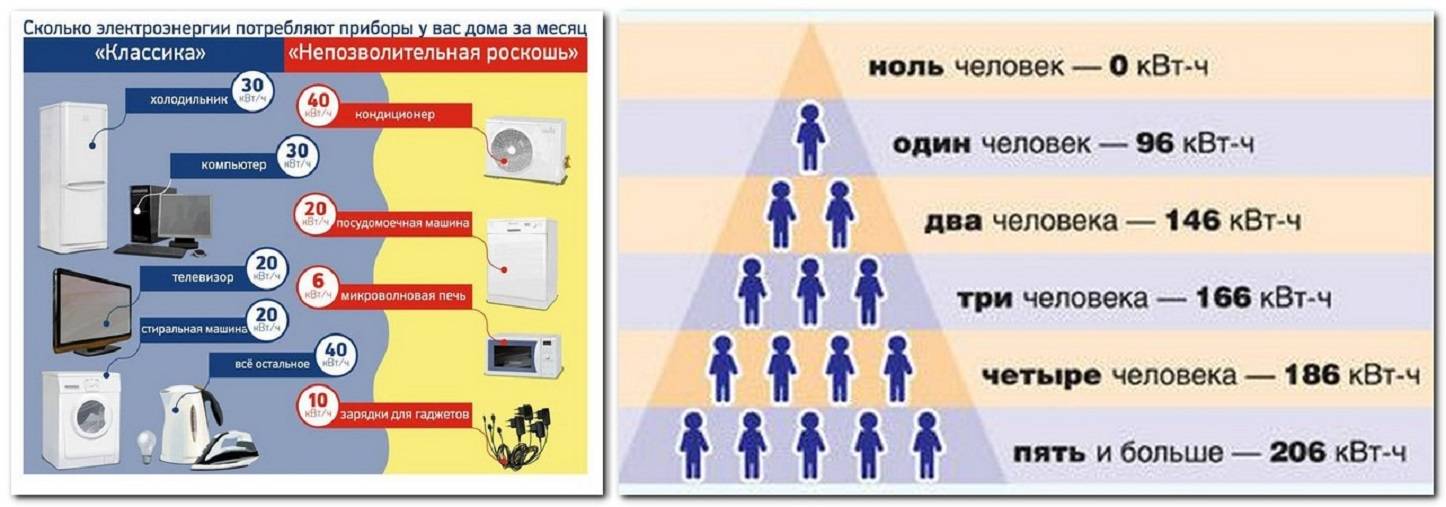
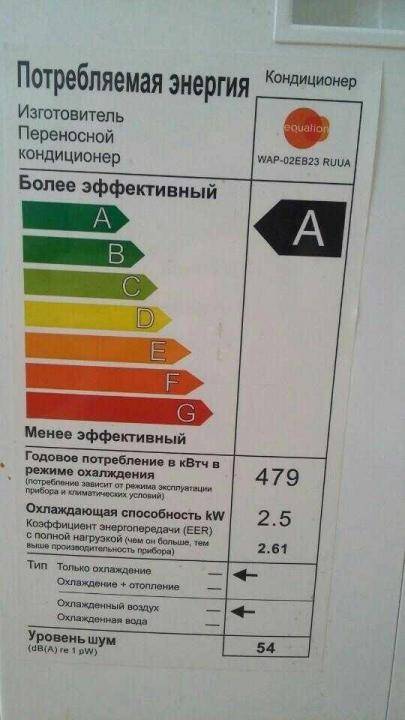
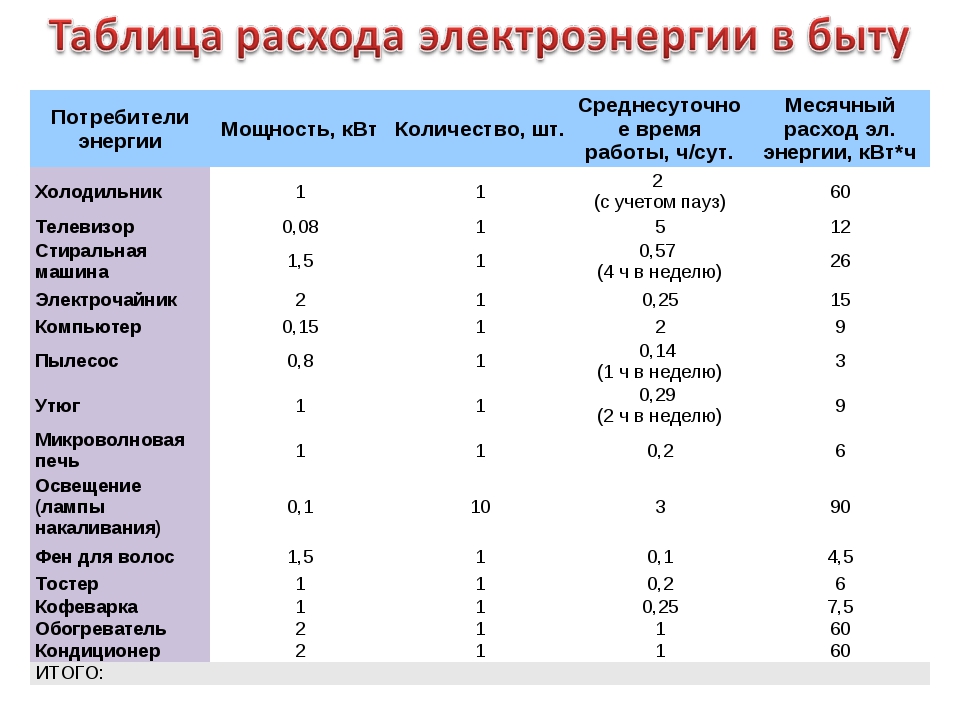
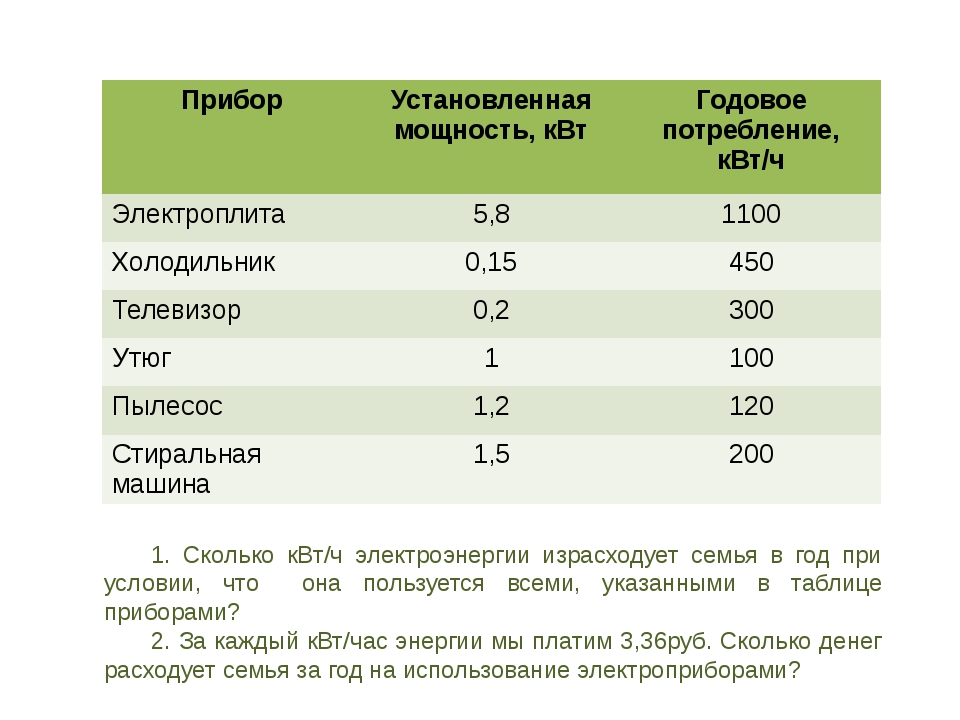
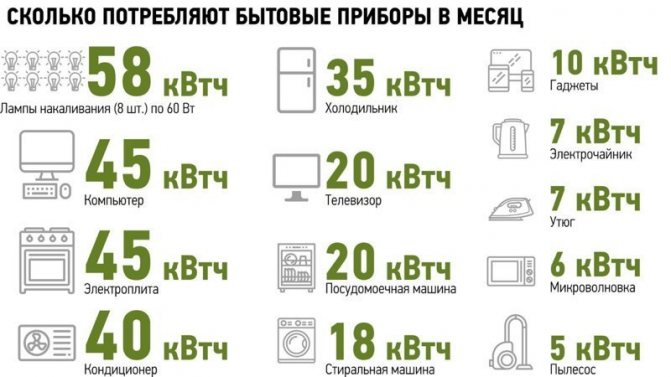
- Example 2
- Collection of initial data for calculation
- Power consumption of the device
- How to reduce air conditioner costs
- Calculation of energy consumption per month, per day
- 1 kW how many W: the concept of physical quantities
- What determines the consumption of electricity
- Power calculation using additional parameters
- Accounting for the influx of fresh air from an open window
- Guaranteed 18 – 20C
- Top floor
- Large glass area
- Cooling power
- Factors affecting the power of refrigerators
- Factors affecting electricity consumption
- Types of electric underfloor heating
- Electrical cable
- Thermomats
- Infrared film
- Rod floor
- Calculation of underfloor heating as the main heating
- Additional criteria for choosing an air conditioner
- Criterion # 1 - type of air conditioner
- Criterion # 2 - the principle of operation
- Criterion #3 - features and brand
- Oven Energy Calculation
- Disadvantages and disadvantages of winter heating
Example 2
There is a tank with a volume of V=5000 l, into which water is poured with a temperature Tnzh =25°C. Within 3 hours it is required to cool the water to a temperature Tkzh=8°C. Estimated ambient temperature 30°С.1. Determine the required cooling capacity.
