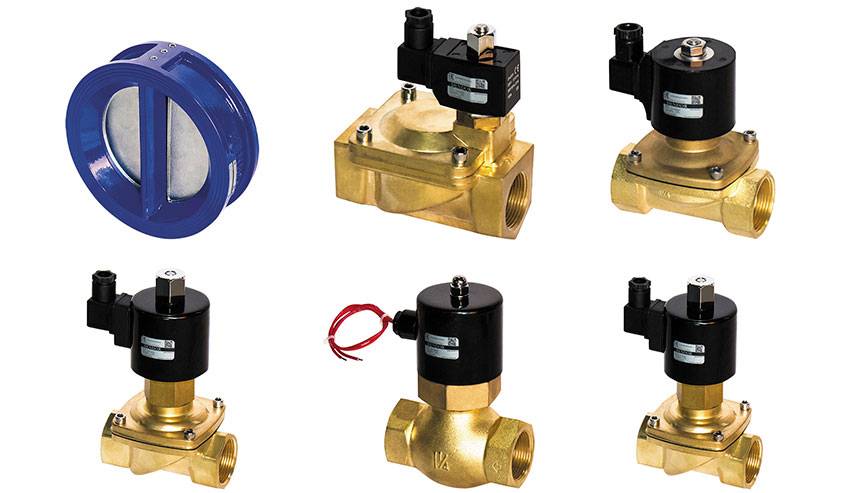
- Types and features
- How to choose a solenoid gas valve?
- Installation nuances
- What to look for when choosing a solenoid valve
- Connecting the solenoid valve to the garden watering system
- Purpose and application of solenoid valves
- Valve device
- The principle of operation of electromagnetic systems
- Description and principle of operation of the solenoid
- Operational features of valves for water
- The principle of operation of the pilot solenoid valve
- The principle of operation of the valve of electromagnetic direct action
- The principle of operation of the bistable valve
- Valve selection
- Armature device
- How the valve works
- Scope of use
- Valve types
- Working principle of GEVAX® solenoid valves for water and air
- Operating principle of the NC solenoid valve with floating diaphragm
- Installation rules
- How to install a do-it-yourself solenoid valve for water (12 Volt, 220V)
- Solenoid valve installation process (220V, 12V): practical tips
- Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Types and features
Magnetic gas valves "Lovato" of the VN series are very diverse in terms of the principles of operation and the features of their application. There are several types and ways to classify this device.
- normally open (NO).This group of valves, after turning off the current supply, remains in the open position. They are used on those pipelines where fuel must be supplied constantly and blocked only in emergency cases;
- normally closed (NC). Such devices are directly opposite to the previous subgroup. From the task to shut off the gas supply after the disappearance of the electrical impulse. It is convenient to install them on household gas appliances, for example, water heaters;
- universal - after a power outage, they can remain both in the closed and in the open position.
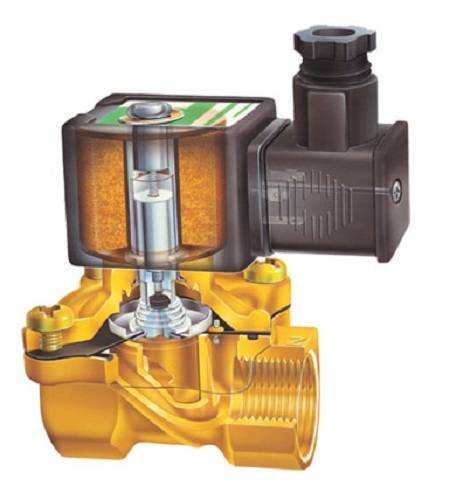

Valve internals
Valve movement principles:
- direct action involves actuating the shutter solely by the movement of the core;
- indirect action suggests that the shutter can be actuated not only by the movement of the core, but also by the stroke of the gas itself. This subtype of Lovato BH series throttles is beneficial for systems with a large fuel flow.
Number of moves:
- two-way - valves in which there are only two holes: inlet and outlet. This type is used in cases where it is only required to supply or shut off the gas supply in the pipeline;
- three-way - devices with three holes: one inlet and two outlets. It is convenient in cases where it is necessary not only to block, but also to redirect the gas flow in the system;
- Four-way valves have one inlet and three outlets. They allow not only blocking or redistributing the gas flow, but also connecting to additional systems.
How to choose a solenoid gas valve?
To select a solenoid gas valve "Lovato" series VN, you need to decide where it will be used and, therefore, what properties it should have.

Pneumatic shut-off valves
When choosing this device, pay attention to the following characteristics:
Electrical service. It is better to choose valves with low power and intrinsic safety, or with additional manual adjustment. Pressure
When choosing a valve, you need to pay attention to the pipeline. It must not be higher than the pressure rating of the accessories.
High pressure can damage the mechanism. Environment. Do not neglect the external conditions in which the valve will be operated. The characteristics of the device itself must necessarily match the environmental conditions, such as humidity, temperature changes, vibration, direct sunlight and other conditions other than normal. The external environment can adversely affect both the entire mechanism as a whole and its individual elements. Mains voltage. It is worth paying special attention to this parameter, since high or low voltage can lead to improper operation or even failure of the valve mechanism.
Prices for solenoid valves "Lovato" series BH fluctuate depending on the size, type and application. For example, the price of equipment for a geyser is in the range of 4-10 dollars, and for a HBO car - from 10 to 15 dollars.

Solenoid gas valves differ in connection method, operating pressure, as well as the installation environment and power supply of the actuator
Similar devices designed for the industrial sector are several times more expensive.
