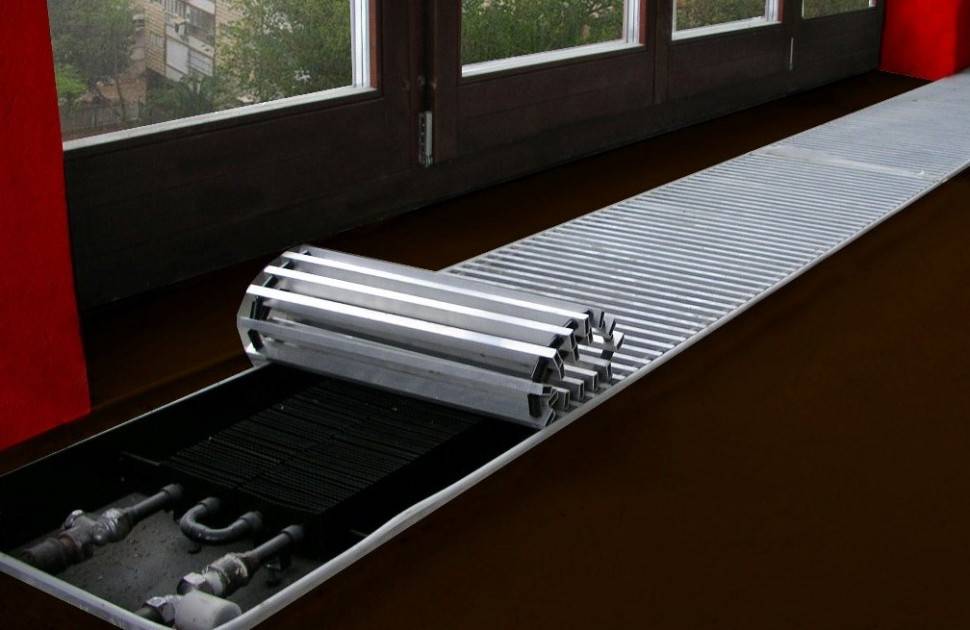
- Installation of the heating structure "Leningradka"
- What is the best material for the pipeline?
- Connection of radiators and pipes
- Starting the heating structure
- Heating network wiring diagrams
- Vertical wiring
- Horizontal wiring
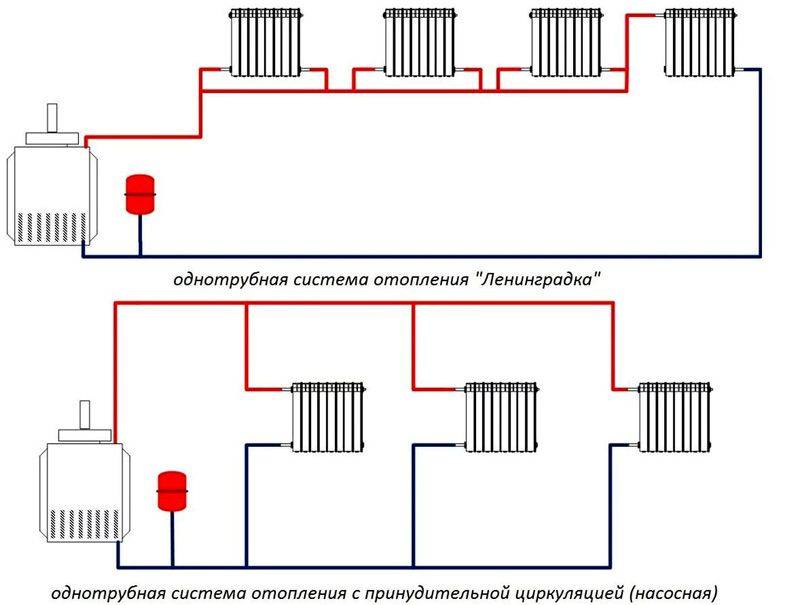
- Gravity and forced circulation
- Characteristics of Leningradka
- A brief overview of the main heating schemes
- Versions
- vertical
- Horizontal
- Leningrad system with a pump
- The principle of operation of the circuit
- Advantages and disadvantages
- Scheme with a pump
- Installation technology of the Leningrad system in a private house
- Selection of radiators and pipelines
- Mounting technology
- DIY installation recommendations
Installation of the heating structure "Leningradka"

Before you start building the heating system of a private house with your own hands, you need to perform a competent and accurate calculation. It will be problematic to do this on your own, so it is better to turn to professionals in this industry. Using the calculation, you can determine the list of equipment and materials necessary for the work.
The main elements of "Leningradka" include the following:
- boiler for heating the coolant;
- metal or polypropylene pipeline;
- radiators (batteries);
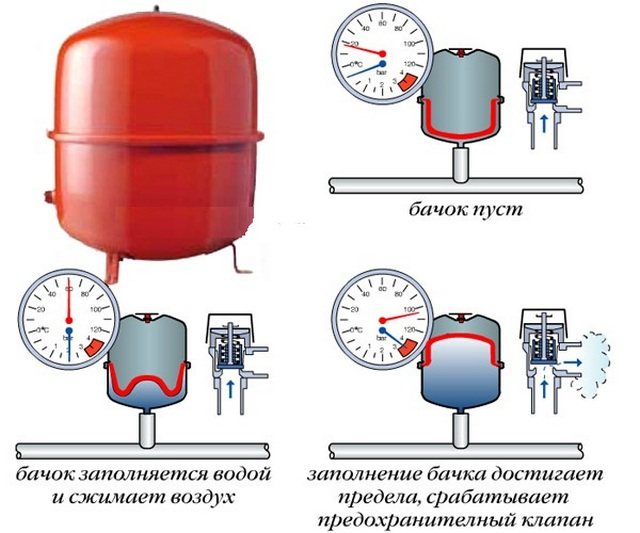
- expansion tank or tank with a valve (for an open system);
- tees;
- a pump for circulating the coolant (in the case of a forced design scheme);
- Ball Valves;
- bypasses with needle valve.
In addition to calculations and the acquisition of materials, one should also take into account the location of the pipeline. If it is planned to be carried out in a wall or in the floor, it will be necessary to prepare special niches - strobes, which should be located around the entire perimeter of the contours. In addition, all pipes must be wrapped with heat-insulating material in order to prevent the temperature of the liquid from dropping before entering the radiators.
What is the best material for the pipeline?
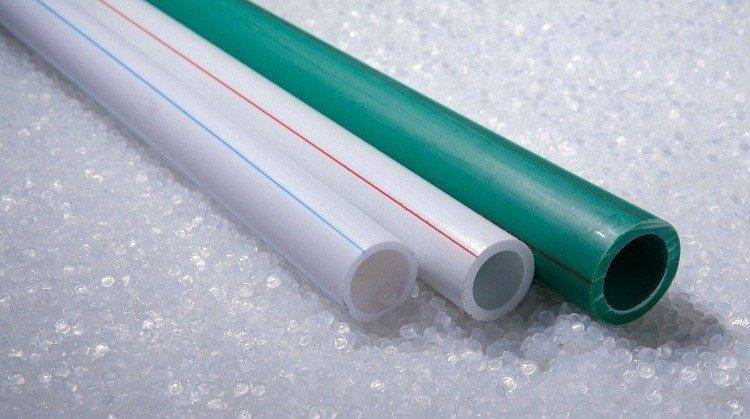



Most often, polypropylene is used as a pipeline for installing Leningradka in a private house. This material is quite simple to install and inexpensive. However, experts do not recommend installing polypropylene pipes in regions where the air temperature drops too low, meaning the Northern Territories.
Polypropylene begins to melt if the coolant temperature rises above 95 degrees, which can lead to pipe ruptures. In such cases, it is more advisable to use metal counterparts, which are rightfully considered the most reliable and durable.
