- Scopes of electrowelded pipes
- Range of steel products
- Types of pipes by linear dimensions
- Types of products by production method
- Classification by type of anti-corrosion coating
- Round constructions
- Main pipe classification
- By material
- Steel
- Cast iron
- Polymer (plastic)
- Asbestos-cement and concrete
- By diameter
- By execution
- According to internal working pressure
- According to the operating temperature of the transferred medium
- By type of insulation
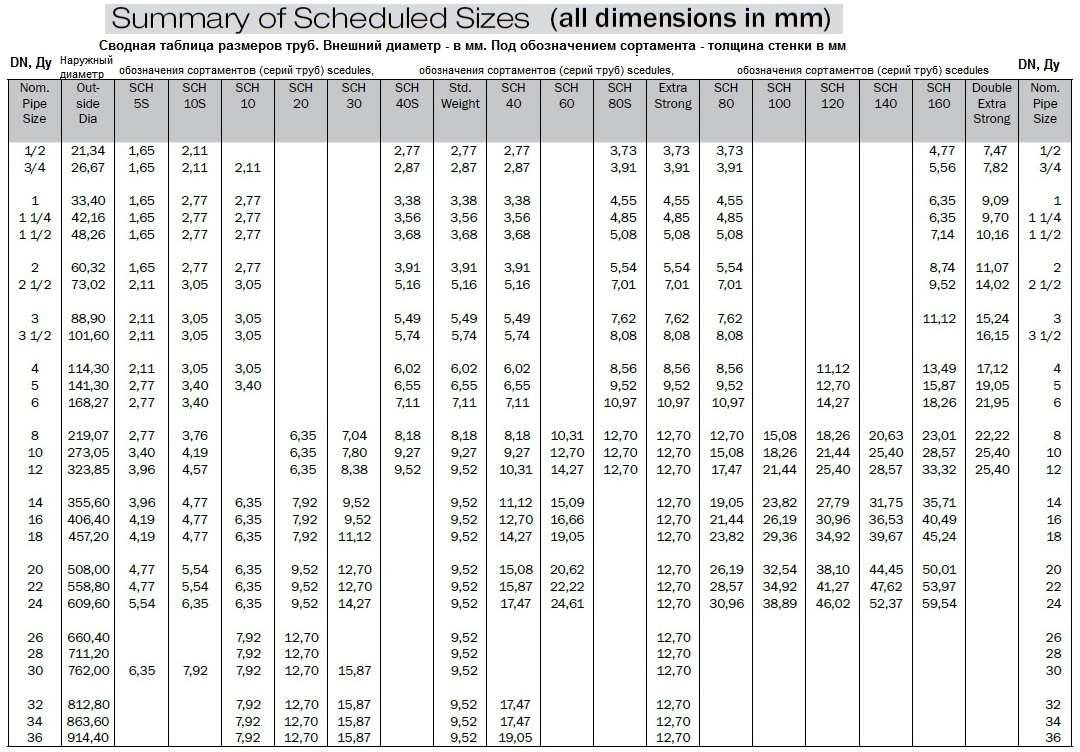
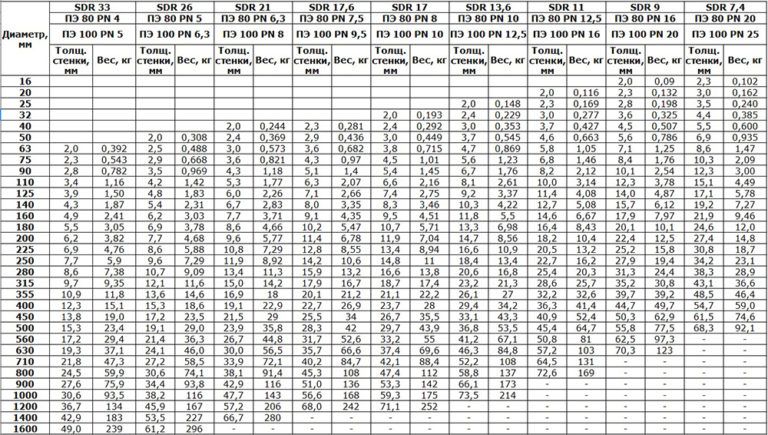
- Specifications of steel water pipes
- Light pipes
- Ordinary pipes
- reinforced pipes
- Threaded pipes
- Features of installation and operation
- Production of steel pipes: basic methods
- How are electrically welded straight seam products made?
