- Starting enricher on a 4t scooter - description and purpose
- What does it consist of
- About product varieties
- Principle of operation
- Replacing the solenoid valve VAZ 2107
- Replacing the filling valve in the washing machine
- Purpose and application of solenoid valves
- Valve device
- The principle of operation of electromagnetic systems
- Principle of operation
- Upgraded mechanism based on magnets
- Purpose and principle of operation of the device
- The magnetic field created by the coil
- Installation and operation rules
- Solenoid valves Danfoss
- Description and principle of operation of the solenoid
- How to install a do-it-yourself solenoid valve for water (12 Volt, 220V)
- Solenoid valve installation process (220V, 12V): practical tips
- Features of Asco Solenoid Valves
- Classification of solenoid valves depending on the features of the device
- Design features, classification of valves
Starting enricher on a 4t scooter - description and purpose
Not all motorcycle enthusiasts know why a solenoid valve on a scooter is needed. This device is also called a starting enricher. He is responsible for the volume of the air-fuel mixture, which is filled through the jet cylinder chamber when starting a cooled motor scooter.A feature of small-capacity motorcycles is the engine's need for an enriched mixture during a cold start of a scooter engine. The fuel entering through the carburetor is mixed with air in a certain concentration thanks to the solenoid valve connected to the carburetor.
If the starting enricher is functioning, and there are no breakdowns of the power unit, starting the engine is not a problem even in the cold season
There is no doubting the importance of the electric valve to ensure trouble-free starting of the engines of modern mopeds and scooters. However, if there are difficulties with starting the engine, interruptions in operation and excessive gluttony of the motor, it can be assumed that there are problems with the starting enricher
That is why it is important to know its device and be able to check its performance.
What does it consist of
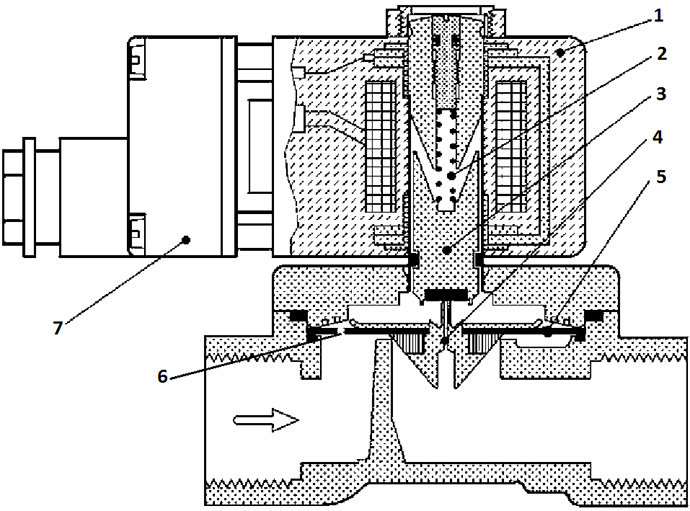
Each valve, regardless of the structural features, is placed in a special case. It is made of durable metal: brass or cast iron. To lighten the weight of the structure, synthetic polymers are sometimes used in modern production, which are not inferior in strength. Among the most common materials are nylon, polypropylene or ecolon. They are also used to make lids.
Fig 2. Valve device
The design of the solenoid valve consists of the following elements:
- Coils
- Plug
- Plunger
- Springs
- stock
- membranes
- fasteners.
The membrane is the main driving element, which is built in the form of a special piston. A design feature is a coil that controls the device in automatic mode.
Fig 3. What the valve consists of
In addition to the main body, the coil is equipped with a separate protective structure.Using copper with an enamel coating, a winding is made. The top layer acts as a protective layer, which avoids an early failure of the coil. Due to the durable metal shell, the mechanism is able to withstand high pressure. Models from reputable manufacturers are popular in piping systems and other designs where high pressures are required.
About product varieties
Classification of products is carried out according to several parameters.
Based on the position of the locking element in the absence of voltage on the coil, there are:
- Normally open, or NO. The passage for liquid or gas is open, and when voltage is applied, it closes.
- Normally closed, or NC. The passage for the medium is blocked, and when voltage is applied, it opens.
Some models are produced universal, and normally the position of the locking element is adjusted during installation and connection to the control network. Such switched devices are called bistable.
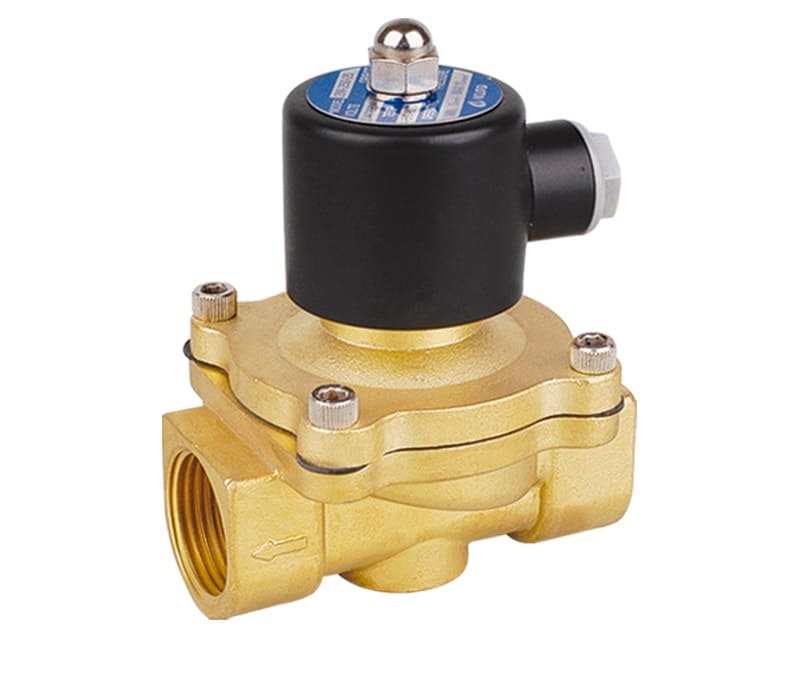

Depending on the working environment, valves are produced for:
- Air.
- Water.
- Pair.
- active media.
- Fuels and lubricants.
Devices for operation in radioactive environments are distinguished by a special selection of materials with increased radiation resistance. The vacuum solenoid valve must provide particularly high tightness
Based on the characteristics of the external environment, the performance of the device can be:
- Normal
- For wet areas.