- temperature difference of the cooled liquid ΔTzh=Tn - Тk=25-8=17°С;
- water consumption G=5/3=1.66 m3/h
- cooling capacity Qo \u003d G x Cp x ρzh x ΔTzh / 3600 \u003d 1.66 x 4.19 x 1000 x 17/3600 \u003d 32.84 kW.
where Срж=4.19 kJ/(kg x°С) is the specific heat capacity of water; ρzh=1000 kg/m3 is the density of water.2. We select the scheme of the water-cooling installation. Single-pump circuit without the use of an intermediate tank. Temperature difference ΔТl =17>7°С, we determine the circulation rate of the cooled liquid n=Срж x ΔTl/Ср x ΔТ=4.2х17/4.2×5=3.4 where ΔТ=5°С is the temperature difference in the evaporator.
Then the calculated flow rate of the cooled liquid G= G x n= 1.66 x 3.4=5.64 m3/h.
3. The temperature of the liquid at the outlet of the evaporator Tc=8°C.
4. We select a water-cooling unit that is suitable for the required cooling capacity at a water temperature at the outlet of the unit of 8°C and an ambient temperature of 28°C After viewing the tables, we determine that the cooling capacity of the VMT-36 unit at Tacr.av. .3 kW, power 12.2 kW.
Collection of initial data for calculation
For calculations, the following information about the building will be needed:
S is the area of the heated room.
Woud - specific power. This indicator shows how much heat energy is needed per 1 m2 in 1 hour. Depending on local environmental conditions, the following values can be taken:
- for the central part of Russia: 120 - 150 W / m2;
- for the southern regions: 70-90 W / m2;
- for northern regions: 150-200 W/m2.
Woud - the theoretical value is used mainly for very rough calculations, because it does not reflect the real heat loss of the building. Does not take into account the area of glazing, the number of doors, the material of the outer walls, the height of the ceilings.
Accurate heat engineering calculation is carried out using specialized programs, taking into account many factors.For our purposes, such a calculation is not needed;
Values to be included in the calculations:
R is the heat transfer resistance or heat resistance coefficient. This is the ratio of the temperature difference along the edges of the building envelope to the heat flux passing through this structure. It has the dimension m2×⁰С/W.
In fact, everything is simple - R expresses the ability of the material to retain heat.
Q is a value showing the amount of heat flow passing through 1 m2 of surface at a temperature difference of 1⁰С per 1 hour. That is, it shows how much heat energy is lost by 1 m2 of the building envelope per hour with a temperature drop of 1 degree. It has the dimension of W/m2×h. For the calculations given here, there is no difference between kelvins and degrees Celsius, since it is not the absolute temperature that matters, but only the difference.
Qcommon- the amount of heat flow passing through the area S of the building envelope per hour. It has the unit W/h.
P is the power of the heating boiler. It is calculated as the required maximum power of the heating equipment at the maximum temperature difference between the outdoor and indoor air. In other words, sufficient boiler power to heat the building in the coldest season. It has the unit W/h.
Efficiency - the efficiency of a heating boiler, a dimensionless value showing the ratio of energy received to energy consumed. In the documentation for the equipment, it is usually given as a percentage of 100, for example, 99%. In calculations, a value from 1 i.e. 0.99.
∆T - shows the temperature difference on both sides of the building envelope.To make it clearer how the difference is correctly calculated, see an example. If outside: -30C, and inside + 22C⁰, then
∆T = 22-(-30)=52С⁰
Or, too, but in kelvins:
∆T = 293 - 243 = 52K
That is, the difference will always be the same for degrees and kelvins, so reference data in kelvins can be used for calculations without correction.
d is the thickness of the building envelope in meters.
k is the coefficient of thermal conductivity of the building envelope material, which is taken from reference books or SNiP II-3-79 "Construction Heat Engineering" (SNiP - building codes and rules). It has the dimension W/m×K or W/m×⁰С.
