- Calculation of gas consumption
- Calculation example
- An example of calculating the consumption of liquefied gas
- Liquefied gas
- Calculation of gas consumption for heating
- We use modern automation
- How to find out the gas consumption for heating a house
- How to reduce gas consumption
- How to calculate main gas consumption
- Calculation for liquefied gas
- Method of calculation for natural gas
- We calculate the gas consumption by heat loss
- Heat loss calculation example
- Boiler power calculation
- By quadrature
- Using a propane-butane mixture
- How to calculate correctly?
- Why Choose Gas
Calculation of gas consumption
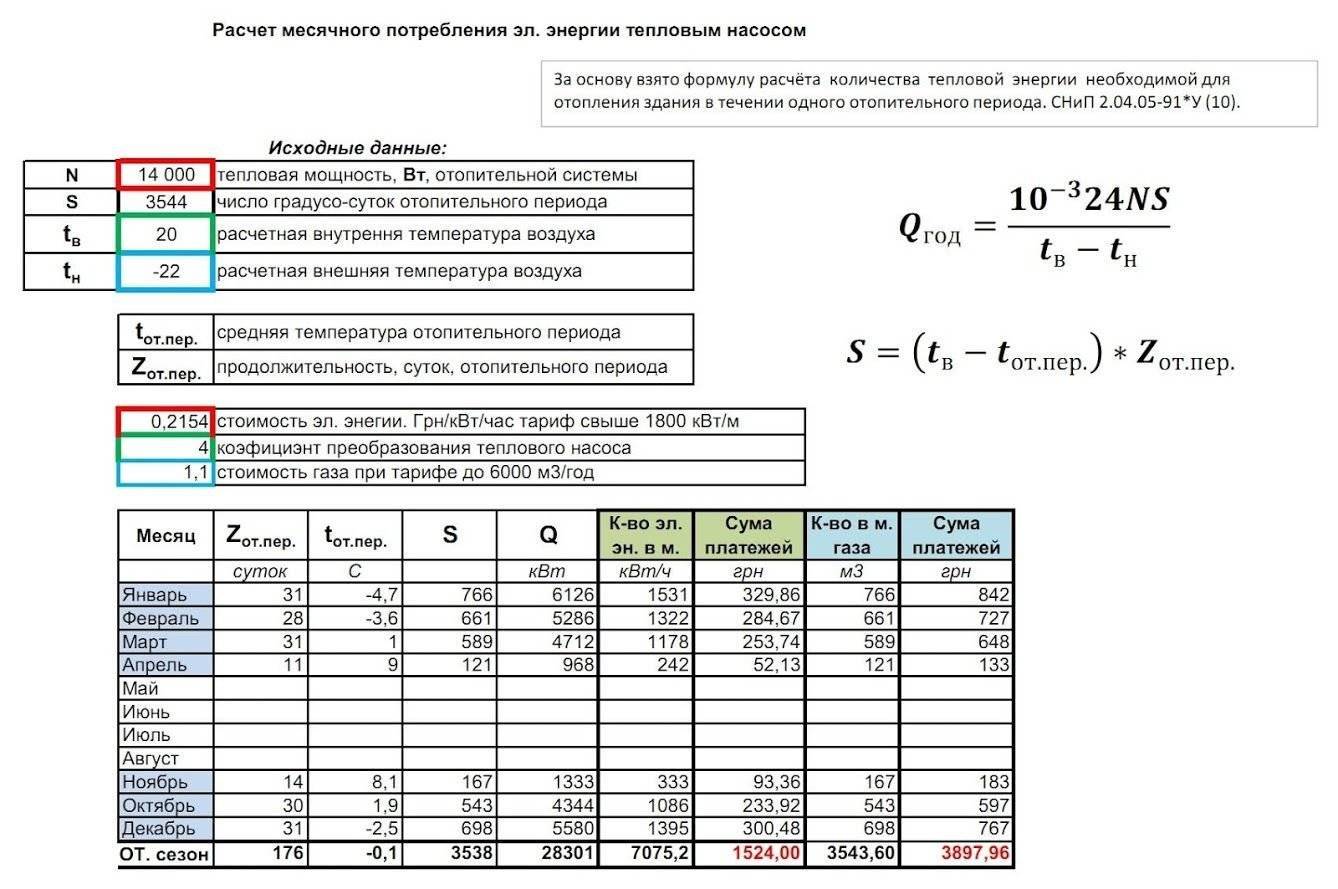
The calculation of gas consumption for heating a house can be done using the following formula:
V = Q / ((q * efficiency) / 100).
