- Quality processing
- Quantitative processing
- What determines our level of intelligence?
- What Your IQ Scores Don't Say
- Success in work
- public value
- Efficiency
- Procedure
- Test for a moron, idiot, imbecile (UO) ^
- Tests for the diagnosis of the cognitive sphere
- Tests for the diagnosis of intelligence and mental development
- How to pass an IQ test for the maximum score
- Description of the technique
- July 22What is IQ and how is it measured
- IQ = 100 - the most common result;
- There are two types of this test:
Quality processing
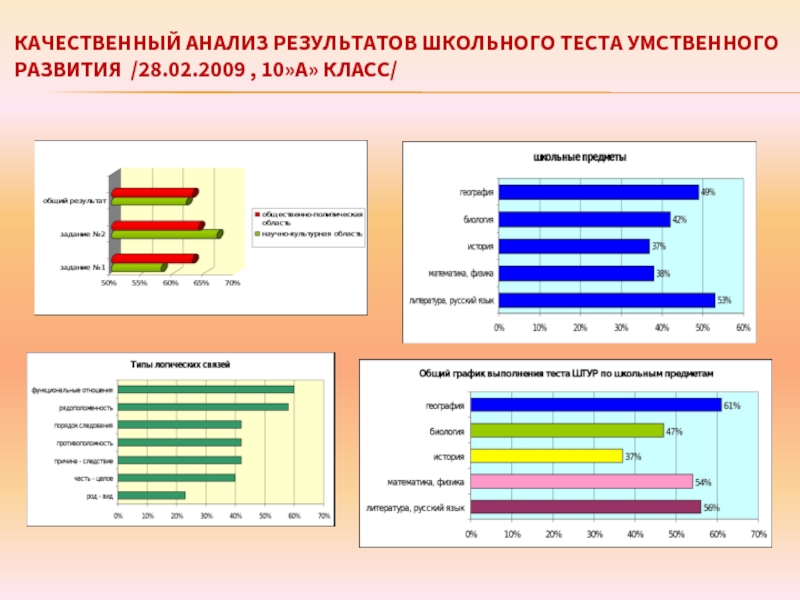
This analysis of test results, both group and individual, makes it possible to determine the most complex logical connections in terms of their type. At the same time, high-quality processing is carried out by a specialist in the following areas:
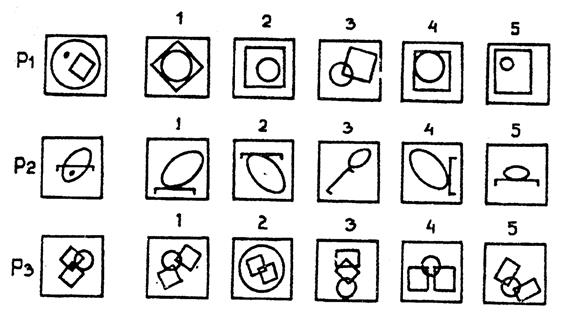
- For a set of tasks of the 3rd subtest, the easiest (worked out), as well as the most complex types of logical connections are identified. Among them are genus-species, cause-effect, whole-part, functional relationships and opposites. The experimenter also highlights typical mistakes that children make. The most and least assimilated areas of biology, physics, mathematics, history, literature and such cycles of school disciplines as physics and mathematics, natural sciences and the humanities are considered.
- For a set of tasks number 4, the specialist must determine which of them the child performed better and which worse. He will also have to analyze the answers to questions concerning abstract and concrete concepts, and which of them cause great difficulties for the student.
- Analyzing the tasks of the 5th set, the experimenter will have to identify the nature of the generalizations, breaking them down according to categorical, specific and specific characteristics. It is also expected to study the nature of typical errors. In what concepts do they occur most often (in concrete or abstract)?

Consider the test material offered to children using the example of form A.
Quantitative processing
How is this method of obtaining the results of the STUR test carried out? During quantitative processing, the experimenter reveals:
- Individual indicators. They are determined for each subtest (with the exception of the fifth). At the same time, a certain score is displayed for the test and subtest. It is determined by counting the number of correctly completed tasks. For example, if a child in the 3rd subtest gave correct answers to 13 tasks, then he is given 13 points.