The following list of formulas shows the relationship of quantities:
- R=d/k
- R= ∆T/Q
- Q = ∆T/R
- Qcommon = Q×S
- P=Qcommon / efficiency
For multilayer structures, the heat transfer resistance R is calculated for each structure separately and then summed up.
Sometimes the calculation of multilayer structures can be too cumbersome, for example, when calculating the heat loss of a double-glazed window.
What you need to consider when calculating the heat transfer resistance for windows:
- glass thickness;
- the number of glasses and air gaps between them;
- type of gas between panes: inert or air;
- the presence of a heat-insulating coating of window glass.
However, you can find ready-made values \u200b\u200bfor the entire structure either from the manufacturer or in the directory, at the end of this article there is a table for double-glazed windows of a common design.
Power consumption of the device
The electricity consumption of the air conditioner does not depend on its type (split system, floor, etc.), except for the inverter type. its design allows you not to turn off and turn on the device for operation.The inverter type is always in operation, only after it has brought the temperature to the desired one, the device reduces speed and is in temperature maintenance mode.
Video about the difference between the inverter type and other types:
The consumption depends on the heat output (BTU-British Thermal Unit) can be 07; 09; etc. (0.7 means that it consumes 0.7-0.8 kW / h; 09 - 0.9-1 kW).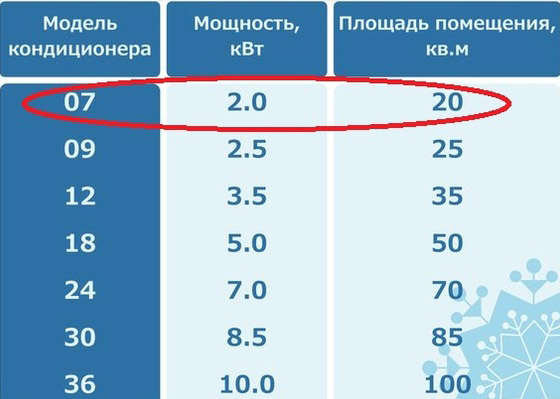
If the area is larger or smaller, the power consumption changes similarly (as shown in the table).
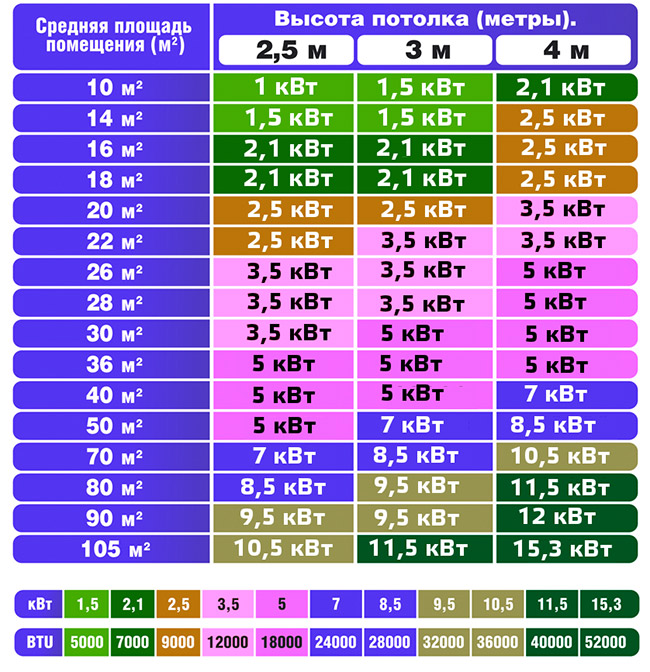
The most energy-saving and efficient air conditioner is class A.
How to choose the right air conditioner depending on the size of your room:
How to reduce air conditioner costs
Experts offer consumers the following figures: air conditioners with a capacity in the range of 2-3.5 kW will consume from 0.5 to 1.5 kW / h
But before turning it on, it is important to know some values:
- the power consumption of the air conditioner for which the socket is designed (Russian is suitable for a current of 6.3 A / 10A, and foreign 10A / 16A);
- the power that the wiring can withstand;
- fuse settings that protect the network from overloads.
