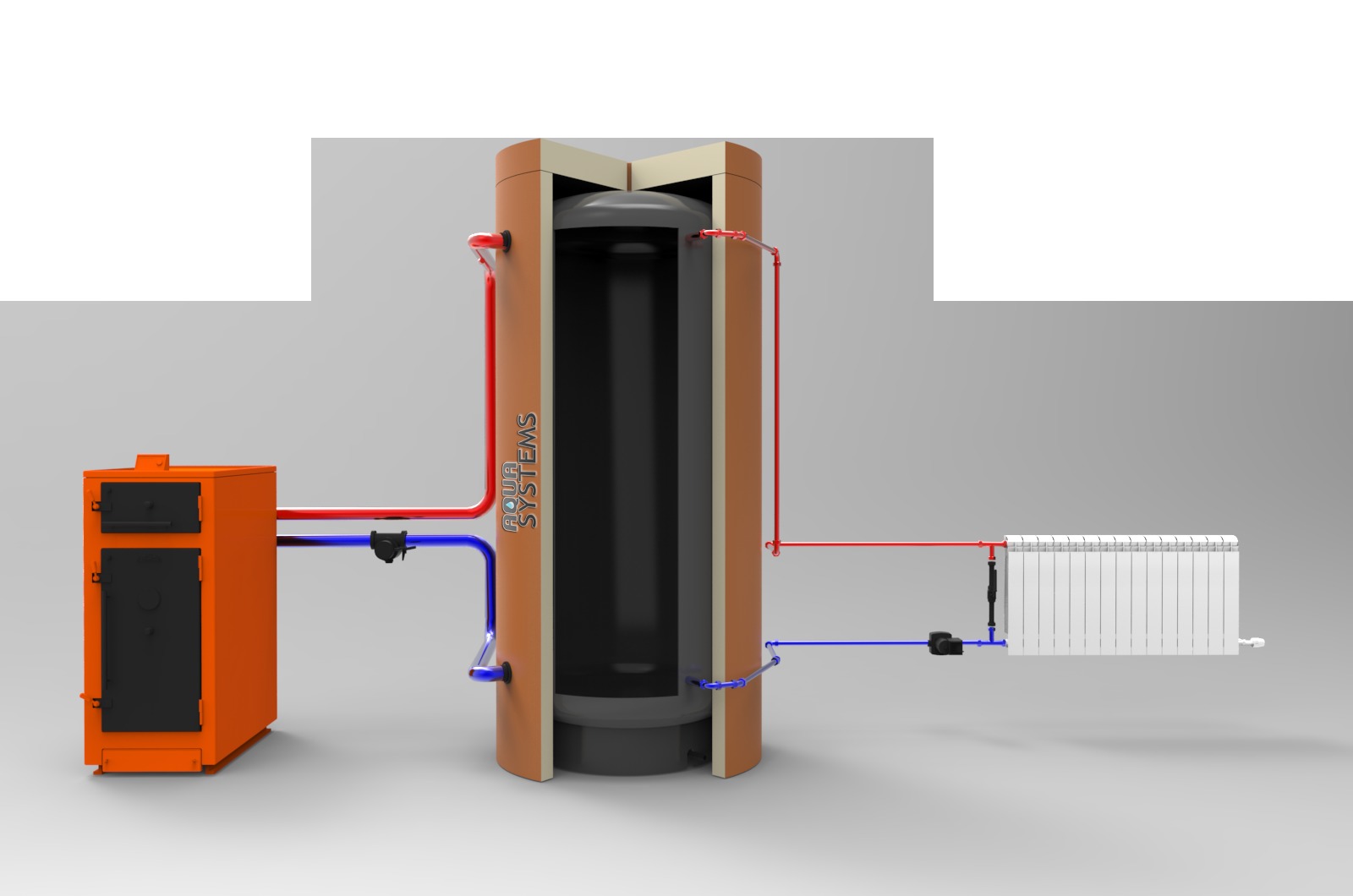
The principle of operation of the system with a solid fuel boiler

The heat released during the combustion of fuel, through the heat exchanger through the pipeline, enters the registers or radiators, which are essentially the same heat exchangers, only they do not receive heat, but, on the contrary, give it to surrounding objects, air, in general, to the heating room.
Cooling down, the coolant - water in the batteries, goes down and again flows into the boiler heat exchanger circuit, where it heats up again. In such a scheme, there are at least two points associated with a large, if not a huge loss of heat:
- direct direction of movement of the coolant from the boiler to the registers and rapid cooling of the coolant;
- a small volume of coolant inside the heating system, which does not allow maintaining a stable temperature;
- the need to constantly maintain a consistently high temperature of the coolant in the boiler circuit.
It is important to understand that such an approach can only be called wasteful. After all, when laying fuel, first at a high combustion temperature in the premises, the air warms up quite quickly
But, as soon as the combustion process stops, the heating of the room will also end, and as a result, the temperature of the coolant will drop again, and the air in the room will cool.
How does a heating system with a heat accumulator work?
