- Welding machine
- Pros and cons
- 4 Regulatory framework for butt welding
- Preparing for welding
- 5 Incoming inspection of pipes, fittings and welding nozzles
- Socket installation
- Qualification Requirements
- Methods for installing polyethylene pipes
- Advantages and disadvantages
- Rules for welding on PE pipes
- Theoretical basis
- Instructions: how to weld plastic pipes
- Preparation of pipes for welding
- Setting up the welding machine
- Heating parts
- Connection of parts
- Cleanup
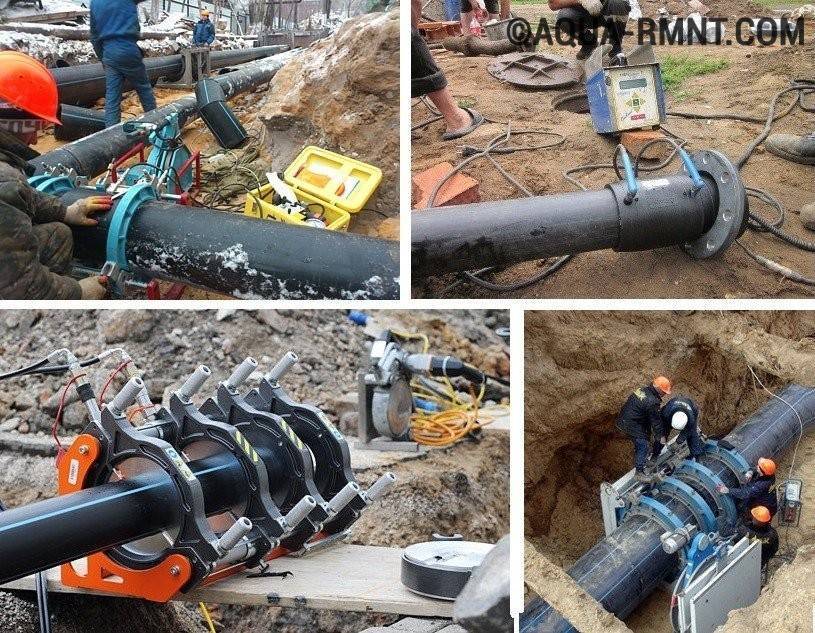
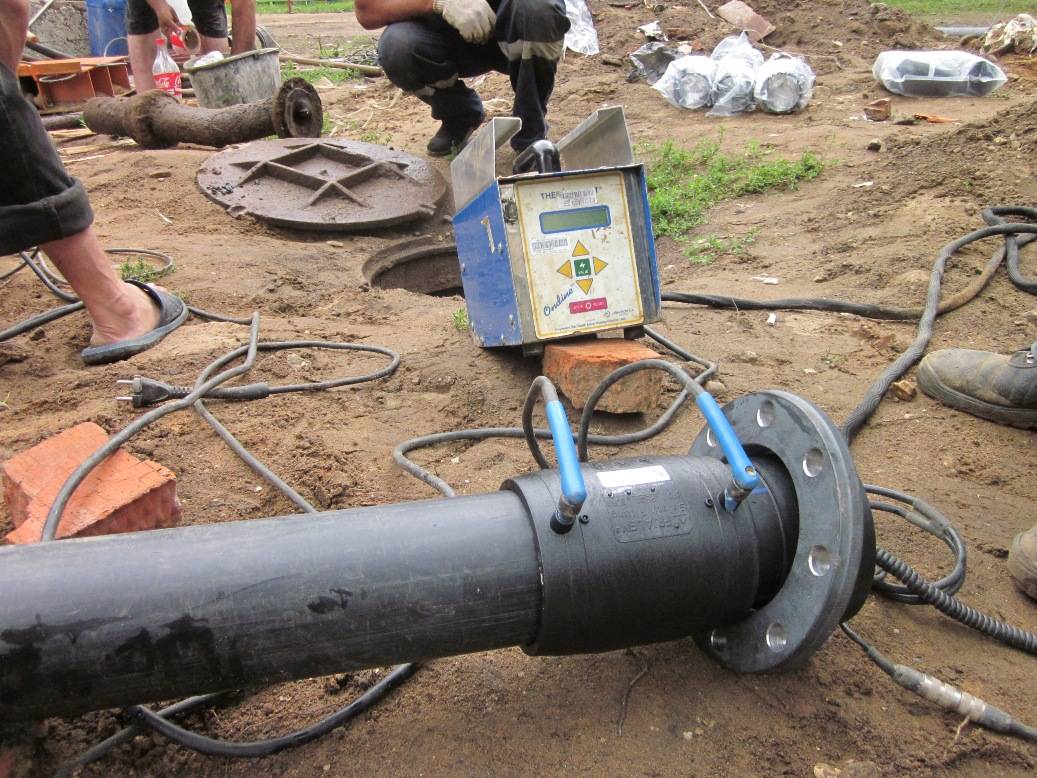
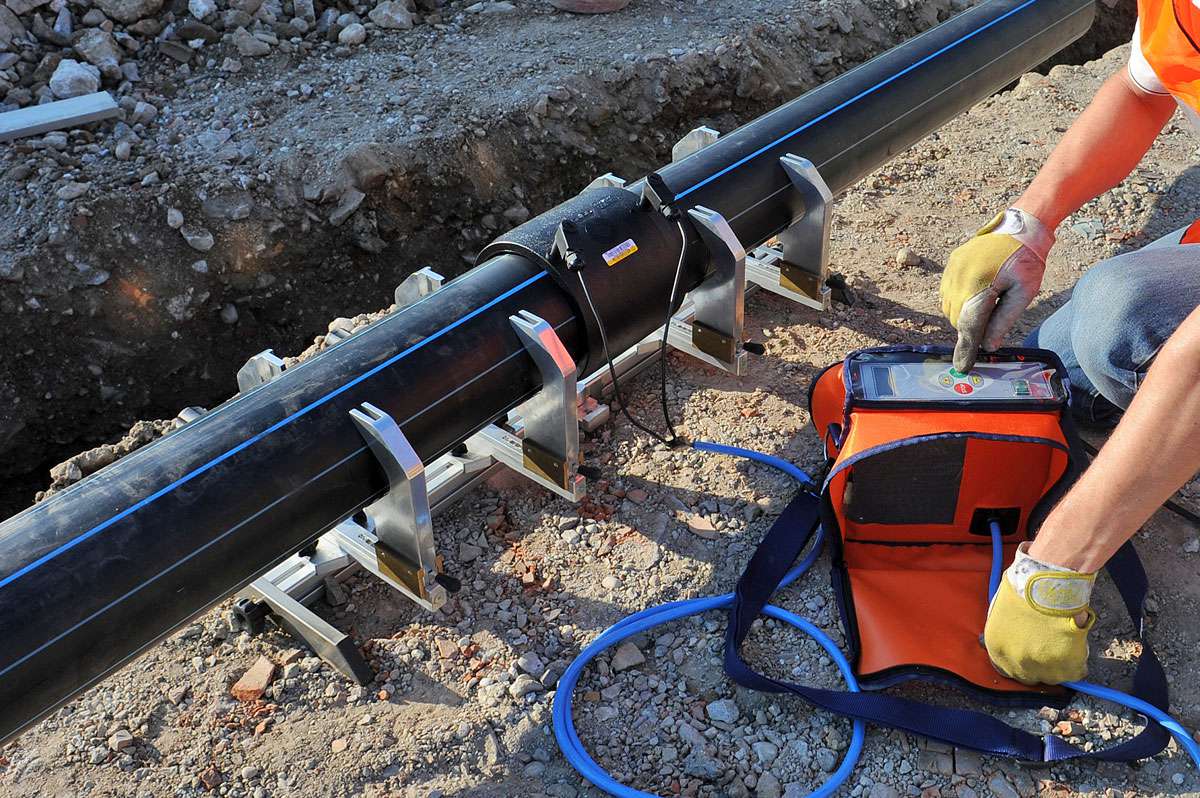
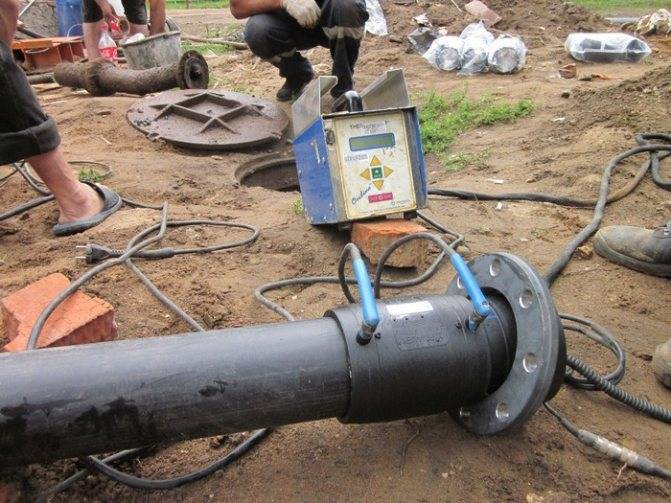
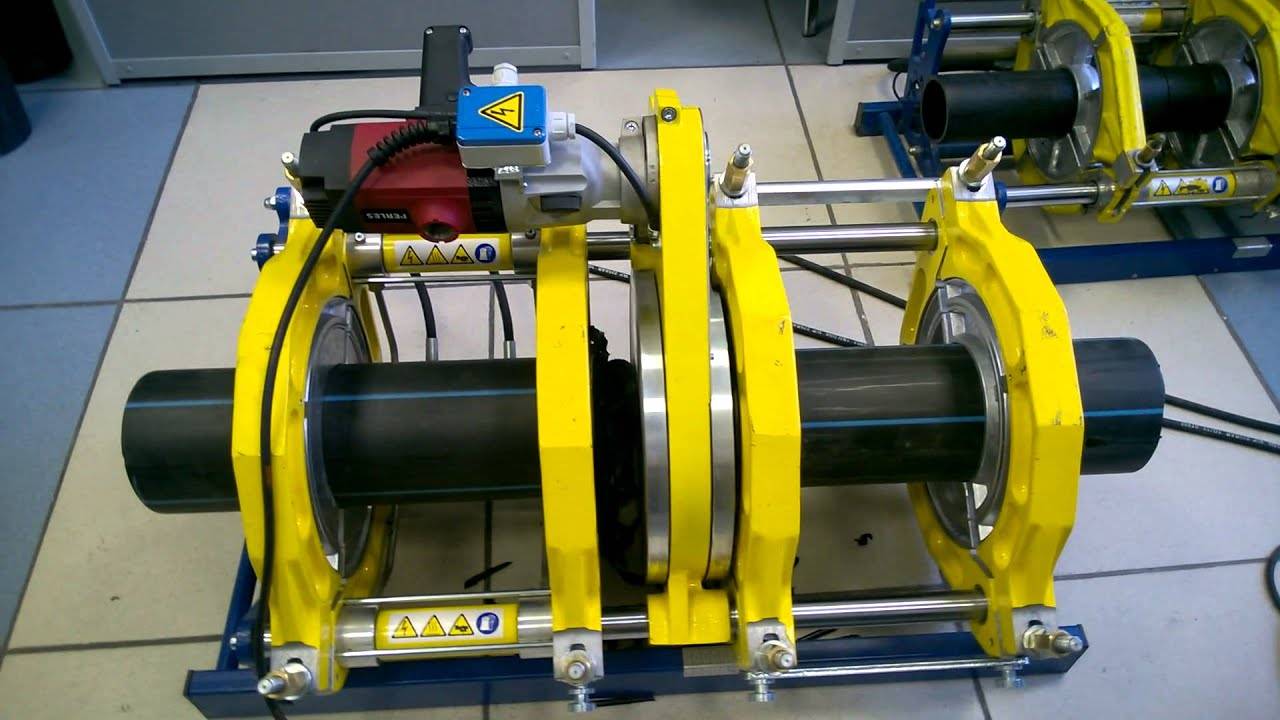
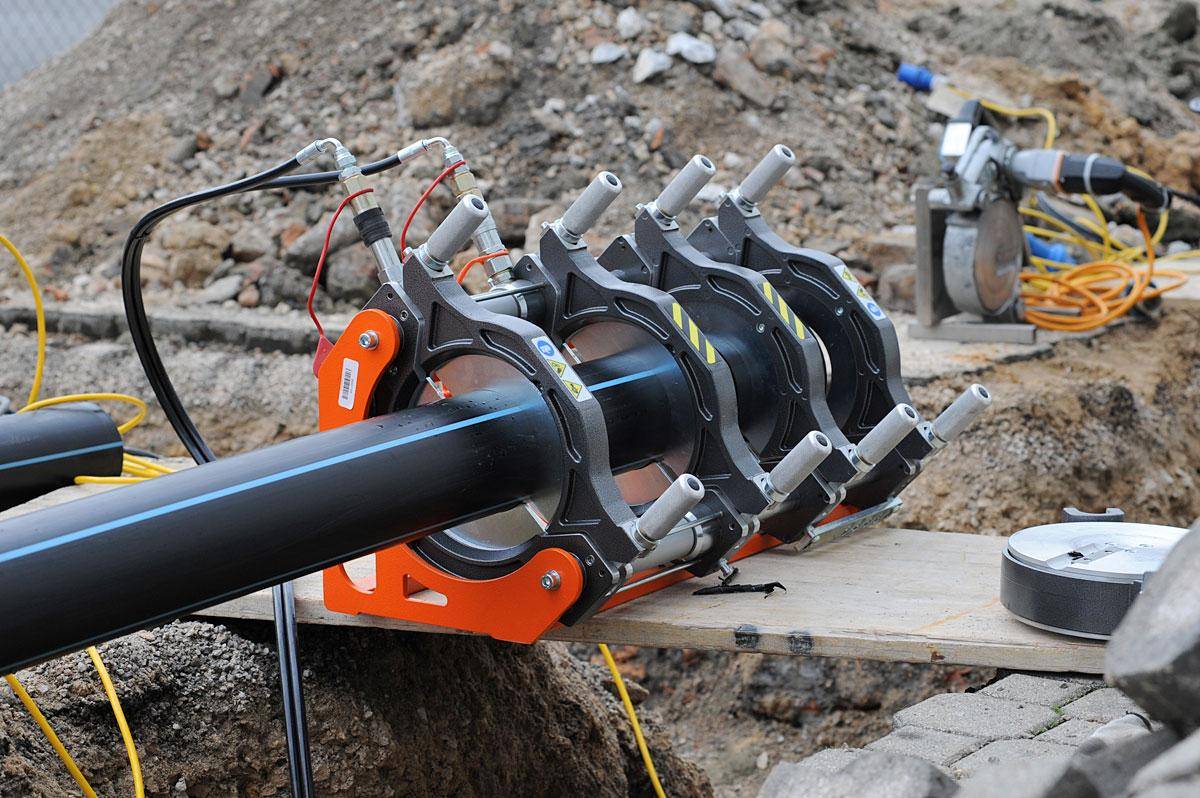
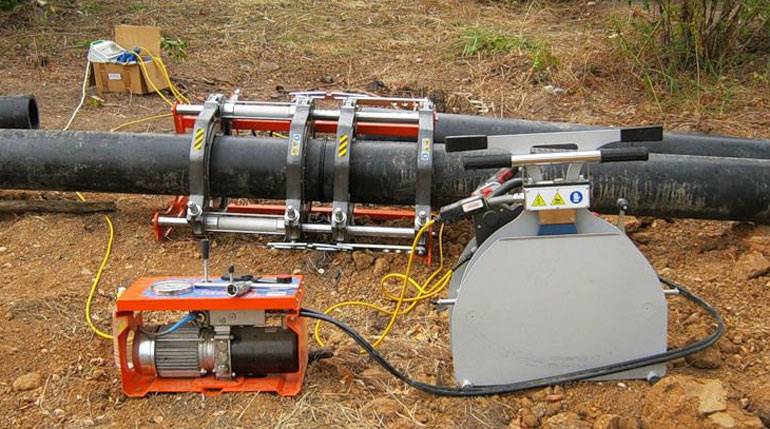
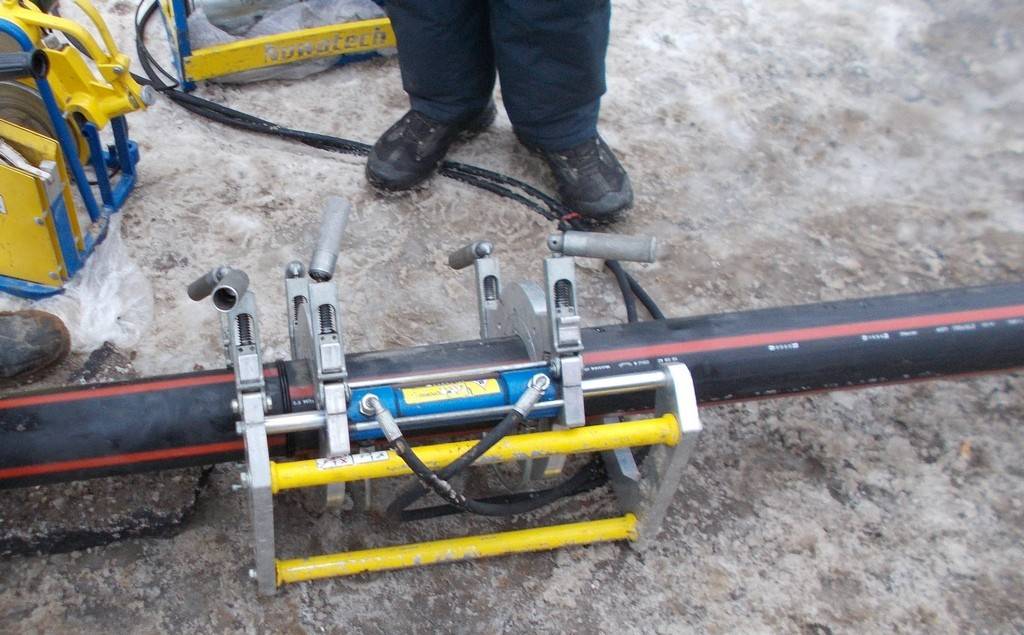
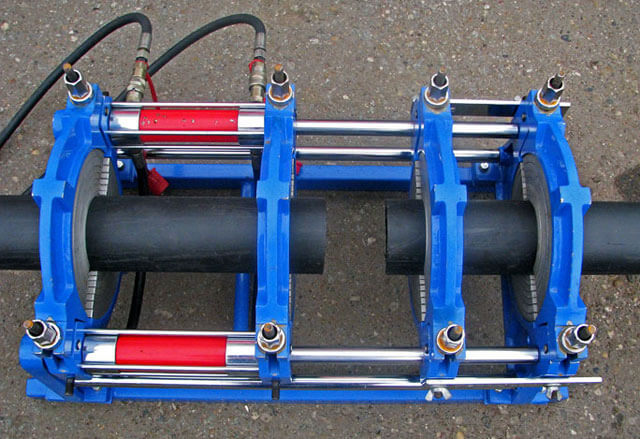
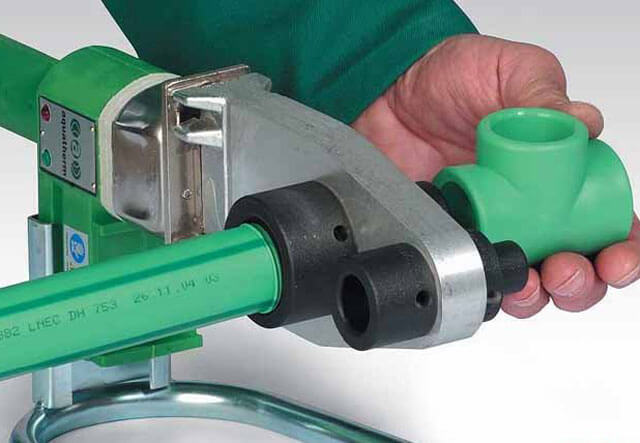
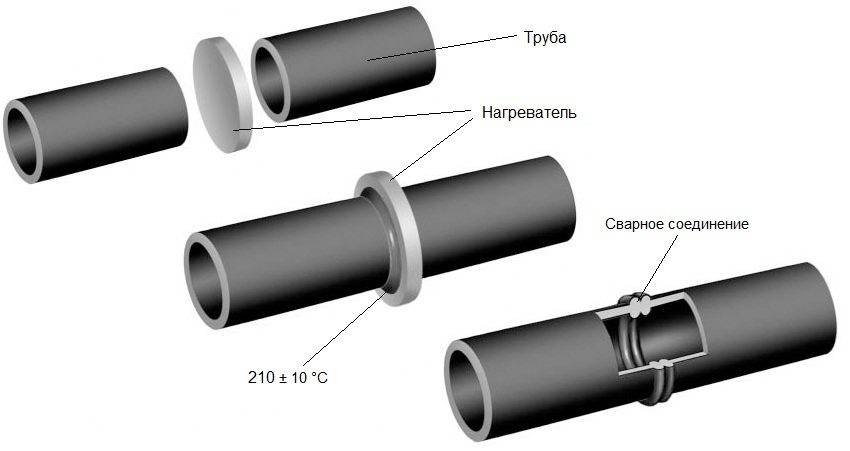
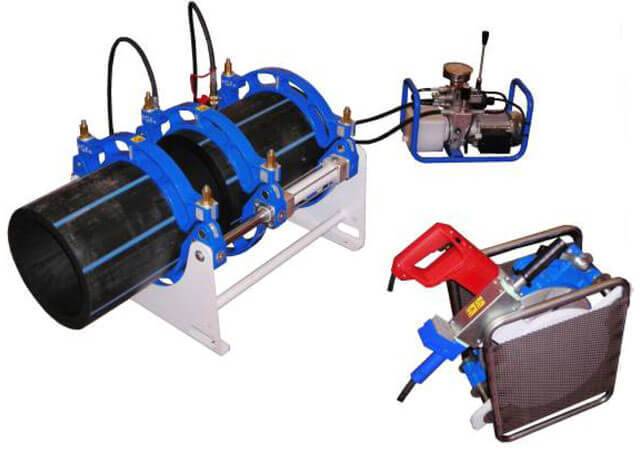
Welding machine
The device for welding HDPE pipes consists of several elements. Each element performs its functions. For example, a centralizer is used to clamp and center pipes. It is equipped with two or four clamps. The planer is used to process the ends. A welding mirror - heats the pipes to the melting point.
