- Connecting the electric boiler to the heating system
- Varieties of circulation pumps
- 1 Complete set and principle of operation
- Water heating systems
- Determination of power
- Calculations
- European calculation method
- 3 About the choice of equipment and the rules for its independent calculation
- General information.
- Pump Installation Recommendations
- Where to put
- forced circulation
- natural circulation
- Mounting Features
- Two-pipe system with top wiring
- Pipeline options
- Top and bottom wiring
- Counter and passing movement of the coolant
- Fan connection diagram
- Piping options in the system
- The specifics of one-pipe and two-pipe schemes
- Top and bottom coolant supply
- Vertical and horizontal risers
- Advantages
- Open and closed heating system
- Conclusions and useful video on the topic
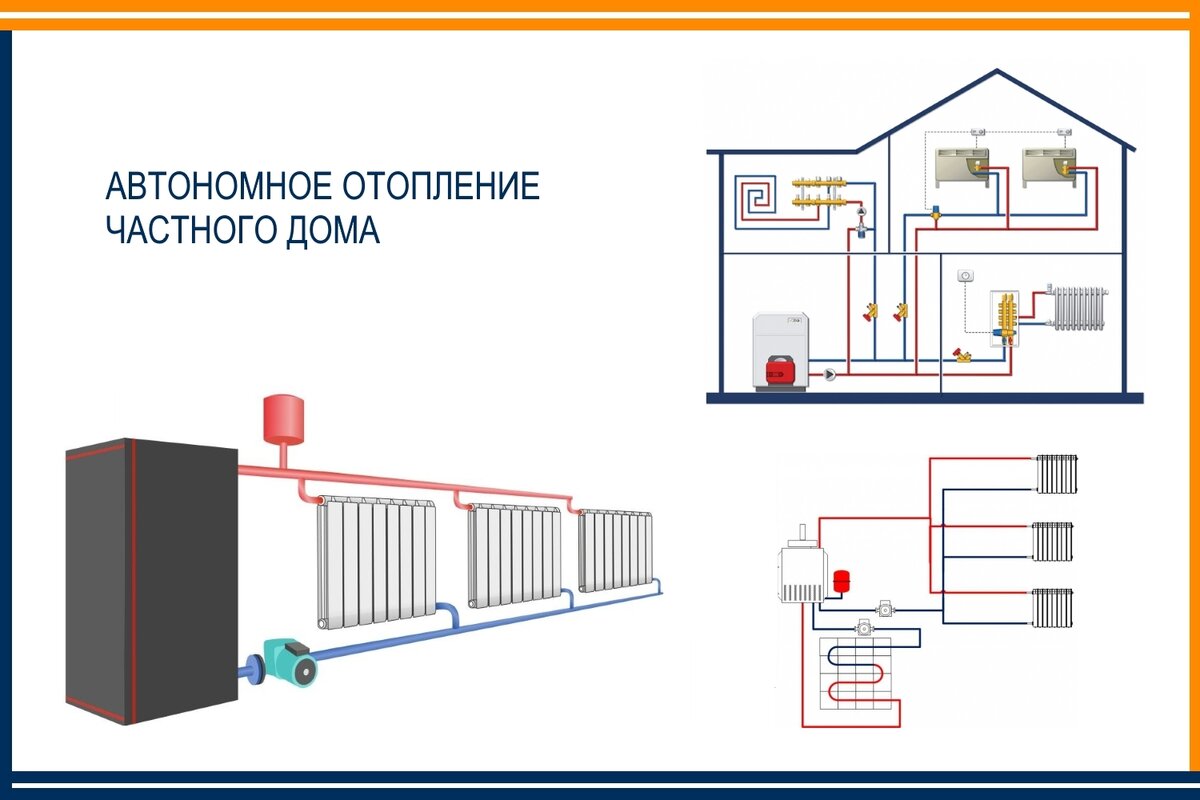
Connecting the electric boiler to the heating system
piping of an electric heating boilerElectric heating convectors: how to choose - little tricks

To reduce the amount of electricity consumed, it is advisable to resort to the following scheme:
- equip a floor heating system that evenly distributes heat throughout the room;
- install a heat accumulator - a heat-insulated storage tank.In it, the water will be heated at night, when a lower electricity tariff is in effect, and during the day it will slowly cool down, giving off heat to the room (for more details: “The correct heating scheme with a heat accumulator”).
Connecting an electric boiler to a heating system: instructions
Varieties of circulation pumps
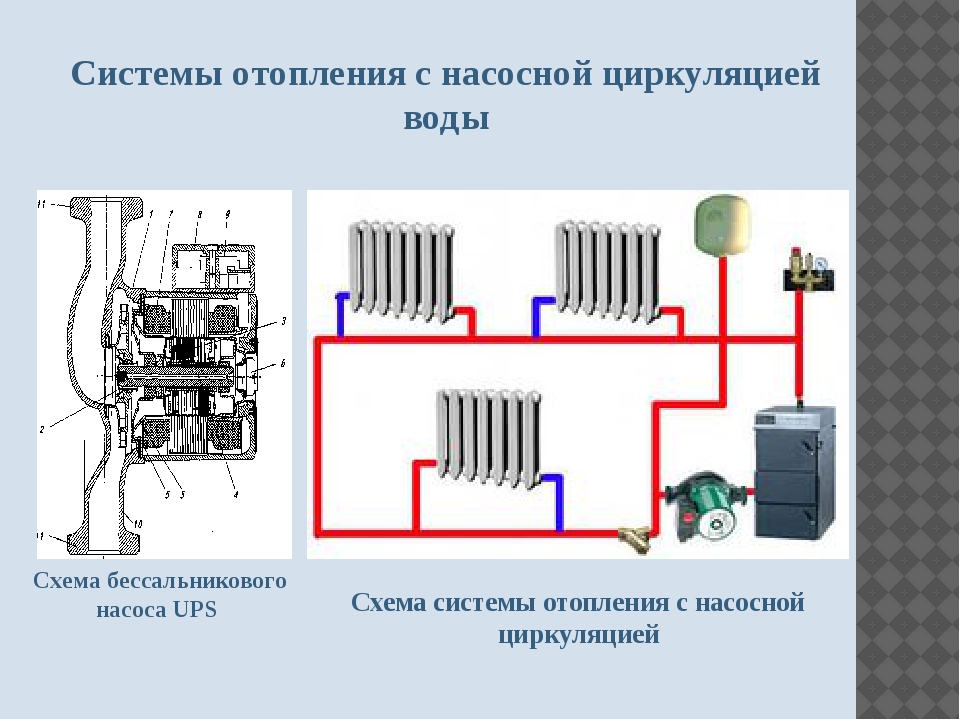
The wet rotor pump is available in stainless steel, cast iron, bronze or aluminium. Inside is a ceramic or steel engine
To understand how this device works, you need to know the differences between the two types of circulation pumping equipment. Although the fundamental scheme of the heating system based on a heat pump does not change, two types of such units differ in their operation features:
- The wet rotor pump is available in stainless steel, cast iron, bronze or aluminium. Inside is a ceramic or steel engine. The technopolymer impeller is mounted on the rotor shaft. When the impeller blades rotate, the water in the system is set in motion. This water simultaneously acts as an engine cooler and lubricant for the working elements of the device. Since the “wet” device circuit does not provide for the use of a fan, the operation of the unit is almost silent. Such equipment only works in a horizontal position, otherwise the device will simply overheat and fail. The main advantages of the wet pump are that it is maintenance-free and has excellent maintainability. However, the efficiency of the device is only 45%, which is a small drawback. But for domestic use, this unit is perfect.
- A dry rotor pump differs from its counterpart in that its motor does not come into contact with the liquid. In this regard, the unit has a lower durability. If the device will work "dry", then the risk of overheating and failure is low, but there is a threat of leakage due to abrasion of the seal. Since the efficiency of a dry circulation pump is 70%, it is advisable to use it for solving utility and industrial problems. To cool the engine, the circuit of the device provides for the use of a fan, which causes an increase in the noise level during operation, which is a disadvantage of this type of pump. Since in this unit water does not perform the function of lubricating the working elements, during the operation of the unit it is periodically necessary to carry out technical inspection and lubricate the parts.
In turn, "dry" circulating units are divided into several types according to the type of installation and connection to the engine:
- Console. In these devices, the engine and housing have their own place. They are separated and firmly fixed on it. The drive and working shaft of such a pump is connected by a coupling. To install this type of device, you will need to build a foundation, and the maintenance of this unit is quite expensive.
- Monoblock pumps can be operated for three years. The hull and engine are located separately, but are combined as a monoblock. The wheel in such a device is mounted on the rotor shaft.
- Vertical. The term of use of these devices reaches five years. These are sealed advanced units with a seal on the front side made of two polished rings.For the manufacture of seals, graphite, ceramics, stainless steel, aluminum are used. When the device is in operation, these rings rotate relative to each other.