- Heat-resistant (for high temperatures).
- Frost-resistant (for extremely low temperatures).
- Explosion-proof. Such devices should not spark when turned on or off. To do this, they use special design solutions and materials.
According to the type of supply voltage, the coils are divided into
- AC, high voltage. They develop great efforts, are used on main pipelines of high pressure and large diameters.
- DC, low voltage. They are used on pipes of small cross section and low pressure.
Read next: How to distinguish a 124 engine from a 126 externally
There is a separate class of high pressure solenoid shut-off valves. They are called cutoffs. They are designed to instantly shut off pipelines or seal containers in case of emergency or emergencies.
And, finally, according to the type of functioning, the valves are divided into
- One-way. Such a valve has only an inlet pipe. Usually they are normally closed and open the way for water or air flow to the external environment. They are used as protection.
- Two-way. The most common type, they have inlet and outlet pipes and are mounted in a pipeline break. They are used to control the flow in one of the circuits of the pipeline system.
- Three-way. They can have one inlet and two outlets or two inlets and one outlet.

Three-way valves of the first type are used to redirect flows from one circuit to another (for example, in a heating system). This allows you to maintain a constant temperature of the working medium without changing the parameters of the heat source. Devices of the second type are used to mix two streams with different temperatures. A typical example is a single-lever ball mixer in the kitchen or in the bathroom.
Principle of operation
A shut-off locking device is often called an anti-flood, meaning its main purpose is to prevent fluid from flowing out of the pipeline.
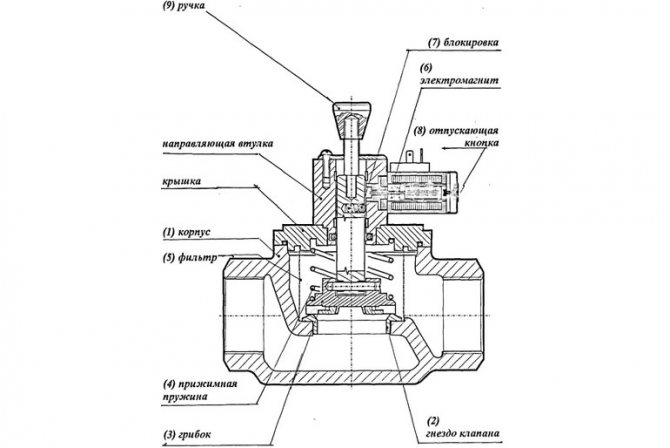
The valve is designed in such a way that upon a manual command of the personnel, a signal given by a sensor or another element, the movement of the medium in a direction not provided for by the design, the locking device quickly operates and the device cuts off the passage of the working medium. A characteristic feature of the apparatus is its rapid response, usually provided by actuation of a spring or other mechanism to close the valve.
For example, in a disposable valve, fluid entering the device impacts the silicone gasket. Under the influence of moisture, it grows in volume, lifts the shutter of the locking mechanism. It blocks the channel and stops the movement of the medium.
Replacing the solenoid valve VAZ 2107
To replace the valve, you only need a 13 wrench and a new valve. Replacing the solenoid valve VAZ 2107 is as follows:
- turn off the ignition;
- unplug the power wire terminal from the valve;
- use the key to unscrew the valve;
- screw the new valve into the carburetor with your fingers;
- tighten the valve with a wrench;
- put on the terminal of the power wire to the outlet on the valve;
- start the engine and check the operation of the valve.
This completes the replacement of the VAZ 2107 solenoid valve. If the engine continues to run erratically, check the carburetor jets and ignition system.
Replacing the filling valve in the washing machine
We advise you to entrust the replacement of the valve to a washing machine repairman.
Manufacturers usually place the valve on the back wall at the top of the washing machine. To make it convenient to get the valve, the cover is removed.This part of the body is fixed with 2 self-tapping screws. They need to be unlocked. The lid is pushed from the front side to the back wall. After that, it is easily removed.
In washing machines where the loading is vertical, the valve is located at the bottom of the back of the body. To get to it, you need to remove part of the housing on the side of the washing machine.
Before you begin to remove the valve, be sure to turn off the water supply. The wire terminals or hoses must be disconnected from it. In the event that fixation is provided with disposable clamps, then they must be prepared in advance. In addition, reusable products can also be used.
The bolts fixing the part must be unscrewed. There are models in which it is securely fastened with latches. In this situation, you will need to pull back the part of the latch that secures the part. The valve turns and pulls out. It is being replaced. Then, in reverse order, the new valve is fixed.