In the given calculation formula, the letters have the following meaning: The q value, which is located in the denominator of the formula, is the calorie content of the consumable combustible material. The value is assumed to be 8 kW/m³; V - what volume of gas is consumed when heating the room; Efficiency is the efficiency factor when burning fuel, it is always indicated as a percentage; Q is the value of the heating load for a room with an area of 150 m2.
Calculation example
In the above example, a living space is proposed, the area of \u200b\u200bwhich is 150 square meters, and the load value is 15 kilowatts.

All calculations of gas consumption for heating are given relative to these values.The building will be heated by an installation that has a closed chamber, and the efficiency is 92%.
With the strongest possible frosts on the street, gas consumption in sixty minutes, i.e. one hour of active operation of the boiler will be 2.04 m³ / h. All calculations are made according to the formula given at the beginning of the title. And in one day, the gas consumption for heating a house with an area of 150 m² will be 2.04 * 24 \u003d 48.96 cubic meters. The calculations were made for the northern latitudes of our country and taking into account the maximum possible frosts. Those. speaking in a more professional language, a calculation was made maximum hourly consumption gas.
During the heating season, ambient temperatures may vary depending on where the subject lives. The temperature can drop to -25ºС, and in some places even to -40ºС. Therefore, the average consumption will be much less than we calculated, and will be in the region of 25 cubic meters per day.
It turns out that in one month of the heating season, a turbocharged boiler, which is installed and used to heat a dwelling located in the middle latitudes of Russia, with an area of 150 cubic meters, will spend 25 * 30 = 750 cubic meters of gas. In the same simple way, using formulas, you can calculate gas consumption for rooms of other sizes.
An example of calculating the consumption of liquefied gas
Most modern heating equipment is designed and operated in such a way as to burn gas and heat the room without changing the burner. Therefore, it will be interesting for people to consider the costs of propane-butane, which is supplied to the population in cylinders or autonomous gas tanks.

This information, in particular all calculations, will be of interest to that segment of the population who want to install autonomous gas heating of the premises due to the lack of main fuel and autonomous gas supply.
To calculate the consumption of liquefied gas for space heating, you need to add the value of the calorific value of this type of combustible material. At the same time, it must be remembered that all volumes of natural gas are calculated either in cubic meters or in liters, and liquefied gas in kilograms, which must later be converted into liters.
The calorific value of liquefied gas will be equal to 12.8 kW per kilogram. This value is equal to 46 megajoules per kilogram. As a result, thanks to the formula, we get an indicator of 0.42 kilograms per hour. This is provided that we used a boiler with an efficiency of 92%, i.e. as in the example above 5/(12.8*0.92).
One liter of liquefied gas propane-butane has a mass of 540 grams. If we translate this value into liters, then we get a value of 0.78 liters of liquefied gas. If we multiply this value by 24, then we will get an indicator for one day, and it will equal 18.7 liters. As the accounting for gas consumption shows, we will get a value of 561 liters per month. This value is for a room of 100 square meters. As our flow meter shows that with a building area of 200 square meters, the flow rate will be 1122 liters, and with a house area of 300 m2, the volume will be 1683 liters.
Liquefied gas
Many boilers are made in such a way that the same burner can be used when changing fuel. Therefore, some owners choose methane and propane-butane for heating. This is a low density material.During the heating process, energy is released and natural cooling occurs under the influence of pressure. The cost depends on the equipment. Autonomous supply includes the following elements:
- A vessel or cylinder containing a mixture of butane, methane, propane - a gas holder.