There is a difference between whether a household or industrial appliance is planned to be delivered. The air conditioner in the apartment will not exceed 2400 W (and will also have a single-phase connection). In contrast, semi-industrial and industrial units can consume electricity up to several hundred kW (three-phase connection is required).
There is one piece of advice that will help reduce energy consumption even at the stage of purchase. We are talking about the acquisition of an inverter model.If you use a similar system, the waste will be reduced by as much as 40% without losing the power of the device. The daily consumption of such an air conditioner will not exceed 0.5 kW, and the monthly fee will be about 390 rubles (according to a six-hour work schedule). When turned on around the clock, it will, of course, increase by 4 times, but again it will be much lower than that of conventional stop-start climate technology.
Calculation of energy consumption per month, per day
The electricity consumption of an air conditioner per hour depends on its electric power, which in turn depends on the type of compressor. How much classic models spend, we said above. Modern split systems use an inverter compressor, these consume 40-60% less, which means that the “nine” will consume about 0.5 kW per hour, etc.

If the split system works 8 hours non-stop, and at night it is turned off, for example, during a hot day, then the "nine" will not consume so much. The actual consumption is related to the start-stop operation. The air conditioner stays idle longer than it works. Then the real daily consumption will be about 6.4 kW (with 8 hours of operation). Expenses per day, at Moscow electricity tariffs for February 2018, will be:
5.38r * 6.4 kW = 34.432 rubles in eight hours.
In a month, if you use the air conditioner every day, the consumption will be:
6.4 * 30 * 5.38r \u003d 1032 rubles per month for 192 kW
As we can see from the calculations, the actual consumption of air conditioners does not cause such high costs, inverter models consume even less:
5.38r * 3.8 \u003d 21 rubles, daily consumption.
Per month:
21*30=620 rubles.
Please note that this calculation is based on 8 hours of work.In extreme heat, the split system can work 24 hours a day, then the costs will be 3 times more.
For example, the consumption of a more powerful "twelfth" air conditioner per day will be almost 24 kW and an expense of 130 rubles. Then his work per month will cost you more than 3,000 rubles.
Do not forget that this is a rough calculation, does not take into account the mode of operation when the temperature in the room has reached the set temperature. The compressor is in standby mode and only the fan is running (it consumes little). However, it gives an idea of upcoming expenses and simplifies budget planning.
To reduce the cost of operation, you need thermal insulation of the apartment and high-quality windows. Then less heat will be given off to the apartment by the environment, and it will be cooler in it in summer, and in winter the heat will not go beyond it. So the energy consumption of the air conditioner will be less, as well as electricity bills.
In conclusion, I would like to note that air conditioning is not such a “gluttonous” consumer. The same iron eats up about 2 kW, and an electric kettle 1.5-2. The maximum electricity consumption falls on the first hours of operation of the split system, when the room is very hot and significant cooling is needed. Less electricity is used to maintain the temperature. Also, consumption depends on the temperature difference in the rooms, with extreme heat, electricity will take more.
Related materials:
- Electricity consumption for underfloor heating
- How to choose an air conditioner for your home
- How to determine the power consumption of electrical appliances
- The best manufacturers of air conditioners
1 kW how many W: the concept of physical quantities
All household appliances use electricity as a power source.The technical passport of each device indicates the rated power without taking into account the conditions and modes of its operation. For low-power devices, this parameter is indicated in watts, and for more powerful devices, the kilowatt value is used. The power of the device indicates the rate of conversion or consumption of energy. This is the ratio of work to the time during which it was performed. The unit of power got its name from the Irish inventor James Watt, who is the creator of the first steam engine.
 Electricity consumption of appliances in standby mode (kWh/year).
Electricity consumption of appliances in standby mode (kWh/year).
The use of the watt is not limited to electrical engineering. This unit is used to determine the torque of power plants, the flow of acoustic and thermal energy, the intensity of ionizing radiation. To understand whether 1 W is a lot or a little, you can consider such examples. Mobile phone transmitters have a power of 1W. For incandescent lamps, this parameter is 25-100 W, for a refrigerator or TV 50-55 W, for a vacuum cleaner - 1000 W, and for a washing machine - 2500 W.
In order not to use many zeros, you should know how many watts are in 1 kW. The prefix "kilo" is a multiple of a thousand. It involves multiplying the value by one thousand. So 1 kW to watts equals 1000.
There is also the concept of vilowatt-hour (kWh). This is a value that indicates the amount of electrical energy that the device consumes per unit of time. In other words, we can say that kWh is the amount of work that the device performs in one hour. To understand the dependence of these quantities, consider an example. The power consumption of the TV is 200 watts.If it works for 1 hour, the device will consume 200 W * 1 hour = 200 W * h. If he works for 3 hours, then during this time he will spend 200 W * 3 hours = 600 W * h.