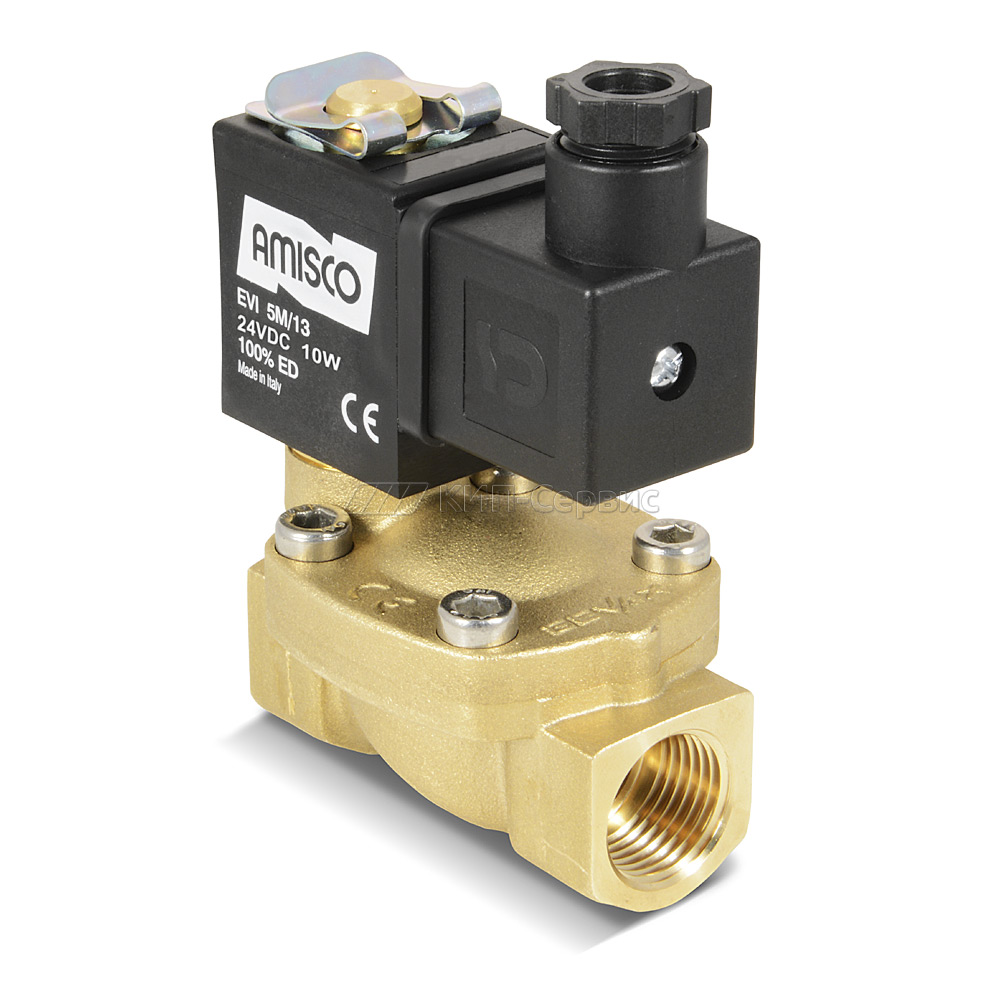
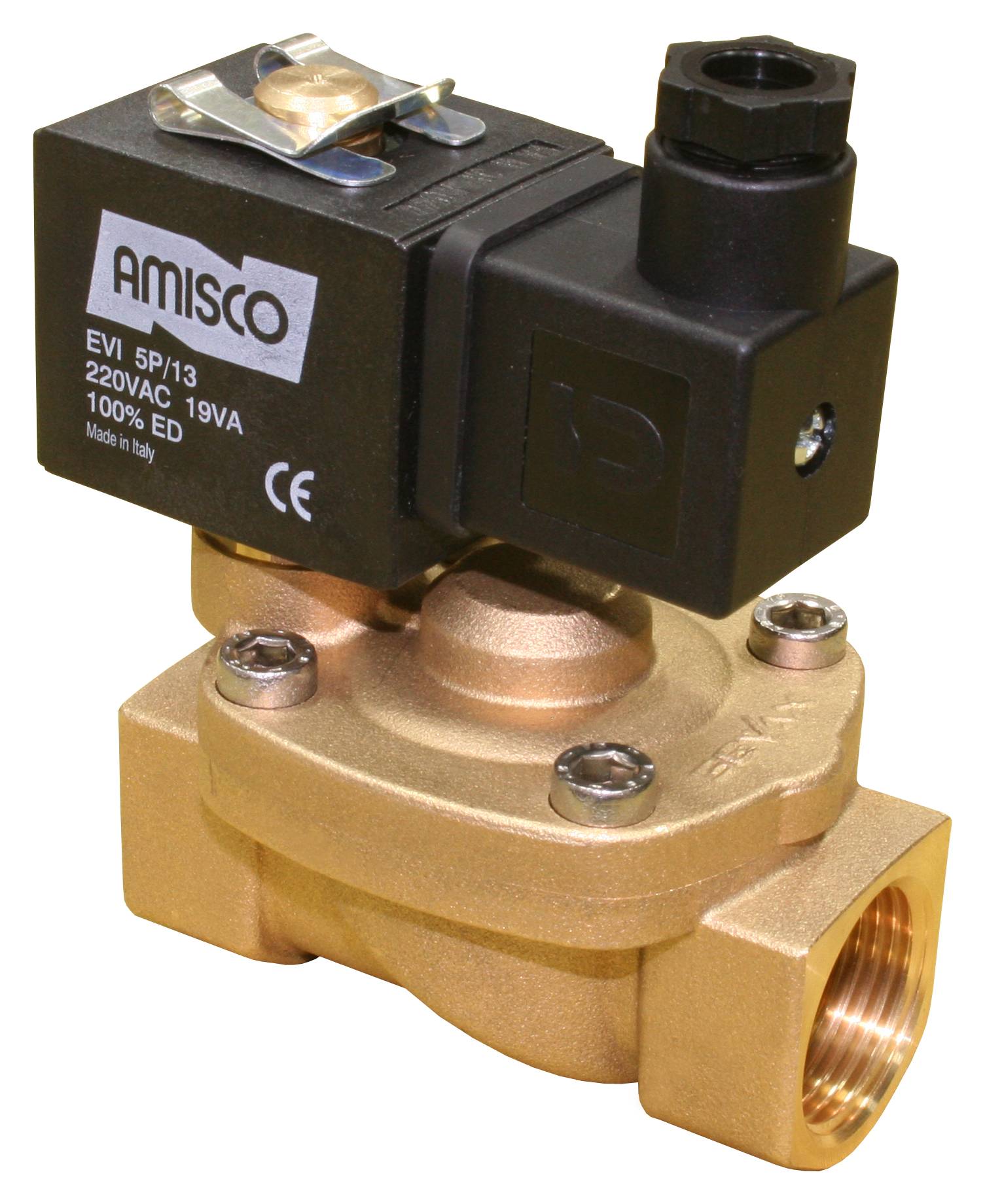
Purpose and application of solenoid valves
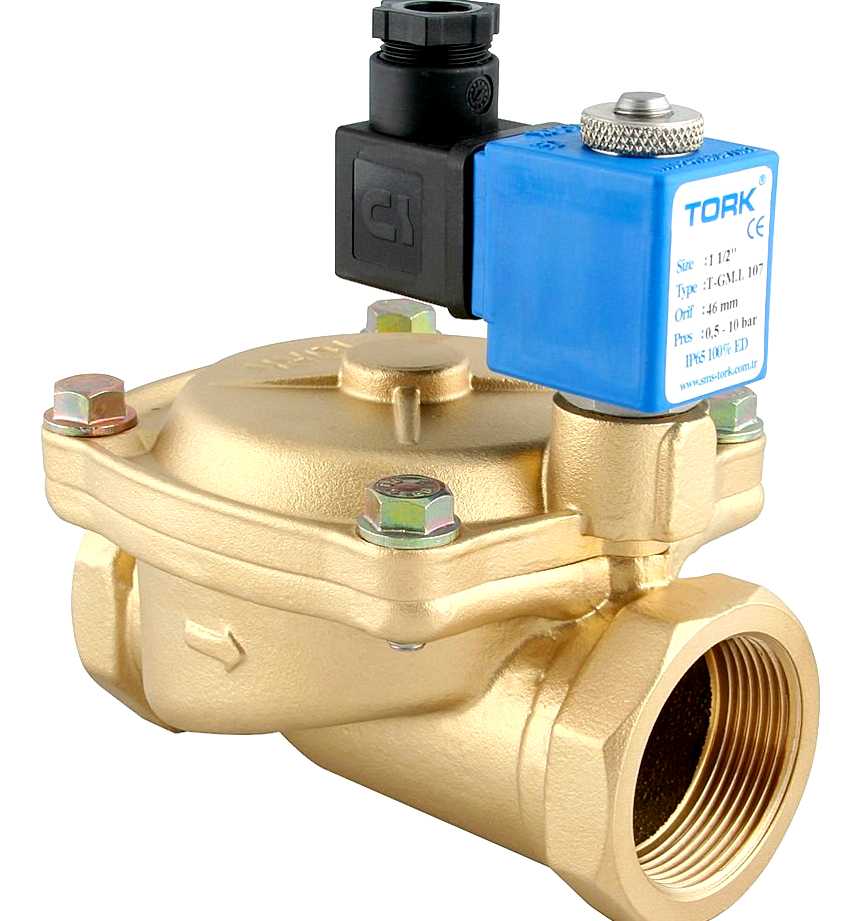
The solenoid valve performs the role of a regulating and shut-off device in the remote control of the transportation of liquid, air, gas and other media flows. At the same time, the process of its use can be both manual and fully automated.
