- Calculation of gas flow from a gas tank
- How to calculate correctly?
- How to find out consumption per month?
- Features of mounting the accounting device
- Which gas stove to install
- General principles for calculating heating power and energy consumption
- And why are such calculations carried out at all?
- We calculate how much gas a gas boiler consumes per hour, day and month
- Table of consumption of known models of boilers, according to their passport data
- Quick Calculator
- Gas consumption by boilers of different power
- Which stove to choose
- How much gas does a gas boiler consume?
- Heat loss
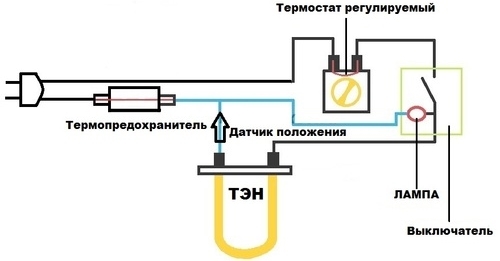
- Automation systems
- Selection of condensing type devices
- Method of calculation for natural gas
- We calculate the gas consumption by heat loss
- Heat loss calculation example
- Boiler power calculation
- By quadrature
- Use of economical condensing gas boilers
- How else can you save gas?
- Information in GOST
Calculation of gas flow from a gas tank
The calculation of the consumption for heating of the mixture from the gas storage used in the heat supply system of the house has its own characteristics and differs from the calculation of the consumption of the main natural gas.
The predicted volume of gas consumption is calculated by the formula:
V = Q / (q × η), where
V is the calculated volume of LPG, measured in m³/h;
Q is the calculated heat loss;
q - the smallest specific value of the heat of combustion of gas or its calorie content. For propane-butane, this value is 46 MJ/kg or 12.8 kW/kg;
η - efficiency of the gas supply system, expressed in absolute value to unity (efficiency / 100). Depending on the characteristics of the gas boiler, the efficiency can range from 86% for the simplest to 96% for high-tech condensing units. Accordingly, the value of η may be from 0.86 to 0.96.
Assume that the heating system is planned to be equipped with a modern condensing boiler with an efficiency of 96%.
Substituting in the original formula the values \u200b\u200baccepted for calculation, we obtain the following averaged volume of gas consumed for heating:
V \u003d 9.6 / (12.8 × 0.96) \u003d 9.6 / 12.288 \u003d 0.78 kg / h.
Since a liter is considered to be a LPG filling unit, it is necessary to express the volume of propane-butane in this unit of measurement. To calculate the number of liters in the mass of a liquefied hydrocarbon mixture, kilograms must be divided by density.
The table shows the values of the test density of liquefied gas (in t / m3), at various average daily air temperatures and in accordance with the ratio of propane to butane expressed as a percentage
The physics of the transition of LPG from liquid to vapor (working) state is as follows: propane boils at minus 40 ° C and above, butane - from 3 ° C with a minus sign. Accordingly, a 50/50 mixture will begin to pass into the gaseous phase at a temperature of minus 20 °C.
For mid-latitudes and a gas tank buried in the ground, such proportions are sufficient. But, in order to protect yourself from unnecessary troubles, it will be optimal in winter conditions to use a mixture with at least 70% propane content - “winter gas”.
Taking for the calculated density of LPG equal to 0.572 t / m3 - a mixture of propane / butane 70/30 at a temperature of -20 ° C), it is easy to calculate the gas consumption in liters: 0.78 / 0.572 \u003d 1.36 l / h.
Daily consumption with such a selection of gas in the house will be: 1.36 × 24 ≈ 32.6 liters, during the month - 32.6 × 30 = 978 liters. Since the obtained value is calculated for the coldest period, then, adjusted for weather conditions, it can be divided in half: 978/2 \u003d 489 liters, on average per month.
The duration of the heating season is calculated from the moment when the average temperature during the day outside does not exceed +8 degrees Celsius for 5 days. This period ends in spring, with stable warming.