A heat accumulator for heating boilers is a part of the heating system designed to increase the time between loading solid fuel into the boiler. It is a reservoir in which there is no air access. It is insulated and has a fairly large volume. There is always water in the heat accumulator for heating, it also circulates throughout the circuit. Of course, an antifreeze liquid can also be used as a coolant, but still, due to its high cost, it is not used in circuits with TA.
In addition to this, in filling the heating system with a heat accumulator with antifreeze it makes no sense, since such tanks are placed in residential premises. And the essence of their application is to ensure that the temperature in the circuit is always stable, and, accordingly, the water in the system is warm. The use of a large heat accumulator for heating in country houses of temporary residence is impractical, and there is little sense from a small reservoir. This is due to the principle of operation of the heat accumulator for the heating system.
- The TA is located between the boiler and the heating system. When the boiler heats up the coolant, it enters the TA;
- then the water flows through the pipes to the radiators;
- The return line returns to the TA, and then immediately to the boiler.
In order for TA to perform its primary function of heat storage, these streams must be mixed. The difficulty lies in the fact that the heat always rises, and the cold tends to fall. It is necessary to create such conditions that part of the heat sinks to the bottom of the heat accumulator in heating system and heated the coolant return lines.If the temperature has evened out in the entire tank, then it is considered fully charged.
After the boiler fired everything that was loaded into it, it stops working and TA comes into play. The circulation continues and it gradually releases its heat through the radiators into the room. All this happens until the next portion of fuel enters the boiler again.
If the heat storage for heating is small, then its reserve will last for a very short time, while the heating time of the batteries increases, since the volume of the coolant in the circuit has become larger. Cons of using for temporary residences:
- the warm-up time increases;
- a larger volume of the circuit, which makes filling it with antifreeze more expensive;
- higher installation costs.
As you understand, filling the system and draining water every time you arrive at your dacha is at least troublesome. Considering that the tank alone will be 300 liters. For the sake of several days a week, it is pointless to take such measures.
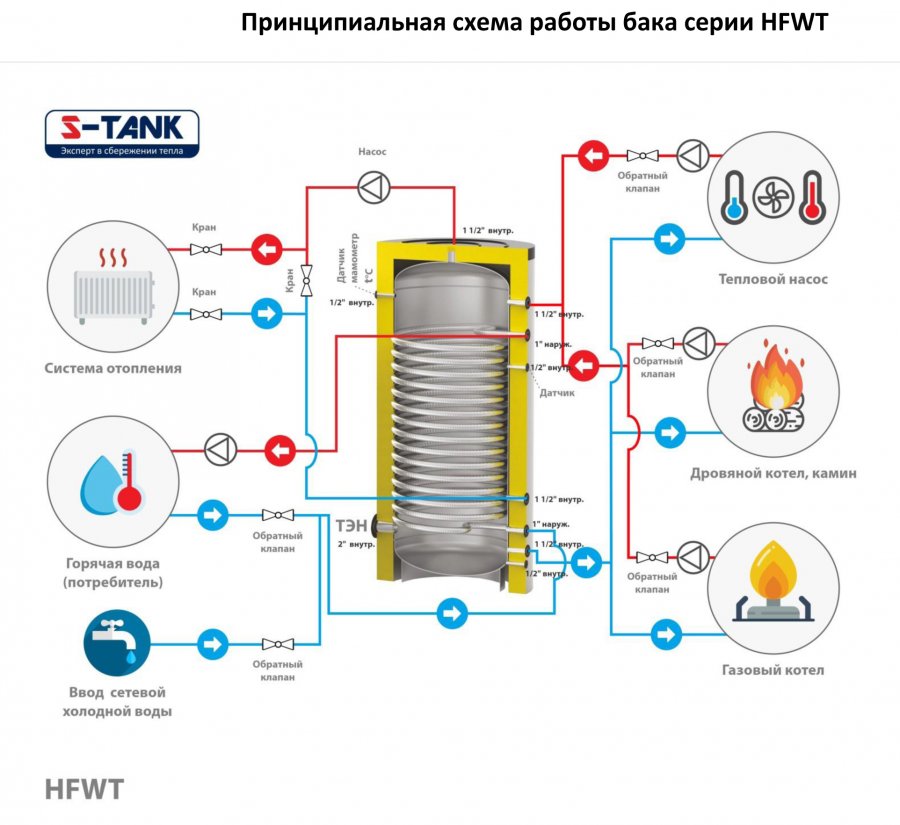
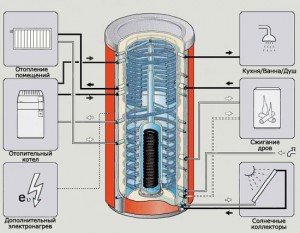
Additional circuits are built into the tank - these are metal spiral pipes. The liquid in the spiral does not have direct contact with the coolant in the heat accumulator for heating the house. These can be contours:
- DHW;
- low-temperature heating (warm floor).
Thus, even the most primitive single-circuit boiler or even a stove can become a universal heater. It will provide the entire house with the necessary heat and hot water at the same time. Accordingly, the performance of the heater will be fully utilized.