The most popular is the Esbe solenoid valve, which has a solenoid valve as its main device. The solenoid valve consists of electric magnets, which are popularly called solenoids.In its design, the solenoid valve resembles an ordinary shut-off valve, but in this case, the position of the working body is controlled without the use of physical effort. The coil takes on the electrical voltage, thereby driving the solenoid valve and the entire system.
The solenoid valve works both in complex technological processes in production, or in utilities, and in everyday life. Using such a device, we can independently regulate the volume of air or liquid supply at a particular point in time. The vacuum valve can also work in rarefied air systems.
Depending on the conditions where the solenoid valve is used, the housing can be manufactured as ordinary and explosion-proof. Such a device is mainly used at points of oil and gas production, as well as at car filling stations and fuel depots.
Water valves are used to automate water purification systems. In addition, the electromagnetic water valve has found its application in maintaining the water level in water tanks.
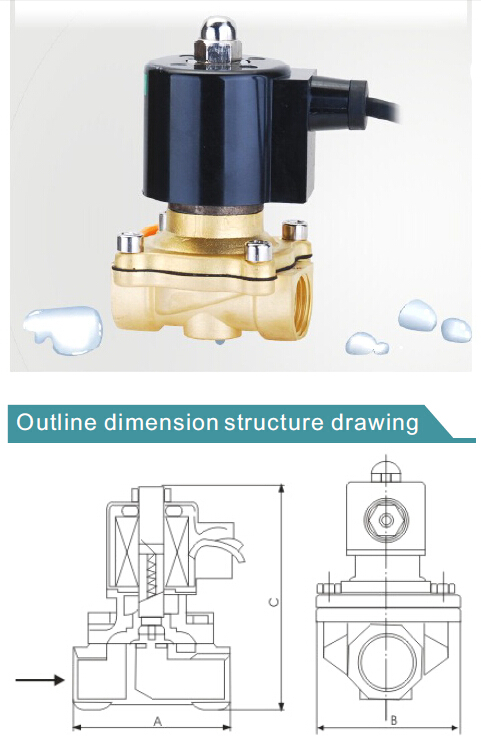
Valve device
The main structural elements of the solenoid valve are:
- frame;
- lid;
- membrane (or piston);
- spring;
- plunger;
- stock;
- an electric coil, also called a solenoid.
Valve device diagram
The body and cover can be made of metal materials (brass, cast iron, stainless steel) or polymeric (polyethylene, polyvinyl chloride, polypropylene, nylon, etc.). Special magnetic materials are used to create plungers and rods. Coils must be hidden under a dustproof and sealed case in order to exclude external influence on the fine work of the solenoid.The winding of the coils is carried out with enameled wire, which is made of electrical copper.
The device is connected to the pipeline by a threaded or flanged method. A plug is used to connect the valve to the mains. For the manufacture of seals and gaskets, heat-resistant rubber, rubber and silicone are used.
Drives with an approximate operating voltage of 220V are supplied with the product. Separate companies carry out orders for the supply of drives with a voltage of 12V and 24V. The drive is equipped with a built-in SFU forced control circuit.
The principle of operation of electromagnetic systems
The electromagnetic inductor works in all known AC and DC voltages (220V AC, 24 AC, 24 DC, 5 DC, etc.). Solenoids are placed in special housings protected from water. Due to the low power consumption, especially for small electromagnetic systems, control using semiconductor circuits is possible.
The smaller the air gap between the stopper and the electromagnetic core, the stronger the magnetic field strength increases, regardless of the type and magnitude of the applied voltage. Electromagnetic systems with alternating current have a much larger rod size and magnetic field strength than systems with direct current.
When voltage is applied and the air gap is at its maximum extent, AC systems, consuming a large amount of energy, raise the stem and the gap closes. This increases the output flow and creates a pressure drop. If a direct current is supplied, then the increase in the flow rate occurs rather slowly, until the voltage value becomes fixed.For this reason, valves can only control low pressure systems, except those with small orifices.
In other words, in a static position, provided that the coil is de-energized and the device is in the closed/open position (depending on the type), the piston is in tight connection with the valve seat. When voltage is applied, the coil transmits a pulse to the actuator and the stem opens. This is possible because the coil generates a magnetic field, which in turn acts on the plunger and is drawn into it.
Principle of operation
The intake valve has two functional states - closed (it happens more often) and open. The valve has a coil, which is energized to form an electromagnetic field, as a result of which the valve opens, letting water into the machine. This principle of inclusion causes another name for the part - a solenoid valve.
As soon as the water fills the tank to the desired level, the control module sends a command to cut off the power supply to the valve. The result will be closing the valve and stopping the water supply.
