- Installation price comparison
- Types of forced circulation of heat carrier in heating
- Why do people choose a two-circuit system?
- Classification of water heating systems according to the principle of operation
- with natural circulation
- Forced circulation scheme
- Mounting methods
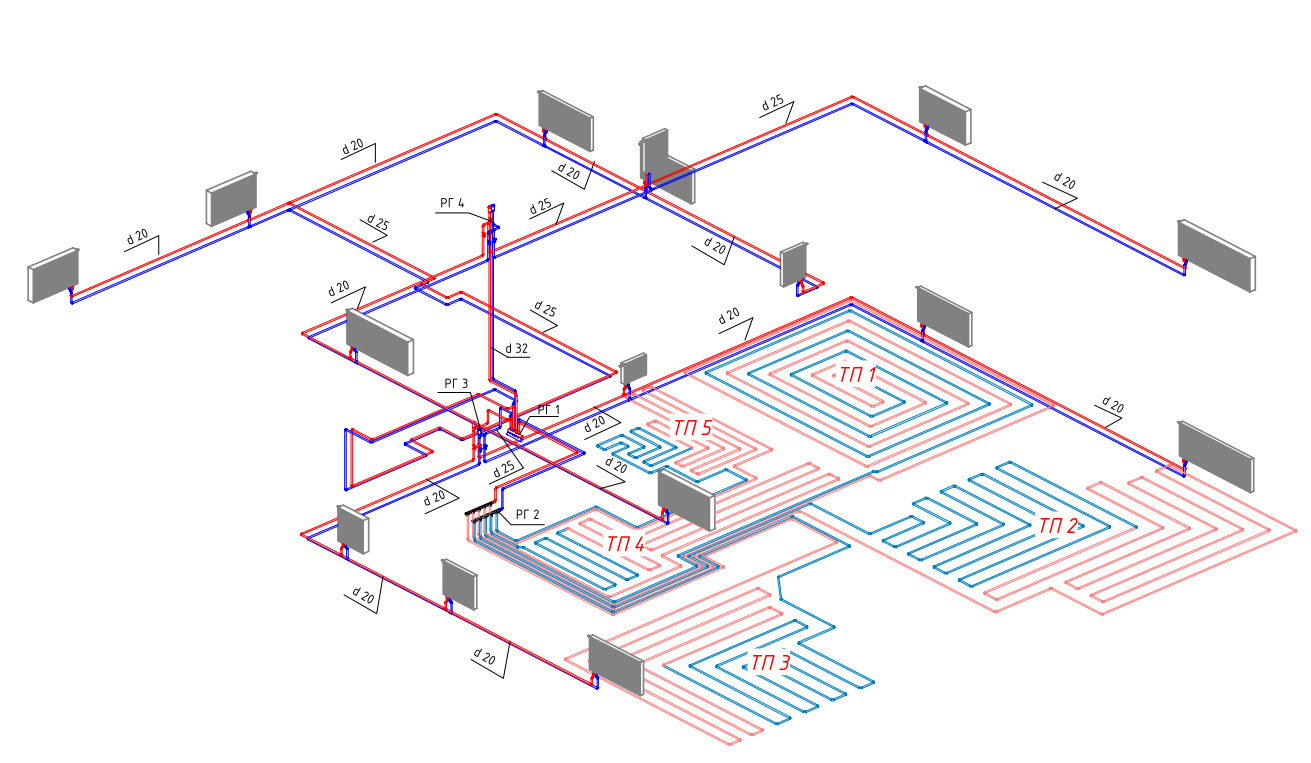
- Collector heating
- Technical requirements
- The principle of operation of closed CO
- Features of the installation process
- Solar panels. Working principle of solar heating system
- Pros and cons
- Construction features
- Pipe slope
- gravity pressure
- Possible obstacles
- Gravity type
- Pipe laying
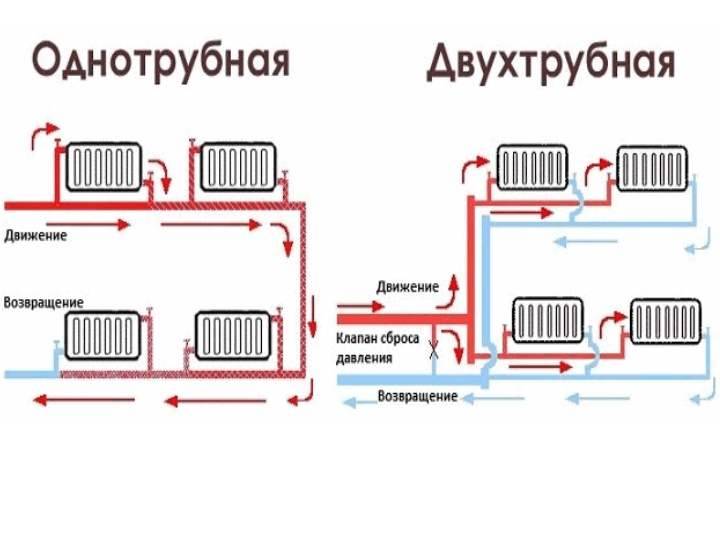
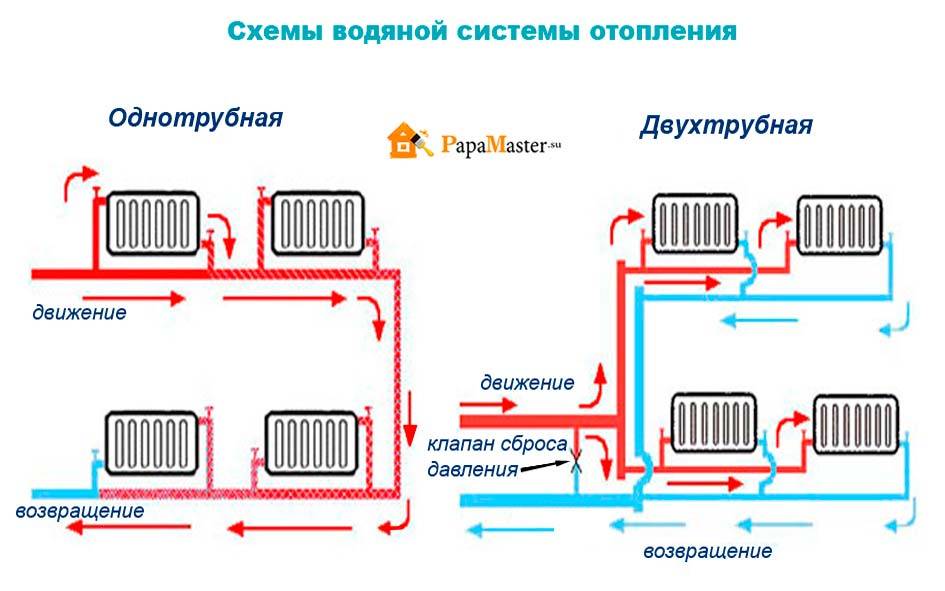
- Method 1. With one pipe
- Method 2. With two pipes
- Method 3. Beam
Installation price comparison
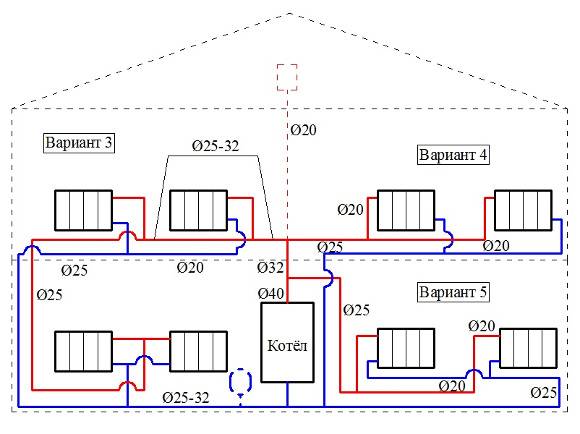
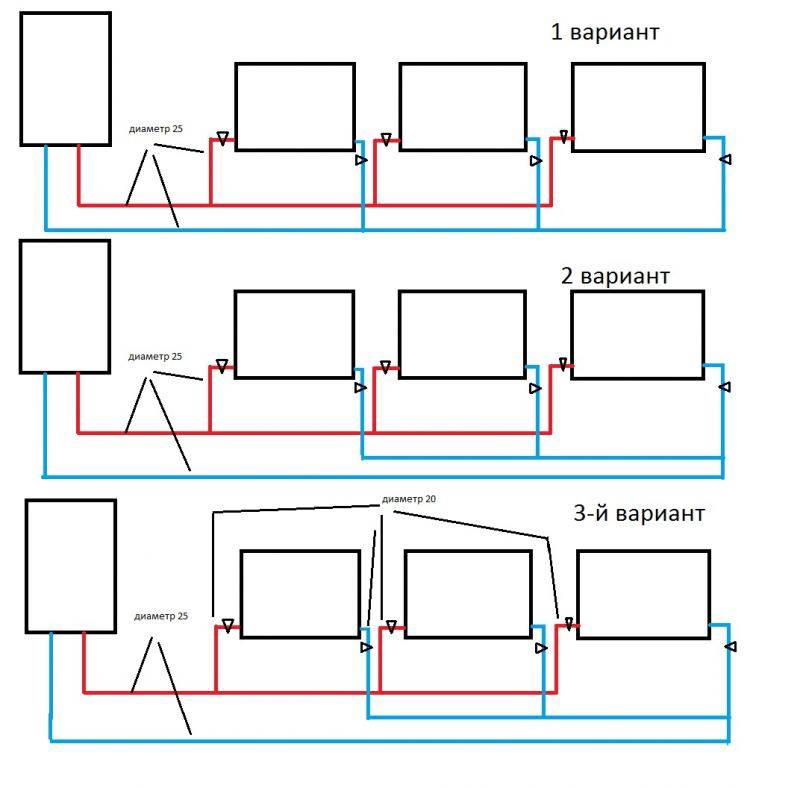
Adherents of single-pipe heating networks like to remind about the cheapness of this type of wiring. The cost reduction compared to the two-pipe scheme is justified by half the number of pipes. We affirm the following: "Leningrad" will cost less than a dead-end system in one case - if heating is soldered from polypropylene.