In serial models manufactured under production conditions, additional heating sources are built in. These are also spirals, only they are called electric heating elements.There are often several of them and they can work from different sources:
- circuit;
- solar panels.
Such heating refers to additional options and is not mandatory, consider this if you decide to make a heat accumulator for heating with your own hands.
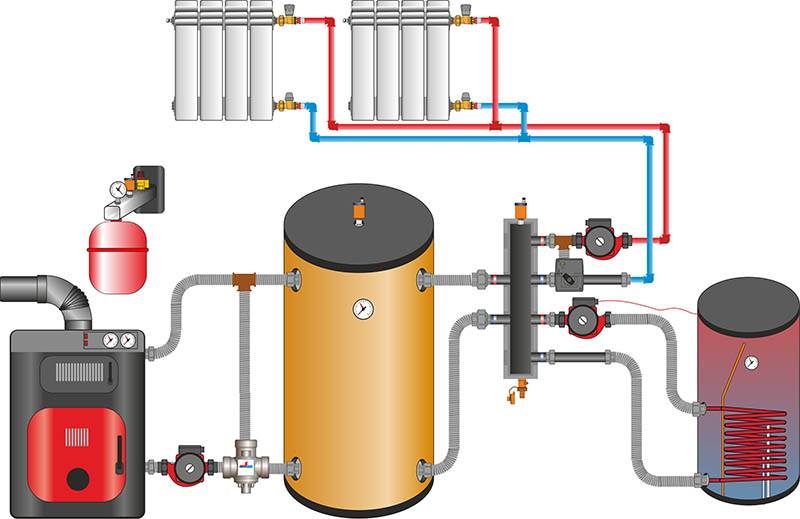
Heat accumulator: purpose and principle of operation
With the purpose of the heat accumulator, everything is more or less clear - it serves to make-up of the heating system hot water in those moments when the boiler is not able to heat water for any reason. In addition, one of the side effects in the operation of this device is the ability to save energy resources - if you allow the heat accumulator to discharge in a timely manner, you can achieve a twenty percent reduction in energy consumption. And this in our age, believe me, is not so little. By the way, if you wish, you can install such a device in a heating system with any boiler - there is, however, one drawback that you have to put up with - these are its dimensions (if there is no special room (furnace), then it will take quite a lot of usable area).
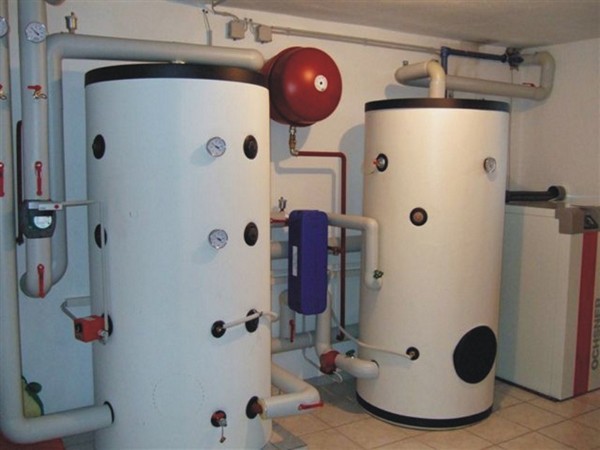

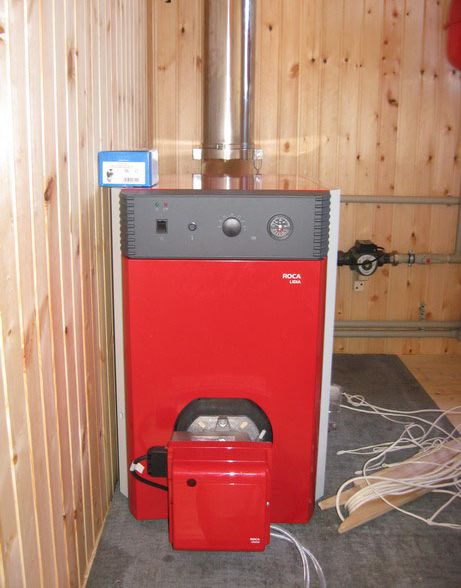
Heat accumulator for solid fuel boiler photo
The heat accumulator for a solid fuel boiler works elementarily simply - in fact, it is a large, well-insulated storage tank, into which the most heated coolant enters during the operation of the boiler. Thanks to, that it crashes into the heating system the first from the stake, the water in it is constantly updated at a high speed and has the highest temperature.When the boiler stops working due to lack of fuel, the water that has cooled in the main pipelines gradually begins to squeeze the hot coolant out of the tank into the system, thereby ensuring its uninterrupted operation for your benefit. It should be understood that the resource of this device is limited, and it will not be enough for a long time. Although, with proper system setup and high-quality insulation of the building, you will be provided with a warm night!

Heat accumulators for heating photo
3 Accessories
The buffer tank for the boiler is presented in the form of a conventional metal barrel, with external thermal insulation
Despite the very simple design, this unit is highly efficient and economical, which is very important in the heating system.