Also on sale there are more powerful devices with two rotors. This dual circuit allows you to increase the performance of the device at maximum load. If one of the rotors exits, the second one can take over its functions. This allows not only to enhance the operation of the unit, but also to save energy, because with a decrease in heat demand, only one rotor works.
1 Complete set and principle of operation
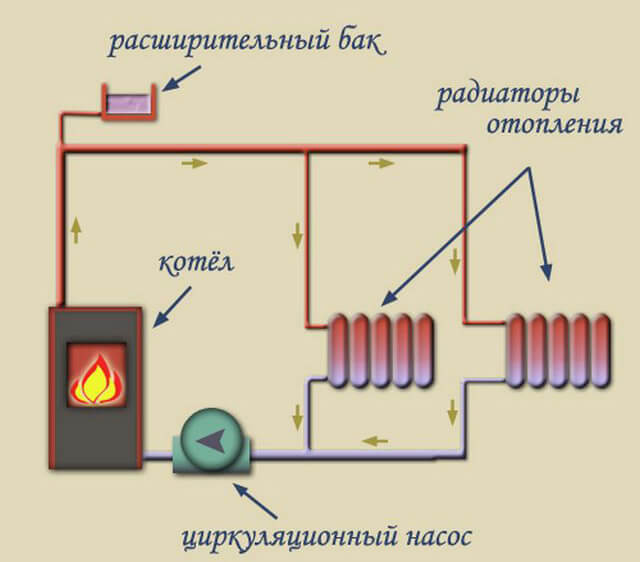
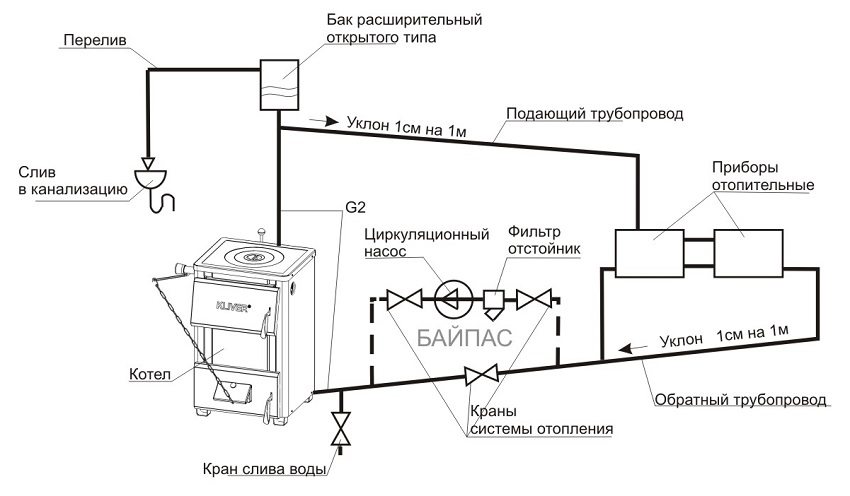
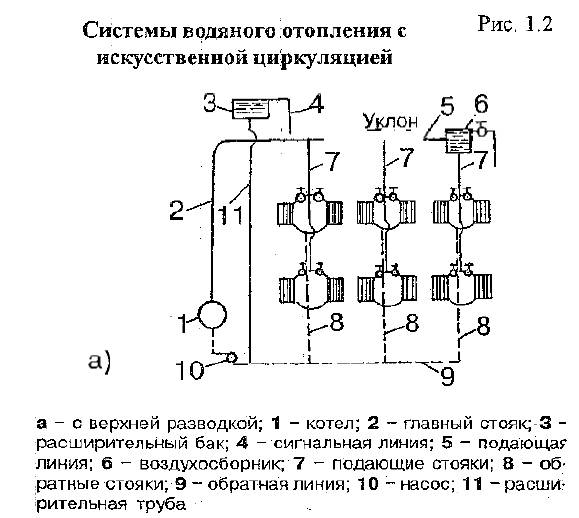
In water heating systems, the main coolant is liquid. It circulates from the boiler plant to the heating radiators, giving off the thermal potential to the surrounding space. Depending on the length of the pipes, the circulation process can continue for quite a long time, which allows heating large buildings. Due to this feature water heating systems are in incredible demand.
Most of the installations are able to function without additional pumping equipment, since the movement of the coolant is carried out by means of thermodynamic principles. In simple words, the circulation process is facilitated by the difference in the densities of hot and cold liquids, as well as the specific slope of the pipeline.
The open system process consists of two stages:
- 1. Coolant supply. The water heated to a certain temperature begins to move from the boiler to the heating radiators.
- 2. Reverse process. The remaining coolant enters the expansion tank, cools down, and then returns, as a result of which the cycle closes.
In systems of a single-pipe type, the supply and return of the coolant occur in the same line. In two-pipe, two pipes are used for this.