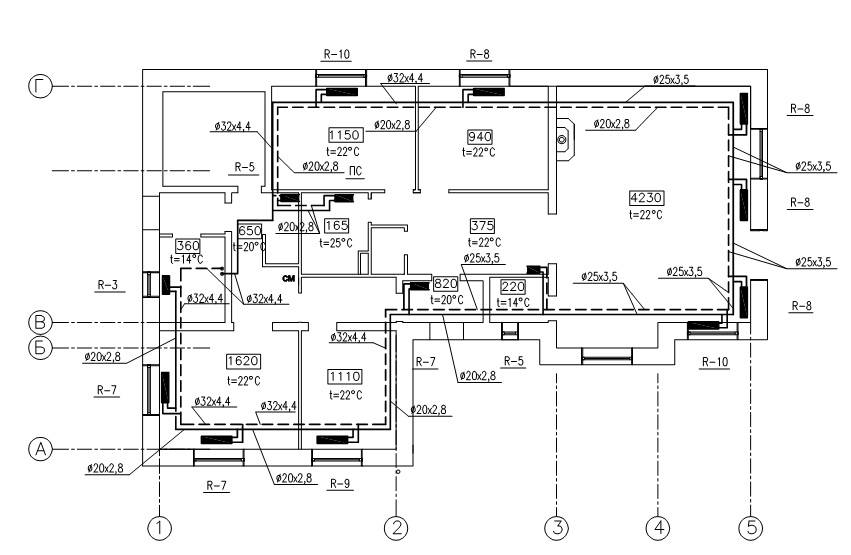
Let's prove our statement with calculations - let's take as an example a one-story dwelling measuring 10 x 10 m = 100 m² (in plan). Let's put the layout of the "Leningrad" on the drawing, count the fittings with pipes, then make a similar estimate of the dead-end wiring.
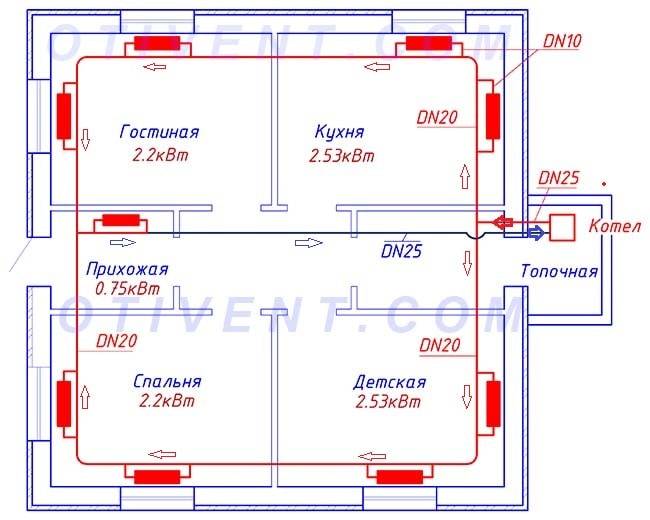
A common return manifold running through the corridor keeps the diameter of the ring line small. If it is removed, the pipe section will increase to Ø25 mm (internal)
So, for a single-pipe heating device, you will need:
- DN20 pipe to the collector (outside Ø25 mm) - 40 m;
- tr. DN25 Ø32 mm for return - 10 m;
- tr. DN10 Ø16 mm for connections - 8 m;
- tee 25 x 25 x 16 (outer size) - 16 pieces;
- tee 25 x 25 x 20 - 1 pc.
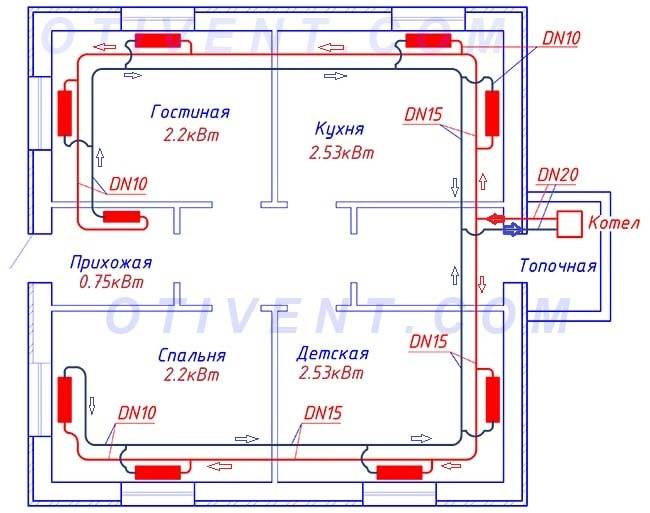
Based on the following layout, we will find out the need for pipes and fittings for a two-pipe network:
- tr. DN15 Ø20 mm - 68 meters (mains);
- tr. DN10 Ø16 mm - 22 m (radiator connections);
- tee 20 x 20 x 16 mm - 16 pcs.