In addition to the material, when choosing a pipeline, it is important to choose its cross section correctly. In this case, the number of radiators used in the circuit is of no small importance. For example, if there are 4–5 elements in the circuit, then the diameter of the pipes for the main line should be 25 mm, and for the bypass this value changes to 20 mm
Thus, the more radiators in the system, the larger the cross section of the pipes. This will make it easier to balance starting the heating system
For example, if there are 4-5 elements in the circuit, then the diameter of the pipes for the main line should be 25 mm, and for the bypass this value changes to 20 mm. Thus, the more radiators in the system, the larger the cross section of the pipes. This will make it easier to balance when starting the heating structure.
Connection of radiators and pipes
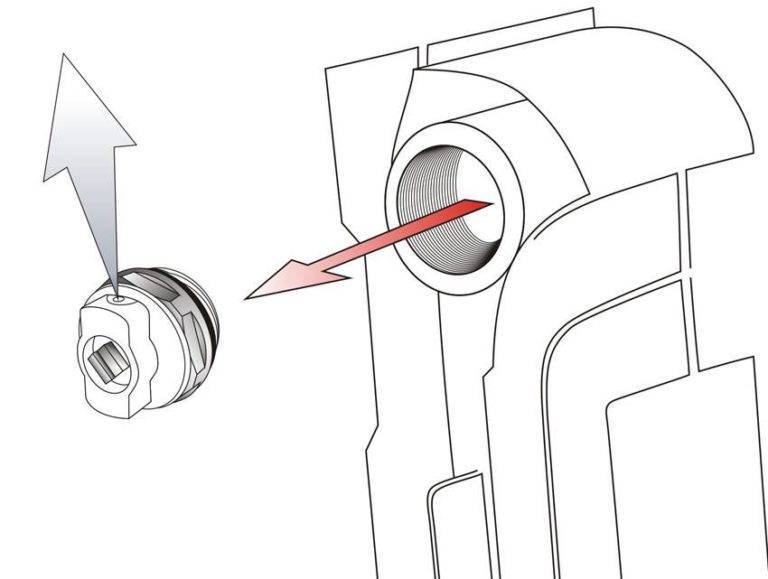
Installation of Mayevsky's crane.
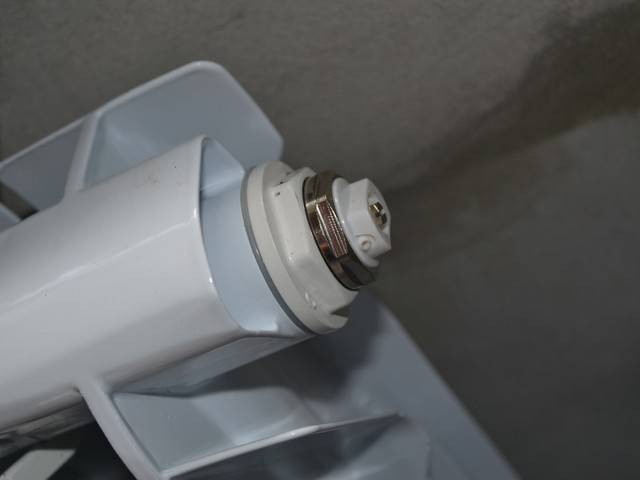


Bypasses are manufactured together with bends and then mounted in the main. At the same time, the distance observed when installing the taps must have an error of 2 mm, so that during the connection of the structural elements, the battery fits.
The backlash that is allowed when pulling up an American is usually 1–2 mm. The main thing is to stick to this value and not exceed it, otherwise it can go downhill and a leak will appear. To obtain more accurate dimensions, you will need to unscrew the valves located at the corners in the radiator and measure the distance between the couplings.
Starting the heating structure
Before starting the Leningradka heating system, it is necessary to open the Mayevsky taps installed on the radiators and let the air out. After that, a control inspection of the structure for the presence of flaws is done. If they are found, they should be eliminated.
After starting the equipment, all connections and nodes are checked, and then the system is balanced. This procedure means equalizing the temperature in all radiators, which is regulated using needle valves. If there are no leaks in the structure, unnecessary noise and the rooms heat up quickly enough, the equipment is installed correctly.
The Leningrad heating system of a private house, although outdated over time, has changed, but is still common, especially in buildings with small dimensions. It is easy to install it yourself, while saving money on attracting specialists and the equipment necessary for the construction.
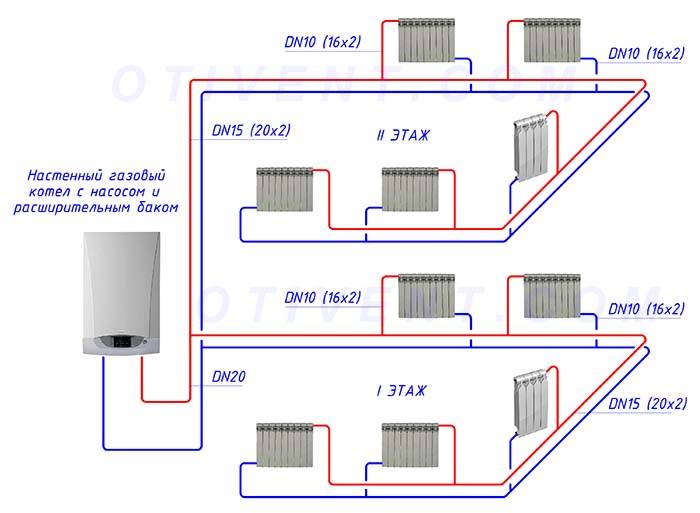
Heating network wiring diagrams
If a decision is made to build a Leningrad heating system for a private house with your own hands, there are several schemes. When choosing a particular variety, it is necessary to take into account the installation features, advantages and disadvantages.
Vertical wiring
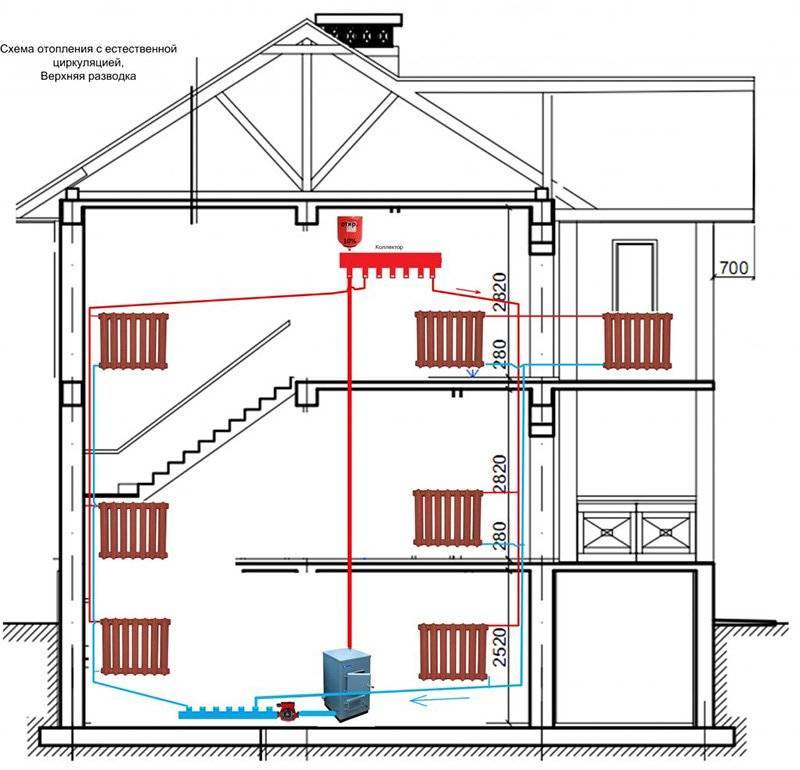
The vertical scheme of the Leningradka single-pipe heating system is used in small two-story houses. You can use atmospheric and closed circuits with natural or forced movement of the coolant.