- Generalization quality. Depending on it, the results of the 5th subtest are evaluated. In this case, the student is given 2, 1 or 0 points. When processing the results according to the STU method, in this case, tables are used with approximate answers entered in them, which are given to tasks for generalization. What is capable of receiving a score of two points is described quite fully. In this case, the experimenter can consider not only direct answers, but also their interpretation. The school mental development test STUR can be estimated at 1 point. The list of such answers is given in the proposed tables less fully.In this case, the subjects have more opportunities to make a choice. 1 point is scored for answers given by the student correctly, but at the same time rather narrowly, as well as those that have categorical generalizations. The experimenter can also put 0. This number of points is given for incorrect answers. When completing the 5th subtest, children can get a maximum of 38 points.
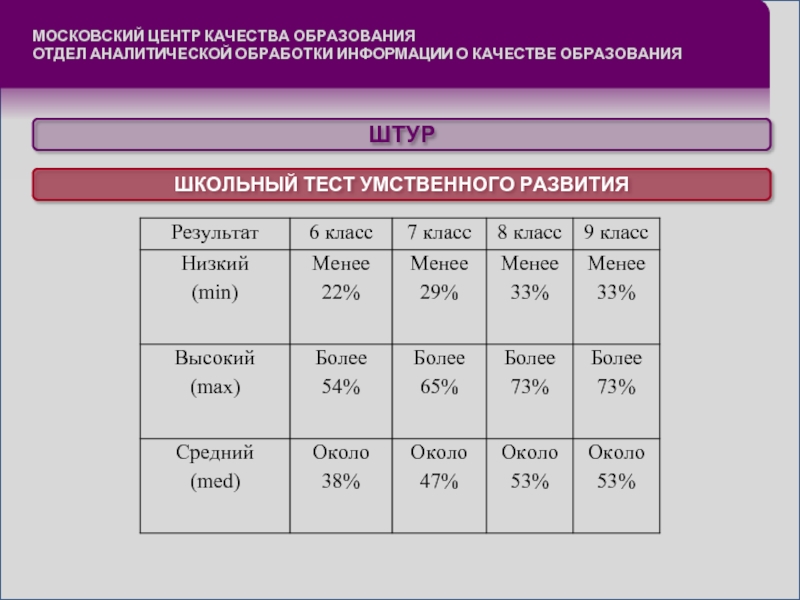
- Individual indicators. In general, they represent the sum of the scores obtained by adding the results of completing tasks for all subtests. As conceived by the authors of the methodology, a test performed 100% is considered the standard of mental development. It is with this indicator that the tasks that were performed correctly by the student should subsequently be compared. You can also find out the percentage of correct answers in the instructions for the described technique for adolescents (ShtUR). This is precisely what determines the quantitative side of the work of the subjects.
- Comparative indicators of group responses. If the experimenter united students in one way or another and analyzes their total score, then in this case he needs to take the arithmetic mean of all scores. According to the test results, students can be divided into 5 subgroups. The first of them will include the most successful, the second - those who are close to them in terms of completing tasks, the third - the middle peasants, the fourth - the least successful, and the fifth - the least successful. After calculating the average score for each of these subgroups, the experimenter builds a coordinate system. At the same time, on the abscissa axis, he marks the numbers of “success” of children, and along the ordinate axis, the percentage of tasks they solved. Having applied the corresponding points, the specialist draws a graph.He will point out the proximity of each of the noted subgroups to the existing socio-psychological standards. A similar type of processing of results is also carried out based on the consideration of the entire test as a whole. The graphs obtained in this way make it possible to draw a conclusion on the method of STUR in the context of students of both the same and different classes.
- The gap in mental development that takes place between the best and worst students in the class. The researchers found that this phenomenon becomes even more pronounced by the 6-8th grade. The best students, growing up, are increasingly approaching the existing socio-psychological standards. The same children who give many wrong answers on the school IQ test continue to remain at the same level. To even out the results, the specialist gives recommendations on conducting more intensive classes with lagging students.
- Group comparison. When analyzing test results, the specialist considers the global assessments of an individual student. At the same time, the level of its development is indicated by such terms as “worse” and “better”, “lower” and “higher”. Also, the specialist puts the total points. At the same time, it should be understood that if they are less than 30 for a child attending the sixth grade, less than 40 for the seventh grade, and they did not reach 45 for the eighth and ninth graders, then such results may indicate a child's low mental intelligence. And what are the good indicators of the test of the methodology for adolescents STUR? This is more than 75 points for a sixth grader, 90 for a seventh grader, and 100 for a child from the 8th grade.
Quantitative indicators of mental development must be combined with qualitative ones.This will allow us to give a psychological interpretation of the unfulfilled and completed tasks according to the SHTR method.
What determines our level of intelligence?