Now let's find the current prices for plumbing fittings and pipes made of 3 materials: reinforced polypropylene PP-R, metal-plastic PEX-AL– PEX and PEX cross-linked polyethylene from well-known manufacturers. The results of the calculations will be entered in the table:
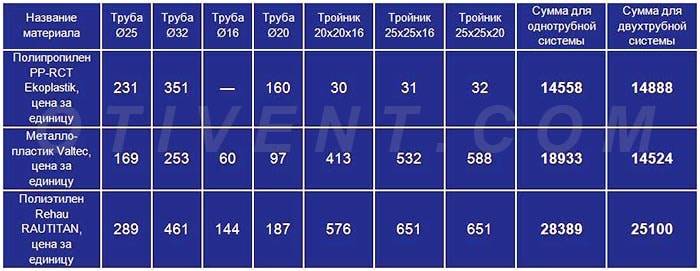
As you can see, the costs for polypropylene tees and pipes are almost the same for both schemes - the shoulder one turned out to be more expensive by only 330 rubles. For other materials, two-pipe wiring definitely wins. The reason lies in the diameters - the prices of pipes with a larger cross section increase sharply compared to the "running" sizes of 16 and 20 mm.
You can take cheaper plumbing from other manufacturers and perform the calculation - the ratio is unlikely to change. Note that we skipped the 90° elbows for the pipe bends and other small items because we don't know the exact number. If you carefully calculate all the materials, the cost of "Leningradka" will increase even more. An expert demonstrating calculations on video came to similar conclusions:
Types of forced circulation of heat carrier in heating
The use of forced circulation heating schemes in two-story houses is used due to the length of the system lines (more than 30 m). This method is carried out using a circulation pump that pumps the liquid of the circuit. It is mounted at the inlet to the heater, where the coolant temperature is the lowest.
With a closed circuit, the degree of pressure that the pump develops does not depend on the number of storeys and the area of \u200b\u200bthe building. The speed of the water flow becomes greater, therefore, when passing through the pipeline lines, the coolant does not cool down much. This contributes to a more even distribution of heat throughout the system and the use of the heat generator in a sparing mode.
The expansion tank can be located not only at the highest point of the system, but also near the boiler. To perfect the scheme, the designers introduced an accelerating collector into it. Now, if there is a power outage and the subsequent stop of the pump, the system will continue to work in convection mode.
- with one pipe
- two;
- collector.
Each can be mounted by yourself or invite specialists.
Variant of the scheme with one pipe
Shutoff valves are also mounted at the battery inlet, which serves to regulate the temperature in the room, as well as necessary when replacing equipment. An air bleed valve is installed on top of the radiator.
Battery valve
To increase the uniformity of heat distribution, radiators are installed along the bypass line. If you do not use this scheme, then you will need to select batteries of different capacities, taking into account the loss of heat carrier, that is, the farther from the boiler, the more sections.
The use of shut-off valves is optional, but without it, the maneuverability of the entire heating system is reduced. If necessary, you will not be able to disconnect the second or first floor from the network to save fuel.
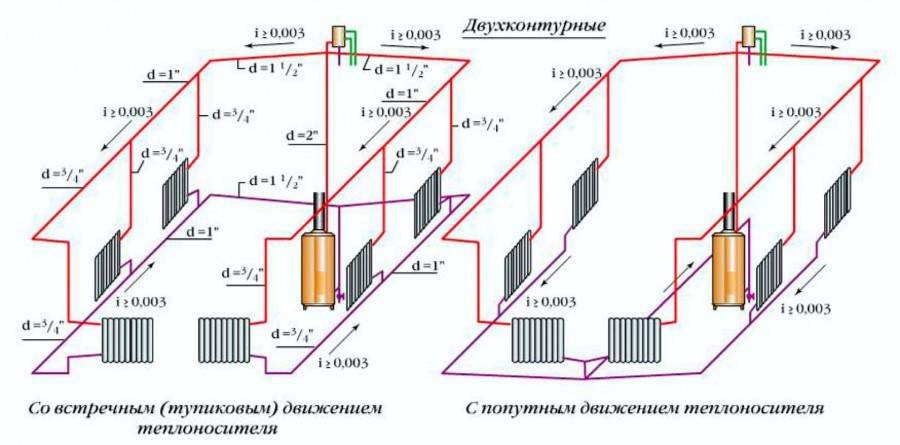
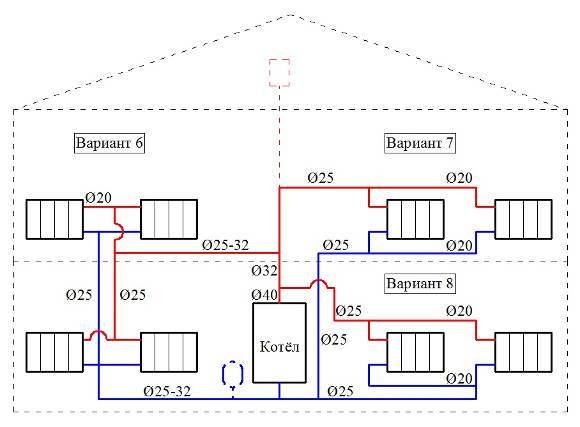
To get away from the uneven distribution of the heat carrier, schemes with two pipes are used.
- dead end;
- passing;
- collector.
Options for dead-end and passing schemes
The associated option makes it easy to control the level of heat, but it is necessary to increase the length of the pipeline.
The collector circuit is recognized as the most effective, which allows you to bring a separate pipe to each radiator. Heat is distributed evenly. There is one minus - the high cost of equipment, as the amount of consumables increases.
Scheme of collector horizontal heating
There are also vertical options for supplying heat carrier, which are found with the lower and upper wiring. In the first case, the drain with the supply of a heat carrier passes through the floors, in the second, the riser goes up from the boiler to the attic, where pipes are routed to the heating elements.
Vertical layout
Two-story houses can have a very different area, ranging from a few tens to hundreds of square meters. They also differ in the location of the rooms, the presence of outbuildings and heated verandas, the position to the cardinal points. Focusing on these and many other factors, you should decide on the natural or forced circulation of the coolant.
A simple scheme of coolant circulation in a private house with a natural circulation heating system.
Heating schemes with natural circulation of the coolant are distinguished by their simplicity.Here, the coolant moves through the pipes on its own, without the help of a circulation pump - under the influence of heat, it rises up, enters the pipes, is distributed over the radiators, cools down and enters the return pipe to go back to the boiler. That is, the coolant moves by gravity, obeying the laws of physics.
