- Types of forced circulation of heat carrier in heating
- Varieties of liquid autonomous heating systems
- Where to put
- forced circulation
- natural circulation
- Mounting Features
- Classification of water heating systems according to the principle of operation
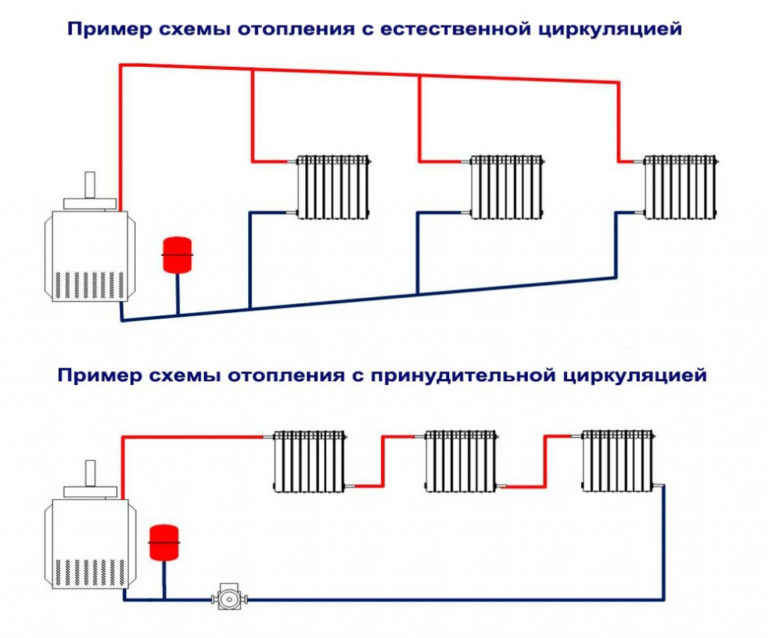
- with natural circulation
- Forced circulation scheme
- Mounting methods
- Collector heating
- The main elements of the heating system
- Boiler
- Universal boilers
- 3 Basic piping schemes - choose the best option
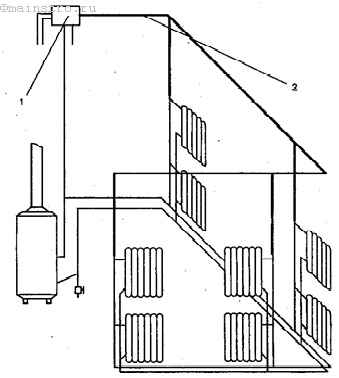
- Heating system with natural circulation
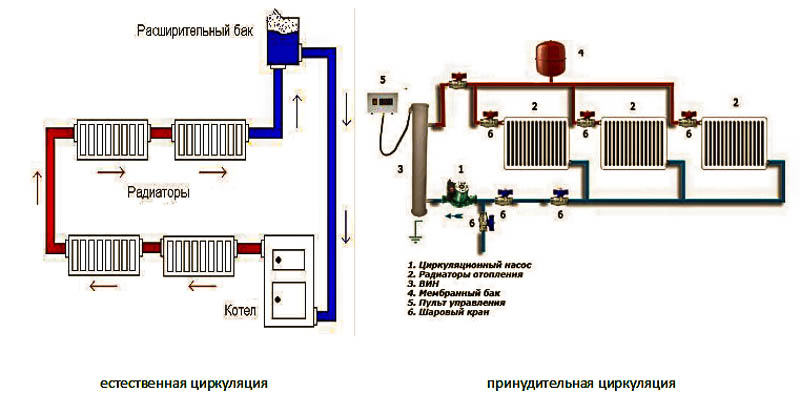
Types of forced circulation of heat carrier in heating
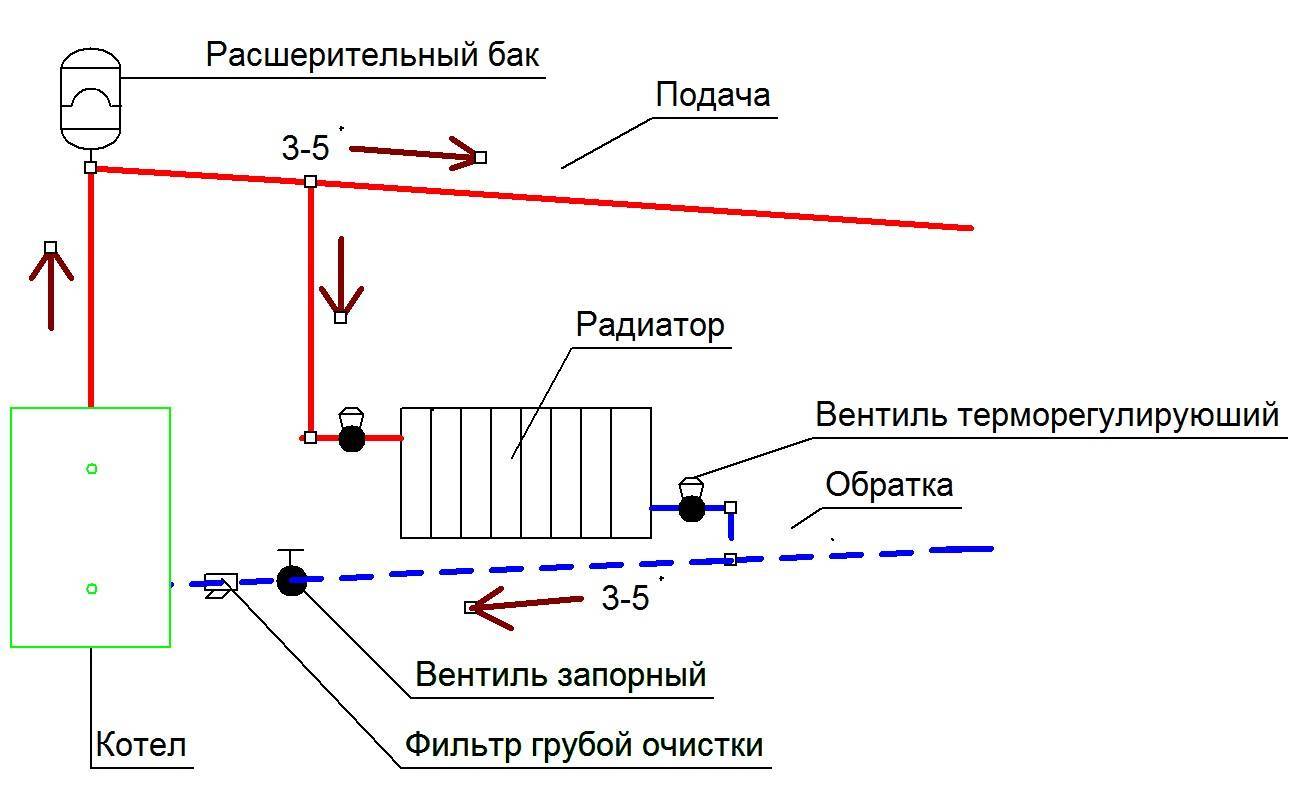
The use of forced circulation heating schemes in two-story houses is used due to the length of the system lines (more than 30 m). This method is carried out using a circulation pump that pumps the liquid of the circuit. It is mounted at the inlet to the heater, where the coolant temperature is the lowest.
With a closed circuit, the degree of pressure that the pump develops does not depend on the number of storeys and the area of \u200b\u200bthe building. The speed of the water flow becomes greater, therefore, when passing through the pipeline lines, the coolant does not cool down much.This contributes to a more even distribution of heat throughout the system and the use of the heat generator in a sparing mode.
The expansion tank can be located not only at the highest point of the system, but also near the boiler. To perfect the scheme, the designers introduced an accelerating collector into it. Now, if there is a power outage and the subsequent stop of the pump, the system will continue to work in convection mode.
- with one pipe
- two;
- collector.
Each can be mounted by yourself or invite specialists.
Variant of the scheme with one pipe
Shutoff valves are also mounted at the battery inlet, which serves to regulate the temperature in the room, as well as necessary when replacing equipment. An air bleed valve is installed on top of the radiator.
