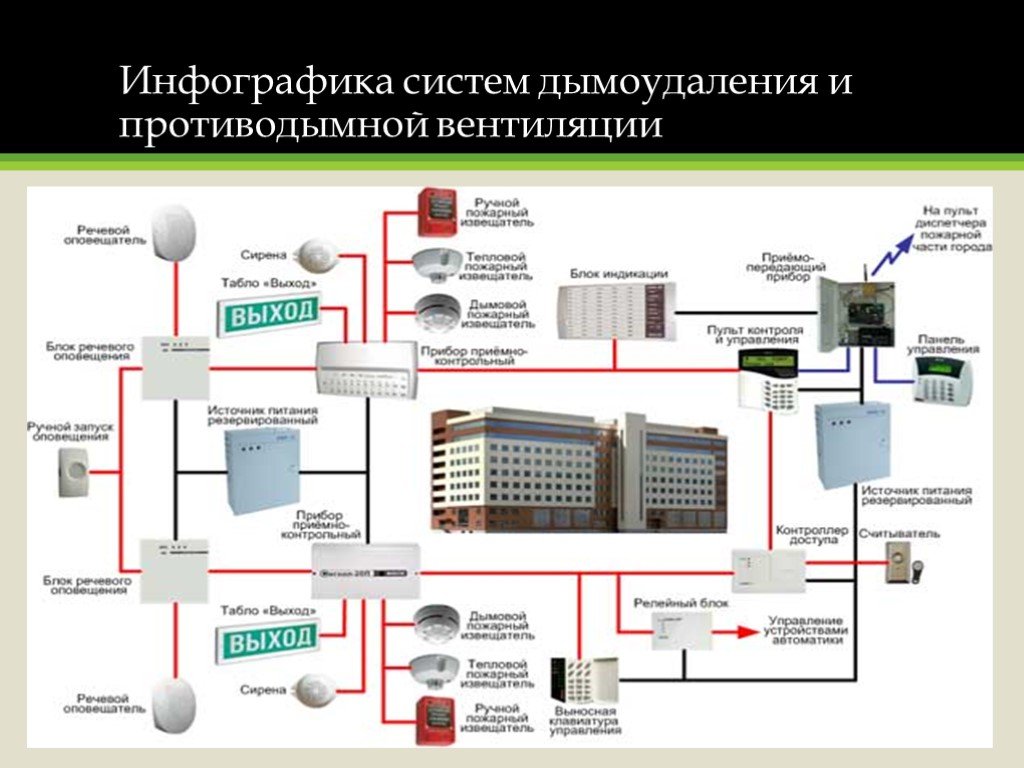
- Types of smoke extraction systems
- Natural air exchange
- Algorithm for starting the smoke exhaust system
- How to install a combustion exhaust system
- Calculation of the combustion temperature of products removed from the corridor
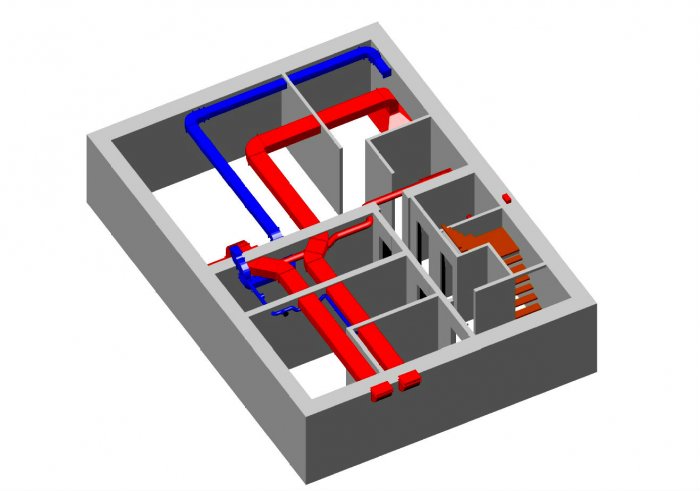
- Device
- Where is smoke ventilation installed?
- Where are SDUs needed?
- Where are SDUs not needed?
- Use in private homes
- Starting the fire protection system from the duty station.
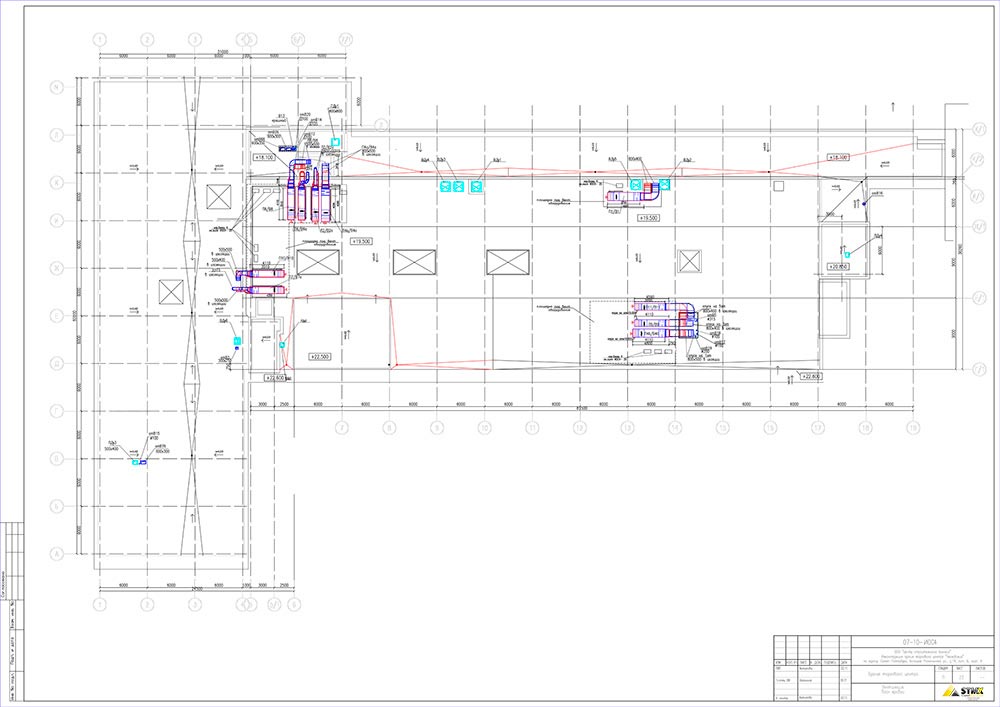
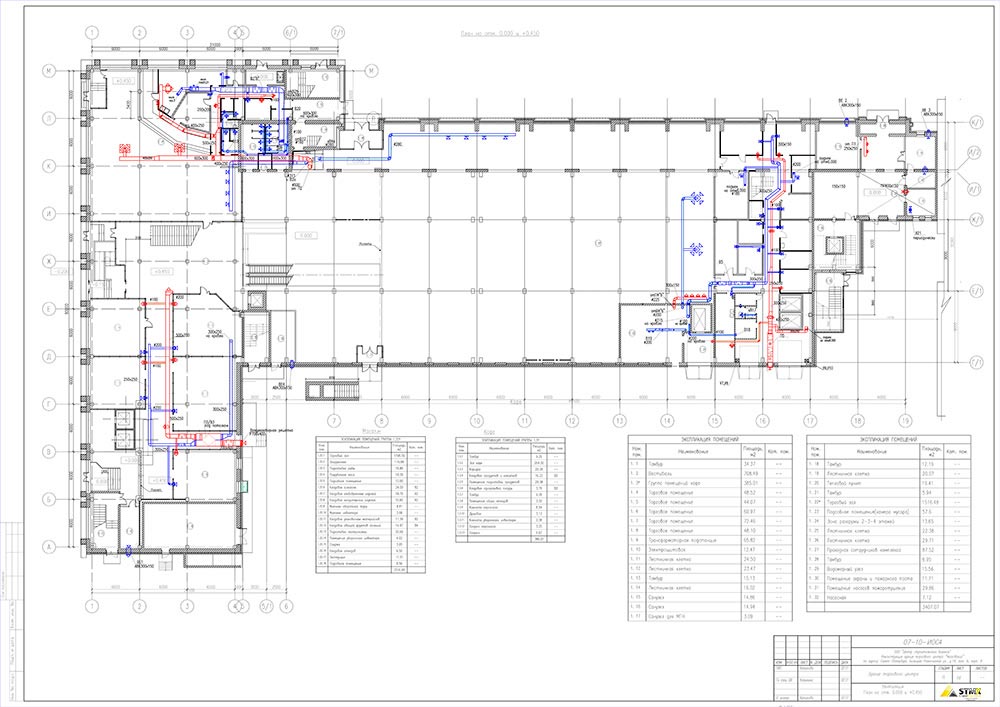
- Installation of a smoke exhaust system
- SDU installation
- Checking the operation of the CDS
- Service
- What is a smoke extraction system?
- Tasks of the CDS
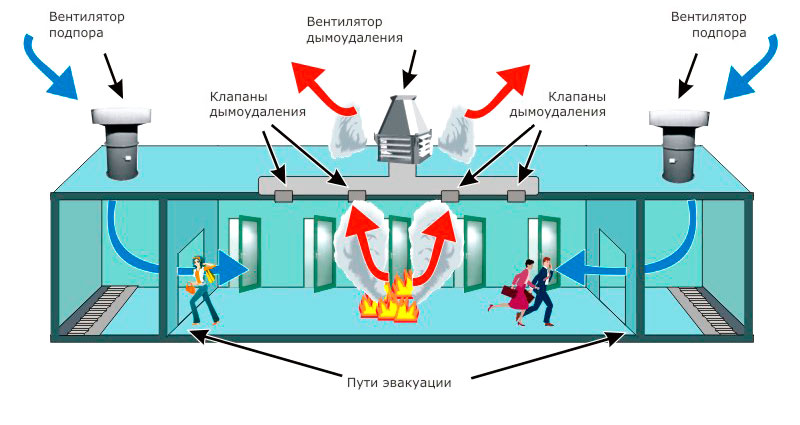
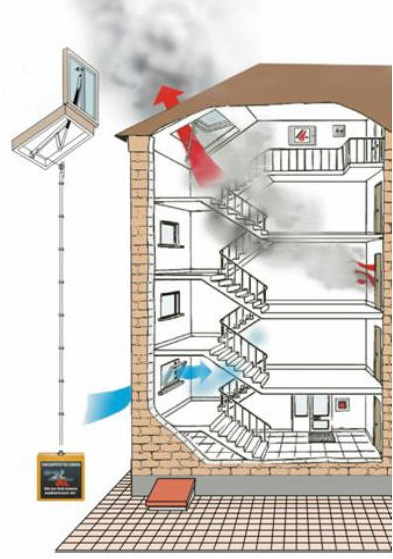
- How does a smoke exhaust system work?
- Types of smoke ventilation
- What is taken into account when designing a CDS?
Types of smoke extraction systems
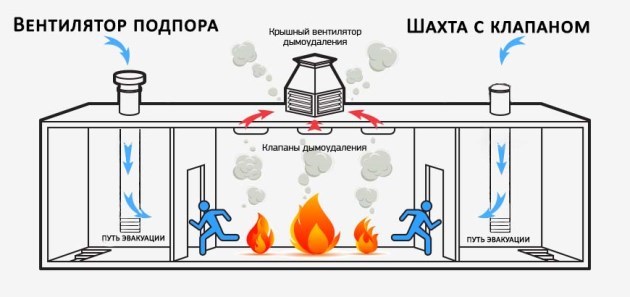
A smoke exhaust system from a room is arranged if there is a high risk of fire and filling the enclosed space with poisonous volatile emissions.
Its installation is rational if it is impossible to remove combustion products by banal ventilation, or even with an open window, the movement of polluted air mass to the windows will be too slow.