In addition, the device is equipped with a device that allows you to create the required force to press the pipe to the welding mirror, as well as to press two pipe sections during pressing. The device control unit allows you to provide the necessary voltage, as well as maintaining the device parameters in a certain interval.

Pros and cons
Like any other professional activity, the work of a plastic welder is characterized by its own distinctive characteristics.Moreover, they are not only positive, but also negative. You need to familiarize yourself with all the features of the professional activity of a specialist in advance so that you do not regret choosing a career in the future.
The advantages include:
- a high level of demand (having received professional training as a plastic welder, you will not be left without work);
- decent wages;
- a short period of training (since welders are trained not in higher, but in secondary vocational schools), etc.
At the same time, it is impossible not to note the existing shortcomings, the main of which is the fact that they will have to work in adverse, often dangerous conditions. For example, harmful fumes can adversely affect the health of an employee.

4 Regulatory framework for butt welding
As can be seen from , until recently in Russia there was considerable confusion with butt welding technology, since several current regulatory documents gave their own interpretation of it, and therefore most welders preferred to trust the slender German DVS technology. And the requirements for butt welding equipment in Russia were not defined by any standard at all.
Since the beginning of 2013, two regulatory documents have come into force in the Russian Federation at once:
- GOST R 55276 - for the technology of butt welding of PE pipes during the installation of water and gas pipelines, based on the translation of the international standard ISO 21307;
- GOST R ISO 12176-1 - for butt welding equipment, based on the translation of the international standard ISO 12176-1.
The adoption of GOST for equipment was certainly useful. Unfortunately, this does not mean that the most low-grade imported equipment was immediately weeded out.But, in any case, a few Russian equipment manufacturers are now forced to work on quality, and the consumer has received a hint on assessing the quality of the purchased equipment.
GOST on the technology of butt welding brought relative order. In any case, it led to the uniformity of the technology of butt welding of PE pipes on the territory of the Russian Federation. But the problems remained.
IMPORTANT! GOST R 55276, along with the traditional low pressure welding mode (similar to DVS 2207-1 and old Russian standards), legalized the high pressure welding mode for polyethylene pipes, which was previously used only in the USA. This mode imposes increased requirements on the equipment, but it can significantly reduce the welding cycle time.
IMPORTANT! GOST R 55276 is hardly suitable for direct use on a construction site, since it is focused not on a welder, but on a developer of a technological chart for welding polyethylene pipes. IMPORTANT! GOST R 55276 did not solve the problem of limitations that the old Russian standards suffered from and to this day all foreign standards suffer
Firstly, the allowable air temperature range is from +5 to +45°C, while a huge part of the territory of the Russian Federation is forced to start welding when the swamps freeze. Secondly, the maximum wall thickness of the pipes is 70 mm, while the wall thickness of actually produced pipes has long ago exceeded 90 mm. And thirdly, the pipe material is only traditional low-pressure polyethylene (HDPE) with a melt flow rate of at least 0.2 g / 10 min (at 190/5), while non-flowing grades of polyethylene have long been used for the production of large diameter pipes medium pressure with MFI below 0.1 g/10 min (at 190/5).For conditions outside the proven limits of air temperature and wall thicknesses, some manufacturers have calculated the technology for welding polyethylene pipes by extrapolating current regulations, but this theoretical technology has not yet been verified by long-term tests. For non-flowing grades of polyethylene, there is no technology for pipe welding, even in theory. As a result, about 80% of all welding is performed in Russia under conditions that go beyond the limitations of proven technology!
