- Types of forced circulation of heat carrier in heating
- Systems with artificial induction of coolant movement
- general information
- Basic moments
- Self-regulation
- Circulation rate
- Ways of water circulation in heating systems
- Natural circulation of the coolant
- Forced coolant circulation
- Two-pipe system with bottom wiring
- Advantages and disadvantages of a two-pipe system with bottom wiring
- Features of mounting a two-pipe system with bottom wiring
- The difference between one-pipe and two-pipe systems
- Features of single-pipe wiring
- 2 Requirements for arrangement and operation
- Gravity circulation
- general information
- Basic moments
- Self-regulation
- Circulation rate
- Classification of water heating systems according to the principle of operation
- with natural circulation
- Forced circulation scheme
- Mounting methods
- Collector heating
- We calculate a single-pipe heating system ourselves
- How to properly install heating
- Theoretical horseshoe - how gravity works
Types of forced circulation of heat carrier in heating
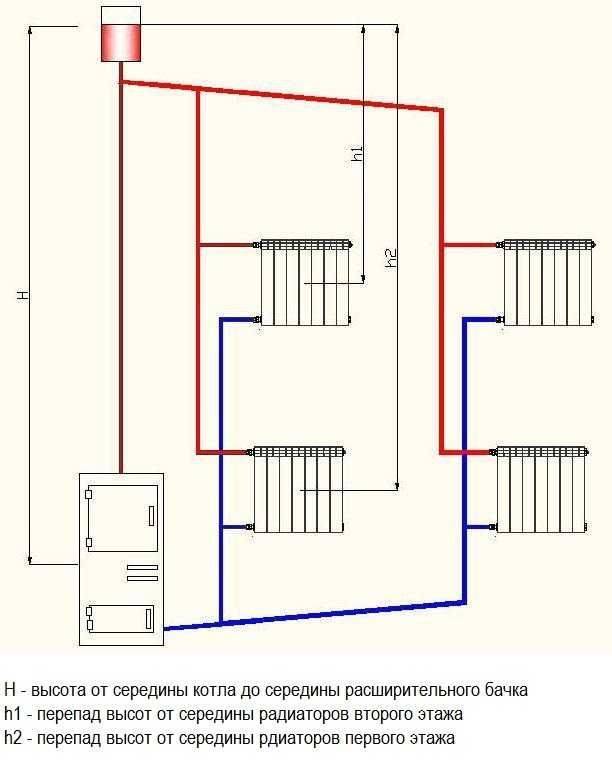
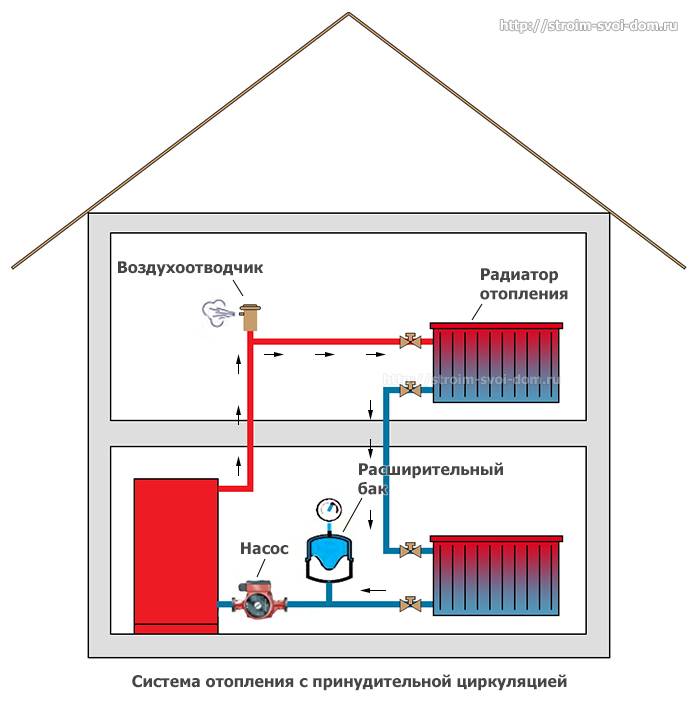
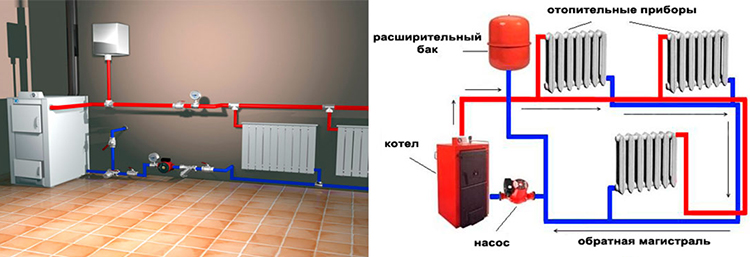
The use of forced circulation heating schemes in two-story houses is used due to the length of the system lines (more than 30 m). This method is carried out using a circulation pump that pumps the liquid of the circuit.It is mounted at the inlet to the heater, where the coolant temperature is the lowest.
With a closed circuit, the degree of pressure that the pump develops does not depend on the number of storeys and the area of \u200b\u200bthe building. The speed of the water flow becomes greater, therefore, when passing through the pipeline lines, the coolant does not cool down much. This contributes to a more even distribution of heat throughout the system and the use of the heat generator in a sparing mode.
The expansion tank can be located not only at the highest point of the system, but also near the boiler. To perfect the scheme, the designers introduced an accelerating collector into it. Now, if there is a power outage and the subsequent stop of the pump, the system will continue to work in convection mode.
- with one pipe
- two;
- collector.
Each can be mounted by yourself or invite specialists.
Variant of the scheme with one pipe
Shutoff valves are also mounted at the battery inlet, which serves to regulate the temperature in the room, as well as necessary when replacing equipment. An air bleed valve is installed on top of the radiator.
Battery valve
To increase the uniformity of heat distribution, radiators are installed along the bypass line. If you do not use this scheme, then you will need to select batteries of different capacities, taking into account the loss of heat carrier, that is, the farther from the boiler, the more sections.
The use of shut-off valves is optional, but without it, the maneuverability of the entire heating system is reduced. If necessary, you will not be able to disconnect the second or first floor from the network to save fuel.
To get away from the uneven distribution of the heat carrier, schemes with two pipes are used.
- dead end;
- passing;
- collector.
Options for dead-end and passing schemes
The associated option makes it easy to control the level of heat, but it is necessary to increase the length of the pipeline.
The collector circuit is recognized as the most effective, which allows you to bring a separate pipe to each radiator. Heat is distributed evenly. There is one minus - the high cost of equipment, as the amount of consumables increases.