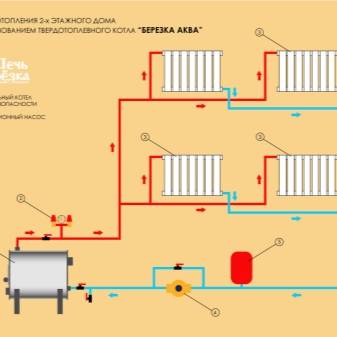
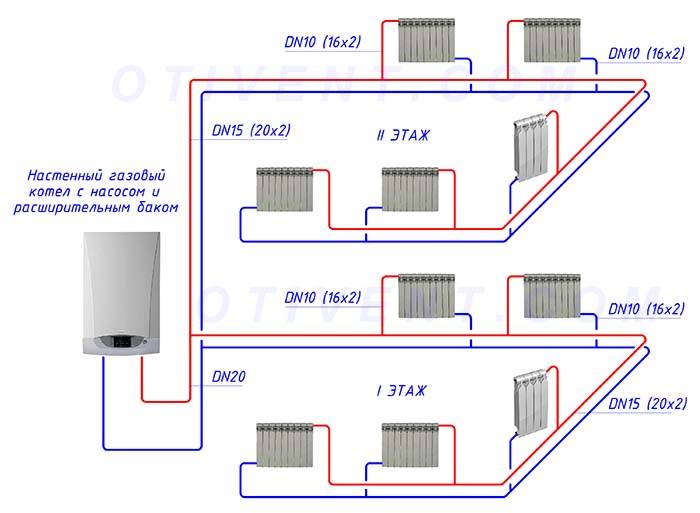
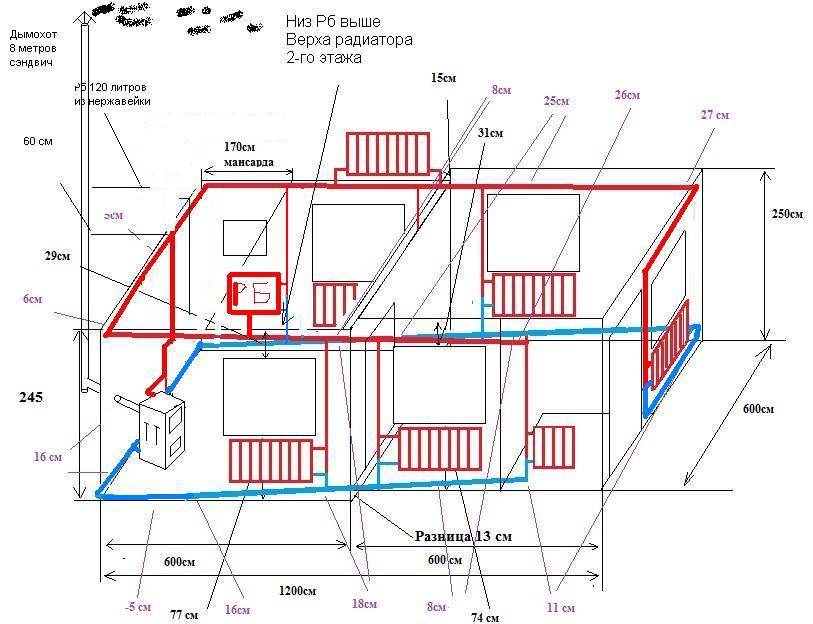
Scheme of a closed two-pipe heating system of a two-story house with forced circulation
- More uniform heating of the entire household;
- Significantly longer horizontal sections (depending on the power of the pump used, it can reach several hundred meters);
- Possibility of more efficient connection of radiators (for example, diagonally);
- Possibility of mounting additional fittings and bends without the risk of pressure drop below the minimum limit.
Thus, in modern two-story houses, it is best to use heating systems with forced circulation. It is also possible to install a bypass, which will help you choose between forced or natural circulation in order to select the most optimal option. We make a choice towards coercive systems, as more effective.
Forced circulation has a couple of disadvantages - this is the need to purchase a circulation pump and the increased noise level associated with its operation.
Why do people choose a two-circuit system?
Such a layout has advantages that need to be mentioned in order to understand why homeowners opt for it. These include:
- Parallel connection of radiators. This allows you to maintain different temperatures in a single room. This allows the system to be used in multi-storey buildings.Plus, if one or more radiators break down, the system will continue to function. With a single-circuit system, this is not possible.
- Ability to connect a large number of radiators. The temperature of the water entering each radiator will be the same no matter how far it is from the boiler.
- The possibility of installing a thermostat. The system monitors the temperature itself and automatically turns on when needed. The owner only needs to set the temperature range.
- Small heat losses. Almost all of the heat produced is not lost, but is used to heat the room. In single-circuit systems, it is wasted.
Of the minuses: many note the large length of pipes and the high cost of installing double-circuit heating in a private house. In fact, a two-circuit system is not more expensive than its single-pipe counterpart due to the small diameter of the pipes themselves. And the benefits are much greater.
Classification of water heating systems according to the principle of operation
According to the principle of operation, heating has natural and forced circulation of the coolant.
with natural circulation
Used to heat a small house. The coolant moves through the pipes due to natural convection.
Photo 1. Scheme of a water heating system with natural circulation. Pipes must be installed at a slight slope.
According to the laws of physics, a warm liquid rises. Water, heated in the boiler, rises, after which it descends through pipes to the last radiator in the system. Cooling down, the water enters the return pipe and returns to the boiler.
The use of systems operating with the help of natural circulation requires the creation of a slope - this simplifies the movement of the coolant. The length of the horizontal pipe cannot exceed 30 meters - the distance from the outermost radiator in the system to the boiler.
Such systems attract with their low cost, no additional equipment is required, they practically do not make noise when they work. The downside is that the pipes need a large diameter and should be laid as evenly as possible (there is almost no coolant pressure in them). It is impossible to heat a large building.
Forced circulation scheme
The scheme using the pump is more complicated. Here, in addition to heating batteries, a circulation pump is installed that moves the coolant through the heating system. It has higher pressure, so:
- It is possible to lay pipes with bends.
- It is easier to heat large buildings (even several floors).
- Suitable for small pipes.
Photo 2. Scheme of a heating system with forced circulation. A pump is used to move the coolant through the pipes.
Often these systems are made closed, which eliminates the ingress of air into the heaters and coolant - the presence of oxygen leads to metal corrosion. In such a system, closed expansion tanks are required, which are supplemented with safety valves and air vent devices. They will heat a house of any size and are more reliable in operation.
Mounting methods
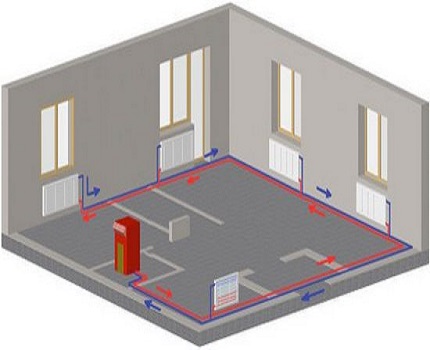
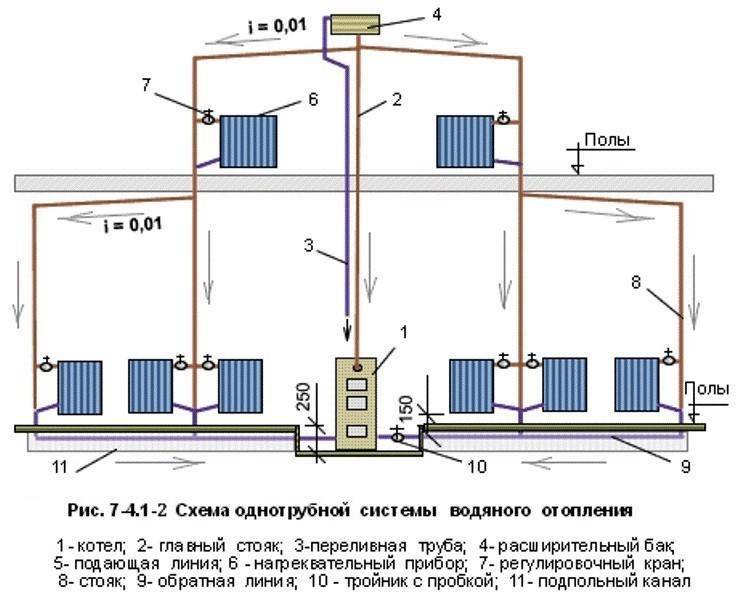
For a small house consisting of 2-3 rooms, a single-pipe system is used. The coolant moves sequentially through all the batteries, reaches the last point and returns through the return pipe back to the boiler. Batteries connect from below.The downside is that the distant rooms warm up worse, as they receive a slightly cooled coolant.