Installation nuances
The solenoid valve "Lovato" of the VN series is installed in the premises after the gas valve. It is recommended to install a filter in front of it to avoid clogging of the valve itself.
When installing the equipment, pay attention to the arrow on the case. It should show the direction of gas flow
The gas pipeline on which the throttle is installed must be located strictly vertically or horizontally. On pipelines with a small diameter, the valve is installed by means of a thread, with a large diameter - using flanges.
What to look for when choosing a solenoid valve
When selecting a solenoid device for gas flow control, it is recommended to take into account a number of characteristics and requirements, the neglect of which can result in operational problems:
the value of the rated working pressure must be suitable for the application. The cost of purchasing a device with a higher pressure rating may be unnecessary or even harmful (if the pressure drop is insufficient);
 Depending on the valve model, the rule of its installation is observed - in the direction of the working medium or against
Depending on the valve model, the rule of its installation is observed - in the direction of the working medium or against
the installation of a two-way valve is carried out exclusively in the direction indicated by the manufacturer of the device. And the two-way solenoid valve works with the flow of the working medium moving in one direction.Attempting to operate in a direction other than that indicated by the manufacturer will either result in unstable operation of the fixture or make it impossible to operate; most models of the device are produced for operation in a clean working environment
Manufacturers indicate exceptions that should be given the closest attention. Setting the electromagnets vertically will help prevent impurities from entering the core tube; most models are operated at rated voltage with deviations not exceeding 10%
- the size must be appropriate so that performance does not suffer;
- the device must be adapted to operate at the minimum / maximum pressure drops at the place of intended installation;
- electrical parameters must be taken into account. Most models allow simple electrical control. A number of models provide for the use of a manual on / off mode in an emergency. Intrinsically safe devices use ultra-low power, eliminating the appearance of sparks in an explosive environment;
- the materials of which the structure is composed must withstand the operating conditions at the place of intended installation;
- The selected device must match the available power source. Replacing the coil does not allow you to remake the valve, designed for a different type of current.
The spread of electromagnetic solenoid valves for gas has been facilitated by the introduction of a number of technological innovations, as a result of which the performance of devices has increased and the cost has decreased.Installing attachments does not require the purchase of additional components, as is the case with ball valves, and requires a minimum investment of time, cost and effort. The electromagnetic solenoid device is designed for long-term operation, withstanding about a million inclusions.
Connecting the solenoid valve to the garden watering system
For a small garden, a -12 volt watering solenoid valve (NT8048) is better suited. It is safe, because if water gets on the contacts and if you touch it with wet hands, there will be no electric shock. The ability to connect it to a 15 Ah battery allows you to work without recharging for a week. It will also be easy to make power from the shield through the network adapter.
Water is supplied from a storage tank installed at a height of at least 2 m. The water in it is drawn from a centralized system. Filling is controlled by a float switch connected to a plug valve. The absence of a pump eliminates many problems. Watering the garden by gravity occurs within a few hours and does not need to be controlled. All irrigation control will be taken over by an electronic timer connected to the outlet.
Purpose and application of solenoid valves
The solenoid valve performs the role of a regulating and shut-off device in the remote control of the transportation of liquid, air, gas and other media flows. At the same time, the process of its use can be both manual and fully automated.
The most popular is the Esbe solenoid valve, which has a solenoid valve as its main device.The solenoid valve consists of electric magnets, which are popularly called solenoids. In its design, the solenoid valve resembles an ordinary shut-off valve, but in this case, the position of the working body is controlled without the use of physical effort. The coil takes on the electrical voltage, thereby driving the solenoid valve and the entire system.
The solenoid valve works both in complex technological processes in production, or in utilities, and in everyday life. Using such a device, we can independently regulate the volume of air or liquid supply at a particular point in time. The vacuum valve can also work in rarefied air systems.
Depending on the conditions where the solenoid valve is used, the housing can be manufactured as ordinary and explosion-proof. Such a device is mainly used at points of oil and gas production, as well as at car filling stations and fuel depots.
Water valves are used to automate water purification systems. In addition, the electromagnetic water valve has found its application in maintaining the water level in water tanks.
