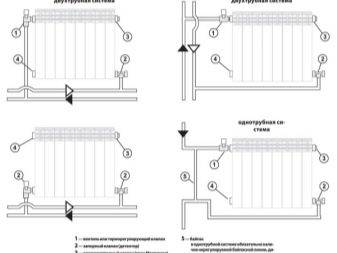
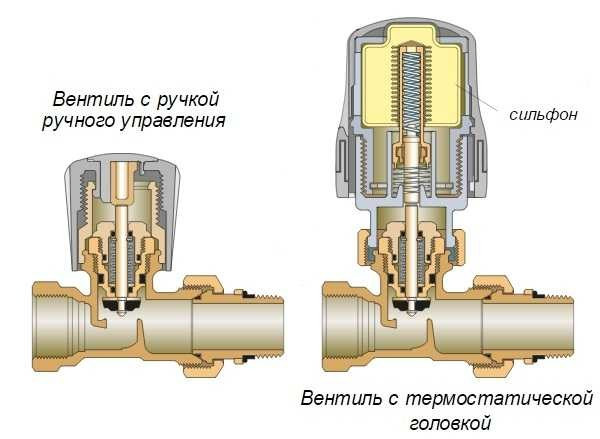
- Radiator connection diagrams
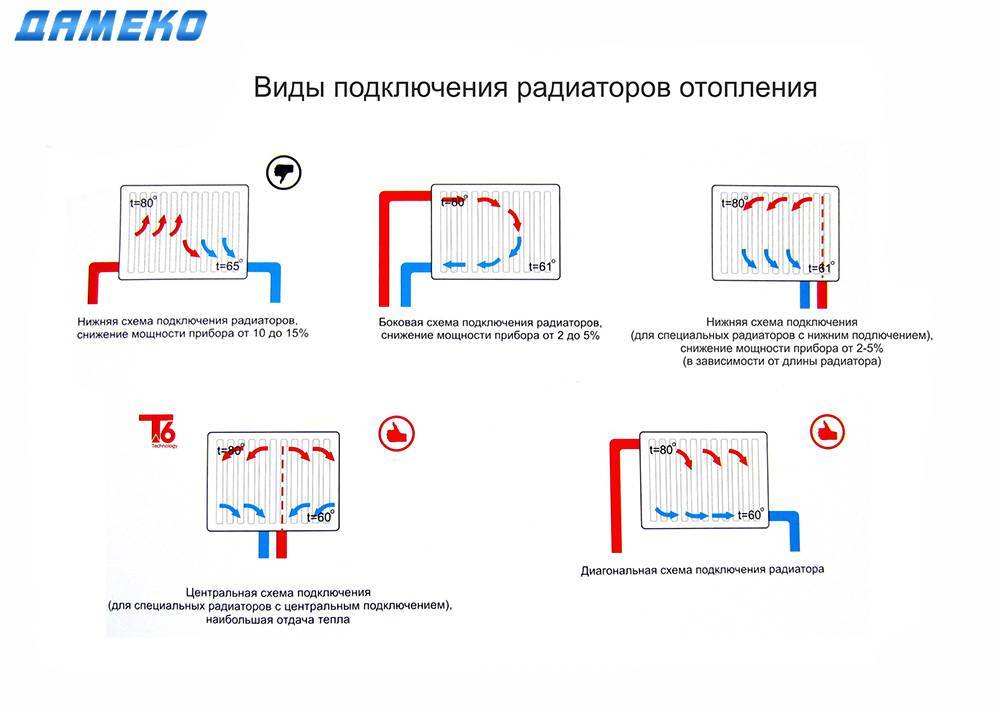
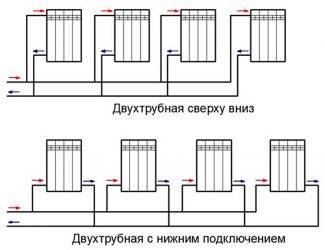
- Radiators with bottom connection
- Radiators with side connection
- Option number 1. Diagonal connection
- Option number 2. Unilateral
- Option number 3. Bottom or saddle connection
- Where is the best place to install a radiator?
- Ways to connect radiators
- Radiator connection options
- How to connect radiators?
- Bottom connection
- Side connection
- Diagonally
- Radiator connection diagrams
- Radiators with bottom connection
- Radiators with side connection
- Option number 1. Diagonal connection
- Option number 2. Unilateral
- Option number 3. Bottom or saddle connection
- What coolant to use
- Schema selection
- Bypass Pros
- Side connection
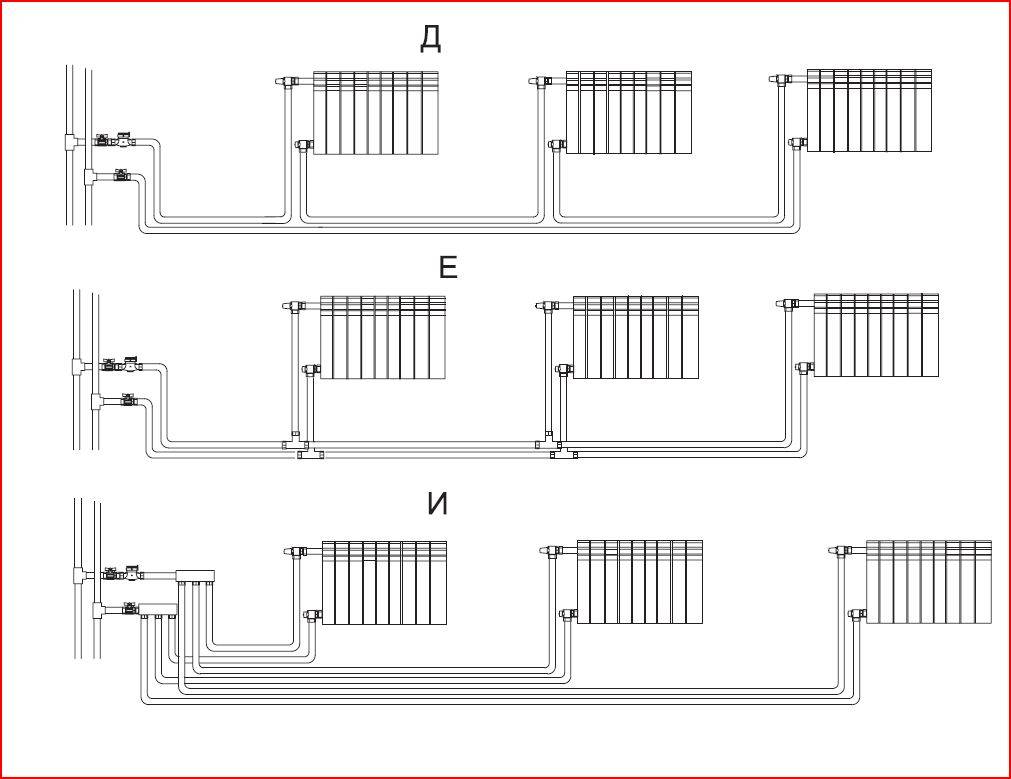
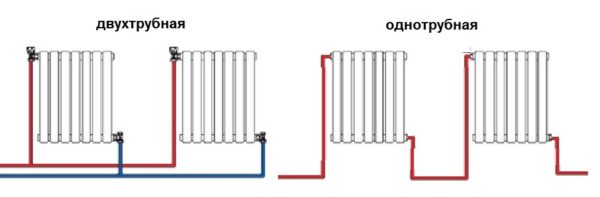
- Heating radiator piping options
- Binding with one-way connection
- Binding with diagonal connection
- Strapping with saddle connection
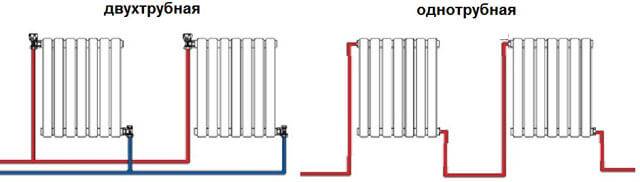
- One-pipe system: "highlights" of connection and real benefits during installation
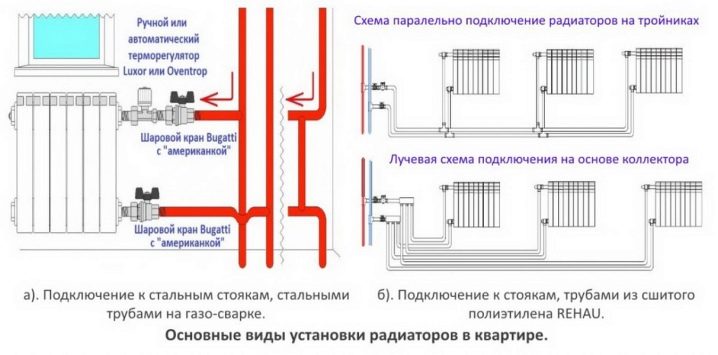
Radiator connection diagrams
How well the radiators will heat up depends on how the coolant is supplied to them. There are more and less effective options.