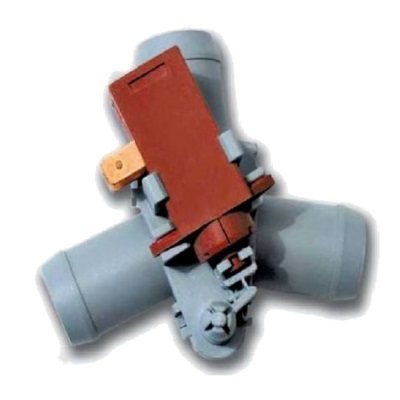

For information on how a single electromagnetic filler (inlet) valve for washing machines looks like, see the following video review.
The intake valves of machines of different models and manufacturers differ in the number of coils. Some valve models have only one coil, others have two coils. Valves with three coils are also common. The number of coils corresponds to the number of sections in the valve through which water is supplied to the dispenser.
Models with a single coil are found in old washing machines in which the work is controlled by a command device (a jet of water is sent to the dispenser mechanically). In modern machines, valves with two and three coils are installed.

Upgraded mechanism based on magnets
Now let's analyze the work based on magnets that our craftsmen suggested. Instead of the usual crankshaft, there is a special one that has magnetic eccentrics made of magnets (or having magnets in its structure). They attract the valve structure and are in constant engagement with it. That is, the valve is always, as it were, magnetized to this part of the shaft. At the right time it closes, at another time it opens.
What does this give us? It's simple - camshafts do not experience spring pressure, do not spend energy on overcoming compression, and therefore a lot of energy is really saved! This is really a breakthrough.
As the manufacturers themselves assure, fuel economy reaches 3-4 liters per 100 kilometers, and thus, if your PRIORA (on mechanics) consumes 8-9 liters in urban mode, then after the rework it will be only 5-6 liters! Just super! Power is also added, according to the inventors, about 20 - 30 hp.
Now guys, video of these folk craftsmen, I did not find more contacts. You can watch their channel on YOUTUBE.
Purpose and principle of operation of the device
The main principle and advantage of using this device is automatism. The design of the valve was conceived in such a way as to shut off the flow of water or other liquid / gas when certain system parameters - temperature, pressure, speed and flow - change without human intervention.This happens due to the electromagnetic field in the area of action of the core (plunger) of the valve. When voltage occurs, it drops or rises, depending on the stipulated conditions.
The working energy that drives the plunger arises from the movement of electrons along the copper winding of the coil. The magnetism that appears when an impulse is applied from an external device is converted into a translational movement that lowers the plunger. The latter blocks the flow of water, avoiding large technological losses. As soon as the situation returns to normal, the voltage disappears and the plunger rises, allowing the water to move further through the pipes.
The magnetic field created by the coil
When an electric current passes through the windings of the coils, it behaves like an electromagnet, and the plunger that is inside the coil is attracted to the center of the coil by the magnetic flux inside the coil body, which in turn compresses a small spring attached to one end of the plunger. The force and speed of the plungers are determined by the strength of the magnetic flux generated inside the coil.
When the supply current is turned off (de-energized), the electromagnetic field previously created by the coil is destroyed, and the energy stored in the compressed spring causes the piston to return to its original rest position. This back and forth movement of the plunger is known as the "stroke" of the solenoids, in other words, the maximum distance the plunger can travel in either the "in" or "out" direction, e.g. 0-30mm.
This type of solenoid is commonly referred to as a linear solenoid because of the linear directional movement and plunger action.Linear solenoids are available in two basic configurations, called "pull type" as it pulls the connected load towards itself when energized, and "push type" which act in the opposite direction, pushing it away from itself when energized. Both the pull and push types are usually of the same design, with a difference in the location of the return spring and the design of the plunger.
 The magnetic field generated inside.
The magnetic field generated inside.
Installation and operation rules
Thanks to the manufacturer's instructions on the body of the device, the installation of the solenoid valve is as simple as possible. It will be easy for a person with skills in working with engineering equipment to install a valve on a pipeline section. Key recommendations for device installation:
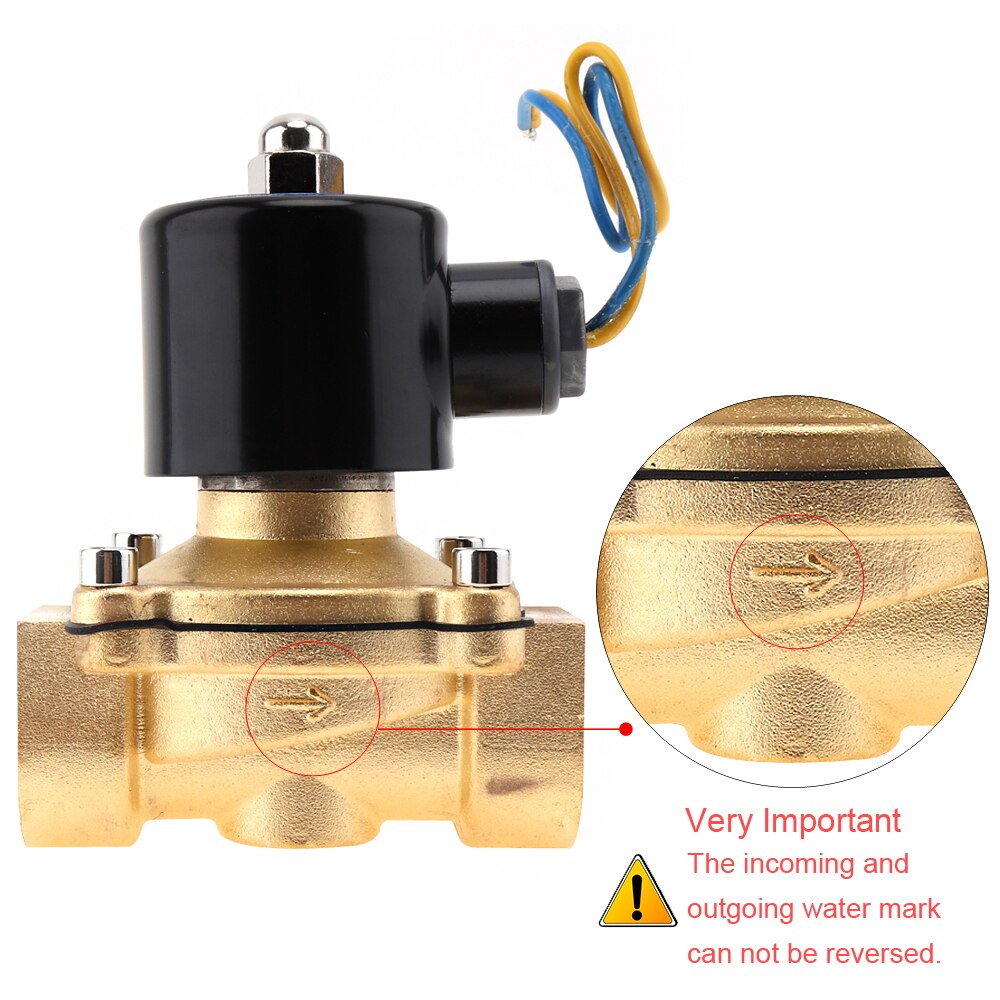
the valve must be positioned strictly in accordance with the arrows on the body of the device, indicating the direction of water flow;
it is recommended to install a dirt filter on the supply section of the pipe in front of the valve itself to trap particles (they must not enter the valve device, because
from them the device quickly fails);
the device is connected to the power source only after it is installed in the pipeline and the connection is checked for tightness;
it is important to ensure that there is no weight load on the device pipes;
when installed outdoors, it is necessary to isolate the device or select a model of the appropriate IP level. Otherwise, the installation of the valve does not differ in principle from other types of valves
For example, when using a device with a threaded connection, it is necessary to make a thread on the pipe using a special tool.Immediately before installation, the pipe must be prepared - cleaned of dirt and burrs, degreased with solvents
Otherwise, the installation of the valve does not differ in principle from other types of valves. For example, when using a device with a threaded connection, it is necessary to make a thread on the pipe using a special tool. Immediately before installation, the pipe must be prepared - cleaned of dirt and burrs, degreased with solvents.
