- Options for a two-pipe system
- Vertical system with bottom wiring
- Vertical system with top wiring
- Horizontal heating system - three main types
- Installation of the system when planning a warm floor
- Two-pipe CO
- "Warm floor
- Primary requirements
- Types of forced circulation of heat carrier in heating
- What is two-pipe wiring
- Two-pipe system with bottom wiring
- Advantages and disadvantages of a two-pipe system with bottom wiring
- Features of mounting a two-pipe system with bottom wiring
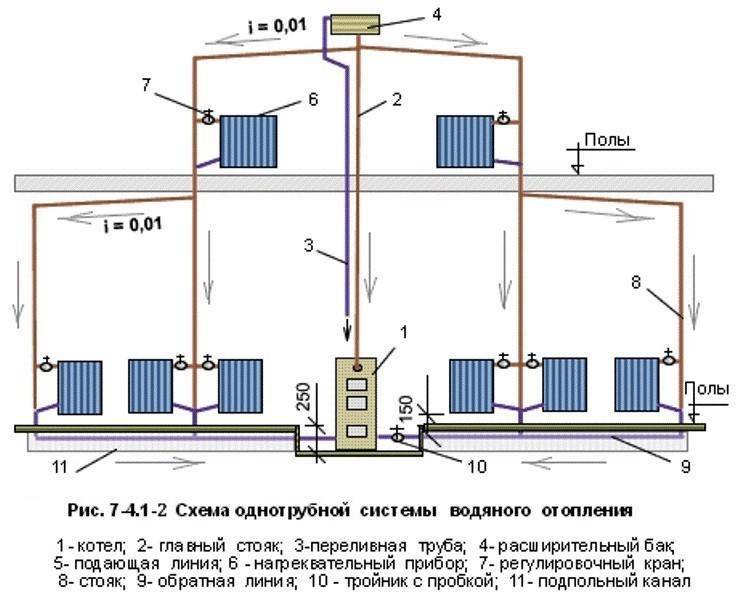
- Types of water heating of a private two-story house with their own hands with diagrams
- Natural variant of heat carrier supply
- Requirements for a room with two boilers
Options for a two-pipe system
The main difference between a two-pipe heating scheme for a private house is the connection of each battery to the mains of both direct and reverse current, which doubles the consumption of pipes. But the owner of the house has the opportunity to regulate the level of heat transfer of each individual heater. As a result, it is possible to provide a different temperature microclimate in the rooms.
When installing a vertical two-pipe heating system, the lower, as well as the upper, heating wiring diagram from the boiler is applicable. Now in more detail about each of them.
Vertical system with bottom wiring
Set it up like this:
- From the heating boiler, a supply main pipeline is launched along the floor of the lower floor of the house or through the basement.
- Further from the main pipe, risers are launched upwards, which ensure that the coolant enters the batteries.
- A return current pipe departs from each battery, which takes the cooled coolant back to the boiler.
When designing the lower wiring of an autonomous heating system, the need for constant removal of air from the pipeline is taken into account. This requirement is met by installing an air pipe, as well as installing an expansion tank, using Mayevsky taps on all radiators located on the top floor of the house.
Vertical system with top wiring
In this scheme, the coolant from the boiler is supplied to the attic through the main pipeline or under the very ceiling of the upper floor. Then the water (coolant) goes down through several risers, passes through all the batteries, and returns back to the heating boiler through the main pipeline.
An expansion tank is installed in this system to periodically remove air bubbles. This version of the heating device is much more effective than the previous method with lower piping, since higher pressure is created in the risers and in the radiators.
Horizontal heating system - three main types
The device of a horizontal two-pipe autonomous heating system with forced circulation is the most common option for heating a private house. In this case, one of three schemes is used:
- Dead end circuit (A). The advantage is the low consumption of pipes.The disadvantage lies in the large length of the circulation circuit of the radiator farthest from the boiler. This greatly complicates the adjustment of the system.
- Scheme with the associated advancement of water (B). Due to the equal length of all circulation circuits, it is easier to adjust the system. During implementation, a large number of pipes will be required, which increase the cost of work, and also spoil the interior of the house with their appearance.
- Scheme with a collector (beam) distribution (B). Since each radiator is connected separately to the central manifold, it is very easy to ensure uniform distribution of all rooms. In practice, the installation of heating according to this scheme is the most expensive due to the high consumption of materials. Pipes are hidden in a concrete screed, which at times increases the attractiveness of the interior. The beam (collector) scheme for distributing heating on the floor is becoming increasingly popular among individual developers.