In the area that we took as an example (Moscow region), such a period averages 214 days.
Gas consumption for heating during the year, when calculated, will be: 32.6 / 2 × 214 ≈ 3488 l.
How to calculate correctly?
You can find out the consumption of blue fuel for heating a house by calorie indicators on the basis of the management company. If this option does not work out, then you can put a conditional figure in the calculations, but it is best to take it with some margin - 8 kW / m³. But it also often happens that sellers give information regarding the specific heat of combustion, expressed in other units, that is, kcal / h. Don't worry, these numbers can be converted to Watts by simply multiplying the data by a factor of 1.163.
Another indicator that directly affects fuel consumption is the possible heat load on the heating system, which is heat loss due to additional building structures of the building, as well as possible losses spent on heating the ventilation air.The most suitable calculation option is to conduct or order detailed and accurate calculations of all existing heat losses. If you do not have the opportunity for such methods, and a rather approximate result will satisfy, then there is an option to recalculate using the “aggregated” method.
- With a ceiling height of up to three meters, you can count on heat of 0.1 kW per 1 sq. m of heated area. As a result, a building of no more than 100 m2 consumes 10 kW of heat, 150 m2 - 15 kW, 200 m2 - 20 kW, 400 m2 - 40 kW of heat energy.
- If calculations are carried out in other units of measurement, then 40-45 W of heat per 1 m³ of the heated building. Its load is checked by multiplying the specified indicator by the volume of all available heated rooms in the building.
The efficiency of the heat generator, which affects the most efficient fuel consumption, is most often noted in the special technical passport of the equipment.
If you have not yet bought a heating unit, you can take into account the efficiency data of gas boilers of various types from the following list:
- gas convector - 85 percent;
- boiler with an open combustion chamber - 87 percent;
- heat generator with a closed combustion chamber - 91 percent;
- condensing boiler - 95 percent.
The initial calculation of the use of liquefied gas for heating can be calculated using the following formulas:
V = Q / (q x efficiency / 100), where:
- q - fuel caloric content level (if it was not possible to find out the data from the manufacturer, it is advised to set the generally accepted rate of 8 kW / m³);
- V is the consumption of the main gas to be found, m³ / h;
- Efficiency - the efficiency of fuel use by the currently available heat source, written as a percentage;
- Q is the possible load on the heating of a private house, kW.
Calculating gas consumption for 1 hour during the coldest times, it is possible to obtain the following answer:
15 / (8 x 92 / 100) = 2.04 m³ / h.
Working 24 hours without interruption, the heat generator will consume the following amount of gas: 2.04 x 24 \u003d 48.96 m³ (for ease of measurement, it is advisable to round up to 49 cubic meters). Of course, during the heating season, the temperature tends to change, so there are very cold days, and there are also warm ones. Because of this, the value of the average daily gas consumption, which we found above, will need to be divided by 2, where we will get: 49/2 = 25 cubic meters.
Having the data already defined above, it is possible to calculate the gas consumption of a turbocharged boiler for 1 month in a house of 150 m², which is located somewhere in central Russia. To do this, we multiply the daily consumption by the number of days in a month: 25 x 30 = 750 m³. By means of the same calculations it is possible to find the gas consumption of larger and smaller buildings
It is important to know that it would be very good to carry out such calculations even before the building is completely built. This will give you the opportunity to carry out activities that could help improve the operating conditions of the premises, while saving on heat consumption.
How to find out consumption per month?
Calculating the gas used is very simple. To do this, you need to have access to the counter. First five digits to a comma on it and are an expense. And now we find out the costs per month: once every 30 days, go to the counter, while fixing the readings. After receiving at least two notes, you need to subtract the previous one from the result of the current month. In this way, you can count for a year, two, three, and so on.

Just be careful when taking testimony: do not climb with your bare hands if something is not visible. Use auxiliary items that do not conduct electricity.