Scheme of collector horizontal heating
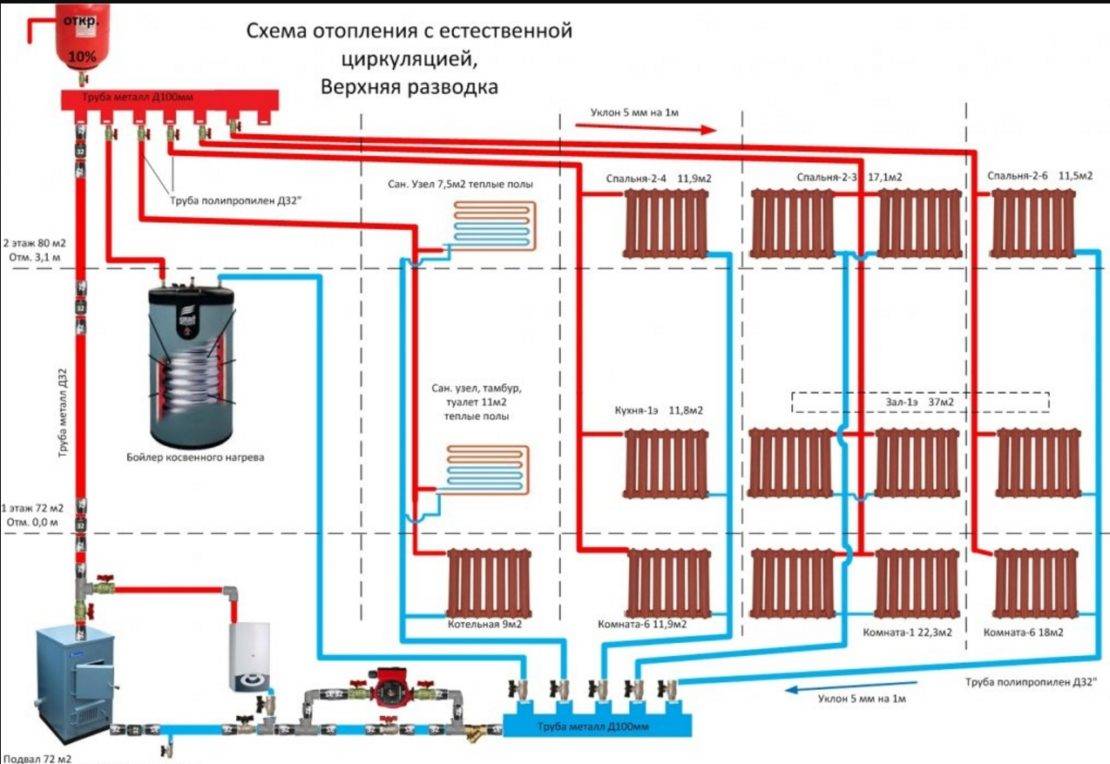
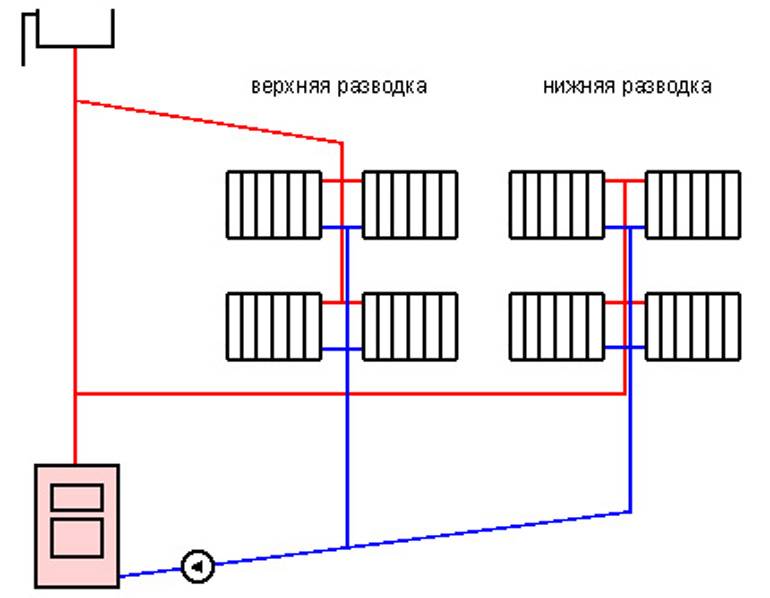
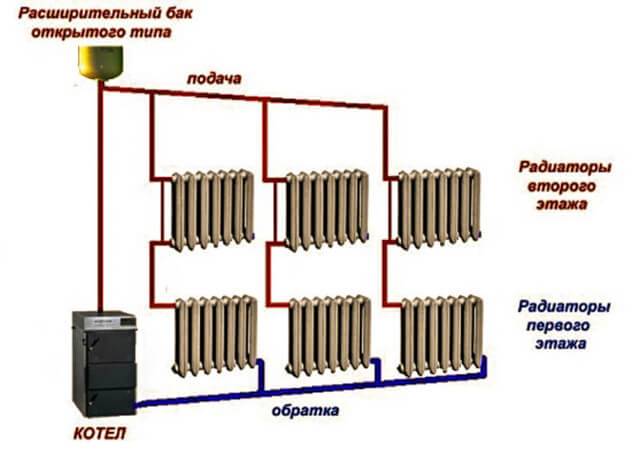
There are also vertical options for supplying heat carrier, which are found with the lower and upper wiring. In the first case, the drain with the supply of a heat carrier passes through the floors, in the second, the riser goes up from the boiler to the attic, where pipes are routed to the heating elements.
Vertical layout
Two-story houses can have a very different area, ranging from a few tens to hundreds of square meters. They also differ in the location of the rooms, the presence of outbuildings and heated verandas, the position to the cardinal points. Focusing on these and many other factors, you should decide on the natural or forced circulation of the coolant.
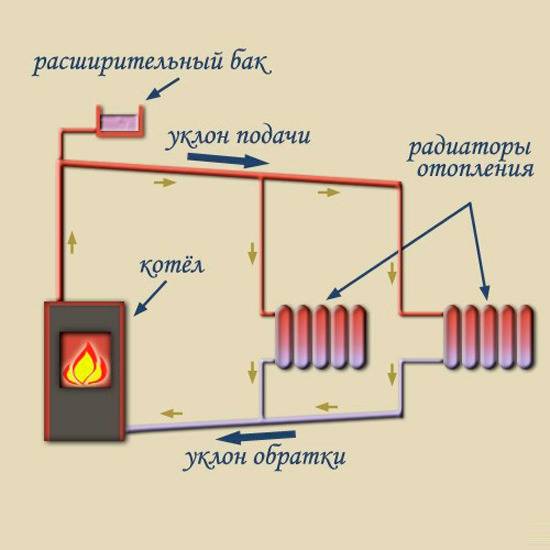
A simple scheme of coolant circulation in a private house with a natural circulation heating system.
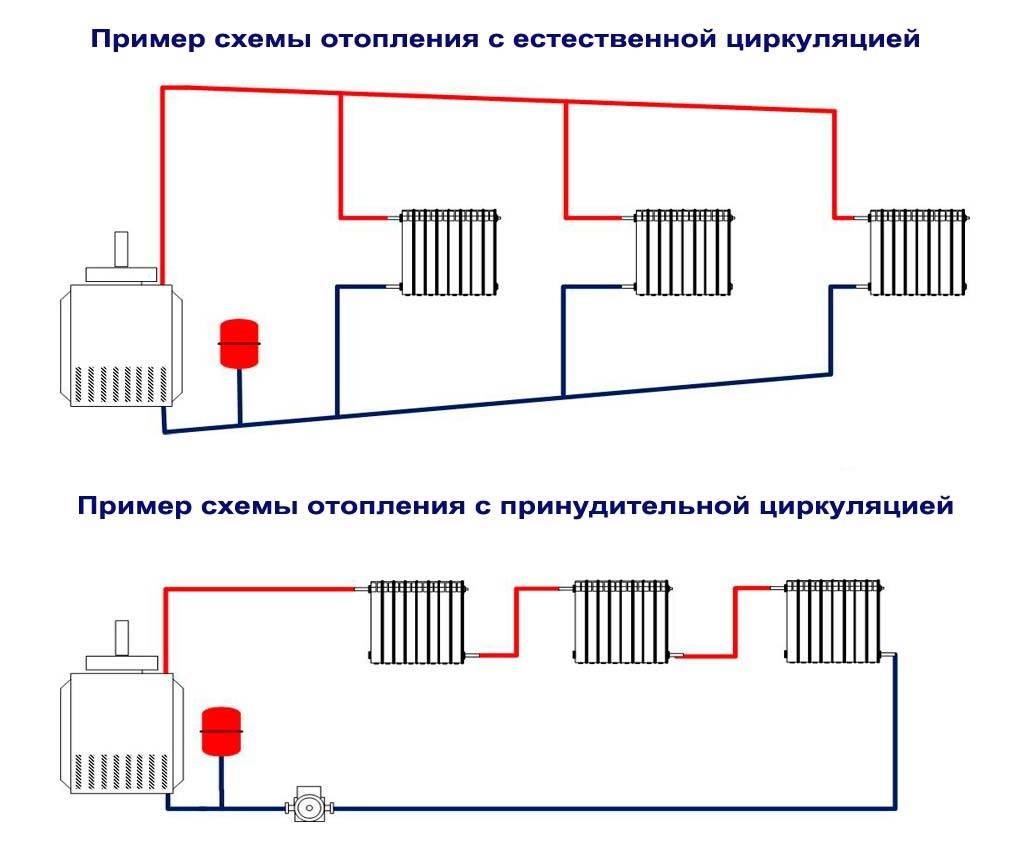
Heating schemes with natural circulation of the coolant are distinguished by their simplicity. Here, the coolant moves through the pipes on its own, without the help of a circulation pump - under the influence of heat, it rises up, enters the pipes, is distributed over the radiators, cools down and enters the return pipe to go back to the boiler. That is, the coolant moves by gravity, obeying the laws of physics.
Scheme of a closed two-pipe heating system of a two-story house with forced circulation
- More uniform heating of the entire household;
- Significantly longer horizontal sections (depending on the power of the pump used, it can reach several hundred meters);
- Possibility of more efficient connection of radiators (for example, diagonally);
- Possibility of mounting additional fittings and bends without the risk of pressure drop below the minimum limit.
Thus, in modern two-story houses, it is best to use heating systems with forced circulation. It is also possible to install a bypass, which will help you choose between forced or natural circulation in order to select the most optimal option. We make a choice towards coercive systems, as more effective.
Forced circulation has a couple of disadvantages - this is the need to purchase a circulation pump and the increased noise level associated with its operation.
Systems with artificial induction of coolant movement
Schemes of an open heating system with a pump in any case imply the use of an appropriate device. This allows you to increase the speed of movement of the liquid and reduce the time to heat the house. The coolant flow in this case moves at a speed of about 0.7 m/s, so heat transfer becomes more efficient and all sections of the heat supply system are heated equally.
When installing an open-type heating system with a pump, several features should be considered:
- The presence of a built-in circulation pump requires connection to the power supply system.For uninterrupted operation during an emergency power outage, it is recommended to install the pump on the bypass.
- The pumping equipment must be installed on the return pipe in front of the entrance to the boiler, at a distance of up to 1.5 meters from it.
- The pump crashes into the pipeline, taking into account the direction of movement of the coolant.