This is how it looks like:
When choosing a typical wiring diagram, it is necessary to take into account many factors, ranging from the area of \u200b\u200bthe house to the materials used in its construction. It is better to resolve such issues with specialists in order to eliminate the possibility of error. After all, we are talking about heating the house, the main condition for comfortable living in private housing.
Installation of the system when planning a warm floor
The main nuances that must be considered when planning the installation of a warm floor:

It is very important to choose the right flooring.Highly! For example, if a screed is laid over a warm floor (and it is mandatory and will be in any case), and a 10-centimeter parquet is placed on top of the screed, then why is this warm floor needed at all if the efficiency of such a system is zero? All such points must be taken into account;
The underfloor heating pipeline is always and under any circumstances mounted exclusively in the screed of the floor itself. Then usually people ask themselves: what should be its thickness? But experts will be able to answer this question only if they have information about all the initial parameters of the house itself and the power required for the heating circuit;
Then usually people ask themselves: what should be its thickness? But experts will be able to answer this question only if they have information about all the initial parameters of the house itself and the power required for the heating circuit;
Even if it is planned to install a warm floor on the ground floor only in some parts, thermal insulation will have to be carried out over the entire surface of the floor, otherwise the heat will go to the basement, thereby wasting energy virtually nowhere and lowering the efficiency of the entire system. Of course, this is provided that there are no living rooms in the basement or that no animals are kept. For the second floor, this condition is optional;
By the way, any water supply scheme will work more efficiently if it has natural rather than forced circulation, which is extremely important. How different are heating systems?