Vertical arrangements are more difficult to implement because piping must be laid on top of walls at a certain slope to create fluid flow. First, the coolant enters the expansion tank from the boiler, and then moves under pressure through pipelines to the heating units. For efficient operation of the heating system, heating equipment is mounted below the level of radiators.
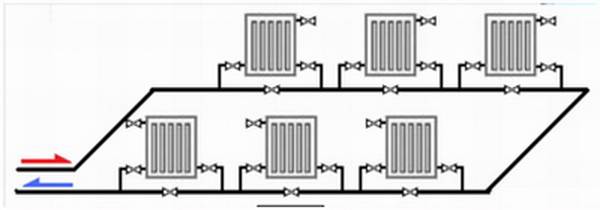
Horizontal wiring

If you decide to use horizontal single-pipe scheme Leningradka heating system, it is used only in compact houses with one floor. All heaters are mounted around the perimeter of the room along the walls.
Components of horizontal systems with forced circulation:
- heating equipment connected to water supply and sewerage pipes;
- a circulation pump installed on a pipeline with a return;
- open expansion tank with a separate pipe for draining the coolant to protect against overflow;
- heating appliances equipped with Mayevsky taps;
- supply and discharge pipes;
- filtering equipment is installed in front of the boiler;
- ball valves for draining the coolant and filling the system with water.
In closed systems, a safety group is additionally installed, consisting of a safety valve, a pressure gauge and an air vent. Here, a closed-type compensation tank with two chambers and a membrane partition is used.
Gravity and forced circulation
Heating networks can be with forced or gravitational circulation of the heat carrier. Heating system Leningradka in a private house from a gas boiler or an electric heater, it happens only with forced current. Otherwise, the likelihood of overheating of the heat exchanger, airing the system increases. For forced circulation, pumping equipment is installed.
To choose the best option, you need to compare both varieties:
In networks with gravitational fluid flow, pipes of a larger diameter are used.
It is important to correctly calculate the cross section of the pipeline, determine its slope and length.
It is advisable to use natural current circuits only in small one-story houses, since they will be inefficient in other buildings.
For the device of a system with forced circulation, pipelines of small cross section can be used. Small pipes are cheaper and look more attractive in the interior.
In gravity systems, the heating equipment is installed at the lowest point, and the expansion tank at the highest, so there must be an insulated attic, as well as a basement or basement floor. In circuits with forced current, the equipment can be installed anywhere.
Gravity networks in two-story houses have one significant drawback - the heaters on the second floor heat up more, so the number of sections has to be increased on the first floor.
Gravity schemes are not used in buildings with attic floors and seasonal residences.
In circuits with forced current, the equipment can be installed anywhere.
Gravity networks in two-story houses have one significant drawback - the heaters on the second floor heat up more, so the number of sections has to be increased on the first floor.
Gravity schemes are not used in buildings with attic floors and seasonal residences.
Characteristics of Leningradka
When choosing an installation, you should pay attention to the fact that it differs in the way the coolant circulates:
- Water moves forcibly. Leningradka with a pump increases circulation, but at the same time consumes electricity.
- Water moves by gravity. The process is carried out due to physical laws. Cyclicity is provided by the temperature difference and under the action of gravity.
The technical characteristics of Leningradka without a pump are inferior to forced ones in terms of the speed of movement of the coolant and the speed of heating.
To improve the properties of the equipment, it is equipped with various devices:
- Ball valves - thanks to them, you can adjust the temperature level for heating the room.
- Thermostats direct the coolant to the desired zones.
- Valves are used to regulate the circulation of water.
These add-ons allow you to upgrade even a previously installed system.
Advantages and disadvantages
The advantages of using include:
- Profitability - the cost of the elements is low, installation can be carried out independently. During operation, energy is saved.
- Availability - parts for assembly are available at any hardware store.
- The heating system of a private house in Leningradka is easily repaired in case of breakdowns.
Among the shortcomings are:
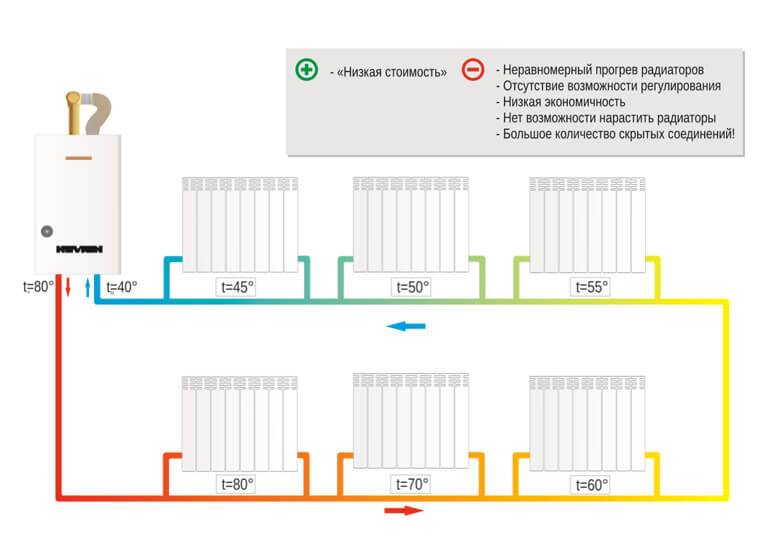
- Installation features. To equalize heat transfer, it is necessary to add several sections to each radiator located far from the boiler.
- Inability to connect to a horizontal installation of underfloor heating or heated towel rails.
- Since pipes with a large cross section are used when forming an external network, the equipment looks unaesthetic.
How to mount correctly?