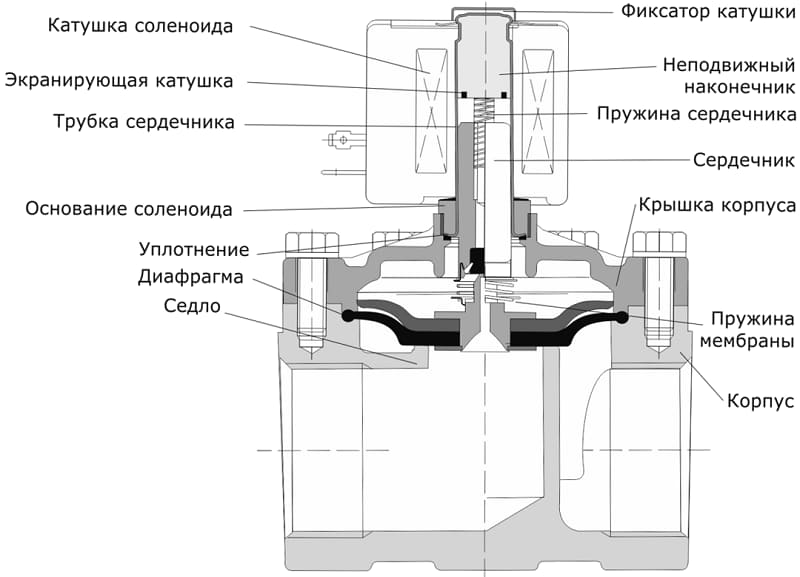
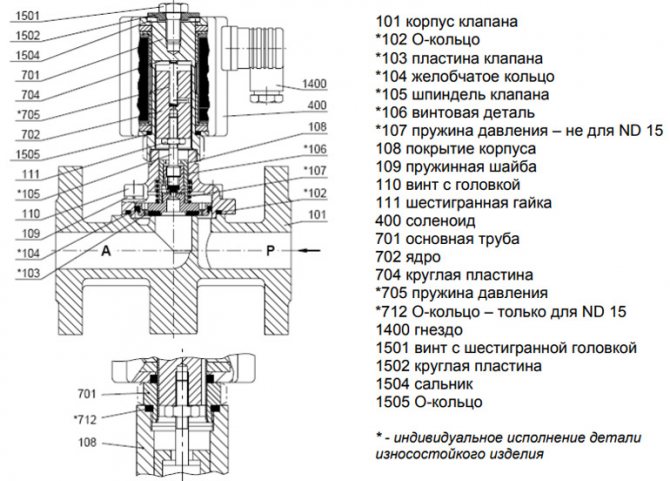
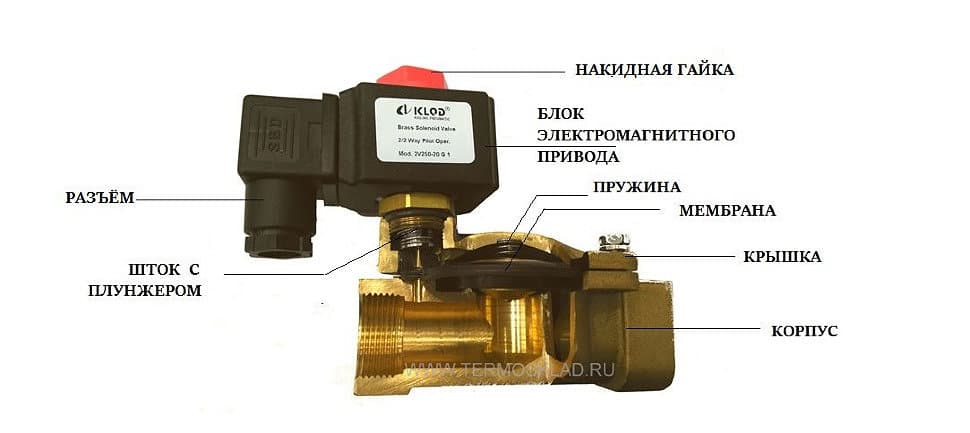
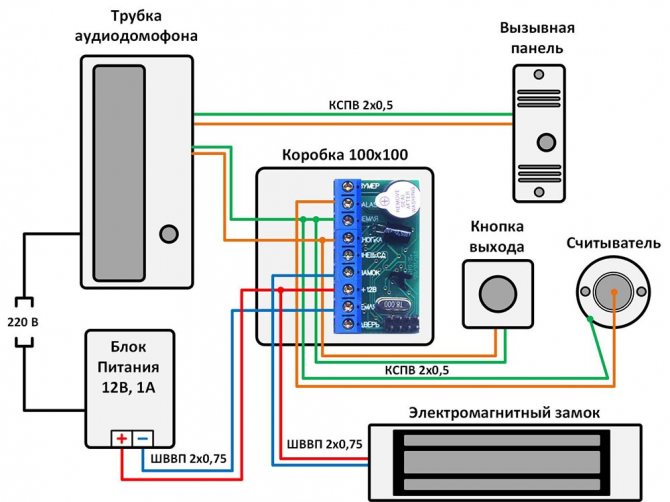
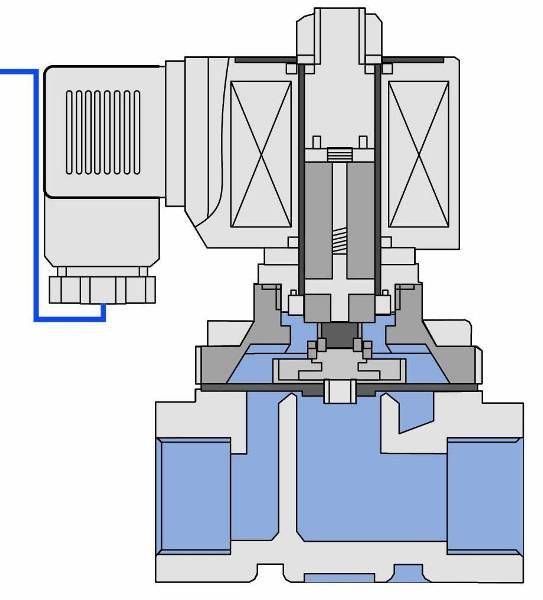
Valve device
The main structural elements of the solenoid valve are:
- frame;
- lid;
- membrane (or piston);
- spring;
- plunger;
- stock;
- an electric coil, also called a solenoid.
Valve device diagram
The body and cover can be made of metal materials (brass, cast iron, stainless steel) or polymeric (polyethylene, polyvinyl chloride, polypropylene, nylon, etc.). Special magnetic materials are used to create plungers and rods.Coils must be hidden under a dustproof and sealed case in order to exclude external influence on the fine work of the solenoid. The winding of the coils is carried out with enameled wire, which is made of electrical copper.
The device is connected to the pipeline by a threaded or flanged method. A plug is used to connect the valve to the mains. For the manufacture of seals and gaskets, heat-resistant rubber, rubber and silicone are used.
Drives with an approximate operating voltage of 220V are supplied with the product. Separate companies carry out orders for the supply of drives with a voltage of 12V and 24V. The drive is equipped with a built-in SFU forced control circuit.