Image gallery
Photo from
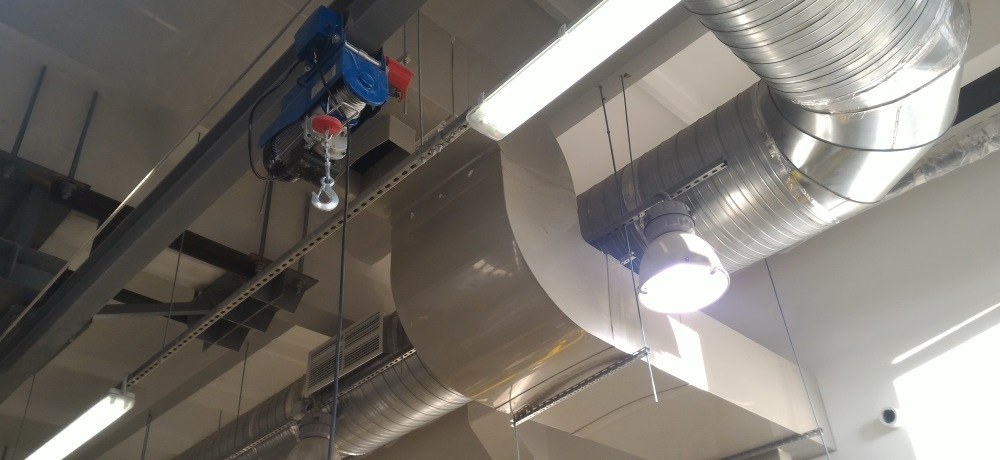
Systems that remove smoke, fumes and airborne toxins are installed in public, industrial and commercial buildings
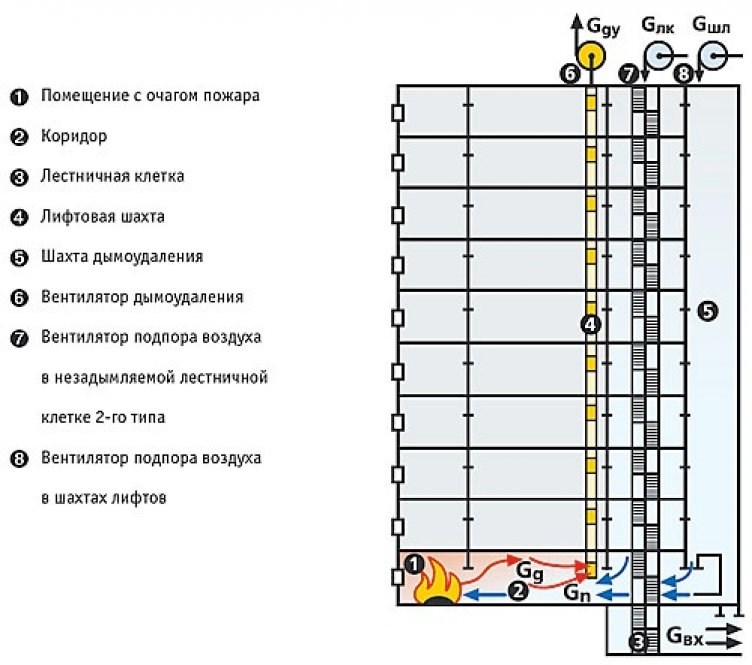
Smoke exhaust systems are built wherever the organization and operation of natural ventilation is impossible: these are stairwells, metro stations, elevators, mines and similar objects that do not have direct communication with the street
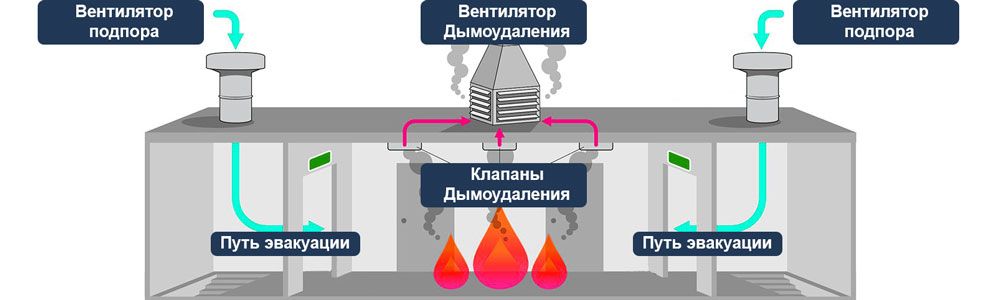
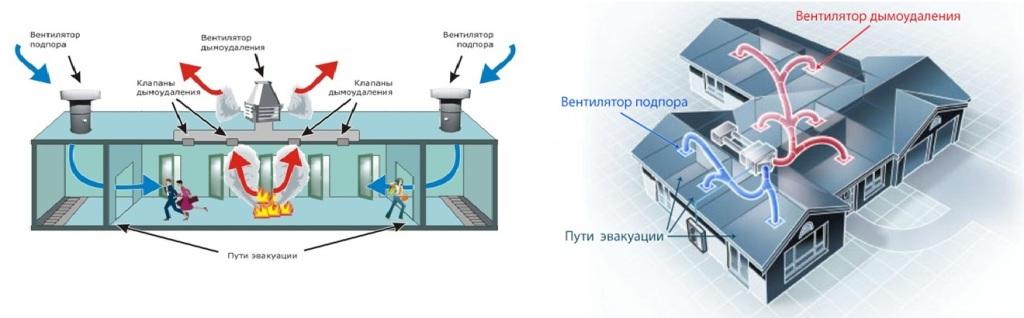
This type of system is designed to provide conditions for the evacuation of people present in the building in the event of an emergency or fire.
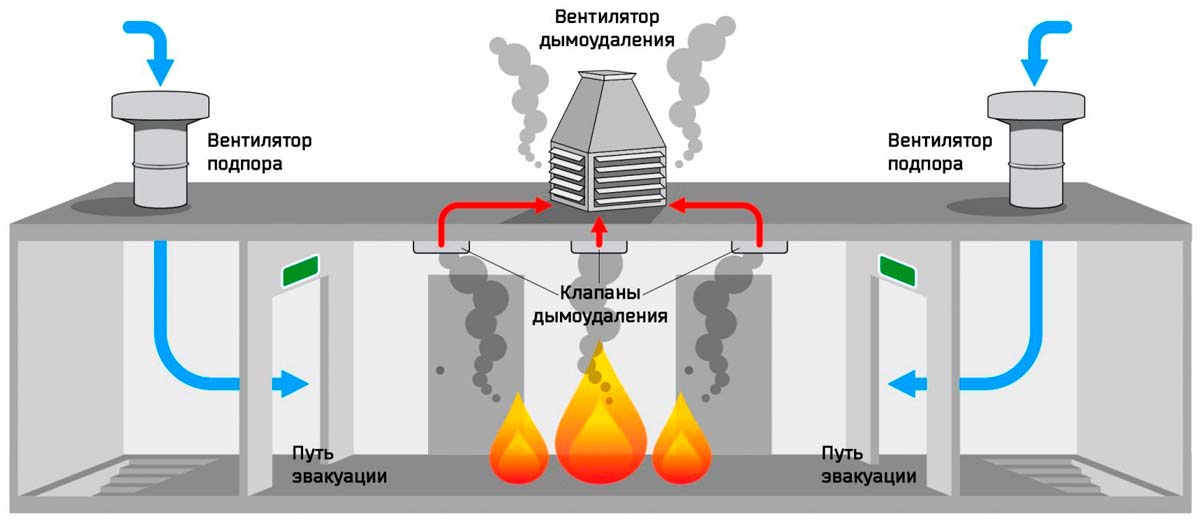
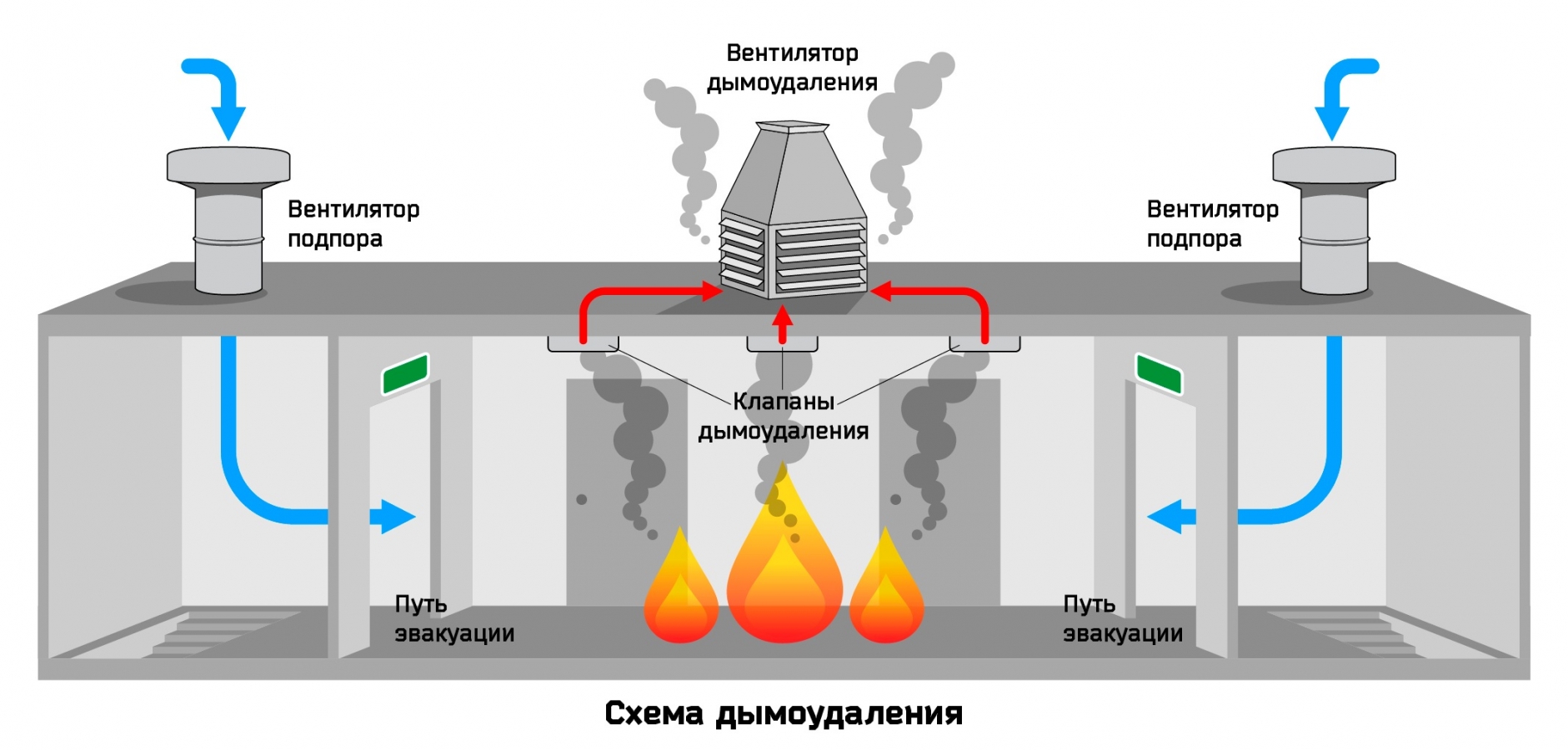
The smoke exhaust system is an integral part of smoke ventilation, working in tandem with the air pressurization system
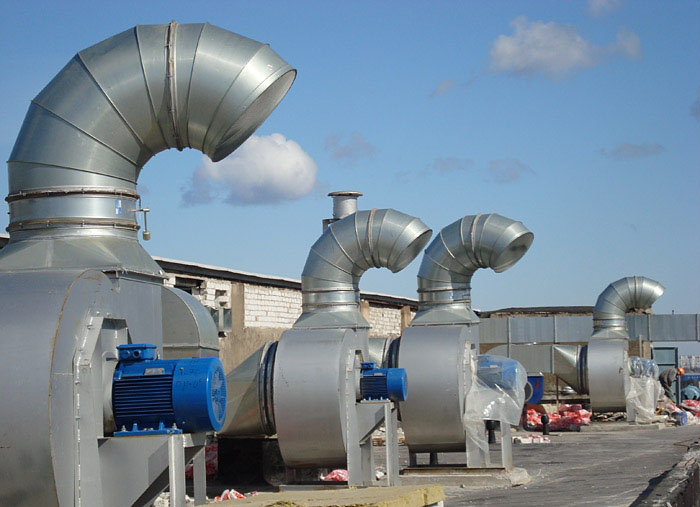
The system that removes smoke and ash is equipped with powerful fans that capture and remove air from the room with a concentration of fumes that is dangerous for people.