- Production of electric welded spiral seam types
- Production of hot-formed seamless products
- Features of the production of cold-formed pipes
- Bonding parts of plastic pipeline
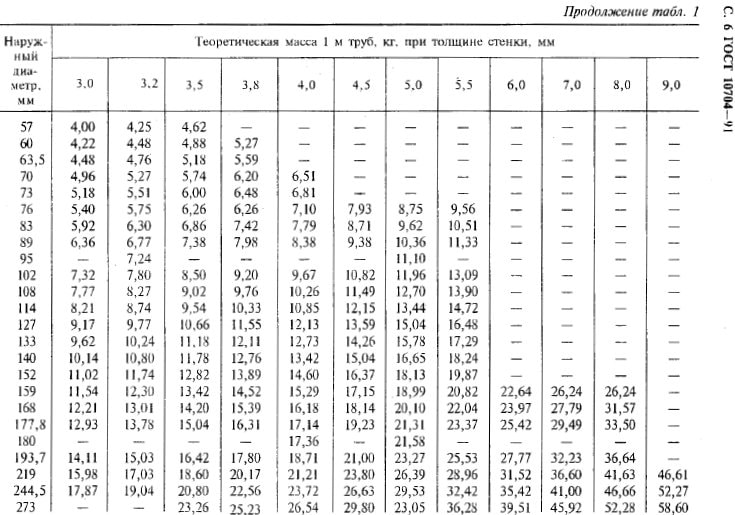
- Standards and assortment
- Hot-formed GOST 8732-78
- Cold-formed GOST 8734-75
Scopes of electrowelded pipes
• Heat exchangers and heaters • Decorations, constructions • Oil and chemical industry • Food industry • Shipbuilding and mechanical engineering • Water transportation systems
Product standards, according to the intended use (stainless steel welded pipes)
| USAGE | E.N. Euro standard | S.S. | ASTM-ASME | DIN | NFA | GOST |
| Chemical industry | EN 10217-7 | 219711 219713 | A 358-SA 358 A 312-SA312 A 269-SA 269 | 17457 | 49147 | GOST 11068-81 |
| food products | EN 10217-7 | A 270 | 11850 | 49249 | ||
| heat exchanger | EN 10217-7 | 219711 219713 | A 249-SA 249 | 17457 2818 | 49247 49244 | GOST 11068-81 |
| Pipeline | EN 10217-7 | A 778 A 269 | 17455 | 49147 | ||
| Drinking water | EN 10312 | DVGW541 | ||||
| Decoration, construction | EN 10296-2 | A 554 | 17455 2395 | 49647 |
Range of steel products
Steel pipes is a general term for a wide range of products. There are several classifications of parts.

The cross section of steel pipes can be of various shapes. In addition to traditional round products, you can find rectangular, six and octagonal, oval, square and other elements for sale.
Types of pipes by linear dimensions
Based on this feature, there are several types of elements:
- According to the outer diameter, all pipes are divided into products of medium diameter (102-426 mm), small diameter (5-102 mm) and capillary (0.3-4.8 mm).
- According to the geometry of the section, square, oval, round, segmental, ribbed, octagonal and hexagonal, rectangular parts, etc.
- Based on the ratio of the outer diameter to the wall width, extra thin-walled, thin-walled, normal, thick-walled and extra thick-walled products are produced.
- Processing class. The first class involves trimming the edges of the pipe and removing burrs. The second class is only cutting parts.
- Elements differ in length, which can be short, measured and unmeasured.
Types of products by production method
All steel products can be produced in one of two ways: with or without welding.Accordingly, the parts can be both with a welded seam and without it. In the first case, the steel sheet is rolled up in various ways, after which it is welded in an inert gas with tungsten electrodes. This is the so-called TIG welding. Alternatively, high frequency welding or HF welding is used.
The steel strip can either be rolled into a tube, which results in a straight seam, or wound in a spiral, resulting in a spiral seam. Water and gas pressure and profile pipes are produced only by the welded method.