The principle of operation of electromagnetic systems
The electromagnetic inductor works in all known AC and DC voltages (220V AC, 24 AC, 24 DC, 5 DC, etc.). Solenoids are placed in special housings protected from water. Due to the low power consumption, especially for small electromagnetic systems, control using semiconductor circuits is possible.
The smaller the air gap between the stopper and the electromagnetic core, the stronger the magnetic field strength increases, regardless of the type and magnitude of the applied voltage. Electromagnetic systems with alternating current have a much larger rod size and magnetic field strength than systems with direct current.
When voltage is applied and the air gap is at its maximum extent, AC systems, consuming a large amount of energy, raise the stem and the gap closes. This increases the output flow and creates a pressure drop.If a direct current is supplied, then the increase in the flow rate occurs rather slowly, until the voltage value becomes fixed. For this reason, valves can only control low pressure systems, except those with small orifices.
In other words, in a static position, provided that the coil is de-energized and the device is in the closed/open position (depending on the type), the piston is in tight connection with the valve seat. When voltage is applied, the coil transmits a pulse to the actuator and the stem opens. This is possible because the coil generates a magnetic field, which in turn affects the plunger and is drawn into it.
Description and principle of operation of the solenoid
The linear solenoid works on the same basic principle as the electromechanical relay described in the previous lesson, and just like relays, they can also be switched and controlled using transistors or MOSFETs. A linear solenoid is an electromagnetic device that converts electrical energy into mechanical pushing or pulling force or movement. A linear solenoid basically consists of an electric coil wound around a ferromagnetically driven cylindrical tube or "plunger" which is free to move or slide "IN" and "OUT" in the coil housing. Types of solenoids are shown in the figure below.

Solenoids can be used to electrically open doors and latches, open or close valves, move and control robotic limbs and mechanisms, and even turn on electrical switches just by energizing its coil.Solenoids are available in a variety of formats, with the most common types being the linear solenoid, also known as linear electromechanical actuator (LEMA) and rotary solenoid.
 Solenoid and scope
Solenoid and scope
Both types of solenoids, linear and rotary, are available in latching (constant voltage) or latching (ON-OFF pulse), with latching types being used in energized or power outage applications. Linear solenoids can also be designed for proportional motion control, where the plunger position is proportional to the power input. When an electric current flows through a conductor, it generates a magnetic field, and the direction of this magnetic field relative to its north and south poles is determined by the direction of current flow within the wire.
This coil of wire becomes an "electromagnet" with its own north and south poles, just like a permanent magnet. The strength of this magnetic field can be increased or decreased either by controlling the amount of current flowing through the coil or by changing the number of turns or loops that the coil has. An example of an "electromagnet" is shown below.
Operational features of valves for water
Provided that it is properly installed, and also subject to all requirements during operation, the solenoid valve is able to serve effectively for a long time, stabilizing the level of water pressure inside the pipeline. The solenoid allows you to extend the life of the pipes due to the uniform distribution of loads.
 When properly installed, the solenoid valve will work effectively for a very long time.
When properly installed, the solenoid valve will work effectively for a very long time.
The main signs and causes of failures in the operation of solenoid valves on the water:
- Loss of power - most often occurs when the control panel cable is damaged.
- The valve does not work - if the spring fails, the device will not be able to function normally and respond to voltage changes.
- The absence of a characteristic click when turned on - the burnt solenoid may be the reason for this.
The most common cause of valve failure is blockage. Therefore, in the event of any malfunction of the device, first of all, you should check the hole where solid particles can accumulate.
On a note! Experts recommend regularly checking the condition of the internal elements of the shut-off valve. This can only be done after the system has been completely emptied. If communications need complex repairs, it is better to hire professionals to do this work.
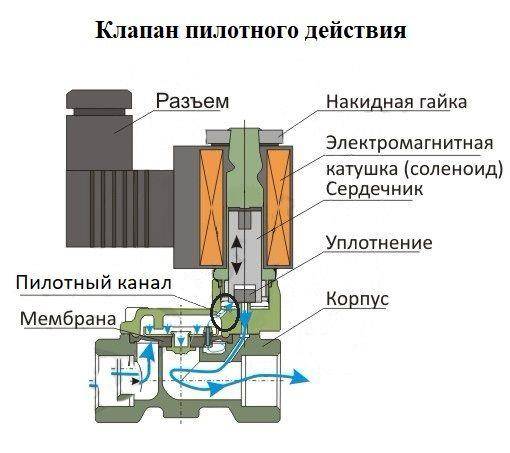
The principle of operation of the pilot solenoid valve
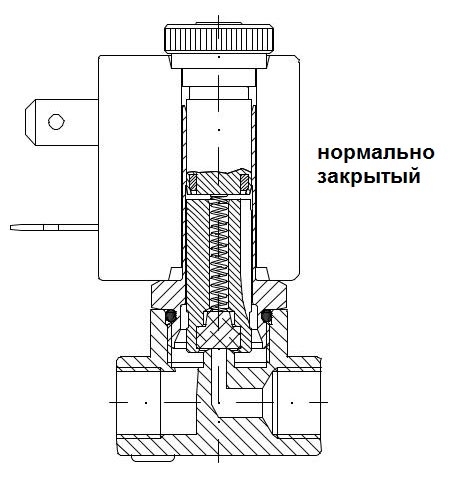
Normally closed valve In the static position, there is no voltage on the coil - the electrovalve is closed. The shut-off element (membrane or piston, depending on the type of valve) is hermetically pressed against the seat of the sealing surface by the force of the spring and the pressure of the working medium. The pilot channel is closed by a spring-loaded plunger. The pressure in the upper cavity of the valve (above the diaphragm) is maintained through the bypass hole in the diaphragm (or through the channel in the piston) and is equal to the pressure at the valve inlet. The solenoid valve is in the closed position until the coil is energized.