- Devices for management.
- A communication system through which fuel moves and is distributed inside a private house.
- Temperature sensors.
- Stop valve.
- Automatic adjustment devices.
The gas holder must be located at least 10 meters from the boiler room. When filling a cylinder of 10 cubic meters, to service a building of 100 m2, you will need equipment with a capacity of 20 kW. Under such conditions, it is enough to refuel no more than 2 times a year. To calculate the approximate gas consumption, you need to insert the value for the liquefied resource into the formula R \u003d V / (qHxK), while the calculations are carried out in kg, which are then converted to liters. With a calorific value of 13 kW / kg or 50 mJ / kg, the following value is obtained for a house of 100 m2: 5 / (13x0.9) \u003d 0.427 kg / hour.
Since a liter of propane-butane weighs 0.55 kg, the formula comes out - 0.427 / 0.55 = 0.77 liters of liquefied fuel in 60 minutes, or 0.77x24 = 18 liters in 24 hours and 540 liters in 30 days. Given that there are about 40 liters of resource in one container, the consumption during the month will be 540/40 = 13.5 gas cylinders.
How to reduce resource consumption?
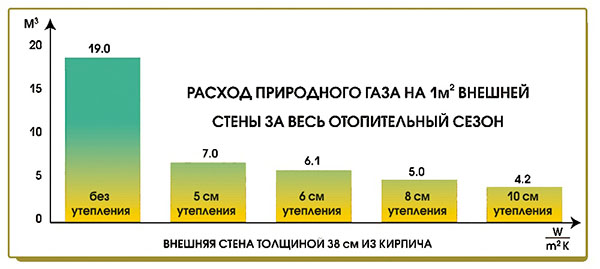
In order to reduce the cost of space heating, homeowners take various measures. First of all, it is necessary to control the quality of window and door openings. If there are gaps, heat will escape from the rooms, which will lead to more energy consumption.
Also one of the weak points is the roof. Hot air rises and mixes with cold masses, increasing the flow in winter.A rational and inexpensive option would be to provide protection from the cold on the roof with the help of rolls of mineral wool, which is laid between the rafters, without the need for additional fixation
It is important to insulate the walls inside and outside the building. For these purposes, there are a huge number of materials with excellent properties. For example, expanded polystyrene is considered one of the best insulators that lends itself well to finishing, it is also used in the manufacture of siding.
For example, expanded polystyrene is considered one of the best insulators that lends itself well to finishing, it is also used in the manufacture of siding.
When installing heating equipment in a country house, it is necessary to calculate the optimal power of the boiler and the system operating on natural or forced circulation. Sensors and thermostats control the temperature, depending on the climatic conditions. Programming will ensure timely activation and deactivation if necessary. A hydraulic arrow for each device with sensors for a single room will automatically determine when it is necessary to start heating the area. The batteries are equipped with thermal heads, and the walls behind them are covered with a foil membrane so that the energy is reflected into the room and does not go to waste. With underfloor heating, the carrier temperature reaches only 50°C, which is also a determining factor in savings.
Plumbers: You'll pay up to 50% LESS for water with this faucet attachment
The use of alternative installations will help reduce gas consumption. These are solar systems and equipment powered by wind power. It is considered most effective to use several options at the same time.
The cost of heating a house with gas can be calculated using a certain formula. Calculations are best done at the design stage of a building, this will help to find out the profitability and feasibility of consumption
It is also important to take into account the number of people living, the efficiency of the boiler and the possibility of using additional alternative heating systems. These measures will save and significantly reduce costs
Calculation of gas consumption for heating
Before you calculate the consumption of natural gas for heating a house or apartment, you need to know one important parameter - the heat loss of a residential building. Well, when it is correctly calculated by specialists at the design stage, this will significantly increase the accuracy of your calculations.