Steel pipes can be made with or without welding. Profile and water and gas pressure pipes always have a seam
Seamless parts are made from steel rods by drilling, cold or hot deformation and casting. In the first case, a steel cylinder is drilled, in the latter case, molten metal is poured into the mold, inside which the rod is installed. However, deformation methods are most often used for production. With the hot method, the rod is heated in an oven to a plastic state and sent to the rollers, where it is brought to the required length and diameter.
Cold deformation assumes that before processing in the rollers the workpiece is cooled, but before the start of the final sizing it is annealed. Thick-walled pipes are produced in this way. Based on the production method, the range of steel pipes is as follows. Electric welded are divided into:
- spiral stitch;
- straight seam;
- profile;
- water and gas pressure.
Accordingly, seamless are divided into cold-formed and hot-formed.
Classification by type of anti-corrosion coating
Corrosion protection can be achieved in various ways. For these purposes, various coatings are used: extruded polyethylene, cement-sand mixture, polyethylene laid in one, two or three layers, epoxy-bitumen mixture or zinc. In the latter case, cold or hot galvanizing is used.
Round constructions

For communication systems, it is not very convenient to use profile products. They do not withstand strong internal loads from the pressure created by the carrier. Even for the arrangement of non-pressure systems, products of a rectangular or square shape cannot be used. This is due to the fact that the angular design significantly reduces the throughput of the pipeline. For these tasks, pipes with a circular cross section are used.
This type of construction is also used in the creation of chimneys. The resistance of the considered stainless steel pipes to high temperatures is especially appreciated. In addition, they are characterized by low roughness and significant throughput. They are often used for the construction of fences and various decorative structures.
Pipe products with a circular cross section are manufactured in two ways:
- Seamless.
- Welded.
The first version of the product has the same strength parameters over its entire surface. In its production, cold or hot blanks are used. They are pulled out by means of special equipment. The assortment and properties of these products are declared by GOST 8731-78.
Seamless products have in most cases a smaller section size. They are mainly used in the oil and chemical industries. In these sectors of the industry, higher requirements are placed on profile pipes.
The electrowelded version of products is divided into two types: spiral-seam and straight-seam. These products are characterized by low cost. The scope of its application is the widest.
Profiles are divided into the following categories according to the direction of their use:
- oil and gas;
- trunk;
- general and special purposes.
Main pipe classification
By material
Steel
Received the greatest distribution due to reliability, rather low price and simplicity of welding. They are used in all types of main pipelines, but, in recent years, the percentage of use of steel pipes has been steadily declining. The main reasons for this are the low corrosion resistance of the material, the need for a large number of expansion joints of various types in pipelines, and the high labor intensity of laying.
Connections of steel pipes are carried out by welding. From corrosion use the method of cathodic protection or coating with bitumen-rubber insulation. For transportation of highly aggressive media, apply steel pipes with internal insulation.
Cast iron
Mainly used in water supply and sanitation systems. Advantages - durability and corrosion resistance including resistance to corrosion under the influence of stray currents. Are applied to highways in the conditions of big loadings on soil. Modern samples are internally coated with a cement-sand composition to reduce the rate of deposit formation.
Considering that corrosion resistance depends on the integrity of the inner and outer coating, the main disadvantage is the brittleness of the material. For the same reason, pipeline strings have limited flexibility, which increases the risk of leaks.
For cast-iron pipes, joints with asbestos-cement sealing are used, they are elastic, resist vibration loads well and are reliable. There are connections on rubber rings without embossing.
Currently, the use of this type of pipe is limited due to the high price and the complexity of laying due to the large weight.

Polymer (plastic)
They are made from polyethylene, polyvinyl chloride, polypropylene, fiberglass, etc. They are mainly used in water supply systems, gas supply systems and heating networks. The type of polymer is selected depending on the sanitary requirements (for drinking water) and operating conditions.
With sufficient rigidity, such pipes are flexible and elastic, which makes it possible to compensate for small shifts in the soil and thermal expansion. Complete inertness to transported media and resistance to all types of corrosion ensure a long service life. For ground laying, pre-insulated pipes are used - resistant to ultraviolet radiation.
Polymer main pipes are the most progressive type, as the chemical industry develops, the scope is constantly expanding
Asbestos-cement and concrete
They are distinguished by high durability of finished structures, corrosion resistance, mechanical strength and relatively low price. The inner surface is resistant to the formation of mineral deposits and the formation of silt. Mainly used for technical water supply, drainage and sewerage systems. Connections for this type of pipes are carried out by couplings with rubber rings.