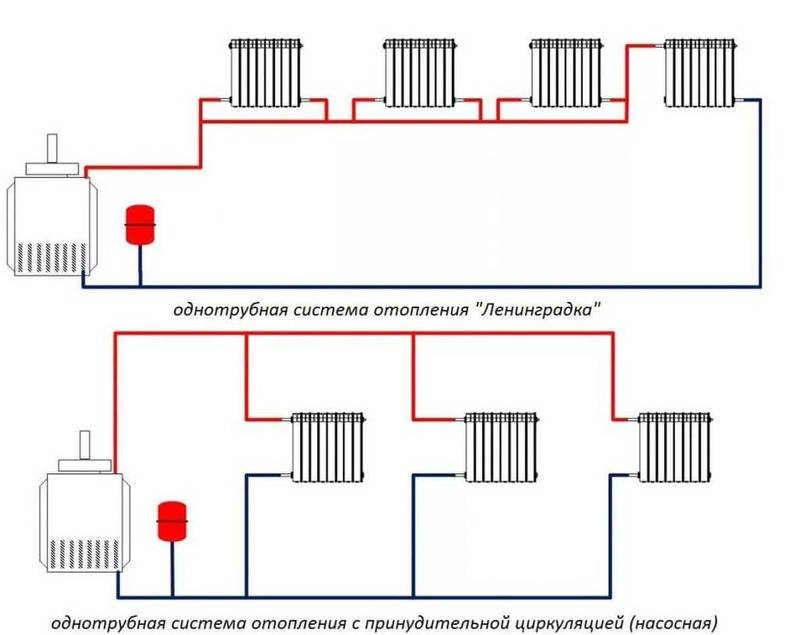
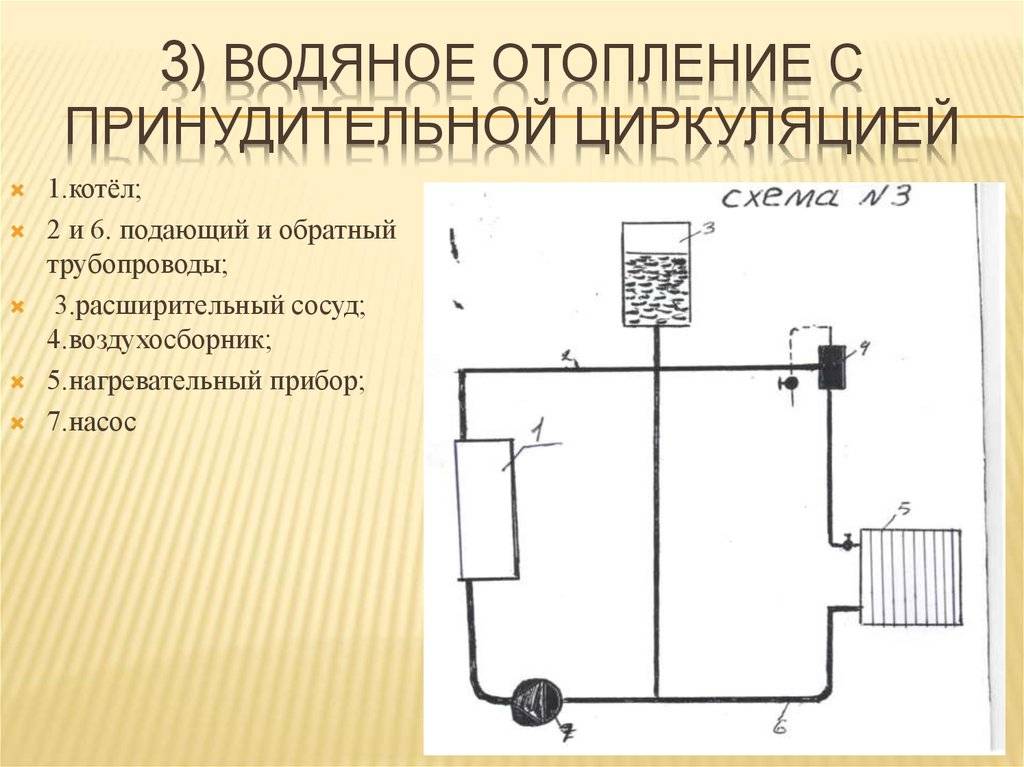
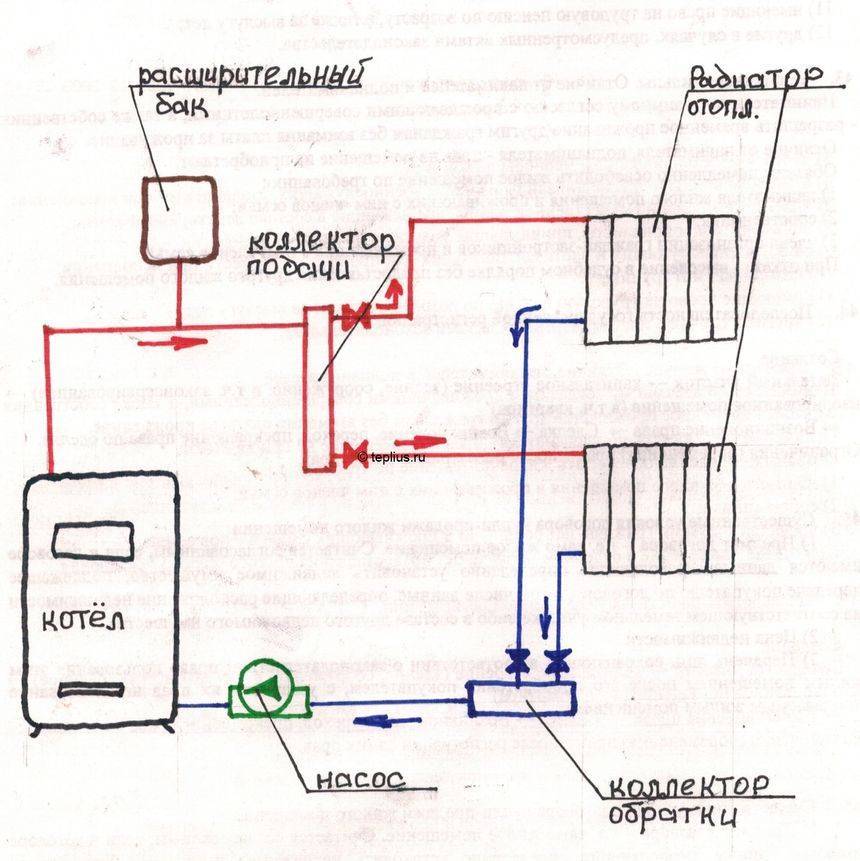
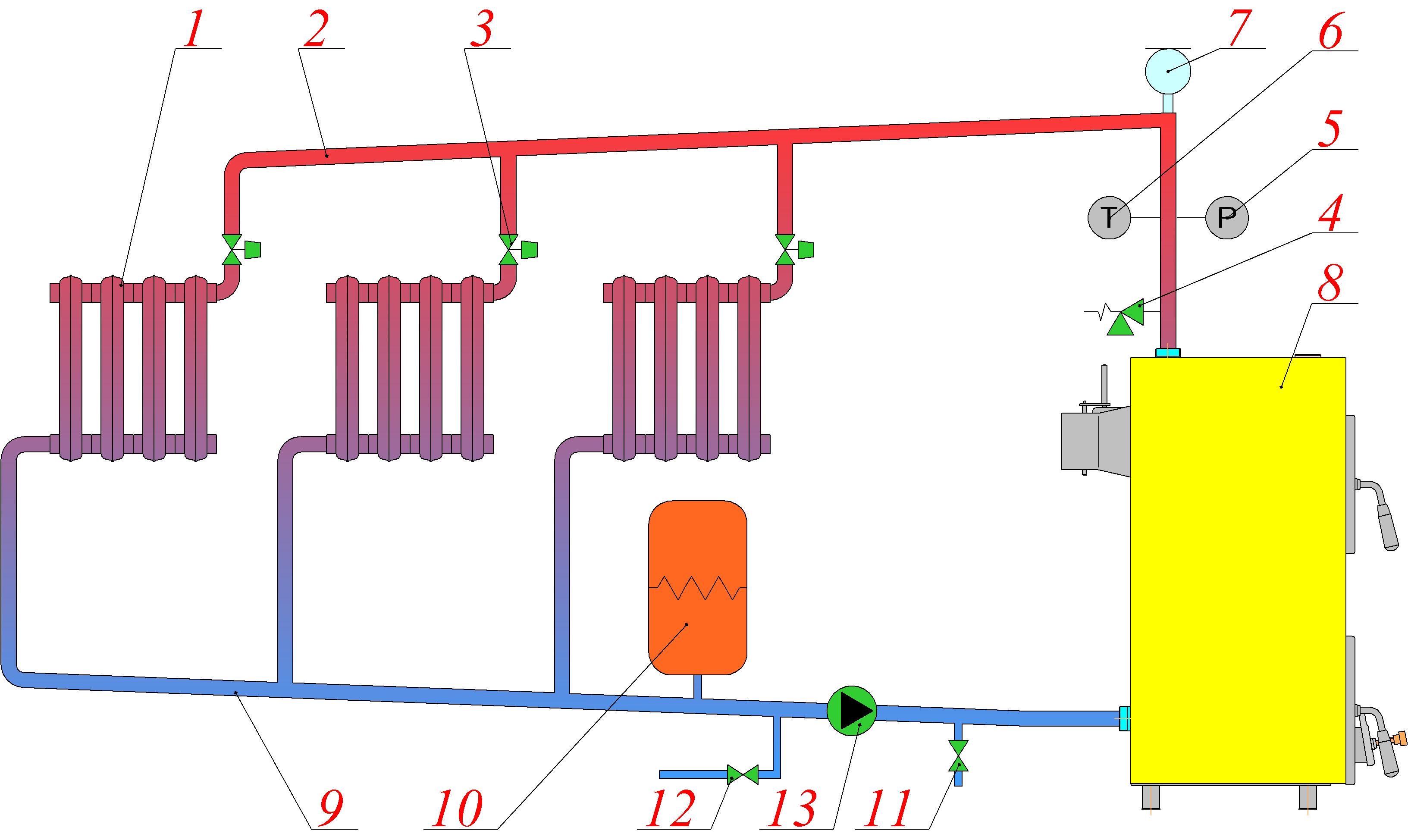
The design of a single-pipe heating system with a pump looks very simple. In the basic configuration, the installation consists of:
- 1. From the boiler unit.
- 2. Heating radiators.
- 3. Expansion tank.
- 4. Pipe systems.
Individual consumers do not install radiators in the house, solving the problem by installing a special pipe with a diameter of 8-10 cm around the perimeter of the building. But, according to experts, such systems are not efficient enough, while they are not very convenient to maintain.
The single-pipe scheme of an open heating system with a pump is volatile. As for the cost of purchasing components in the form of pipes, fittings and related equipment, they are relatively low.
Water heating systems
Water heating is a method of space heating using a liquid heat carrier (water or water-based antifreeze). Heat is transferred to the premises using heating devices (radiators, convectors, pipe registers, etc.).
Unlike from steam heating, water is in a liquid state, which means it has a lower temperature. Thanks to this, water heating is safer. Radiators for water heating are larger than those for steam. In addition, when heat is transferred by means of water over a long distance, the temperature drops sharply. Therefore, they often make a combined heating system: from the boiler room, with the help of steam, heat enters the building, where it heats the water in the heat exchanger, which is already supplied to the radiators.