For example, what will be the difference between the heating system of a one-story brick private house with polypropylene pipes (polypropylene pipes are now popular) and a two-story wooden house, which is heated by an electric boiler?
For example, what will be the difference between the heating system of a one-story brick private house with polypropylene pipes (polypropylene pipes are now popular) and a two-story wooden house, which is heated by an electric boiler?

The general scheme of the underfloor heating device in the house
In any case, the heating system in a one-story house will be a priori simpler from a technical point of view than in houses with two or more floors. And if we take huge houses, the area of \u200b\u200bwhich starts from 500 m², then everything is so complicated and completely confusing that it seems that even a nuclear physicist will not immediately figure out where to insert this or that fitting and with what pumps water or some kind of other coolant.
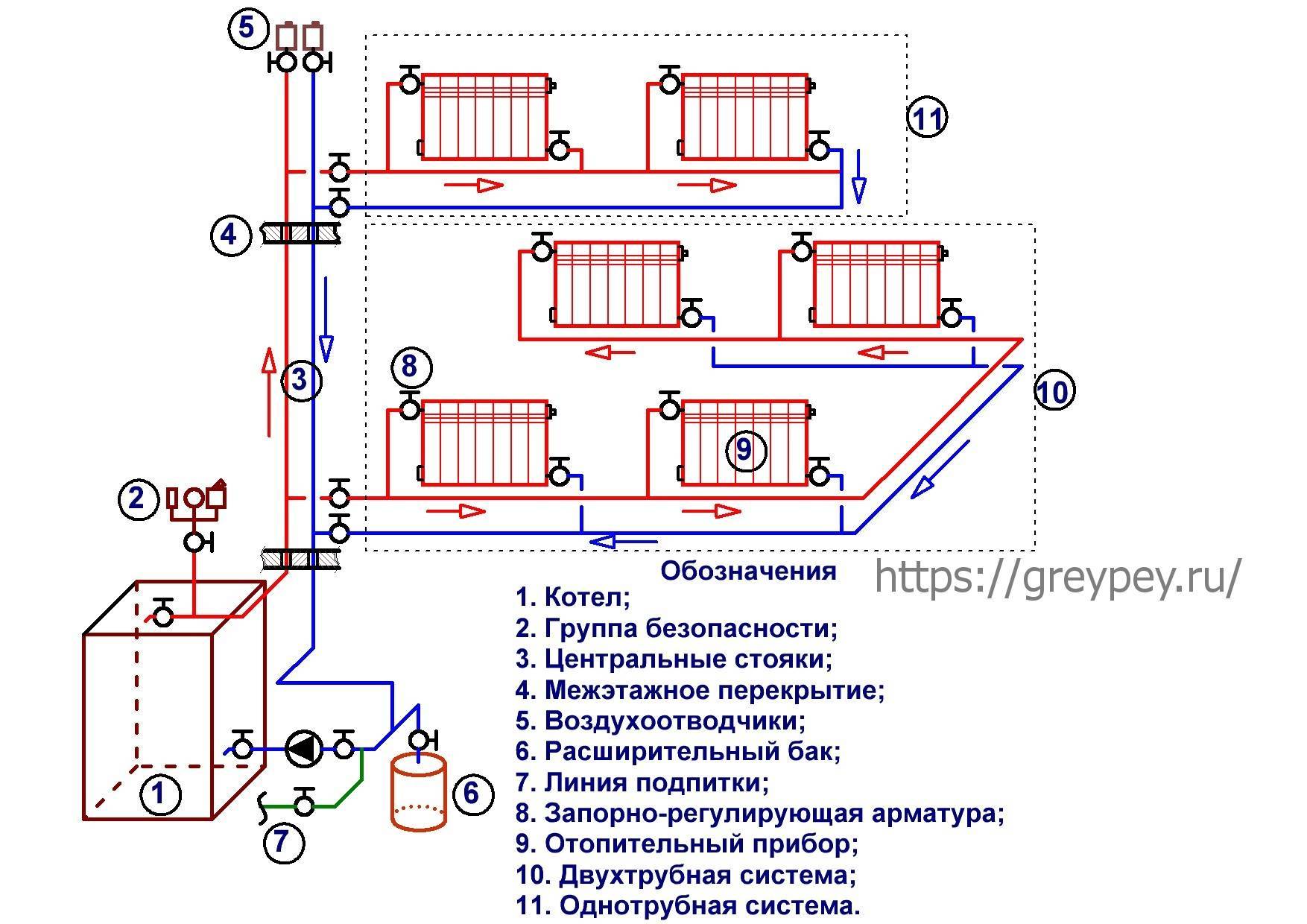
Two-pipe CO
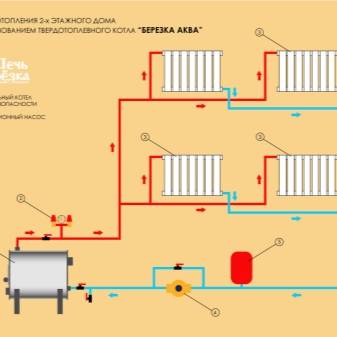
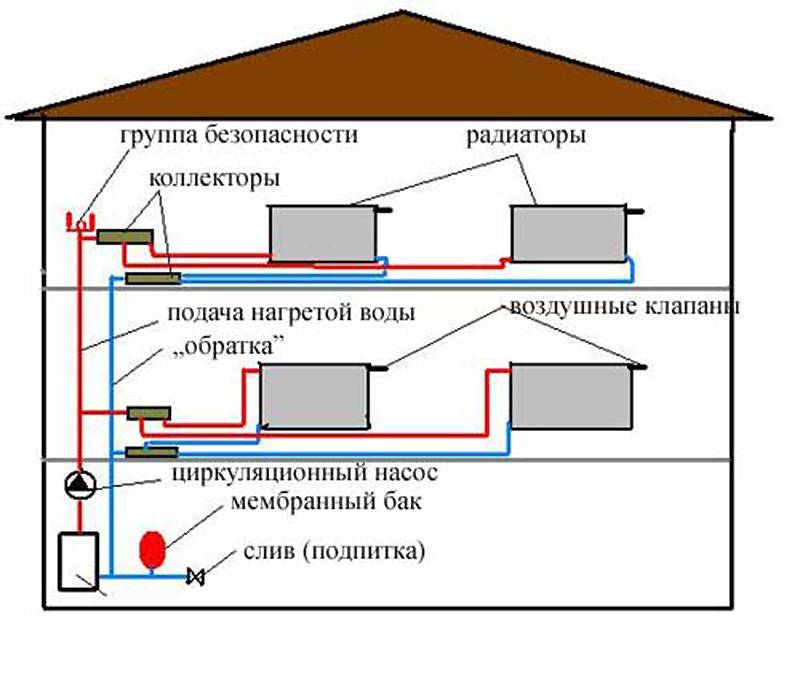
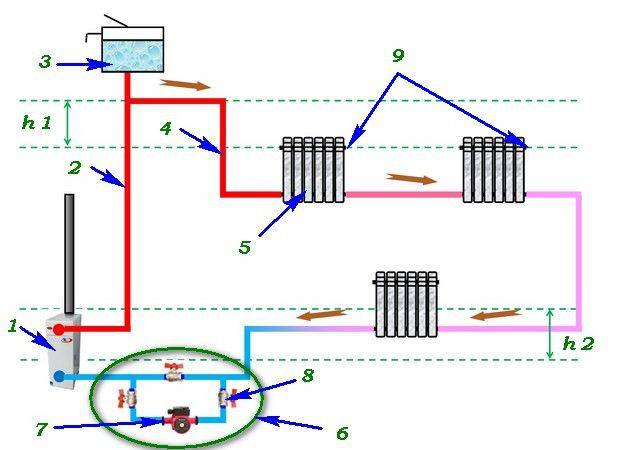
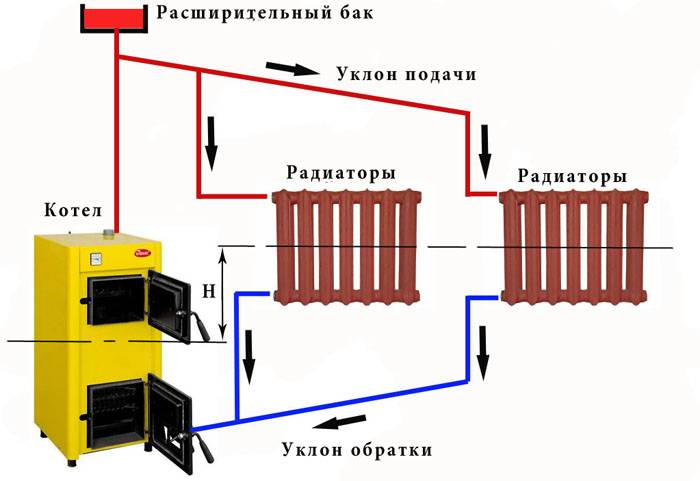
In two-pipe circulation circuits, hot water is supplied from the boiler and the cooled coolant is returned to the boiler through two independent pipelines, called, respectively, supply and return. Unlike a single-pipe Leningrad, heating two-pipe systems are able to supply radiators on both floors of a private two-story building with a coolant of the same temperature, which favorably affects the microclimate of the home.
The figure below shows a diagram of the movement of the water coolant through the heating devices on both floors:
- red line - hot water circuit;
- the blue line is the circuit with cooled water coming out of the radiators.
Scheme of the movement of the coolant in a two-pipe CO of a two-story house
The following factors are considered to be the most weighty arguments in favor of a two-pipe system in front of Leningrad:
- uniform heating of rooms on both floors of a private house;
- the ability to adjust the temperature range in each room in automatic mode, coordinating the work of CO with the heating boiler.
"Warm floor

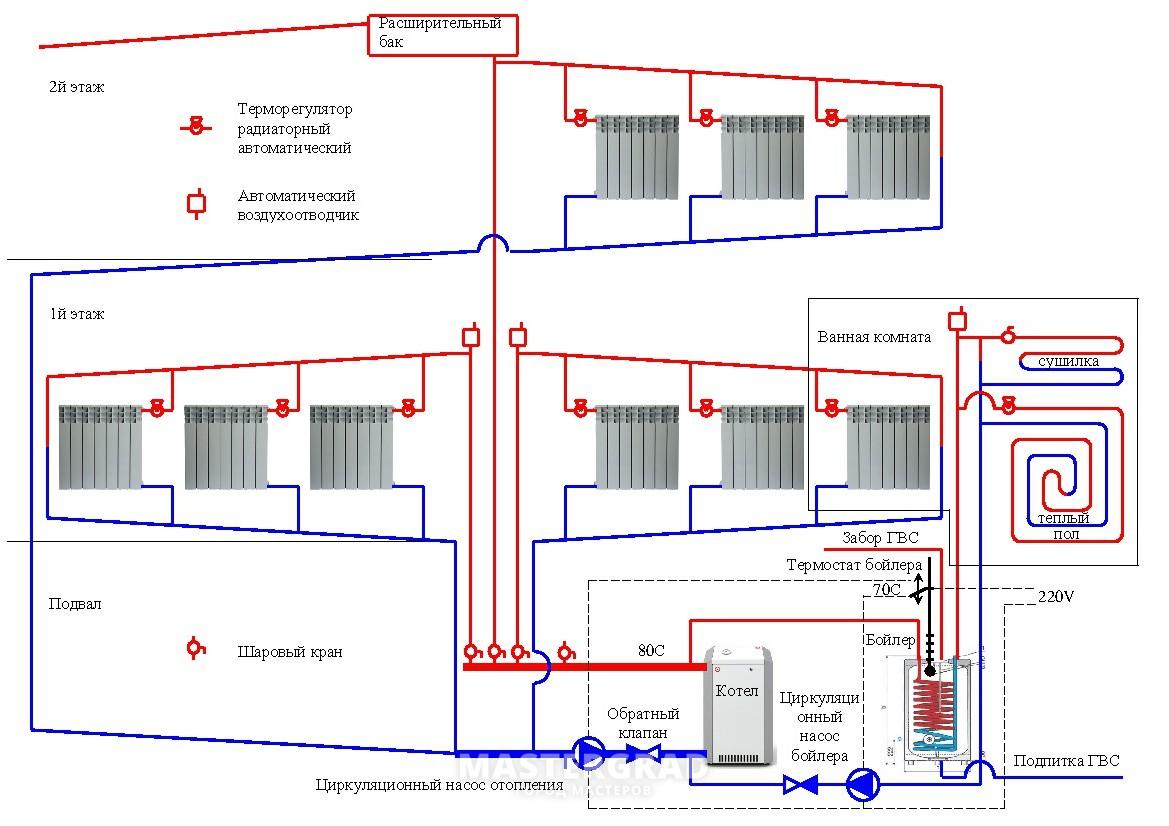
include in the scheme and system "warm" floor
Installation of the system should be carried out already during the overhaul, since the pipes are laid in a cement-sand screed. Of course, this can also be done afterwards, using heat-distributing aluminum plates that provide uniform heating of the floor. Accordingly, for underfloor heating on the same floor in several rooms, a collector connection is used, which was mentioned above. Among the advantages of such a system, it is worth highlighting the following:
- rational distribution of heat;
- comfort in winter;
- low water temperature required for system operation.
Finally, it remains to add that the heating scheme must fully comply with the profile documentation, and is certified by the relevant authorities. If you are in doubt about something, then it is better to entrust all the work to specialists.
Primary requirements
If the system is designed taking into account SNiP, there will be no problems with it. But this is not enough. A well-thought-out configuration has the following qualities:
- Energy efficiency (economical). This characteristic is especially important in climatic zones with a low average annual temperature and a long heating period. Maintaining a comfortable microclimate in the house is one of the main items of expenditure for homeowners.
- Reliability and fault tolerance.Stopping the system in the middle of the heating season is hazardous to the health of residents. And regular temperature drops and prolonged freezing cause irreparable damage to the building.
- Maximum security. All possible negative scenarios should be foreseen and the risk of their occurrence should be minimized.
- Autonomy and ease of use. A well-thought-out heating system should do without human intervention for as long as possible.