The fans of the system are equipped with check valves to prevent the reverse movement of smoke and thermal decomposition products.
A well-designed smoke exhaust system should fully cope with the removal of products of combustion products suspended in the air, ensuring safe evacuation until the arrival of the Ministry of Emergencies
The design of smoke exhaust systems is influenced by the requirements for clean air, the purpose of the building, vibration standards, local meteorological data, operational safety
Application of smoke exhaust systems
Scope of use of chimneys
Application of smoke removal
Part of smoke ventilation
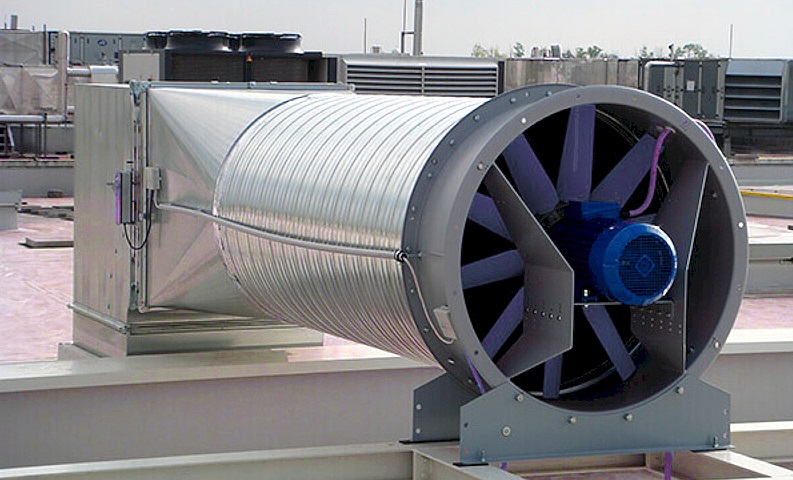
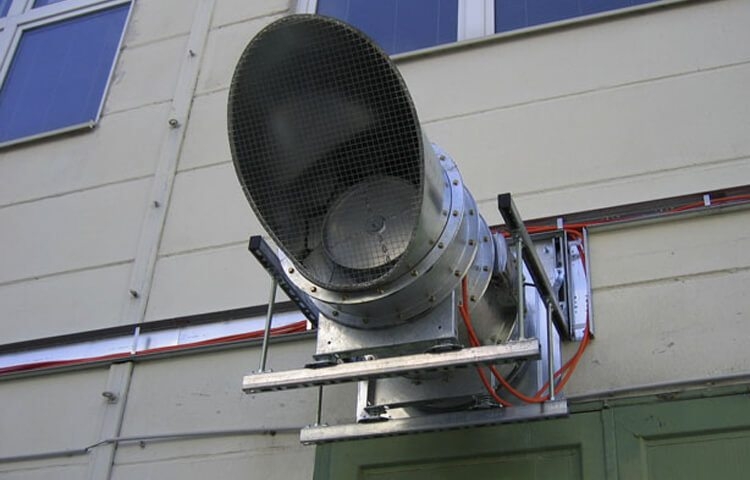
Smoke extraction fan
Smoke extraction device
Device Requirements
Design Factors
According to the method of removing smoky air from the premises, the systems can be divided into two types:
- Static.
- Dynamic.
Their functionality is configured on fundamentally different processes.The static CDS at the time of fire detection turns off the ventilation and oxygen supply from the outside and blocks the smoke in one room, preventing its spread.
If there is a possibility of filling the room with toxic gases during a fire, you should not save on a smoke exhaust system (+)
At the same time, the temperature in the room heats up to critical levels of 1000 degrees Celsius. If people are evacuated from the building through this room, it is dangerous and can lead to poisoning, burns and evacuation difficulties.
Dynamic CDS work differently. There is an increase in air circulation due to the operation of powerful fans and the removal of carbon monoxide, which prevents the accumulation of smoke. The level of smoke is reduced, but the concentration of carbon monoxide still occurs. The air temperature also continues to rise. The main purpose of the dynamic CDS is to buy time for the evacuation. She excels at this goal.
If we talk about the price criteria, then static CDS are cheaper than dynamic ones. This is one of those cases where it is better not to skimp on security. When using dynamic systems, the chances of avoiding poisoning by volatile toxins are higher. It is worth noting that both types of systems are allowed for installation by fire safety rules.
Even the simplest ventilation significantly increases the chances of survival in a fire. It is precisely because of the lack of SDU in old high-rise buildings that there is a need for their modernization. The same applies to old buildings adapted for storage and production needs.
Natural air exchange
A necessary condition for natural air exchange is supply and exhaust shafts and air ducts, which perform the function of balancing the inflow and outflow of extracts. Creation of thrust by heat difference in the room and outside is carried out with the general requirements for tightness and adequacy of throughputs. At the same time, the requirements of sanitary and technical safety standards are taken into account.
You need to pay attention to things like:
- number of storeys,
- relative position of surrounding structures,
- sound Effects,
- cleanliness of the environment.
In summer, it happens that the natural order of ventilation stops working due to the lack of drops and pressure. Accordingly, there is a need for forced ventilation. The classic version consists of three outputs:
- inflow;
- Hood;
- Supply and exhaust complex for the extraction of suspensions.
Depending on the nature of air exchange, there is:
- local ventilation;
- general purpose.
The first class includes desktop and window appliances. The second category includes systems that create the movement of gases over the entire area of the object. Desktop and fortochny - channelless. In the second case, we mean channel devices with circulation through special channels. The channel type can be both separate and monoblock in one case. Functionally, these types are divided into recuperative and recirculating (they have recirculation).
Other varieties:
- heated;
- with mixed cooling in summer;
- with air conditioning.
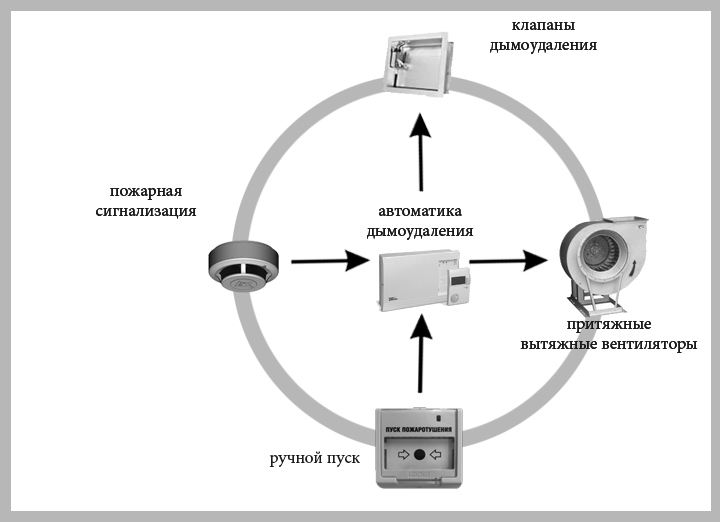
Algorithm for starting the smoke exhaust system
The type of fire ventilation start depends on the type of building:
- The CDS and backwater in the fire zone are the first to operate. After that, all other sensors are started.
- In large public and industrial premises, where there are many SDU installations, the launch of individual networks is spread over time.
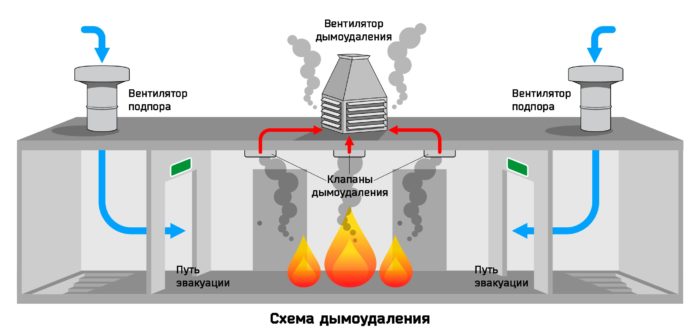
This algorithm allows you to reduce the simultaneous load on the network. By lowering the load, the accuracy of the operation of the devices is achieved.
The triggering algorithm affects the choice of equipment. Modules can be used to control actuated valves and supports:
- address command;
- monitor;
- command and monitor.
The last version of the equipment not only manages, but also controls the launch, the functionality of the CDS.
How to install a combustion exhaust system
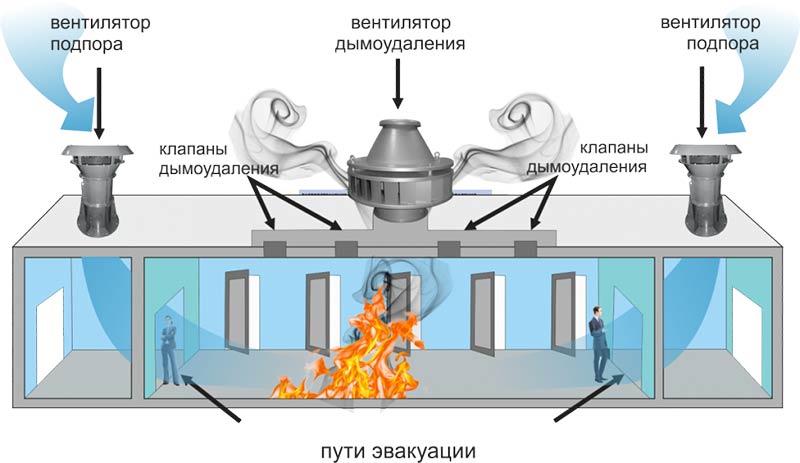
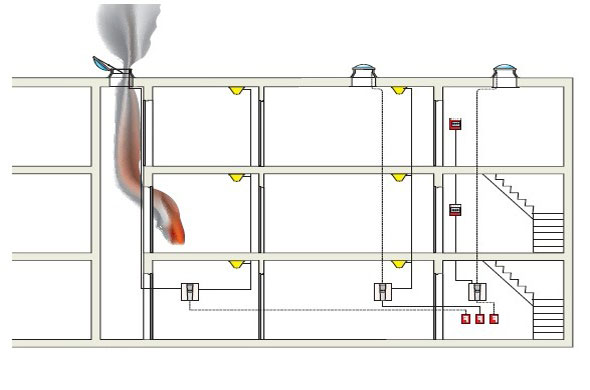
In addition to the threat of poisoning, smoke causes disorientation and panic during evacuation. There are specially designated places where the smoke removal system should run. First of all, they include:
- Staircases and landings.
- Foyer.
- Corridors, passages and galleries.
- Entrances.
In addition to the evacuation purpose, the SDU allows fire brigades to enter the building. This allows them to find the source of ignition, localize it and eliminate it. This is primarily beneficial for the owner of the building, as it allows minimizing possible damage from fire.