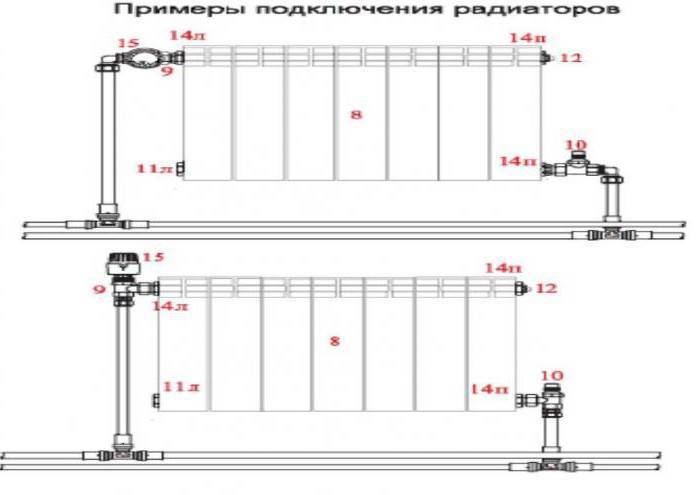
Radiators with bottom connection
All heating radiators have two types of connection - side and bottom. There can be no discrepancies with the lower connection.There are only two pipes - inlet and outlet. Accordingly, on the one hand, a coolant is supplied to the radiator, on the other hand it is removed.
Bottom connection of heating radiators with one-pipe and two-pipe heating systems
Specifically, where to connect the supply, and where the return is written in the installation instructions, which must be available.
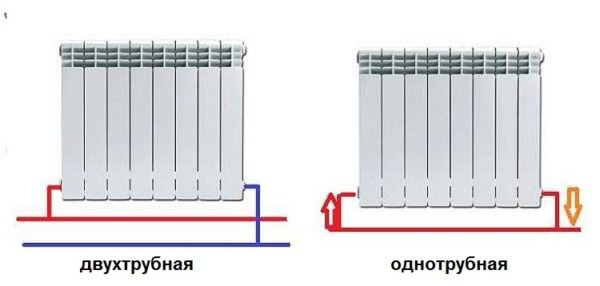
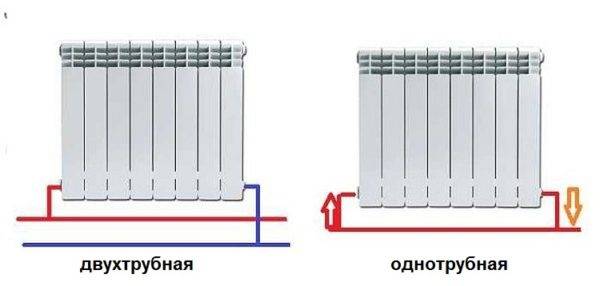
Radiators with side connection
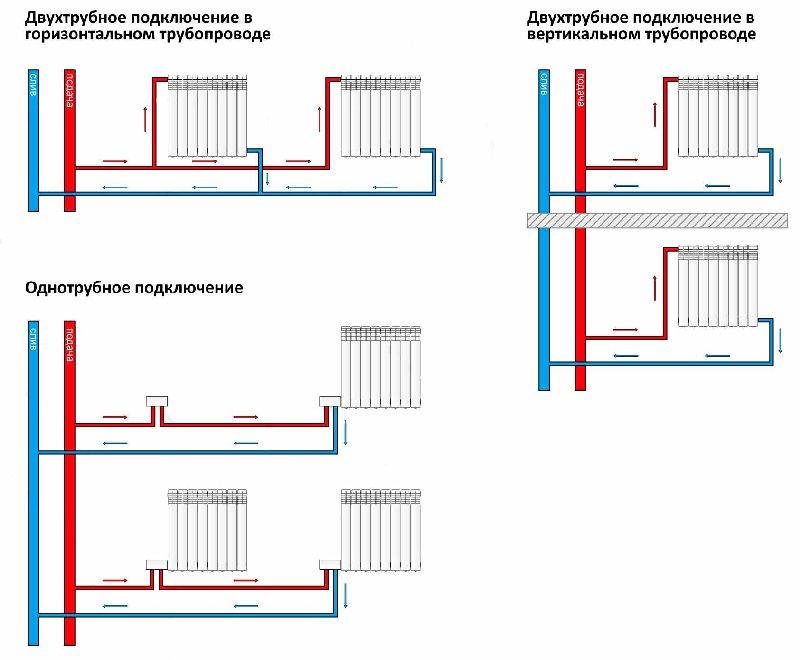
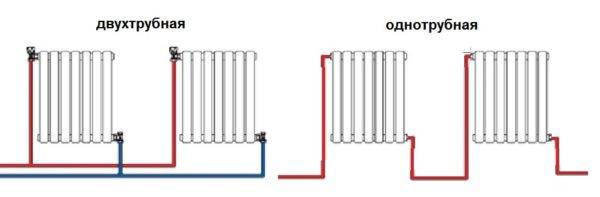
With a lateral connection, there are much more options: here the supply and return pipelines can be connected to two pipes, respectively, there are four options.
Option number 1. Diagonal connection
Such a connection of heating radiators is considered the most effective, it is taken as a standard, and this is how manufacturers test their heaters and the data in the passport for thermal power - for such an eyeliner. All other connection types are less efficient at dissipating heat.
Diagonal connection diagram for heating radiators with a two-pipe and one-pipe system
This is because when the batteries are connected diagonally, the hot coolant is supplied to the upper inlet on one side, passes through the entire radiator and exits from the opposite, lower side.
Option number 2. Unilateral
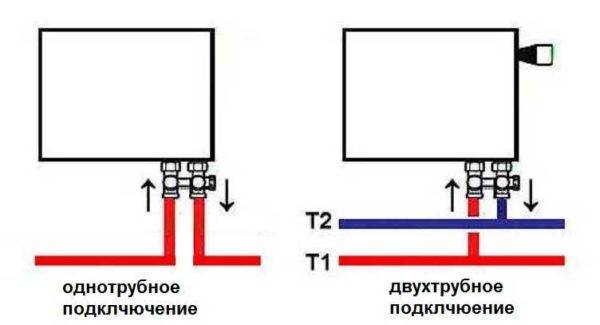
As the name implies, pipelines are connected on one side - supply from above, return - from below. This option is convenient when the riser passes to the side of the heater, which is often the case in apartments, because this type of connection usually prevails. When the coolant is supplied from below, such a scheme is used infrequently - it is not very convenient to arrange pipes.