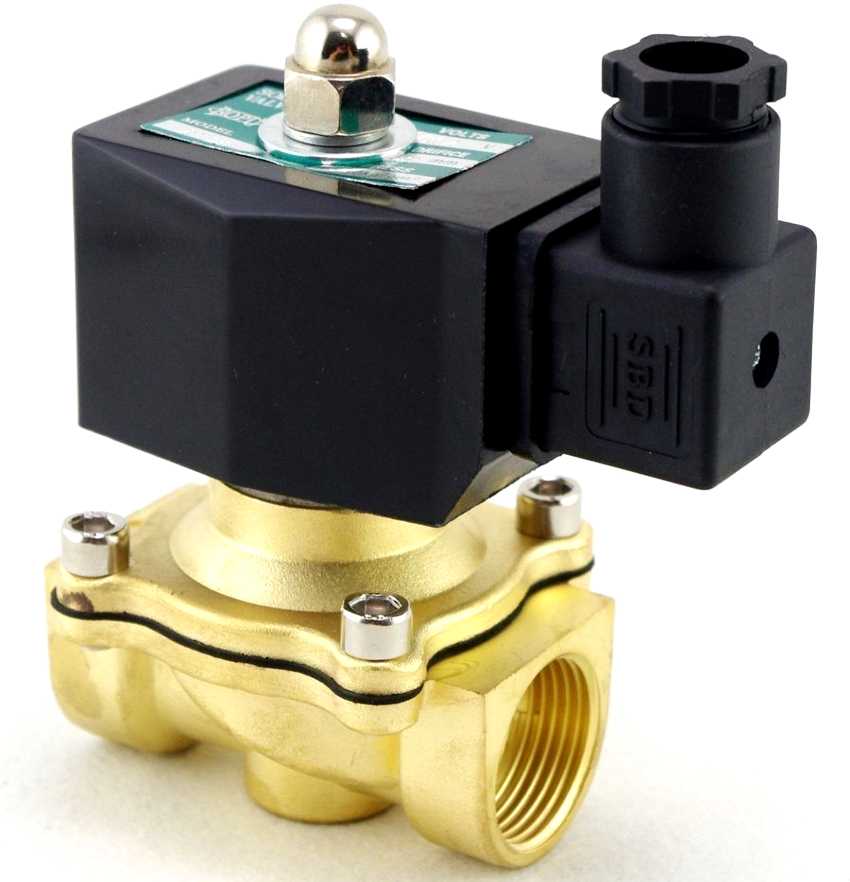
When using water supply and heating systems, no one is immune from the occurrence of emergencies. The electromagnetic (solenoid) valve for water allows minimizing the risks and losses in the event of a breakthrough. This device allows you to quickly block or, conversely, open the flow of water in a few seconds, being at a distance. Let us analyze in detail how the electromagnetic valve is arranged, types, principles of its operation and installation.