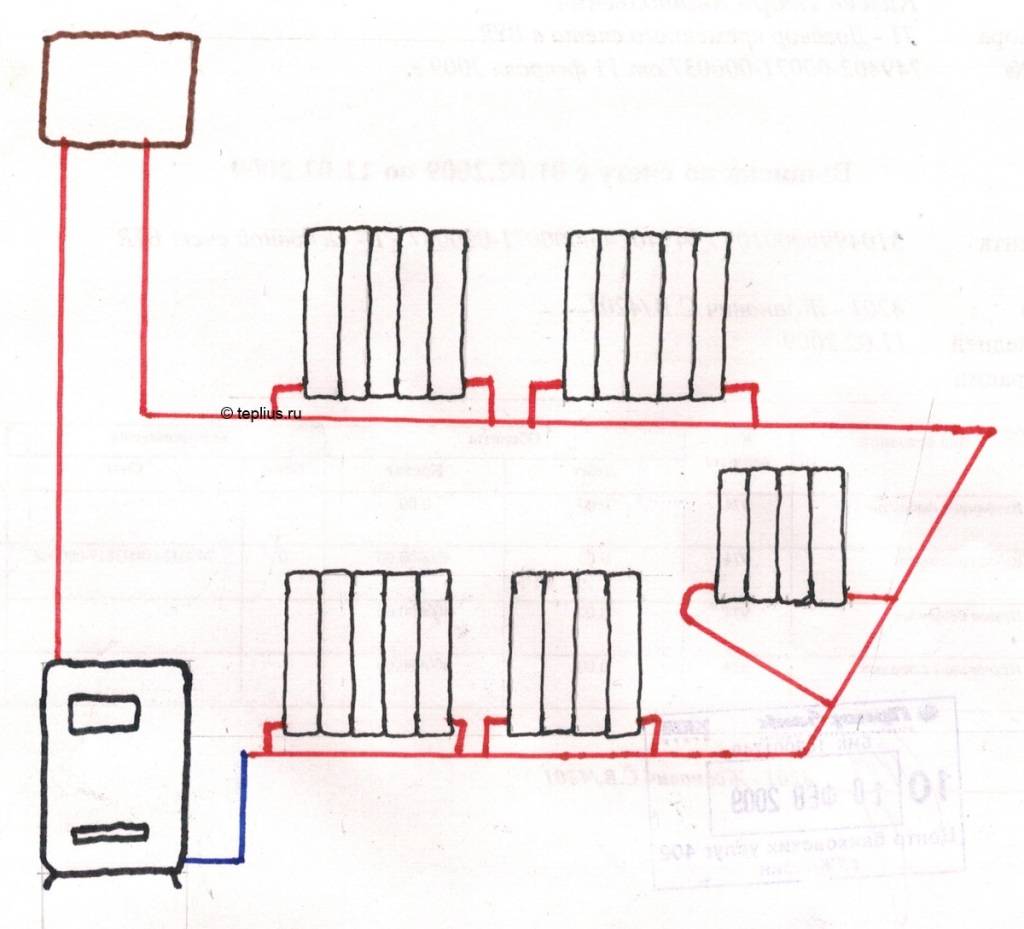
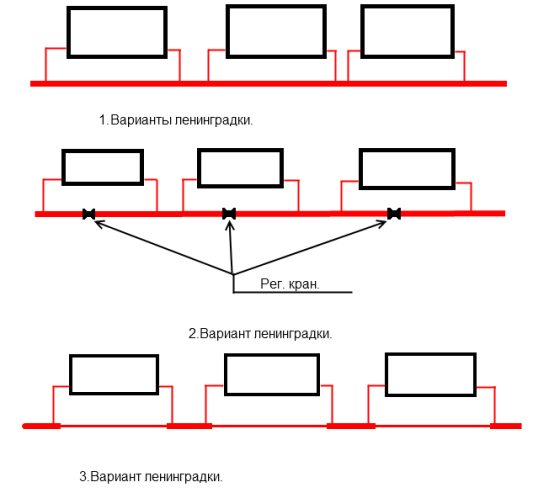
Installing Leningradka is quite feasible with your own hands, for this, 1 of the methods is selected:
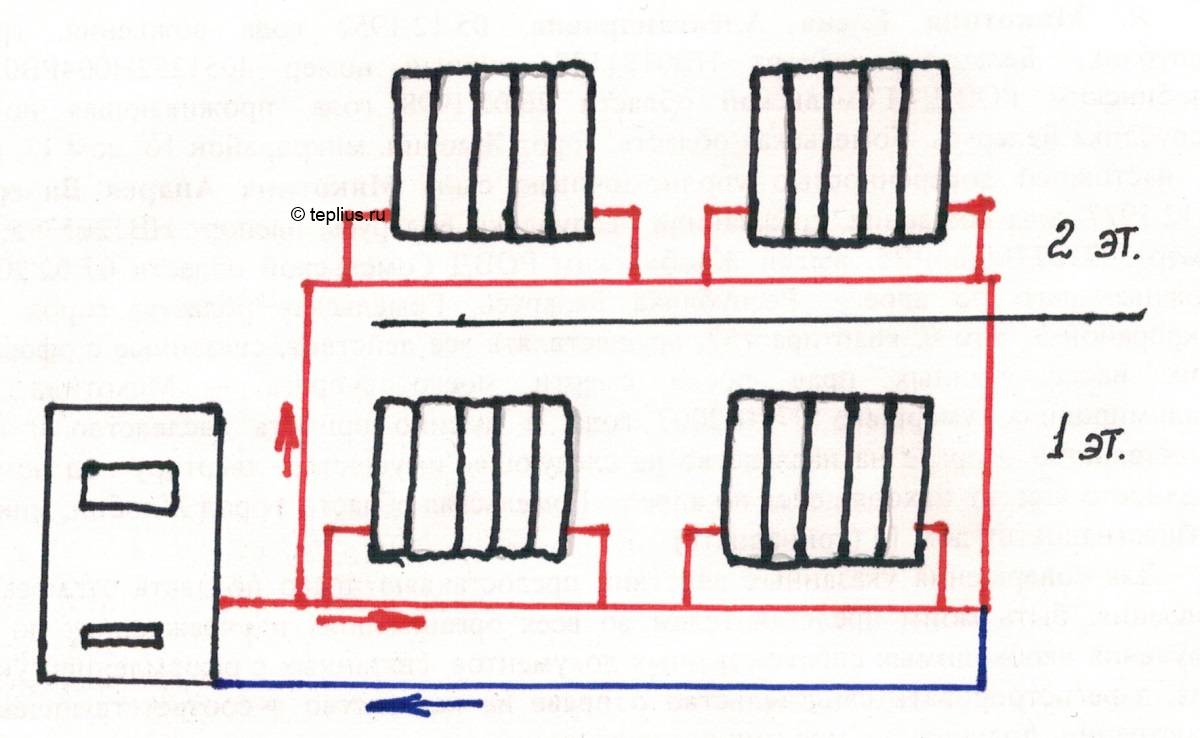
1. Horizontal. A prerequisite is the laying of a floor covering in the structure or on top of it, it is necessary to choose at the design stage.
The supply network is installed at a slope to ensure the free movement of water. All radiators must be located on the same level.
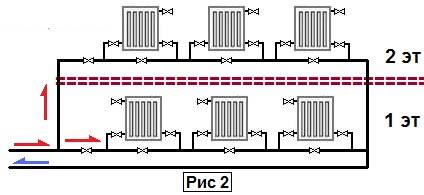
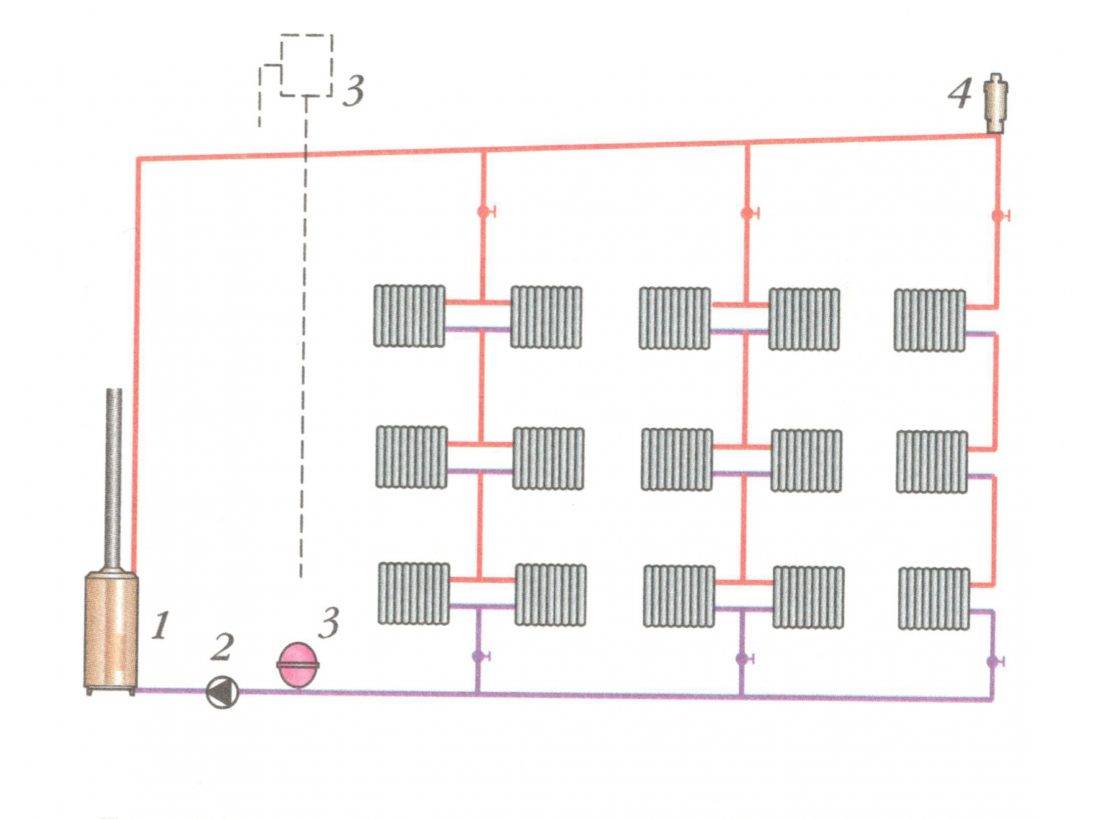
2. Vertical is used in case of using forced type equipment. The advantage of this method lies in the rapid heating of the coolant even when installing pipes with a small cross section. Functioning occurs due to the installation of a circulation pump.If you want to do without it, then you should purchase pipes with a large diameter and place them under a slope. The Leningradka vertical water heating system is mounted with bypasses, which allow repairing individual elements of the equipment without shutting it down. The length must not exceed 30 m.