Battery valve
To increase the uniformity of heat distribution, radiators are installed along the bypass line. If you do not use this scheme, then you will need to select batteries of different capacities, taking into account the loss of heat carrier, that is, the farther from the boiler, the more sections.
The use of shut-off valves is optional, but without it, the maneuverability of the entire heating system is reduced. If necessary, you will not be able to disconnect the second or first floor from the network to save fuel.
To get away from the uneven distribution of the heat carrier, schemes with two pipes are used.
- dead end;
- passing;
- collector.
Options for dead-end and passing schemes
The associated option makes it easy to control the level of heat, but it is necessary to increase the length of the pipeline.
The collector circuit is recognized as the most effective, which allows you to bring a separate pipe to each radiator. Heat is distributed evenly.There is one minus - the high cost of equipment, as the amount of consumables increases.
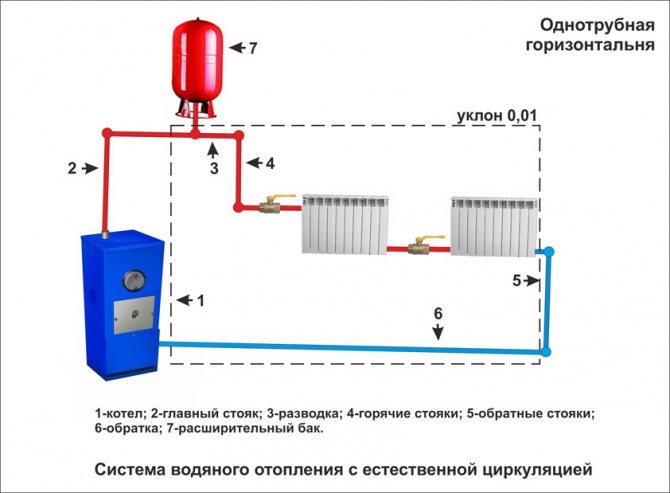
Scheme of collector horizontal heating
There are also vertical options for supplying heat carrier, which are found with the lower and upper wiring. In the first case, the drain with the supply of a heat carrier passes through the floors, in the second, the riser goes up from the boiler to the attic, where pipes are routed to the heating elements.
Vertical layout
Two-story houses can have a very different area, ranging from a few tens to hundreds of square meters. They also differ in the location of the rooms, the presence of outbuildings and heated verandas, the position to the cardinal points. Focusing on these and many other factors, you should decide on the natural or forced circulation of the coolant.
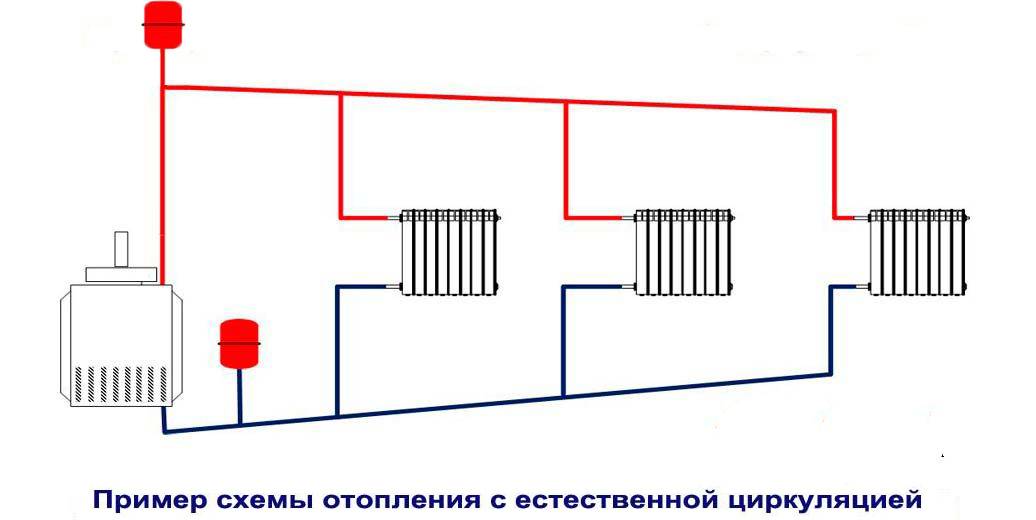
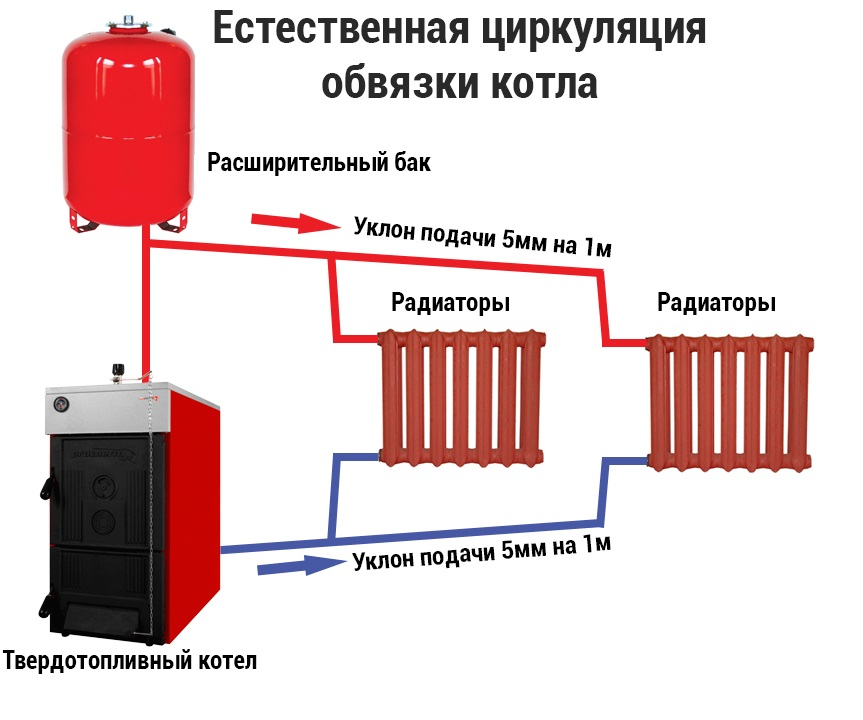
A simple scheme of coolant circulation in a private house with a natural circulation heating system.