Intelligence is the ability to learn and solve problems. Intelligence includes human cognitive abilities: sensation, perception, memory, representation, thinking, imagination.
Scientists also have not established the influence on the intelligence of race or nationality. Ushakov in the book "The Psychology of Intelligence and Giftedness" cites the following data: black orphans raised in foster families with access to better education have higher IQs. It is likely that intelligence in this case was more influenced by social factors than hereditary ones. This is confirmed by studies of twins with an identical set of genes, which Steward Richie cites. While twins are children, their IQ level is approximately equal, and this can be explained by genetics. As children grow older, they begin to create an environment for themselves: someone spends time reading books and other activities, someone wanders around idle. Then, with the same heredity, the level of IQ ceases to be equal. It turns out that with age we have more control over our environment. And the environments we create affect IQ levels.
Other facts speak about the influence of external factors on the intellect. The average IQ is higher in countries with a high standard of living. The quality of food and medical care, the availability of education, crime rates and social attitudes in society can also affect IQ levels.
Surprisingly, the average level of IQ is gradually growing both in the world and in individual countries.This process is called the Flynn effect, after the scientist who collected the data on these changes. The Flynn effect is paradoxical: the average IQ rises every 10 years. For genetic and evolutionary changes, this is too short a period of time. In addition, these data do not allow a strong connection between intelligence and heredity, race, nationality, gender, and brain characteristics. It turns out that people become "smarter" for various reasons, and the level of intelligence does not depend on anything specific.
What Your IQ Scores Don't Say
Success in work
With the help of tests, psychologists wanted to predict how well a person is suitable for a certain activity. In fact, it turned out that IQ scores do not predict success at work. Human activity is too complex and does not fit into the scale of one test. Therefore, special methods have been developed for assessing mathematical abilities, memory, creativity and career guidance.
public value
Mental abilities - albeit important, but only one of the human resources. Much more important is how you manage your abilities. Record holders of IQ tests created the Mensa International organization: only 2% of the test subjects with the highest intelligence scores are taken there. Members of Mensa have not yet become famous for their outstanding scientific discoveries or other contributions to social development.
Efficiency
IQ scores do not indicate a person's ability to interact effectively with others, quickly adapt to new conditions, take responsibility and find the strength to move forward despite setbacks. In the industrial age, knowledge and memory played a leading role, now these functions are taken over by the smartphone.Therefore, exclusively human abilities are of particular value: to understand and express emotions, to show empathy and flexibility, to take into account the interests of different groups and to think critically. Unlike general intelligence, these abilities (soft skills) can be developed through educational practices and training.
Procedure
This test is group. The time allotted for each subtest is limited and is sufficient for all students. For proper testing, it is necessary to strictly follow the instructions, control the time of subtests (using a stopwatch), and not help the test subjects in completing tasks.
For proper testing, it is necessary to strictly follow the instructions, control the time of subtests (using a stopwatch), and not help the test subjects in completing tasks.
Group testing should involve two experimenters. One of them reads the instructions and keeps track of the testing time, the other watches the students, preventing them from violating the instructions.
Subtest times:
| Subtest | Number of tasks in the subtest | Execution time, min |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Awareness 1 | | |
| 2. Awareness 2 | | |
| 3. Analogies | | |
| 4. Classifications | | |
| 5. Generalizations | | |
| 6. Number series | | |
Before testing, the experimenter explains its purpose and creates an appropriate attitude in the subjects. To do this, he addresses them with the following words:
“Now you will be offered tasks that are designed to reveal the ability to reason, compare objects and phenomena of the world, find common and different in them. These tasks are different from what you have to do in class.
To complete the assignments, you will need a pen and forms, which we will distribute to you. You will complete different sets of tasks. Before the presentation of each set, a description of this type of tasks is given and the way to solve them is explained using examples.
Each set of tasks has a limited amount of time to complete. It will be necessary to start and finish the work on our command. All assignments must be completed in order. Don't stay too long on one task. Try to work quickly and without errors!”.
After reading this instruction, the experimenter distributes test notebooks and asks them to fill in the columns in which the following information is entered: the student's last name and first name, the date of the experiment, the class and number of the school where he studies. After checking the correctness of filling in these columns, the experimenter invites students to put aside their pens and listen carefully to him. Then he reads the instruction and analyzes the examples of the first subtest, then asks if there are any questions. In order for the testing conditions to be always the same, when answering questions, the experimenter should simply read out again the corresponding place in the text of the instruction. After that, they are instructed to turn the page and start doing tasks.