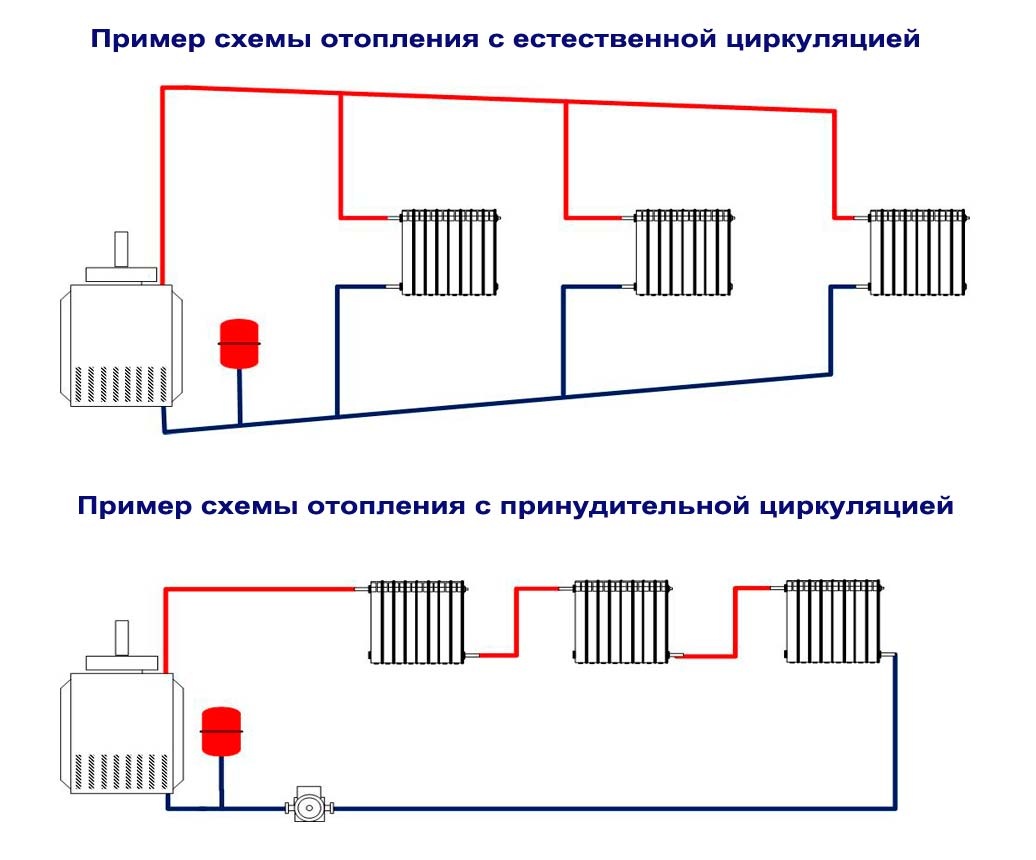
In water heating systems, water circulation can be either natural or artificial. Systems with natural water circulation are simple and relatively reliable, but have low efficiency (this depends on the correct design of the system).
The disadvantage of water heating is also air jams, which can form after draining the water during heating repairs and after severe cold snaps, when the temperature in the boiler rooms is raised and part of the air dissolved in it is released from it. To combat them, special trigger valves are installed. Before the start of the heating season, air is released through these valves due to excess water pressure.
Heating systems are distinguished by many features, for example: - by the method of wiring - with top, bottom, combined, horizontal, vertical wiring; - according to the design of the risers - one-pipe and two-pipe;
- in the direction of movement of the coolant in the main pipelines - dead-end and associated; - according to hydraulic modes - with a constant and variable hydraulic mode; - according to the atmosphere - open and closed.
Determination of power
Factors to consider when choosing a pump include:
- power of heating radiators;
- speed of movement of the coolant;
- total length of the pipeline;
- flow section of pipelines;
- boiler power.
Calculations
To more accurately determine the power of the pump, you can use the rule of manufacturers who "tied" 1 kW of power to 1 liter of pumped water. So, a 25 kW pump can circulate a maximum of 25 liters of coolant.
Sometimes a simplified selection scheme is used, based on the area of \u200b\u200bthe heated room:
- for heating a building with an area of up to 250 m2, they buy a pump with a capacity of 3.5 cubic meters of water per hour and a pressure force of 0.4 atmospheres;
- from 250 to 350 m2 - with a capacity of 4.5 cubic meters per hour and a pressure force of 0.6 atmospheres;
- from 350 m2 - with a capacity of 11 cubic meters per hour and a pressure force of 0.8 atmospheres.
European calculation method
When choosing equipment, you can use another technique - standard housing projects developed in the European Union. So, for 1 m2 of space there should be a pump power of 97 watts, provided that the air temperature outside is 25C ° (minus), or 101 watts - if the temperature drops to 30C ° (minus).
This standard applies to buildings with a height of three floors or more. When arranging a private house up to two floors high, the pump power per 1 m2 of area should be 173 watts at outdoor temperatures up to 25 ° C and 177 watts - below 25 ° C.
3 About the choice of equipment and the rules for its independent calculation
The key indicator that determines the efficiency of the circulation pump is its power. For a domestic heating system, you do not need to try to purchase the most powerful installation. It will only hum strongly and waste electricity.

Mounted circulation pump
You need to correctly calculate the power of the unit based on the following data:
- indicator of hot water pressure;
- section of pipes;
- productivity and throughput of the heating boiler;
- coolant temperature.
The flow of hot water is determined simply. It is equal to the power of the heating unit.If you, for example, have a 20 kW gas boiler, no more than 20 liters of water will be consumed per hour. The pressure of the circulation unit for the heating system for every 10 m of pipes is about 50 cm. The longer the pipeline, the more powerful the pump must be purchased
Here you should immediately pay attention to the thickness of tubular products. The resistance to water movement in the system will be stronger if you install small pipes. In pipelines with a diameter of half an inch, the flow rate of the coolant is 5.7 liters per minute at the generally accepted (1.5 m / s) speed of movement of water, with a diameter of 1 inch - 30 liters
But for pipes with a cross section of 2 inches, the flow rate will already be at the level of 170 liters. Always choose the diameter of the pipes in such a way that you do not have to overpay extra money for energy resources
In pipelines with a diameter of half an inch, the flow rate of the coolant is 5.7 liters per minute at the generally accepted (1.5 m / s) speed of water movement, with a diameter of 1 inch - 30 liters. But for pipes with a cross section of 2 inches, the flow rate will already be at the level of 170 liters. Always select the diameter of the pipes in such a way that you do not have to overpay extra money for energy resources.
The flow rate of the pump itself is determined by the following ratio: N/t2-t1. Under t1 in this formula is understood the temperature of the water in the circulation pipes (usually it is 65–70 ° С), under t2 - the temperature provided by the heating unit (at least 90 °). And the letter N indicates the power of the boiler (this value is available in the equipment passport). The pump pressure is set according to the standards accepted in our country and Europe. It is believed that 1 kW of power of the circulation unit is quite enough for high-quality heating of 1 square of the area of a private dwelling.
General information.
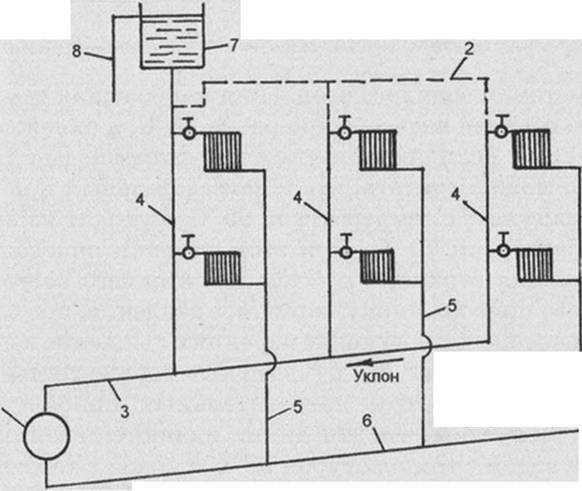
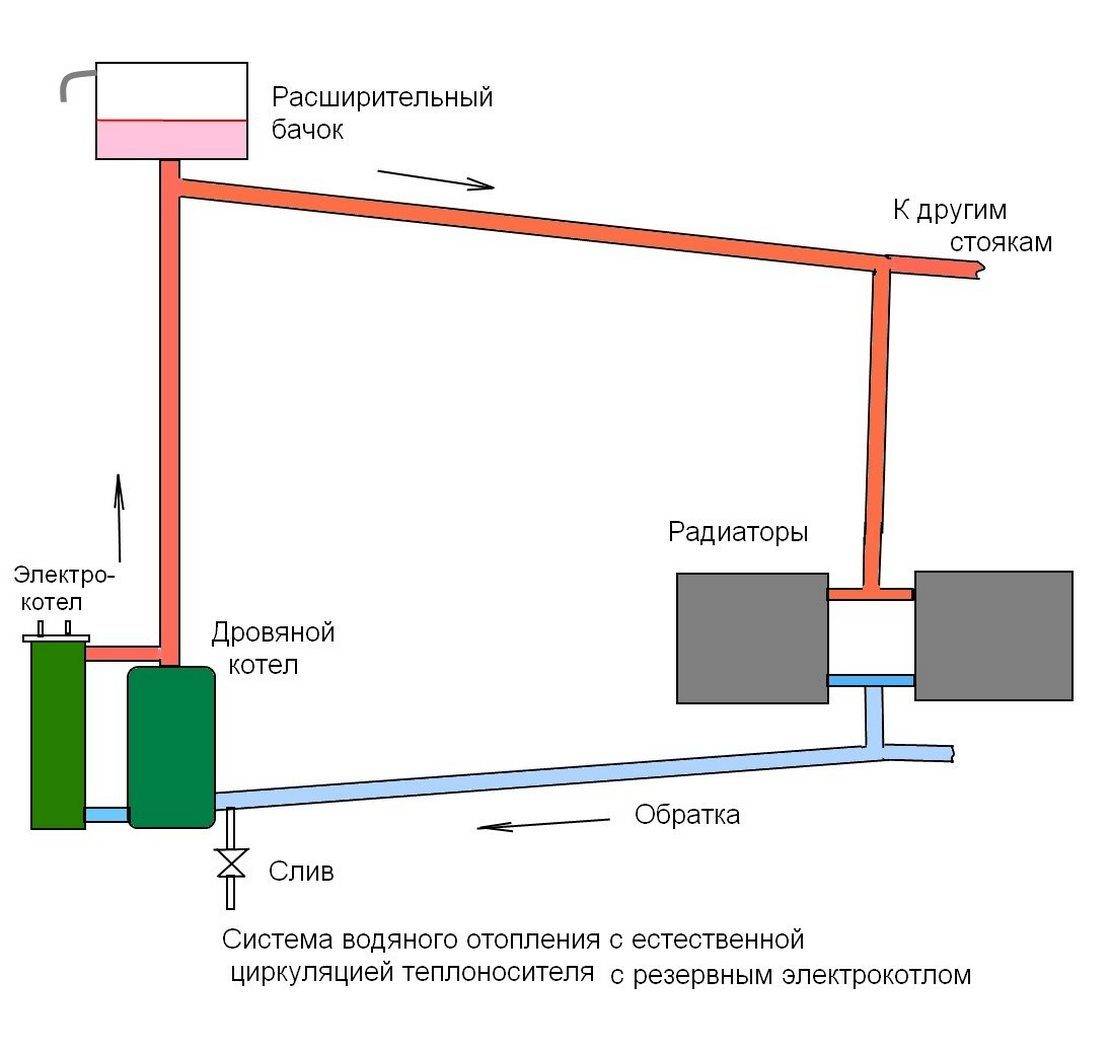
The fact that the heating circuit of a one-story house with natural circulation has practically no moving elements allows it to be operated without major repairs for a long time. If the distribution of CO is carried out using galvanized or polymer pipes, then the terms can reach fifty years.