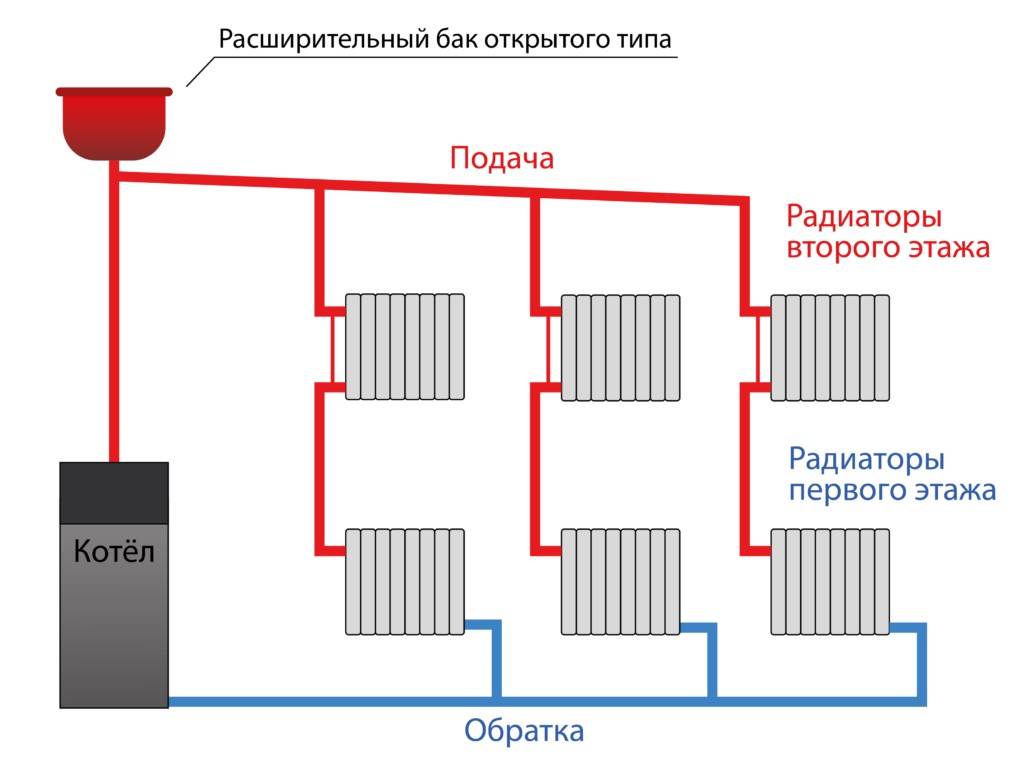
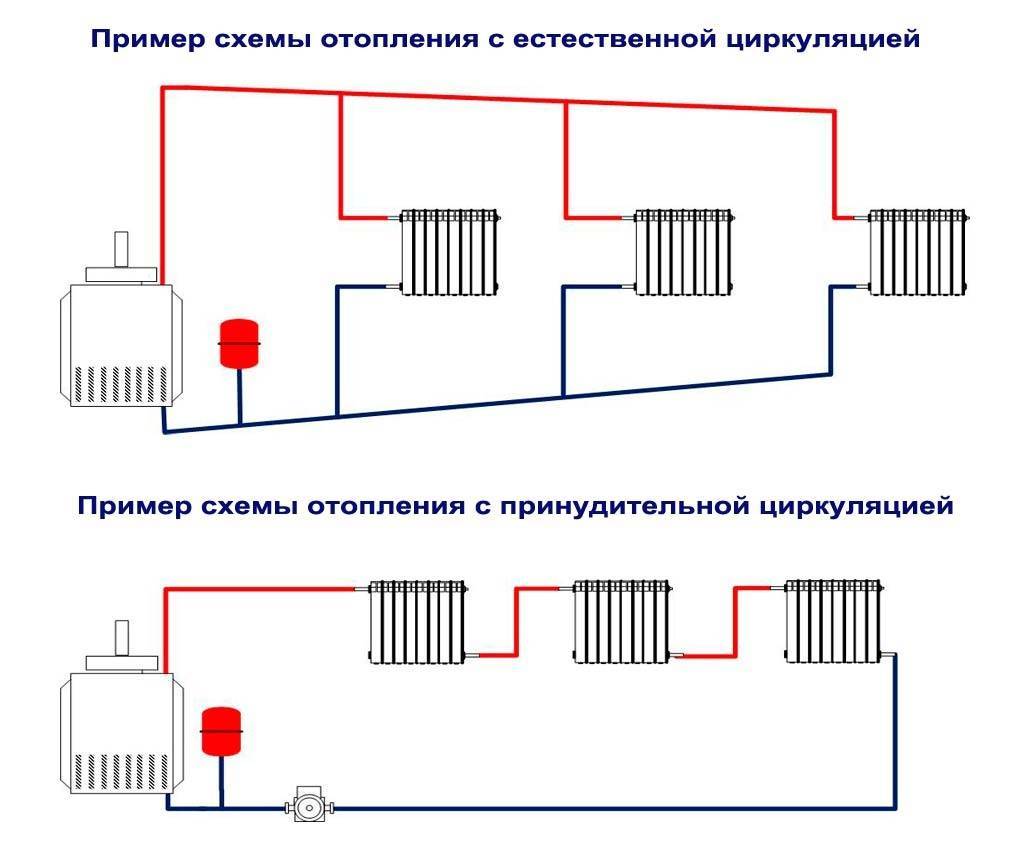
Heating schemes with natural circulation of the coolant are distinguished by their simplicity. Here, the coolant moves through the pipes on its own, without the help of a circulation pump - under the influence of heat, it rises up, enters the pipes, is distributed over the radiators, cools down and enters the return pipe to go back to the boiler. That is, the coolant moves by gravity, obeying the laws of physics.
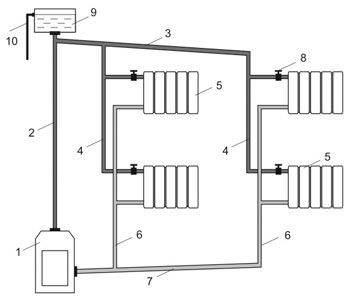
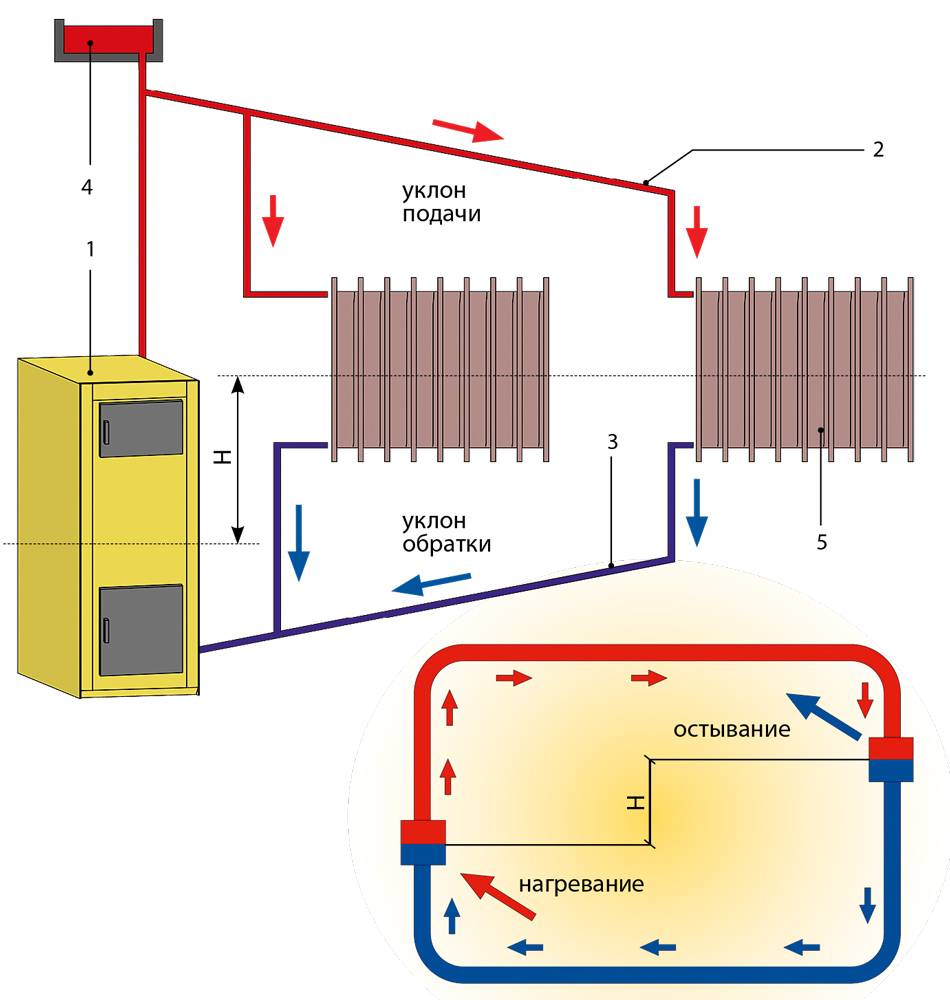
Scheme of a closed two-pipe heating system of a two-story house with forced circulation
- More uniform heating of the entire household;
- Significantly longer horizontal sections (depending on the power of the pump used, it can reach several hundred meters);
- Possibility of more efficient connection of radiators (for example, diagonally);
- Possibility of mounting additional fittings and bends without the risk of pressure drop below the minimum limit.
Thus, in modern two-story houses, it is best to use heating forced circulation systems. It is also possible to install a bypass, which will help you choose between forced or natural circulation in order to select the most optimal option. We make a choice towards coercive systems, as more effective.
Forced circulation has a couple of disadvantages - this is the need to purchase a circulation pump and the increased noise level associated with its operation.