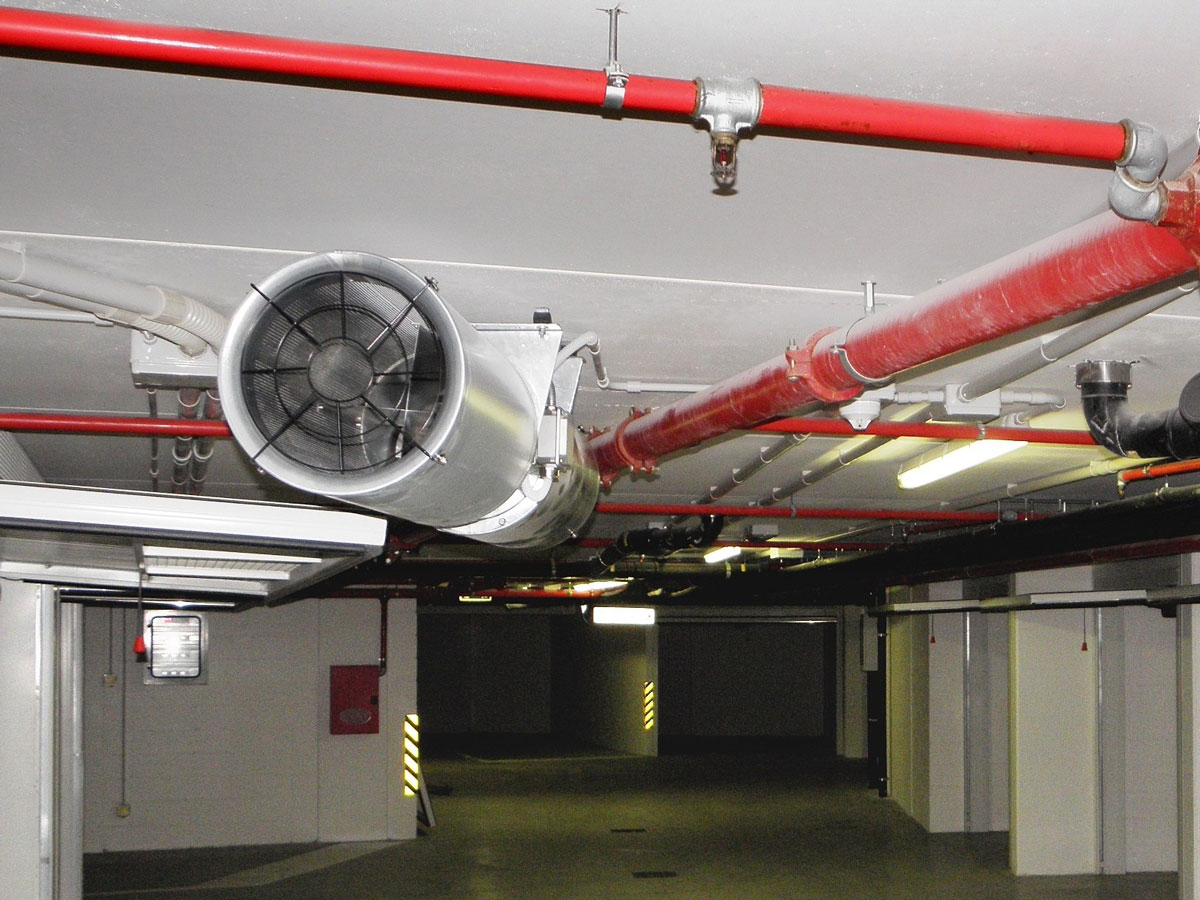
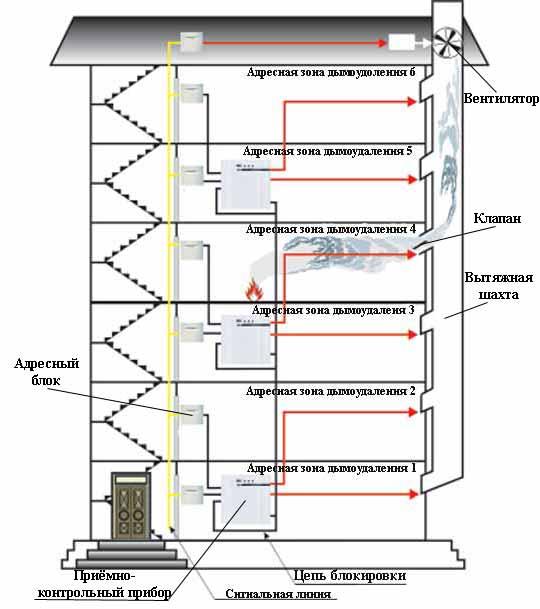
Installation work begins with the laying of chimneys and ventilation. This stage consists of mounting individual modules. First, special clamps are installed in the ceiling, to which each module is attached.

Branches are installed as needed. As a rule, these are elements having one or two channels. Such a branching must be installed in each zone where, according to the regulations, air masses must circulate.Channel openings are closed with a special grating. Chimneys transport the products of combustion to larger smoke shafts.
Each smoke shaft leads to an exhaust fan, which is installed directly on the roof of the building. Fans are mounted directly at the exit of smoke shafts. They are mounted in strict observance of the recommendations of the manufacturer.
Above the fan there is a small section of shaft that leads to a roof hatch. Hatches must be installed in accordance with the manufacturer's recommendations.

In parallel with the chimneys, pipes for pressurizing air are mounted. They can be mounted next to chimneys
Please note that the air vents must not be located side by side. If you do not follow this rule, then the efficiency of the system will drop sharply. Wiring over the chimney
It must be a three-phase cable with a voltage of 380 volts. It is connected to electronics. This is necessary for the automatic opening of the hatches and valves of the system. The cable must not come into contact with the heated parts of the chimney and in close proximity to them. Most often, the cable is attached above the parallel branch of the air boost
Wiring is pulled over the chimney. It must be a three-phase cable with a voltage of 380 volts. It is connected to electronics. This is necessary for the automatic opening of the hatches and valves of the system. The cable must not come into contact with the heated parts of the chimney and in close proximity to them. Most often, the cable is attached above the parallel branch of the air pressure.
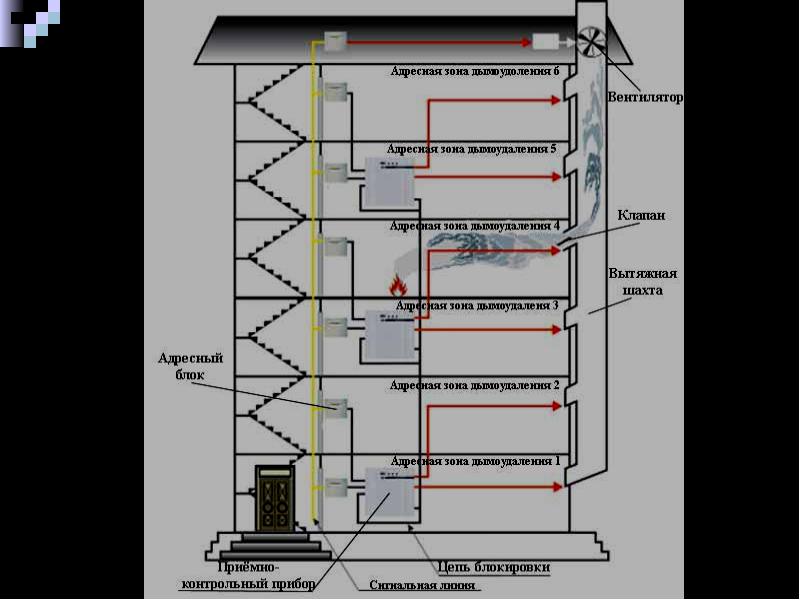
This protects against a short circuit that occurs when the wire is melted. Incorrect wiring leads to failure of the entire smoke extraction system.The final stage of installation work is the connection of an alarm or sensor system. In buildings with large areas, zoning is done. Separate control units are responsible for each section. There are systems where ventilation and smoke removal must be started manually.
Calculation of the combustion temperature of products removed from the corridor
Consider the distance from the fire to the nearest valve
Distance from the room with the seat of fire to the smoke damper
Corridor configuration
AngularRectilinearCircular
Maximum smoke layer thickness, m Corridor area, m2 Corridor length, m Type of fire
Fires regulated by air exchange are understood as fires that occur with a limited oxygen content in the gaseous environment of the room and an excess of combustible substances and materials. The oxygen content in the room is determined by the conditions of its ventilation, i.e. the area of supply openings or the flow rate of air entering the fire room with the help of mechanical ventilation systems.
Fires regulated by the fire load are understood as fires that occur with an excess of oxygen in the air in the room and the development of a fire depends on the fire load. These fires in their parameters approach fires in open space.
Ventilation-controlled fireLoad-controlled fire
Selecting a Value Entry Option
Enter value Calculate value
Specific reduced fire load, related to the floor area of the room, kg/m2
Specific reduced fire load, referred to the area of the heat-receiving surface of the enclosing building structures of the room, kg/m2
Mass of the fire load of the room, kg
Floor area of the room, m2
Room volume, m3
The total area of the openings of the room, m2
Substances and materials in the fire load
Add
Device
The need, composition and arrangement of such a rather complex variety of supply and exhaust ventilation systems are regulated by the following rules and regulations:
- SP 60.13330 "SNiP 41-01-2003*", regulating the requirements for heating, ventilation of the air environment of buildings (as amended on February 10, 2017), which included a block of new requirements for smoke protection systems.
- SP 7.13130.2013, which establishes the PB requirements for such systems.
- NPB 239-97 on checking the fire resistance of air ducts.
- NPB 241-97 on fire dampers for ventilation systems.
- NPB 253-98, which establishes safety standards for fans of smoke exhaust systems.
- NPB 250-97 on the requirements for fire elevators installed in buildings, structures for various purposes.
- Guidelines of the Ministry of Emergency Situations of 2008 on the calculation of the parameters of smoke removal. This document is not a guide, but is successfully applied in the design.
According to these standards, the installation of such systems - supply and exhaust ventilation systems, which are controlled automatically or in manual mode, is required from the following fire compartments / premises of protected objects:
- Halls / corridors of public or residential buildings above 28 m.
- Tunnels, corridors of buried and underground floors that do not have insolation, buildings of any purpose, if premises with a constant presence of people open into them.
- Corridors longer than 15 m without lighting in industrial, warehouse buildings of the explosion hazard category A–B2 from two floors; workshops of category B3; public complexes of six floors or more.
- Common corridors of buildings with smoke-free stairwells.
- Corridors of apartment buildings without natural lighting, if the distance from the entrance of the farthest apartment to the non-smokeable staircase H1 is more than 12 m.
- Atriums of public complexes above 28 m; passages/atriums with doors/balconies above 15 m.
- Stairs L2 of hospitals in the presence of lanterns that automatically open when smoke detectors of APS installations/systems are triggered.
- Industrial premises, warehouses with workplaces, without natural lighting or with it through windows / lanterns that are not provided with automatic drives for opening.
- Premises not provided with insolation: any public with a mass presence of people; over 50 sq. m. with jobs in the presence of combustible substances; commercial premises; wardrobes over 200 sq. m.
It is acceptable to design the removal of the smoke flow through the corridor serving rooms up to 200 sq. m., if they are for industrial use and belong to fire and explosion categories B1–B3 or are intended for storage of combustible materials.
It is not required to design/install smoke exhaust systems from the following rooms:
- Less than 200 sq. m., if they are protected by stationary fire extinguishing systems, with the exception of categories A, B.
- With powder/gas AUPT systems.
- From the corridors, if all the rooms adjacent to them are provided with smoke exhaust.