The EC automatically assumes a low inlet and outlet pressure drop. Naturally, the coolant experiences a certain resistance to its movement, passing through heating devices and pipes. With this in mind, the optimal radius for the normal operation of the CO with the EC was determined, thirty meters. But we must understand that the figure is rather conditional and may fluctuate.
Due to the design features, the heating system with natural circulation of a one-story house has a high inertia. From the moment the boiler is ignited until the temperature in the premises of the building stabilizes, at least several hours pass. The reason is simple. First, the boiler heat exchanger warms up and only then does the slow movement of the coolant begin.
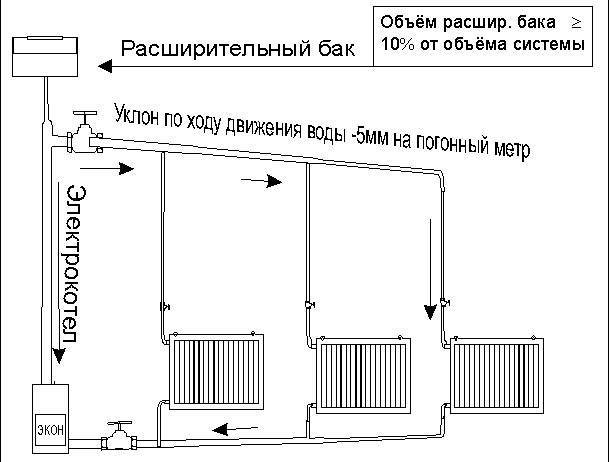
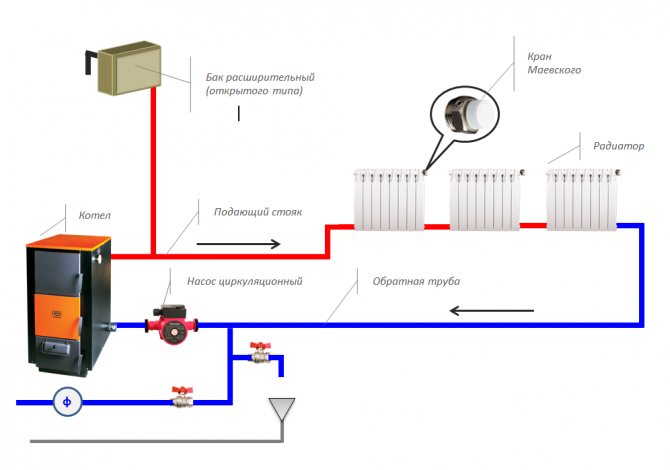
Scheme of heating a house with natural circulation
It is important that in those places where the CO pipes are laid horizontally, they have a mandatory slope in the direction of the coolant flow. This achieves the movement of water in the system without stagnation and the automatic removal of air from the system to its highest point, which is located in the expansion tank
It is carried out according to one of three options: open, with a built-in air vent or sealed.
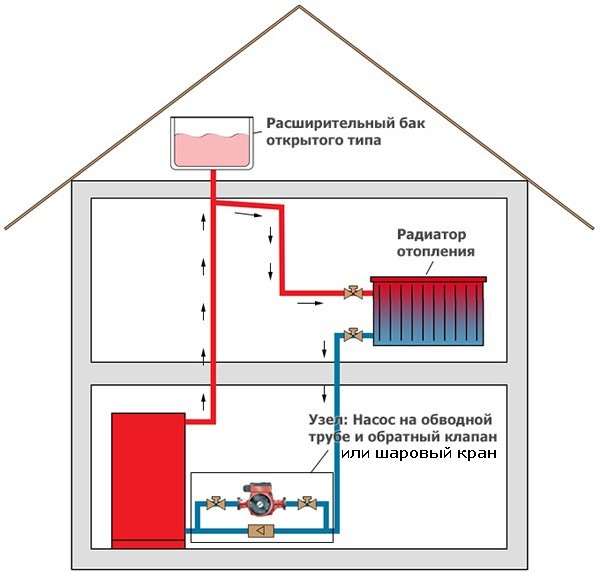
Pump Installation Recommendations
In order to ensure the normal circulation of fluid in the heating system, you need to make the right choice of the place where the pump will be installed.A place in the water suction area should be determined where excess hydraulic pressure is always present.
Most often, the highest point of the pipeline is selected, from which the expansion tank rises to a height of about 80 cm. The use of this method is possible if the room is high. It is usually practiced to install an expansion tank in the attic, provided that it is insulated for the winter.
In the second case, the tube is transferred from the expansion tank and cuts into the return pipe instead of the supply pipe. Near this place is the suction pipe of the pump, so the most favorable conditions are created for forced circulation.
The third installation option is to tie the pump into the supply pipeline, immediately after the point where water enters from the expansion tank. The use of such a connection is possible if a particular model is resistant to high water temperatures.
Where to put
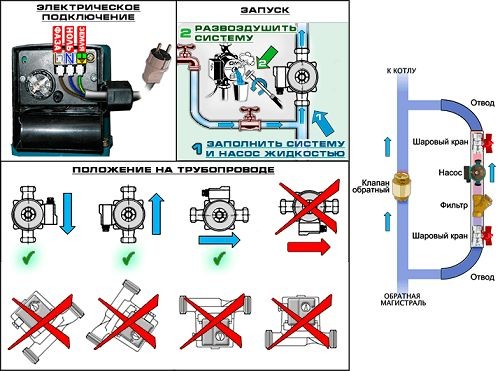
It is recommended to install a circulation pump after the boiler, before the first branch, but it does not matter on the supply or return pipeline. Modern units are made from materials that normally tolerate temperatures up to 100-115 ° C. There are few heating systems that work with a hotter coolant, therefore considerations of a more “comfortable” temperature are untenable, but if you are so calmer, put it in the return line.
Can be installed in the return or direct pipeline after/before the boiler up to the first branch
There is no difference in hydraulics - the boiler, and the rest of the system, it does not matter whether there is a pump in the supply or return branch.What matters is the correct installation, in the sense of tying, and the correct orientation of the rotor in space
Nothing else matters
There is one important point at the installation site. If there are two separate branches in the heating system - on the right and left wings of the house or on the first and second floors - it makes sense to put a separate unit on each, and not one common one - directly after the boiler. Moreover, the same rule is preserved on these branches: immediately after the boiler, before the first branch in this heating circuit. This will make it possible to set the required thermal regime in each of the parts of the house independently of the other, as well as save on heating in two-story houses. How? Due to the fact that the second floor is usually much warmer than the first floor and much less heat is required there. If there are two pumps in the branch that goes up, the speed of the coolant is set much less, and this allows you to burn less fuel, and without compromising the comfort of living.
There are two types of heating systems - with forced and natural circulation. Systems with forced circulation cannot work without a pump, with natural circulation they work, but in this mode they have a lower heat transfer. However, less heat is still much better than no heat at all, so in areas where electricity is often cut off, the system is designed as hydraulic (with natural circulation), and then a pump is slammed into it. This gives high efficiency and reliability of heating. It is clear that the installation of a circulation pump in these systems has differences.