Varieties of liquid autonomous heating systems
Heating systems for heating an individual house using water and non-freezing liquids (antifreeze) as a coolant differ in a number of ways, the main differences are:
By type of fuel used. The most popular types of energy for heating heat carriers are electricity, gas, liquid combustible hydrocarbon mixtures (diesel fuel, fuel oil, oil, kerosene), a large number of solid combustible materials - firewood, coal, peat briquettes and pellets of various compositions. Electricity can be generated both from energy companies and independently using solar panels, wind or hydraulic generators.
By type of heat generators. In modern heating systems, heating boilers are used to transfer energy to the coolant, which have design features and differences between analogues for each type of fuel.With a lack of funds, many craftsmen assemble independent heating with their own hands, using instead of factory boilers self-assembled structures mainly on solid fuels, a typical example is a metal stove in a residential area with an expansion tank in the attic and a steel piping system with radiators.
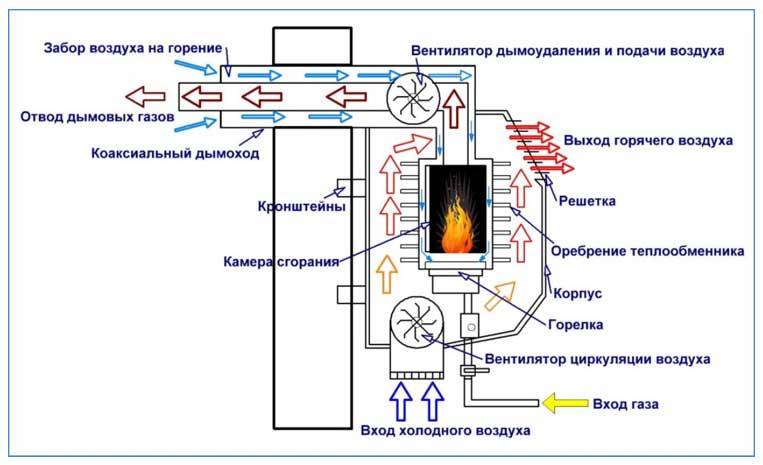
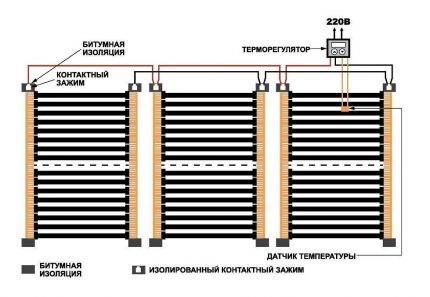
Rice. 7 The principle of operation and the main components of the gas convector
According to the material of the pipeline. Polymeric pipes made of PP polypropylene, cross-linked polyethylene and PEX metal-plastic are gradually replacing metal products; at old buildings, external steel pipelines are still used to supply water to radiators. Some homeowners, with significant financial resources, make the coolant supply through copper pipelines completely or in separate sections. Modern advanced systems are mounted from special thin-walled steel pipes using a crimping technology for connecting elements of sanitary fittings using fittings.
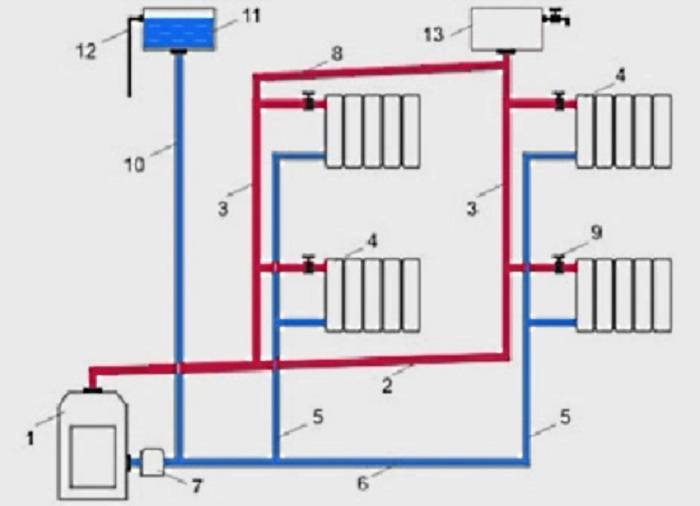
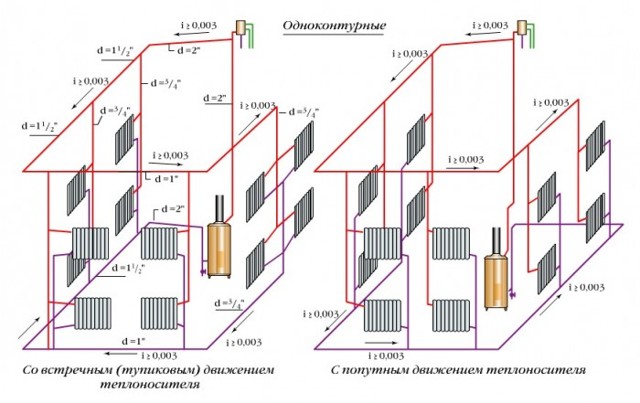