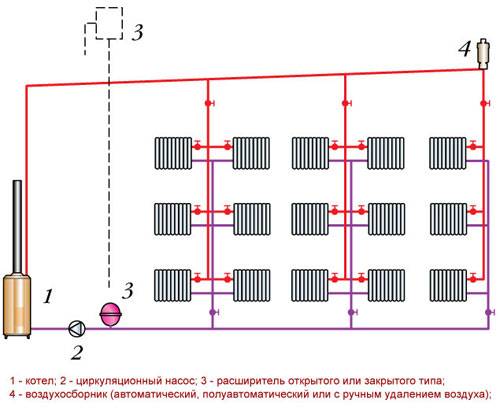
Peculiarities heating system installation Leningradka are reduced to following the sequence of work:
- Install the boiler and connect it to a common line. The pipeline must run around the entire perimeter of the building.
- The expansion tank is a must. To connect it, a vertical pipe is cut. It should be located near the heating boiler. The tank is installed above all other elements.
- Radiators are cut into the supply network. They are supplied with bypasses and ball valves.
- Close the equipment on the heating boiler.
A video review of the Leningradka heating distribution system will help you understand the order of work and follow their sequence.
“A few years ago we moved to live outside the city. We have a single-pipe heating system installed in a two-story house similar to Leningradka. For normal circulation, I connected the equipment to the pump. There is enough pressure for heating the 2nd floor, it is not cold. All rooms are well heated. Easy to install, no expensive materials required.
Grigory Astapov, Moscow.
“When choosing heating, I studied a lot of information. According to reviews, Leningradka approached us due to the savings in materials. Radiators chose bimetallic. It works smoothly, fully copes with the heating of a two-story house, but the equipment should be cleaned periodically. After 3 years, our radiators stopped working at full capacity.It turns out that garbage was clogged on the approaches to them. After cleaning, the operation resumed.
Oleg Egorov, St. Petersburg.
“The Leningradka heating distribution system has been working with us for more than a year. Generally satisfied, easy installation and easy maintenance. I took polypropylene pipes with a diameter of 32 mm, the boiler runs on solid fuel. We use antifreeze diluted with water as a coolant. The equipment fully copes with the heating of a house of 120 m2.
Alexey Chizhov, Yekaterinburg.
A brief overview of the main heating schemes
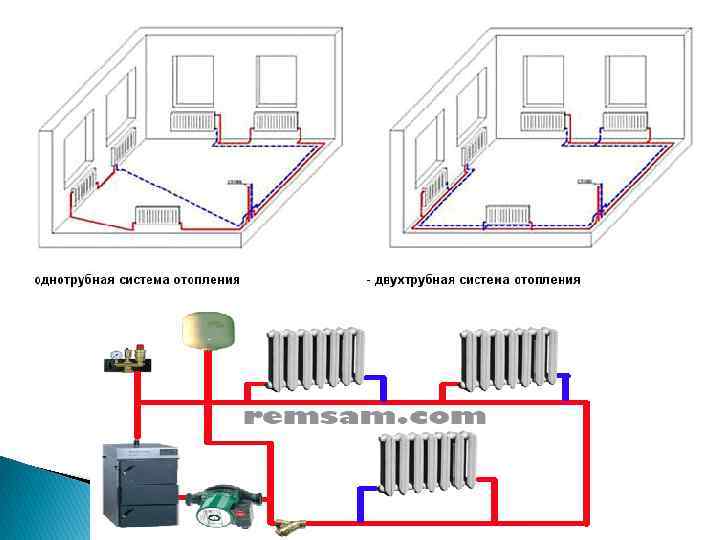
To understand what we are talking about, we will briefly describe two basic heating schemes:
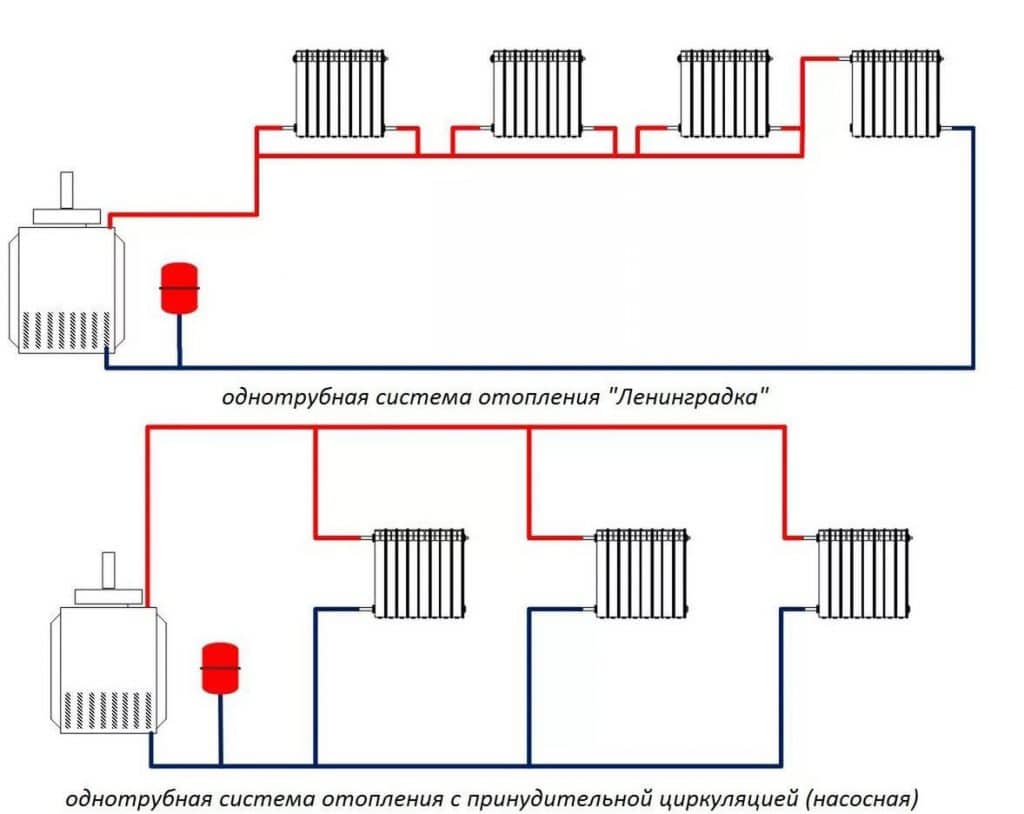
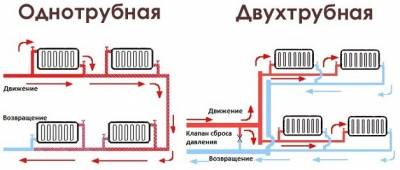
Single-pipe - distribution and return collection of the coolant occurs through a single line to which the heating devices are connected in series. For each subsequent radiator, water comes already decently cooled down in the previous one. Heating, collected according to a single-pipe scheme, is practically not amenable to adjustment by room. Uneconomical, uncomfortable, but easy to install and relatively cheap due to low pipe consumption.