All heating systems with underfloor heating are forced - without a pump, the coolant will not pass through such large circuits
forced circulation
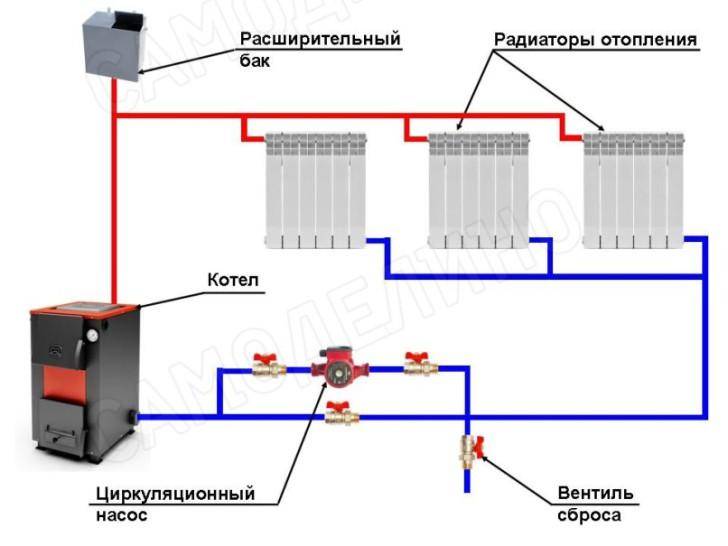
Since a forced circulation heating system is inoperative without a pump, it is installed directly into the gap in the supply or return pipe (of your choice).
Most problems with the circulation pump arise due to the presence of mechanical impurities (sand, other abrasive particles) in the coolant. They are able to jam the impeller and stop the motor. Therefore, a strainer must be placed in front of the unit.

Installing a circulation pump in a forced circulation system
It is also desirable to install ball valves on both sides. They will make it possible to replace or repair the device without draining the coolant from the system. Turn off the taps, remove the unit. Only that part of the water that was directly in this piece of the system is drained.
natural circulation
The piping of the circulation pump in gravity systems has one significant difference - a bypass is required. This is a jumper that makes the system operational when the pump is not running. One ball shut-off valve is installed on the bypass, which is closed all the time while pumping is in operation. In this mode, the system works as a forced one.
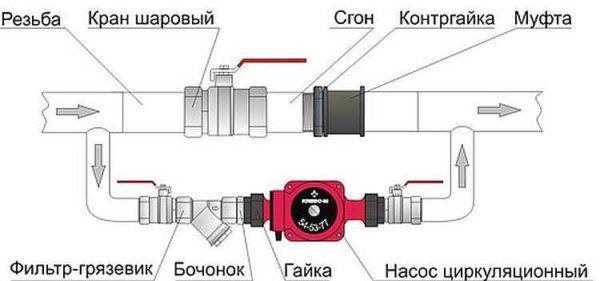
Scheme of the installation of the circulation pump in a natural circulation system
When electricity fails or the unit fails, the faucet on the jumper is opened, the faucet leading to the pump is closed, the system works like a gravitational one.
Mounting Features
There is one important point, without which the installation of the circulation pump will require alteration: it is required to turn the rotor so that it is directed horizontally. The second point is the direction of the flow. There is an arrow on the body indicating in which direction the coolant should flow. So turn the unit around so that the direction of movement of the coolant is “in the direction of the arrow”.
The pump itself can be installed both horizontally and vertically, only when choosing a model, see that it can work in both positions. And one more thing: with a vertical arrangement, the power (created pressure) drops by about 30%. This must be taken into account when choosing a model.
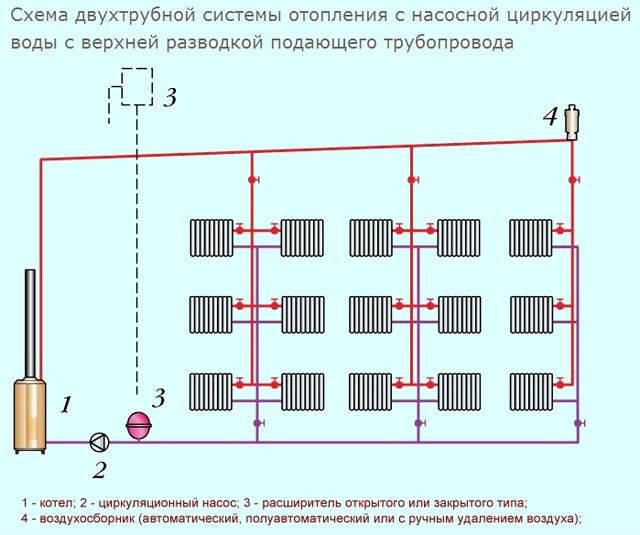
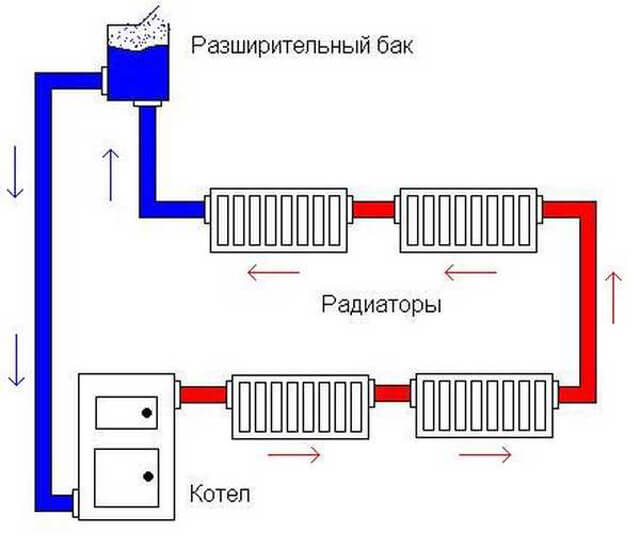
Two-pipe system with top wiring
The main supply pipeline is laid under the ceiling, the return line is laid along the floor. This explains the constantly high pressure in the system, allows the use of pipes of the same diameter even when forming a gravity-flow type structure. The expansion tank must be installed in the attic, be sure to insulate it, or placed between the ceiling - the lower part remains in the heated room, the upper one - in the attic.
Experts recommend mounting the upper highway above the level of window openings. In this case, it is possible to place the expansion tank under the ceiling, provided that the riser is high enough to pressurize the system. The return pipe is laid out on the floor or lowered under it.
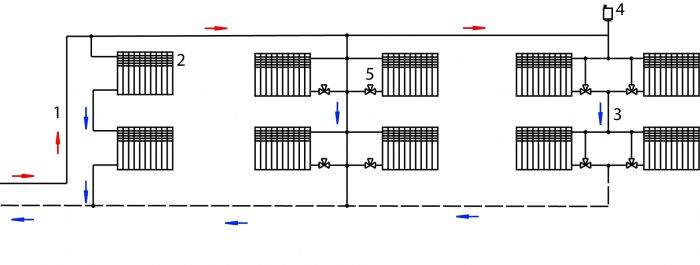
In the case of the upper wiring, the upper pipes remain in sight, which does not improve the appearance of the room, and part of the heat remains at the top and is not used to heat the premises.You can put the pipes of the passing line under the radiators, and to ensure normal circulation, install a pump, which allows the use of pipes of small diameter.