According to the method of supplying the coolant to the heat exchangers. There are 2 main ways to supply heated liquid to the pipes of heating radiators - one-pipe and two-pipe, sometimes a combined connection is used. To connect the underfloor heating pipeline, collector wiring is used, which allows several circuits to be connected to one distribution unit, systems from a large number of radiators are connected through hydraulic arrows or radiator manifolds. When connecting heat exchange radiators, various piping layouts are used - radial, dead-end, associated, special horizontal (Leningrad).
There are also various ways to connect the inlet and outlet pipes of heat exchange radiators to the heat main - vertical, horizontal, diagonal, bottom.
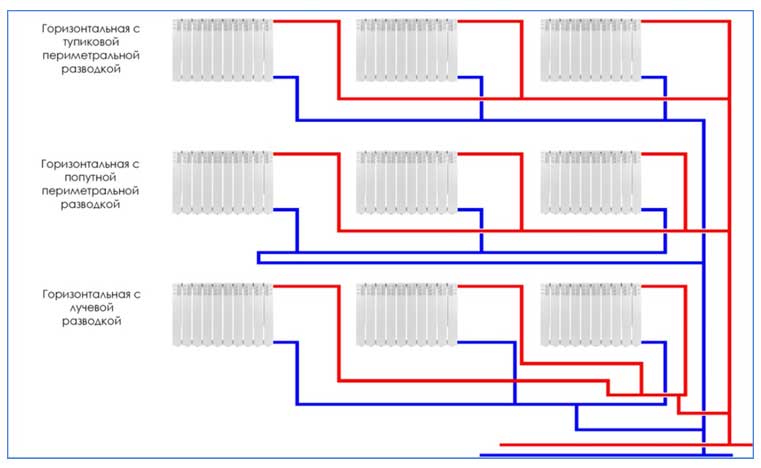
Rice. 8 Piping diagrams
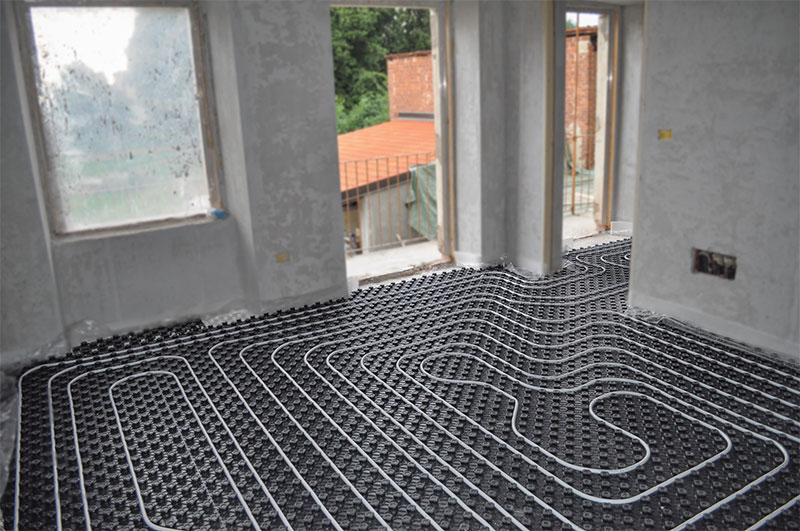
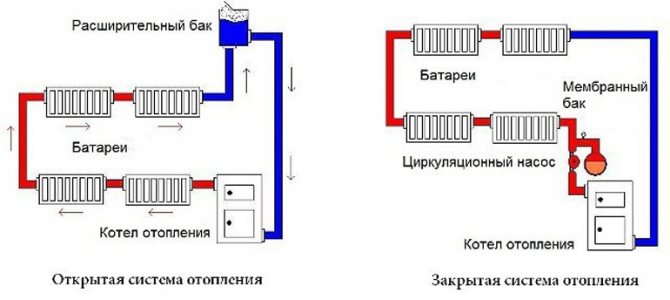
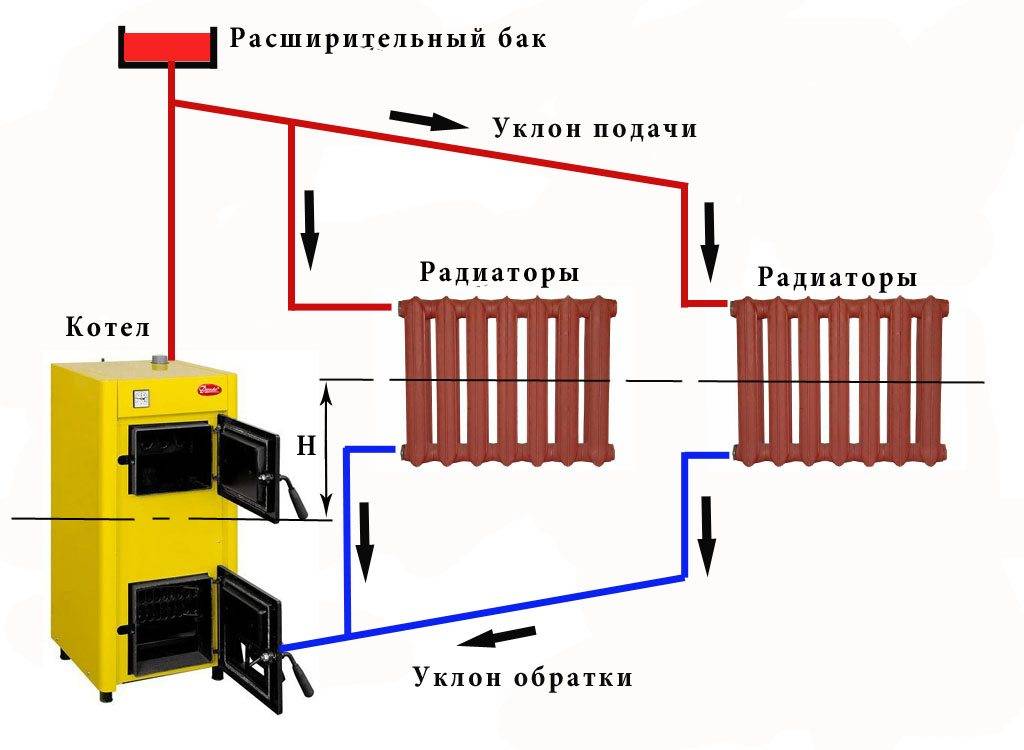
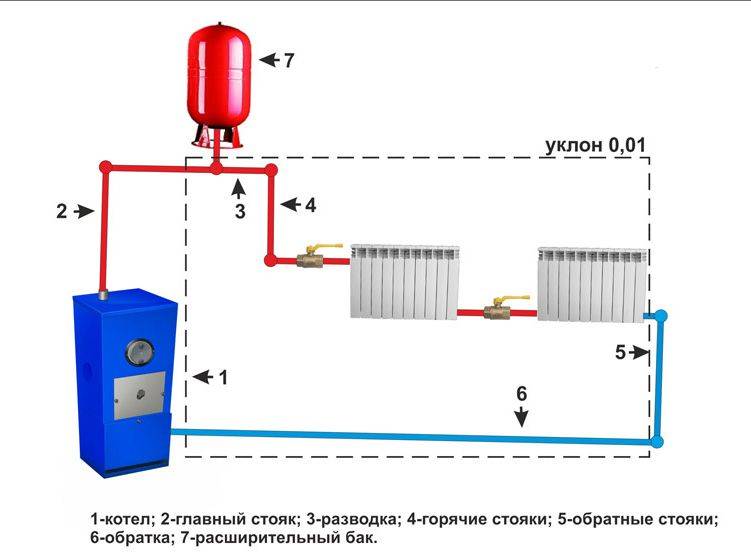
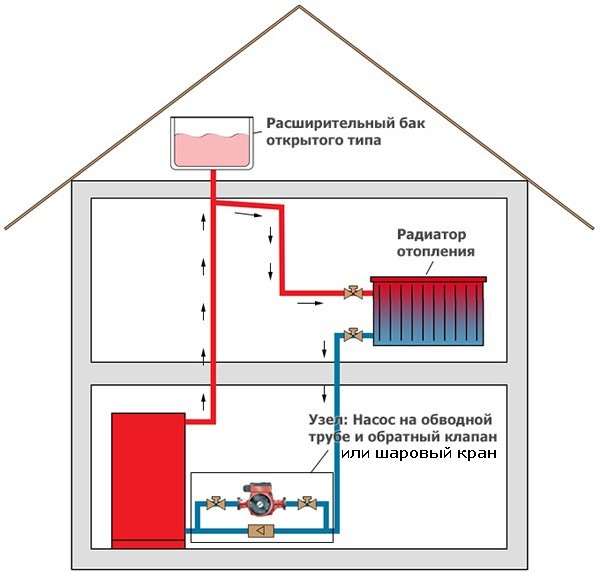
According to the location of the storage tank. The expansion tank, which is an important element of any heating system, can be factory-made sealed (red accumulator) and mounted in the circuit in any convenient place - such systems are called closed, since there is no direct access to the coolant. The movement of liquid through the pipeline in systems of this type is carried out using a circulating electric pump installed at the bottom near the boiler next to the hydraulic accumulator.
In another type of heating systems, called gravity, the storage tank is installed at the top in the attic, the pipelines have a slight slope when approaching the radiators, at their exit a small angle of inclination is maintained towards the boiler. The circulation of liquid in the system occurs by gravity due to the fact that heated water or antifreeze have a lower density and therefore are pushed upward by denser cold layers.
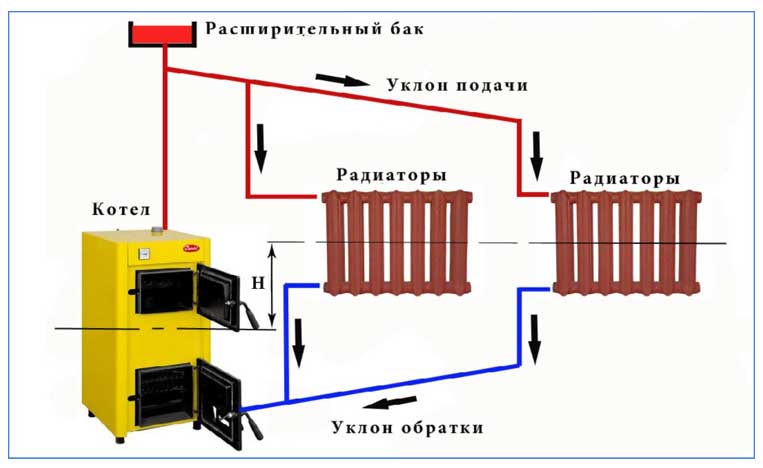
Rice. 9 Open heating system
Where to put
It is recommended to install a circulation pump after the boiler, before the first branch, but it does not matter on the supply or return pipeline. Modern units are made from materials that normally tolerate temperatures up to 100-115 ° C. There are few heating systems that work with a hotter coolant, therefore considerations of a more “comfortable” temperature are untenable, but if you are so calmer, put it in the return line.