What determines the consumption of electricity
The consumption of electrical energy with the help of an air conditioner does not depend on its type, the presence of a heating system. Inverter type after temperature stabilization, reduce speed and maintain temperature.
Electricity consumption depends on the set temperature, enabled functions and operating time
But here it is important to understand that an insignificant power consumption is obtained per hour. When it comes to long-term costs, they can vary greatly.
The consumption also depends on the compressor potential (during a lower speed, less energy is consumed and the most profitable are inverter devices), the temperature difference between the street and the room (costs increase in summer heat or frost), the load of the cooling system on the split and various additional functions .
Power calculation using additional parameters
Under certain circumstances, the value of the required cooling capacity obtained in the typical calculation has to be adjusted to take into account certain circumstances.
Accounting for the influx of fresh air from an open window

If the user cannot imagine his existence without fresh air and plans to constantly ventilate the room during the operation of the air conditioner, he should increase the Q1 value by 30% in the calculation of the cooling capacity.
One should not think that an air conditioner, calculated taking into account this amendment, can be operated with the windows wide open - a household appliance, even the most powerful one, will not last long in such conditions.
It is understood that the window will only be slightly ajar (metal-plastic windows - in the ventilation mode). Even better is to equip the room with a supply valve, the performance of which can be precisely regulated.
Guaranteed 18 – 20C
The above formula for calculating Q1 is focused on providing a 10-degree difference between the temperatures outside and in the room. It is this difference that is believed to provide sufficient comfort and at the same time is safe: getting into the room from the street, a person does not risk catching a cold.
But some users, even in 40 degree heat, would like to have 18 - 20 degrees in the room. Then, when calculating, they should increase Q1 by 20% - 30%.
Top floor

In apartments on the upper floors, the area of enclosing structures through which outside heat enters the room has been increased - a roof has been added.
Moreover, due to the dark color, it heats up quite strongly in the sun.
Therefore, residents of such apartments should increase the value of Q1 by 10% - 20%.
Large glass area
In the presence of glazing with an area of \u200b\u200bmore than 2 square meters. m of solar heat enters the room more than provided by the formula, and this must also be taken into account by amending. For each additional sq. m of glazing to the estimated refrigeration capacity should be added:
- in low light: 50 - 100 W;
- at average illumination: 100 - 200 watts.
With intense illumination, 200 - 300 watts are added.
If you have enough money to buy a quality air conditioner, you can consider an inverter split system. Inverter air conditioner - what is it and what are its advantages?
Read more about how your air conditioner works in heating mode here. How to turn on the unit for heat?
Do you know how air conditioning works? If interested, read this article about the principle of operation of split systems.
Cooling power
An air conditioner is a classic example of a heat pump. Its compressor forces the refrigerant to circulate through the circuit, which gives off heat in the condenser and takes it in the evaporator. Thus, the cooling capacity of the air conditioner is the amount of heat that it takes from the room and releases it in the condenser of the external unit of the split system.
The air is cooled as it passes through the evaporators of the indoor unit under the influence of the fan. The air from the room does not go anywhere, and does not come from anywhere - it just cools. Only the best air conditioners have the added option of supplying fresh air from outside to the premises.
Factors affecting the power of refrigerators
The power consumption of a refrigerator depends on the following number of factors:
- Compressor type. Modern inverter installations are characterized by fast start-up and minimal energy consumption. Previously produced and some cheap models still use inefficient rotary piston counterparts.
- number of compressors. The larger the capacity of the compartments, the more freon is required, and the more compressor units are installed.
- The volume of refrigerators and freezers.
- Basic and additional functionality.The ice maker, ventilation, fast freezing and other additional functions lead to increased electricity consumption.
- settings. The lower the temperature can be set inside the chambers, the more powerful equipment is required.
The amount of total electricity that a refrigerator can consume primarily depends on the type and number of compressors used. This is the heart of the cooling cabinet. With its help, the refrigerant is pumped through the system.
At the same time, it turns on only from the signal of temperature sensors. The latter, in turn, work/switch off as the internal space of the chambers heats up/cools.
Factors affecting electricity consumption
In order to correctly calculate the heating with electricity and, accordingly, find out which boiler model it is desirable to purchase in a particular case, a number of points must be taken into account:
- the volume of the room to be heated;
- type of device required (single or double circuit);
- supply voltage;
- current value;
- section of the supply cable;
- unit power for;
- tank capacity;
- the amount of coolant for which the heating circuit is designed;
- operating time of the equipment during the heating season;
- cost of one kWh;
- daily duration of work at maximum load.