To open the valve, voltage is applied to the coil.The plunger, under the influence of a magnetic field, rises and opens the pilot channel. Since the diameter of the pilot port is larger than the bypass port, the pressure in the upper cavity of the valve (above the diaphragm) decreases. Under the influence of the pressure difference, the diaphragm or piston rises and the valve opens. The valve will remain in the open position as long as the coil is energized.
valve normally open
The principle of operation of a normally open valve is the opposite - in a static position, the valve is in the open position, and when voltage is applied to the coil, the valve closes. To keep a normally open valve closed, voltage must be applied to the coil for a long time.
For proper operation of any pilot operated valves, a minimum pressure drop is required, ΔP is the pressure difference between the inlet and outlet of the valve. Pilot valves are called valves of indirect action, because. in addition to applying voltage, it is necessary to fulfill the conditions for pressure drop. Suitable in most cases, for operation in water supply systems, heating systems, hot water systems, pneumatic control systems, etc. - wherever there is pressure in the pipeline.
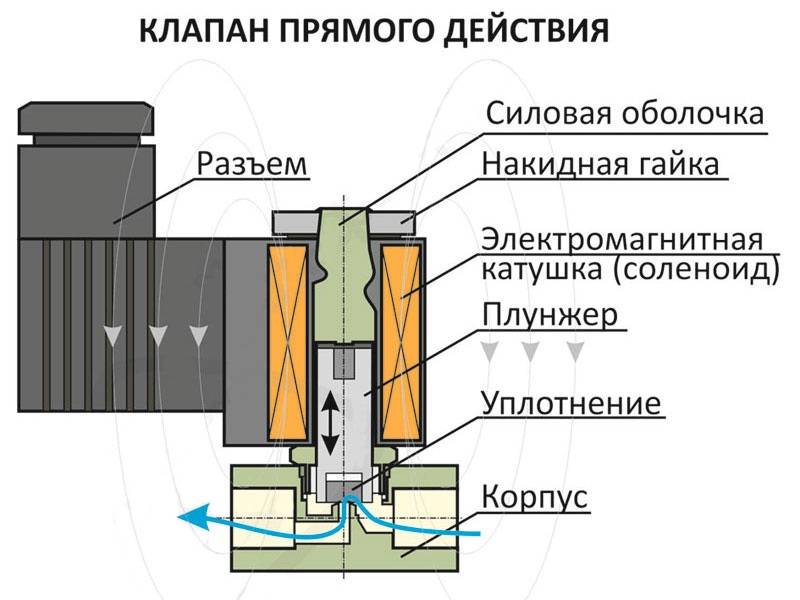
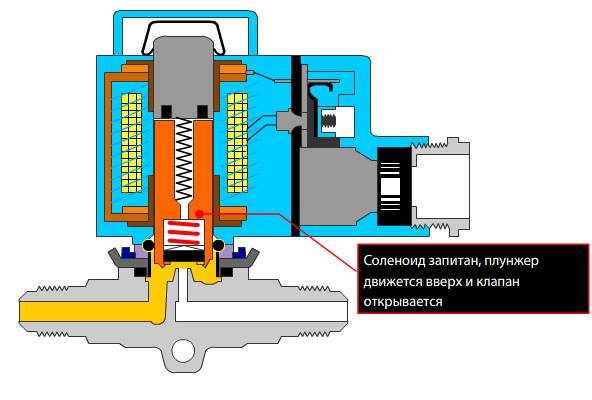
The principle of operation of the valve of electromagnetic direct action
A direct acting solenoid valve does not have a pilot port. The elastic membrane in the center has a rigid metal ring and is connected to the plunger through a spring. When the valve is opened, under the influence of the magnetic field of the coil, the plunger rises and removes the force from the membrane, which instantly rises and opens the valve.When closing (no magnetic field), the spring-loaded plunger descends and with force presses the membrane through the ring to the sealing surface.
For a direct acting solenoid valve, no minimum differential pressure across the valve is required, ΔPmin=0 bar. Direct acting valves can work both in systems with pressure in the pipeline, and on drain tanks, storage receivers and in other places where pressure is minimal or absent.
The principle of operation of the bistable valve
The bistable valve has two stable positions: "Open" and "Closed". Switching between them is carried out sequentially by applying a short pulse to the valve coil. A feature of the control is the need to supply pulses of variable polarity, so bistable valves operate only from DC sources. The coil does not need to be energized to hold the open or closed position! Structurally, bistable pulse valves are designed as pilot valves, i.e. minimum pressure drop required.
Solenoid valve (English solenoid valve) is a functional and reliable pipeline fittings. The service life of special electromagnetic coils is up to 1 million inclusions. The time required to actuate a diaphragm solenoid valve is on average between 30 and 500 milliseconds, depending on diameter, pressure and version. Solenoid valves can be used as shut-off devices for remote control, and for safety, as shut-off, switching or shut-off solenoid valves.
Valve selection
Before proceeding with the selection of a valve, it is necessary to find out the design of the fittings, the principle of its operation and the scope.