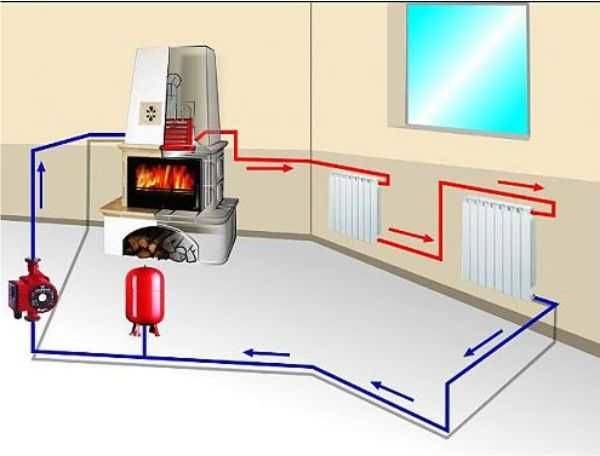
Can be installed in the return or direct pipeline after/before the boiler up to the first branch
There is no difference in hydraulics - the boiler, and the rest of the system, it does not matter whether there is a pump in the supply or return branch. What matters is the correct installation, in the sense of tying, and the correct orientation of the rotor in space
Nothing else matters
There is one important point at the installation site. If there are two separate branches in the heating system - on the right and left wings of the house or on the first and second floors - it makes sense to put a separate unit on each, and not one common one - directly after the boiler. Moreover, the same rule is preserved on these branches: immediately after the boiler, before the first branch in this heating circuit. This will make it possible to set the required thermal regime in each of the parts of the house independently of the other, as well as save on heating in two-story houses. How? Due to the fact that the second floor is usually much warmer than the first floor and much less heat is required there. If there are two pumps in the branch that goes up, the speed of the coolant is set much less, and this allows you to burn less fuel, and without compromising the comfort of living.
There are two types of heating systems - with forced and natural circulation. Systems with forced circulation cannot work without a pump, with natural circulation they work, but in this mode they have a lower heat transfer. However, less heat is still much better than no heat at all, so in areas where electricity is often cut off, the system is designed as hydraulic (with natural circulation), and then a pump is slammed into it.This gives high efficiency and reliability of heating. It is clear that the installation of a circulation pump in these systems has differences.

All heating systems with underfloor heating are forced - without a pump, the coolant will not pass through such large circuits
forced circulation
Since a forced circulation heating system is inoperative without a pump, it is installed directly into the gap in the supply or return pipe (of your choice).
Most problems with the circulation pump arise due to the presence of mechanical impurities (sand, other abrasive particles) in the coolant. They are able to jam the impeller and stop the motor. Therefore, a strainer must be placed in front of the unit.

Installing a circulation pump in a forced circulation system
It is also desirable to install ball valves on both sides. They will make it possible to replace or repair the device without draining the coolant from the system. Turn off the taps, remove the unit. Only that part of the water that was directly in this piece of the system is drained.
natural circulation
The piping of the circulation pump in gravity systems has one significant difference - a bypass is required. This is a jumper that makes the system operational when the pump is not running. One ball shut-off valve is installed on the bypass, which is closed all the time while pumping is in operation. In this mode, the system works as a forced one.
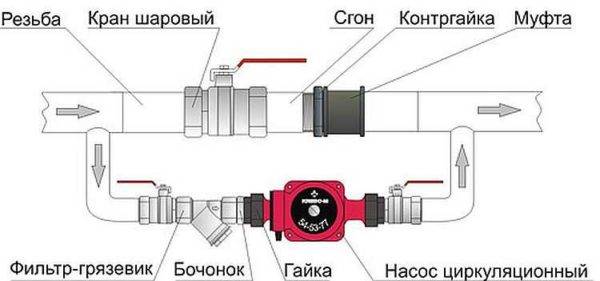
Scheme of installation of a circulation pump in a system with natural circulation
When electricity fails or the unit fails, the faucet on the jumper is opened, the faucet leading to the pump is closed, the system works like a gravitational one.
Mounting Features
There is one important point, without which the installation of the circulation pump will require alteration: it is required to turn the rotor so that it is directed horizontally. The second point is the direction of the flow. There is an arrow on the body indicating in which direction the coolant should flow. So turn the unit around so that the direction of movement of the coolant is “in the direction of the arrow”.
The pump itself can be installed both horizontally and vertically, only when choosing a model, see that it can work in both positions. And one more thing: with a vertical arrangement, the power (created pressure) drops by about 30%. This must be taken into account when choosing a model.
Classification of water heating systems according to the principle of operation
According to the principle of operation, heating has natural and forced circulation of the coolant.
with natural circulation
Used to heat a small house. The coolant moves through the pipes due to natural convection.
Photo 1. Scheme of a water heating system with natural circulation. Pipes must be installed at a slight slope.
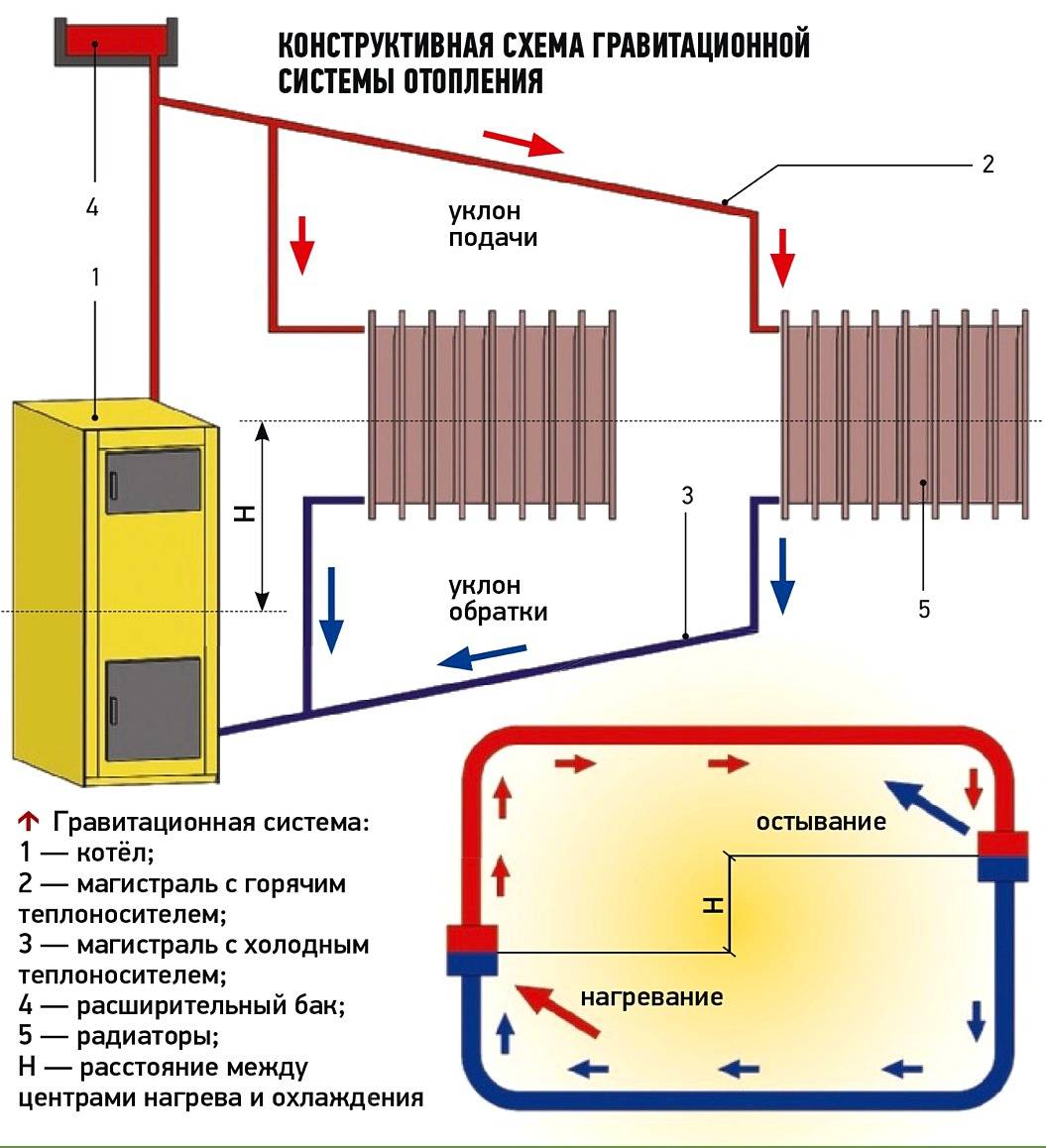
According to the laws of physics, a warm liquid rises. Water, heated in the boiler, rises, after which it descends through pipes to the last radiator in the system. Cooling down, the water enters the return pipe and returns to the boiler.