- Full control. In a well-implemented system, everything can be configured. Even the microclimate in each individual room.
- Aesthetics and noiselessness. The presence of heating engineering networks in the house should give out only the temperature in the rooms. And the work of the electric pump is well audible even during the day. And if this is not corrected, the tenants will stop sleeping at night.

Types of forced circulation of heat carrier in heating
The use of forced circulation heating schemes in two-story houses is used due to the length of the system lines (more than 30 m). This method is carried out using a circulation pump that pumps the liquid of the circuit. It is mounted at the inlet to the heater, where the coolant temperature is the lowest.
With a closed circuit, the degree of pressure that the pump develops does not depend on the number of storeys and the area of \u200b\u200bthe building. The speed of the water flow becomes greater, therefore, when passing through the pipeline lines, the coolant does not cool down much. This contributes to a more even distribution of heat throughout the system and the use of the heat generator in a sparing mode.
The expansion tank can be located not only at the highest point of the system, but also near the boiler. To perfect the scheme, the designers introduced an accelerating collector into it.Now, if there is a power outage and the subsequent stop of the pump, the system will continue to work in convection mode.
- with one pipe
- two;
- collector.
Each can be mounted by yourself or invite specialists.
Variant of the scheme with one pipe
Shutoff valves are also mounted at the battery inlet, which serves to regulate the temperature in the room, as well as necessary when replacing equipment. An air bleed valve is installed on top of the radiator.
Battery valve
To increase the uniformity of heat distribution, radiators are installed along the bypass line. If you do not use this scheme, then you will need to select batteries of different capacities, taking into account the loss of heat carrier, that is, the farther from the boiler, the more sections.