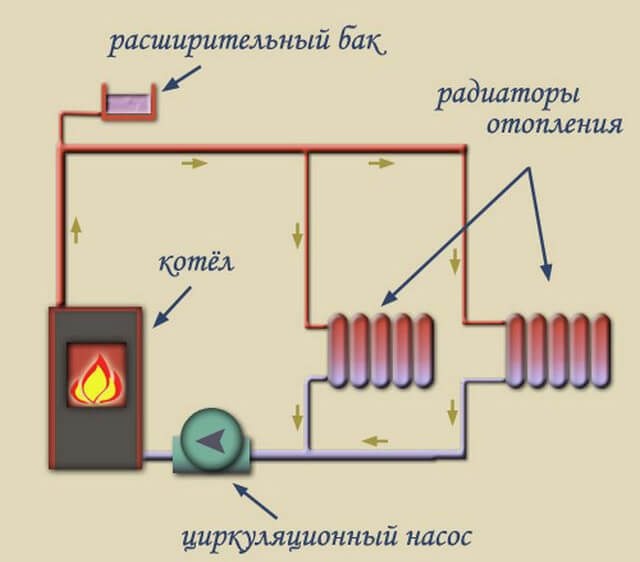
general information
Basic moments
The absence of a circulation pump and generally moving elements and a closed circuit, in which the amount of suspensions and mineral salts is finite, makes the service life of this type of heating system very long. When using galvanized or polymer pipes and bimetallic radiators - at least half a century.
Natural heating circulation means a fairly small pressure drop. Pipes and heaters inevitably provide a certain resistance to the movement of the coolant. That is why the recommended radius of the heating system we are interested in is estimated at about 30 meters. Clearly, this does not mean that with a radius of 32 meters the water will freeze - the border is rather arbitrary.
The inertia of the system will be quite large. Several hours may elapse between the ignition or start-up of the boiler and the stabilization of the temperature in all heated rooms. The reasons are clear: the boiler will have to warm up the heat exchanger, and only then will the water begin to circulate, and rather slowly.
All horizontal sections of pipelines are made with a mandatory slope in the direction of water movement. It will ensure the free movement of cooling water by gravity with minimal resistance.
What is no less important - in this case, all air plugs will be forced out to the upper point of the heating system, where the expansion tank is mounted - sealed, with an air vent, or open.

All air will collect at the top.
Self-regulation
Home heating with natural circulation is a self-regulating system. The colder it is in the house, the faster the coolant circulates. How it works?
The fact is that the circulation pressure depends on:
Differences in height between the boiler and the bottom heater. The lower the boiler is relative to the lower radiator, the faster the water will overflow into it by gravity. The principle of communicating vessels, remember? This parameter is stable and unchanged during the operation of the heating system.
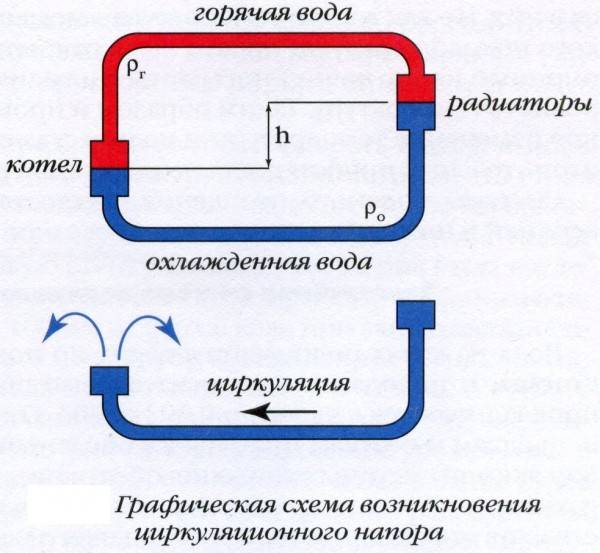
The diagram demonstrates the principle of operation of heating clearly.
With a drop in the temperature of the coolant, its density increases, and it begins to quickly displace the heated water from the lower part of the circuit.
Circulation rate
In addition to pressure, the circulation rate of the coolant will be determined by a number of other factors.
- Wiring pipe diameter. The smaller the internal section of the pipe, the greater the resistance it will provide to the movement of fluid in it. That is why for wiring in the case of natural circulation, pipes with a deliberately oversized diameter are taken - DN32 - DN40.
- Pipe material. Steel (especially corroded and covered with deposits) resists the flow several times more than, for example, a polypropylene pipe with the same cross section.
- The number and radius of turns. Therefore, the main wiring is best done as straight as possible.
- The presence, number and type of valves, various retaining washers and pipe diameter transitions.

Each valve, each bend causes a pressure drop.
It is precisely because of the abundance of variables that an accurate calculation of a heating system with natural circulation is extremely rare and gives very approximate results. In practice, it is enough to use the recommendations already given.
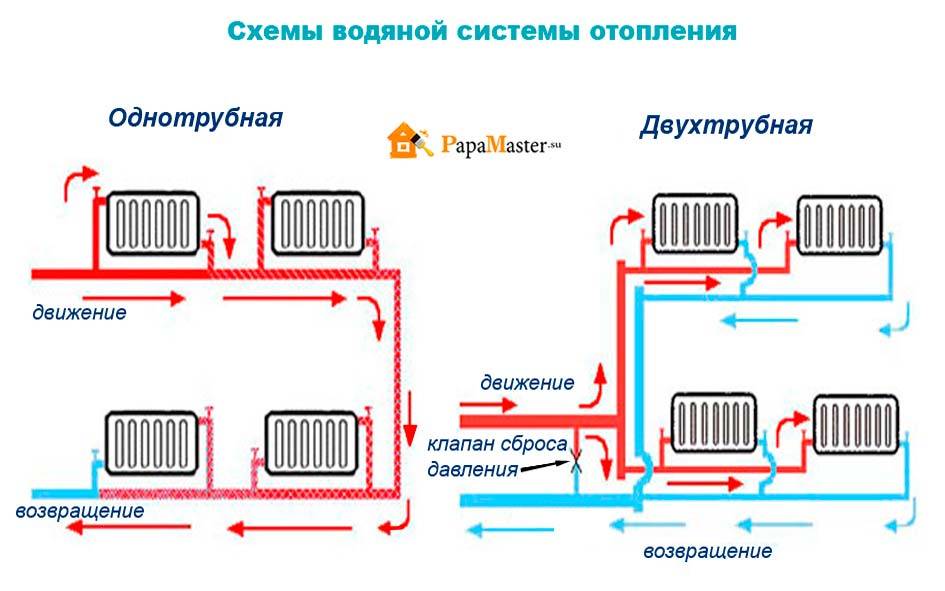
Ways of water circulation in heating systems
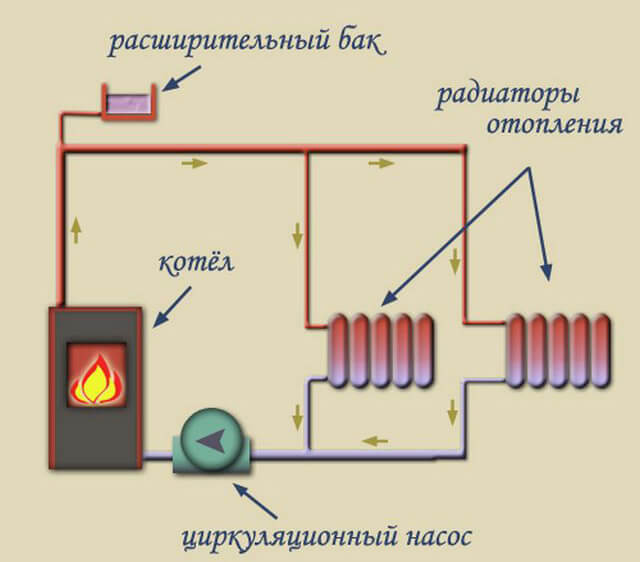
The movement of fluid along a closed circuit (contours) can occur in a natural or forced mode. The water heated by the heating boiler rushes to the batteries. This part of the heating circuit is called the forward stroke (current). Once in the batteries, the coolant cools down and is sent back to the boiler for heating. This interval of the closed route is called reverse (current). To accelerate the circulation of the coolant along the circuit, special circulation pumps are used, cut into the pipeline on the "return". Models of heating boilers are produced, the design of which provides for the presence of such a pump.