Lateral connection for two-pipe and one-pipe systems
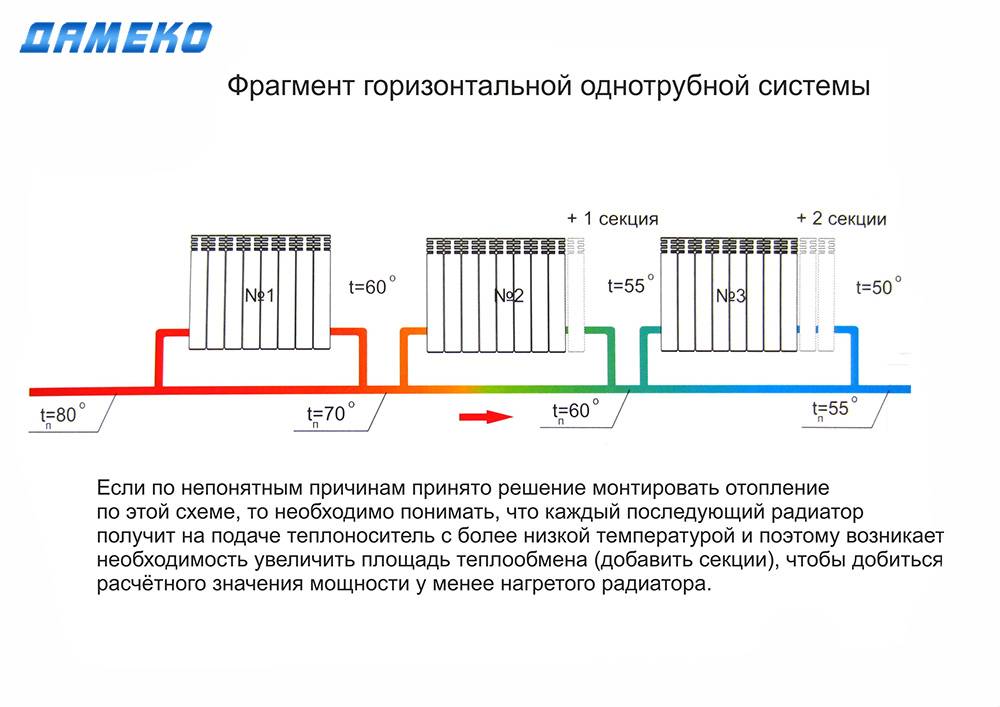
With this connection of radiators, the heating efficiency is only slightly lower - by 2%.But this is only if there are few sections in the radiators - no more than 10. With a longer battery, its farthest edge will not heat up well or even remain cold. In panel radiators, to solve the problem, flow extensions are installed - tubes that bring the coolant a little further than the middle. The same devices can be installed in aluminum or bimetallic radiators, while improving heat transfer.
Option number 3. Bottom or saddle connection
Of all the options, the saddle connection of heating radiators is the most inefficient. Losses are approximately 12-14%. But this option is the most inconspicuous - the pipes are usually laid on the floor or under it, and this method is the most optimal in terms of aesthetics. And so that the losses do not affect the temperature in the room, you can take a radiator a little more powerful than required.
Saddle connection of heating radiators
In systems with natural circulation, this type of connection should not be done, but if there is a pump, it works well. In some cases, even worse than the side. Just at some speed of movement of the coolant, vortex flows arise, the entire surface heats up, and heat transfer increases. These phenomena have not yet been fully studied, therefore it is not yet possible to predict the behavior of the coolant.
Where is the best place to install a radiator?
This question is important, because before connecting the battery must be installed and fixed in a certain place. Everyone knows that usually heaters are located under the windows, but why this is done, people are beginning to be interested in personally organizing the heating of the home and when installing batteries in apartments or country houses.The fact is that much more cold enters the room through the window than through the outer walls. Cold air from the windows will immediately descend to the lower zone and begin to spread along the floor, causing a feeling of cold if a heater is not placed in its path.
If you correctly place the battery under the light opening so that its length is from 70 to 90% of the width of the window, then the cold air flow from it will immediately warm up. At the same time, it is recommended to take the height of the heater at least 110 mm less than the distance from the window sill to the floor, so that when it is installed from below, a gap of at least 60 mm remains, and from above - 50 mm. The minimum offset from the inner surface is 25 mm.
In corner rooms, where there is an additional outer wall and heat losses are much higher, you should install and connect a radiator not only under the window, but also near the cold wall. Its task is to compensate for the heat lost by the side enclosing structure. The installation height in this case does not play a decisive role, you just need to navigate by the level of the batteries under the windows.
In the corner rooms, you need to correctly distribute the power of the radiators that will stand under the windows and near the wall. To do this, it is necessary to calculate in advance the heat loss through the light openings and external fences of the room.
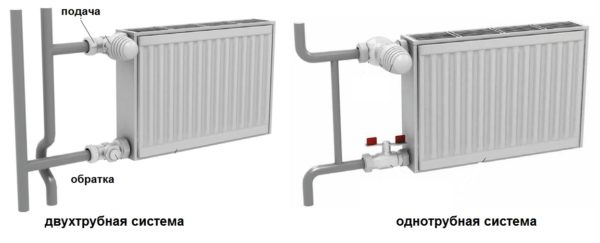
Ways to connect radiators
There are several options for connecting radiators, but they all fall into two broad categories - side and bottom. The bottom connection can be made in the only way, which looks very simple: there are two pipes, one of which is connected to the radiator inlet, and the second to the outlet.The scheme for connecting a heating radiator in an apartment is always described in the documentation attached to it.
The side scheme for connecting batteries in an apartment has more options, including:
- Diagonal connection;
- One way connection;
- Bottom (saddle) connection.
Each option should be given special attention.
Radiator connection options
To know how to properly connect a heating battery, you need to consider that in addition to the types of piping, there are several schemes for connecting batteries to the heating system. These include the following options for connecting heating radiators in a private house:
In this case, the connection of the outlet and supply pipes is made on one side of the radiator. This method of connection allows you to achieve uniform heating of each section at minimal cost for equipment and a small amount of coolant. Most often used in multi-storey buildings, with a large number of radiators.
Useful information: If the battery, connected to the heating system in a one-way scheme, has a large number of sections, the efficiency of its heat transfer will be significantly reduced due to the weak heating of its remote sections. It is better to ensure that the number of sections does not exceed 12 pieces. or use another connection method.
It is used when connecting to a heating system with a large number of sections. In this case, the supply pipe, as in the previous connection option, is located at the top, and the return pipe is at the bottom, but they are located on opposite sides of the radiator.Thus, heating of the maximum battery area is achieved, which increases heat transfer and improves the efficiency of space heating.
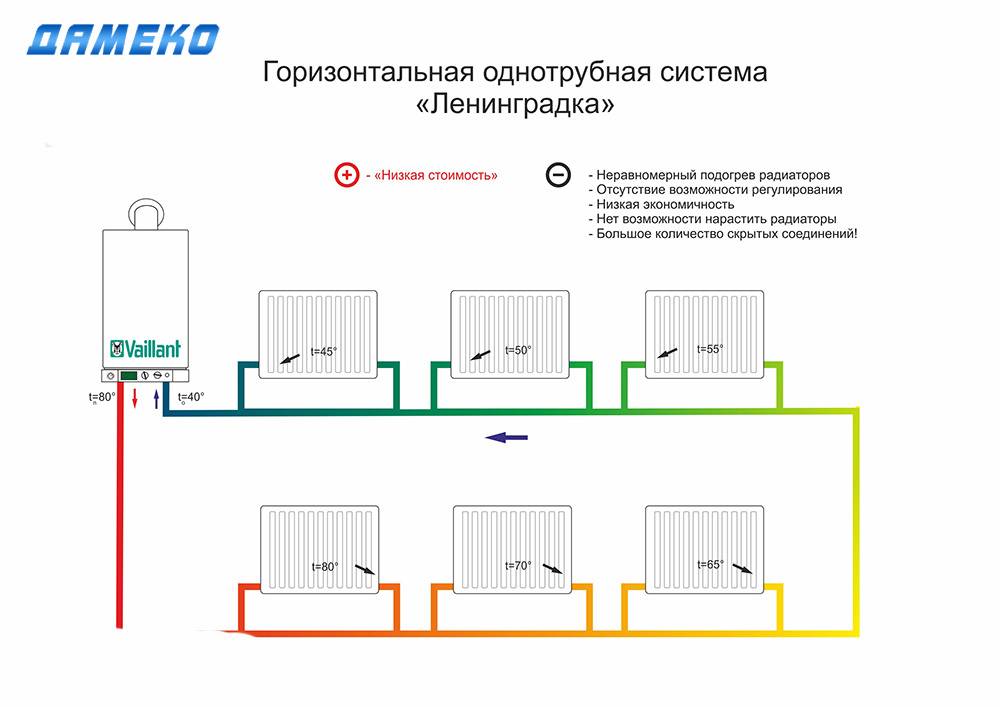
This connection scheme, otherwise called "Leningrad", is used in systems with a hidden pipeline laid under the floor. In this case, the connection of the inlet and outlet pipes is made to the lower branch pipes of the sections located at opposite ends of the battery.