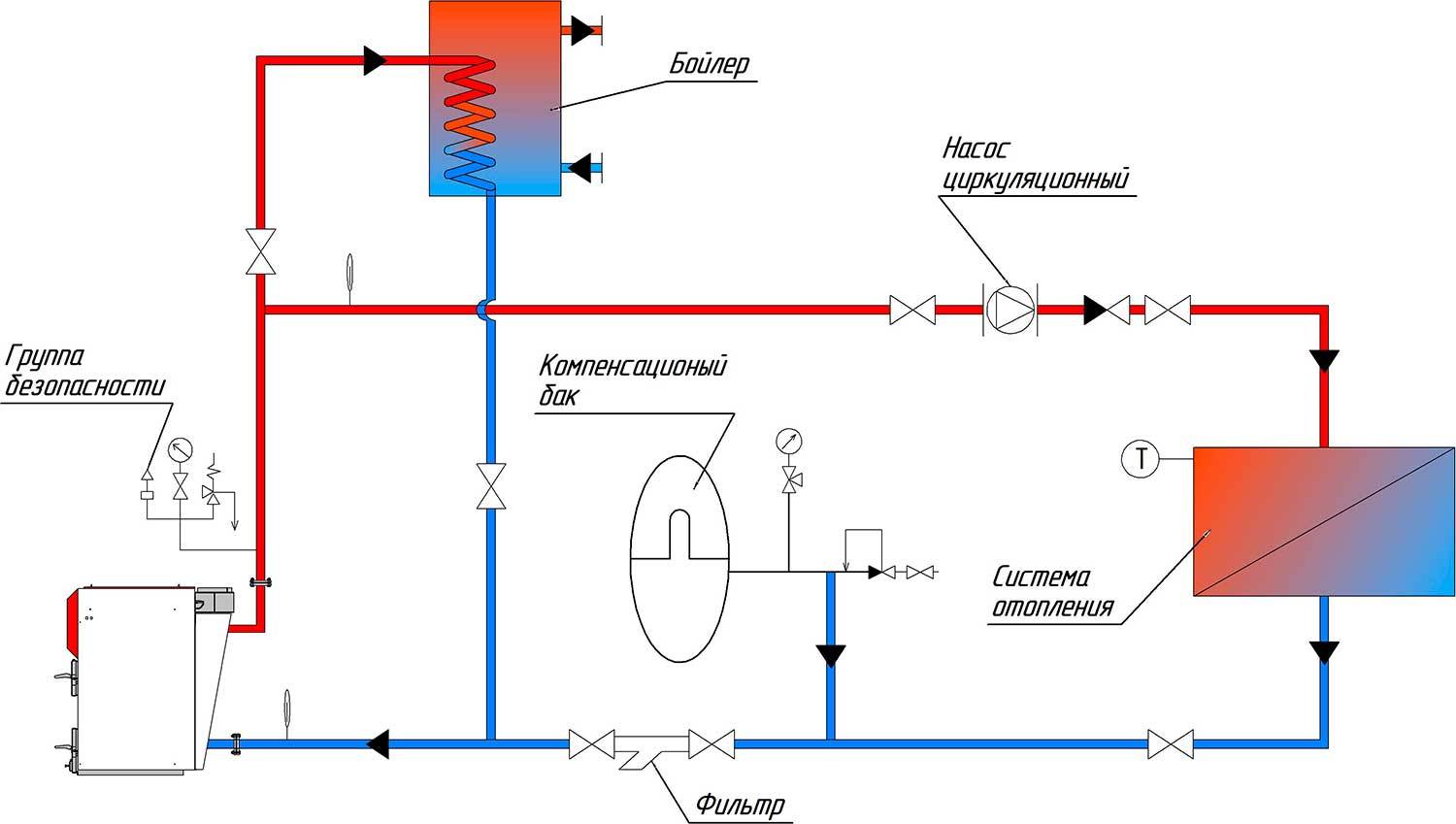
In two-story buildings of a private type, the upper wiring is considered effective and helps to achieve good heating in all rooms. The expansion tank is placed at the highest point, the boiler - in the basement. Such a height difference guarantees the efficiency of transporting the coolant, the availability of connecting a tank to provide hot water supply - water circulation will ensure a constant flow of hot water to all appliances.
If you install a gas or non-volatile boiler in the house, then the circuit becomes autonomous. To reduce costs, consider combining a one- and two-pipe heating system. For example, make a warm (single-circuit) floor on the second floor, and equip a double-circuit structure on the first floor.
Advantages of the scheme in:
- speed of movement of the coolant;
- maximum and even heating of the premises;
- eliminating the risk of air pockets.
The disadvantages include the high consumption of components, the lack of energy for heating large rooms and the difficulty in placing an expansion tank.
Pipeline options
There are two types of two-pipe wiring: vertical and horizontal. Vertical pipelines are usually located in multi-storey buildings. This scheme allows you to provide heating for each apartment, but at the same time there is a large consumption of materials.
Top and bottom wiring
The distribution of the coolant is carried out according to the upper or lower principle. With the upper wiring, the supply pipe runs under the ceiling and goes down to the radiator.The return pipe runs along the floor.
With this design, the natural circulation of the coolant occurs well, thanks to the height difference, it has time to pick up speed. But such wiring has not been widely used due to external unattractiveness.
The scheme of a two-pipe heating system with a lower wiring is much more common. In it, the pipes are located at the bottom, but the supply, as a rule, passes slightly above the return. Moreover, pipelines are sometimes carried out under the floor or in the basement, which is a great advantage of such a system.
This arrangement is suitable for schemes with forced movement of the coolant, since during natural circulation the boiler must be at least 0.5 m lower than the radiators. Therefore, it is very difficult to install it.
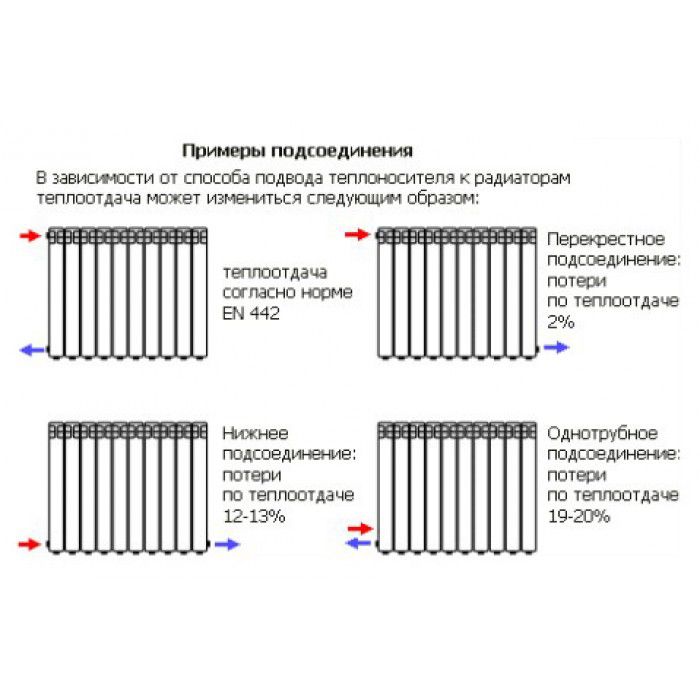
Counter and passing movement of the coolant
The scheme of two-pipe heating, in which hot water moves in different directions, is called oncoming or dead-end. When the movement of the coolant is carried out through both pipelines in the same direction, it is called an associated system.
In such heating, when installing pipes, they often resort to the principle of a telescope, which facilitates adjustment. That is, when assembling the pipeline, sections of pipes are laid in series, gradually reducing their diameter. With the oncoming movement of the coolant, thermal valves and needle valves for adjustment are always present.
Fan connection diagram
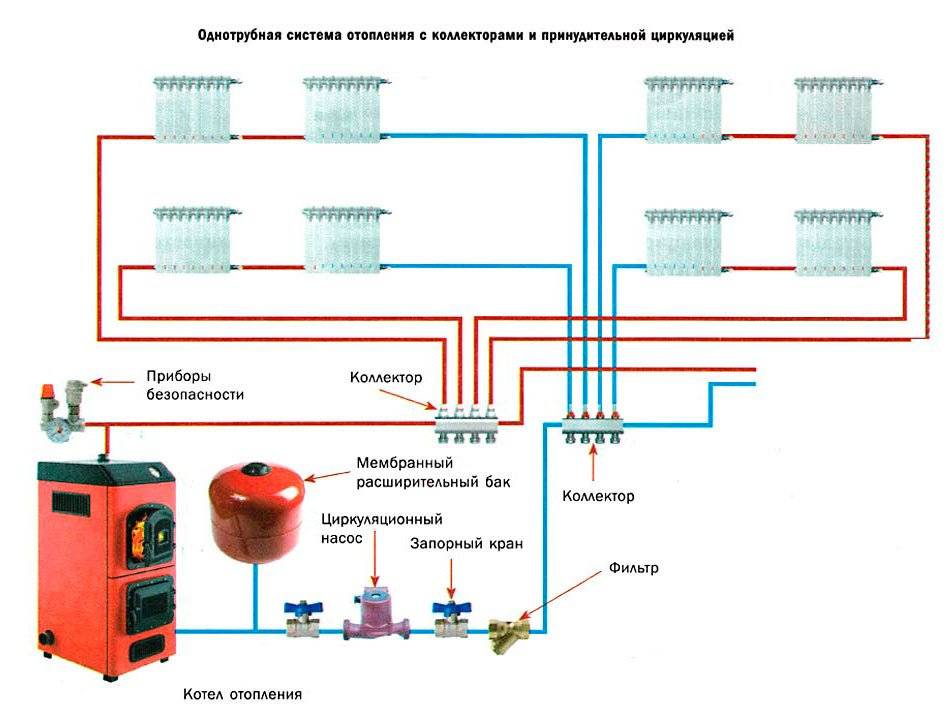
The fan or beam scheme is used in multi-storey buildings to connect each apartment with the possibility of installing meters. To do this, a collector is installed on each floor with a pipe outlet for each apartment.
Moreover, only whole sections of pipes are used for wiring, that is, they do not have joints.Thermal metering devices are installed on pipelines. This allows each owner to control their heat consumption. During the construction of a private house, such a scheme is used for floor-by-floor piping.
To do this, a comb is installed in the boiler piping, from which each radiator is connected separately. This allows you to evenly distribute the coolant between the devices and reduce its loss from the heating system.