Two-pipe - supply and return are carried out through separate lines, which leads to an increase in pipe consumption and an increase in the cost of the system. However, with such a series-parallel circuit, the influence of previous devices on subsequent devices is minimal, the temperature of the coolant entering the radiators differs slightly. This avoids unproductive heat consumption, makes it possible to accurately regulate the heating of each room or zone.
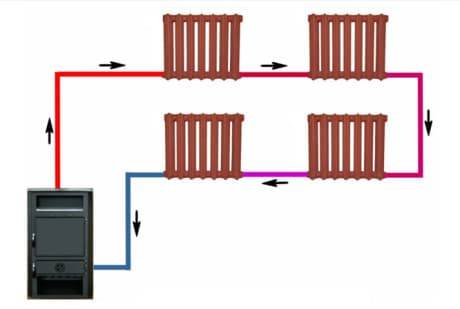
Versions
Depending on the orientation of the Leningradka highway, it happens:
- vertical;
- horizontal.
vertical
Used for multi-storey buildings. Each circuit substitutes a vertical riser, passing from the attic to the basement on all floors. Radiators are connected sideways parallel to the main line and in series on each floor.

The effective height of the "Leningradka" vertical type is up to 30 meters. If this threshold is exceeded, the distribution of the coolant is disturbed. It is not advisable to use such a connection for a private house.
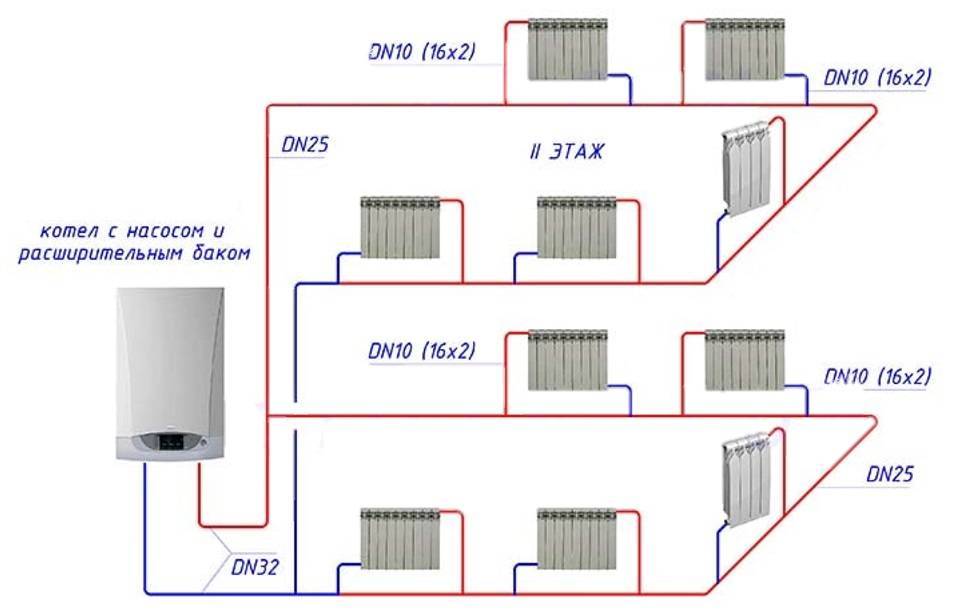
Horizontal
The best option for an autonomous heating system of a private house with one or two floors. The highway bypasses the building along the contour and closes to the boiler. Radiators are installed with a bottom or diagonal connection, with the top point oriented to the hot end of the line, and the bottom point to the cold end. Radiators are supplied with a Mayevsky crane for air release.
The circulation of the coolant can be:
- natural;
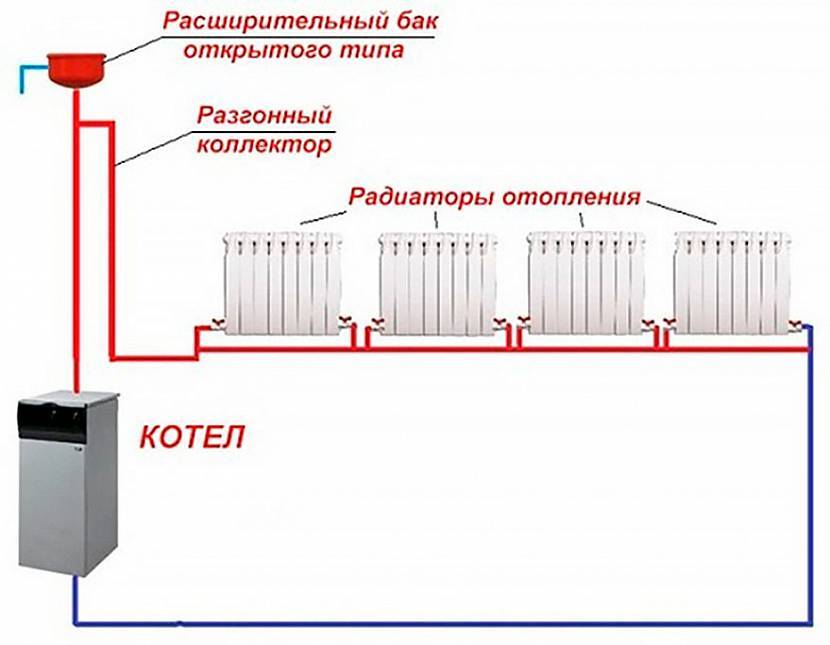
- forced.

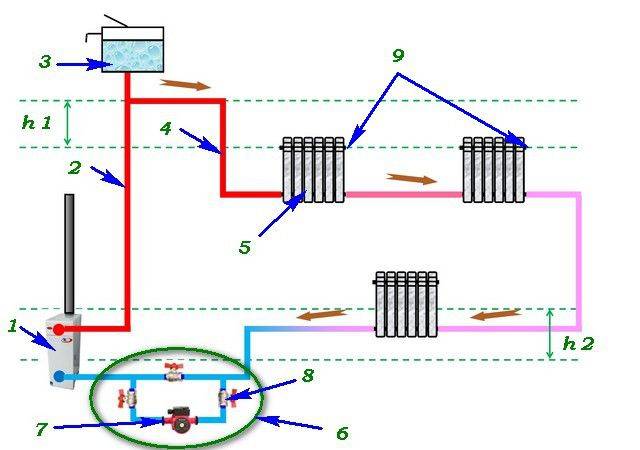
In the first case, the pipes are distributed along the contour with a mandatory slope of 1–2 degrees. The hot outlet from the boiler is located at the top of the system, the cold outlet is at the bottom. To increase circulation, the section of the line from the boiler to the first radiator or the point of inclusion of an open expansion tank is laid with a slope upwards, and then evenly downwards, closing the circuit.