But in practice, such data is often not available, because few homeowners pay due attention to the design

The amount of heat loss of the building is determined by the power of the heating system and the boiler itself or a gas convector. Therefore, when choosing a gas boiler for a cottage or when installing autonomous heating for an apartment, you have to use the following averaged methods for determining heat loss and equipment power:
- According to the general square of the building. The essence of the method is that for heating each square meter, 100 W of heat is required with a ceiling height of up to 3 m. At the same time, for the southern regions, a specific value of 80 W / m² is taken, and in the northern regions, the consumption rate can reach 200 W / m².
- According to the total volume of heated premises. Here, from 30 to 40 W are allocated for heating 1 m³, depending on the region of residence.
It turns out that heating a dwelling with an area of 100 m² requires about 10-12 kW of heat per hour during severe cold weather and when the house is located in the middle lane.Accordingly, for a cottage of 150 m², about 15 kW of thermal energy will be required, for 200 m² - 20 kW, and so on. Now you can also calculate what maximum gas consumption the gas boiler will show on the coldest days, for which the formula is used:
V = Q / (q x efficiency / 100), where:
- V is the volume flow rate of natural gas per hour, m³;
- Q is the value of heat loss and power of the heating system, kW;
- q is the lowest specific calorific value of natural gas, averaging 9.2 kW/m³;
- Efficiency - the efficiency of a gas boiler or convector.
We use modern automation
Well, and obvious things: you can save gas by correctly setting the heating in time. For example, if you are not at home from morning to evening, then in the boiler (if it supports such a function) you can set a low temperature on the thermostat and program an increase in power at a certain time. And if you are not at home for weeks or even months, then ideally you need to set the temperature of the coolant to 3-5 degrees. And let the house be cold. The main thing is that the pipes do not freeze.
Modern technologies in this regard have gone far ahead. Many boilers can be equipped with modern automation, which will allow you to control the device remotely. You can use your smartphone to command the boiler to change the mode while at work. To do this, special GSM-modules are installed on the equipment. And there are many such smart systems. With proper use of them, the real cost of heating can be reduced. Sometimes savings can reach 30, 40 and even 50%. Of course, it depends on how often you are at home and what the temperature is outside.
How to find out the gas consumption for heating a house
How to determine the flow gas for heating a house 100 m 2, 150 m 2, 200 m 2?
When designing a heating system, you need to know what it will cost during operation.
That is, to determine the upcoming fuel costs for heating. Otherwise, this type of heating may subsequently be unprofitable.
How to reduce gas consumption
A well-known rule: the better the house is insulated, the less fuel is spent on heating the street. Therefore, before starting the installation of the heating system, it is necessary to perform high-quality thermal insulation of the house - the roof / attic, floors, walls, replacing windows, hermetic sealing contour on the doors.
You can also save fuel by using the heating system itself. Using warm floors instead of radiators, you will get more efficient heating: since heat is distributed by convection currents from the bottom up, the lower the heater is located, the better.
In addition, the normative temperature of floors is 50 degrees, and radiators - an average of 90. Obviously, floors are more economical.
Finally, you can save gas by adjusting the heating over time. It makes no sense to actively heat the house when it is empty. It is enough to withstand a low positive temperature so that the pipes do not freeze.
Modern boiler automation (types automation for gas heating boilers) allows remote control: you can give a command to change the mode through a mobile provider before returning home (what is Gsm modules for boilers heating). At night, the comfortable temperature is slightly lower than during the day, and so on.
How to calculate main gas consumption
The calculation of gas consumption for heating a private house depends on the power of the equipment (which determines the gas consumption in gas heating boilers). Power calculation is performed when choosing a boiler. Based on the size of the heated area.It is calculated for each room separately, focusing on the lowest average annual temperature outside.
To determine the energy consumption, the resulting figure is divided approximately in half: throughout the season, the temperature fluctuates from a serious minus to plus, gas consumption varies in the same proportions.
When calculating the power, they proceed from the ratio of kilowatts per ten squares of the heated area. Based on the foregoing, we take half of this value - 50 watts per meter per hour. At 100 meters - 5 kilowatts.