The disadvantage of this scheme is heat loss, reaching 12-14%, which can be compensated by the installation of air valves designed to remove air from the system and increase battery power.
Heat loss depends on the choice of the method of connecting the radiator
For quick dismantling and repair of the radiator, its outlet and inlet pipes are equipped with special taps. To adjust the power, it is equipped with a temperature control device, which is installed on the supply pipe.
What are the technical characteristics of aluminum heating radiators. you can learn from a separate article. It also contains a list of popular manufacturers.
And about what constitutes an expansion tank for closed-type heating. read in another article. Volume calculation, installation.
Tips for choosing an instantaneous water heater for a faucet are here. Device, popular models.
As a rule, the installation of the heating system and the installation of heating radiators is carried out by invited specialists. However, using the listed methods for connecting heating radiators in a private house, this can be done independently, strictly observing the technological sequence of this process.
If you perform these works accurately and competently, ensuring the tightness of all connections in the system, there will be no problems with it during operation, and installation costs will be minimal.
The photo shows an example of a diagonal way to install a radiator in a country house
The procedure for this will be as follows:
- We dismantle the old radiator (if necessary), having previously blocked the heating line.
- We mark the place of installation. The radiators are fixed on brackets that need to be attached to the walls, taking into account the regulatory requirements described earlier. This must be taken into account when marking.
- Attach brackets.
- We collect the battery. To do this, we install adapters on the mounting holes in it (they come with the device).
Attention: Usually two adapters are left-handed and two are right-handed!
- To plug unused collectors, we use Mayevsky taps and locking caps. To seal the joints, we use sanitary flax, winding it on the left thread counterclockwise, on the right - clockwise.
- We fasten ball-type valves to the junctions with the pipeline.
- We hang the radiator in place and connect it to the pipeline with mandatory sealing of the joints.
- We make pressure testing and trial start-up of water.
Thus, before connecting a heating battery in a private house, it is necessary to determine the type of wiring in the system and its connection scheme. At the same time, installation work can be performed independently, taking into account the established standards and process technology.
How the installation of heating batteries in a private house is carried out, the video will show you clearly.
How to connect radiators?
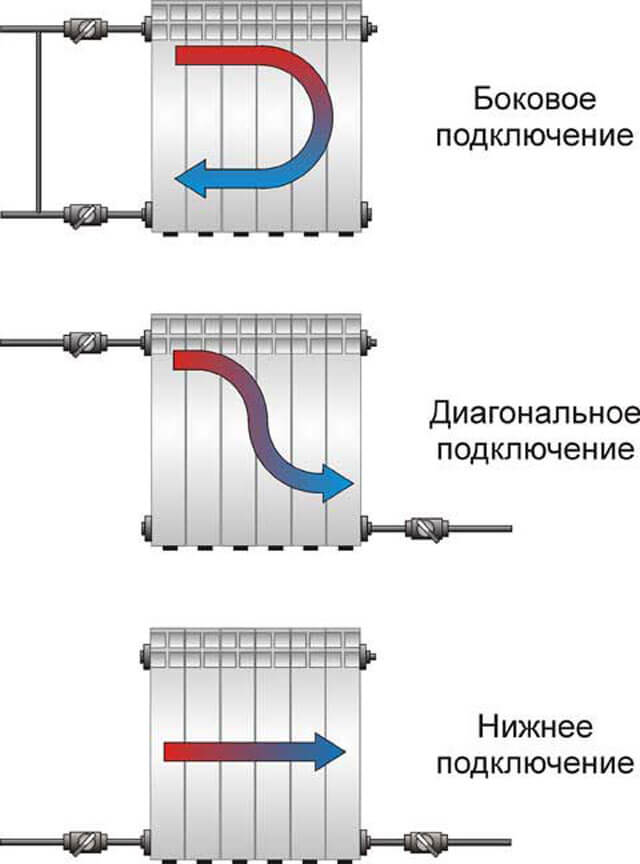
You can connect devices in various ways: from the side, from below, diagonally.
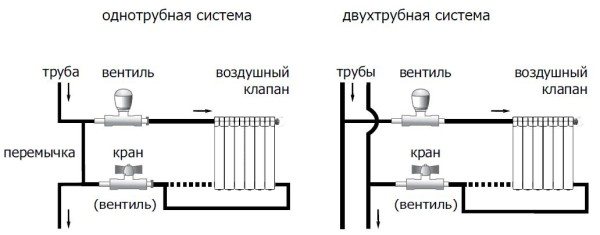
Bottom connection
With this method, pipes are most often laid along the bottom of the wall or under the floor. Hidden wiring rather for design purposes, so as not to spoil the appearance of the room.
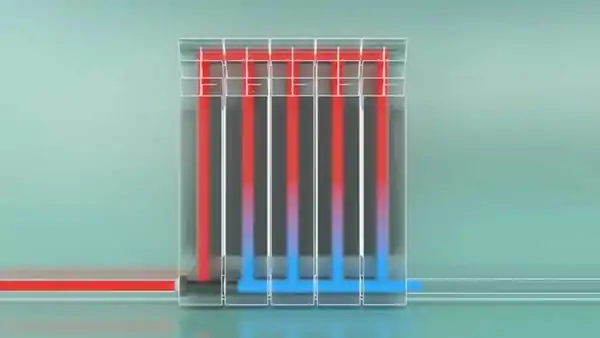
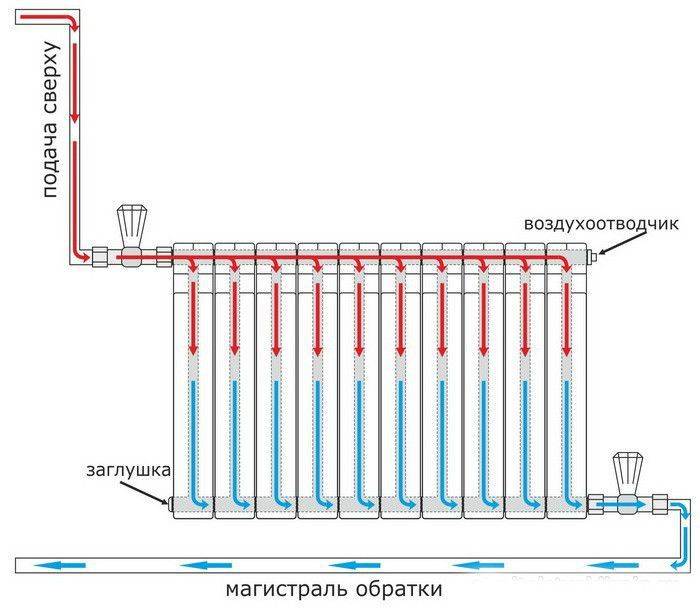
Photo 1. Scheme showing the movement of the coolant through the radiator with the lower method of connection to a single-pipe system.
The method is used for the forced type of water circulation. In the system, a height difference is injected, the heat rises up, then falls, and at the level of the windows it diverges through the heating elements.
Pros:
- the possibility of hidden installation;
- ease of installation;
- has a built-in thermostat.
Minuses:
- significant heat loss;
- the need to install an air vent on each radiator;
- low efficiency.
First, the batteries themselves are attached to the walls, then pipes are brought to them. Below are two pipes: for inlet and outlet. After passing through the heating element, the water returns back to the boiler.
There are universal batteries with four holes, they can be connected in any way.