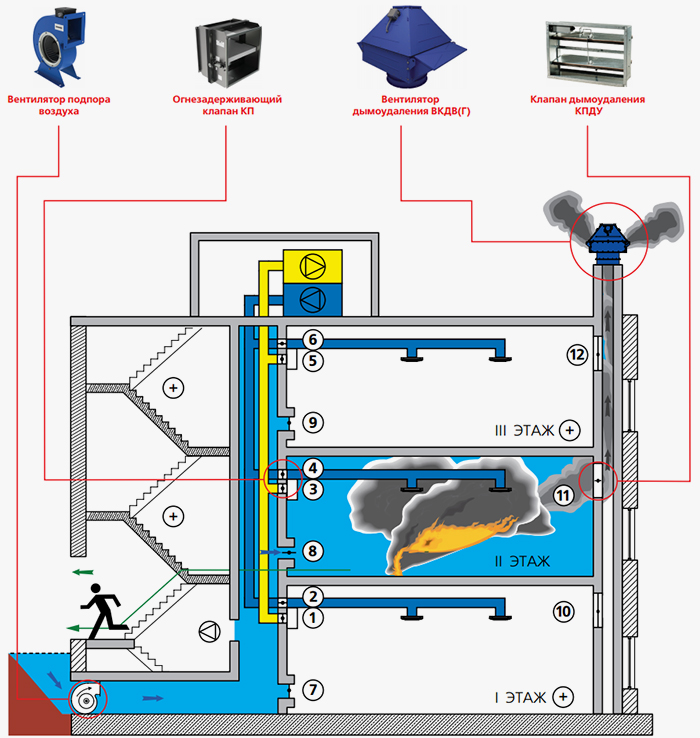
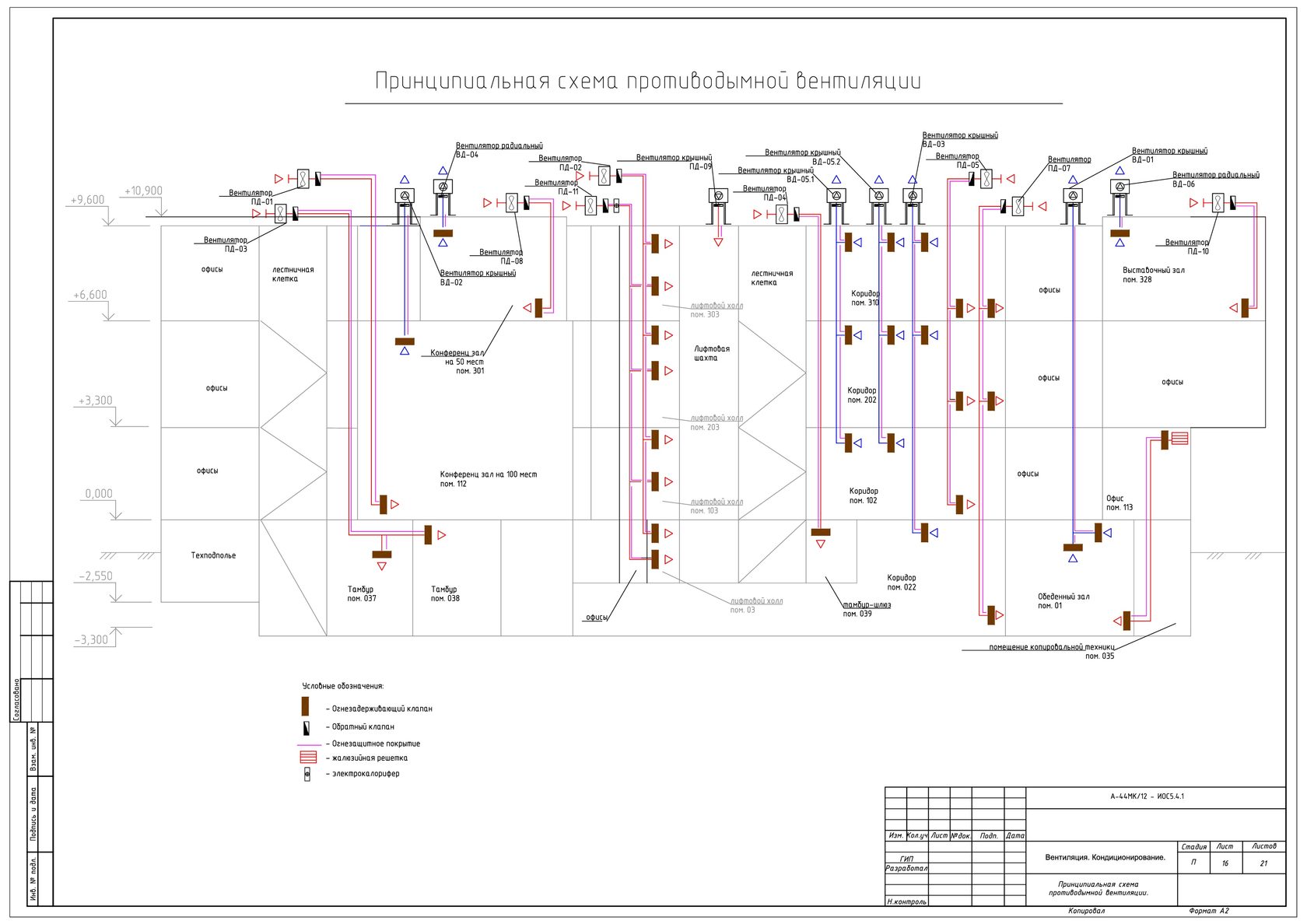
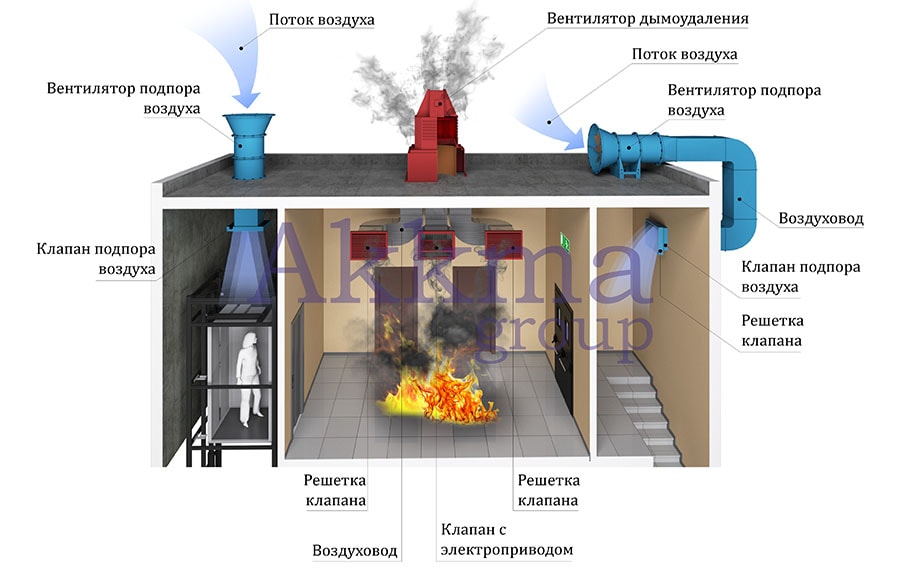
Devices, smoke exhaust and air supply systems are of several types with the following device:
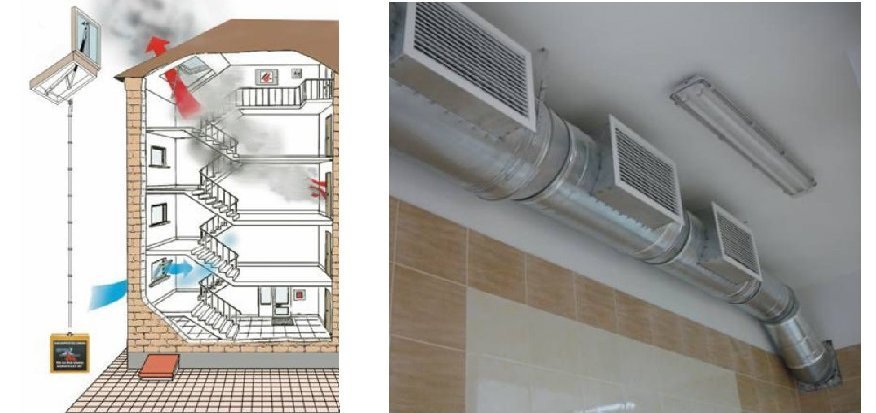
- Windows, lanterns for lighting premises with an incentive drive, opening in manual and automatic modes.
- Exhaust smoke ventilation from rooms, foyers, lobbies, corridors.
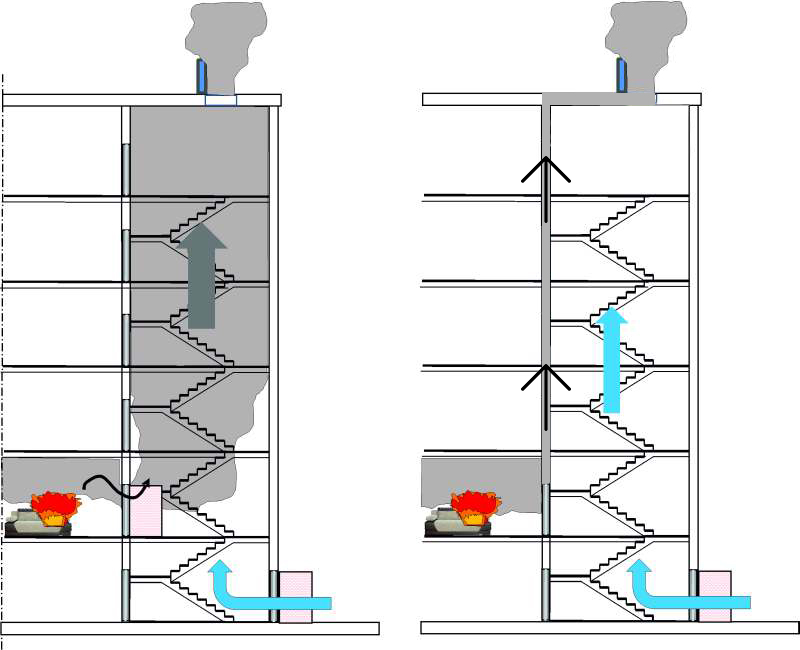
- Supply ventilation designed for forced air flow into internal staircases, vestibules, elevator shafts of passenger / freight elevators of buildings and structures, displacing / eliminating combustion products from entering them with strong air pressure.