Fuel is calculated according to the formula A = Q / q * B, where:
- A - the desired amount of gas, cubic meters per hour;
- Q is the power required for heating (in our case, 5 kilowatts);
- q - minimum specific heat (depending on the brand of gas) in kilowatts. For G20 - 34.02 MJ per cube = 9.45 kilowatts;
- B - the efficiency of our boiler. Let's say 95%. The required figure is 0.95.
We substitute the numbers in the formula, we get 0.557 cubic meters per hour for 100 m 2. Accordingly, gas consumption for heating a house of 150 m 2 (7.5 kilowatts) will be 0.836 cubic meters, gas consumption for heating a house of 200 m 2 (10 kilowatts) - 1.114, etc. It remains to multiply the resulting figure by 24 - you get the average daily consumption, then by 30 - the average monthly.
Calculation for liquefied gas
The above formula is also suitable for other types of fuel. Including for liquefied gas in cylinders for a gas boiler. Its calorific value, of course, is different. We accept this figure as 46 MJ per kilogram, i.e. 12.8 kilowatts per kilogram. Let's say the boiler efficiency is 92%. We substitute the numbers in the formula, we get 0.42 kilograms per hour.
Liquefied gas is calculated in kilograms, which are then converted to liters.To calculate the gas consumption for heating a house of 100 m 2 from a gas tank, the figure obtained by the formula is divided by 0.54 (the weight of one liter of gas).
Further - as above: multiply by 24 and by 30 days. To calculate the fuel for the entire season, we multiply the average monthly figure by the number of months.
Average monthly consumption, approximately:
- consumption of liquefied gas for heating a house of 100 m 2 - about 561 liters;
- consumption of liquefied gas for heating a house of 150 m 2 - approximately 841.5;
- 200 squares - 1122 liters;
- 250 - 1402.5 etc.
A standard cylinder contains about 42 liters. We divide the amount of gas required for the season by 42, we find the number of cylinders. Then we multiply by the price of the cylinder, we get the amount needed for heating for the entire season.
Method of calculation for natural gas
The approximate gas consumption for heating is calculated based on half the capacity of the installed boiler. The thing is that when determining the power of a gas boiler, the lowest temperature is laid. This is understandable - even when it is very cold outside, the house should be warm.
You can calculate the gas consumption for heating yourself
But it is completely wrong to calculate the gas consumption for heating according to this maximum figure - after all, in general, the temperature is much higher, which means that much less fuel is burned. Therefore, it is customary to consider the average fuel consumption for heating - about 50% of the heat loss or boiler power.
We calculate the gas consumption by heat loss
If there is no boiler yet, and you estimate the cost of heating in different ways, you can calculate from the total heat loss of the building. They are most likely familiar to you. The methodology here is as follows: they take 50% of the total heat loss, add 10% to provide hot water supply and 10% to heat outflow during ventilation. As a result, we get the average consumption in kilowatts per hour.
Then you can find out the fuel consumption per day (multiply by 24 hours), per month (by 30 days), if desired - for the entire heating season (multiply by the number of months during which the heating works). All these figures can be converted into cubic meters (knowing the specific heat of combustion of gas), and then multiply cubic meters by the price of gas and, thus, find out the cost of heating.