Natural circulation of the coolant
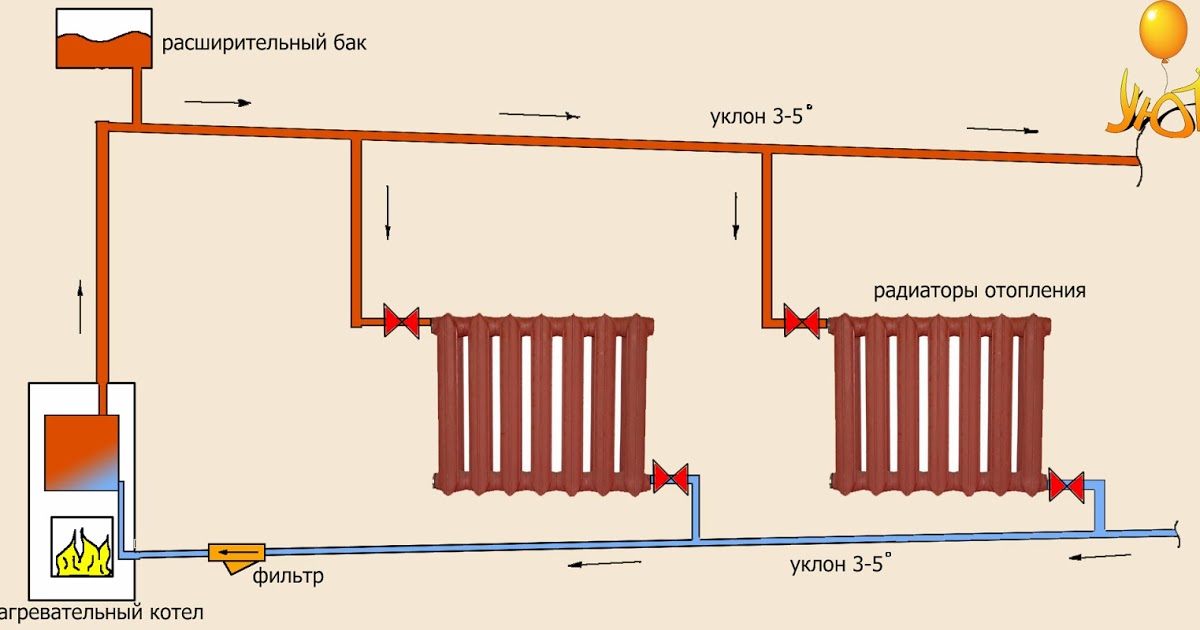
With natural circulation, the movement of water in the system goes by gravity. This is possible due to the physical effect that occurs when the density of water changes. Hot water has a lower density. The liquid going in the reverse direction has a high density, and therefore easily displaces the water that has already heated up in the boiler. The hot coolant rushes up the riser, and then is distributed along horizontal lines, drawn at a slight slope of no more than 3-5 degrees.The presence of a slope and allows the movement of fluid through the pipes by gravity.
The heating scheme, based on the natural circulation of the coolant, is the simplest, and therefore it is easy to implement in practice. In addition, in this case, no other communications are required. However, this option is suitable only for private houses of a small area, since the length of the circuit is limited to 30 meters. The disadvantages include the need to install pipes of larger diameter, as well as low pressure in the system.
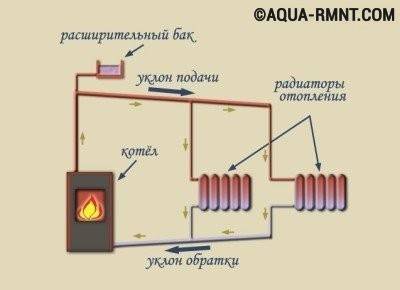
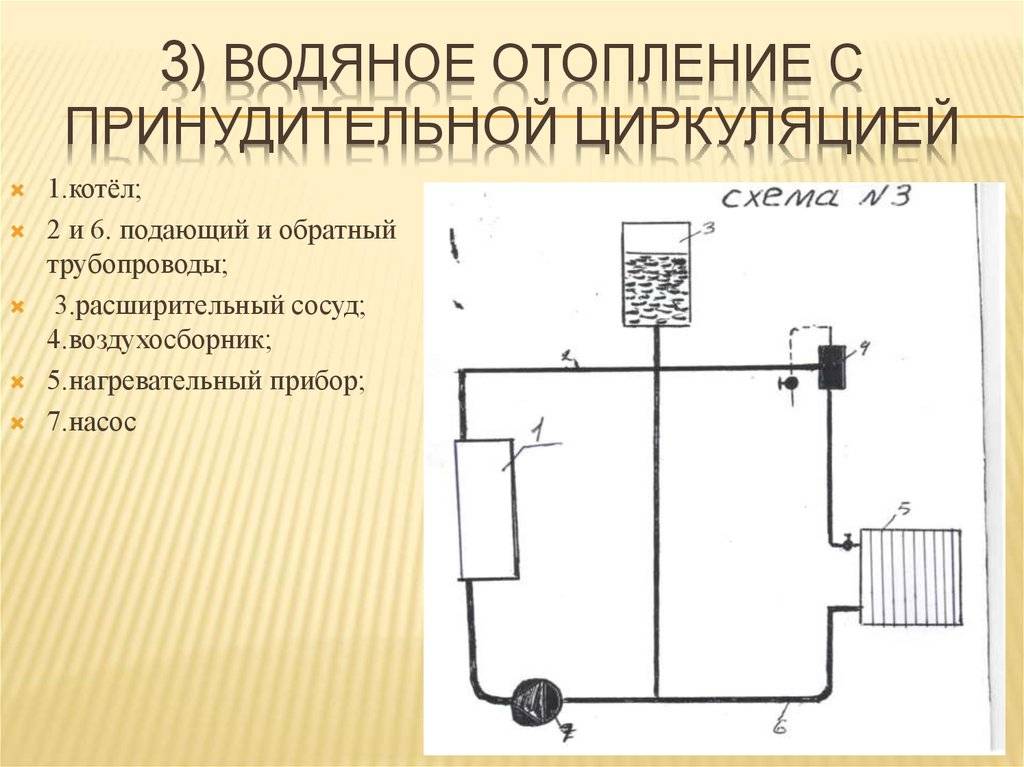
Forced coolant circulation
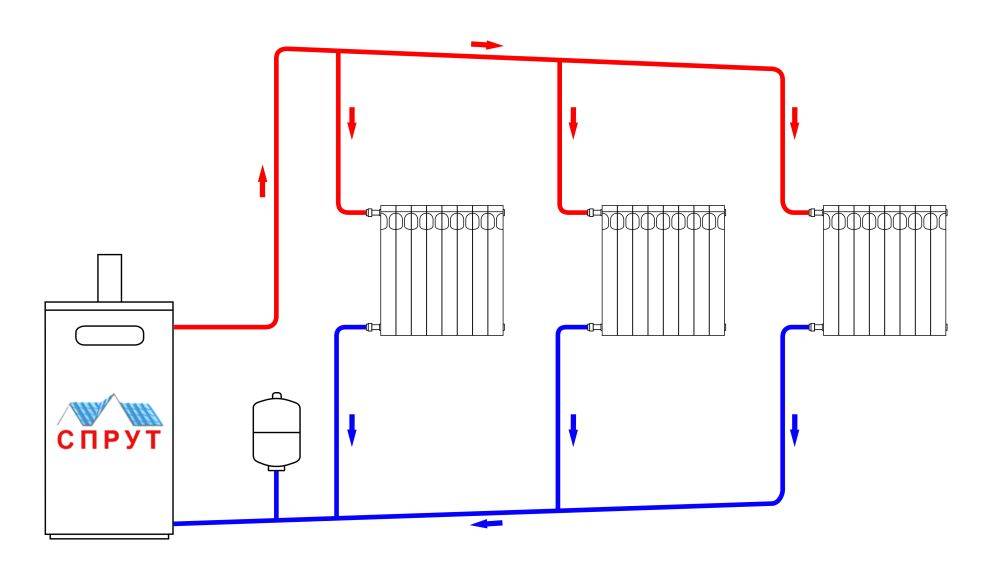
In autonomous heating systems with forced circulation of water (coolant) in a closed circuit, a circulation pump is mandatory, which provides an accelerated flow of heated water to the batteries, and cooled water to the heater. The movement of water is possible due to the pressure difference that occurs between the direct and reverse flow of the coolant.
When installing this system, it is not required to observe the slope of the pipeline. This is an advantage, but a significant drawback lies in the energy dependence of such a heating system. Therefore, in the event of a power outage in a private house, there must be a generator (mini-power plant) that will ensure the functioning of the heating system in an emergency.
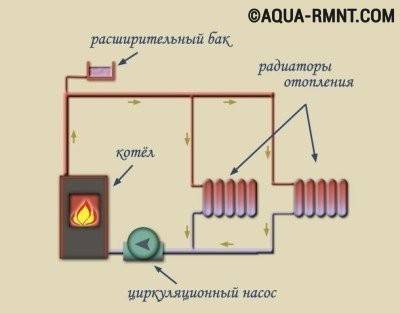
A scheme with forced circulation of water as a heat carrier can be used when installing heating in a house of any size. In this case, a pump of suitable power is selected and its uninterrupted power supply is ensured.