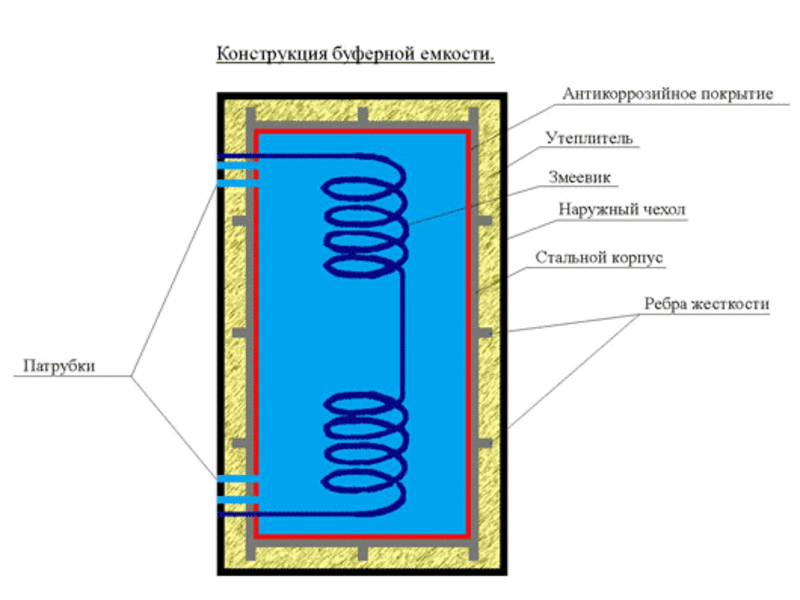
In order for such an apparatus to function correctly, you need to know what elements it consists of and what function they all perform:
Spiral heat exchanger. This element is installed only in those models that are connected to the heating system with several types of heat carriers at once (powerful solar collectors, heat pump). For its manufacture exclusively stainless steel is used.
Capacious tank. Available in enamelled sheet metal or stainless steel. Special pipes depart from the tank, which intended for connection to the system heating and heat generator
It is important to understand that the duration of its operation depends on the material from which the tank is made.
Built-in DHW coil. Some modern models, in addition to maintaining the heating temperature of the filled coolant, heat water for domestic purposes.
Do-it-yourself heat accumulator: diagrams and description of the process
If you decide to create a heat accumulator with your own hands, you must:
- Perform a capacity calculation.
- Determine the appropriate design - the container can be cylindrical or rectangular.
- Prepare the necessary materials and components.
- Assemble and check the device for leaks.
- Connect the container to the heating system.
The volume of the tank will determine how long the heat will last in the room during the shutdown of the boiler. The photo shows the calculation of the volume for a room of 100 m²:

The optimal storage for storing the heated coolant will be a cylindrical tank with convex bottoms. This form allows you to store a fairly large amount of water. Such containers can only be manufactured in the factory.
A home master will greatly facilitate the task if he finds an opportunity and uses a ready-made container. For this you can use:
- Cylinders for storage and transportation of gas.
- Unused containers that are intended for operation under pressure.
- Receivers that were installed in the pneumatic system of railway transport.
But, of course, the use of homemade tanks is also acceptable. For their manufacture, sheet metal with a thickness of at least 3 mm is used. Inside the container, an 8-15-meter copper tube, 2-3 cm in diameter, pre-bent into a spiral, is placed. A pipe is placed on top of the tank for draining hot water, and the same for cold water at the bottom. Each is equipped with a tap to control the flow of fluid.

The normal operation of the thermal storage is based on the movement of hot and cold coolant inside, the time of "charging" the battery. It should be carried out strictly horizontally, and at the time of "discharge" - vertically.
To ensure such a movement, it is necessary to ensure that a few simple rules are followed:
- The boiler circuit must be connected to the storage tank through a circulation pump.
- The heating system is supplied with a working fluid using a separate pumping unit and a mixer, which includes a three-way valve - it takes the required volume of water from the storage tank.
- The pumping unit, which is installed in the boiler circuit, cannot be inferior in efficiency to the unit that supplies the working fluid to the heating devices.
Warming of the heat accumulator
How are containers insulated? For solution to this problem is the best consider basalt wool, the thickness of which is 60–80 mm. Styrofoam or extruded polystyrene foam is not recommended. Another reason why cotton wool is used is its fire safety. Thermal insulation is installed between the tank and a metal casing, which is made of sheet metal - it must be painted.
What is a heat accumulator and what is it for?
The heat accumulator is a steel hermetic insulated tank made of black steel, having branch pipes - two upper and two lower ones in order to connect the source and consumer of heat. Heat accumulator for heating reviews show that this is an effective device. And it serves to accumulate excess energy that the heat source (boiler) emits.
 Heat accumulator for heating
Heat accumulator for heating
So, if your solid fuel boiler operates in the optimal combustion mode (at full power) from fuel loading to its complete combustion, then there will be a maximum effect. Thus, the resulting heat enters the heating system. But the system does not always need so much heat. It is for these purposes that the buffer capacity of the heating system exists.