By diameter
To the main, according to Russian standards, according to GOST 20295-85, include pipes with a diameter of more than 114 mm.According to the European classification, pipes made of any material with a diameter of more than 200 mm are defined as main pipes.
In the oil industry, depending on the diameter of pipes for main oil pipelines, there is a division into classes:
- I – diameter over 1000 mm,
- II - from 500 to 1000mm,
- III - from 300 to 500 mm,
- IV - less than 300mm.

By execution
According to the Russian classification, pipes of “ordinary” and “northern” execution are distinguished.
- In the cold-resistant version, requirements are imposed on the impact strength and the proportion of the viscous component in the fracture, the fulfillment of which must be ensured at a temperature of minus 20 ° C, and for samples with a U-shaped concentrator at minus 60 ° C
- In the usual version, the requirements are relaxed to 0 and minus 40°C, respectively.
According to internal working pressure
- Pressure. For water supply, gas supply, heating networks, oil and gas pipelines.
- Non-pressure. Are used in systems of water disposal and the sewerage.
In the gas industry, depending on the operating pressure, pipes are distinguished for two classes of main gas pipelines:
- Class I - operating modes under pressure from 2.5 to 10 MPa (from 25 to 100 kgf / cm2),
- Class II - operating mode in the range from 1.2 to 2.5 MPa (from 12 to 25 kgf / cm2).
According to the operating temperature of the transferred medium
- Used in cold pipelines (less than 0 °C).
- In normal networks (from +1 to +45 °C).
- In hot pipelines (above 46 °C).
By type of insulation
In order to protect against corrosion, coatings are used that have the properties of a dielectric (protection against corrosion generated by stray currents), water resistance, heat resistance, elasticity and mechanical strength.

Specifications of steel water pipes
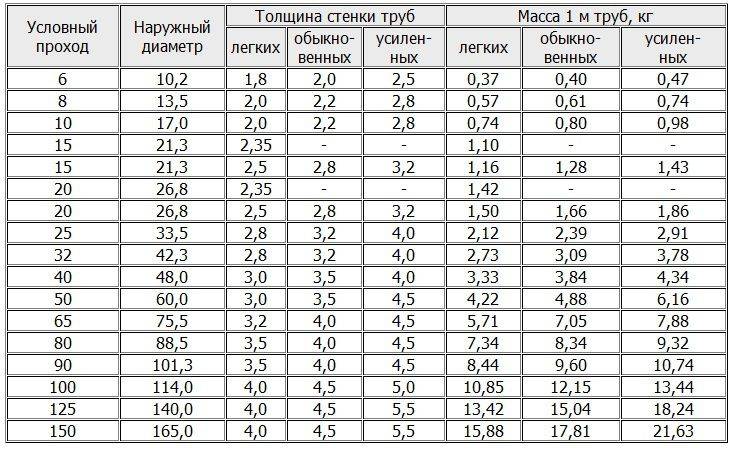
State VGP standards also apply to such technical characteristics as length and weight.
According to GOST 3262 75, the length of the finished product can vary between 4-12 m
Taking into account this parameter, this type of product is divided into 2 categories:
- measured length or a multiple of the measured length - all products in the batch have one size (a deviation of 10 cm is permissible);
- unmeasured length - in a batch there may be products of different lengths (from 2 to 12 m).
The cut of the product for plumbing should be done at a right angle. The permissible bevel of the end is called a deviation of 2 degrees.
There are special requirements for galvanized products. This zinc coating shall be a continuous thickness of at least 30 µm. There may be areas on the threads and ends of the finished product that are not zinc plated. Places with a bubble coating and various inclusions (oxides, hardzinc) are strictly prohibited - such products are considered defective.
According to the wall thickness of the product are divided into 3 types:
- lungs;
- ordinary;
- reinforced.
Light pipes
Feature of light pipes is the small wall thickness. Of all the possible varieties of VGP, light types of this rolled metal product have the smallest thickness. This indicator varies from 1.8 mm to 4 mm and directly depends on the outer diameter of the product.
The weight of 1 meter in this case is also characterized by the lowest rates. Products with an outer diameter of 10.2 mm in the amount of 1 m weigh only 0.37 kg. Thin-walled products should be chosen if the object is subject to increased requirements in terms of weight. However, water supply using such rolled metal has a limited scope. The liquid pressure in such pipes should be no more than 25 kg / sq. cm.When marking products with light weight, they are designated with the letter “L”.