IMPORTANT! GOST R 55276 did not solve the problem of limitations that the old Russian standards suffered from and to this day all foreign standards suffer. Firstly, the allowable air temperature range is from +5 to +45 ° С, while a huge part of the territory of the Russian Federation is forced to start welding when the swamps freeze
Secondly, the maximum wall thickness of the pipes is 70 mm, while the wall thickness of actually produced pipes has long ago exceeded 90 mm. And thirdly, the pipe material is only traditional low-pressure polyethylene (HDPE) with a melt flow rate of at least 0.2 g / 10 min (at 190/5), while non-flowing grades of polyethylene have long been used for the production of large diameter pipes medium pressure with MFI below 0.1 g/10 min (at 190/5). For conditions outside the proven limits of air temperature and wall thicknesses, some manufacturers have calculated the technology for welding polyethylene pipes by extrapolating current regulations, but this theoretical technology has not yet been verified by long-term tests. For non-flowing grades of polyethylene, there is no technology for pipe welding, even in theory. As a result, about 80% of all welding is performed in Russia under conditions that go beyond the limitations of proven technology!
Previous
2
Track.
Preparing for welding
Before starting welding, you need to prepare in advance all the necessary equipment and tools. You will need:
- welding with cables and holder;
- mask (most often forgotten);
- mittens or leggings (canvas, tarpaulin, suede);
- metal brush;
- hammer to remove slag.
Visually check the welding cables for damage to the insulation, otherwise a short circuit may occur or there is a great risk of electric shock. Choose the best option for you: a welding helmet or a welding shield with a handle, as each of them has its own advantages (beginners are advised to use a shield). Mittens should never be made of flammable material or synthetics. When splashed, they instantly melt (ignite), are difficult to remove and can stick to the skin.
5 Incoming inspection of pipes, fittings and welding nozzles
SP 40-102-2000, in addition to checking packaging, marking pipes and fittings, external inspection, prescribes "measuring and comparing the outer and inner diameters and wall thickness of pipes with the required ones." What are the "required" dimensions is indicated below: "the measurement results must correspond to the values \u200b\u200bspecified in the technical documentation for pipes and fittings."
And now attention: an incident! In Russia, to date, there is no GOST that accurately describes the geometry of polypropylene pipes and fittings intended for socket welding.Even the long-awaited GOST R 52134-2003 "PRESSURE PIPES FROM THERMOPLASTICS AND CONNECTING PARTS TO THEM FOR WATER SUPPLY AND HEATING SYSTEMS", finally adopted in the spring of 2004, does not take into account that the outer diameter of pipes for socket welding must necessarily be greater than the nominal diameter of the pipeline by a very specific amount.
And the geometry of polypropylene fittings in the specified GOST is not described at all.
All Russian polypropylene pipes and fittings are produced on the basis of technical specifications, the development of which the manufacturer himself orders for authorized organizations. So with what to compare the sizes of pipes and fittings during incoming inspection?
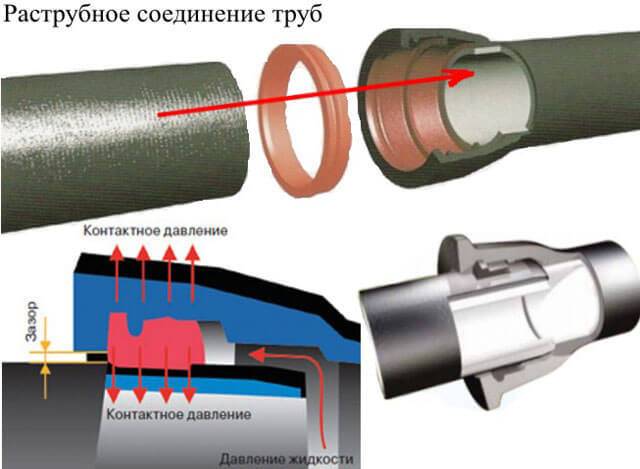
Everything is very simple! Reference normative document describing the geometry of a heated tool (welding nozzles) for socket welding - DVS 2208-1 (Germany). The main idea is that both the mandrel and the sleeve of the heated tool in their middle part have a diameter corresponding to the nominal diameter of the pipeline being welded (Fig. 15). Both working surfaces of the nozzles are conical, the taper is about 0.5º.
Reference normative document describing the geometry of polypropylene pipes and fittings for socket welding - DIN 16962 "Connections and components for pressure pipelines made of polypropylene". The main idea is that a plastic pipe can be inserted into the sleeve of a heated tool only through force and only when the outer surface of the pipe is melted (Fig. 16). And so that the mandrel of the heated tool can be introduced into the fitting also only through force and only when the inner surface of the fitting is melted.
| Rice. 15 Welding nozzle geometry | Rice. 16 Pipe and fitting geometry |
Therefore, the most relevant and simplest part of the input control of polypropylene pipes and fittings is to check that a cold pipe cannot be introduced into a cold fitting. In addition, it must be ensured that neither the cold fitting nor the cold pipe can be combined with the cold nozzle.
If this is not the case, it is not possible to connect your pipe to your fittings using socket (socket) welding technology.
In practice, welding nozzles, even Chinese or Turkish ones, rarely have irregular geometry. All of them are processed on CNC machines according to the requirements of DVS 2208-1. If a polypropylene fitting (or pipe) is freely combined, then in 99.99% of cases the reason is a defective fitting (or pipe).
When choosing nozzles, it makes sense to pay attention, first of all, to the quality of the Teflon coating. The anti-adhesive properties of Teflon can be tested with a leaky ballpoint pen.
If you manage to leave a drop of paste on the Teflon, it's bad. A drop of paste will not stick to a good Teflon coating, it will remain on the pen shaft. And how durable the coating is - only time will tell.
Another sign of a cheap nozzle is when the working surface is not smooth, but in embossed rings. Poor quality turning will cause rapid wear of the Teflon on the raised ribs.
And further. All decent nozzles have a through air channel in the side part. For example, a polypropylene plug simply cannot be put on a welding nozzle if there is no air channel.