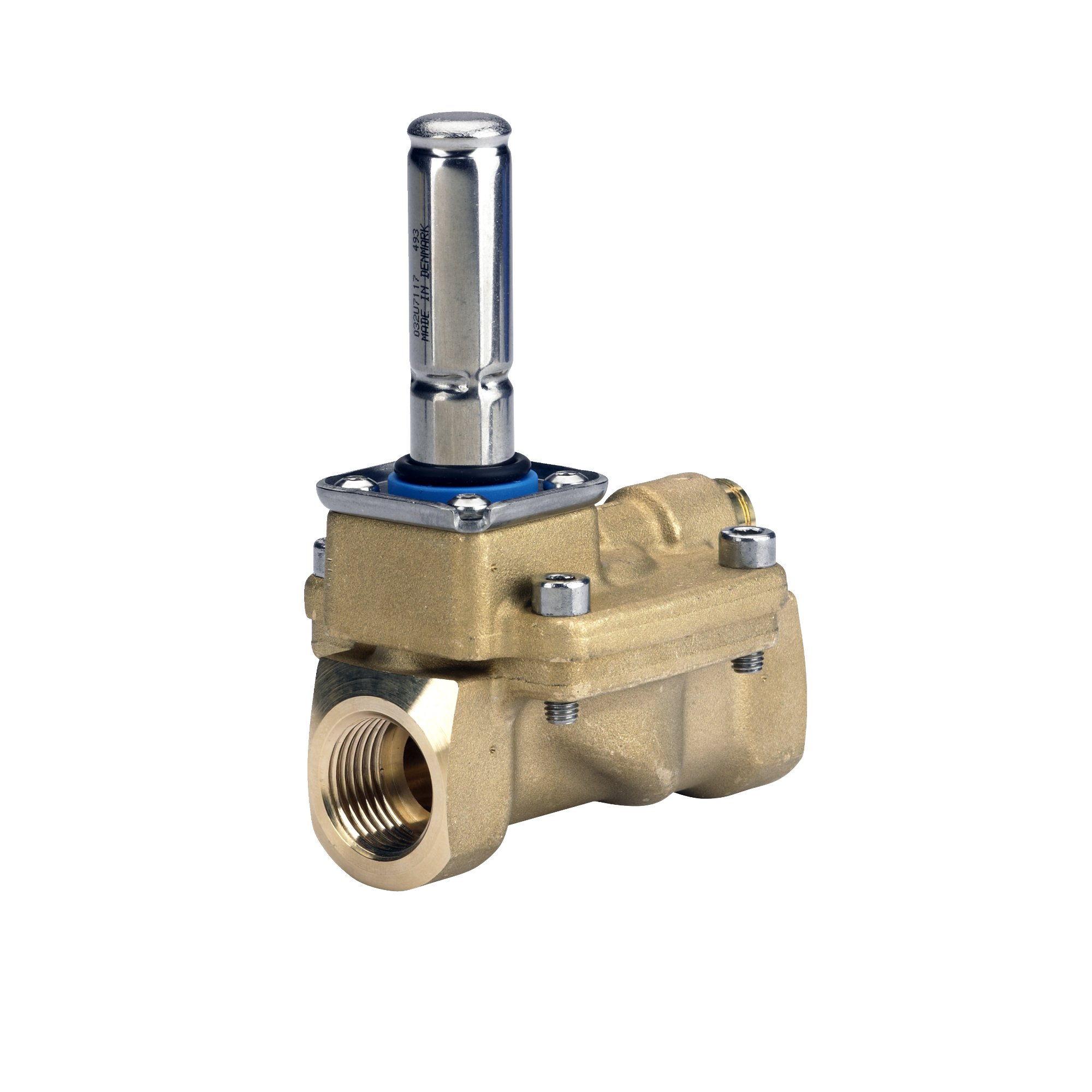
Solenoid valves Danfoss
Danfoss valves are fitted to a wide variety of equipment, from pumps installed at gas stations to machines found in dry cleaners. The small size of these devices does not affect their reliability at all. Danfoss manufactures an extensive range of valves. Thanks to this, in stores you can find such modifications that other manufacturers make exclusively by special order.
 Danfoss solenoid valves are small in size, but this does not affect their level of reliability at all.
Danfoss solenoid valves are small in size, but this does not affect their level of reliability at all.
Advantages of Danfoss solenoid valves:
- an extensive range of general purpose devices;
- even standard modifications can solve many problems faced by the industry;
- The product range allows you to select devices that can come into contact with very aggressive media, such as valves, the body of which is made of stainless steel and provided with protection class IP67.
If necessary, Danfoss can modify products according to the customer's specifications. Thanks to this, optimal solutions can be found for any industrial task. Moreover, representatives of the buyer company can take part in the development process.
The shut-off devices are supplied with a complete package of technical documentation, as well as simplified guides to enable customers to select a valve with suitable characteristics. The production process involves specialists who are experts in the field of regulation of gas, steam and liquids. Therefore, the products are distinguished by high functionality, reliability and safety.
 Danfoss manufactures both direct acting and servo operated solenoid valves.
Danfoss manufactures both direct acting and servo operated solenoid valves.
On sale you can find electromagnetic locking devices of direct action and equipped with a servo drive. Danfoss EV220B two-way solenoid valves are in particular demand, which are designed to control neutral gases, water, air, oils. Some modifications from this line can control steam and slightly aggressive media.
Description and principle of operation of the solenoid
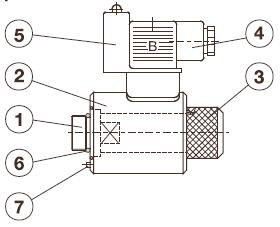
The linear solenoid works on the same basic principle as the electromechanical relay described in the previous lesson, and just like relays, they can also be switched and controlled using transistors or MOSFETs. A linear solenoid is an electromagnetic device that converts electrical energy into mechanical pushing or pulling force or movement. A linear solenoid basically consists of an electric coil wound around a ferromagnetically driven cylindrical tube or "plunger" which is free to move or slide "IN" and "OUT" in the coil housing. Types of solenoids are shown in the figure below.
Solenoids can be used to electrically open doors and latches, open or close valves, move and control robotic limbs and mechanisms, and even turn on electrical switches just by energizing its coil. Solenoids are available in a variety of formats, with the most common types being the linear solenoid, also known as linear electromechanical actuator (LEMA) and rotary solenoid.
Solenoid and scope
Both types of solenoids, linear and rotary, are available in latching (constant voltage) or latching (ON-OFF pulse), with latching types being used in energized or power outage applications. Linear solenoids can also be designed for proportional motion control, where the plunger position is proportional to the power input.When an electric current flows through a conductor, it generates a magnetic field, and the direction of this magnetic field relative to its north and south poles is determined by the direction of current flow within the wire.
This coil of wire becomes an "electromagnet" with its own north and south poles, just like a permanent magnet. The strength of this magnetic field can be increased or decreased either by controlling the amount of current flowing through the coil or by changing the number of turns or loops that the coil has. An example of an "electromagnet" is shown below.
How to install a do-it-yourself solenoid valve for water (12 Volt, 220V)
You can handle the installation of a solenoid valve (12 Volt, 220V) on water yourself. To avoid mistakes in the process of this, it is advisable to adhere to some rules:
- it is not allowed to install a locking device equipped with a coil that is capable of performing the function of a lever;
- all work on the installation or dismantling of the valve can only be carried out after the system is completely de-energized;
- care must be taken to ensure that the weight of the piping does not exert pressure on the valve body.
Locking devices can be used in open areas, for example, at local treatment facilities, which can often be found in suburban areas. In this case, the electromagnetic device needs additional protection. For these purposes, a standard FUM tape is suitable. It must also be used if work is carried out at low temperatures.
Related article:
When connecting the device to the power supply, be sure to use a flexible cable. The recommended cross-section of the conductors is 1 mm.
In the process of installing the device with your own hands, it is necessary to control the direction of the arrow on the body of the solenoid valve
Solenoid valve installation process (220V, 12V): practical tips
Before proceeding to direct installation, you need to determine what type of connection will be used for this.