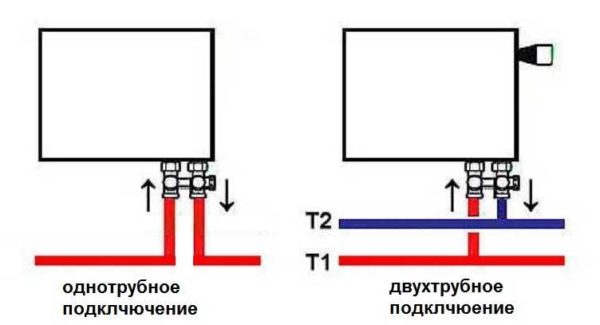
Side connection
Lateral connection is also called one-sided, since both pipes fit on one side of the heater. This usually happens in urban apartments. The method is effective for small sections.
Pros:
- quite effective heating;
- easy installation.
Minuses:
- reduced performance for large heatsinks;
- fast clogging of distant sections.
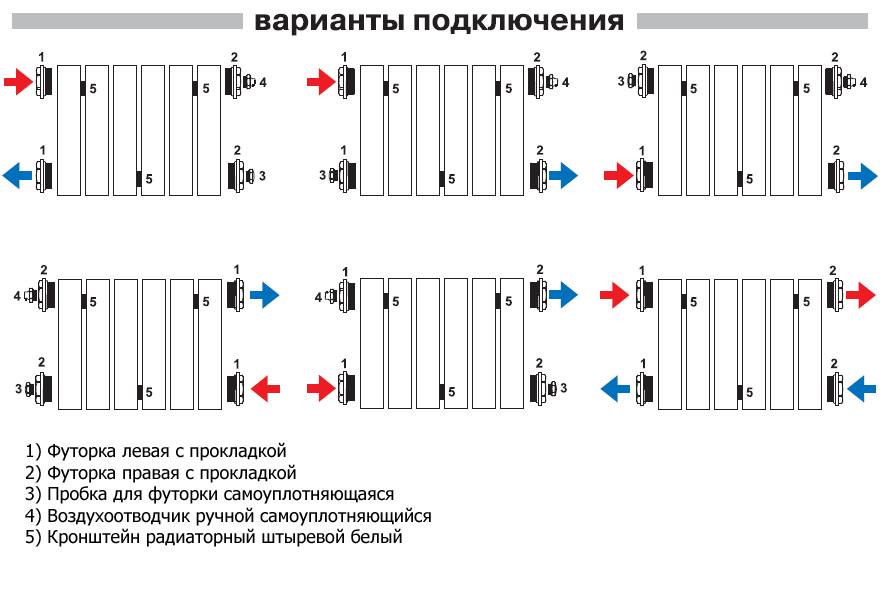
Side connection can be of two options:
- direct; in this case, the pipes are brought from below;
- angular; pipes come out of the wall.
The inlet and outlet pipes approach the battery from one side.At the junctions, it is desirable to install ball valves, which, if necessary, turn off the radiator.
Diagonally
An effective scheme that operates with natural water circulation, but is not used in multi-storey buildings, because there is a forced water supply system. With a diagonal connection, the radiator warms up evenly and gradually from top to bottom. The name comes from the location of the nozzles opposite each other, from corner to corner.
Pros:
- uniform distribution of heat;
- maximum heat transfer;
- the possibility of heating large radiators.
Minuses:
- Pipes fit from different sides, it is difficult to hide them.
- The battery needs to be level. Pipes are supplied from two different sides: water supply - from above, outlet - from below. It is desirable to install valves on the nozzles so that, if necessary, you can disconnect the battery.
Radiator connection diagrams
How well the radiators will heat up depends on how the coolant is supplied to them. There are more and less effective options.
Radiators with bottom connection
All heating radiators have two types of connection - side and bottom. There can be no discrepancies with the lower connection. There are only two pipes - inlet and outlet. Accordingly, on the one hand, a coolant is supplied to the radiator, on the other hand it is removed.
Bottom connection of heating radiators with one-pipe and two-pipe heating systems
Specifically, where to connect the supply, and where the return is written in the installation instructions, which must be available.
Radiators with side connection
With a lateral connection, there are much more options: here the supply and return pipelines can be connected to two pipes, respectively, there are four options.
Option number 1. Diagonal connection
Such a connection of heating radiators is considered the most effective, it is taken as a standard, and this is how manufacturers test their heaters and the data in the passport for thermal power - for such an eyeliner. All other connection types are less efficient at dissipating heat.
Diagonal connection diagram for heating radiators with a two-pipe and one-pipe system
This is because when the batteries are connected diagonally, the hot coolant is supplied to the upper inlet on one side, passes through the entire radiator and exits from the opposite, lower side.
Option number 2. Unilateral
As the name implies, pipelines are connected on one side - supply from above, return - from below. This option is convenient when the riser passes to the side of the heater, which is often the case in apartments, because this type of connection usually prevails. When the coolant is supplied from below, such a scheme is used infrequently - it is not very convenient to arrange pipes.

Lateral connection for two-pipe and one-pipe systems
With this connection of radiators, the heating efficiency is only slightly lower - by 2%. But this is only if there are few sections in the radiators - no more than 10. With a longer battery, its farthest edge will not heat up well or even remain cold. In panel radiators, to solve the problem, flow extensions are installed - tubes that bring the coolant a little further than the middle.The same devices can be installed in aluminum or bimetallic radiators, while improving heat transfer.
Option number 3. Bottom or saddle connection
Of all the options, the saddle connection of heating radiators is the most inefficient. Losses are approximately 12-14%. But this option is the most inconspicuous - the pipes are usually laid on the floor or under it, and this method is the most optimal in terms of aesthetics. And so that the losses do not affect the temperature in the room, you can take a radiator a little more powerful than required.
Saddle connection of heating radiators
In systems with natural circulation, this type of connection should not be done, but if there is a pump, it works well. In some cases, even worse than the side. Just at some speed of movement of the coolant, vortex flows arise, the entire surface heats up, and heat transfer increases. These phenomena have not yet been fully studied, therefore it is not yet possible to predict the behavior of the coolant.
What coolant to use
A significant influence on the service life of devices and the efficiency of the heating system is exerted by the type of coolant used. The internal structure of bimetallic heaters allows the use of liquids that have low quality and purity standards. Similar coolants are used in centralized heating systems.
The use of low-quality water with the presence of chemically active elements adversely affects all elements of the heating system. Calcium and magnesium salts dissolved in the coolant are detrimental to radiators, which cause the appearance of scale and insoluble deposits on the inner surface.
Corrosion can occur under the influence of the following factors:
- increased water hardness;
- the value of the degree of pH, not corresponding to the requirements of operation;
- a large number of organic particles contained in the water;
- oxygen entering the device.
In order to avoid negative impact on batteries, the manufacturer warns about the need to use water in accordance with clause 4.8. SO 153–34.20.501 - 2003.
For bimetallic radiators, it is permissible to use water and antifreeze as a coolant with a pH level in the range of 6.5–9.5.
The use of antifreeze in heating systems has its own characteristics:
- It is recommended to use it in private homes, where it is possible to turn off the heating due to problems with electricity, in order to prevent the coolant from freezing.
- The use has a positive effect on the condition of seals and gaskets, prolonging their service life.
- The environmentally friendly product does not have a negative impact on human health.
- Subject to all rules of use, the service life can reach 10 years.
- Since this liquid has a higher viscosity than water, it is necessary to consider purchasing a more powerful circulation pump for the heating system.
- It is not recommended to use antifreeze in heating systems where zinc pipes are installed in order to prevent the occurrence of a chemical reaction that leads to a decrease in the performance of the equipment.
- Constant monitoring of the acidity of the coolant is required. Exceeding the pH recommended for radiators increases the likelihood of corrosion.
- Antifreeze has a high fluidity, so it is necessary to use high-quality intersectional paronite and silicone gaskets.