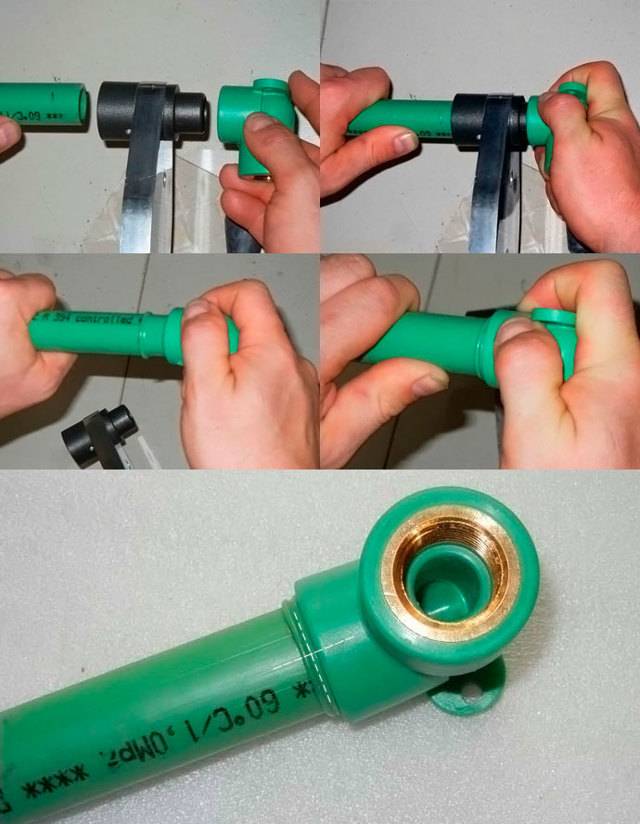
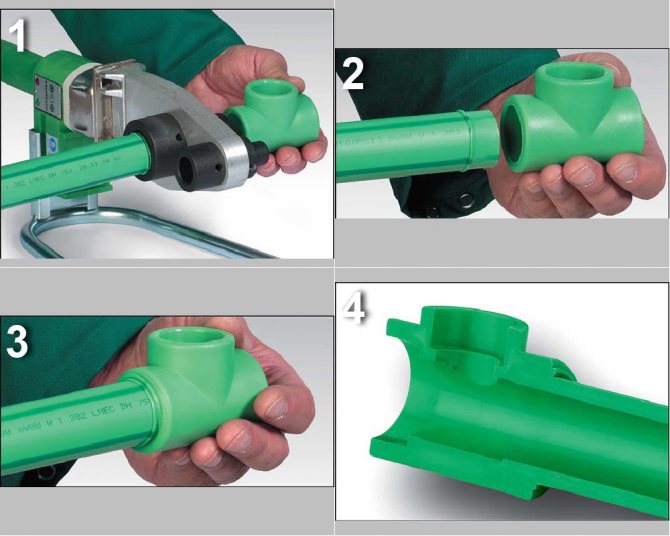
Socket installation
It should be noted that in domestic documents you will not find any standards for socket soldering. It is only described in European standards DVS 2207-15.Step-by-step instructions on how to weld HDPE pipes with couplings:
Before starting work, you will need to prepare communication. To do this, the outer surface is cleaned of various contaminants: dust, grease. This can be done with a damp cloth and an alcohol solution or a special mixture. It is sold in plumbing stores;
After the junction is put in order. The density of fastening depends on the smoothness of the cut. You should walk along the end of the pipe with sandpaper or clean it with a crumpled newspaper
After the joint of the HDPE pipes is cut to form a chamfer of 1 mm at 45 degrees, this is very important for tight fastening; Photo - docking
Next, you need to install the taps in the coupling
It is divided into two halves: the first is put on the pipe (this is the mandrel), and the second segment is inserted into the second (this is the sleeve)
It should be noted that putting on the coupling should only be started after the tool has been heated; Photo - connection
The preheated nozzle is threaded onto the communication as quickly as possible, after which the second outlet is inserted into it;
You need to advance the segments very carefully, but quickly, otherwise you can overheat the polyethylene. If everything is done correctly, then liquid plastic will begin to come out from under the coupling.
After finishing heating and welding, remove the coupling and fix the pipes on a solid surface.
Flanges are even easier to work with. They are threaded connections for installation. Accordingly, a thread is cut out at one end of the communication, into which the element is screwed, and a pipe is already put on it. The junction is heated with a hairdryer or a muff.
Photo - flange pnd
Qualification Requirements
In order to get a position as a plastics welder, you need to undergo professional training. At the same time, you can learn a profession in almost any college or technical school in a technical direction. The period of study is 3 years
At the same time, during the educational process, you should not only focus on theoretical training, but also pay attention to obtaining the skills and abilities necessary for further work. So, the employer in the process of searching for an employee takes into account not only formal signs (the presence of a diploma), but also real skills
A plastics welder must be able to:
- to carry out the technological process of welding;
- to make reinforcing tapes;
- carry out the necessary marking of the product;
- assemble welding equipment;
- carry out repairs (if necessary);
- be able to apply various welding methods in practice;
- carry out blind embossing of products, etc.
The employee must know:
- technological features of the welding process;
- physical and chemical properties of plastic materials;
- design and technical characteristics of the welding equipment used;
- safety precautions;
- legislative documents regulating the activities of a plastic welder, etc.
However, this list of requirements is not final. It can be changed and supplemented depending on the specific place of work, as well as on the wishes of the employer. That is why, in order to stand out among the general mass of applicants for the position of a plastic welder and to quickly move up the career ladder, you need to constantly improve your practical and theoretical levels.Thus, you will remain a sought-after and relevant specialist in the labor market.
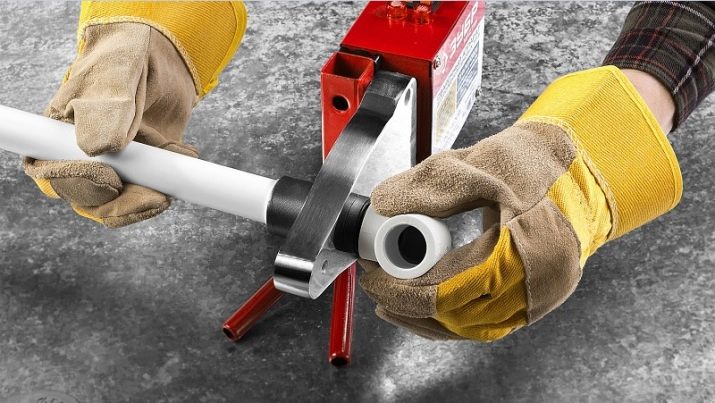

Methods for installing polyethylene pipes
There are two main types of piping connections. These are welded one-piece and detachable connections. When choosing one of the types of connections, it is necessary first of all to take into account the operating conditions of the pipeline. For example, when building a highway, butt welding is used. And when installing a pipeline with low pressure, detachable connections are used in it due to simpler installation.
Welding end-to-end polyethylene pipes used to securely connect individual elements of the pipeline. In this case, it can be used by the method of joining parts end-to-end or with the help of an electric coupling.

Advantages and disadvantages
The undoubted advantage of socket welding of polypropylene pipes is a 100% guarantee of the quality of the seam. In fact, a monolithic product is obtained. Often, with intentional destruction, a fracture occurs anywhere, but not at the place of welding.