Two-pipe systems are more perfect - a pipe is laid to the far radiator, and taps are made from it to the rest of the radiators. The coolant at the outlet of the radiators enters the return pipe and moves to the boiler. This scheme evenly heats all rooms and allows you to turn off unnecessary radiators, but the main disadvantage is the complexity of installation.
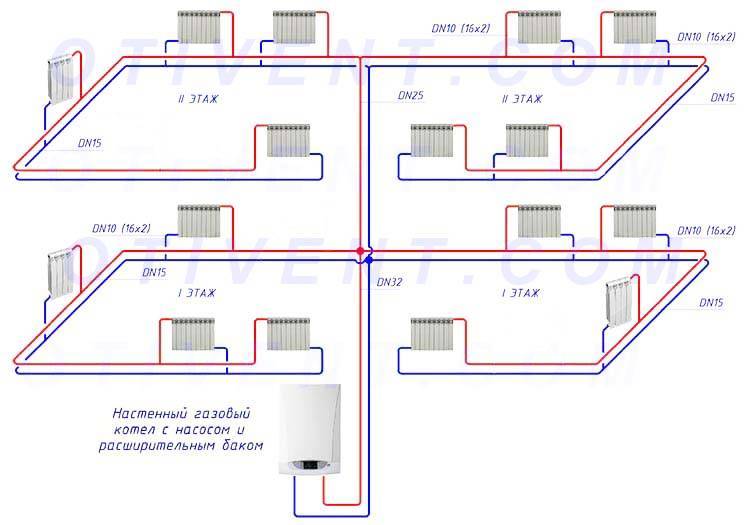
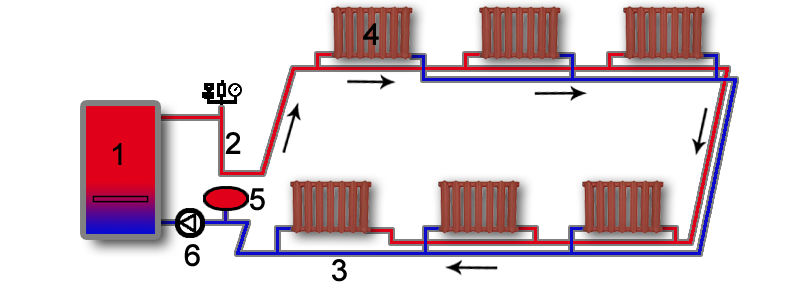
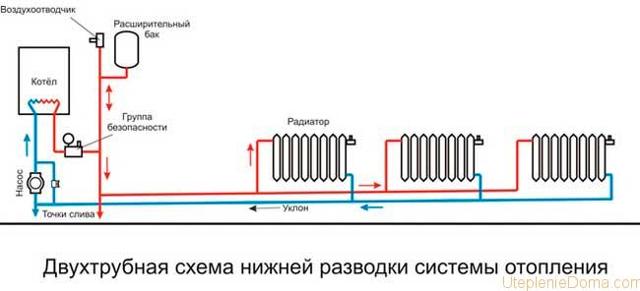
Collector heating
The main disadvantage of a one- and two-pipe system is the rapid cooling of the coolant; the collector connection system does not have this drawback.
Photo 3. Water collector heating system. A special distribution unit is used.
The main element and basis of collector heating is a special distribution unit, popularly called a comb. Special plumbing fittings necessary for the distribution of the coolant through separate lines and independent rings, a circulation pump, safety devices and an expansion tank.
The manifold assembly for a two-pipe heating system consists of 2 parts:
- Input - it is connected to a heating device, where it receives and distributes hot coolant along the circuits.
- Outlet - connected to the return pipes of the circuits, it is necessary to collect the cooled coolant and supply it to the boiler.
The main difference between the collector system is that any battery in the house is connected independently, which allows you to adjust the temperature of each or turn it off. Sometimes mixed wiring is used: several circuits are connected independently to the collector, but inside the circuit the batteries are connected in series.
The coolant delivers heat to the batteries with minimal losses, the efficiency of this system increases, which makes it possible to use a boiler of lower power and consume less fuel.
But the collector heating system is not without drawbacks, these include:
- Pipe consumption. You will need to spend 2-3 times more pipe than when connecting batteries in series.
- The need to install circulation pumps. Requires high pressure in the system.
- Energy dependence. Do not use where there may be power outages.
Technical requirements
Designing modern heating systems is a responsible process. In such a scheme, an important role is played by the chimney. It is used to ensure that all combustion products go outside.
There are some requirements for chimneys:
- Joints and joints must be treated with fire-resistant materials.
- The chimney must be gas-tight.
- Its size must correspond to the power of the heat generator.
- The cross section of the chimney can be determined in accordance with the standards in the list of acts SNiP 41-01-2003 "Heating, ventilation, air conditioning", as well as SP 7.13130.2013 "Heating, ventilation, air conditioning".
- The length and diameter of the chimney itself must fully comply with the recommendations of the boiler manufacturers.
- It must be placed vertically.
- Above the roof, the chimney can protrude no more than 50 centimeters. If the distance between the ridge and the pipe is less than three meters, the pipe may be located on the same level as the ridge.
- It also needs to be protected from various atmospheric precipitation with the help of nozzles, for example, umbrellas or deflectors.
- Laying a chimney through living quarters is not permitted.
Various materials are used for the manufacture of chimneys. They can be brick, or metal, less often - ceramic. If brick is used, then the design takes place even before the house is built. Nowadays, stainless steel chimneys are most often used, as this is a fairly durable material. It is for this reason that a ceramic pipe is least likely to be installed, since it is quite fragile.