At the same time, the experimenter imperceptibly turns on the stopwatch (so as not to fix their attention on this and not create a feeling of tension in them).
After the time allotted for the first subtest, the experimenter decisively interrupts the work of the subjects with the word "stop", inviting them to put down their pens, and begins to read the instructions for the next subtest.
During testing, it is necessary to control whether the subjects turn the pages correctly and fulfill other requirements of the experimenter.
Test for a moron, idiot, imbecile (UO) ^
Answer the questions of the test for a moron, idiot, imbecile quickly, do not look for the right answers - they are not here.
So, take an online mental retardation test:
1
Is it easy to get your attention, distract from something?
Yes
It depends
Not
2. Do you remember information quickly and for a long time?
Fast and long
Fast but not for long
Slowly but for a long time
Slowly and briefly
3
Do you have abstract thinking?
Yes
Not
Don't know
4. Do you have any speech disorders?
Yes
A little
Not
5. How rich is your vocabulary?
very rich
Not really
poor
6. How rich and varied is your speech?
very rich
Not really
Bedna
7. Is it difficult for you to retell in detail what you have read or heard?
Not difficult
embarrassing
Very hard
8. Do you memorize material mechanically or meaningfully?
More mechanical
It depends
More meaningful
9. Do you have negativism (unreasonable resistance to requests, demands, behavior opposite to people's expectations)?
Often
Sometimes
Rarely
Never
10. Have you graduated from a comprehensive school?
Yes, I have a secondary general or vocational education
Completed incomplete secondary education
Graduated from remedial school
I study in high school, I will finish my secondary education
I study at school, I will finish incomplete secondary education
Studying in a correctional school (class)
I study at a school (college) with secondary education
Studying at a school without secondary education
11. Are you an independent person?
Yes, completely
Most, but not all
Little independence
Practically dependent
12. Are you suggestible (is it easy to convince you of anything)?
Yes
Sometimes
Rarely
Not
13. Were the subjects easy for you: physics and mathematics?
Easily
More or less
Not easy
Hard
14. Can it be said about you that you have more practical skills than theoretical knowledge?
Yes
Equal skills and knowledge
More knowledge than skill
Few of both
15. Have you mastered any profession, specialty?
Yes
mastering
Gonna master
Not
16. Are you dependent on the opinions and influence of other people?
Yes
Sometimes
Not
17. Do others use you for their own purposes?
Often
Sometimes
Not
18. Do you often use template expressions, speech stamps in a conversation?
Yes
Sometimes
Not
19. Does it happen that you argue (argue, discuss) about what you don’t really understand?
Often
Periodically
Rarely
Almost not
20. Do you easily suppress your biological desires?
Easily
It depends
Not easy
I find it extremely difficult to suppress them.
21. Is your behavior promiscuous?
Often
Sometimes
Rarely
Never
22. Is it possible to notice some clumsiness, sweeping in your movements?
Yes
I think yes
I think no
Not
23. Do you have any neurological disorders (not mental)?
Yes
Not
Don't know
24. Do you have anomalies of physical development?
Yes
Not
Don't know
25. Could you call yourself a low-conflict person?
Yes
Not
Don't know
26. Can I say about you that you are obedient and manageable?
Yes
Sometimes
Not
27. Do you pay much attention to your appearance?
Yes
Sometimes
Not
28. Where are your food and sexual instincts?
On the first
Not at first
On the last
29.Do you have mental disorders?
Yes
Not
Don't know
30. Do you have any immediate relatives with mental or neurological disorders?
Yes
Not
Don't know
Plugin Sponsor: Girls Tests
Similar tests:
Online dementia test (dementia)
Mental development of the child (drawing test)
Tests for the diagnosis of the cognitive sphere
The technique "Recognition of figures" is intended for diagnosing the features of perception.
Method for determining short-term memory.
Technique "Random Access Memory".
Technique "Figurative memory".
Method A.R. Luria "Learning 10 words" is designed to determine the state of memory, attention, fatigue.
The "Story reproduction" technique is designed to determine the level of semantic memory, its volume, as well as the ability to memorize texts.
The technique "Mediated memorization" (proposed by L.S. Vygotsky and A.R. Luria, developed by A.N. Leontiev) is intended to determine the features of mediated memorization, thinking.
The "Pictogram" technique is intended to study the features of mediated memorization and its productivity, as well as the nature of mental activity, the level of formation of conceptual thinking.
The technique "Correction test" (Bourdon's test) is designed to study the degree of concentration and stability of attention.
The Schulte Table technique is designed to determine the stability of attention and the dynamics of performance.