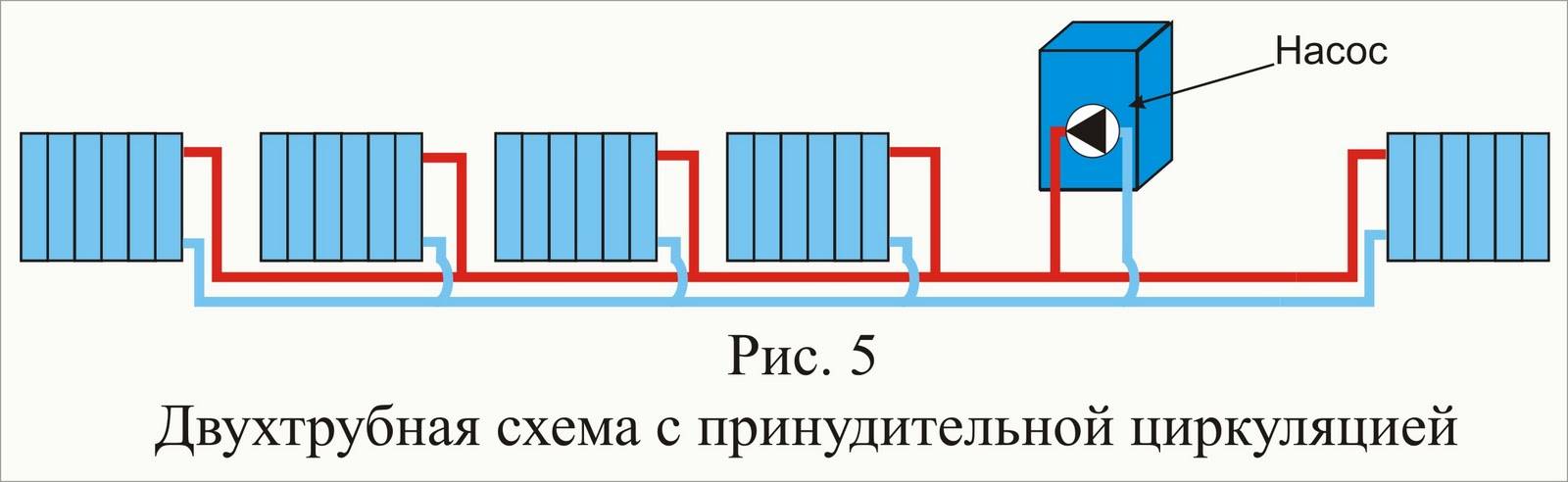
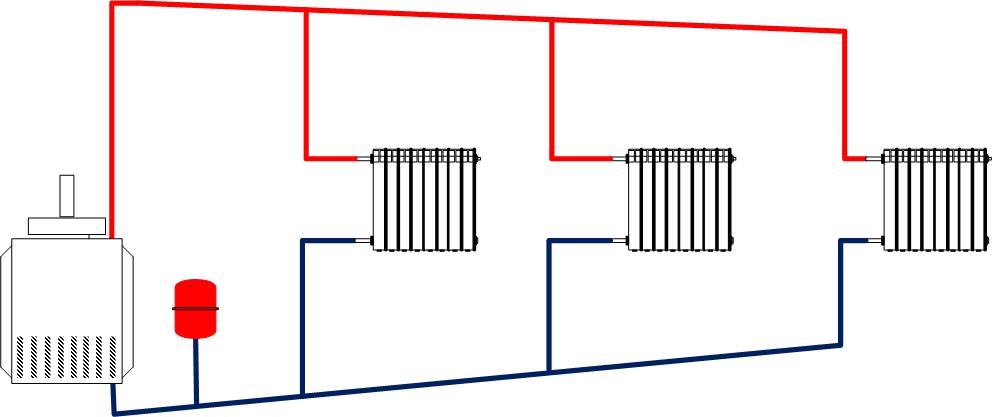
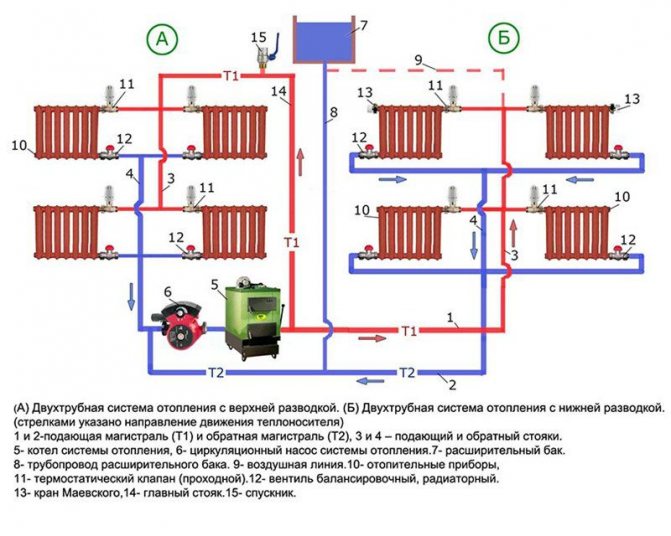
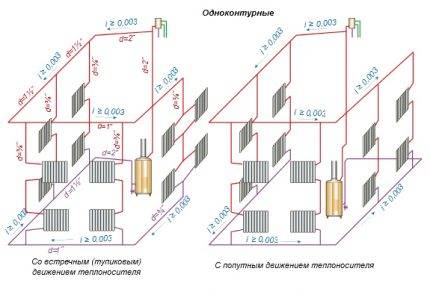
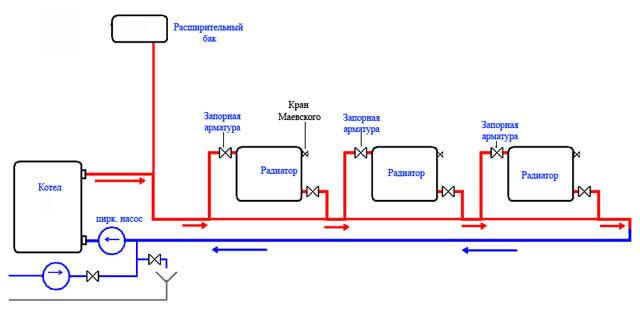
Two-pipe system with bottom wiring
Next, we will consider two-pipe systems, which are distinguished by the fact that they provide an even distribution of heat even in the largest households with many rooms. It is the two-pipe system that is used to heat multi-storey buildings, in which there are a lot of apartments and non-residential premises - here such a scheme works great. We will consider schemes for private houses.
Two-pipe heating system with bottom wiring.
A two-pipe heating system consists of a supply and return pipes. Radiators are installed between them - the radiator inlet is connected to the supply pipe, and the outlet to the return pipe. What does it give?
- Uniform distribution of heat throughout the premises.
- Possibility to regulate the temperature in the rooms by completely or partially blocking individual radiators.
- Possibility of heating multi-storey private houses.
There are two main types of two-pipe systems - with lower and upper wiring. To begin with, we will consider a two-pipe system with a bottom wiring.
Lower wiring is used in many private homes, as it allows you to make heating less visible. The supply and return pipes pass here next to each other, under the radiators or even in the floors. Air is removed through special Mayevsky taps. Heating schemes in a private house made of polypropylene most often provide for just such a wiring.
Advantages and disadvantages of a two-pipe system with bottom wiring
When installing heating with a lower wiring, we can hide the pipes in the floor.
Let's see what positive features two-pipe systems with bottom wiring have.
- The possibility of masking pipes.
- The possibility of using radiators with a bottom connection - this somewhat simplifies installation.
- Heat losses are minimized.
The ability to at least partially make heating less visible attracts many people. In the case of the bottom wiring, we get two parallel pipes running flush with the floor. If desired, they can be brought under the floors, providing for this possibility even at the design stage of the heating system and the development of a project for the construction of a private house.
If you use radiators with a bottom connection, it becomes possible to almost completely hide all the pipes in the floors - the radiators are connected here using special nodes.
As for the disadvantages, they are the need for regular manual removal of air and the need to use a circulation pump.
Features of mounting a two-pipe system with bottom wiring
Plastic fasteners for heating pipes of different diameters.
In order to mount the heating system according to this scheme, it is necessary to lay the supply and return pipes around the house. For these purposes, there are special plastic fasteners on sale. If radiators with side connection are used, we make a tap from the supply pipe to the upper side hole, and take the coolant through the lower side hole, directing it to the return pipe. We put air vents next to each radiator. The boiler in this scheme is installed at the lowest point.
It uses a diagonal connection of radiators, which increases their heat transfer. Lower connection of radiators reduces heat output.
Such a scheme is most often made closed, using a sealed expansion tank.The pressure in the system is created using a circulation pump. If you need to heat a two-story private house, we lay pipes on the upper and lower floors, after which we create a parallel connection of both floors to the heating boiler.
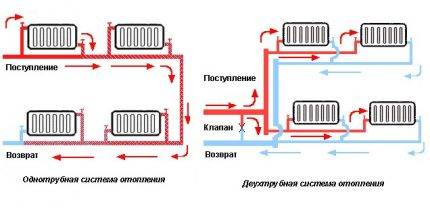
The difference between one-pipe and two-pipe systems
Water heating systems are divided into two main types - these are single-pipe and two-pipe. The differences between these schemes lies in the method of connecting heat-releasing batteries to the main.