Schema selection
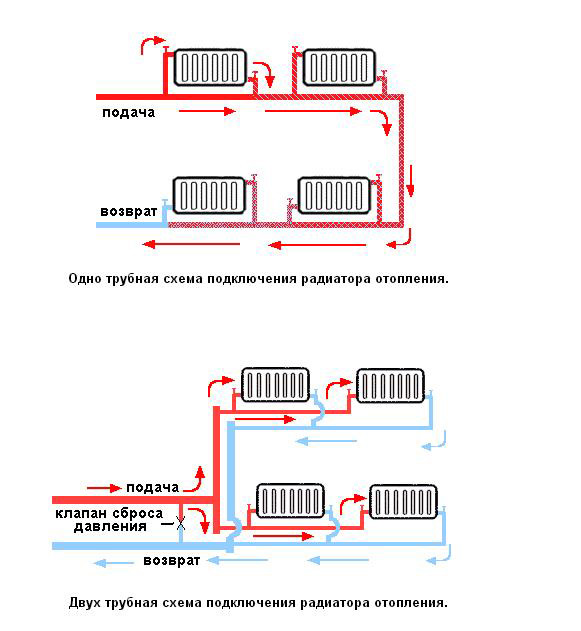
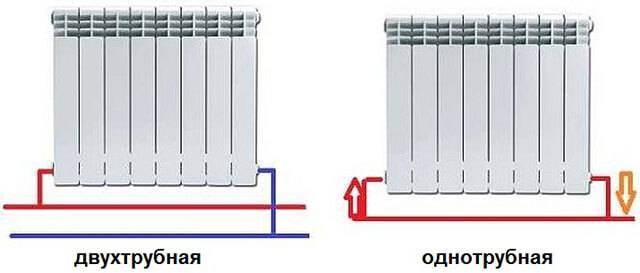
The choice of piping depends on the connection system: one-pipe and two-pipe, and the method of water circulation in the pipes: natural and forced (using a circulation pump).
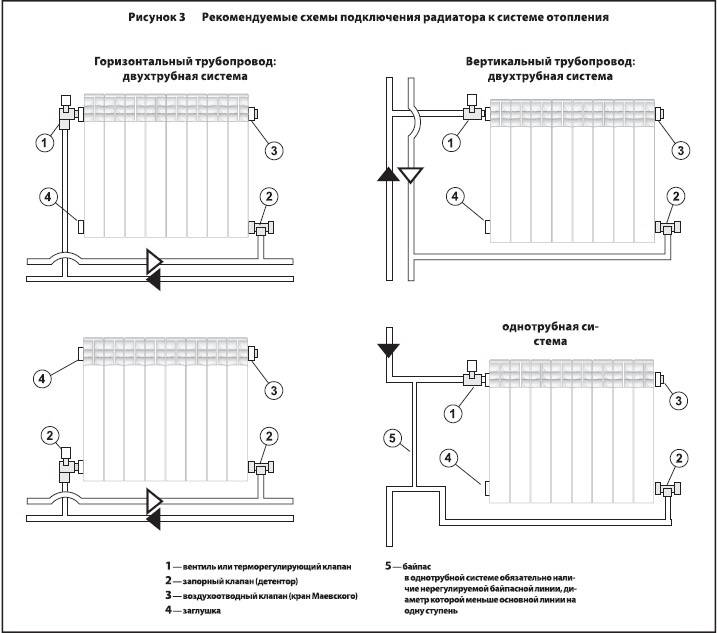
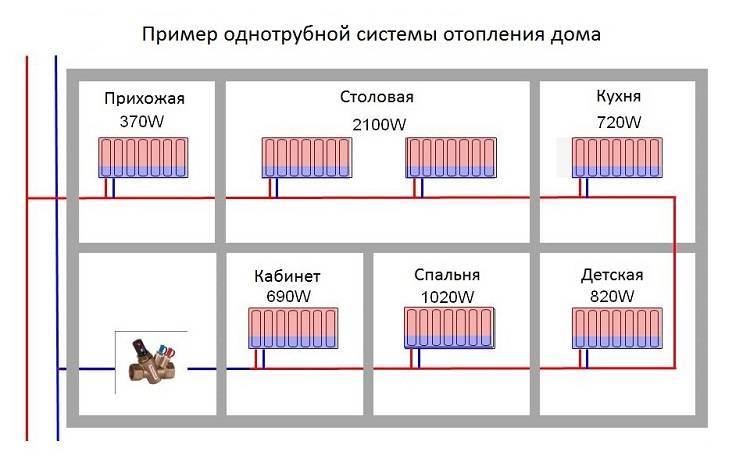
Single-pipe - based on the serial connection of radiators. Hot water, heated by the boiler, passes through all the heating sections through one pipe and goes back to the boiler. Types of wiring for a single-pipe circuit: horizontal (with forced circulation of water) and vertical (with natural or mechanical circulation).
The pipe with horizontal wiring is installed parallel to the floor, the radiators should be located on the same level. The liquid is supplied from below, it is output in the same way. The circulation of water is carried out by means of a pump.
With vertical wiring, the pipes are perpendicular to the floor (vertically), heated water is supplied upwards, and then it descends down the riser to the radiators. Water circulates independently, under the influence of high temperatures.
The two-pipe system is based on the parallel connection of radiators to the circuit, that is, hot water is individually supplied to each battery through one pipe, and water is released through the second. Types of wiring - horizontal or vertical. Horizontal wiring is carried out according to three schemes: flow, dead-end, collector.
Connection of convectors to the heating system is carried out in the following ways: bottom, top, one-sided and diagonal (cross). The circulation of liquid inside it depends on the installation plan of the battery.
For one-pipe and two-pipe systems, vertical wiring is mainly used for houses containing two or more floors.
Bypass Pros
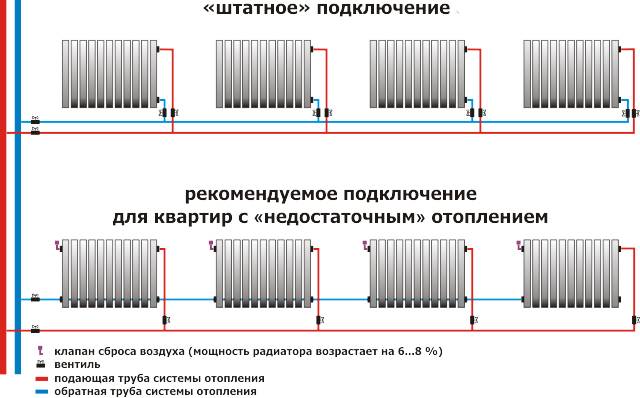
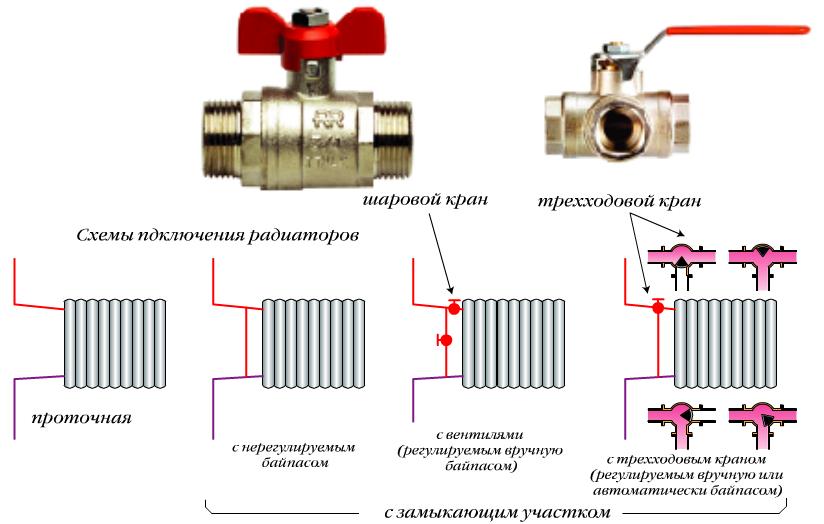
It is sometimes difficult for a homeowner to make a decision on the recommendation of specialists when installing a one-pipe heating system to install a bypass. The principle is simple: a bypass pipe is included in the design (this is the bypass), which will save material resources and allow local repair of the radiator without shutting down the entire system. The latter is relevant for owners of private houses and for residents of typical high-rise buildings of the last century.