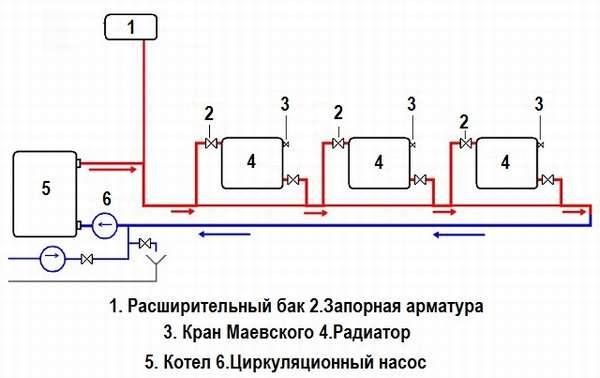
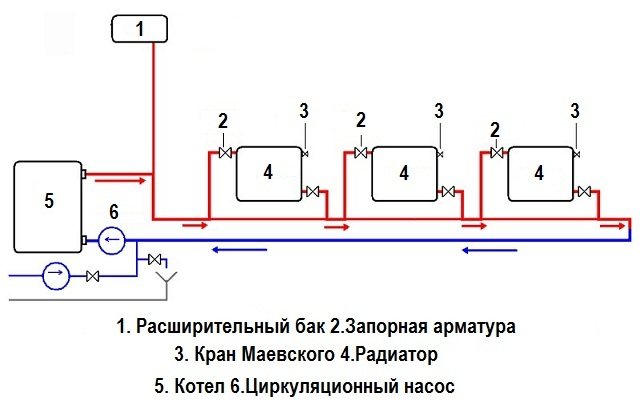
- boiler (hot output);
- open-type expansion tank (top point of the system);
- heating circuit;
- branch pipe with a ball valve for draining and filling the system (the lowest point of the system);
- ball valve;
- boiler (cold input).

1 - heating boiler; 2 - expansion tank of open type; 3 - radiators with bottom connection; 4 - Mayevsky crane; 5 - heating circuit; 6 - valve for draining and filling the system; 7 - ball valve
There is no need for a one-story house to make the upper and lower wiring of the main, a lower wiring with a slope is enough. The coolant circulates mainly along the contour of the common pipe and boiler. Hot coolant enters the radiators due to the pressure drop caused by the water temperature drop.
The expansion tank provides the required coolant pressure in the system. An open-type tank is installed under the ceiling or in the attic. A membrane-type tank for a closed heating system is installed on the return after connecting parallel circuits, but before the boiler and pump.
Forced circulation is preferable. There is no need to observe the slope, you can perform a hidden installation of the main pipe. The expansion tank of the membrane type allows you to accurately set the pressure in the system.
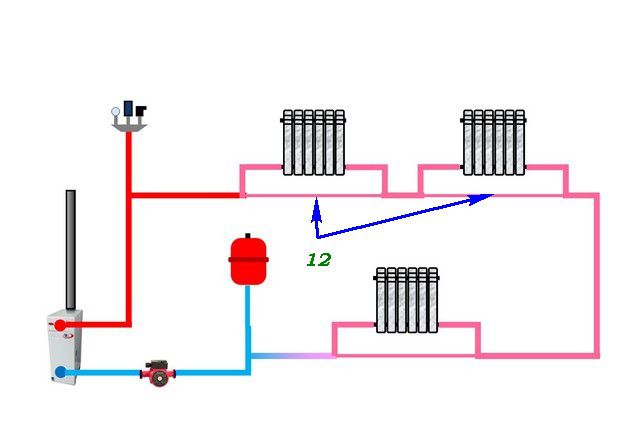
- boiler (hot output);
- five-pin fitting for connecting a pressure gauge, air vent and explosion valve;
- heating circuit;
- branch pipe with a ball valve for draining and filling the system (the lowest point of the system);
- expansion tank;
- pump;
- ball valve;
- boiler (cold input).

1 - heating boiler; 2 - security group; 3 - radiators with diagonal connection; 4 - Mayevsky crane; 5 - expansion tank of membrane type; 6 - valve for draining and filling the system; 7 - pump
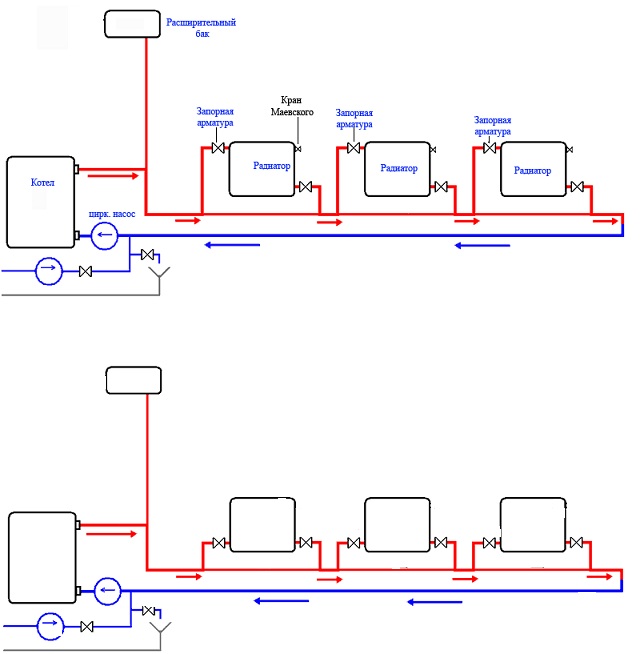
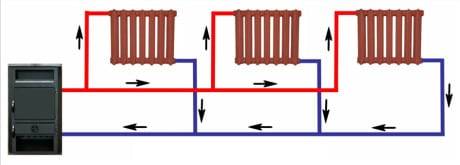
Leningrad system with a pump

The main advantage of a single-pipe circuit is the possibility of autonomous operation and the movement of the coolant by gravity.
However, the effectiveness of such heating depends on several factors, each of which can slow down the movement of water in the radiators, reduce the air temperature in the rooms.
For example, the speed of the coolant depends on the temperature difference at the inlet and outlet of the boiler. The larger it is, the higher the pressure difference will be and the faster the flow will move.
However, with a relatively small outdoor cooling, at +8 +10 ° C, there is no need to heat the water too much. +50 +60 °C is enough. And at this temperature, the flow rate will be noticeably lower than when heated to +80 °C.
For a single-pipe gravity flow scheme, a specific location of the boiler is required - as low as possible, in the basement or semi-basement. And the high location of the distribution manifold - in the attic. Which is not possible in every building.
And yet - gravity is impossible in large houses with a heating area of more than 150 square meters. m. Therefore, for large buildings, an additional device is built into the single-pipe heating circuit - a circulation pump.
The pump provides forced circulation of the coolant. It pushes water through the pipes by rotating small blades. Operates from a separate power source - an electrical outlet. Provides the movement of the coolant, regardless of the temperature of the water heating, the location of the boiler and the height of the pipe at the outlet. In a house with any heating area.
The principle of operation of the circuit

Under the outer casing of the pump is the motor and rotation blades. When connected to a common pipeline, the blades are rotated by an electric motor.
Their rotation forces the water in the pipe to move further. The next portion of water enters the vacant place, which also passes through the pump blades.
So the coolant moves in a circle, pushed by the working blades.
The pump is built into the system before entering the boiler. Here - the minimum natural flow rate, and hence the most appropriate location of forced circulation.
Advantages and disadvantages
The main advantage of a heating circuit with a circulation pump is its guaranteed operation at any temperature and at any location / connection of emitter batteries. As well as the ability to heat a house of different sizes, with one or more floors.
Among the shortcomings of the circuit with a pump is the dependence of heating on electricity.