Choosing a heat accumulator
TA is chosen when designing a heating system. Thermal engineers will help you choose the right heat accumulator. But, if it is impossible to use their services, you will have to choose on your own. It is not difficult to do this.
Heat accumulator for solid fuel boiler
The main criteria for the selection of this device are considered to be the following :
- pressure in the heating system;
- the volume of the buffer tank;
- external dimensions and weight;
- equipment with additional heat exchangers;
- the possibility of installing additional devices.
Water pressure (pressure) in the heating system is the main indicator. The higher it is, the warmer it is in the heated room.
Given this parameter, when choosing a heat accumulator for solid fuel boilers, attention is paid to the maximum pressure that it can withstand. The heat accumulator for a solid fuel boiler, shown in the photo, is made of stainless steel and can withstand high water pressure. Buffer capacity
The ability to accumulate heat for the heating system during operation depends on it. The larger it is, the more heat will accumulate in the container. Here you need to take into account that it is pointless to raise the limit to infinity. But if the water is less than the norm, the device simply will not perform the function of heat accumulation assigned to it.Therefore, for the correct choice of a heat accumulator, it will be necessary to calculate its buffer capacity. We'll show you how it's done a bit later.
The volume of the buffer tank. The ability to accumulate heat for the heating system during operation depends on it. The larger it is, the more heat will accumulate in the container. Here you need to take into account that it is pointless to raise the limit to infinity. But if the water is less than the norm, the device simply will not perform the function of heat accumulation assigned to it. Therefore, for the correct choice of a heat accumulator, it will be necessary to calculate its buffer capacity. A little later, it will be shown how it is performed.
External dimensions and weight. These are also important indicators when choosing a TA. Especially in an already built house. When the calculation of the heat accumulator for heating is made, delivery to the installation site is carried out, there may be a problem with the installation itself. In terms of overall dimensions, it may simply not fit into a standard doorway. In addition, large-capacity TAs (from 500 liters) are installed on a separate foundation. A massive device filled with water will become even heavier. These nuances must be taken into account. But it's easy to find a way out. In this case, two heat accumulators for solid fuel boilers are purchased with a total volume of buffer tanks equal to the calculated one for the entire heating system.
Equipment with additional heat exchangers. In the absence of a hot water system in the house, its own water heating circuit in the boiler, it is better to immediately purchase a TA with additional heat exchangers. For those living in the southern regions, it will be useful to connect a solar collector to the TA, which will become an additional free source of heat in the house.A simple calculation of the heating system will show how many additional heat exchangers it is desirable to have in a heat accumulator.
Possibility to install additional devices. This implies the installation of heating elements (tubular electric heaters), instrumentation (instruments), safety valves and other devices, ensuring uninterrupted and safe operation of the buffer tank in the device. For example, in case of emergency attenuation of the boiler, the temperature in the heating system will be maintained by heating elements. Depending on the volume of space heating, they may not create a comfortable temperature, but they will definitely prevent defrosting of the system.
The presence of instrumentation will allow timely attention to possible problems that have arisen in the heating system
Important
When choosing a heat accumulator for heating, pay attention to its thermal insulation. It depends on the conservation of the received heat.
Heat accumulator piping schemes
We dare to assume that if you are interested in this article, then most likely you decided to make a heat accumulator for heating and tie it yourself. You can come up with a lot of connection schemes, the main thing is that everything works. If you correctly understand the processes taking place in the circuit, then you can quite experiment. How you connect the HA to the boiler will affect the operation of the entire system. Let's first analyze the simplest heating scheme with a heat accumulator.
Simple TA piping diagram
In the figure you see the direction of movement of the coolant
Please note that upward movement is prohibited.To prevent this from happening, the pump between the TA and the boiler must pump a larger amount of coolant than the one that stands up to the tank. Only in this case will a sufficient retracting force be formed, which will take part of the heat from the supply
The disadvantage of such a connection scheme is the long heating time of the circuit. To reduce it, you need to create a boiler heating ring. You can see it in the following diagram.
Only in this case will a sufficient retracting force be formed, which will take part of the heat from the supply. The disadvantage of such a connection scheme is the long heating time of the circuit. To reduce it, you need to create a boiler heating ring. You can see it in the following diagram.