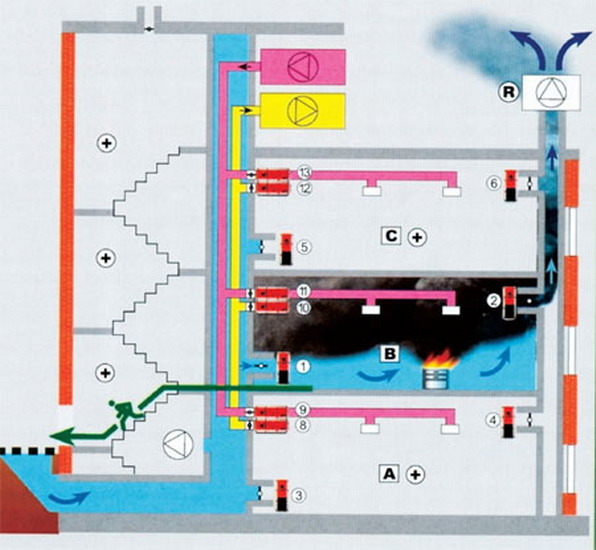
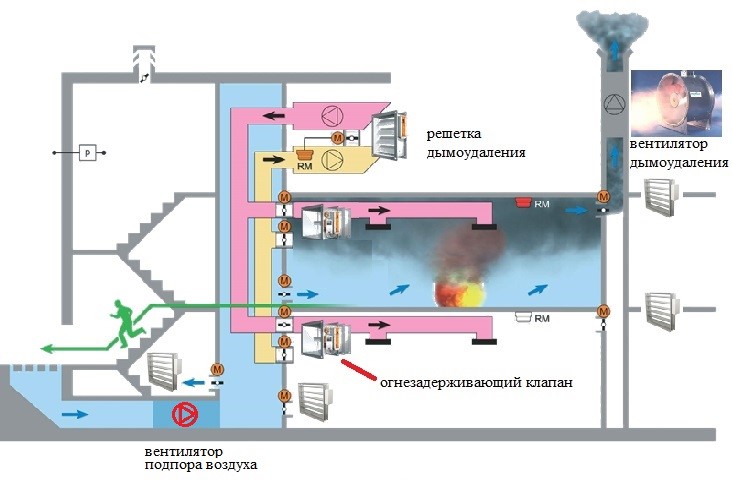
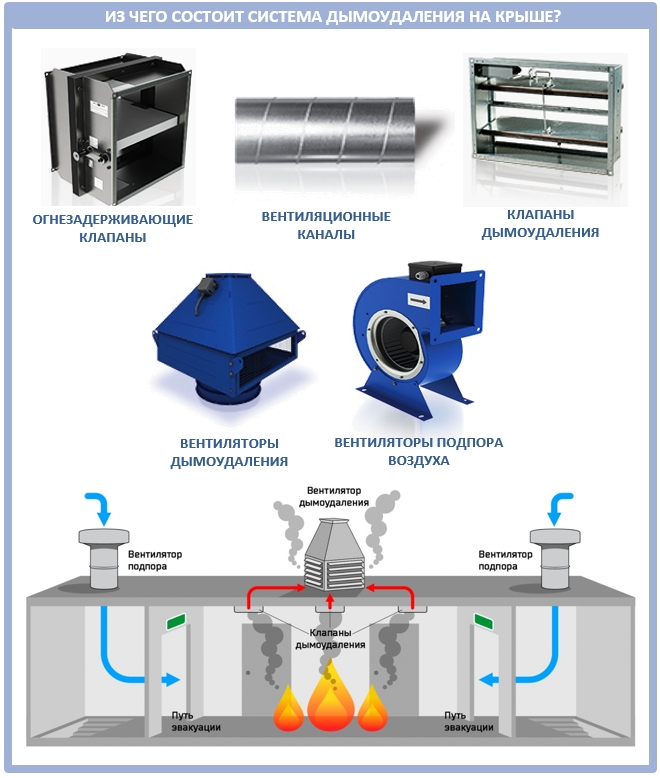
Smoke exhaust/forced air supply systems in case of fire include:
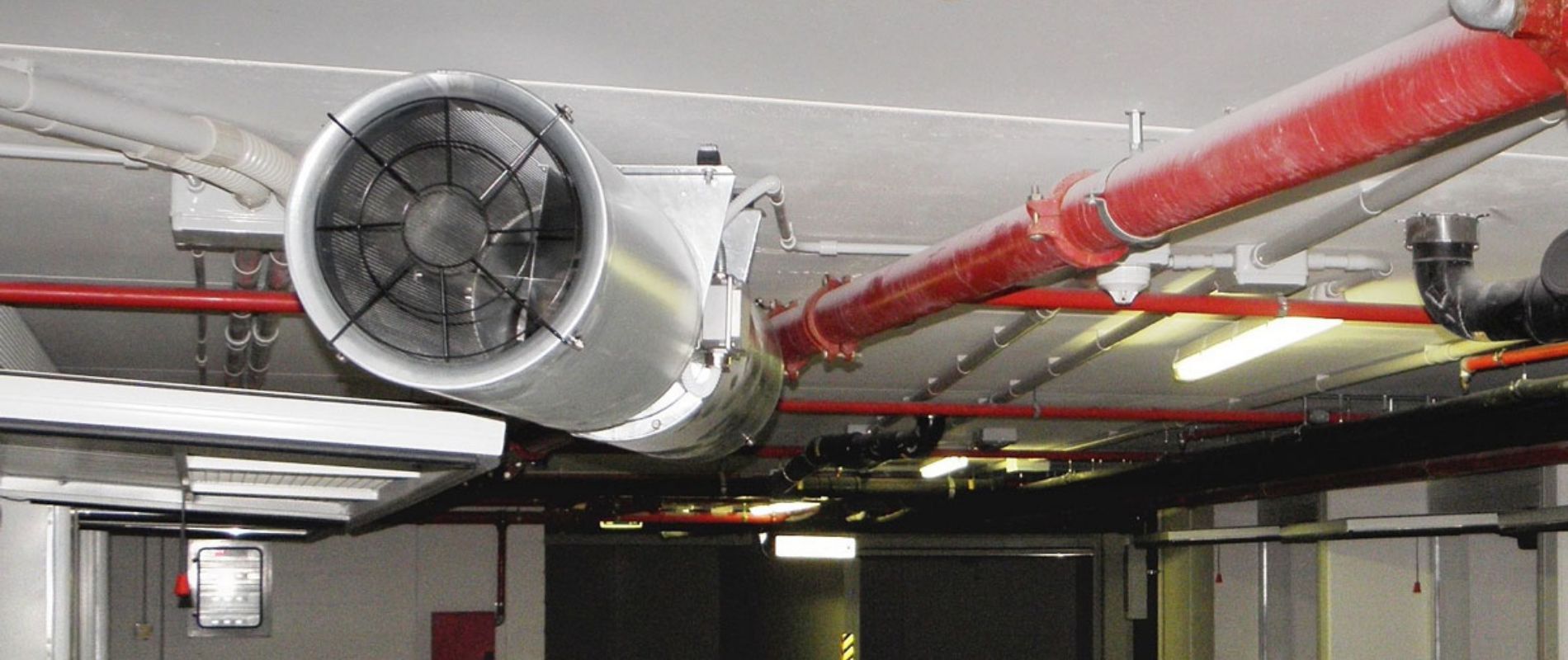
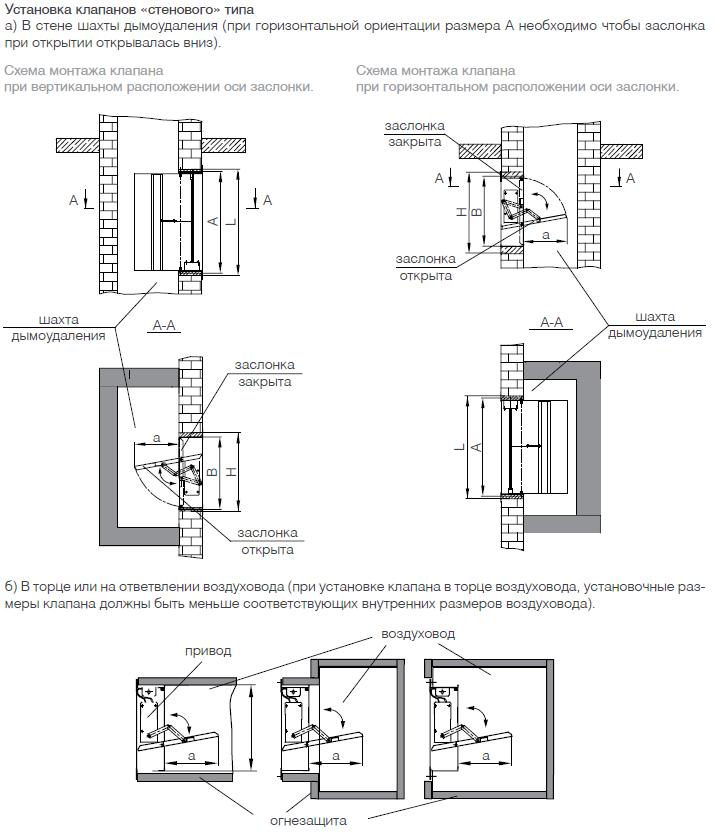
- Smoke dampers, also called smoke extractors.
- Fans to remove dense smoke flow.
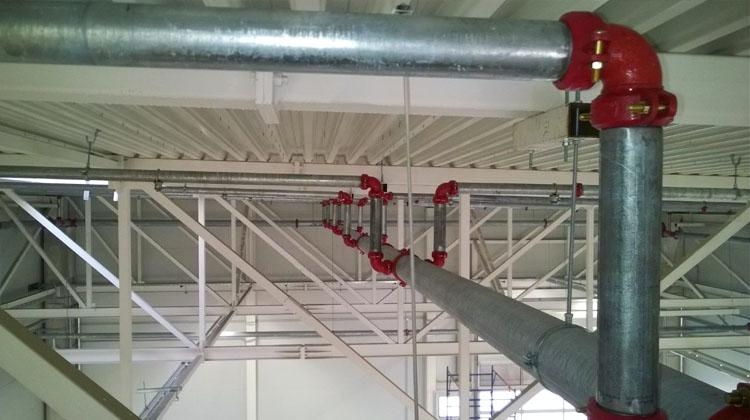
- Mines, main channels, fire-resistant smoke exhaust ventilation ducts.
- Forced air fans, most often mounted on the roof of buildings / structures.
- Fire-retardant dampers mounted on the exhaust system of the general air exchange of the premises to limit / exclude the spread of fire through the ventilation ducts.
The effectiveness of protecting buildings/structures in the event of a fire, the possibility of carrying out a quick safe evacuation of people from them, limiting the spread of fire, thermal effects, combustion products directly depends on the synchronism of the joint operation of smoke exhaust systems / forced inflow of clean air; therefore, the device, the principles of their work should be designed so that they complement each other as much as possible.
Where is smoke ventilation installed?
There are buildings and premises where smoke exhaust systems are needed. Sometimes you can do without them.
Where are SDUs needed?
Systems must be installed:
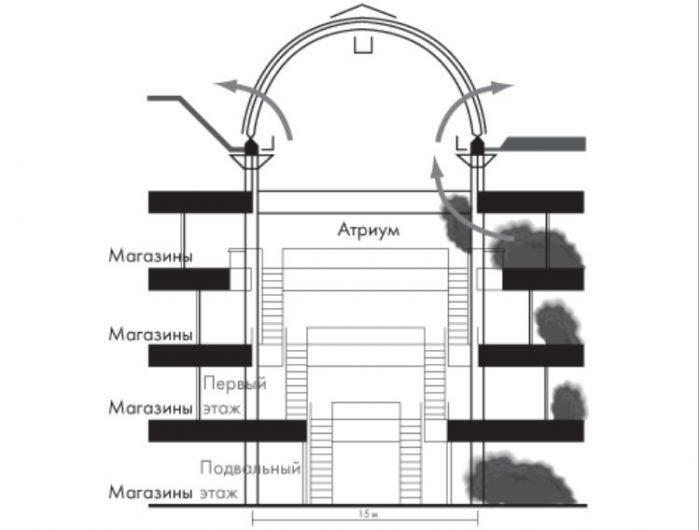
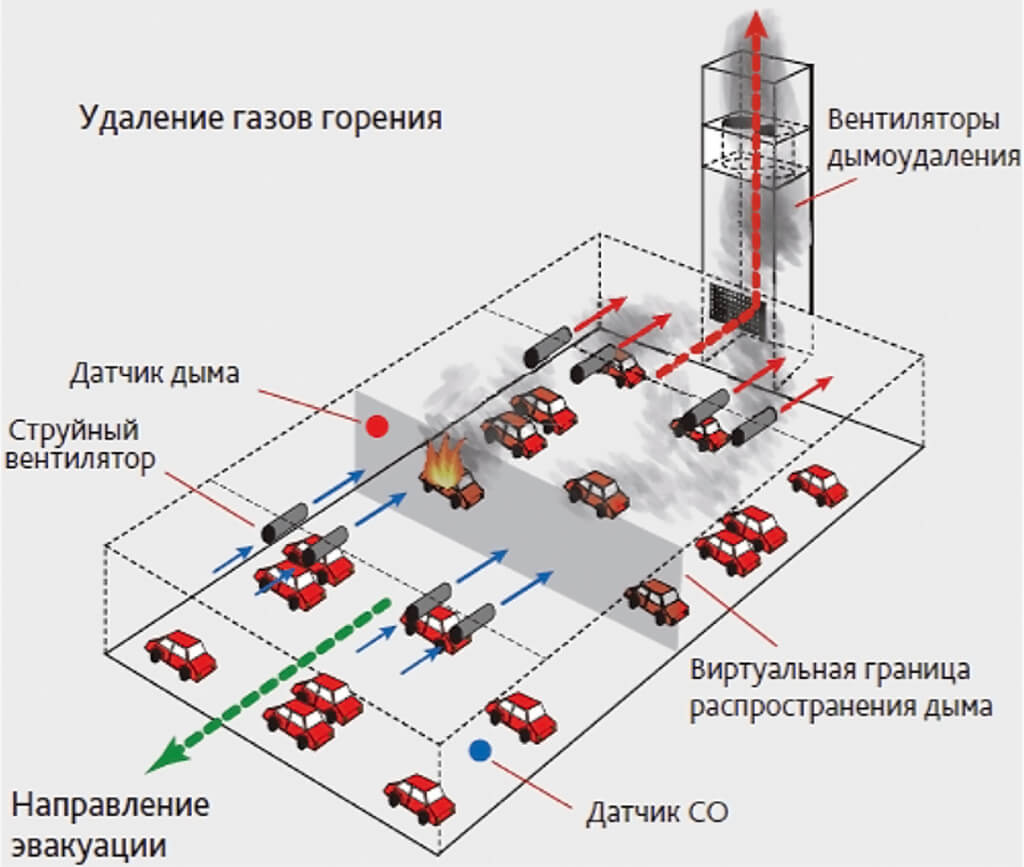
- In passages (atriums), in warehouses with racks, if the height is more than 5.5 m, and materials that can catch fire are stored indoors.