Ordinary pipes
Rolled metal of this type has an ordinary wall thickness. This indicator varies between 2-4.5 mm. The main influence on this characteristic is the diameter of the product.
Ordinary steel pipes are considered the most common, they should be chosen in cases where there are no special requirements for laying water pipes.
The list of advantages of this type of rolled metal should include:
- optimal weight - in comparison with thick-walled products, such products can reduce the total weight of the finished structure;
- the allowable pressure has the same indicator as for thin-walled ones (25 kg / sq.m), however, hydraulic shocks are acceptable here;
- average cost - achieved due to the weight indicator.
When marking a special designation of an ordinary pipe, there is no. The letter designation is assigned only to light and reinforced products.
reinforced pipes
Products of this type include those steel pipes that have an increased wall thickness - from 2.5 mm to 5.5 mm. The weight of such a finished structure will be very different from the weight category of a structure made of light and even ordinary products.
However, such water and gas pipeline systems also have an advantage - they are suitable for objects with high pressure (up to 32 kg / sq. cm). When marking such pipes, the designation “U” is used.
Threaded pipes
The quality of threaded steel pipes is controlled by GOST 6357 and must fully comply with accuracy class B.
To achieve high quality products, the thread must meet several important requirements:
- be clear and clean;
- the presence of burrs and flaws is not allowed;
- a small amount of blackness may be present on the threads of the thread (if the thread profile is reduced by no more than 15%);
- according to GOST, there may be broken or incomplete threads on the thread (their total length should not exceed 10% of the total);
- the gas supply pipe may have a thread, the useful length of which is reduced by 15%.
Features of installation and operation
Laying a cable in a metal corrugation is not a big problem, provided that the installer has experience and sufficient qualifications. So, if you do not have the knowledge necessary to complete the work, it is better to use the help of electricians.
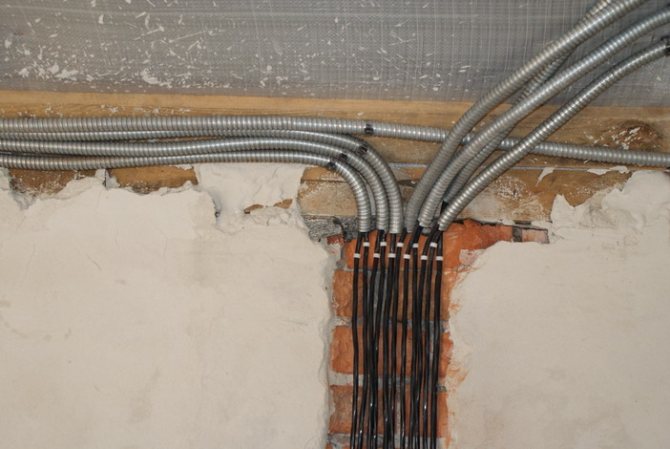

Installation of electrical wiring in the corrugation can be carried out on any surface
Concealed electrical wiring is traditionally installed in apartments and residential buildings. In this case, the corrugation with cables is placed in strobes previously prepared for this purpose, which, after installation, are sealed and plastered. Alternatively, external electrical wiring can be used, which is usually hidden under false ceilings or under drywall.
If the laying of electrical wires is planned in the cement screed of the subfloor, the cable laying product should be of a heavy type - it is designed for a sufficiently high mechanical load.
When it comes to laying central highways, the cable is pulled into the corrugation before it is laid. If we are talking about branches for switches or sockets, it is quite possible to pull the broach later.
When fastening external wiring, special clips are used.Their size is selected in strict accordance with the diameter of the corrugation itself. In the strobe, mounting on alabaster and other quick-hardening solutions is permissible.
Production of steel pipes: basic methods
Steel pipes are made in several ways.
The most common manufacturing options are:
- electrowelded with a direct seam;
- electric welded with a spiral seam;
- hot-worked without a seam;
- cold rolled without a seam.
The choice of a suitable metal processing method depends on the quality of raw materials and equipment available from the manufacturer.
A separate standard regulates water and gas pipes. However, this does not happen because there is a special manufacturing method for this material, but only based on the field of application.