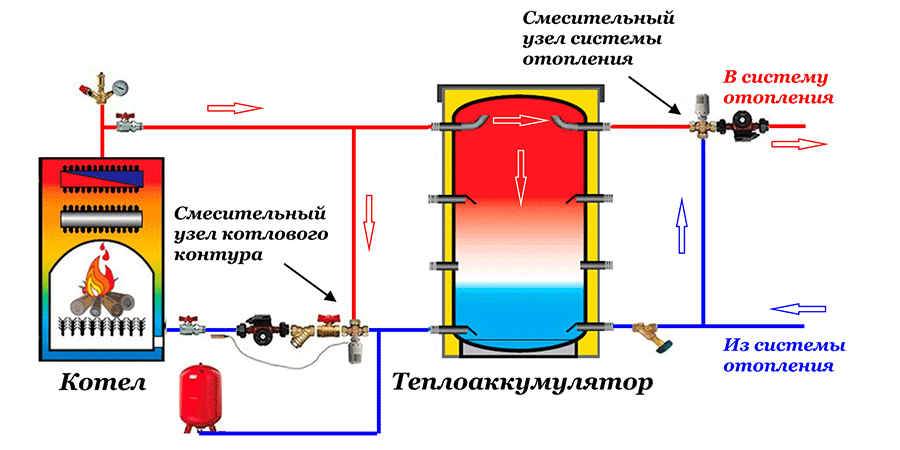
TA piping scheme with a boiler heating circuit
The essence of the heating circuit is that the thermostat does not mix water from the TA until the boiler warms it up to the set level. When the boiler is warmed up, part of the supply goes to the TA, and the part is mixed with the coolant from the reservoir and enters the boiler. Thus, the heater always works with an already heated liquid, which increases its efficiency and the heating time of the circuit. That is, the batteries will get warm faster.
This method of installing a heat accumulator in the heating system allows you to use the circuit in offline mode when the pump will not work.
Please note that the diagram shows only the nodes for connecting the TA to the boiler. The circulation of the coolant to the radiators occurs in a different way, which also passes through the TA. The presence of two bypasses allows you to play it safe twice:
The presence of two bypasses allows you to play it safe twice:
- the check valve is activated if the pump is stopped and the ball valve on the lower bypass is closed;
- in the event of a pump stop and a failure of the check valve, circulation is carried out through the lower bypass.
In principle, some simplifications can be made in such a construction. Given the fact that the check valve has a high flow resistance, it can be excluded from the circuit.
TA piping scheme without check valve for gravity system
In this case, when the light disappears, you will need to manually open the ball valve. It should be said that with such a wiring, the TA should be above the level of the radiators. If you do not plan that the system will work by gravity, then the piping of the heating system with a heat accumulator can be performed according to the scheme shown below.