Features of mounting the accounting device
The installation of the meter must be carried out exclusively by specialists with the appropriate qualifications, compliance with the required installation standards and requirements is mandatory. As for the cost of installation work, it depends on a number of individual characteristics, including the specific model of the device, the location of gas pipelines and gas-powered equipment.
Which gas stove to install
When installing the stove, you should be aware that the main gas is supplied to the apartments at a pressure of 1.5 kPa (15 mbar) and the stove itself is set to a predetermined value, and the liquefied gas gas tank reducer is usually set to a gas boiler pressure of approximately 2.3-5 kPa (23-50 mbar). Because of this, increased pressure arises, which can be judged by the red flame (normally it is blue) coming out of the burners of the gas stove, and the black "marks" of soot that appeared on the bottom of the pans. There are two ways to solve this problem: install a lowering pressure stabilizer or purchase a stove that matches the gas pressure.
General principles for calculating heating power and energy consumption
And why are such calculations carried out at all?
The use of gas as an energy carrier for the functioning of the heating system is advantageous from all sides. First of all, they are attracted by quite affordable tariffs for "blue fuel" - they cannot be compared with the seemingly more convenient and safe electric one.In terms of cost, only affordable types of solid fuels can compete, for example, if there are no special problems with harvesting or acquiring firewood. But in terms of operating costs - the need for regular delivery, organization of proper storage and constant monitoring of the boiler load, solid fuel heating equipment completely loses to gas connected to the mains supply.
In a word, if it is possible to choose this particular method of heating a home, then it is hardly worth doubting the expediency of installing a gas boiler.
According to the criteria of efficiency and ease of use, gas heating equipment currently has no real rivals
It is clear that when choosing a boiler, one of the key criteria is always its thermal power, that is, the ability to generate a certain amount of thermal energy. To put it simply, the purchased equipment, according to its inherent technical parameters, should ensure the maintenance of comfortable living conditions in any, even the most unfavorable conditions. This indicator is most often indicated in kilowatts, and, of course, is reflected in the cost of the boiler, its dimensions, and gas consumption. This means that the task when choosing is to purchase a model that fully meets the needs, but, at the same time, does not have unreasonably high characteristics - this is both unprofitable for the owners and not very useful for the equipment itself.
When choosing any heating equipment, it is very important to find a "golden mean" - so that there is enough power, but at the same time - without its completely unjustified overestimation
It is important to understand one more thing correctly.This is that the indicated nameplate power of a gas boiler always shows its maximum energy potential.
With the right approach, it should, of course, somewhat exceed the calculated data on the required heat input for a particular house. Thus, the very operational reserve is laid down, which, perhaps, will someday be needed under the most unfavorable conditions, for example, during extreme cold, unusual for the area of \u200b\u200bresidence. For example, if calculations show that for a country house the need for thermal energy is, say, 9.2 kW, then it would be wiser to opt for a model with a thermal power of 11.6 kW.
Will this capacity be fully demanded? - it is quite possible that it is not. But its stock does not look excessive.
Why is this explained in such detail? But only to ensure that the reader has clarity with one important point. It would be completely wrong to calculate the gas consumption of a particular heating system, based solely on the passport characteristics of the equipment. Yes, as a rule, in the technical documentation accompanying the heating unit, the energy consumption per unit of time (m³ / h) is indicated, but again this is more of a theoretical value. And if you try to get the desired consumption forecast by simply multiplying this passport parameter by the number of hours (and then days, weeks, months) of operation, then you can come to such indicators that it will become scary!..
It is not advisable to take passport values of gas consumption as a basis for calculations, since they will not show the real picture
Often, the consumption range is indicated in the passports - the boundaries of the minimum and maximum consumption are indicated.But this, probably, will not be of great help in carrying out calculations of real needs.
But it is still very useful to know the gas consumption as close to reality as possible. This will help, firstly, in planning the family budget. And secondly, the possession of such information should, voluntarily or involuntarily, encourage zealous owners to search for energy saving reserves - perhaps it is worth taking certain steps to reduce consumption to the possible minimum.