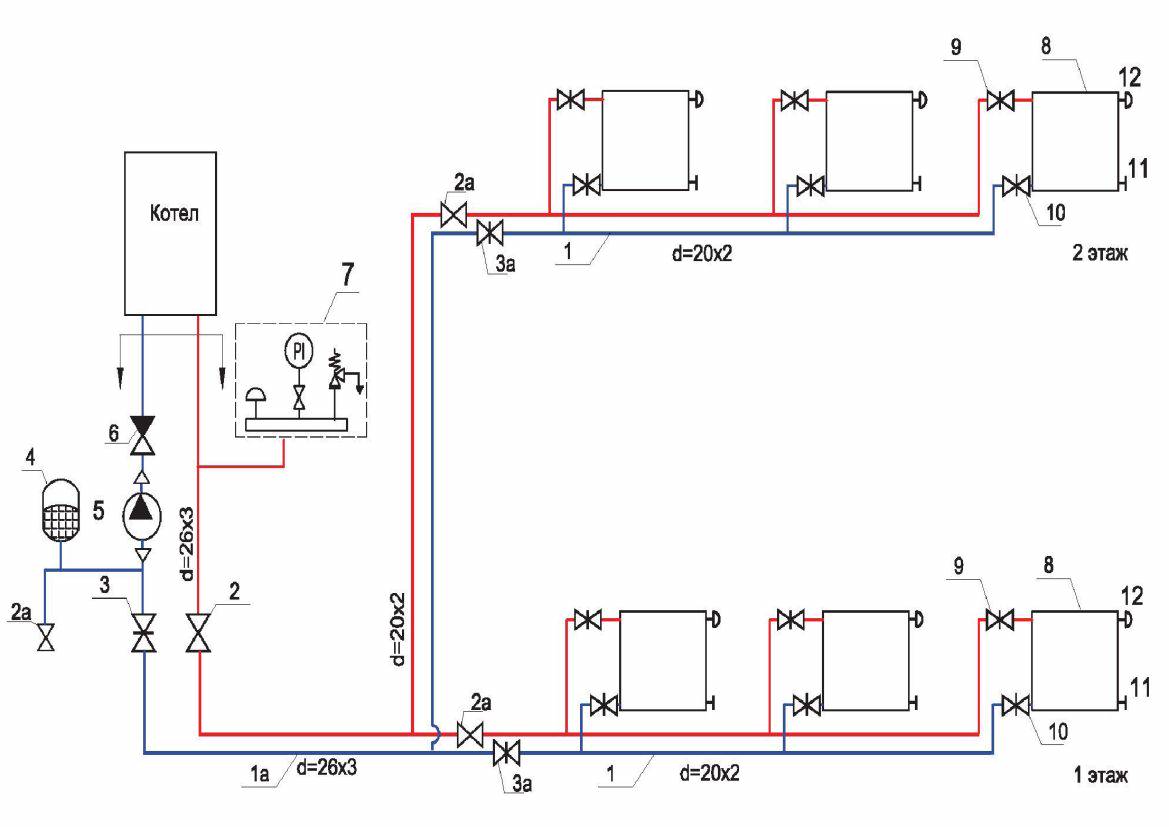
The principle of operation of closed CO
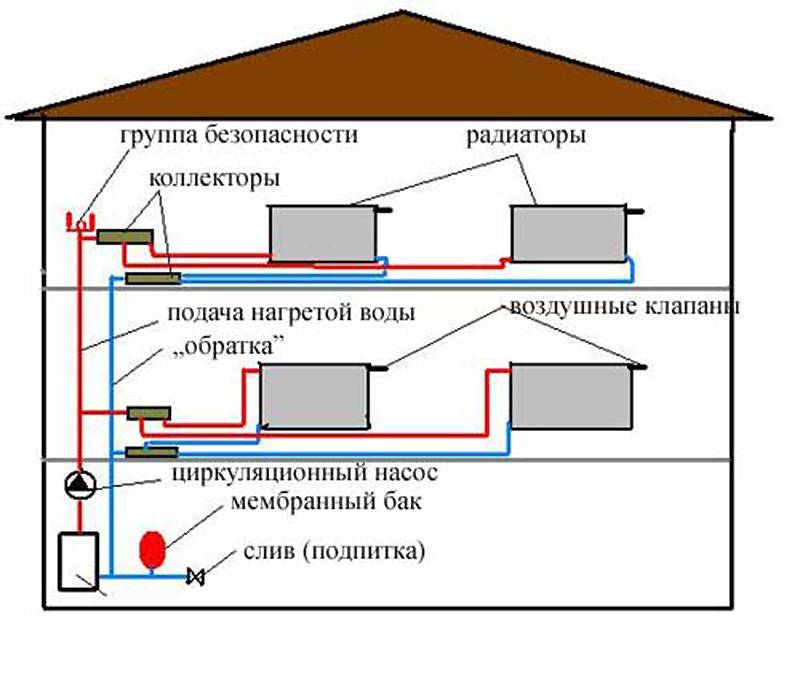
A closed (otherwise - closed) heating system is a network of pipelines and heating devices in which the coolant is completely isolated from the atmosphere and moves forcibly - from the circulation pump. Any SSO must include the following elements:
- heating unit - gas, solid fuel or electric boiler;
- safety group consisting of a pressure gauge, safety and air valve;
- heating devices - radiators or contours of underfloor heating;
- connecting pipelines;
- a pump that pumps water or non-freezing liquid through pipes and batteries;
- coarse mesh filter (mud collector);
- closed expansion tank equipped with a membrane (rubber "pear");
- stopcocks, balancing valves.
Typical diagram of a closed heating network of a two-story house
The algorithm of operation of a closed-type system with forced circulation looks like this:
- After assembly and pressure testing, the pipeline network is filled with water until the pressure gauge shows a minimum pressure of 1 bar.
- The automatic air vent of the safety group releases air from the system during filling.He is also engaged in the removal of gases that accumulate in pipes during operation.
- The next step is to turn on the pump, start the boiler and warm up the coolant.
- As a result of heating, the pressure inside the SSS increases to 1.5–2 bar.
- The increase in the volume of hot water is compensated by a membrane expansion tank.
- If the pressure rises above the critical point (usually 3 bar), the safety valve will release excess fluid.
- Once every 1-2 years, the system must undergo a procedure for emptying and flushing.
The principle of operation of the ZSO of an apartment building is absolutely identical - the movement of the coolant through pipes and radiators is provided by network pumps located in an industrial boiler room. There are also expansion tanks, the temperature is controlled by a mixing or elevator unit.
How a closed heating system works is explained in the video:
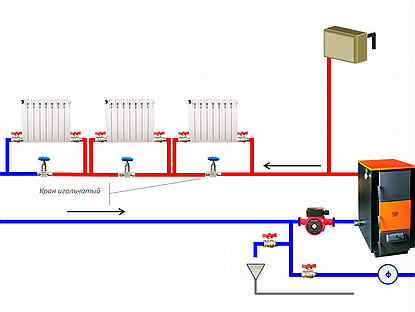
Features of the installation process
The pump should be installed in the area with the lowest temperature, that is, on the "return" near the boiler.
If installed on the “supply” line, the polymer parts of the supercharger will quickly fail due to overheating.
And if the coolant boils, the circulation will stop altogether (which will further aggravate overheating), since the pump is unable to pump steam.
Before the pump, a coarse filter (mud filter) is installed, and after it - a pressure gauge. Another pressure gauge is usually installed after the boiler as part of the safety group.
Since the expansion tank in a forced circulation system is closed, it does not have to be installed at the highest point of the circuit.Usually it is also connected to the "return" somewhere near the boiler.
In the event of a blockage in the circuit, it is necessary to provide a bypass with a bypass valve, through which the pump will pump the coolant "through itself", that is, in a small circle, bypassing the circuit. If this is not done, a zone of high pressure will form before the blockage, which will significantly accelerate the wear of the pump.
In order not to mess with the bypass, you can install a pump with the ability to smoothly adjust the engine speed and an automatic regulator.
5
The more pipes, the better!
The advantages and disadvantages of the systems described above lead us to two conclusions. Firstly, if you need an optimal heating scheme for a three-story house with forced circulation, then you will not find anything better than collector wiring. But in one-story houses, the two-pipe option is considered the optimal scheme. In this case, it is possible to minimize the consumption of fittings and remain with a heat supply network that is sensitive to control. A single-pipe system will cost less, but it will not save on fuel by regulating the temperature in the batteries. Therefore, the more pipes, the better.

Closed two-pipe system
Now regarding the closed or open version of the assembly. In the two-pipe case, an open heating system with forced circulation does not give a chance for serious fuel savings. An open expansion tank gives off heat to the atmosphere and does not allow the circulation to be accelerated to decent speeds. Another thing is a closed two-circuit scheme. It requires a little more effort during installation, but the ability to increase pressure and accelerate the circulation of the coolant to an acceptable level provides a chance for good fuel savings.After all, if the coolant goes through the pipes under high pressure, then it enters the boiler while still warm.
Solar panels. Working principle of solar heating system
Solar heating can also be included in the list where all the new technologies for home heating are present. In this case, not only photovoltaic panels, but also solar collectors can be used for heating. Photovoltaic panels have practically fallen out of use, since collector-type batteries have a much higher efficiency indicator.
Heating the latest heating systems for a private house, which are powered by solar energy, include components such as a collector - a device consisting of a series of tubes, these tubes are attached to a tank that is filled with coolant.