In fact, pipes of this type are a universal electric welded product with a straight seam. Typically, this type is used in communication systems with moderate pressure.
How are electrically welded straight seam products made?
A steel sheet (strip) rolled into a tight roll is unwound and cut into longitudinal strips of the desired length and width. The resulting fragments are welded into an endless belt, thus ensuring continuity in production.
Then the tape is deformed in rollers and the workpiece is turned into a round section product with open edges. The connecting seam is welded by the arc method, induction currents, plasma, laser or electron beams.

The seam on a steel pipe, made in an inert gas environment with a tungsten electrode (the active element of electric arc welding), is quite strong and durable. However, processing takes a long time.Pipe welding with high-frequency induction currents is carried out almost 20 times faster, therefore the price of such products is always much lower
After all the manipulations, the round steel pipe is calibrated in the rollers and a delicate non-destructive control of the strength and integrity of the seam is carried out by ultrasound or eddy currents. If no errors are found during the testing process, the workpiece is cut into fragments of the planned length and sent to the warehouse.
Production of electric welded spiral seam types
The production of steel spiral-seam pipes follows the same principle as straight-seam pipes, only simpler mechanisms are used for the manufacture of products. The main difference is that the cut steel strip is rolled up with the help of rollers not as a tube, but as a spiral. This ensures high connection accuracy at all stages.

On pipes with a spiral seam, in the event of an emergency, a main longitudinal crack does not form, which is recognized by experts as the most dangerous deformation of any communication system
The spiral seam is considered more reliable and gives the pipe increased tensile strength. The disadvantages include the increased length of the seam, requiring additional costs for welding consumables and more time for connection.
Production of hot-formed seamless products
As a blank for creating a seamless (solid-drawn) steel pipe by hot deformation, a monolithic cylindrical billet is used.
It is heated at high temperature in an industrial furnace and driven through a piercing press.The unit turns the product into a sleeve (hollow cylinder), and subsequent processing with several rollers gives the element the desired wall thickness and a suitable diameter.

The wall thickness of the pipe material made of steel produced by hot deformation reaches 75 mm. Pipes of this quality are used in difficult operating conditions and in communication systems where strength and reliability are the main priority.
At the last stage, the hot steel pipe is cooled, cut according to the specified parameters and transferred to the finished product warehouse.
Features of the production of cold-formed pipes
The initial stage of the process of manufacturing seamless steel pipes by cold deformation is identical to the "hot" version. However, after running through the piercing mill, the sleeve is immediately cooled and all other operations are carried out in a cold environment.
When the pipe is fully formed, it must be annealed, first heating it to the steel recrystallization temperature, and then cooling it again. After such measures, the viscosity of the structure increases, and the internal stresses that inevitably arise during cold deformation leave the metal itself.

Cold-formed steel pipes can be used to lay a highly reliable communication system, in which the risk of leakage is minimized.
Now on the market are seamless cold-rolled pipes with a wall thickness of 0.3 to 24 mm and a diameter of 5 - 250 mm. Their advantages include a high level of tightness and the ability to withstand high pressure.
Bonding parts of plastic pipeline
By gluing, PVC pipes are connected to the socket.For better grip, the socket inside and the tail of the inserted pipe are treated with emery so that the surface becomes rough. Next, the chamfer is removed, the treated parts are degreased using methylene chloride as a primer.
Before making a connection, check the pipes for compatibility. The smaller diameter pipe should fit freely into the socket, but not too much. Then the line marks the border for applying glue - this will help to dock the parts without errors.
On the surface of the elements to be joined - 2 thirds of the socket recess, as well as a fully calibrated end of the pipe, glue is evenly applied in a thin layer. The pipe is inserted into the socket and rotated a quarter of a turn to improve contact between the connected elements. The docked parts are held until the glue sets.
For gluing PVC pipes, special aggressive adhesives are used. The process is similar to welding, but without high-temperature exposure, it is replaced by a chemical reaction, as a result of which the surfaces of the connected parts of the pipes dissolve and turn them into one whole by copolymerization
The process takes only 20-30 seconds. If a uniform layer of glue appears on the joint, it is immediately removed with a piece of clean cloth. From gluing to complete stabilization of the joint and testing of the pipeline for tightness, at least a day must pass.