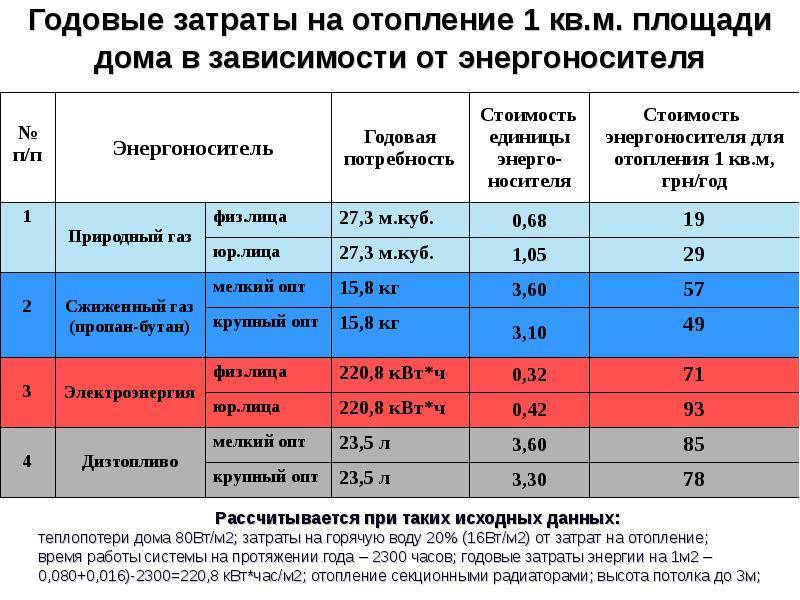
| The name of the crowd | unit of measurement | Specific heat of combustion in kcal | Specific heating value in kW | Specific calorific value in MJ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Natural gas | 1 m 3 | 8000 kcal | 9.2 kW | 33.5 MJ |
| Liquefied gas | 1 kg | 10800 kcal | 12.5 kW | 45.2 MJ |
| Hard coal (W=10%) | 1 kg | 6450 kcal | 7.5 kW | 27 MJ |
| wood pellet | 1 kg | 4100 kcal | 4.7 kW | 17.17 MJ |
| Dried wood (W=20%) | 1 kg | 3400 kcal | 3.9 kW | 14.24 MJ |
Heat loss calculation example
Let the heat loss of the house be 16 kW / h. Let's start counting:
- average heat demand per hour - 8 kW / h + 1.6 kW / h + 1.6 kW / h = 11.2 kW / h;
- per day - 11.2 kW * 24 hours = 268.8 kW;
-
per month - 268.8 kW * 30 days = 8064 kW.
Convert to cubic meters. If we use natural gas, we divide the gas consumption for heating per hour: 11.2 kW / h / 9.3 kW = 1.2 m3 / h. In calculations, the figure 9.3 kW is the specific heat capacity of natural gas combustion (available in the table).
Since the boiler has not 100% efficiency, but 88-92%, you will have to make more adjustments for this - add about 10% of the figure obtained. In total, we get the gas consumption for heating per hour - 1.32 cubic meters per hour. You can then calculate:
- consumption per day: 1.32 m3 * 24 hours = 28.8 m3/day
- demand per month: 28.8 m3 / day * 30 days = 864 m3 / month.
The average consumption for the heating season depends on its duration - we multiply it by the number of months that the heating season lasts.
This calculation is approximate. In some month, gas consumption will be much less, in the coldest - more, but on average the figure will be about the same.
Boiler power calculation
Calculations will be a little easier if there is a calculated boiler capacity - all the necessary reserves (for hot water supply and ventilation) are already taken into account. Therefore, we simply take 50% of the calculated capacity and then calculate the consumption per day, month, per season.
For example, the design capacity of the boiler is 24 kW. To calculate the gas consumption for heating, we take half: 12 k / W. This will be the average need for heat per hour. To determine the fuel consumption per hour, we divide by the calorific value, we get 12 kW / h / 9.3 k / W = 1.3 m3. Further, everything is considered as in the example above:
- per day: 12 kW / h * 24 hours = 288 kW in terms of the amount of gas - 1.3 m3 * 24 = 31.2 m3
-
per month: 288 kW * 30 days = 8640 m3, consumption in cubic meters 31.2 m3 * 30 = 936 m3.
Next, we add 10% for the imperfection of the boiler, we get that for this case the flow rate will be slightly more than 1000 cubic meters per month (1029.3 cubic meters). As you can see, in this case everything is even simpler - fewer numbers, but the principle is the same.
By quadrature
Even more approximate calculations can be obtained by the quadrature of the house. There are two ways:
- It can be calculated according to SNiP standards - for heating one square meter in Central Russia, an average of 80 W / m2 is required. This figure can be applied if your house is built according to all requirements and has good insulation.
- You can estimate according to the average data:
- with good house insulation, 2.5-3 cubic meters / m2 are required;
-
with average insulation, gas consumption is 4-5 cubic meters / m2.