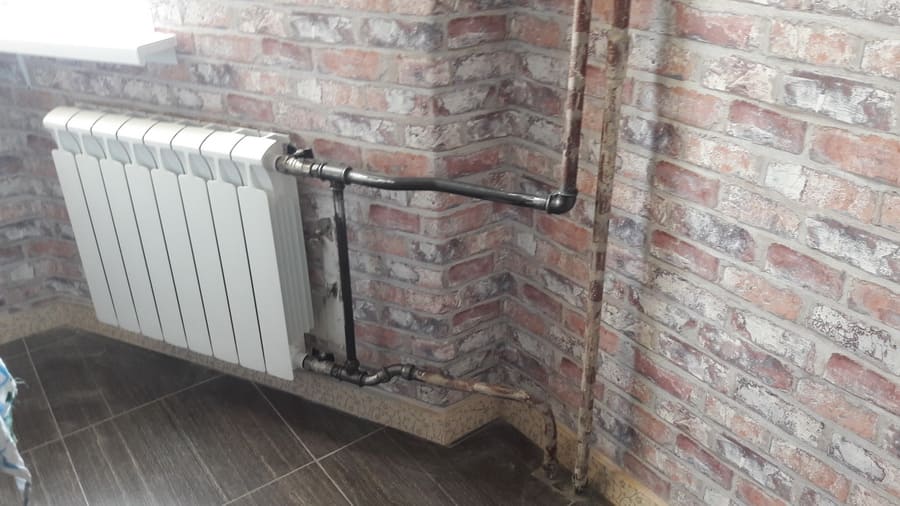
Photo 1. Radiator connected to the heating system. The arrows indicate the location of the bypass and ball valves.
For owners of a large living space with a single-pipe heating system, it will be advisable to connect a "stroke". It is a piece of pipe that is installed in the immediate vicinity of the radiator. The pipe diameter is one position lower than the section of the main pipeline. This is due to the fact that when the carrier is supplied, water prefers to rush along channels of a larger diameter. Thus, it becomes possible to safely start repairing leaking radiator units for home heating.
A gravity-fed system does not provide a comfortable (and adjustable) temperature in living quarters, which is where a bypass is needed. Masters mount a bypass pipe with a circulation pump and temperature sensors located in it. It does not matter if the power supply is interrupted - the bypass will direct the water flows according to the principle of "gravity" and in emergency mode. The bypass pipe saves the homeowner up to 25% of the electricity bill, alternating gravity and forced circulation of the coolant.
Attention! Install the circulation pump in the bypass pipe, adhering to the rule of "curvilinearity": the more bends, the lower the thermal conductivity of the heating system. The bypass is “surrounded” on both sides by ball valves to protect the water supply to a specific radiator
The bypass is “surrounded” on both sides by ball valves to protect the water supply to a specific radiator.
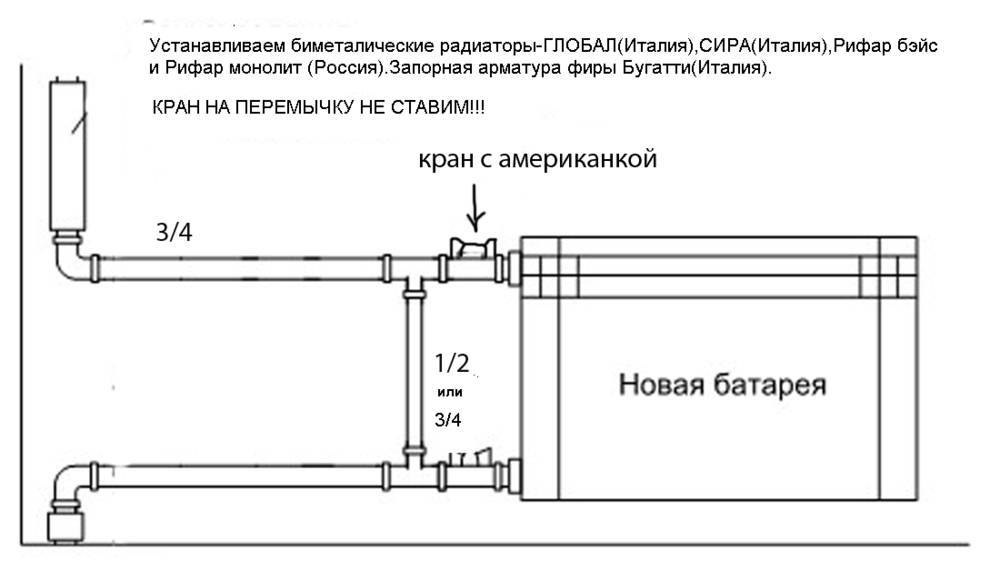
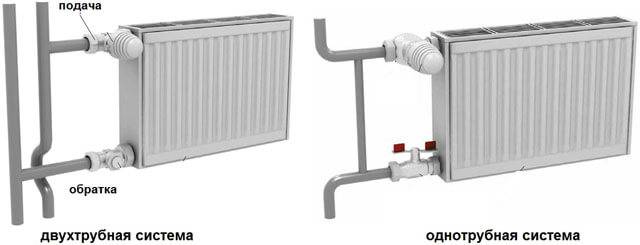
Side connection
This connection option is considered more complicated, since water supply and return are possible through two nozzles. Therefore, it is necessary to know how to properly connect an aluminum heating radiator.
In accordance with this, installation is carried out in several ways:
- With a diagonal connection, hot water enters the radiator through the upper pipe from the side and, passing through the entire heating element, exits into the lower pipe from the other side. In this way, radiators are tested at the factory, it is taken as the basis for determining the power of devices. Therefore, the diagonal connection of the battery with the pipes of the heating system can be called the most effective, other methods are characterized by lower productivity.
- One-way connection means that the supply and return pipes are connected on the same side. The coolant enters the upper pipe and exits through the lower pipe. This method is ideal for apartments in which the heating system riser is located on the side of the heat exchangers. With a lower connection to the heating radiator, installation and operation difficulties may arise.The disadvantage of this connection is the poor heating of long radiators, however, for devices with no more than 10 sections, a one-way connection is just as effective as the previous method.
- The saddle or bottom connection of a heating radiator to a two-pipe system is characterized by the lowest efficiency, heat losses in this case can be up to 14%. However, this method allows you to mask the pipes of the system under the floor, therefore, the appearance of the room looks more aesthetically pleasing.
More powerful radiators help reduce heat loss. It is not recommended to use the saddle connection in systems where the medium moves naturally through the pipes. But in systems with forced circulation of the coolant, the connection diagram for heating radiators with a lower connection works well. The circulation pump built into the heating system causes the water to move faster, which leads to the appearance of eddy currents that heat the surface of the radiator.
Heating radiator piping options
Installation of heating radiators involves their connection to pipelines. There are three main connection methods:
- saddle;
- unilateral;
- diagonal.
Connection options
If you install radiators with a bottom connection, you have no choice. Each manufacturer strictly ties the supply and return, and its recommendations must be strictly followed, because otherwise you simply won’t get heat. There are more options with lateral connection (read more about them here).