Depending on the power of a single-phase boiler (4, 6, 10, 12 kW), the approximate cable cross-section should be 4, 6, 10, 16 mm², respectively. For three-phase heaters with a power of 12, 16, 22, 27, 30 kW, choose a cable with a cross-sectional area of 2.5, 4, 6, 10, 16 mm².
Despite the fact that there are no special requirements for conventional boilers, when installing a unit with a capacity of more than 10 kW, this must be agreed with the Energy Supervision Authority and electricity distribution companies. The fact is that with high power it is necessary to connect a 3-phase line and obtain permission to pay for electricity at a household tariff.
Types of electric underfloor heating
Today, there is a huge range of electric type floor systems on the market. All of them are divided into several types.
Below we will analyze in detail the technical characteristics of each type, calculate the electricity consumption depending on the type of room per 1 m2 per hour, per month. We will also find out how the finish coating affects energy consumption.
Electrical cable
An electrical cable is a wire that is laid arbitrarily, but more often according to the “snail” or “snake” pattern. From above, the structure is poured with a concrete screed, which reduces the height of the room by an average of 5 cm. The specific power of such a cable is from 0.01 to 0.06 kW / m2, its choice depends on the frequency of turns.

The energy consumption of one meter of cable is from 10 to 60 watts. To cover 1 m2 of surface, about 5 meters of wire are required, thus, on average, 120 - 200 W of electricity is needed for heating.
Thermomats
Heating mats are a cable construction, which is laid according to a certain pattern on a special grid. Mounted more often under the screed, and is perfect for laying in rooms with high humidity.
This model is designed for rooms with low ceilings, since the thickness of the “pie” is only 3 cm. The power of the mat is up to 0.2 kW / m2.
The average consumption per square meter of the heating mat is 120 - 200 watts.
Infrared film

Infrared warm floor - a thin film of polymer coated with a carbon layer. When heated, carbon radiates heat.
IR film does not affect the height of ceilings. On average, about 150 - 400 W of electricity is wound to warm up 1 m2 of film.
Rod floor
Rod floor - refers to the infrared type, but instead of carbon plates contains rods. Its power consumption is 120 - 200 W per square meter.
Calculation of underfloor heating as the main heating
But how do you know if there is enough heat from the electric floor to warm the entire room and house? To do this, you need to calculate your heat loss. Of course, in each case, everything is individual, and a lot of factors will affect the error.
However, you can roughly focus on the requirements of SNiP.
They say that the normal heat loss for a standard residential apartment is 1kWh over an area of 10m2.
At the same time, the height of the ceilings is a maximum of 3 m, and the walls, floor and everything else must be insulated again in accordance with SNiP.
Let's take the same calculated data as before. The area of the room is 20m2.
Accordingly, on such an area, heat loss will be - 2 kW / h

Your task is to block the received data. That is, you must lay mats of a certain power and on a certain area so that the final result from such installation is either equal to or exceeds the calculated heat loss of the room.
We know that the useful area that can be used for mats or heating cable in a room is 8m2.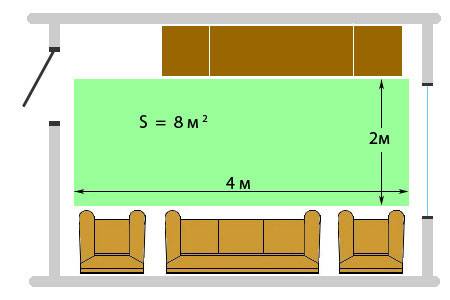
Based on this, we calculate how much power the warm floor needs to be chosen so that it is enough to warm the room as the main source of heat.
Total for our room we have:
Ptp = 2 / 8 = 0.25 kW/m2
Moreover, if you live in a climatic zone, when the temperature outside can drop to -30 degrees for several days, it is recommended to add another + 25% to this power.
If such a powerful mat or cable is not available, then try to increase the usable laying area and recalculate.
Additional criteria for choosing an air conditioner
In addition to the power characteristics of the system and the energy efficiency class, before buying, you should decide on the following parameters:
- type of air conditioner;
- the principle of operation of the unit;
- functionality;
- manufacturer firm.
Let's take a closer look at each of these criteria.
Criterion # 1 - type of air conditioner
For domestic use, monoblocks and split systems are used. The first category includes window models and compact portable appliances. Air conditioners built into the window have lost their former popularity.