Each owner can assess the degree of insulation of his house, respectively, you can estimate what gas consumption will be in this case. For example, for a house of 100 sq. m.with average insulation, 400-500 cubic meters of gas will be required for heating, 600-750 cubic meters per month for a house of 150 square meters, 800-100 cubic meters of blue fuel for heating a house of 200 m2. All this is very approximate, but the figures are based on many factual data.
Using a propane-butane mixture
Autonomous heating of private houses with liquefied propane or its mixture with butane has not yet lost its relevance in the Russian Federation, although in recent years it has noticeably increased in price
It is all the more important to calculate the future consumption of this type of fuel for those homeowners who plan such heating. The same formula is used for the calculation, only instead of the net calorific value of natural gas, the value of the parameter for propane is set: 12.5 kW with 1 kg of fuel
The efficiency of heat generators when burning propane remains unchanged.
Below is an example calculation for the same building of 150 m², only heated with liquefied fuel. Its consumption will be:
- for 1 hour - 15 / (12.5 x 92 / 100) = 1.3 kg, per day - 31.2 kg;
- on average per day - 31.2 / 2 \u003d 15.6 kg;
- on average per month - 15.6 x 30 \u003d 468 kg.
When calculating the consumption of liquefied gas for heating a house, it must be taken into account that fuel is usually sold by volume measures: liters and cubic meters, and not by weight. This is how propane is measured when filling cylinders or a gas tank. This means that it is necessary to convert mass into volume, knowing that 1 liter of liquefied gas weighs about 0.53 kg. The result for this example will look like this:
468 / 0.53 \u003d 883 liters, or 0.88 m³, of propane will have to be burned on average per month for a building with an area of 150 m².
Given that the retail price of liquefied gas is an average of 16 rubles.for 1 liter, heating will result in a considerable amount, about 14 thousand rubles. per month for the same cottage for one and a half hundred squares. There is reason to think about how best to insulate the walls, and take other measures aimed at reducing gas consumption.
Many homeowners expect to use fuel not only for heating, but also for providing hot water
These are additional costs, they must be calculated, plus it is important to take into account the additional load on heating equipment
The thermal power required for hot water supply is easy to calculate. It is necessary to determine the required amount of water per day and use the formula:
- c is the heat capacity of water, equal to 4.187 kJ/kg °C;
- t1 — initial water temperature, °C;
- t2 is the final temperature of the heated water, °С;
- m is the amount of water consumed, kg.
As a rule, economical heating occurs up to a temperature of 55 ° C, and this must be substituted into the formula. The initial temperature is different and lies in the range of 4-10 °C. For a day, a family of 4 people needs approximately 80-100 liters for all needs, subject to economical use. It is not necessary to convert the volume into mass measures, since in the case of water they are almost the same (1 kg \u003d 1 l). It remains to substitute the obtained value QDHW in the above formula and determine the additional gas consumption for hot water.
How to calculate correctly?
You can find out the consumption of blue fuel for heating a house by calorie indicators on the basis of the management company. If this option does not work out, then you can put a conditional figure in the calculations, but it is best to take it with some margin - 8 kW / m³. But it also often happens that sellers give information regarding the specific heat of combustion, expressed in other units, that is, kcal / h.Don't worry, these numbers can be converted to Watts by simply multiplying the data by a factor of 1.163.
Another indicator that directly affects fuel consumption is the possible heat load on the heating system, which is heat loss due to additional building structures of the building, as well as possible losses spent on heating the ventilation air. The most suitable calculation option is to conduct or order detailed and accurate calculations of all existing heat losses. If you do not have the opportunity for such methods, and a rather approximate result will satisfy, then there is an option to recalculate using the “aggregated” method.
- With a ceiling height of up to three meters, you can count on heat of 0.1 kW per 1 sq. m of heated area. As a result, a building of no more than 100 m2 consumes 10 kW of heat, 150 m2 - 15 kW, 200 m2 - 20 kW, 400 m2 - 40 kW of heat energy.