Heating scheme with solar collectors
According to their design features, solar collectors can be of the following varieties: vacuum, flat or air. Sometimes a component such as a pump can be included in such modern heating systems of a country house. It will be designed to provide mandatory circulation along the coolant circuit. This will contribute to more efficient heat transfer.
In order for solar heating technology to be the most efficient, some rules must be followed. Firstly, such new technologies for heating a country house can only be used in regions where it is sunny at least 15-20 days a year. If this indicator is lower, then additional new types of heating of a private house should be installed. The second rule dictates that the collectors be placed as high as possible.You need to orient them so that they absorb as much solar heat as possible.
The most optimal angle of the collector to the horizon is considered to be 30-45 0 .
To prevent unnecessary heat loss, it is necessary to insulate all pipes that connect the heat exchanger to the solar collectors.
Thus, we see that the development of technology does not stand still, and novelties in home heating are as much a necessity as the modernization of equipment that we use every day.
Innovations in the heating system use something completely new and unusual for us - thermal energy from different sources.
Modern types of heating a private house sometimes amaze the imagination, however, in modern times, each of us can already purchase or make such modern heating for a country house or a private one with our own hands. New in heating a private house are efficient systems that continue to develop the field of heating equipment, and we hope that all the most effective options are yet to come.
The heating system in a newly built house is the basis for many other activities in private homes. After all, it is heating that is the condition under which it is possible to carry out internal finishing work and the construction and installation of communications. This process is especially necessary when the construction of a house is delayed and all activities related to internal work fall on the cold season.
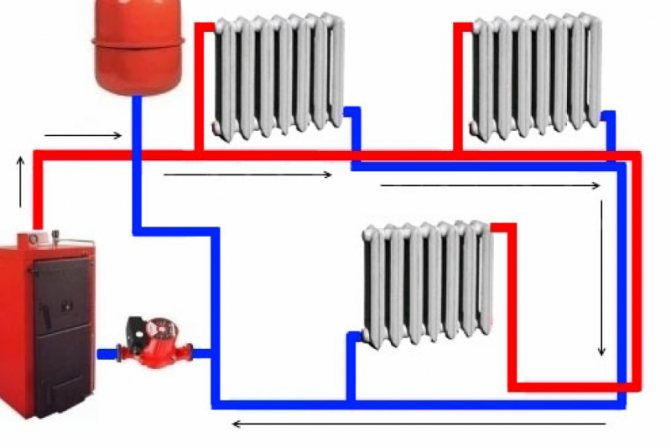
The scheme of heating the house with a gas boiler.
Many homeowners are forced to put them off due to the fact that the houses do not yet have an adequate heating system.Therefore, even at the stage of building a house, and even better before it, it is necessary to carefully consider all the options related to the organization of the heating system in the house. Depending on the style in which your house will be decorated and how often you intend to use the finished structure, it is necessary to select materials for construction and, accordingly, determine which heating system is suitable for these specific conditions. Both traditional and modern heating systems for private houses can be selected.
Pros and cons
Due to the use of a pump, a forced circulation heating system has a rather large range of advantages:
- The ability to use pipes of any diameter - the quality of the system is not tied to the diameter of the pipes, since the pump guarantees a constant speed of movement of the coolant and the same heating of all zones of the system, regardless of the size of the products used. This makes it possible to ensure uninterrupted operation of the system even with low-cost pipes of reduced diameter.
- Simplified installation - there is no need to strictly maintain a certain angle of pipe laying, as is the case with a system with a natural circulation type, which makes it possible to do the installation of equipment yourself.
- Independent temperature control - it is possible to set a specific temperature in each separate room of a one-story house, regardless of the temperature in the neighboring room.
- No temperature fluctuations - thanks to the pump, there are no significant temperature fluctuations in the system, which significantly increases the service life of all devices and components.
 Heating pipes in a private house
Heating pipes in a private house
Among the main disadvantages:
Dependence of heating on power supply - due to the use of a circulation pump, the heating system requires a mandatory connection to the mains.
Advice. You can protect the pump from emergency power outages using an uninterruptible power supply.
Uncomfortable noise level - the operation of the pumping unit is accompanied by not very pleasant noise.
Without a doubt, the heating system with forced circulation is superior in many respects to the option with natural movement of the coolant. That is why it is most often chosen for one-story houses
But in order for this choice to bring only positive results, it is important to correctly organize the heating, so carefully study the available schemes for the system device - they are all in front of you
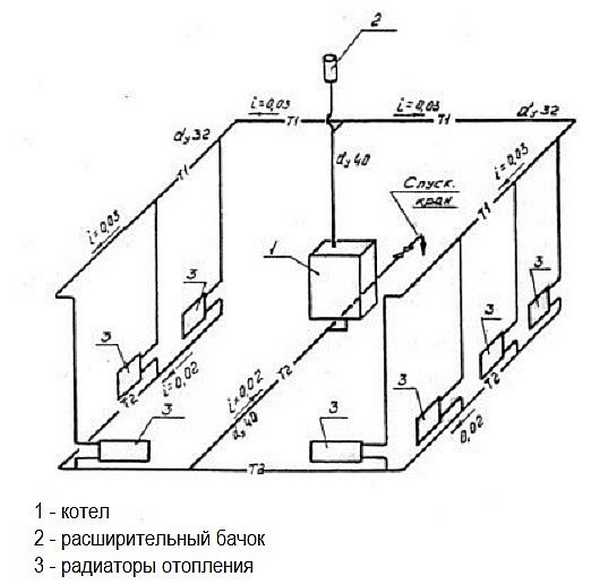
Construction features

To organize the movement of fluid by gravity, do the following:
The heating boiler is located as low as possible - on the ground floor or in the basement. The distributing manifold is raised higher - under the ceiling or in the attic of the building.
Thus, the water receives the maximum height allowed for this building. What creates the maximum possible gravitational head of the coolant in the pipes.
Mount devices with wide internal gaps. Pipes of increased diameter - not less than 40 mm in cross section. Radiators with a wide internal passage - traditional cast iron batteries. If necessary installation of locking devices - put ball valves, which in the open position minimally narrow the internal lumen.
- Pipe laying is carried out with a minimum number of turns, corners, without coils and without spirals.
- The supply and return lines are laid with a slope.
Attention! The principles listed above allow you to organize the natural pressure of water and its movement at the required speed. Let's list the devices which assemble a gravity heating circuit:. We list the devices from which a gravity heating circuit is assembled:
We list the devices from which a gravity heating circuit is assembled:
- Heating boiler - can operate on various types of fuel - gas, wood, coal, electricity.
- Radiators - direct heating devices - radiate heat into the space of the room.
- Main supply and return pipe.
- The distribution manifold is located above the boiler. The water heated in the boiler enters it, then it moves (distributed) into the main pipe.
- Expansion tank - for temporary storage of coolant, which expands and increases in volume when heated. It is located at the highest point of the system, is performed in the open.
- Swivel ball valves - at the inlet and outlet of heating radiators.
- A tap for draining water (also a ball valve) is at the lowest point of the system.
Now let's take a closer look at how they provide the maximum possible pressure.
Pipe slope
For the natural circulation of the coolant, a number of measures are taken that facilitate its movement inside radiators and pipes. One of these measures is laying the supply and return pipes at a slight slope. The size of the slope is chosen - 2-3 ° per linear meter.
The indicated degrees of slope do not visually violate the geometry of pipe laying, but ensure the movement of water by gravity. They also allow you to drain the fluid from the system if you need to replace the battery, repair.
gravity pressure

Gravitational pressure arises as the difference in water pressure in different segments of the pipeline.