Gorbov's technique "Red-black table" is designed to assess the switching and distribution of attention.
The method of studying the level of attention (proposed by P.Ya. Galperin and S.L. Kabylitskaya) is aimed at studying the level of attention and self-control of schoolchildren in grades 3-5.The method "Intellectual lability" is intended for diagnosing the switching of attention.
Methodology "Interpretation of Proverbs" is intended to study the level of thinking.
The technique "Simple analogies" allows you to identify the nature of logical connections and relationships between concepts in children over 10 years old.
The technique "Complex analogies" is intended for the diagnosis of thinking.
The method "Comparison of concepts" is aimed at studying the operations of comparison, analysis and synthesis in childhood and adolescence.
The technique of "Identification of essential features" allows you to identify the features of thinking.
Tests for the diagnosis of intelligence and mental development
Methods for determining the level of mental development of children 7-9 years old E.F. Zambiciavichene.
Verbal test G. Eysenck
Designed to assess the intellectual abilities of persons aged 18 to 50 years with an education not lower than secondary.
D. Wexler test
Designed for the study of mental development. Currently, there are three forms of Wechsler scales designed for different ages. It is believed that the test can be used to diagnose school readiness and assess the causes of underachievement. In our country, the Wexler test was adapted by A. Yu. Panasyuk (1973) and later published in an updated edition in St. Petersburg (Yu. I. Filimonenko, V. I. Timofeev, 1992).
J. Raven test
Designed for the study of mental development. "Raven's Progressive Matrices" is a non-verbal test developed by L. Penrose and J. Raven in 1936 in black and white and in 1949 in color. The black-and-white version of the test is designed to examine children from 8 years old and adults up to 65 years old. The test consists of 60 matrices or compositions with a missing element.
Culture-Free Intelligence Test by R. Cattell
Designed to measure the level of intellectual development, regardless of the influence of factors of the surrounding social environment.
Group Intelligence Test (GIT) by J. Wanda
The test was translated and adapted for a sample of Russian schoolchildren in LPI (M. K. Akimova, E. M. Borisova et al., 1993). Designed to diagnose the mental development of students in grades 3-6. The test reveals how much the subject at the time of the examination has mastered the words and terms offered to him in the tasks, as well as the ability to perform certain logical actions with them - all this characterizes the level of mental development of the subject, which is essential for successful completion of the school course. GIT contains 7 subtests: execution of instructions, arithmetic tasks, addition of sentences, determination of similarities and differences of concepts, number series, analogies, symbols.
School Test of Mental Development (SIT)
Developed by the team of K.M. Gurevich for diagnosing the mental development of students in grades 7-9. The tasks of the STC include concepts that are subject to compulsory assimilation in subjects of three cycles: mathematical, humanitarian and natural sciences.
Intelligence structure test by R. Amthauer
It was created in 1953 (last revised in 1973). The test is designed to measure the level of intellectual development of persons aged 13 to 61 years. The test consists of nine subtests, each of which is aimed at measuring different functions of intelligence. Six subtests diagnose the verbal sphere, two - spatial imagination, one - memory.The test contains 9 subtests: awareness, classifications, analogies, generalizations, arithmetic problems, numerical series, spatial representations (2 subtests), memorization of verbal material.
ASTUR (for Applicants and Senior Students Test of Mental Development)
The test includes 8 subtests: 1. Awareness. 2. Double analogies. 3. Lability. 4. Classifications. 5. Generalization. 6. Logic circuits. 7. Number series. 8. Geometric shapes.
How to pass an IQ test for the maximum score
The average IQ of a test is calculated by the number of people who passed it with a score of 100 or so. The test scoring system is constantly being revised, because humanity is getting smarter by about 3 points every ten years. The growth of the average score is associated with an increase in the number of educated people and the transition from manual to mental work.
The researchers noticed that the results of a particular person are influenced by his ability and desire to perform the test as best as possible. The higher the level of intelligence of the subject, the stronger the influence of his motivation on the test result. A person with lower abilities, no matter how hard you try, will not show a high result. If a person with high intellectual potential does not try to solve problems, he will not show his true abilities.
The result of the test will be higher if you practice doing such tasks - this is the effect of learning. As in any test, the emotional mood plays a role, so it is better to start tasks in a good mood.
The distribution of the results of the subjects: 70% demonstrate average scores, another quarter - slightly above or below average, units - extremely high or low scores.
Description of the technique
The school intelligence test consists of six sets of tasks, or subtests, namely:
- “awareness” (two tasks);
- "analogies";
- "generalization";
- "classification";
- "number lines".