With a threaded connection, the outlet and inlet pipes have an internal or external thread. By using fittings of the appropriate size and configuration, the valve can be integrated into the piping system. This option is considered the most convenient if the valve is installed by hand.
Flanged connections use branch pipes that have flanges at the ends. The same elements must be present on the pipes. The tightening of parts is carried out with the help of bolts. Flange connection allows you to create a high flow rate in the system, as well as a considerable pressure. Most often it occurs on highways with medium and high pressure.
Instructions detailing the installation process are included with each valve package. If everything is done correctly, the device will work properly, providing protection against leaks. When installing the device, it is necessary to leave a little extra space in the installation area. This is necessary so that, if necessary, you can remove and replace the solenoid. In addition, the presence of free space will allow you to control the operation of the valve, using a mechanism that provides manual stem lift.
Each solenoid valve comes with detailed instructions for installing the device
It is advisable to install a filter at the inlet to the valve.It will trap solid particles larger than 800 microns. Only a normally closed valve should be installed in front of the expansion valve. To exclude the possibility of water hammer when opening the locking device, it is necessary to leave as little space as possible between it and the expansion valve.
It is not recommended to use adapters before and after the valve. These elements can narrow the diameter of the pipeline, increasing the risk of water hammer. Adapters are best placed in front of the expansion valve. Installing a T-tube vertically in the solenoid valve to act as a damper can reduce the amount of water hammer that occurs when closing. In addition, the presence of such a tube will increase the service life of the device. The damper is essential if the pipeline has a long length and a small diameter.
Features of Asco Solenoid Valves
The American company Asco is one of the leading manufacturers of hydropneumatic, electromagnetic and shut-off valves, as well as pneumatic cylinders, pneumatic automation and other automation devices.
Product advantages:
- instrumentation and control equipment is manufactured on modern production lines with a wide range of functionality;
- if necessary, valves can be easily repaired, and the process itself does not take much time;
- high level of reliability;
- ability to withstand contact with aggressive environments and extreme loads.
The manufacturer produces more than 5000 standard types of shut-off valves. In addition, Asco produces special modifications and versions of these devices, the number of which exceeds 20,000.All of them are designed to meet the different needs of customers. At the same time, the manufacturer complies with the strictest quality requirements, monitoring all stages of production, including the development process, sales, and service.
 The quality of Asco solenoid valves is confirmed by ISO 9002 and 9001 certificates. Note! Before entering the store shelves, products are carefully checked for manufacturing defects, and also tested. The highest quality of valves is confirmed by ISO 9002 and 9001 certificates.
The quality of Asco solenoid valves is confirmed by ISO 9002 and 9001 certificates. Note! Before entering the store shelves, products are carefully checked for manufacturing defects, and also tested. The highest quality of valves is confirmed by ISO 9002 and 9001 certificates.
Classification of solenoid valves depending on the features of the device
Solenoid valves are distinguished by a significant variety of design features, and therefore there is an extensive field for classification.
They differ in the operating environment used on the systems where the devices are installed:
- water;
- air;
- gas;
- couple;
- fuel, such as gasoline.
In difficult conditions, where there is a possibility of an emergency, explosion-proof valve models are used
The composition of the working environment and the features of the room determine the features of the performance:
- ordinary;
- explosion-proof. It is customary to install devices of this kind at objects that are classified as explosive and fire hazardous.
According to the control features, there is a division of solenoid valves into devices:
- direct action. This is the simplest design, which is characterized by reliability and speed. It does not have a pilot channel. With an instantaneous rise of the membrane, the device opens. In the absence of a magnetic field, a spring-loaded plunger is lowered, pressing the membrane.The direct acting valve does not require a minimum pressure drop, it creates the necessary action on the spool stem due to the pulling force of the coil located at the top of the device;
- having membrane (piston) strengthening. Unlike direct action devices, they use the transported medium itself to function as an additional energy supplier. These valves have two spools. The purpose of the main spool is to directly cover the hole for which the seat of the body is allocated. The control spool closes the relief hole(s), through which the pressure is released from the cavity above the membrane (piston). This causes the main spool to rise and open the main passage.
According to the location of the locking mechanism at the moment when the coil is in a de-energized state, it is customary to separate the so-called pilot devices as belonging to a certain type:
- normally closed (NC). For NC valves, when the solenoid is de-energized, the passage for the working medium is closed. That is, the static position implies the absence of voltage on the solenoid, the closed state of the device. Due to the difference in diameter between the pilot and bypass channels, the pressure above the membrane decreases in favor of the first one. The pressure difference ensures that the membrane (piston) rises and the valve opens, remaining in this position as long as voltage is applied to the coil;
- normally open (NO). On the contrary, in normally open valves, when the coil is in a de-energized state, the working medium can move along the passage in a given direction.By keeping the NO valve closed, a constant voltage supply to the coil must be ensured.
Normally closed valve shuts off the flow of the working medium in a de-energized state
There are also models of the device in which, when a control pulse is applied to the coil, switching from the open position to the closed position and in the opposite direction is provided. Such an electrovalve is called bistable. Such a solenoid device requires a differential pressure and a constant current source to function. Depending on the number of pipe connections, it is customary to name solenoid valves:
- two-way. Such devices have one inlet and outlet pipe connection. Two-way devices are both NC and NO;
- three-way. Equipped with three connections and two flow sections. They can be produced as NC, NO or universal. Three-way valves are used to alternately supply pressure / vacuum to control valves, single-acting cylinders, automatic actuators;
- four-way. Four or five pipe connections (one for pressure, one or two for vacuum, two for the cylinder) ensure the operation of double-acting cylinders, automatic drives.
Design features, classification of valves
By type, valves are divided into open and closed. In open models, when the coil is de-energized, the passage is open; for closed valves, in this case, the passage is automatically closed.Modern manufacturers offer customers convenient designs of solenoid valves, which, if necessary, can be adjusted to a specific mode of operation (depending on need) - open, closed.
Depending on the pulse applied to the coil, solenoid valves can be pulsed and stable in design. These models, if necessary, can switch from open to closed position and vice versa. Depending on the systems in which the valves are installed, they are capable of operating with steam, air, gasoline and other fuels.
Depending on the room where the valves are used, they can be manufactured in conventional or explosive versions. The latter type of structures is used in various industries, namely: in fuel depots, gas stations, oil and gas production systems, as well as in other explosive and fire hazardous objects of the national economy.