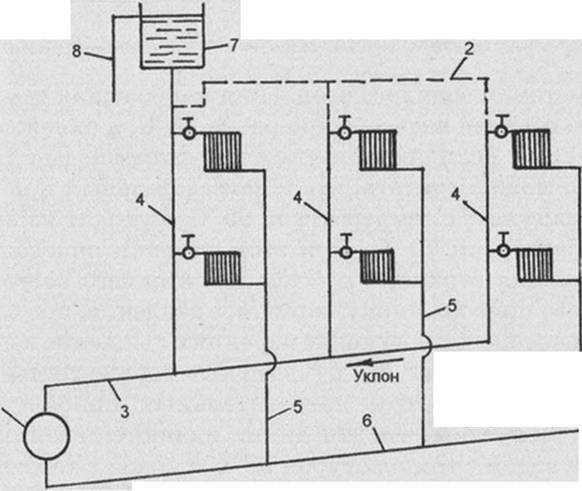
The use of systems operating with the help of natural circulation requires the creation of a slope - this simplifies the movement of the coolant. The length of the horizontal pipe cannot exceed 30 meters - the distance from the outermost radiator in the system to the boiler.
Such systems attract with their low cost, no additional equipment is required, they practically do not make noise when they work. The downside is that the pipes need a large diameter and should be laid as evenly as possible (there is almost no coolant pressure in them). It is impossible to heat a large building.
Forced circulation scheme
The scheme using the pump is more complicated. Here, in addition to heating batteries, a circulation pump is installed that moves the coolant through the heating system. It has higher pressure, so:
- It is possible to lay pipes with bends.
- It is easier to heat large buildings (even several floors).
- Suitable for small pipes.
Photo 2. Scheme of a heating system with forced circulation. A pump is used to move the coolant through the pipes.
Often these systems are made closed, which eliminates the ingress of air into the heaters and coolant - the presence of oxygen leads to metal corrosion. In such a system, closed expansion tanks are required, which are supplemented with safety valves and air vent devices. They will heat a house of any size and are more reliable in operation.
Mounting methods
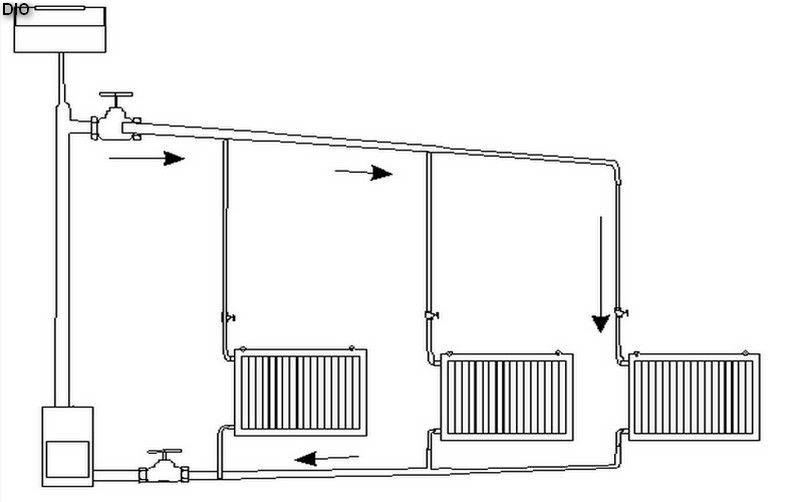
For a small house consisting of 2-3 rooms, a single-pipe system is used. The coolant moves sequentially through all the batteries, reaches the last point and returns through the return pipe back to the boiler. Batteries connect from below. The downside is that the distant rooms warm up worse, as they receive a slightly cooled coolant.
Two-pipe systems are more perfect - a pipe is laid to the far radiator, and taps are made from it to the rest of the radiators.The coolant at the outlet of the radiators enters the return pipe and moves to the boiler. This scheme evenly heats all rooms and allows you to turn off unnecessary radiators, but the main disadvantage is the complexity of installation.
Collector heating
The main disadvantage of a one- and two-pipe system is the rapid cooling of the coolant; the collector connection system does not have this drawback.
Photo 3. Water collector heating system. A special distribution unit is used.
The main element and basis of collector heating is a special distribution unit, popularly called a comb. Special plumbing fittings necessary for the distribution of the coolant through separate lines and independent rings, a circulation pump, safety devices and an expansion tank.
The manifold assembly for a two-pipe heating system consists of 2 parts:
- Input - it is connected to a heating device, where it receives and distributes hot coolant along the circuits.
- Outlet - connected to the return pipes of the circuits, it is necessary to collect the cooled coolant and supply it to the boiler.
The main difference between the collector system is that any battery in the house is connected independently, which allows you to adjust the temperature of each or turn it off. Sometimes mixed wiring is used: several circuits are connected independently to the collector, but inside the circuit the batteries are connected in series.
The coolant delivers heat to the batteries with minimal losses, the efficiency of this system increases, which makes it possible to use a boiler of lower power and consume less fuel.
But the collector heating system is not without drawbacks, these include:
- Pipe consumption.You will need to spend 2-3 times more pipe than when connecting batteries in series.
- The need to install circulation pumps. Requires high pressure in the system.
- Energy dependence. Do not use where there may be power outages.
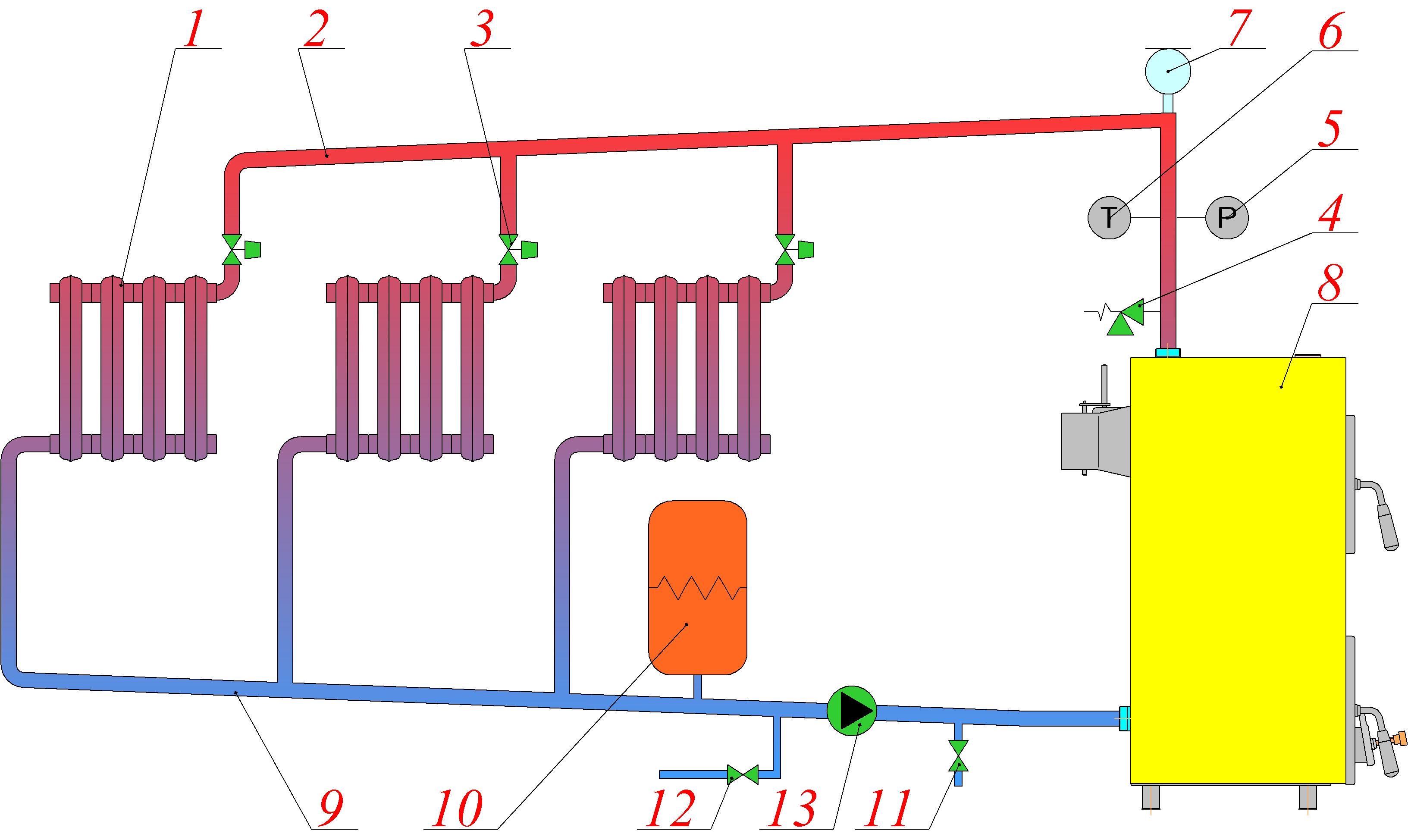
The main elements of the heating system
The heating system, which can work offline, consists of a huge number of different elements. In order to clearly understand and imagine the principle of operation of such a system, one should understand the purpose and principle of operation of its individual components.