- In the halls and corridors of buildings with more than 9 storeys, the exception is industrial buildings where they work with combustible substances. They need SDU.
- Materials that can ignite are stored in production and storage areas where people are constantly present. Smoke exhaust systems are needed for any wooden warehouse, as well as a building built from any other combustible material.
- In the basement or basement floors of any buildings where people are constantly in these rooms. The first example is the basement of a residential building, where shops, workshops, offices, etc. are located. However, if access is provided directly to the street, then smoke ventilation is not needed.
- Corridors that are longer than 15 meters and have outward opening windows are not provided. SDU is not required for industrial buildings where there are no combustible substances. There is no need to install the system when the premises leading to the corridors are not intended for permanent work of people, and the doors are smoke and gas tight.

The CDS are mandatory for schools, hospitals, gyms and other public buildings. Such ventilation is needed for rooms that do not have opening external windows:
- for offices, trading floors of shops, regardless of their area, for dressing rooms over 200 m2;
- for premises whose area exceeds 50 m2: archives, libraries, reading rooms, auditoriums, restaurants, classrooms, etc.
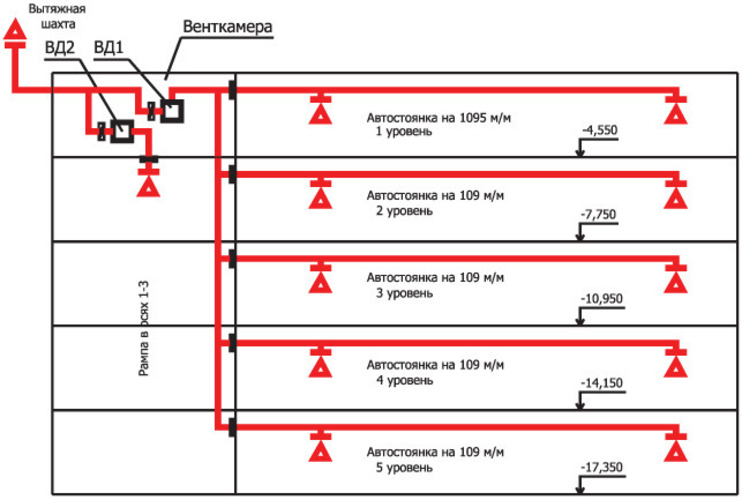
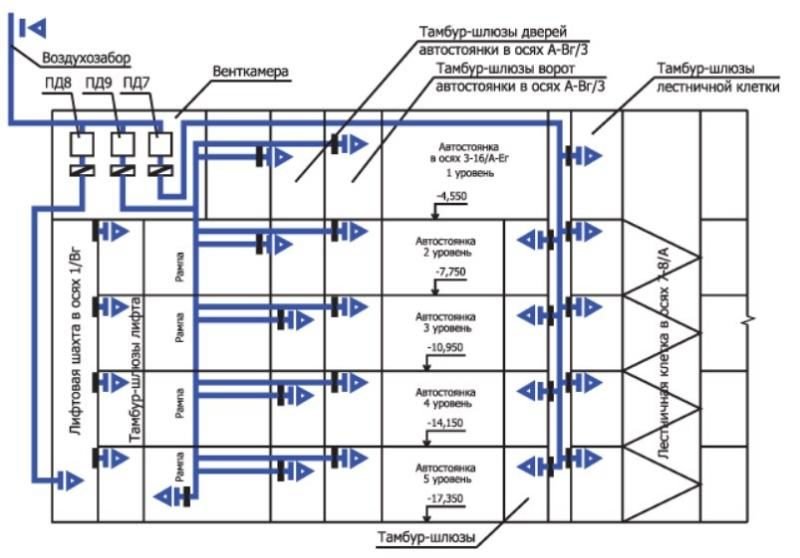
Installation of smoke ventilation is a mandatory condition for all rooms with access to a smoke-free staircase.This is an internal structure designed to evacuate people in case of fire in buildings with a height of more than 28 m (over 9 floors). SDU is a mandatory attribute of covered parking lots, as well as closed ring ramps.
Where are SDUs not needed?

In some rooms, a smoke exhaust system may not be installed. First of all, this applies to buildings already equipped with autonomous fire extinguishing systems of water, foam or powder type. There are exceptions: these are parking lots, car services.
Use in private homes
The regulations do not provide for the installation of smoke ventilation in the private sector. It is believed that open windows are sufficient to remove smoke from low-rise buildings. However, there is an exception: these are non-residential objects. For example, private hotels, clinics, boarding houses or schools.

Since the number of people in a residential building, as a rule, is small, the usual ventilation system completely copes with its duty during a fire. It allows residents to freely leave the premises and the building. In this case, only the installation of a fire alarm is required.
An alternative is an electronic system that can control the opening of doors and windows when sensors are triggered. In this case, the main task is the choice of sensors. Since some models are characterized by a low threshold, such a system may not be very effective. Therefore, the choice of devices should be as correct as possible.
Starting the fire protection system from the duty station.
So, is it necessary or not to drag remote start wires from control cabinets to the security post?
For greater reliability, it would not hurt.
But in each security system there is a corresponding control panel for engineering systems, which allows, at least by pressing a button, to turn on the entire range of system tools.
Frontier went the furthest, creating the remote control "Border-PDU".
Unfortunately, it is rare to find such a panel at the facility.
It costs 7500r and this money is likely to be saved.
The thing is that it is possible to formally control all outputs and engineering systems from the keyboard of the network controller.
But to be does not mean to appear - it is unlikely that ordinary duty personnel will be able to manage anything.
Controlling something from the S2000M panel is fantastic.
But from the instrument panel "Frontier-2OP" control is implemented very conveniently.
So we live in continuous formalities.
Installation of a smoke exhaust system
Before designing and calculations, be sure to study the recommendations of the Ministry of Emergencies. These documents contain tables of properties of different materials, formulas for calculating all parameters of smoke ventilation.
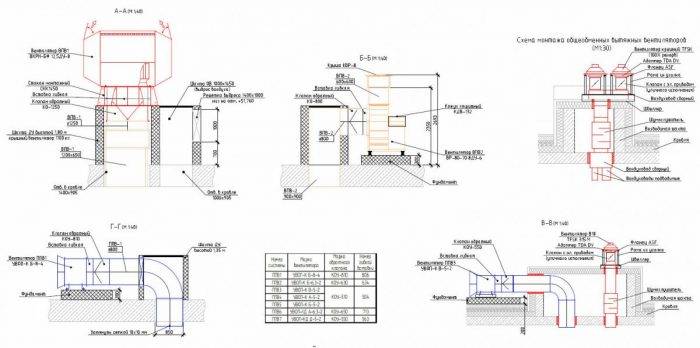
The power of the system must be sufficient for the room in which it is installed. The maximum air circulation speed is clearly limited: it is 1 m/s. This requirement is explained by the fact that a strong air flow contributes to an increase in the source of ignition. This parameter is adjusted by changing the sections of the valves. There is an area requirement: at least one device for every 600-800 m2. Since the system uses forced ventilation, there are no serious restrictions regarding the installation of air ducts. It is allowed to make more than 2 turns of the flue pipes.
SDU installation
Since smoke creates panic in areas intended for evacuation of people, makes it difficult for firefighters to work, the systems are mounted in specially designated places. These include:
- platforms and flights of stairs;
- galleries, corridors, passages;
- entrances.
Installation begins with the assembly of chimney pipes and ventilation. First of all, special clamps are fixed on the ceiling, then individual modules are sequentially attached to them. All joints are sealed. According to the regulations, in each zone it is necessary to install branchings - elements with one or two channels. Their openings are closed with gratings.
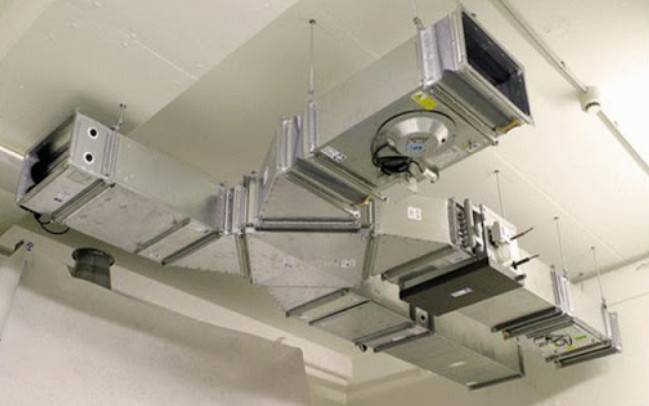

Each such chimney passes into smoke shafts, which are large. The last elements are brought to the roof, where fans are mounted into the system (at the outlet). A small free area is left between the devices and the smoke hatch in the mine. Vertical fan models do not need protective hatches.
In parallel, retaining air ducts are mounted. They can be located in close proximity to chimneys, but the openings of these pipes should not be located nearby. A three-phase power cable with a non-combustible braid is pulled over the backwater branch. Electronics are connected to the wiring, which provides automatic opening of valves and hatches.
Checking the operation of the CDS
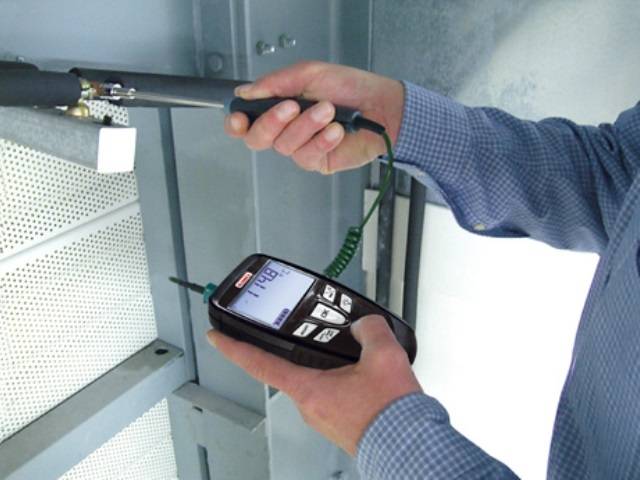

This operation is mandatory, and it is carried out twice: immediately after the installation is completed and during the check of the system by control authorities. This process involves sequential testing of each part of the design. In the future, scheduled inspections will be carried out by supervisory authorities.