Scheme of piping TA for a circuit with forced circulation
In TA, the correct movement of water is created, which allows ball after ball, starting from the top, to warm it up. Perhaps the question arises, what to do if there is no light? We talked about this in an article about alternative power sources for a heating system. It will be more economical and more convenient. After all, gravity circuits are made of large-section pipes, and besides, not always convenient slopes must be observed. If you calculate the price of pipes and fittings, weigh all the inconveniences of installation and compare it all with the price of a UPS, then the idea of installing an alternative power source becomes very attractive.
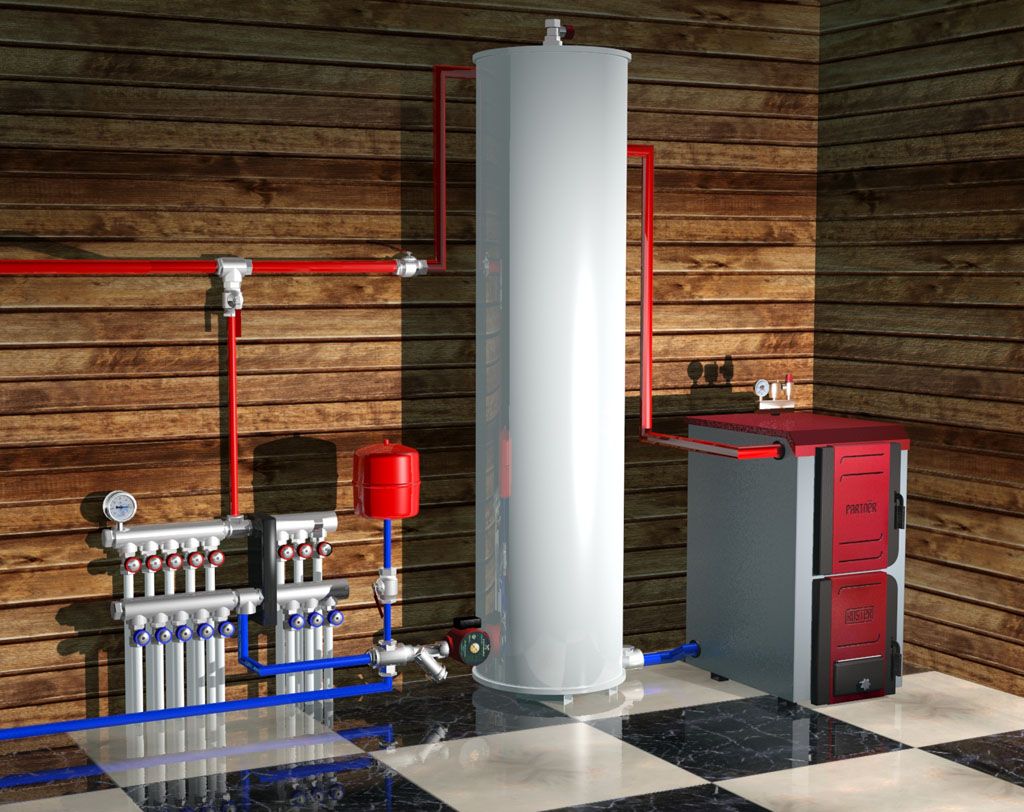
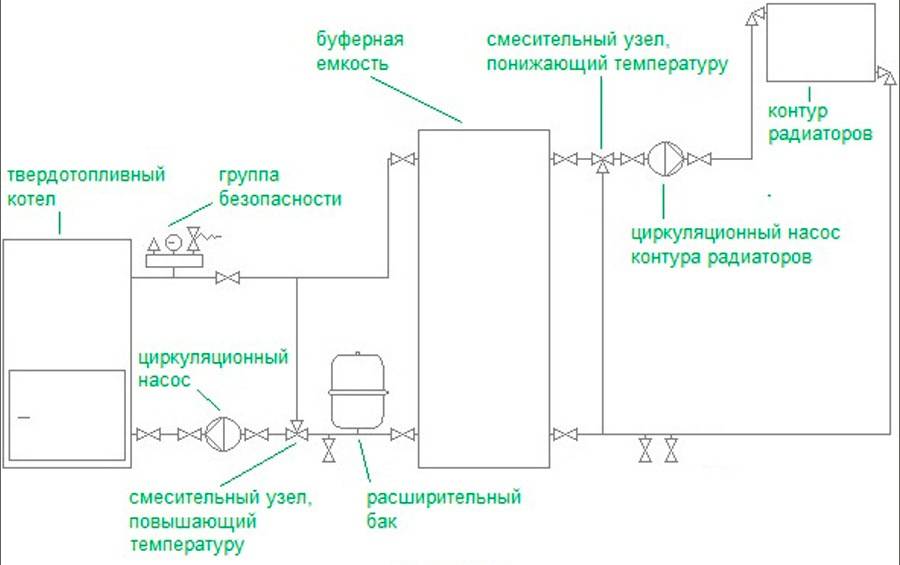
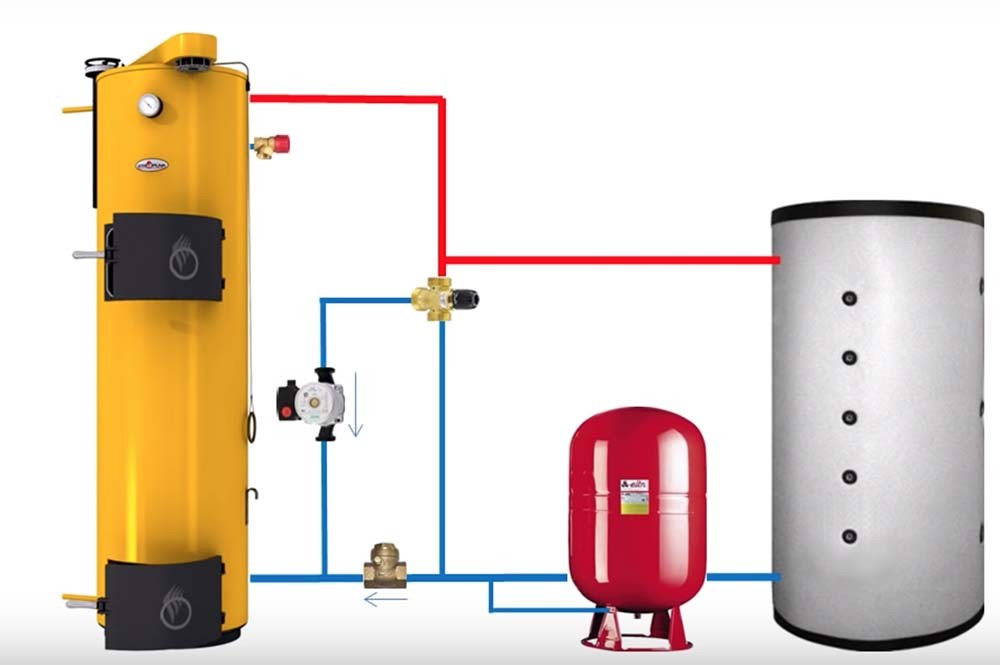
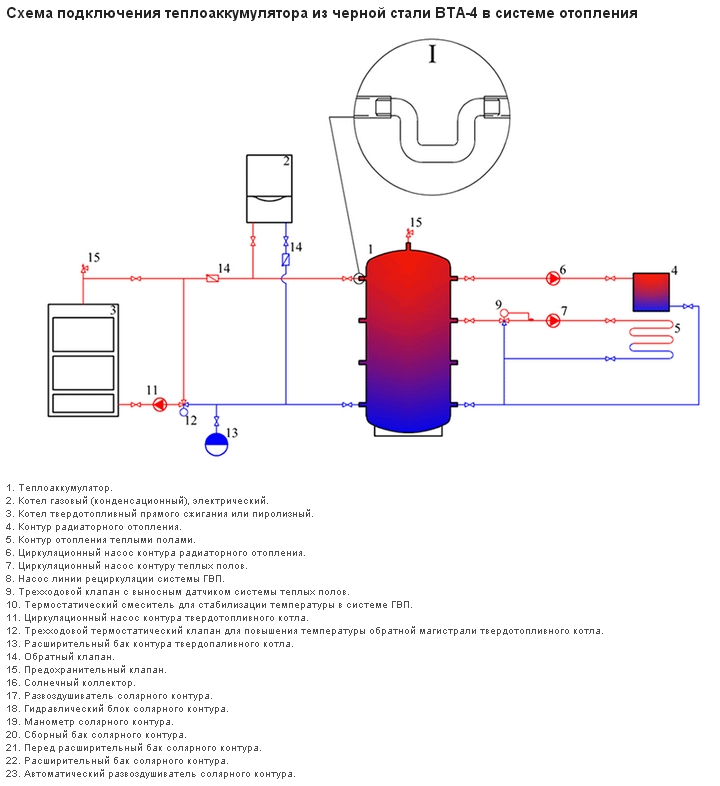
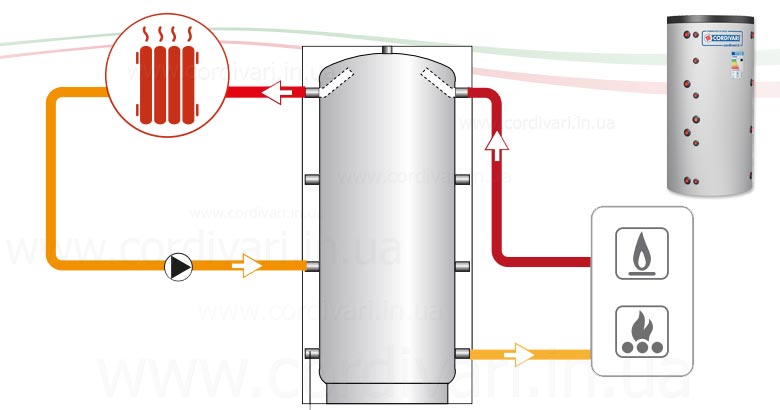
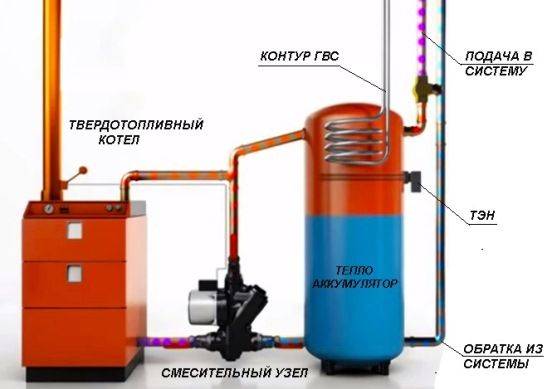
Scheme with a solid fuel boiler and a heat accumulator
 In this scheme, TA is an intermediate link between the boiler and the heating circuit. The coolant is heated in a solid fuel boiler, it passes through a safety group, which is immediately on the supply.Protection against low-temperature corrosion is provided: the circulation pump will pump the coolant in a closed circuit through the bypass until its temperature at the boiler inlet reaches 65 °C.
In this scheme, TA is an intermediate link between the boiler and the heating circuit. The coolant is heated in a solid fuel boiler, it passes through a safety group, which is immediately on the supply.Protection against low-temperature corrosion is provided: the circulation pump will pump the coolant in a closed circuit through the bypass until its temperature at the boiler inlet reaches 65 °C.