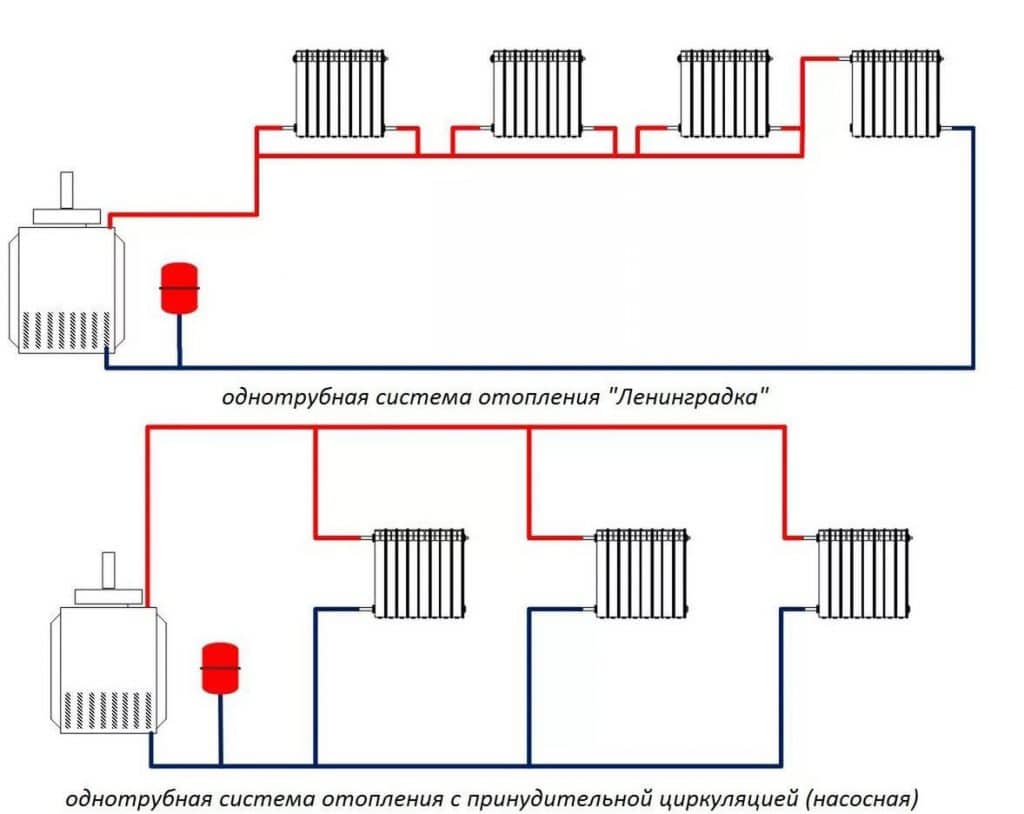
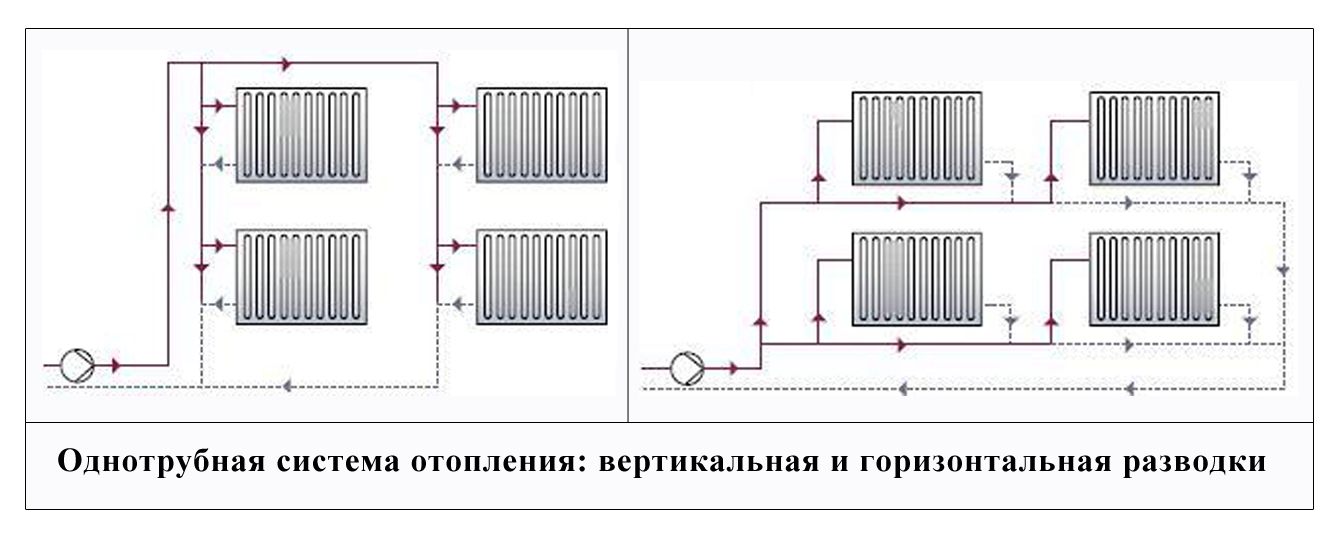
The single-pipe heating main is a closed ring circuit. The pipeline is laid from the heating unit, the radiators are connected to it in series, and lead back to the boiler.
Heating with one line is simply mounted and does not have a large number of components, therefore, it can significantly save on installation.
 Single-pipe heating circuits with natural movement of the coolant are suitable only with upper wiring. A characteristic feature - in the schemes there are risers of the supply line, but there are no risers for the return
Single-pipe heating circuits with natural movement of the coolant are suitable only with upper wiring. A characteristic feature - in the schemes there are risers of the supply line, but there are no risers for the return
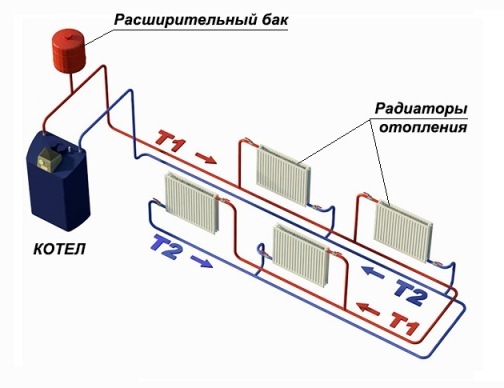
The movement of the coolant of two-pipe heating is carried out along two highways. The first one serves to deliver the hot coolant from the heating device to the heat-releasing circuits, the second one - to drain the cooled water to the boiler.
Heating batteries are connected in parallel - the heated liquid enters each of them directly from the supply circuit, therefore it has almost the same temperature.
In the radiator, the coolant gives off energy and, when cooled, goes into the outlet circuit - the "return". Such a scheme requires twice the number of fittings, pipes and fittings, however, it allows you to arrange complex branched structures and reduce heating costs by individually adjusting radiators.
The two-pipe system effectively heats large areas and multi-storey buildings. In low-rise (1-2 floors) houses with an area of \u200b\u200bless than 150 m², it is more expedient to arrange one-pipe heat supply from both an aesthetic and economic point of view.
 The two-pipe scheme for connecting radiators is not widely used in the individual heat supply of private houses, since it is more difficult to install and maintain. In addition, double the number of pipes looks unaesthetic
The two-pipe scheme for connecting radiators is not widely used in the individual heat supply of private houses, since it is more difficult to install and maintain. In addition, double the number of pipes looks unaesthetic
Features of single-pipe wiring
It is quite simple to install all the details of the system inside the house. In this case, it starts from the water supply point and ends at the heating equipment. Diagonal connection is the most effective, so it is chosen more often. An expansion tank must be placed in the building.
There is also a simpler option that is easy to implement on your own. In this case, it is necessary to put the door on the flight of stairs. This will isolate the floors from each other. This option is quite effective, although not very aesthetic.
Advice! Before wiring, it is necessary to study various schemes. Then it will be much easier to decide on the choice of system.
2 Requirements for arrangement and operation
According to the design features, two-pipe devices are a little more complicated and more expensive. But this is justified by some pluses that cover the shortcomings of the single-pipe version. Water is heated to a uniform temperature, and then simultaneously flows to all appliances.In turn, the cooled coolant is returned through the return pipe, and does not pass through the next radiator.

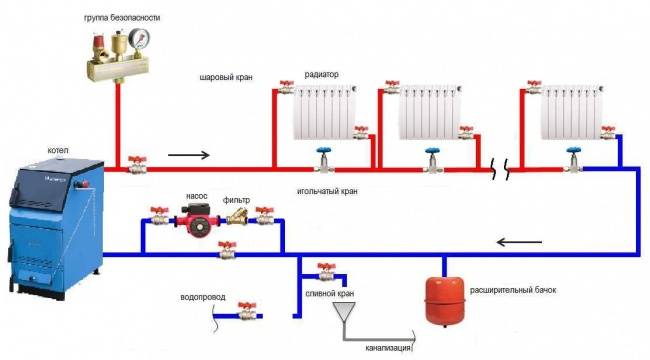
When equipping an open heating system with a pump and an expansion tank, it is necessary to highlight several rules and requirements for the work ahead. They are as follows:
- 1. At the installation stage, the boiler installation must be fixed at the lowest point of the line, and the expansion tank at the highest.
- 2. Ideally, the boiler should be located in the attic. During the cold period, the tank and the supply riser need to be insulated.
- 3. When laying the highway, a large number of turns, connecting and shaped elements should be avoided.
- 4. In gravitational systems, the circulation of the coolant is carried out at a low speed - no more than 0.1-0.3 m per second. Because of this, it is necessary to warm up the water gradually, avoiding boiling. Otherwise, the service life of the pipes will be significantly reduced.
- 5. If the heating system is not in operation during the cold season, it is better to drain the coolant. This approach will prevent premature damage to pipes, radiators and the boiler.
- 6. The volume of coolant in the expansion tank must be monitored and restored as the liquid is exhausted. If this is not done, the risk of air pockets will increase, which will reduce the efficiency of the radiators.
- 7. The best option for a coolant is water. The fact is that antifreeze contains toxic substances in its composition, and when interacting with the atmosphere, they can harm human health. This type of liquid can be used when it is not possible to drain the coolant during the cold period.