Binding with one-way connection
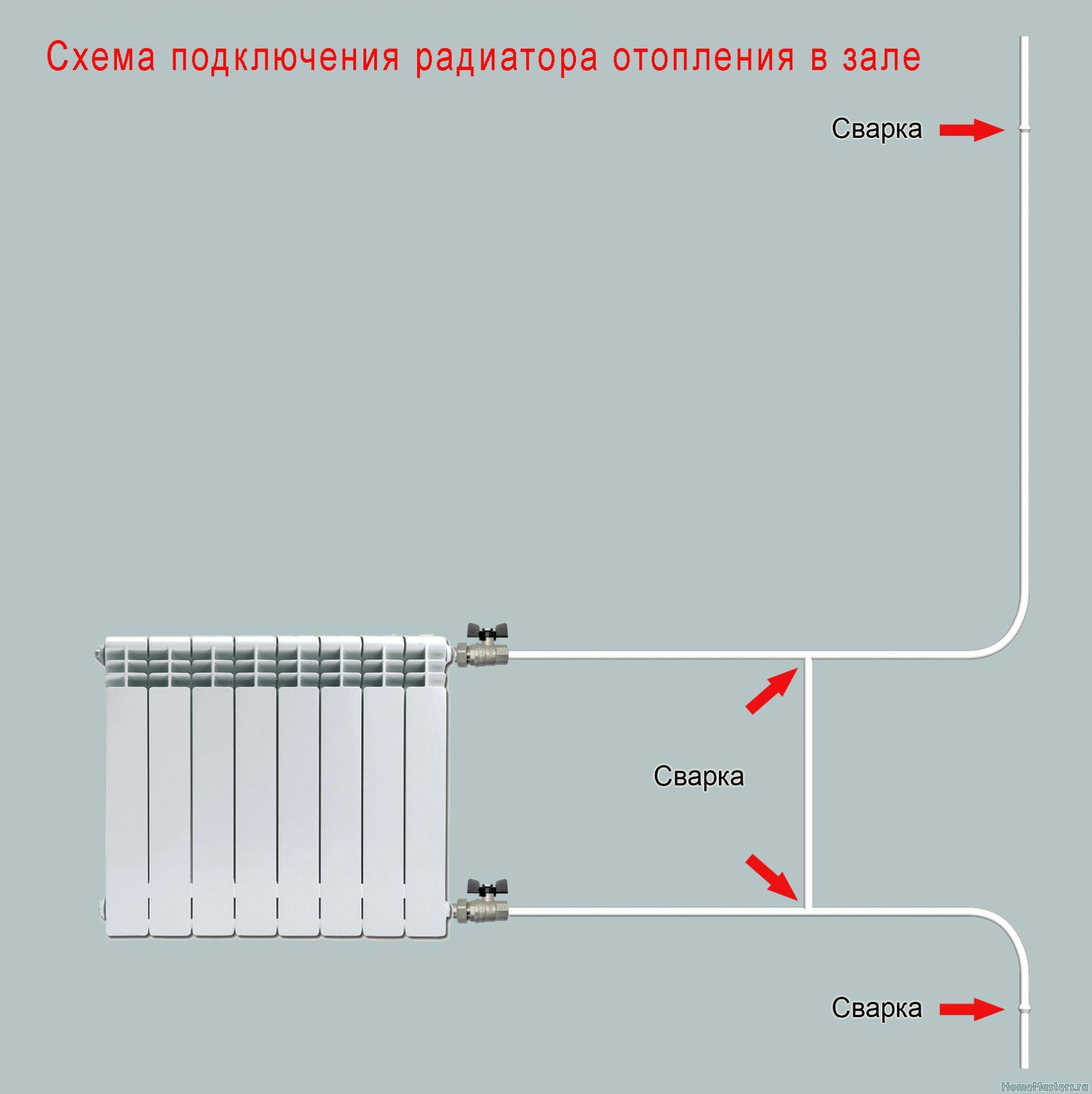
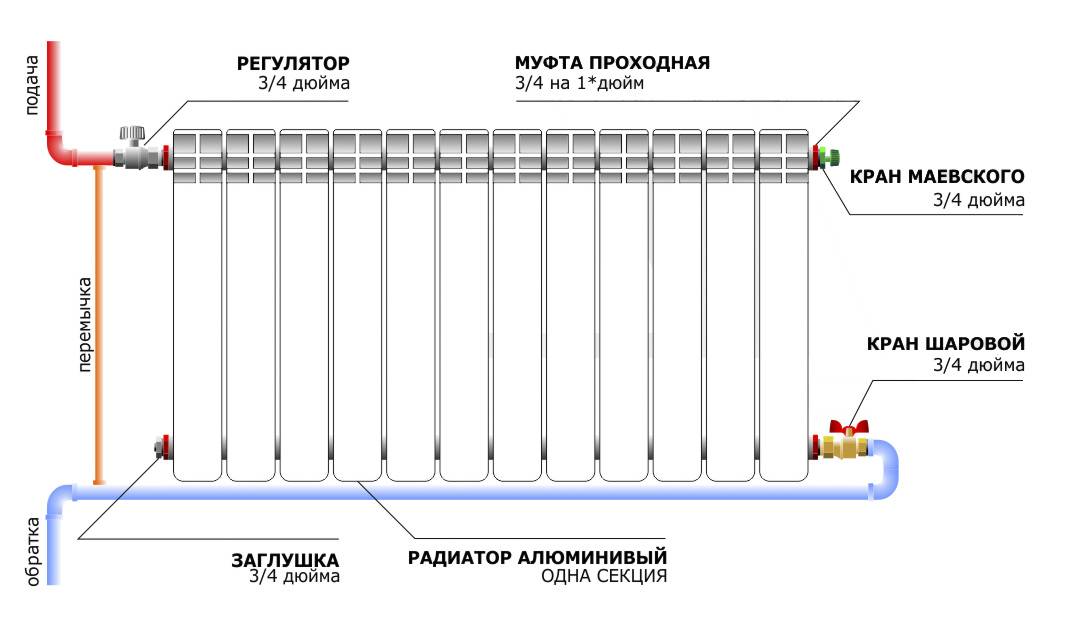
One-way connection is most often used in apartments. It can be two-pipe or one-pipe (the most common option).Metal pipes are still used in apartments, so we will consider the option of tying the radiator with steel pipes on the spurs. In addition to pipes of a suitable diameter, two ball valves, two tees and two spurs are needed - parts with external threads at both ends.
Side connection with bypass (one-pipe system)
All this is connected as shown in the photo. With a single-pipe system, a bypass is required - it allows you to turn off the radiator without stopping or lowering the system. You can’t put a tap on the bypass - you will block the movement of the coolant along the riser with it, which is unlikely to please the neighbors and, most likely, you will fall under a fine.
All threaded connections are sealed with fum-tape or linen winding, on top of which packing paste is applied. When screwing the tap into the radiator manifold, a lot of winding is not required. Too much of it can lead to the appearance of microcracks and subsequent destruction. This is true for almost all types of heating appliances, except for cast iron. When installing all the rest, please, without fanaticism.
Option with welding
If you have the skills / ability to use welding, you can weld the bypass. This is what the piping of radiators in apartments usually looks like.
With a two-pipe system, a bypass is not needed. The supply is connected to the upper entrance, the return is connected to the lower one, taps, of course, are needed.
One-way piping with a two-pipe system
With lower wiring (pipes are laid along the floor), this type of connection is made very rarely - it turns out inconvenient and ugly, it is much better to use a diagonal connection in this case.
Binding with diagonal connection
Installing heating radiators with a diagonal connection is the best option in terms of heat transfer. She is the highest in this case. With a lower wiring, this type of connection is implemented easily (example in the photo) - supply from one side at the top, return from the other at the bottom.
A single pipe system with vertical risers (in apartments) does not look so good, but people put up with it because of the higher efficiency.
Coolant supply from above
Please note that with a one-pipe system, a bypass is again required. Coolant supply from below
Coolant supply from below
Strapping with saddle connection
With lower wiring or hidden pipes, installing heating radiators in this way is the most convenient and most inconspicuous.
With saddle connection and bottom single-pipe wiring, there are two options - with and without bypass. Without a bypass, the taps are still installed, if necessary, you can remove the radiator, and install a temporary jumper between the taps - a drive (a piece of pipe of the desired length with threads at the ends).
Saddle connection with one-pipe system
With vertical wiring (risers in high-rise buildings), this type of connection can be seen infrequently - too large heat losses (12-15%).
One-pipe system: "highlights" of connection and real benefits during installation
Initially, a single-pipe heat supply connection system was the only profitable one: heating radiators were connected according to the physical parameters of a “serial connection”.
The choice was based on economical pricing:
- The cost of purchasing conductors for the coolant was halved in comparison with a two-pipe system.
- Savings were achieved when buying fittings, fittings, taps.
- Radiators of all existing brands were suitable for this system: from cast-iron classics to "advanced" bimetal.
There were some negative moments: the radiators, looped in series, heated up unevenly, the last one in the circuit did not correspond to the set (expected) temperature parameters. This was the case until specialists discovered the principle of a "bypass pipe", known as a bypass.