- If calculations are carried out in other units of measurement, then 40-45 W of heat per 1 m³ of the heated building. Its load is checked by multiplying the specified indicator by the volume of all available heated rooms in the building.
The efficiency of the heat generator, which affects the most efficient fuel consumption, is most often noted in the special technical passport of the equipment.
If you haven't bought yet unit for heating, then you can take into account the efficiency data of gas boilers of various types from the following list:
- gas convector - 85 percent;
- boiler with an open combustion chamber - 87 percent;
- heat generator with a closed combustion chamber - 91 percent;
- condensing boiler - 95 percent.
Initial settlement use of liquefied gas for heating can be calculated using the following formulas:
V = Q / (q x efficiency / 100), where:
- q - fuel caloric content level (if it was not possible to find out the data from the manufacturer, it is advised to set the generally accepted rate of 8 kW / m³);
- V is the consumption of the main gas to be found, m³ / h;
- Efficiency - the efficiency of fuel use by the currently available heat source, written as a percentage;
- Q is the possible load on the heating of a private house, kW.
Calculating gas consumption for 1 hour during the coldest times, it is possible to obtain the following answer:
15 / (8 x 92 / 100) = 2.04 m³ / h.
Working 24 hours without interruption, the heat generator will consume the following amount of gas: 2.04 x 24 \u003d 48.96 m³ (for ease of measurement, it is advisable to round up to 49 cubic meters). Of course, during the heating season, the temperature tends to change, so there are very cold days, and there are also warm ones. Because of this, the value of the average daily gas consumption, which we found above, will need to be divided by 2, where we will get: 49/2 = 25 cubic meters.
Given the data already defined above, one can calculate gas consumption at a turbocharged boiler for 1 month in a house of 150 m², which is located somewhere in the territory of central Russia. To do this, we multiply the daily consumption by the number of days in a month: 25 x 30 = 750 m³. By means of the same calculations it is possible to find the gas consumption of larger and smaller buildings
It is important to know that it would be very good to carry out such calculations even before the building is completely built. This will give you the opportunity to carry out activities that could help improve the operating conditions of the premises, while saving on heat consumption.
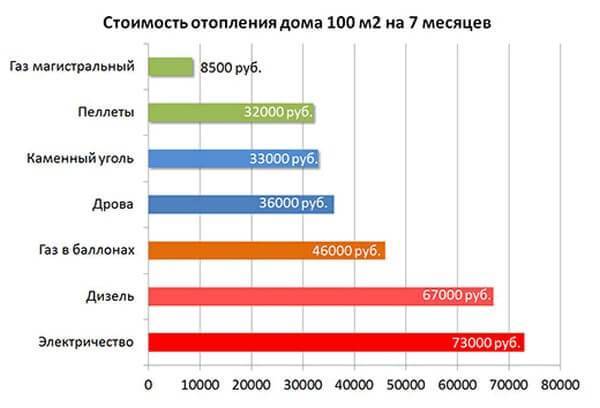
Why Choose Gas
In the last century, firewood was chosen as an economically viable type of fuel.With the development of mechanics and technology, the palm passed to coal. The discovery of deposits of natural combustible gas has replaced coal, and there are fewer harmful emissions into the atmosphere.
The era of the development of green energy and the exploitation of renewable energy sources in the form of solar radiation and wind has come. But not everywhere the number of windy days is enough to generate and accumulate the electricity needed to heat the water boiler. Solar panels are still expensive. A person adheres to a conservative and inexpensive way of heating a home - natural gas.

| Pollutant | Emissions from incineration, maximum | |
| Hard coal, g/t | Natural gas, g/m3 | |
| Ash | % of operating mass of fuel | No |
| Carbon dioxide CO2 | 3000 | 2000 |
| Nitrogen oxides in terms of NO2 | 14 | 11 |
| Sulfur oxides in terms of SO2 | 0,19 | — |
| Benzopyrene | 0,014 | 0,001 |
As can be seen from the table, the content of substances hazardous to human health in gas is lower than in coal. Therefore, natural blue fuel is used to heat housing.