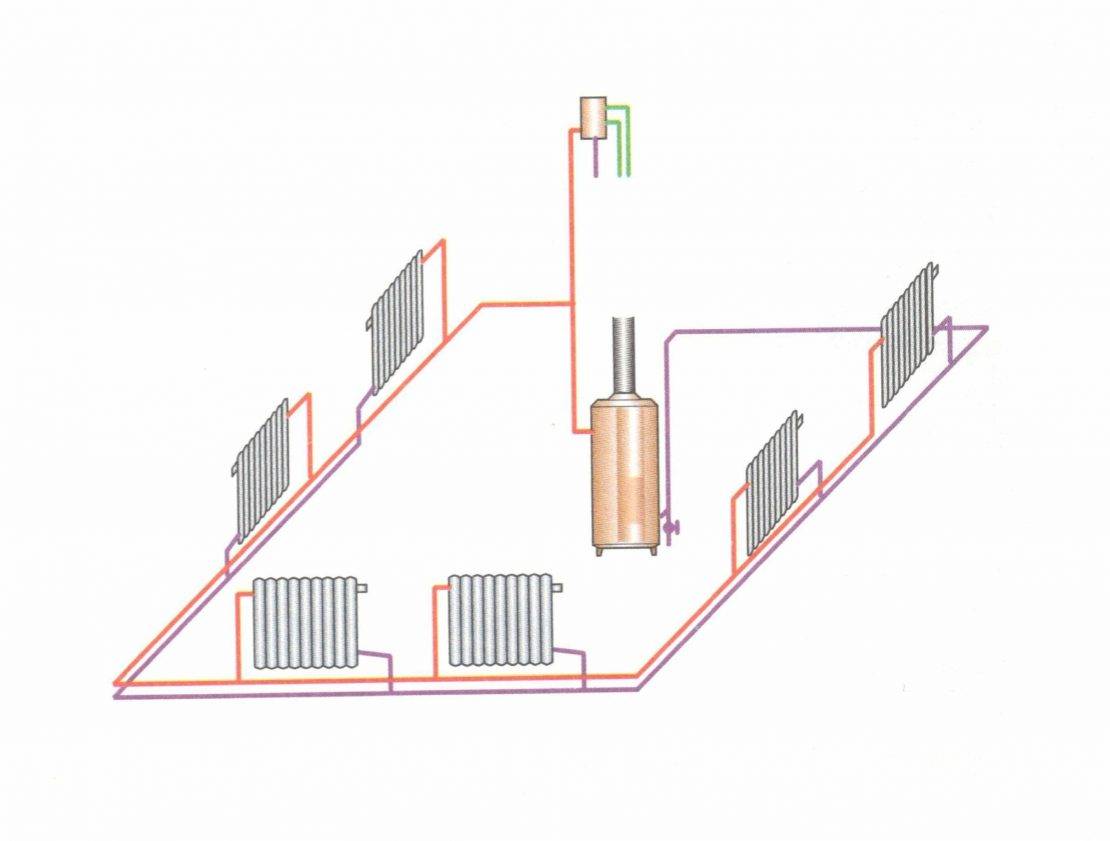
Scheme with a pump
The circuit diagram includes the same devices and elements as a conventional one-pipe system. And it also has a pump. It can be embedded in two ways:
- Directly into the water return pipe. With such a tie-in, the movement of the coolant by gravity is impossible.
- Through branch pipes - with such a tie-in, the pump is connected in parallel to the common line. If it is turned off, water can move through the main pipe without obstruction. Thus, it is possible to combine autonomous and dependent systems in one scheme. When the pump is connected, the coolant will circulate forcibly. When it is turned off, water will flow through the pipe by gravity.
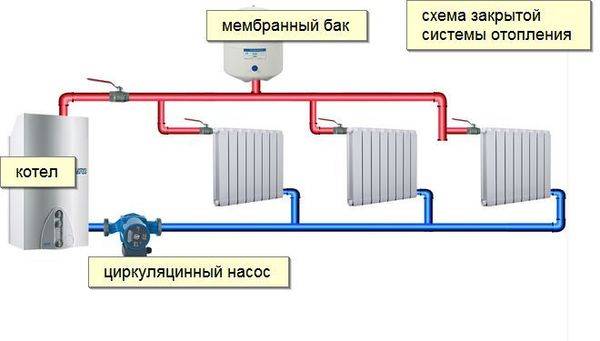
Photo 2. Scheme of a closed-type single-pipe heating system using a circulation pump.
Installation technology of the Leningrad system in a private house

Now let's figure out how heating is done in a private house Leningradka. If you plan to carry out a hidden laying of pipelines, then you need to prepare the strobes in the walls in advance.To protect against heat loss, the pipeline must be insulated. If visible wiring is done, then the pipes do not need to be insulated.
Selection of radiators and pipelines
Heating wiring Leningradka in a private house can be made of steel or polypropylene pipes. The latter variety is quick and easy to install, but not suitable for northern latitudes. This is due to the fact that here the coolant is heated to a higher temperature, which can lead to pipe rupture. In the northern regions, only steel pipelines are used.
Depending on the number of heating devices, the diameter of the pipes is chosen:
- If the number of radiators does not exceed 5 pieces, then pipes with a diameter of 2.5 cm are sufficient. For a bypass, pipes with a cross section of 20 mm are taken.
- With a number of heaters within 6-8 pieces, pipelines with a cross section of 32 mm are used, and the bypass is made of elements with a diameter of 25 mm.
Since the temperature of the coolant at the inlet to the battery differs by 20 ° C from its temperature at the outlet, it is important to accurately calculate the number of sections. Then the water from the radiator mixes again with the coolant at a temperature of 70 ° C, but still one will be a few degrees cooler when it enters the next heater. Thus, with each passage of the battery, the temperature of the coolant decreases
Thus, with each passage of the battery, the temperature of the coolant decreases.
To compensate for the described heat losses, the number of sections in each next heating unit is increased in order to increase the heat transfer of the device. When calculating the first device, 100 percent of the power is laid. The second fixture needs 110% power, the third needs 120%, and so on.In other words, with each subsequent unit, the required power is increased by 10%.
Mounting technology

In the Leningrad system, all heating devices are installed on bypasses. That is, the installation of each battery in the line on special pipe bends. For correct installation, measure the distance between adjacent taps (the error is a maximum of 2 mm). This will make it easy to install Americans with angled cocks and batteries.
Tees are installed on the taps, and one open hole is left for mounting the bypass. To fix another tee, you need to measure the distance between the centers of the branches. Moreover, in the measurement process, it is necessary to take into account the dimensions after installing the bypass.
In the process of welding steel pipelines, they try to avoid sagging from the inside. During the installation of the bypass on the line, a more complex section is first welded, because sometimes it is almost impossible to start a soldering iron between the pipe and the tee.
Heating appliances are fixed on corner valves and combined type couplings. Then install the bypass. The length of its branches is measured separately. If necessary, cut off excess pieces, re-install the combined couplings.
Before the first start you need bleed the air out systems. To do this, open the Mayevsky taps on the radiators. After starting, the network is balanced. By adjusting the needle valves, the temperature in all heaters is equalized.
DIY installation recommendations
When installing the Leningradka system yourself, it is important to take into account the following recommendations from qualified specialists:
- The assembly of the circuit should take place without any particular difficulties, the installation of a closed ring is carried out approximately at floor level. The design must be given a slight slope for the natural circulation of the working medium without a circulation pump. However, it should be remembered that all heat exchangers must be at the same horizontal level.
- Each battery in the system is equipped with a Mayevsky crane. This must be done in any case, if the system has a common automatic air vent or expansion tank.
- The masking of the main pipe and the tie-in pipe in the floor or in the wall must be accompanied by mandatory thermal insulation. This will avoid unnecessary losses of thermal energy and reduce heating costs for the entire building.
- Shut-off and control valves should be separated. It is not recommended to install ball valves on the bypass, they are mounted at the inlet and outlet of the heat exchanger.
The fact is that such valves can be on or off, that is, in the open or closed position. Operation in other modes for ball valves is contraindicated, they quickly become unusable. In other words, it is best to use ball valves as shutoff valves.
If fine adjustment of the flow rate of the working medium is required, it is recommended to use needle valves. These parts are designed for installation on bypasses or tie-ins of an additional circuit.
"Leningradka" can be called the simplest heating system, but self-assembly is best done under the guidance of a professional craftsman. Despite the detailed installation rules on the Internet or the attached instructions, the subtleties and nuances of resolving the issue of how to make Leningradka heating with your own hands can only be taken into account by a master with many years of experience.