If the water temperature at the inlet to the boiler is below 65 °C, then condensate will begin to appear on the walls of the pipes passing inside the boiler. This will lead to increased corrosion, and the device will quickly fail.
After that, the valve on the bypass closes and the coolant begins to heat the water in the storage tank. After the fuel burns out, the boiler circuit is closed. Fence starts coolant to the heating circuit from the top of the tank. Its temperature is regulated by a thermostatic three-way valve that dilutes hot water with cold return water. After passing through all the heating radiators, the water returns to the lower part of the heat accumulator. The system is closed, the medium is moved by means of circulation pumps.
Key functions of heat storage
The principle of operation of the heat accumulator
The heat accumulator has many useful features, including:
- providing the user with hot water;
- normalization of the temperature regime in heated rooms;
- increasing the efficiency of the heating system with a simultaneous decrease in heating costs;
- the possibility of combining several heat sources into a single circuit;
- accumulation of excess energy that the boiler produces, etc.
With all its advantages, heat accumulators have only 2 disadvantages, namely:
- the resource of the accumulated warm liquid directly depends on the volume of the tank used, but under any circumstances it remains strictly limited and ends quite quickly, so it is imperative to consider the issue of arranging an additional heating system;
- larger drives require a lot of space to install, for example, a boiler room.
Heat accumulator tank for solid fuel boiler WIRBEL CAS-500Device for efficient operation of a solid fuel boiler and charging a thermal storage tankInstallation scheme