We calculate how much gas a gas boiler consumes per hour, day and month
In the design of individual heating systems for private houses, 2 main indicators are used: the total area of \u200b\u200bthe house and the power of the heating equipment. With simple averaged calculations, it is considered that for heating every 10 m2 of area, 1 kW of thermal power + 15-20% of the power reserve is sufficient.
How to calculate the required boiler outputIndividual calculation, formula and correction factors
It is known that the calorific value of natural gas is 9.3-10 kW per m3, hence it follows that about 0.1-0.108 m3 of natural gas is needed per 1 kW of thermal power of a gas boiler. At the time of writing, the cost of 1 m3 of main gas in the Moscow region is 5.6 rubles / m3 or 0.52-0.56 rubles for each kW of boiler heat output.
But this method can be used if the passport data of the boiler are unknown, because the characteristics of almost any boiler indicate the gas consumption during its continuous operation at maximum power.
For example, the well-known floor-standing single-circuit gas boiler Protherm Volk 16 KSO (16 kW power), running on natural gas, consumes 1.9 m3 / hour.
- Per day - 24 (hours) * 1.9 (m3 / hour) = 45.6 m3.In value terms - 45.5 (m3) * 5.6 (tariff for MO, rubles) = 254.8 rubles / day.
- Per month - 30 (days) * 45.6 (daily consumption, m3) = 1,368 m3. In value terms - 1,368 (cubic meters) * 5.6 (tariff, rubles) = 7,660.8 rubles / month.
- For the heating season (suppose, from October 15 to March 31) - 136 (days) * 45.6 (m3) = 6,201.6 cubic meters. In value terms - 6,201.6 * 5.6 = 34,728.9 rubles / season.
That is, in practice, depending on the conditions and heating mode, the same Protherm Volk 16 KSO consumes 700-950 cubic meters of gas per month, which is about 3,920-5,320 rubles / month. It is impossible to accurately determine the gas consumption by the calculation method!
To obtain accurate values, metering devices (gas meters) are used, because the gas consumption in gas heating boilers depends on the correctly selected power of the heating equipment and the technology of the model, the temperature preferred by the owner, the arrangement of the heating system, the average temperature in the region for the heating season, and many other factors , individual for each private house.
Table of consumption of known models of boilers, according to their passport data
| Model | power, kWt | Max consumption of natural gas, cubic meters m/hour |
| Lemax Premium-10 | 10 | 0,6 |
| ATON Atmo 10EBM | 10 | 1,2 |
| Baxi SLIM 1.150i 3E | 15 | 1,74 |
| Protherm Bear 20 PLO | 17 | 2 |
| De Dietrich DTG X 23 N | 23 | 3,15 |
| Bosch Gas 2500 F 30 | 26 | 2,85 |
| Viessmann Vitogas 100-F 29 | 29 | 3,39 |
| Navien GST 35KN | 35 | 4 |
| Vaillant ecoVIT VKK INT 366/4 | 34 | 3,7 |
| Buderus Logano G234-60 | 60 | 6,57 |
Quick Calculator
Recall that the calculator uses the same principles as in the example above, the actual consumption data depends on the model and operating conditions of the heating equipment and can only be 50-80% of the data calculated with the condition that the boiler operates continuously and at full capacity .
Gas consumption by boilers of different power
Fuel consumption depends primarily on the power of the device. An important factor affecting the consumption is the principle of operation - convection or condensing, double-circuit or single-circuit, equipment with a coaxial or traditional chimney, technical condition of the unit, quality of the consumed gas, degree of insulation of the heated room, use of the device only for heating or for heating and heating water .
The wall-mounted unit with a condensing principle of operation, a closed combustion chamber and a coaxial chimney gives the lowest gas consumption. How to calculate the consumption of a gas boiler during the heating period? When calculating, one should take into account - a single-circuit or double-circuit boiler, the duration of the heating period, the efficiency of the unit, the area of \u200b\u200bthe heated building, the height of the ceilings.