Image gallery
Photo from
PVC pipes intended for gluing are produced with sockets, which allow making a socket connection. Fittings are produced for them, connected to pipes in the same socket method
The surfaces that will be in contact with each other are first treated with sandpaper, then degreased with methylene chloride, which dissolves the polymer, only after that glue is applied
Glue, most often it is the GIPC-127 composition, is applied in a thin uniform layer on the entire pipe surface to be joined and 2/3 of the surface of the socket or fitting
All connection actions should take no more than 3 minutes. We quickly connect the parts, turn around the axis by 1/4 turn and return to place. If the bonding is done properly, then a thin bead of adhesive should protrude along the edge of the sleeve / bell
PVC pipes for bonding
Processing pipes before joining
Rules for applying glue to PVC parts
Joining glued parts
To repair existing pipelines, fittings are used in the form of repair couplings or products with an elongated socket. A section of the pipe is cut out, chamfered at the ends, special glue is applied to the ends. The sleeve is put on the bottom of the pipeline.
A coupling with a long socket is put on the top of the pipeline until it stops, if required, a fitting is mounted on it. Move the coupling together with the fitting down until it joins the bottom of the pipeline. The sliding sleeve is moved upwards so that it closes the joint area.
The repair coupling differs from the usual connecting one in that it does not have a side inside, therefore, during the repair process, the socket of any pipe can be moved through it
If even after this a leak is observed, the joint is filled with silicone sealant. The bottom and top are determined depending on the direction of movement of the transported substance.
This is interesting: We choose a heater for pipes - for water supply, sewerage and heating
Standards and assortment
Seamless steel pipes are produced according to two standards depending on the production method:
- Hot-formed pipes are produced in accordance with GOST 8732-78;
- Cold-formed pipes are manufactured in accordance with GOST 8734-75.
What do the standards say about these types of pipes?
Hot-formed GOST 8732-78
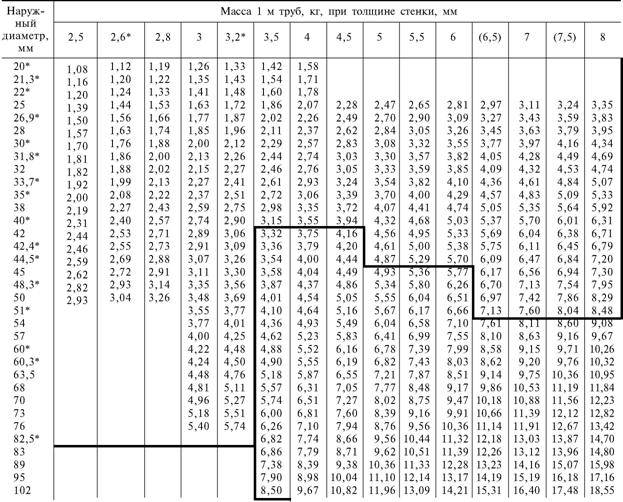
The range of steel pipes of this standard includes diameters from 20 millimeters to 550. The minimum wall thickness is 2.5 millimeters; the thickest-walled pipe has a wall thickness of 75 millimeters.
Pipes can be made in random lengths from 4 to 12.5 meters or to measure lengths within the same limits. Production of pipes of multiple measured length is possible. Size range - the same 4-12.5 meters; for each cut, an allowance of 5 millimeters is made.
The curvature of an arbitrary section of the pipe must be within one and a half millimeters for pipes with a wall thickness of less than 20 millimeters; two millimeters for walls in the range of 20-30 mm and 4 millimeters for walls thicker than 30 mm.
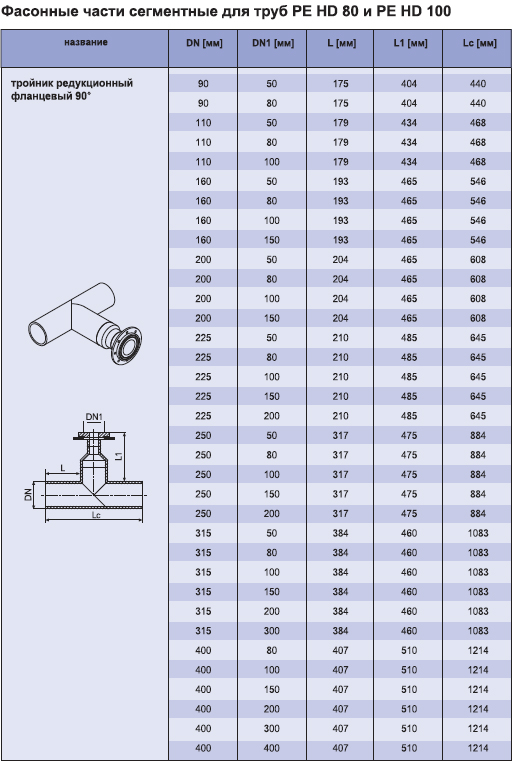
The standard regulates the maximum deviations for the outer diameter of the pipe and the thickness of its walls. The full range table and the table of maximum deviations in the production of pipes can be found in the appendix to the article.