In the event of failure of the CDS, the owner is obliged to ensure that the equipment is repaired as soon as possible. Preventive work is carried out by representatives of the organization that installed the system. If faulty equipment causes death of people, then the owner of the building will be held criminally liable, the reason is a violation of fire safety standards.
Service
Regular testing of the CDS performance is a mandatory requirement. In case of violations of the operating rules, foreign objects can get into the ventilation pipes, garbage left by the craftsmen who did the work poorly is not excluded. If the litter accumulates a lot, then a problem may arise: in this case, the air supply will either be difficult or stop altogether. For these reasons, regular and thorough preventive examinations are the only way to prevent loss of life if an emergency occurs.

Do the following on a monthly basis:
- check the operability, as well as the technical condition of the alarm;
- inspect all connections, evaluate the operation of equipment, valves;
- carry out diagnostics of all devices;
- troubleshoot.
During quarterly events, inspection and cleaning of all elements of the system, checking its operation from a backup power source, and inspecting cables for possible damage are added to these stages. All stages are documented: the results of each check, according to the work schedule, are recorded in the log book.
Smoke ventilation is an extremely important element of the fire protection complex. The following video will tell you how the smoke exhaust system works:
What is a smoke extraction system?
SDU - multi-level ventilation, is an emergency complex of equipment and air ducts that solve one problem - they help to evacuate smoke from the room as quickly as possible. Such systems are installed in multi-storey residential, public buildings, but very rarely they are mounted in private homes.

Tasks of the CDS
Smoke exhaust systems are required to perform several functions at once. They are:
- minimize smoke on escape routes;
- prevent further spread of the flame;
- quickly reduce the temperature in rooms engulfed in fire;
- constantly monitor the level of smoke, notify of a fire;
- provide an optimal microclimate in other rooms where there is no fire.
After detecting an area with smoke, the SDUs automatically transfer all elements of the system to the operating mode. They maintain the minimum concentration of oxygen, which is necessary for the possibility of a quick evacuation of people.
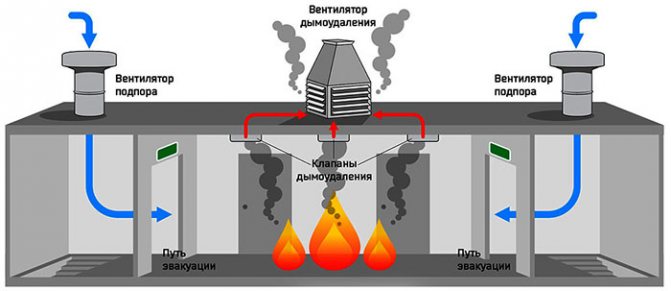
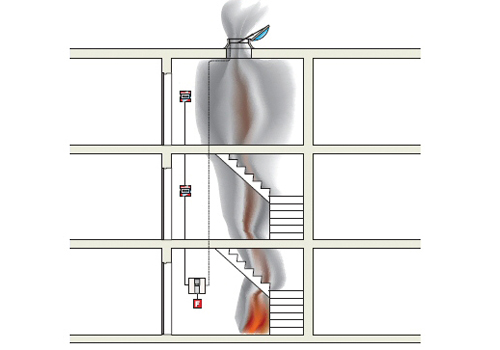
How does a smoke exhaust system work?
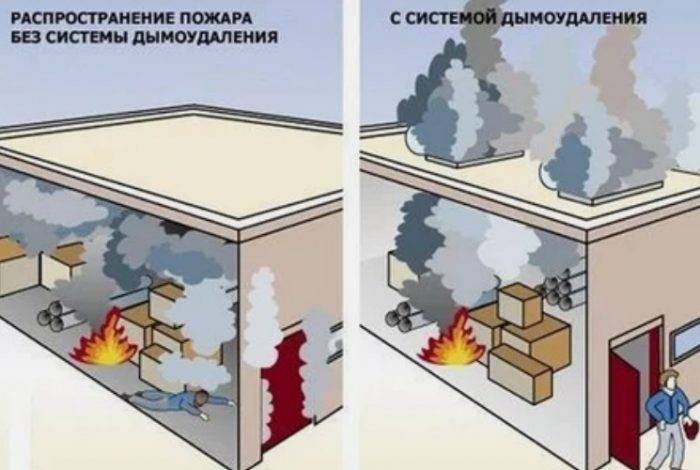
The second name of SDU is smoke ventilation. It consists of an exhaust and an inflow, which must compensate for the removed smoky air. Until 2009, such systems were not installed in buildings, however, due to the increased incidence of serious fires, since 2013 their installation has become mandatory.
The smoke exhaust system works just like any other ventilation system. Warm masses rise up, cold air sinks down. This creates natural traction. To increase its power, special fans are used in the SDU, the tasks of which are to remove smoke and quickly replace it with clean air.
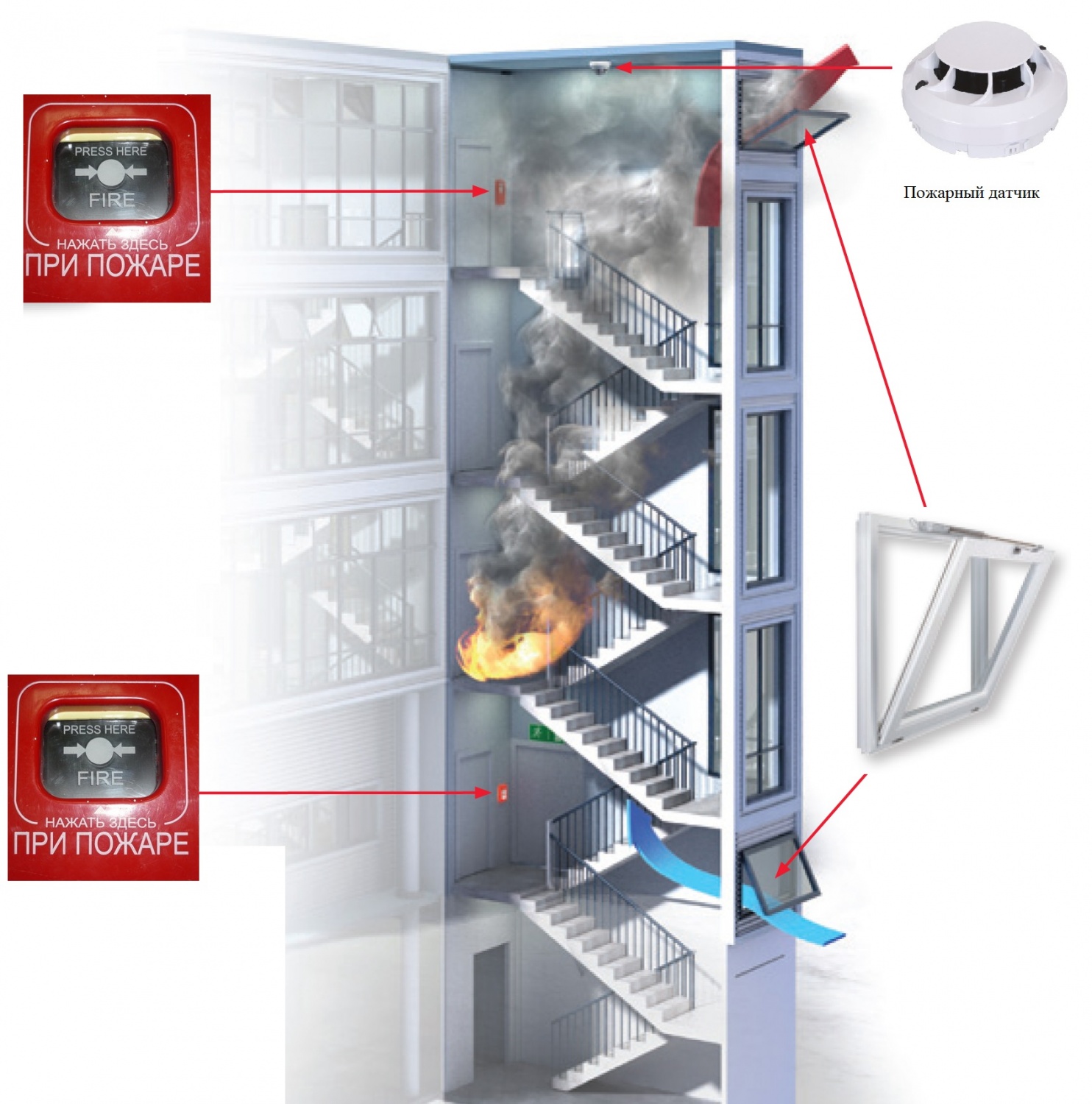
The work of the SDU can be conditionally divided into several stages:
- after a fire source appears, a smoke sensor is triggered;
- this signal is sent to the control panel for fire safety systems, then the ventilation stops, the fire protection valves close;
- where a fire source is detected, smoke exhaust valves open at the same time;
- fans are included in the work: those that remove smoke, and backwater devices (air injection).
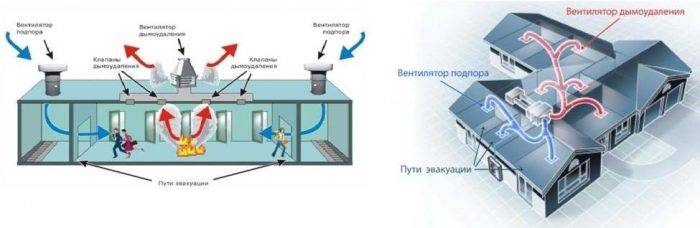
The smoke exhaust system turns on automatically when the fire alarm goes off. After switching to the operating mode, it begins to remove combustion products, preventing their spread to other rooms. Backwater fans are devices that supply fresh air to corridors, platforms, evacuation elevators and other places designed to save people who are in the building at the time of the fire.
Types of smoke ventilation
Smoke exhaust systems are static and dynamic.
- Static CDS are intended only for localization of the source of fire. In this case, the equipment performs an emergency shutdown of the ventilation of the building, preventing the penetration of combustion products and smoke into other rooms. The minus of the systems is low efficiency, since they are not able to guarantee the removal of smoky air from the room, a serious danger to people, since the temperature in the source of ignition can reach 1000 °.
- Dynamic CDS are devoid of the shortcomings of static systems. They ensure the removal of smoke and the inflow of fresh air into the areas of the facility. In this case, special fans are used. There can be several devices - for exhaust and inflow. However, there is another option - a device that alternately works to remove smoke and supply fresh air.The main task of these systems is to provide relatively normal conditions for emergency evacuation of people.

The choice of a smoke exhaust system depends only on the features of the object - structural and architectural. Static CDS are much cheaper, but dynamic ventilation is more likely to avoid poisoning by toxins. If we talk about fire safety rules, then both types are allowed to be installed.
What is taken into account when designing a CDS?
Several factors must be taken into account before starting the calculations. These include:
- the most important characteristics of the building: area, number of storeys, evacuation plan in case of fire;
- glazing features: number of windows, their location, total area;
- smoke permeability of building materials, thermal insulation, facade.
The calculation method is complex, so this stage requires the involvement of competent specialists. The company has the right to develop the project only in one case: if its employees have received a license from the Ministry of Emergency Situations of the Russian Federation. The drawn up plan must also be approved by the Ministry of Emergency Situations.