The use of shut-off valves is optional, but without it, the maneuverability of the entire heating system is reduced. If necessary, you will not be able to disconnect the second or first floor from the network to save fuel.
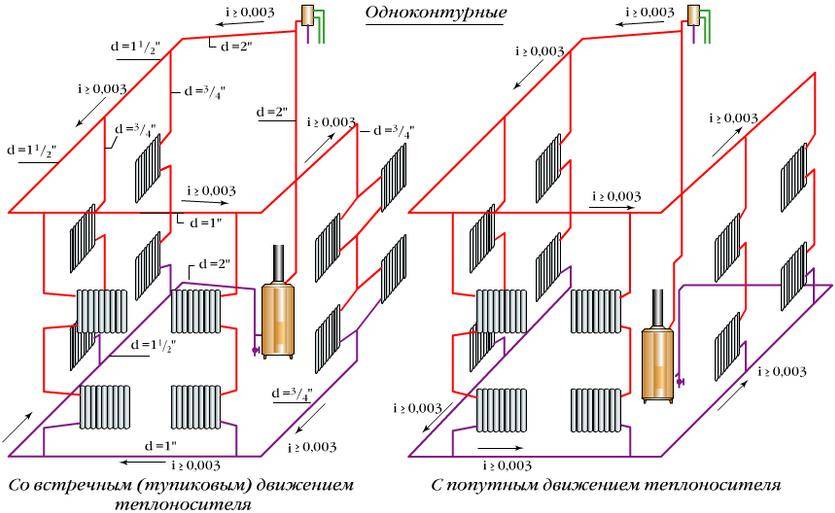
To get away from the uneven distribution of the heat carrier, schemes with two pipes are used.
- dead end;
- passing;
- collector.
Options for dead-end and passing schemes
The associated option makes it easy to control the level of heat, but it is necessary to increase the length of the pipeline.
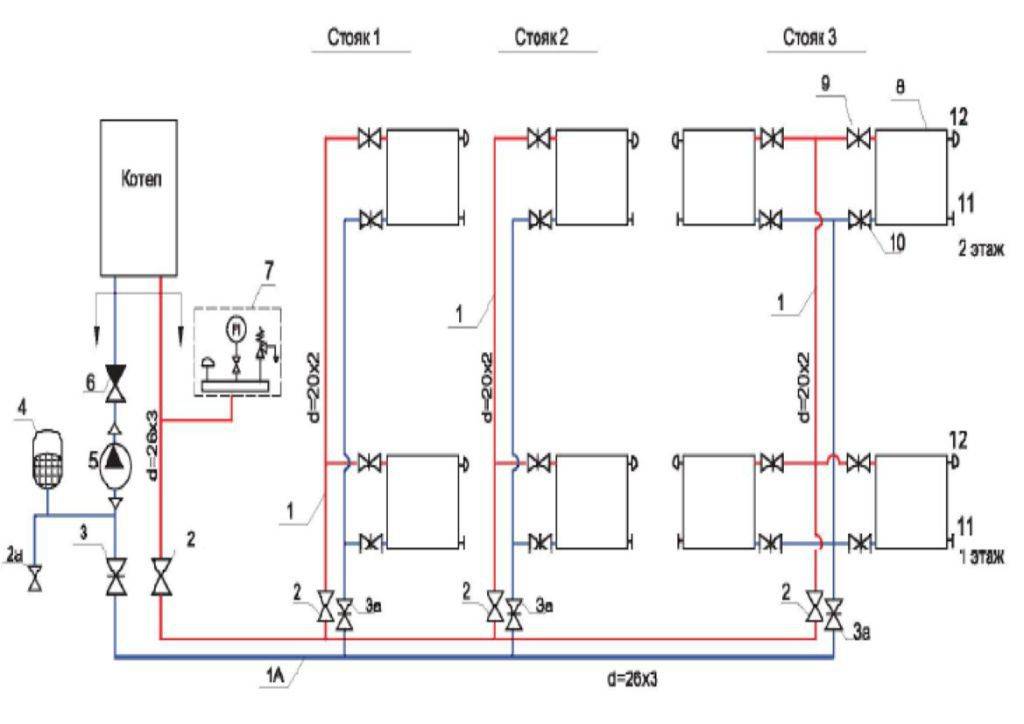
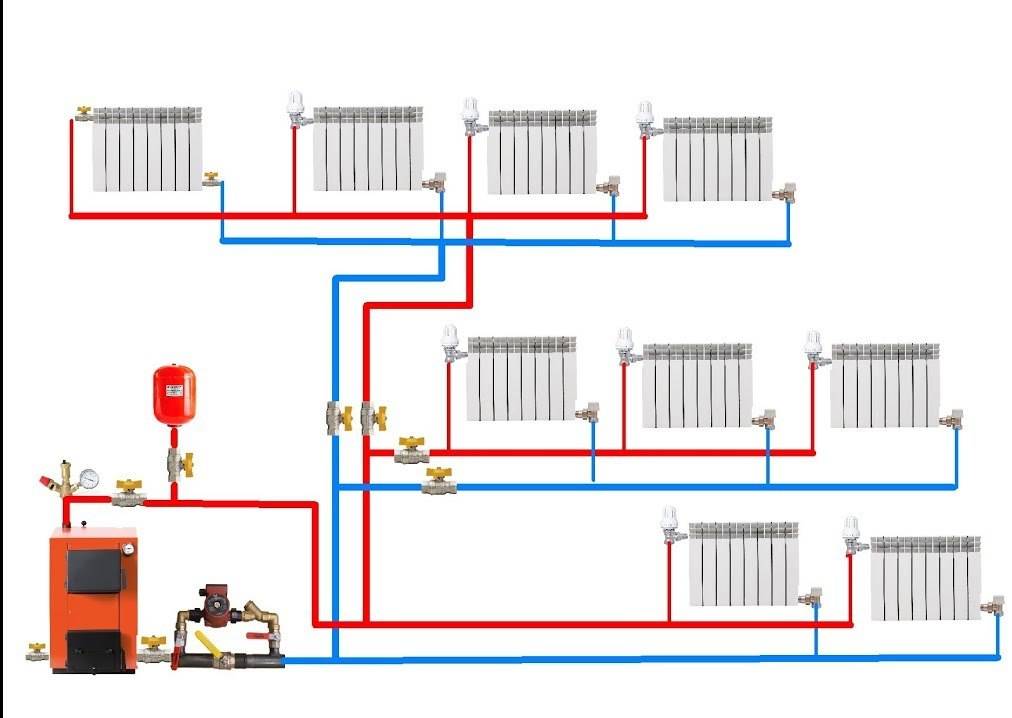
The collector circuit is recognized as the most effective, which allows you to bring a separate pipe to each radiator. Heat is distributed evenly. There is one minus - the high cost of equipment, as the amount of consumables increases.