Armature device
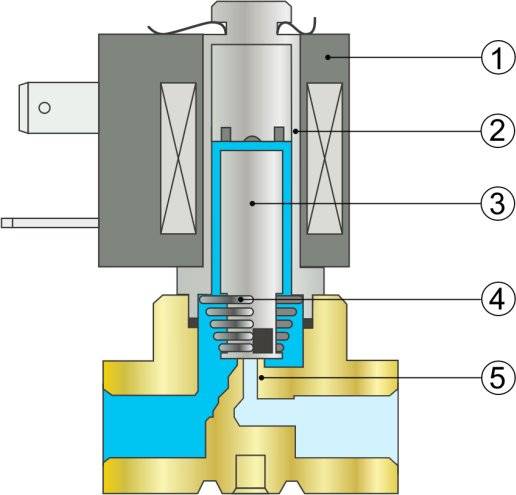
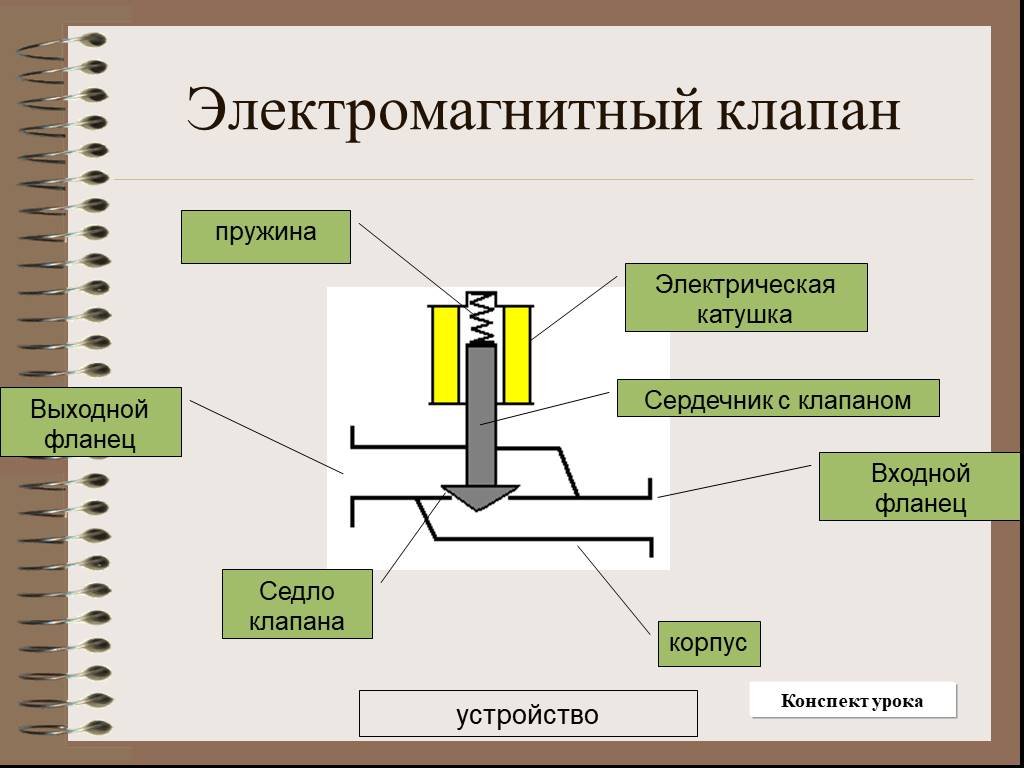
A solenoid or solenoid valve consists of the following elements:
- valve bodies, which can be made of brass, bronze and other materials that are not subject to corrosion;
- piston and rod made of materials with magnetic properties sufficient for the operation of the device;
- membranes - a sensitive element that gives signals about the occurrence of an emergency;
Membranes can be made from various materials, which affects the technical parameters of the fittings.
- an electromagnetic coil (solenoid) located in a protective housing.
Components of the solenoid valve
How the valve works
Valve working principle:
- in the normal position, depending on the type of device, the valve spring is in a lowered / raised state;
- when an electromagnetic signal is applied to the valve coil (220v), the spring rises, passing an excessive fluid flow, or rises to block the flow, respectively;
- after the stress is removed, the reinforcement components return to their normal state.
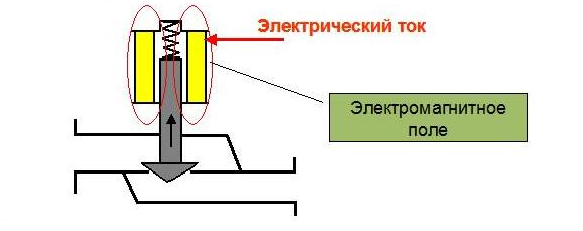
Solenoid valve action diagram
Scope of use
What is a solenoid valve for? Armature is used:
in water supply systems for mixing flows and achieving the optimum temperature or emergency shutdown of the system;

Solenoid valve on the water supply pipes to the dwelling
- in heating systems to reduce losses during liquid evaporation;
- in sewer networks, especially in public places. Armature is also installed to reduce losses;
- in irrigation systems.Installation of a solenoid valve allows you to set the time intervals for water supply for watering plants;
- in washing equipment for domestic and industrial use to ensure uninterrupted operation of the drain.