There are no qualification requirements for the welding operator, anyone can do it.
For products with a diameter of up to 40 mm, cheap manual welding equipment is used.
Requires a high heating temperature of the surfaces to be joined (up to 260 ⁰С). At the same time, it has a short heating time and a high welding speed.
It is impossible to weld thin-walled products due to excessively rapid heating, which leads to such deformations that it is not possible to insert the pipe into the coupling.
Significant force is required when aligning the pipe and fitting with the heater or with each other after heating.With diameters greater than 50 mm, manual connection is practically impossible, the use of mechanical and other devices is required.
Uneconomical in the construction of the main pipeline.
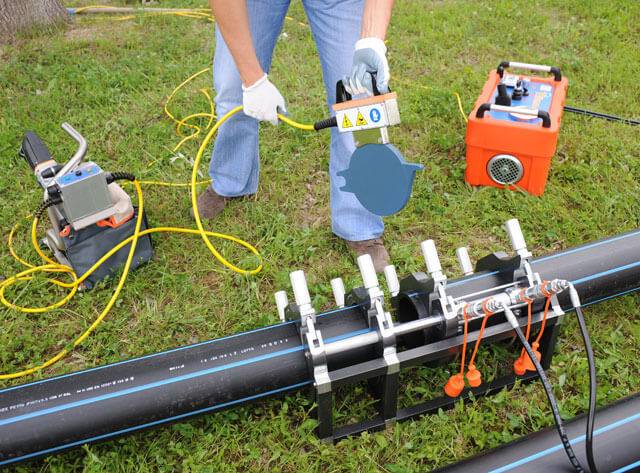
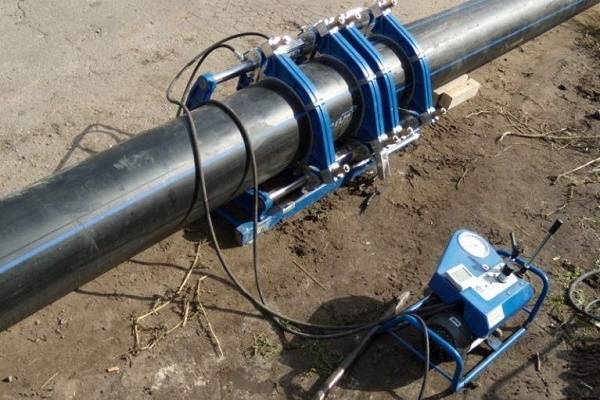
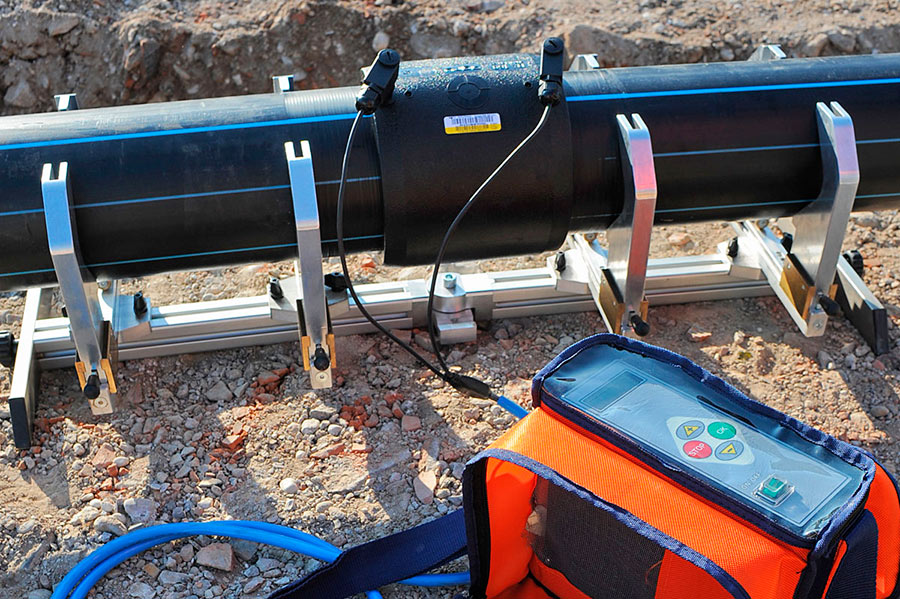
Rules for welding on PE pipes
When butt welding of PE pipes is performed, there are three main methods:
- at the butt;
- into the socket;
- through the clutch.
Each of the methods has its own technological features, but in any case, the welding process must be carried out in compliance with a number of requirements:
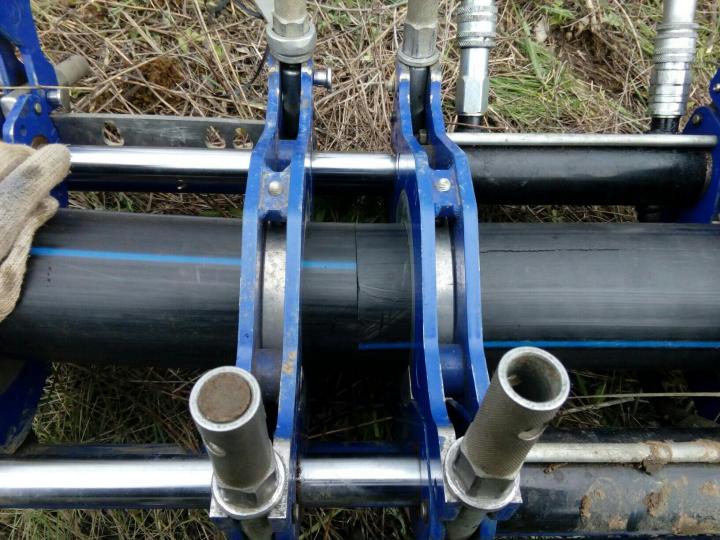
First you need to properly purchase polyethylene pipes. All of them must belong to the same batch and manufacturer. The difference between a quality and a defective product may not be noticeable, therefore, in any case, preference should be given to factory production. Even a millimeter discrepancy in the diameter of two joined pipes can lead to defects in the subsequent operation of the system.
Also, the use of products manufactured under identical conditions determines the full compliance of the pipes in terms of chemical composition and thickness. These indicators affect the time of welding, or rather, the warm-up stage. The discrepancy between the two pipes to each other can lead to the fact that one of them will melt more, and the second, on the contrary, will not reach the desired conditions.
In this case, the butt joint will not be strong enough.
How clean the material is is also very important. Any technology for welding PE pipes involves working with a perfectly clean surface.
The smallest sand, dust, dirt and other solid particles can lead to an insufficiently sealed joint.