Naturally, if the heat exchanger is clogged with scale and the room is not insulated, then during the operation of the boiler there will be a large consumption (excess) of fuel (gas) per hour. Below we give the maximum figures for fuel consumption during the heating period of boilers of different capacities, taking into account that it lasts 210 days.
Knowing the consumption figures per hour, you can calculate the amount of fuel used per day and per day. Considering the given values of fuel consumed and the price of gas in your area, the amount you pay for central heating, you can calculate whether it is profitable to install a gas boiler in an apartment.
Which stove to choose
Also, factors such as:
- Number and power of burners. For example, if you do not need to cook meals for a large group/family all day long, a model with 2 low power burners is suitable for you. And then the controlling device will need an inexpensive one. With 4 burners, it's a little more difficult.
- Plate operation method.
- The number of residents and their habits.
- Time of year and season. For example, in winter frosts, gas heating takes about 300 cubic meters. liquefied gas. In summer - 30-40 cubic meters. And about 10% is gas waste due to burners. The other 90% is spent on water. And in such scenarios, such a stove consumes 3-4 cubic meters per month. fuel.
How much gas does a gas boiler consume?
When buying any equipment, first of all, pay attention to the efficiency of its work. The criterion by which heating gas boilers are chosen is gas consumption. The consumption of natural gas is directly dependent on the power of the boiler, its efficiency, as well as on the load placed on the boiler equipment, namely: on the size of the heated areas and the volume of hot water consumed
In the table below you can see how the fuel consumption of gas heating boilers depends on their power
The consumption of natural gas is directly dependent on the power of the boiler, its efficiency, as well as on the load placed on the boiler equipment, namely: on the size of the heated areas and the volume of hot water consumed. In the table below, you can see how the fuel consumption of gas heating boilers depends on their power.
Heat loss
When calculating the heating project and when choosing the power of gas equipment, it is necessary to take into account possible heat losses.The gas consumption of gas heating boilers directly depends on heat loss. The formula for calculating the power of a heating unit, taking into account heat losses, is extremely simple: for heating 1 sq. meters of area with a ceiling height of up to 3 meters must be supplied with 100 watts of thermal energy. Moreover, drafts and obvious gaps must be excluded from the list of heat losses.
Automation systems
Modern boiler plants are equipped with a programmable built-in timer that allows you to adjust the air temperature in the house during the day and week. The temperature can be automatically lowered at night and raised during the day. On days when there are no people in the house, the air heating is also reduced. Such prudence allows you to reduce the fuel consumption of a gas boiler.
Selection of condensing type devices
A condensing boiler, including a wall-mounted boiler, has a lower gas consumption than a traditional unit. The fact is that condensing boilers make full use of the thermal energy that is released during the condensation of water vapor formed in the products of fuel combustion. Exhaust gases have a high temperature. And the design of condensing boilers allows it to be additionally used. The water supplied to the boiler unit is first heated by exhaust gases, and then by a gas burner. The cost of such devices is higher due to the more complex design and functionality. But during the operation of condensing boilers, the percentage of gas savings is from 15 to 17%, which will eventually pay off all additional costs.
Method of calculation for natural gas
The approximate gas consumption for heating is calculated based on half the capacity of the installed boiler.The thing is that when determining the power of a gas boiler, the lowest temperature is laid. This is understandable - even when it is very cold outside, the house should be warm.
You can calculate the gas consumption for heating yourself
But it is completely wrong to calculate the gas consumption for heating according to this maximum figure - after all, in general, the temperature is much higher, which means that much less fuel is burned. Therefore, it is customary to consider the average fuel consumption for heating - about 50% of the heat loss or boiler power.
We calculate the gas consumption by heat loss
If there is no boiler yet, and you estimate the cost of heating in different ways, you can calculate from the total heat loss of the building. They are most likely familiar to you. The methodology here is as follows: they take 50% of the total heat loss, add 10% to provide hot water supply and 10% to heat outflow during ventilation. As a result, we get the average consumption in kilowatts per hour.