In addition, two equivalent forms, “A” and “B”, are included in the SHTUR methodology.
In order for the testing to be carried out correctly, it is necessary to strictly follow the instructions, as well as control the time of the task, which is carried out using a stopwatch. In addition, during the test, the specialist should not help the subjects.
Instructions for the SHTU method provide for the following task completion times:
- The first subtest - "awareness" - contains 20 items. The time for their implementation is 8 minutes.
- The second subtest is also "awareness". It includes 20 tasks that students must complete in 4 minutes.
- The third subtest is "analogies". These are 25 tasks that must be completed in 10 minutes.
- The fourth subtest is "classifications". It provides for the execution of 20 tasks within 7 minutes.
- The fifth subtest is "generalizations". It includes 19 tasks, which take 8 minutes to complete.
- The sixth subtest is "number series". Here the student has to consider 15 tasks in 7 minutes.
July 22What is IQ and how is it measured
The concept of "intelligence quotient" and the abbreviation IQ are familiar to almost everyone today. And everyone is aware that this very coefficient can be assessed using special tests. But this is where the knowledge of many people who are far from psychology and related sciences ends.
So what is IQ, how is it measured and is it necessary do it at all?
Let's start with a little historical digression. At the beginning of the 20th century in France, the state commissioned the psychologist Alfred Binet with tests to determine the mental abilities of children. To this end, Binet developed a test, which is known today as the "IQ Test"
The test quickly became popular, but not in France, but in the USA. As early as 1917, the US military began using IQ tests to classify soldiers. More than 2 million people passed this exam. Then IQ tests began to be used by universities and private companies, which used them to screen applicants and potential employees.
The results of numerous studies have allowed foreign experts to make the following generalizations:
50% have an IQ between 90 and 110;
25% have an IQ above 110 and 25% below 90.
IQ = 100 - the most common result;
14.5% have an IQ = 110–120;
7% — 120–130;
3% — 130–140;
0.5 - over 140.
An IQ below 70 indicates mental retardation.
Among high school students in American schools, the most common result is IQ = 115, among excellent students - 135-140. People who are under 19 or 60 tend to score lower on tests.
The IQ level speaks more about the speed of thought processes (test tasks must be completed in a limited period of time), and not about the ability to think or the originality of thinking. Therefore, testing intelligence in everything today is losing its former popularity.
To successfully cope with the tasks of IQ tests, the following psychological features are necessary: the ability to focus attention, highlight the main thing and distract from the secondary; memory, vocabulary and practical knowledge of the native language; imagination and the ability to mentally manipulate objects in space; possession of logical operations with numbers and verbally expressed concepts, perseverance, finally. If you compare this list with the definitions of intelligence, you will notice that they do not exactly match. If you compare this list with the definitions of intelligence, you will notice that they do not exactly match.
If you compare this list with the definitions of intelligence, you will notice that they do not exactly match.
Thus, what intelligence tests measure is not exactly intelligence! Even the special term "psychometric intelligence" has been coined - that is what intelligence tests measure.
Despite this, the IQ test is still one of the main ways to measure intelligence. What does he represent?
There are two types of this test:
The first is designed to assess the intellectual abilities of children from 10 to 12 years old.
The second is to assess the intellectual abilities of children from 12 years old and adults. Only the complexity of the questions changes, but the methodology is the same.
Each test consists of a fairly large number of different problems, and to get a score of 100-120 you do not need to solve them all, usually about half is enough.
In the usual measurement of "general" intelligence, it does not matter which ones and in what order are solved.
Therefore, it is important for the tested person to immediately, at the first reading, determine which task to solve and which one to skip. You can return to missed tasks if there is time.The one who manages to choose "their" tasks gets a great advantage over the one who tries to scrupulously solve in a row.
The one who manages to choose "their" tasks gets a great advantage over the one who tries to scrupulously solve in a row.
You have exactly 30 minutes to complete the test. The most reliable and reliable results, indicating the abilities of a person, are obtained in the range from 100 to 130 points, outside these limits, the assessment of the results is not sufficiently reliable.
In conclusion, it should be said that, according to a number of psychologists, tests developed in the West for determining the IQ are not entirely suitable for Russia. The main reason is the difference in the structure of the intelligence of different countries. The Russians are dominated by the so-called "figurative" style of thinking, that is, the Russian more often "thinks" with his heart, and not with his head. It remains only to wait for ours to offer their own methods for assessing intelligence. While they are not...