Piping options in the system
The efficiency, economy and aesthetics of the heat supply system depend on the layout of heating devices and connecting pipes. The choice of wiring is determined based on the design features and area of \u200b\u200bthe house.
The specifics of one-pipe and two-pipe schemes
The heated water flows to the radiators and back to the boiler in various ways. In a single-circuit system, the coolant is supplied through one large-diameter line. The pipeline passes through all radiators.
Advantages of a self-circulating single-pipe system:
- minimum consumption of materials;
- ease of installation;
- limited number of pipes inside the dwelling.
The main disadvantage of a scheme with a single pipe that performs the duties of supply and return is the uneven heating of heating radiators. The intensity of heating and heat transfer of the batteries decreases as they are farther from the boiler.
With a long wiring chain and a large number of radiators, the last battery may be completely inefficient. "Hot" heating devices are recommended to be installed in the rooms of the north side, children's rooms and bedrooms
The two-pipe heating scheme is confidently gaining ground.Radiators connect the return and supply pipelines. Local rings are formed between the batteries and the heat source.
- all heaters are evenly heated;
- the ability to adjust the heating of each radiator separately;
- reliability of the scheme.
A two-circuit system requires large investments and labor costs. It will be more difficult to install two branches of communications on building structures.
The two-pipe system is easily balanced, ensuring that the coolant is supplied at the same temperature to all heating devices. Rooms are heated evenly
Top and bottom coolant supply
Depending on the location of the line supplying the hot coolant, a distinction is made between upper and lower piping.
In open heating systems from the top wiring, there is no need to use devices for venting air. Its excess is discharged through the surface of the expansion tank that communicates with the atmosphere.
With the upper wiring, warm water rises through the main riser and is transferred through the distributing pipelines to the radiators. The device of such a heating system is advisable in one- and two-story cottages and private houses.
The heating system with the lower wiring is quite practical. The supply pipe is located at the bottom, next to the return. The movement of the coolant in the direction from the bottom up. Water, having passed through the radiators, is sent through the return pipeline to the heating boiler. The batteries are equipped with Mayevsky cranes to remove air from the line.
In heating systems with lower wiring, it becomes necessary to use air exhaust devices, the simplest of which is the Mayevsky crane
Vertical and horizontal risers
According to the type of position of the main risers, vertical and horizontal methods of piping are distinguished. In the first version, the radiators of all floors are connected to vertical risers.
Vertical wiring is used in the arrangement of houses with two, three or more floors with an attic, within which it is possible to lay and insulate the pipeline
Features of "vertical" systems:
- lack of air congestion;
- suitable for heating high-rise buildings;
- floor connection to the riser;
- the complexity of installing apartment heat meters in multi-storey buildings.
Horizontal wiring provides for the connection of radiators of one floor to a single riser. The advantage of the scheme is that fewer pipes are used for the device, the installation cost is lower.
Horizontal risers are usually used in one- and two-story rooms. The arrangement of the system is relevant in panel-frame houses and residential buildings without piers
Advantages
A system equipped with a circulation pump is free from these disadvantages. It is excellent for heating rooms ranging from 200 to 800 m2. Its benefits include:
- no requirements for the configuration of the heating circuit - for the circulation of the coolant, it is not necessary to create narrowed places in the pipeline, install pipes at an angle and use other techniques;
- rapid acceleration of the liquid - the circulation of heated water in the circuit begins immediately after the pump is turned on. As a result, the rooms of a private house warm up to the desired temperature in just a few minutes;
- high efficiency - due to the rapid circulation of the coolant, heat losses are reduced.The problem is solved when one of the rooms warms up more than the others. Due to this, fuel is consumed more economically;
- reliable operation - the simple design of the pump eliminates the occurrence of accidental breakdowns.
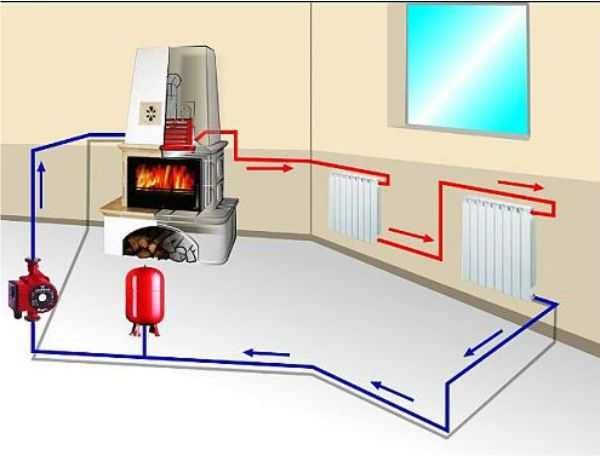
If it is planned to equip a system with natural circulation with a pump, its scheme remains practically unchanged.
It is only required to mount the pump itself, as well as transfer the expansion tank from the water supply circuit to the circuit through which it returns to the boiler.
Open and closed heating system
If an open type expansion tank is installed, then the system is called open. In the simplest version, it is some kind of container (pan, small plastic barrel, etc.) to which the following elements are connected:
- connecting pipe of small diameter;
- a level control device (float), which opens / closes the make-up tap when the amount of coolant drops below a critical level (in the figure below, it works on the principle of a toilet flush tank);
- air release device (if the tank is without a lid, it is not necessary);
- drain hose or circuit for removing excess coolant if its level exceeds the maximum.
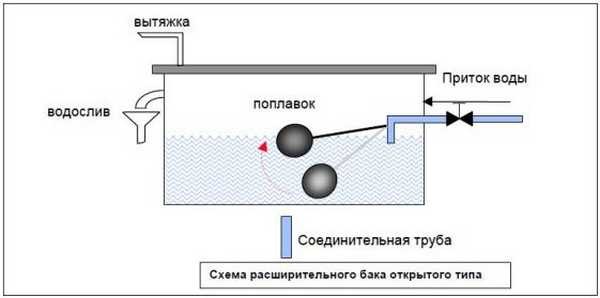
One of the open expansion tanks
Today, open systems are being made less and less, and all because a large amount of oxygen is constantly present in it, which is an active oxidizing agent and accelerates corrosion processes. When using this type, heat exchangers fail many times faster, pipes, pumps and other elements are destroyed. In addition, due to evaporation, it is necessary to constantly monitor the level of the coolant and periodically add it.Another drawback is that it is not recommended to use antifreezes in open systems - due to the fact that they evaporate, that is, they harm the environment, and also change their composition (concentration increases). Therefore, closed systems are becoming more and more popular - they exclude the supply of oxygen, and the oxidation of elements occurs many times slower, because it is believed that they are better.
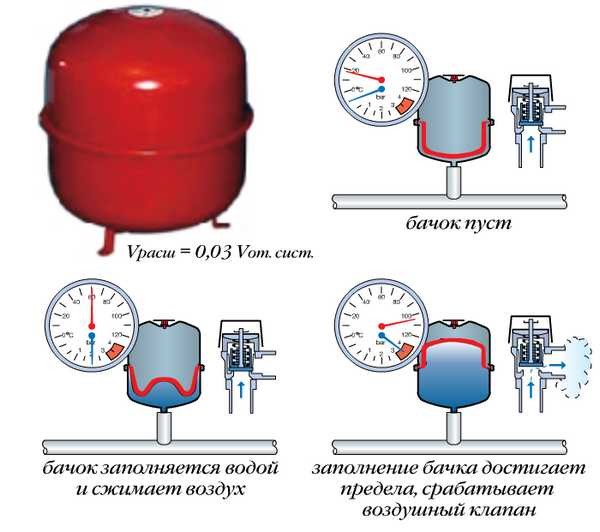
The membrane type tank is installed in closed heating systems
In closed systems, membrane-type tanks are installed. In them, the sealed container is divided into two parts by an elastic membrane. At the bottom is the coolant, and the upper part is filled with gas - ordinary air or nitrogen. When the pressure is low, the tank is either empty or contains a small amount of liquid. With increasing pressure, an increasing amount of coolant is forced into it, which compresses the gas contained in the upper part. So that when the threshold value is exceeded, the device does not break, an air valve is installed in the upper part of the tank, which operates at a certain pressure, releasing part of the gas, and equalizes the pressure.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Rules for installing heating equipment in the video:
The video explains the features of a two-pipe heating system and demonstrates different installation schemes for devices:
Connection Features heat accumulator in the heating system in the video:
p> If you know all the connection rules, there will be no difficulties with the installation of the circulation pump, as well as when connecting it to the power supply at home.
The most difficult task is to insert a pumping device into a steel pipeline.However, using a set of lerok for creating threads on pipes, you can independently arrange the arrangement of the pumping unit.
Do you want to supplement the information presented in the article with recommendations from personal experience? Or maybe you saw inaccuracies or errors in the reviewed material? Please write to us about it in the comments block.
Or have you successfully installed the pump and want to share your success with other users? Tell us about it, add a photo of your pump - your experience will be useful to many readers.