Then you can find out the fuel consumption per day (multiply by 24 hours), per month (by 30 days), if desired - for the entire heating season (multiply by the number of months during which the heating works). All these figures can be converted into cubic meters (knowing the specific heat of combustion of gas), and then multiply cubic meters by the price of gas and, thus, find out the cost of heating.
| The name of the crowd | unit of measurement | Specific heat of combustion in kcal | Specific heating value in kW | Specific calorific value in MJ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Natural gas | 1 m 3 | 8000 kcal | 9.2 kW | 33.5 MJ |
| Liquefied gas | 1 kg | 10800 kcal | 12.5 kW | 45.2 MJ |
| Hard coal (W=10%) | 1 kg | 6450 kcal | 7.5 kW | 27 MJ |
| wood pellet | 1 kg | 4100 kcal | 4.7 kW | 17.17 MJ |
| Dried wood (W=20%) | 1 kg | 3400 kcal | 3.9 kW | 14.24 MJ |
Heat loss calculation example
Let the heat loss of the house be 16 kW / h. Let's start counting:
- average heat demand per hour - 8 kW / h + 1.6 kW / h + 1.6 kW / h = 11.2 kW / h;
- per day - 11.2 kW * 24 hours = 268.8 kW;
-
per month - 268.8 kW * 30 days = 8064 kW.
Convert to cubic meters. If we use natural gas, we divide the gas consumption for heating per hour: 11.2 kW / h / 9.3 kW = 1.2 m3 / h. In calculations, the figure 9.3 kW is the specific heat capacity of natural gas combustion (available in the table).
Since the boiler has not 100% efficiency, but 88-92%, you will have to make more adjustments for this - add about 10% of the figure obtained. In total, we get the gas consumption for heating per hour - 1.32 cubic meters per hour. You can then calculate:
- consumption per day: 1.32 m3 * 24 hours = 28.8 m3/day
- demand per month: 28.8 m3 / day * 30 days = 864 m3 / month.
The average consumption for the heating season depends on its duration - we multiply it by the number of months that the heating season lasts.
This calculation is approximate. In some month, gas consumption will be much less, in the coldest - more, but on average the figure will be about the same.
Boiler power calculation
Calculations will be a little easier if there is a calculated boiler capacity - all the necessary reserves (for hot water supply and ventilation) are already taken into account. Therefore, we simply take 50% of the calculated capacity and then calculate the consumption per day, month, per season.
For example, the design capacity of the boiler is 24 kW. To calculate the gas consumption for heating, we take half: 12 k / W. This will be the average need for heat per hour. To determine the fuel consumption per hour, we divide by the calorific value, we get 12 kW / h / 9.3 k / W = 1.3 m3. Further, everything is considered as in the example above:
- per day: 12 kW / h * 24 hours = 288 kW in terms of the amount of gas - 1.3 m3 * 24 = 31.2 m3
-
per month: 288 kW * 30 days = 8640 m3, consumption in cubic meters 31.2 m3 * 30 = 936 m3.
Next, we add 10% for the imperfection of the boiler, we get that for this case the flow rate will be slightly more than 1000 cubic meters per month (1029.3 cubic meters). As you can see, in this case everything is even simpler - fewer numbers, but the principle is the same.
By quadrature
Even more approximate calculations can be obtained by the quadrature of the house. There are two ways:
- It can be calculated according to SNiP standards - for heating one square meter in Central Russia, an average of 80 W / m2 is required. This figure can be applied if your house is built according to all requirements and has good insulation.
- You can estimate according to the average data:
- with good house insulation, 2.5-3 cubic meters / m2 are required;
-
with average insulation, gas consumption is 4-5 cubic meters / m2.
Each owner can assess the degree of insulation of his house, respectively, you can estimate what gas consumption will be in this case. For example, for a house of 100 sq. m. with average insulation, 400-500 cubic meters of gas will be required for heating, a house of 150 square meters will take 600-750 cubic meters per month, for home heating with an area of 200 m2 - 800-100 cubic meters of blue fuel. All this is very approximate, but the figures are based on many factual data.