Valve types
Solenoid valves can be classified according to several criteria:
- Depending on the mechanism of action, valves are divided into fittings:
- direct action. The locking element of the valve operates under the control of the core, which is energized;
- pilot action. Such fittings are supplemented with a pilot valve, which controls the shut-off element;
Armature with additional control valve
- according to the position of the locking element, there are:
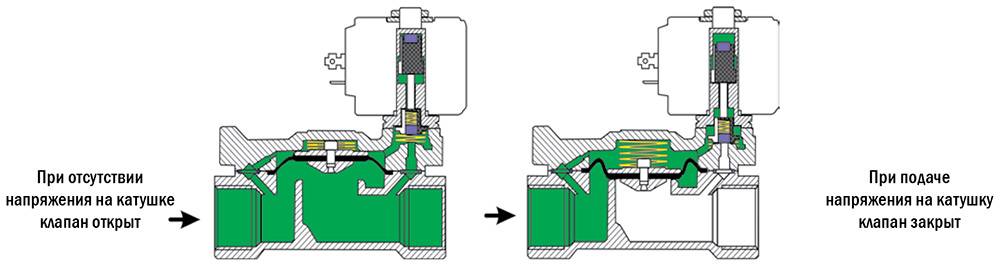
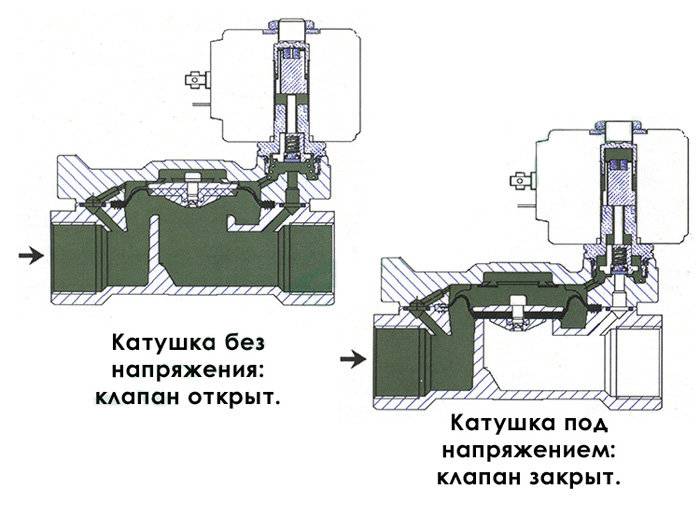
Open solenoid valve in standard position

The principle of operation of a closed solenoid valve
- by the number of pipes:
- one-way - valves with one branch pipe. Used for emergency shutdown;
- two-way - have two nozzles. The fittings can be used both for shutting off / opening the flow, and for mixing;
- three-way - three nozzles. Able to perform both the function of mixing, and the functions of regulation and overlap.
Three port solenoid valve
When selecting a valve, it is also recommended to take into account the technical characteristics, since a mismatch between the requirements of the pipeline system and the data of the valve can lead to valve failure and premature wear.
About different types of valve, fittings and the principle of operation are described in detail in the video.
Working principle of GEVAX® solenoid valves for water and air
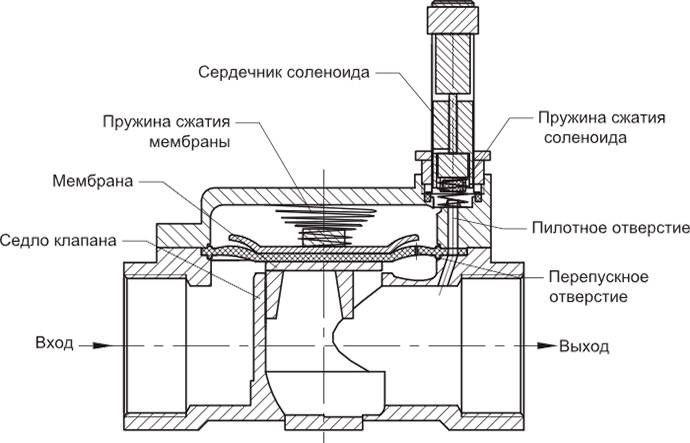
Valves - electromagnetic (solenoid) 2/2-way normally closed indirect action for water and air with a floating membrane.
The advantage of indirect acting solenoid valves with a floating diaphragm is the low power consumption: it is only needed to open a small pilot hole. The membrane that covers the orifice
will open under the action of the pressure of the working environment.
Operating principle of the NC solenoid valve with floating diaphragm
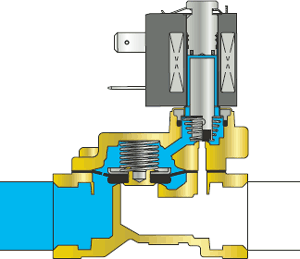 | 1 In the rest position, water or air entering the solenoid valve passes through the diaphragm bypass and fills the cavities above the diaphragm and above the pilot port. The pilot hole is closed by a plunger fixed to the core of the solenoid valve. The core is held in its original position by the elastic force of the spring. The membrane, pressed against the seat by a spring, closes the through hole. The medium pressure at the inlet (under the membrane) and above the membrane is the same. The solenoid valve is closed, the medium does not pass further. |
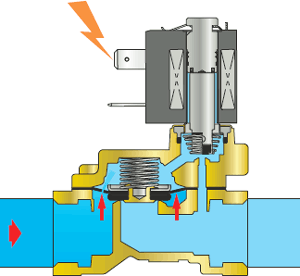 | 2 When voltage is applied to the electromagnetic coil of the valve (in the line they are presented in the version of 12v, 24v or 220v), a magnetic field is created in the core tube, which leads to the retraction of the core and the opening of the pilot Water (or air, gas) from the cavities above the diaphragm and the open pilot hole begins to exit the solenoid valve through the pilot hole. The pilot hole is wider than the bypass, so the medium exits the internal cavities faster than it fills them again. The pressure of the medium in the internal cavities (including above the membrane) drops and becomes less than the pressure of the medium at the inlet of the solenoid valve. As a result, the pressure of the incoming medium is stronger than the pressure of the spring pressing the membrane to the seat: the membrane rises and opens the through hole. The solenoid valve is open, medium flows through the valve. |
 | 3 As long as the coil is energized, the core with the plunger is raised, the pilot hole is open, and the pressure above the membrane and the spring force are less than the pressure of the incoming working medium. The pressure force of the working medium leaves the diaphragm in the raised position, and the medium flows freely through the solenoid valve. |
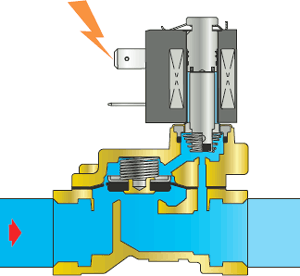
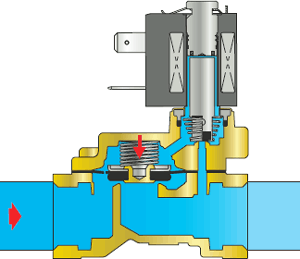 | 4 To close the solenoid valve, the voltage supply to the coil must be interrupted. The magnetic field disappears in the core tube. The core is lowered again under the action of the spring, and the plunger attached to it closes the pilot hole. |
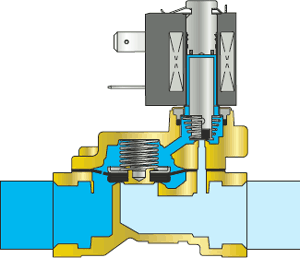 | 5 The working medium ceases to exit through the pilot hole and accumulates in the internal cavities of the solenoid valve, incl. above the membrane. The pressure at the inlet (under the membrane) and above the membrane becomes the same, and under the force of the spring (and under the pressure of the working medium), the membrane is pressed against the seat and closes the through hole. |
| 6 The solenoid valve is closed, the medium does not pass further. |
Installation rules
The valve can be connected in two ways:
- used in the household
When using a threaded connection, special attention is paid to sealing the joints;
- mainly used in the construction of large-diameter trunk networks.

Fittings for flange mounting
When choosing any installation method, it is recommended to consider the following aspects:
- the movement of water in the valve must occur strictly in the direction indicated on the valve body;