In a system with natural movement of the coolant, gravitational pressure is created by heating the water and raising it to the height of the attic or the second floor of the house. This ensures gravity and heating operation.
The value of gravitational pressure is determined by the height of the rise of water and the temperature difference.
Attention! The stronger the heating of the coolant in the boiler, the greater the pressure difference will be, and the sooner the water will move through the pipes
Possible obstacles
For effective natural circulation, they try to reduce the number of factors that impede gravitational pressure.

The scheme is organized with a minimum number of corners and turns. Instead of pipe bends at right angles, smooth turns are made whenever possible. In order for the water not to meet obstacles, the narrowing of the gaps and valves are removed.
The internal sections of the radiators must be large enough. The consequence of wide gaps is an increased volume of the coolant, as well as the inertia of the heating operation.
Gravity type
Such a heating scheme for a one-story house is the simplest classic option. It has both advantages and disadvantages. The gravity heating scheme of a one-story house is based on the layout of the house. The circle of circulation should envelop the entire structure. The disadvantages of this system include massive pipes. Without them, the circulation of the coolant will be inefficient. In this case, you should not use heating radiators or replace pipes with thinner ones. This will lead to the maximum decrease in the flow rate and the cessation of water circulation.Thus, the temperature in the dwelling will decrease significantly. For this reason, the simplest gravity heating scheme for a one-story house includes a boiler and a drain that entangles the entire house. You can also increase the area of \u200b\u200bthe heater. To do this, not one, but two thick taps are launched. Many are interested in the question of how to organize the connection yourself. To do this, you will need instructions for wiring the water system. Thanks to her, all the work can be done by one person, even if he has minimal building experience. At the same time, the system should be fault-tolerant and cheap. 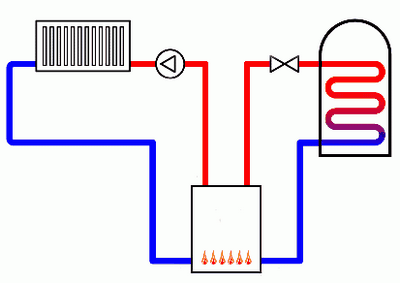
Pipe laying
The scheme of the heating system of a one-story house, in addition to heating equipment and heating radiators, provides for the mandatory presence of pipes that are used to transport the coolant from the boiler to the heating panels.
There are three common schemes in total, each of which will be described in detail below.
Method 1. With one pipe
The simplest, most efficient and commonly used installation method.
The scheme of a single-pipe heating system for a one-story house is designed as follows:
- A main pipe with a diameter of at least 32 mm is installed along the perimeter of the walls of the house. It must be mounted at an angle so that the cooling coolant, under the action of gravity, independently returns to the boiler for subsequent heating. (See also Piping: features.)
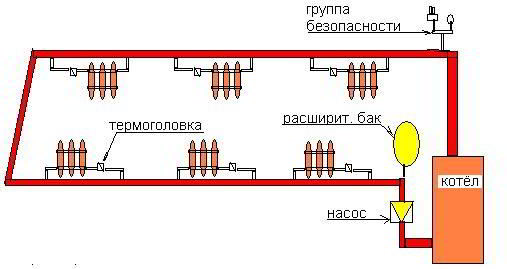
On the photo - single-pipe scheme heating systems for a small house
- Heating panels are attached to the resulting ring using pipes of a smaller diameter (20 mm). It is advisable to connect them through shut-off valves with thermostats.So you get the opportunity to regulate the temperature of each heating radiator separately.
In the upper part of the heating panel, it is necessary to provide for the installation of an air valve, which will prevent the “airing” of the heating system, which negatively affects the efficiency of the heating system.

Heating radiator connected to the main pipe
Such a home heating scheme has many positive aspects:
- its installation does not cause difficulties even for inexperienced craftsmen;
- to install such a scheme, you need to purchase the minimum possible number of pipes and other parts;
- all thermal energy is consumed only indoors, its unproductive losses are excluded;
- if you use a forced circulation heating scheme - a one-story house or a city apartment - such a solution will keep the system working even in the event of a short power outage.
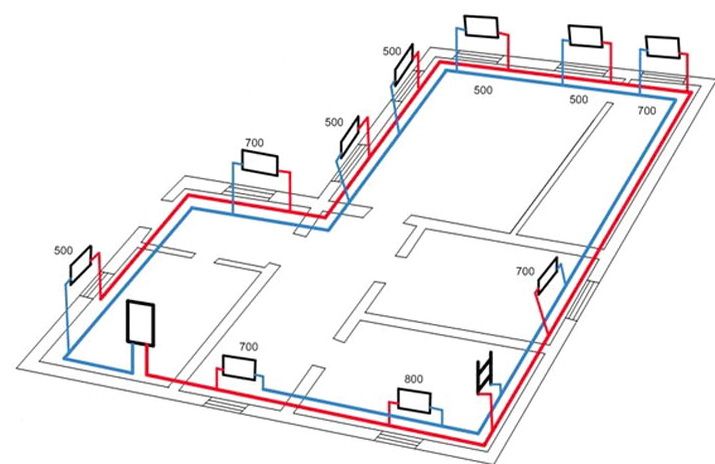
Method 2. With two pipes
In this case, as the name implies, one pipe is used to supply hot water, and another pipe is used to transport it to the boiler.
The scheme of a two-pipe heating system of a one-story house is mounted in the following order:
- two parallel pipes are stretched throughout the house - they can be installed in an open way, hidden under the floor covering, walled up in a wall or decorated with a box;
- heating radiators and other similar equipment, as it were, “crash” into pipelines, creating jumpers.
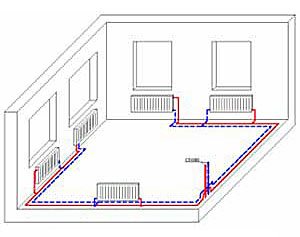
Diagram of a two-pipe heating system for a small house
Hot water will heat those rooms more efficiently if the heating panels are closer to the boiler.To balance the circuit, shut-off valves are often used, controlled manually or with the help of temperature controllers.
The disadvantages of such a solution are obvious:
- increased consumption of parts required for heating installation;
- the danger of failure of individual segments of the network as a result of freezing of the coolant (this often happens if the valves are opened all the way, limiting the access of water to the heating radiators closest to the boiler).
Method 3. Beam
It is very effective in terms of temperature control in individual rooms, but the most expensive and difficult to install. Such a scheme is more often used to provide heat to large residential buildings, where forced circulation of water in the pipeline is provided.
The installation instructions are as follows:
- in the boiler room or other suitable place, two collectors are installed, connected to pipes supplying and discharging the coolant;
- from these collectors there is a pair of pipes to each heating radiator in the house.
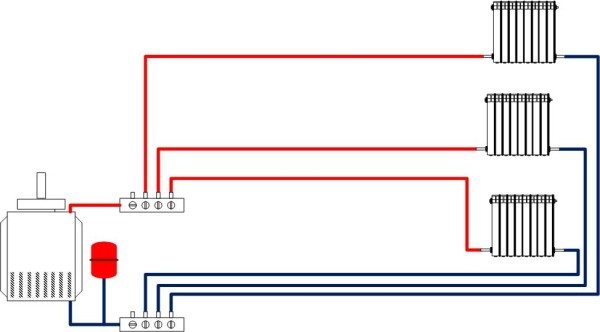
Radial piping scheme
The advantages of this system have already been mentioned, and as for the disadvantages, they are obvious:
- for installation, it is necessary to purchase a large number of parts and other equipment;
- it is necessary to decide where to hide the incoming and outgoing pipelines.