The most thick-walled pipes are produced according to this standard.
Cold-formed GOST 8734-75
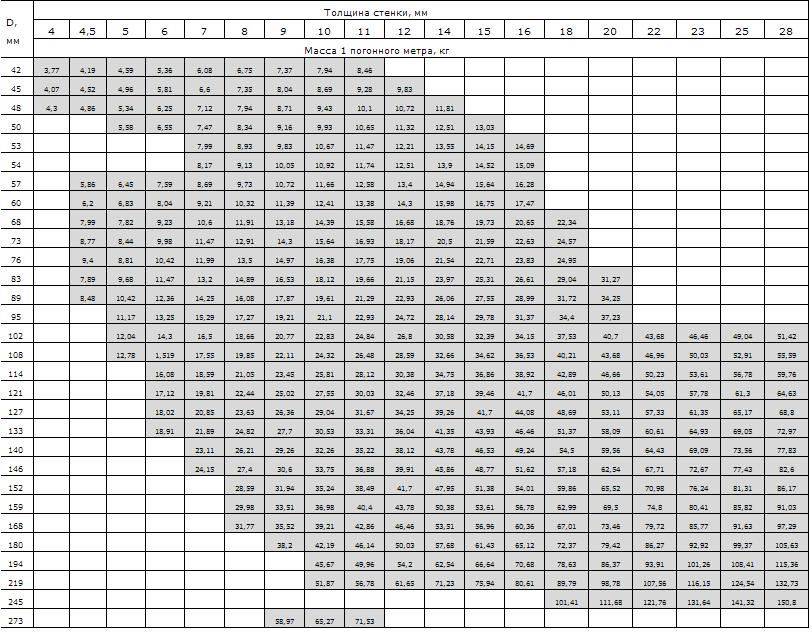
Pipes are produced with a diameter of 5 up to 250 mm with walls from 0.3 to 24 millimeters.
In the range table (also present in the appendices), the pipes are clearly divided into four groups according to wall thickness.
- Pipes with a ratio of outer diameter to wall thickness of more than 40 are especially thin-walled;
- Pipes, in which the ratio of the outer diameter to the wall thickness in the range from 12.5 to 40, is referred to as thin-walled by the standard;
- Thick-walled pipes have this ratio in the range of 6 - 12.5;
- Finally, with an outer diameter to wall thickness ratio of less than six, pipes are considered to be particularly thick-walled.
In addition, pipes with a diameter of 20 mm or less can be classified into two categories based on the absolute value of their wall thickness: pipes with walls thinner than 1.5 millimeters are thin-walled, if the walls are thinner than 0.5 mm, pipes are classified as especially thin-walled.
What else does the standard say?
- Pipes with a diameter to wall ratio of more than fifty with a diameter of more than 100 mm and pipes with an outer diameter to wall thickness ratio of less than four are delivered only after the technical documentation has been agreed with the customer;
- Slight ovality and wall variation of pipes are acceptable. The limitation is the tolerances for the diameter and thickness of the walls (they are also given in the appendix): if the difference in wall thickness and ovality do not take the pipe beyond these tolerances, then everything is in order.
- The curvature of an arbitrary pipe section per linear meter should not exceed 3 millimeters for pipes from 4 to 8 millimeters, 2 millimeters for pipes in the diameter range of 8 to 10 mm and one and a half millimeters for pipes over 10 millimeters.
- By agreement with the customer, it is possible to supply pipes without final heat treatment. But ONLY by convention: in general, annealing is mandatory.

Cold-formed thin-walled pipes have the highest strength at low weight