- it is possible to install the device only in an accessible place in order to control its performance and, if necessary, independently switch operating modes;
- do not mount the valve in places where condensate accumulates or in areas with increased vibration;
- it is recommended to install a filter in front of the valve to protect the constituent elements of the valve.
No special care is required for the valve. In the event of a breakdown of the fittings, repairs are carried out exclusively by professionals.
How to install a do-it-yourself solenoid valve for water (12 Volt, 220V)
You can handle the installation of a solenoid valve (12 Volt, 220V) on water yourself. To avoid mistakes in the process of this, it is advisable to adhere to some rules:
- it is not allowed to install a locking device equipped with a coil that is capable of performing the function of a lever;
- all work on the installation or dismantling of the valve can only be carried out after the system is completely de-energized;
- care must be taken to ensure that the weight of the piping does not exert pressure on the valve body.
Locking devices can be used in open areas, for example, at local treatment facilities, which can often be found in suburban areas. In this case, the electromagnetic device needs additional protection. For these purposes, a standard FUM tape is suitable. It must also be used if work is carried out at low temperatures.
Related article:
When connecting the device to the power supply, be sure to use a flexible cable. Recommended core cross section - 1 mm.
In the process of installing the device with your own hands, it is necessary to control the direction of the arrow on the body of the solenoid valve
Solenoid valve installation process (220V, 12V): practical tips
Before proceeding to direct installation, you need to determine what type of connection will be used for this.
With a threaded connection, the outlet and inlet pipes have an internal or external thread. By using fittings of the appropriate size and configuration, the valve can be integrated into the piping system. This option is considered the most convenient if the valve is installed by hand.
Flanged connections use branch pipes that have flanges at the ends. The same elements must be present on the pipes. The tightening of parts is carried out with the help of bolts. Flange connection allows you to create a high flow rate in the system, as well as a considerable pressure. Most often it is found on highways with medium and high pressure.
Instructions detailing the installation process are included with each valve package. If everything is done correctly, the device will work properly, providing protection against leaks. When installing the device, it is necessary to leave a little extra space in the installation area. This is necessary so that, if necessary, you can remove and replace the solenoid. In addition, the presence of free space will allow you to control the operation of the valve, using a mechanism that provides manual stem lift.
Each solenoid valve comes with detailed instructions for installing the device
It is advisable to install a filter at the inlet to the valve. It will trap solid particles larger than 800 microns.Only a normally closed valve should be installed in front of the expansion valve. To exclude the possibility of water hammer when opening the locking device, it is necessary to leave as little space as possible between it and the expansion valve.
It is not recommended to use adapters before and after the valve. These elements can narrow the diameter of the pipeline, increasing the risk of water hammer. Adapters are best placed in front of the expansion valve. Installing a T-tube vertically in the solenoid valve to act as a damper can reduce the amount of water hammer that occurs when closing. In addition, the presence of such a tube will increase the service life of the device. The damper is essential if the pipeline has a long length and a small diameter.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Solenoid Valve Device Overview:
How a 220 V direct-acting solenoid valve is arranged and works:
Types of solenoid valves according to the principle of operation:
The remote control solenoid valve is unpretentious and reliable in operation. It is designed for several tens of thousands of operations (it will work properly for 20–25 years) and does not require specialized maintenance.
Such a device costs under water in the range of 3-6 thousand rubles, but it helps to solve many problems. At the same time, it is not difficult to mount it yourself, you just need to choose the right valve according to its characteristics and materials.
Would you like to supplement the above material with useful information or point out an inconsistency or error? Or would you like advice on choosing the optimal model solenoid valve? Please write your advice and comments in the comments block.
If you still have questions on the topic of the article, ask our experts below under this publication.