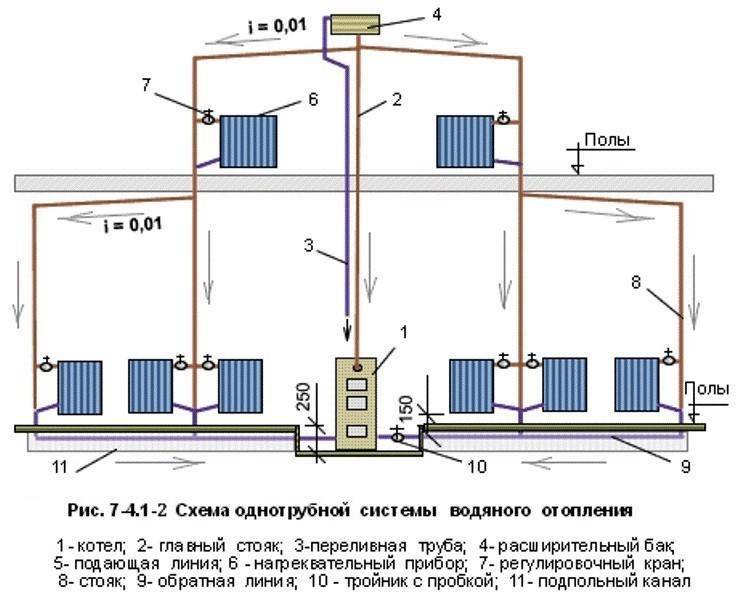
Current design standards are regulated by SNiP number 2.04.01-85. In circuits with gravitational circulation of liquid, the diameter of the pipe section is significantly larger than in systems with a pump.
Gravity circulation
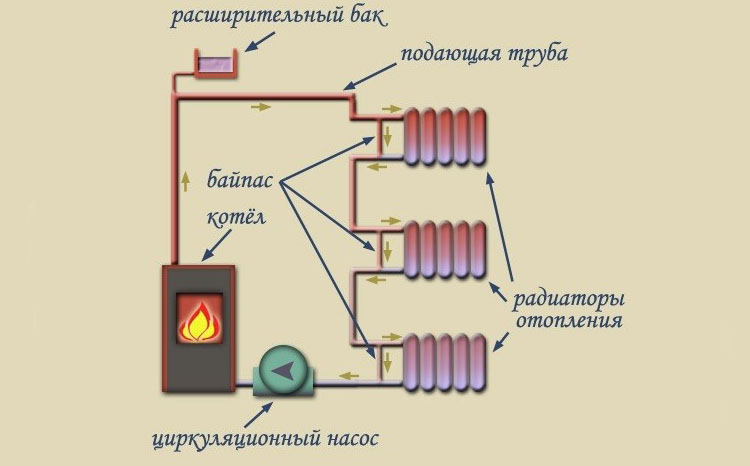
In systems where the coolant circulates naturally, there are no mechanisms to promote fluid movement. The process is carried out due to the expansion of the heated coolant. In order for this type of scheme to work effectively, an accelerating riser with a height of 3.5 meters or more is installed.
The main in the heating system with natural circulation of the liquid has some length restrictions, in particular, it should not exceed 30 meters. Therefore, such heat supply can be used in small buildings, in this case houses are considered the best option, the area of \u200b\u200bwhich does not exceed 60 m2. The height of the house and the number of floors are also of great importance when installing an accelerating riser. One more factor should be taken into account, in a natural circulation type heating system, the coolant must be heated to a certain temperature; in low-temperature mode, the required pressure is not created.
The scheme with the gravitational movement of a fluid has certain possibilities:
- Combination with underfloor heating systems. In this case, a circulation pump is installed on the water circuit leading to the heating elements. Otherwise, the operation is carried out in the usual mode, without stopping even in the absence of power supply.
- Boiler work. The device is installed in the upper part of the system, but at a lower level than the expansion tank is located.In some cases, a pump is installed on the boiler so that it runs smoothly. However, it should be understood that in such a situation the system becomes forced, which makes it necessary to install a check valve to prevent fluid recirculation.
general information
Basic moments
The absence of a circulation pump and generally moving elements and a closed circuit, in which the amount of suspensions and mineral salts is finite, makes the service life of this type of heating system very long. When using galvanized or polymer pipes and bimetallic radiators - at least half a century.
Natural heating circulation means a fairly small pressure drop. Pipes and heaters inevitably provide a certain resistance to the movement of the coolant. That is why the recommended radius of the heating system we are interested in is estimated at about 30 meters. Clearly, this does not mean that with a radius of 32 meters the water will freeze - the border is rather arbitrary.
The inertia of the system will be quite large. Several hours may elapse between the ignition or start-up of the boiler and the stabilization of the temperature in all heated rooms. The reasons are clear: the boiler will have to warm up the heat exchanger, and only then will the water begin to circulate, and rather slowly.
All horizontal sections of pipelines are made with a mandatory slope in the direction of water movement. It will ensure the free movement of cooling water by gravity with minimal resistance.
What is no less important - in this case, all air plugs will be forced out to the upper point of the heating system, where the expansion tank is mounted - sealed, with an air vent, or open.

All air will collect at the top.
Self-regulation
Home heating with natural circulation is a self-regulating system. The colder it is in the house, the faster the coolant circulates. How it works?
The fact is that the circulation pressure depends on:
Differences in height between the boiler and the bottom heater. The lower the boiler is relative to the lower radiator, the faster the water will overflow into it by gravity. The principle of communicating vessels, remember? This parameter is stable and unchanged during the operation of the heating system.
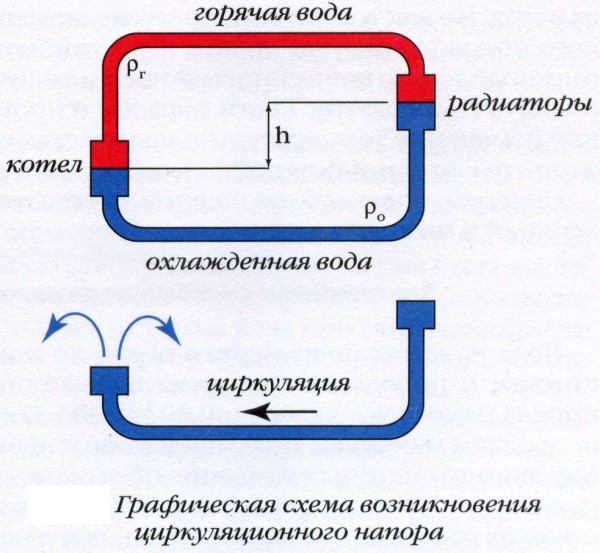
The diagram demonstrates the principle of operation of heating clearly.
Curious: that is why the heating boiler is recommended to be installed in the basement or just as low as possible indoors. However, the author has seen a perfectly functioning heating system in which the heat exchanger in the furnace furnace was noticeably higher than the radiators. The system was fully operational.
Differences in the density of water at the outlet of the boiler and in the return pipeline. Which, of course, is determined by the temperature of the water. And it is precisely thanks to this feature that natural heating becomes self-regulating: as soon as the temperature in the room drops, the heaters cool down.
With a drop in the temperature of the coolant, its density increases, and it begins to quickly displace the heated water from the lower part of the circuit.
Circulation rate
In addition to pressure, the circulation rate of the coolant will be determined by a number of other factors.
- Wiring pipe diameter. The smaller the internal section of the pipe, the greater the resistance it will provide to the movement of fluid in it. That is why for wiring in the case of natural circulation, pipes with a deliberately oversized diameter are taken - DN32 - DN40.
- Pipe material. Steel (especially corroded and covered with deposits) resists the flow several times more than, for example, a polypropylene pipe with the same cross section.
- The number and radius of turns. Therefore, the main wiring is best done as straight as possible.
- The presence, quantity and type of valves. a variety of retaining washers and pipe diameter transitions.

Each valve, each bend causes a pressure drop.
It is precisely because of the abundance of variables that an accurate calculation of a heating system with natural circulation is extremely rare and gives very approximate results. In practice, it is enough to use the recommendations already given.
Classification of water heating systems according to the principle of operation
According to the principle of operation, heating has natural and forced circulation of the coolant.
with natural circulation
Used to heat a small house. The coolant moves through the pipes due to natural convection.
Photo 1. Scheme of a water heating system with natural circulation. Pipes must be installed at a slight slope.
According to the laws of physics, a warm liquid rises. Water, heated in the boiler, rises, after which it descends through pipes to the last radiator in the system. Cooling down, the water enters the return pipe and returns to the boiler.
The use of systems operating with the help of natural circulation requires the creation of a slope - this simplifies the movement of the coolant. The length of the horizontal pipe cannot exceed 30 meters - the distance from the outermost radiator in the system to the boiler.
Such systems attract with their low cost, no additional equipment is required, they practically do not make noise when they work. The downside is that the pipes need a large diameter and should be laid as evenly as possible (there is almost no coolant pressure in them). It is impossible to heat a large building.
Forced circulation scheme
The scheme using the pump is more complicated. Here, in addition to heating batteries, a circulation pump is installed that moves the coolant through the heating system. It has higher pressure, so:
- It is possible to lay pipes with bends.
- It is easier to heat large buildings (even several floors).
- Suitable for small pipes.
Photo 2. Scheme of a heating system with forced circulation. A pump is used to move the coolant through the pipes.