They are being replaced by more modern modifications, devoid of the shortcomings of their predecessors: noisy operation, reduced illumination due to window clutter, limited choice of location
Indisputable advantages of window "coolers": low cost and maintainability. Such a unit is more suitable for seasonal country use than for an apartment.

Advantages of a mobile monoblock: the possibility of transportation, ease of installation. Cons: large dimensions, high noise level, "binding" to the output channel
Split systems confidently occupy a leading position among household air conditioning complexes.
According to the form of execution, two categories of splits are distinguished:
- Duplex construction. A pair of modules is connected by a freon closed line. The complex is easy to operate and virtually silent. Various design options for the indoor unit are available, the case does not occupy a usable area in the room.
- Multi-system. The external module ensures the operation of two to five indoor units.
The use of a multi-complex allows you to set various air conditioning parameters in individual rooms.
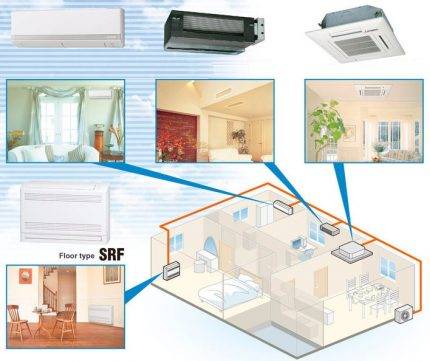 The disadvantage of the climate system is the dependence of indoor units on a single outdoor unit. If it breaks, all rooms will remain without cooling
The disadvantage of the climate system is the dependence of indoor units on a single outdoor unit. If it breaks, all rooms will remain without cooling
Criterion # 2 - the principle of operation
There are conventional and inverter models.
- When the temperature rises, the air conditioner turns on.
- After cooling to the designated aisle, the unit is switched off.
- The operating cycle of switching on/off is repeated continuously.
But the inverter air conditioner operates more “smoothly”. After starting, the room cools down, but the appliance continues to operate at reduced power, maintaining the desired temperature.
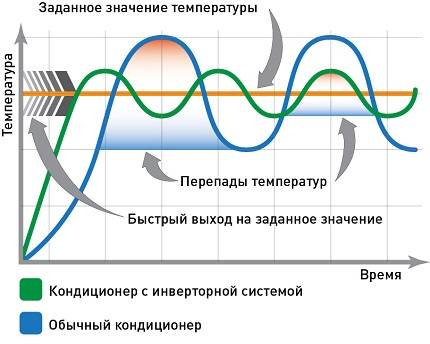
The inverter version of the split is 30-40% more economical than a conventional air conditioner. The energy efficiency value of the EER of some models reaches values up to 4-5.15
Due to the absence of "sharp" cyclic operation, inverter air conditioners are quiet and durable.
You also do not know what is better to choose - an inverter or a conventional air conditioner? In this case, we recommend that you familiarize yourself with their main differences, as well as the pros and cons of each option.
Criterion #3 - features and brand
Manufacturers, in an effort to win the favor of customers, equip split systems with additional options.
Well, if the air conditioner has the following functions:
- fan distribution of air flow;
- automatic restoration of device settings;
- remote control;
- built-in timer.
Another of the functions of the air conditioner that is in demand among users is the influx of fresh air. Many manufacturers offer such models.

Air conditioners of popular brands are represented by a wide range of models of different price categories - from the budget economy class to the premium segment split systems
The manufacturer of the equipment plays a significant role in the choice - the better the reputation of the brand, the higher the quality indicators and reliability of the equipment.
The ranking of leading manufacturers is dominated by foreign companies: Daikin, LG, Sharp, Hitachi, Panasonic and General Climat. We reviewed the best models of air conditioners in the next article.
Oven Energy Calculation
In order to calculate the electricity consumption of the oven, how much it consumes, you need to know how often the oven is used, in what modes, how long, what tariffs. And so the calculation is purely individual. Most often, ovens are bought that consume average power, which means that their operation is 60% of the maximum, that is, 800–850 W / h. To find out how much the oven incurs per month, you need to multiply the number of kilowatts consumed by the oven by the number of hours of its operation per month. Or the sum of the hours of energy consumed will need to be multiplied by the average value of the operating power (800 watts). So, thanks to this method, you can get information about how many kilowatts are consumed by the oven.

Disadvantages and disadvantages of winter heating
Now let's talk about the disadvantages.Do not think that by choosing a machine with the highest COP, you will get an ideal heating system that outperforms everyone else.
A significant drawback of all condos is their noisy work. There is no getting away from the noise and getting rid of it.