Boiler
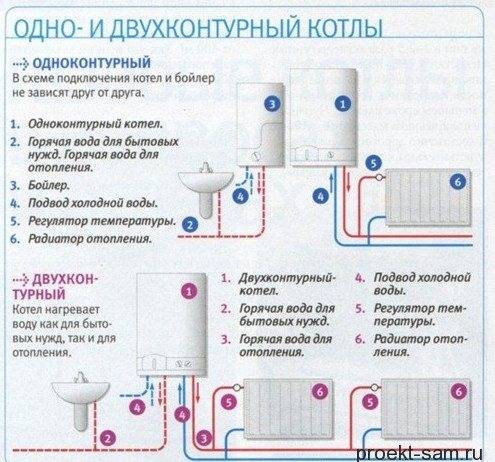
The boiler is the most important part of any heating system, since it is in it that the combustion of fuel occurs and heat appears. To date, two types of boilers are manufactured, which differ from each other in their functional features: single and double-circuit. It is these types that are used in most projects of private houses with a boiler room.
Single-circuit boilers can perform one single function - heating the house, while double-circuit boilers can also heat water. Despite the fact that a double-circuit boiler is more popular, it is considered less reliable than a single-circuit boiler. The reason is as follows: if the double-circuit boiler fails, then the whole house will remain not only without heat, but also with hot water. If a single-circuit boiler fails, then the house will be left without heat, but a small supply of hot water will still be present.
The difference between single-circuit and double-circuit boilers
Double-circuit boilers are equipped with special devices, thanks to which water is heated, and in single-circuit devices it is heated directly in the boiler itself, then moves along the radiators, after which it returns to the boiler again.
Depending on the type of installation, boilers are divided into floor and wall. Suspended boilers, where mainly gas atmospheric burners are used, are much better adapted to fluctuations in gas pressure in the main pipelines (since floor-mounted ones fail much faster in such situations).
Installation diagram of a single-circuit wall-mounted heating boiler
Universal boilers
Such boilers allow the use of almost any type of fuel, but a specialized boiler will be the most efficient, for example, for solid fuel or for heating with diesel fuel. The heat supply project is obliged to show the owner of the house what the efficiency of different boilers is, how much gas, coal, firewood or diesel fuel will cost.
Of course, universal boilers may seem like obsolete devices to some, but fuel industry technologies are constantly evolving. For example, a boiler designed for special fuel briquettes is a high-tech and quite environmentally friendly heating system. Of course, there will be smoke and other products of wood combustion, but everything is not as critical as it was in London in the 18th century, when the sky was not visible from the smoke of fireplaces. Technology has changed, and quite dramatically.
3 Basic piping schemes - choose the best option
Heating circuits, assuming the natural circulation of the coolant, have two main options (diagrams) for the device:
- single-pipe, when the supply and discharge of fluid from the batteries occurs through one pipe;
- two-pipe - the supply of coolant and its removal from the radiators is carried out by various pipelines.

A single pipe system is easier to install
The single pipe circuit is easy to install. A riser departs from the boiler, which is raised as high as possible within the room. From the upper point of the riser, an accelerating pipe departs and descends almost to the floor level, smoothly passing into the supply pipeline. Batteries are alternately connected to the communication along its course using two pipes of a smaller diameter (with a two-inch pipeline, ¾ inch bends are usually used). Having “served” all the radiators, the pipeline turns into a “return”, which goes to the boiler. A single-pipe wiring system is good only for its simplicity of construction and relative aesthetics (the pipes are visible, but located low). Then there are some shortcomings.
Due to the fact that the cooled coolant from the batteries flows into the same pipe from which the hot liquid comes, the temperature of the water after passing through each radiator drops quite quickly. If communication delivers a coolant with a temperature of 85 degrees to the first battery (for example), then the heater farthest from the boiler can only be counted on at 60 degrees. Hence the uneven heating, which has to be compensated by adding sections to the batteries moving away from the boiler, so the extreme radiators are often bulky and heavy (especially if cast iron).
It is possible to connect batteries with single-pipe wiring only from below (inlet and outlet), and this is the most inefficient way to connect radiators (they warm up unevenly, which affects the quality of heating).Diagonal connection of radiators is possible if the supply pipe is laid above the batteries, but this is already a two-pipe scheme.
With a two-pipe wiring, a supply pipe located under the ceiling departs from the riser. Branch pipes descend from it to each battery (connected in the upper position). At the bottom there is a second, return pipe, into which the outlet pipes from the radiators flow (they are connected to the radiators in the lower position diagonally). From the point of view of aesthetics, the picture is not very good, but in terms of efficiency, such a system is much better. Liquid of the same temperature is suitable for each battery, which ensures uniform heating of all rooms, plus it is possible to connect more number of heaters.
Heating system with natural circulation

Water heating systems according to the nature of the movement of the coolant are divided into 2 types:
- Forced circulation system;
- Natural circulation system.
Forced circulation of water in the heating system is provided by a pumping unit installed separately or built into the heating boiler. Natural circulation is realized due to the thermophysical properties of water.
The principle of natural circulation is based on the occurrence of the movement of water of different densities. The water is heated in the boiler and rises up the supply pipeline. Since water is an incompressible liquid, a portion of hot water, when rising, shifts the mass of water of the entire system. At the same time, a portion of cold water enters the boiler, heats up and rises again. As a result, a constant regime of fluid movement in the network is formed due to heating of the coolant in the boiler. The circulation is supported by the slope of the pipelines.
The advantage of this type of heating is complete independence from the availability of electricity. Natural heating of a private house has a number of disadvantages:
- Low speed of movement of the coolant;
- Difficulty in regulating system temperature;
- Restrictions in the choice of materials for installation;
- Exceptionally open pipe laying method.
The instrument piping scheme for natural circulation is single-pipe, sequential. Therefore, each radiator in the circuit is colder than the previous one. The construction of a jumper in this case is impossible. The low water speed reduces the uniformity of heating of the heating devices - the radiators near the boiler are hot, the last ones in the row are barely warm.
Adjustment of the heating temperature is possible only enlarged - regulation of the flow rate to a separate circuit (group of radiators).
The limitation in the choice of material is caused by the need to use pipes with a diameter of at least 40 mm. Smaller diameter pipes can practically stop circulation. The use of polymer pipes is not recommended - they serve as a heat insulator, while steel pipes act as heating surfaces. As heating appliances use cast-iron radiators or registers made of steel pipes with a diameter of 70 - 100 mm.