Often these systems are made closed, which eliminates the ingress of air into the heaters and coolant - the presence of oxygen leads to metal corrosion. In such a system, closed expansion tanks are required, which are supplemented with safety valves and air vent devices. They will heat a house of any size and are more reliable in operation.
Mounting methods
For a small house consisting of 2-3 rooms, a single-pipe system is used. The coolant moves sequentially through all the batteries, reaches the last point and returns through the return pipe back to the boiler. Batteries connect from below. The downside is that the distant rooms warm up worse, as they receive a slightly cooled coolant.
Two-pipe systems are more perfect - a pipe is laid to the far radiator, and taps are made from it to the rest of the radiators.The coolant at the outlet of the radiators enters the return pipe and moves to the boiler. This scheme evenly heats all rooms and allows you to turn off unnecessary radiators, but the main disadvantage is the complexity of installation.
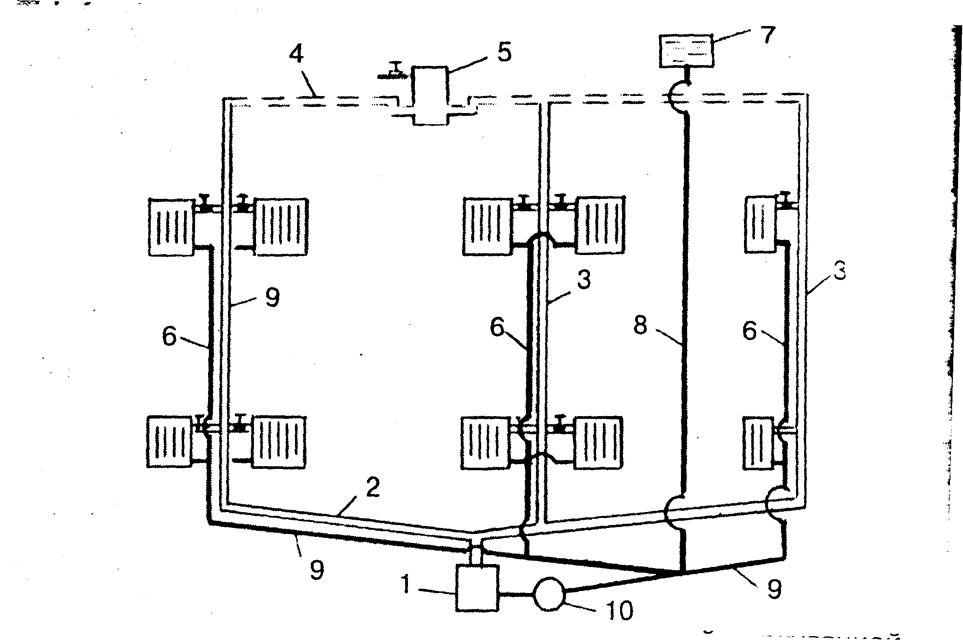
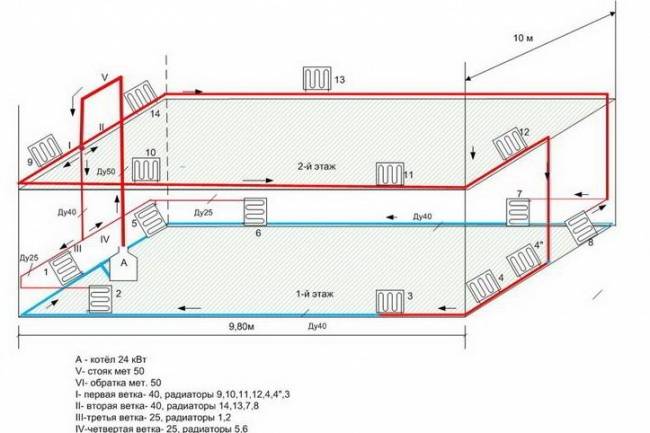
Collector heating
The main disadvantage of a one- and two-pipe system is the rapid cooling of the coolant; the collector connection system does not have this drawback.
Photo 3. Water collector heating system. A special distribution unit is used.
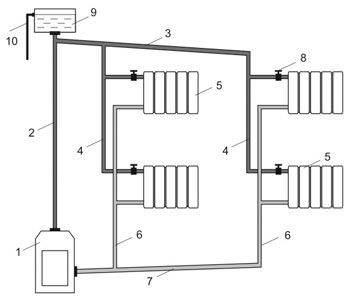
The main element and basis of collector heating is a special distribution unit, popularly called a comb. Special plumbing fittings necessary for the distribution of the coolant through separate lines and independent rings, a circulation pump, safety devices and an expansion tank.
The manifold assembly for a two-pipe heating system consists of 2 parts:
- Input - it is connected to a heating device, where it receives and distributes hot coolant along the circuits.
- Outlet - connected to the return pipes of the circuits, it is necessary to collect the cooled coolant and supply it to the boiler.
The main difference between the collector system is that any battery in the house is connected independently, which allows you to adjust the temperature of each or turn it off. Sometimes mixed wiring is used: several circuits are connected independently to the collector, but inside the circuit the batteries are connected in series.
The coolant delivers heat to the batteries with minimal losses, the efficiency of this system increases, which makes it possible to use a boiler of lower power and consume less fuel.
But the collector heating system is not without drawbacks, these include:
- Pipe consumption.You will need to spend 2-3 times more pipe than when connecting batteries in series.
- The need to install circulation pumps. Requires high pressure in the system.
- Energy dependence. Do not use where there may be power outages.
We calculate a single-pipe heating system ourselves
The main stages in the calculation of water heating:
- calculation of the required boiler power;
- calculation of the power of all heating devices that will be connected to the system;
- pipe sizing.
Boiler power indicators are calculated taking into account heat loss through the floors, walls and roof of the house
When determining the power, you need to pay attention to the surface area, the material of manufacture, as well as the difference in temperatures outside and inside the room during heating the house
Calculation of battery power and pipe size
You can calculate the required pipe diameter as follows:
- Determine the circulation pressure, which depends on the height and length of the pipes, as well as the temperature difference of the liquid at the outlet of the boiler;
- calculate the pressure loss in straight sections, turns and in each heating device.
It is very difficult for a person without special knowledge to perform such calculations, as well as to calculate the entire heating scheme with natural circulation. A small mistake will lead to huge heat losses. Therefore, it is best to entrust the calculations and subsequent installation of the heating system to specialists.
How to properly install heating
In order for the finished heating system with natural circulation to function correctly and efficiently, it is important to follow certain rules when installing it.
In general, the installation scheme looks like this:
- Heating radiators must be installed under the windows, preferably at the same level and with the necessary indents.
- Next, install the heat generator, that is, the selected boiler.
- Install the expansion tank.
- Pipes are laid and the previously fixed elements are joined into a single system.
- The heating circuit is filled with water and a preliminary check of the tightness of the connections is carried out.
- The final stage is to start the heating boiler. If everything works correctly, then the house will be warm.
Pay attention to some nuances:
- The boiler must be located at the lowest point in the system.
- The pipes must be installed with a slope towards the return flow.
- There should be as few turns in the pipeline as possible.
- To increase the efficiency of heating, pipes with a large diameter are needed.
We hope this article will be useful for you, and you will be able to independently mount a heating system without a circulation pump in your country house.
Theoretical horseshoe - how gravity works
The natural circulation of water in heating systems operates due to gravity. How does this happen:
- We take an open vessel, fill it with water and begin to heat it up. The most primitive option is a pan on a gas stove.
- The temperature of the lower liquid layer rises, the density decreases. The water becomes lighter.
- Under the influence of gravity, the upper heavier layer sinks to the bottom, displacing the less dense hot water. The natural circulation of fluid begins, called convection.
Example: if you heat 1 m³ of water from 50 to 70 degrees, it will become 10.26 kg lighter (below, see the table of densities at various temperatures).If heating continues to 90 °C, then the cube of liquid will lose 12.47 kg, although the temperature delta remains the same - 20 °C. Conclusion: the closer the water is to the boiling point, the more active the circulation occurs.
Similarly, the coolant circulates by gravity through the home heating network. The water heated by the boiler loses weight and is pushed up by the cooled coolant that has returned from the radiators. The flow velocity at a temperature difference of 20–25 °C is only 0.1…0.25 m/s versus 0.7…1 m/s in modern pumping systems.
The low speed of fluid movement along highways and heating devices causes the following consequences:
- The batteries have time to give off more heat, and the coolant cools down by 20–30 °C. In a conventional heating network with a pump and a membrane expansion tank, the temperature drops by 10–15 degrees.
- Accordingly, the boiler must produce more heat energy after the burner starts. Keeping the generator at a temperature of 40 ° C is pointless - the current will slow down to the limit, the batteries will become cold.
- To deliver the required amount of heat to the radiators, it is necessary to increase the flow area of the pipes.
- Fittings and fittings with high hydraulic resistance can worsen or completely stop gravity flow. These include non-return and three-way valves, sharp 90° turns and pipe constrictions.
- The roughness of the inner walls of pipelines does not play a big role (within reasonable limits). Low fluid velocity - low resistance from friction.
- A solid fuel boiler + gravity heating system can work without a heat accumulator and a mixing unit. Due to the slow flow of water, condensate does not form in the firebox.
As you can see, there are positive and negative moments in the convection movement of the coolant. The former should be used, the latter should be minimized.