Use of economical condensing gas boilers
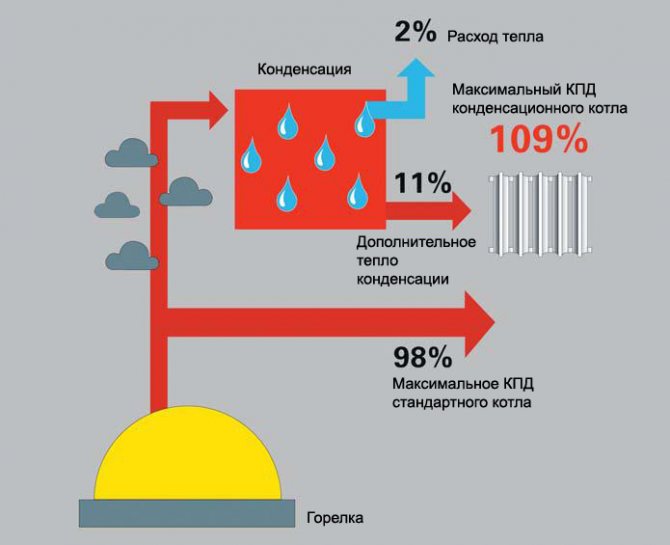
Condensing boilers have high efficiency with less fuel consumption
When using a 24 kW gas boiler, gas consumption can hit your pocket hard, so it’s better to buy modern economical options for heating equipment. Condensers are popular.The principle of their operation is simple: water vapor from the ignition of the fuel condenses, as a result of which thermal energy is released. Its unit uses it completely, so it saves up to 20% of fuel.
The advantage of such equipment is stable operation even in the event of a decrease in fuel pressure in the network. It works almost silently. However, if it is not possible to purchase such a boiler, simply following the recommendations of experts will significantly reduce fuel consumption.
How else can you save gas?
1. Insulate your home as much as possible. The complex process should include insulation of the roof, walls, windows, basements.
2. Turn off gas appliances when not in use.
3. Cook at the right burner setting for the dish you have chosen. Note that the highest temperature is at the tips of the flame. The more you turn on the gas, the less efficiently it will burn, i.e. with less heat - more consumption.
4. Upgrade your heating system. Call an expert to adjust your boiler for optimal performance or exchange it for the most economical model. Condensing gas heating devices are leading in terms of efficiency. Also, to save money, you can install the simplest regulators on radiators, which will allow you to change the temperature in a particular room - depending on its purpose and time of day.
5. Set the minimum temperature when you are away. For example, for a couple of hours during the day, the boiler may turn off, and by the time you return, warm up the house.
6. Replace old gas equipment with more modern ones, with automatic regulation and safety.
You can purchase gas equipment and gas consumption meters at the exhibition center.
The company's specialists will help you choose gas appliances that are suitable directly for your home, as well as install them and draw up all the necessary documents.
Information in GOST
Information about the power of burners is strictly regulated by GOSTs, and if the stove has the appropriate certificates and is allowed for installation in an apartment or residential building, it must comply with these parameters. So, in residential buildings it is allowed to install gas stoves with 2, 3 or 4 burners, the standard power of which should be:
- 0.6 kW - reduced;
- 1.7 kW - average;
- 2.6 kW - high.
Information about the power of the burners is in GOST
Additionally, it is worth calculating the power of the oven, the average indicators of which are within 2.5 kW. The final parameters will be about 10 kW. Many people ask how the power of a gas burner can be increased if it is insufficient or if it is necessary to transfer the stove from liquefied gas to the main. Despite the fact that many experts give advice on how to do this correctly and what manipulations should be carried out with the valves, the burner itself, the gearbox, all these techniques are illegal and unacceptable in relation to gas appliances. Such re-equipment can lead to accidents at home and huge fines from the gas service. If the power of the plate is insufficient, the equipment must be replaced with a new one.