It is also important to take into account the weather conditions when working outdoors, because high humidity during precipitation, overheating of elements under the open rays of the sun and hypothermia in frost can lead to a deterioration in the strength characteristics of the seam.
Finally, a very important stage of work is the cooling of the created seam. Up to the complete cooling of the heated polymer, it is necessary to fix the products relative to each other.
Theoretical basis
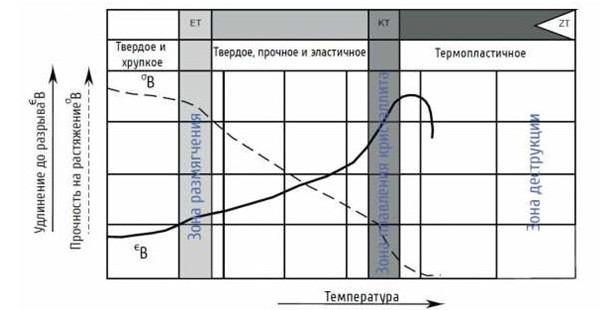
Extrusion welding is applicable only to materials with a large temperature range at which their viscous-flowing state is maintained, such as polyethylene, fluorolone, plasticized polyvinyl chloride, polystyrene. Such materials that can be heated above the pour point are called thermoplastics. The temperature range between melting and thermal degradation (destruction of the material) for thermoplastics is 50-180°C degrees.
The strength of the connection obtained by the extrusion method reaches 80-100% of the calculated strength of the parts themselves, but it strongly depends on the temperature of the additive. The filler material is heated to a temperature exceeding its pour point (Tm) by 30-60°C degrees. The heat consumption of the additive is made for losses to the environment, for melting the joined edges of the parts and for maintaining the viscous state of the mass itself.
It should be noted that in this case the heating temperature of the parts should not exceed the temperature of the thermal destruction of the material, since this will lead to a decrease in the strength of the connection and decrease.
The diagram below shows the process of changing the structure of the polymer with increasing temperature.
Only connections made of thermoplastics made of the same material are to be joined. In this case, the additive must be made of the same substance as the surfaces to be joined. In the event that the parts to be welded have different yield strengths, the yield strength of the additive must be equal to the average value of the PT of the parts to be joined.
PVC and PVDF have a small range of melting and destruction temperatures, so their connection must take place under careful temperature control. For welding of such materials, extruders with a screw are required, which thoroughly mixes the viscous mass, and welding must be carried out in one step, without periodic shutdowns and heating of the extruder.
Extrusion welding can be used to form continuous extended seams on reinforced materials and films. With this connection, the extrusion mass enters the connection of the films, which are pulled through the rolling rolls. The seam to be joined is then passed through pressure rolls to form the weld seam.
To minimize heat loss, extrusion welding should be carried out with the largest possible diameter of the filler rod and a high filler feed rate.
Please note that extruder welding is prohibited for use on pressure pipelines.
In Russia, the rules for extrusion welding are regulated by the GOST 16310-80 standard, this standard regulates the types of joints, operating temperature range, part thicknesses, edge sizes and other technical parameters.
In world practice, the use of the German standard DVS 2207-4 is widespread, which more widely regulates extrusion welding.
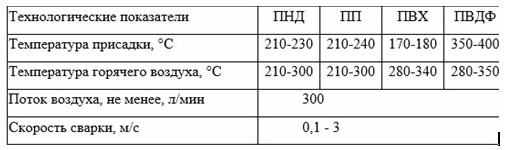
Examples of technical welding parameters are given in the table.
Instructions: how to weld plastic pipes
Learning to weld plastic pipelines into the socket is necessary in practice. Pipe blanks and components for systems are always bought with a margin. To acquire skills in working on equipment, plastic elements are cut into small pieces. The technological process consists of several stages, each of them is considered separately.
Preparation of pipes for welding
Cut the plastic into fragments in accordance with the wiring diagram. The edges are made at right angles. First they make markings, then they crash into plastic. Only after that, with a sharp effort, the workpiece is cut completely. The elements are laid out on a clean, flat surface in an order convenient for welding. Necessary connecting elements are placed nearby: fittings, bends, tees, couplings.
Each joint is cleaned before welding so that there are no burrs left, degreased. Pipes with a foil layer must be folded - the metal layer is completely cut off at the junction.
Setting up the welding machine
Attach nozzles of the required diameter to the soldering iron. The welding tool is firmly placed on a flat surface so that it does not wobble. The heating regulator is moved to the desired position. For welding plastic pipes, the soldering iron is heated from +255 to 280 ° C, regardless of the thickness of the pipelines. Only the heating time of the parts during welding, the interval of holding the joint until hardening changes.
 Included with the welding machine are nozzles for pipes of various diameters
Included with the welding machine are nozzles for pipes of various diameters
Heating parts
When welding, both elements are heated simultaneously: pipe blanks from the outside (they are inserted into the heating element), fittings from the inside (they are put on the heater).The parts are advanced with moderate effort until they stop - the iron pads. From the moment of contact, the heating time is counted, the interval depends on the diameter of the pipe billet:
| Workpiece diameter, mm | Heating time, sec | Nozzle depth, mm |
|---|---|---|
| 20 | 8 | 14 |
| 25 | 9 | 16 |
| 32 | 10 | 20 |
| 40 | 12 | 21 |
| 50 | 18 | 22,5 |
| 63 | 24 | 24 |
Joint holding time from 4 to 8 seconds. The data given in the special propylene welding tables is indicative. Before installing the pipeline, the heating and holding time is set experimentally. Plastic should not be heated to the entire depth of the wall, so that there are no internal sagging. Experimental blanks are made small so that the inner surface of the socket joint is visible.
Connection of parts
The polymer pipe and fitting heated on the nozzles must be connected quickly, with effort, avoiding distortions. Do this in one motion, without turning. Workpieces for welding with a diameter of more than 50 mm (for a drainage system) are connected using a centering tool; high-quality connections cannot be obtained manually. The blanks are held in the hands until the plastic hardens. After that, the formed knot is left to cool completely for 3-10 minutes, depending on the thickness of the workpieces.
 The parts heated on the nozzles must be connected quickly, with effort, avoiding distortions
The parts heated on the nozzles must be connected quickly, with effort, avoiding distortions
Cleanup
With a file, the outer influxes of the polymer are carefully removed. They should not be large with proper heating and compression. There should be no internal sagging at the seams, this is a marriage. After installing the plumbing, you need to make sure that the seams are reliable. Water is supplied to the system not earlier than an hour of exposure. If a leak is detected, the joint is cut out, and a new flange connection is made in its place.