Scheme of collector horizontal heating
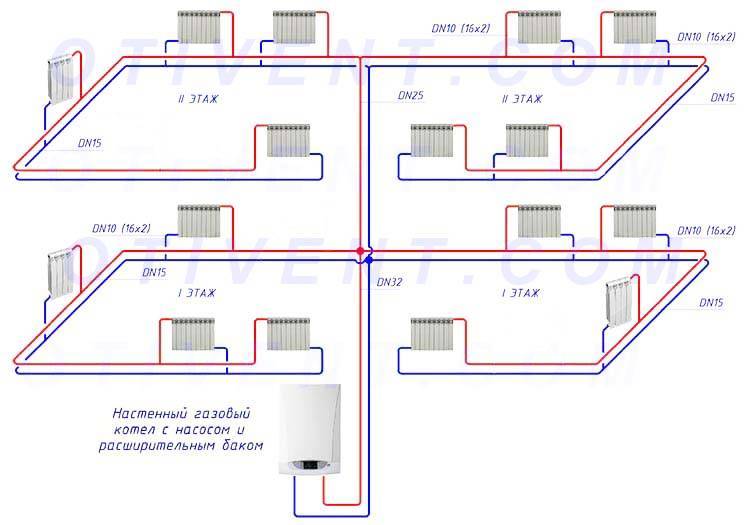
There are also vertical options for supplying heat carrier, which are found with the lower and upper wiring. In the first case, the drain with the supply of a heat carrier passes through the floors, in the second, the riser goes up from the boiler to the attic, where pipes are routed to the heating elements.
Vertical layout
Two-story houses can have a very different area, ranging from a few tens to hundreds of square meters. They also differ in the location of the rooms, the presence of outbuildings and heated verandas, the position to the cardinal points. Focusing on these and many other factors, you should decide on the natural or forced circulation of the coolant.
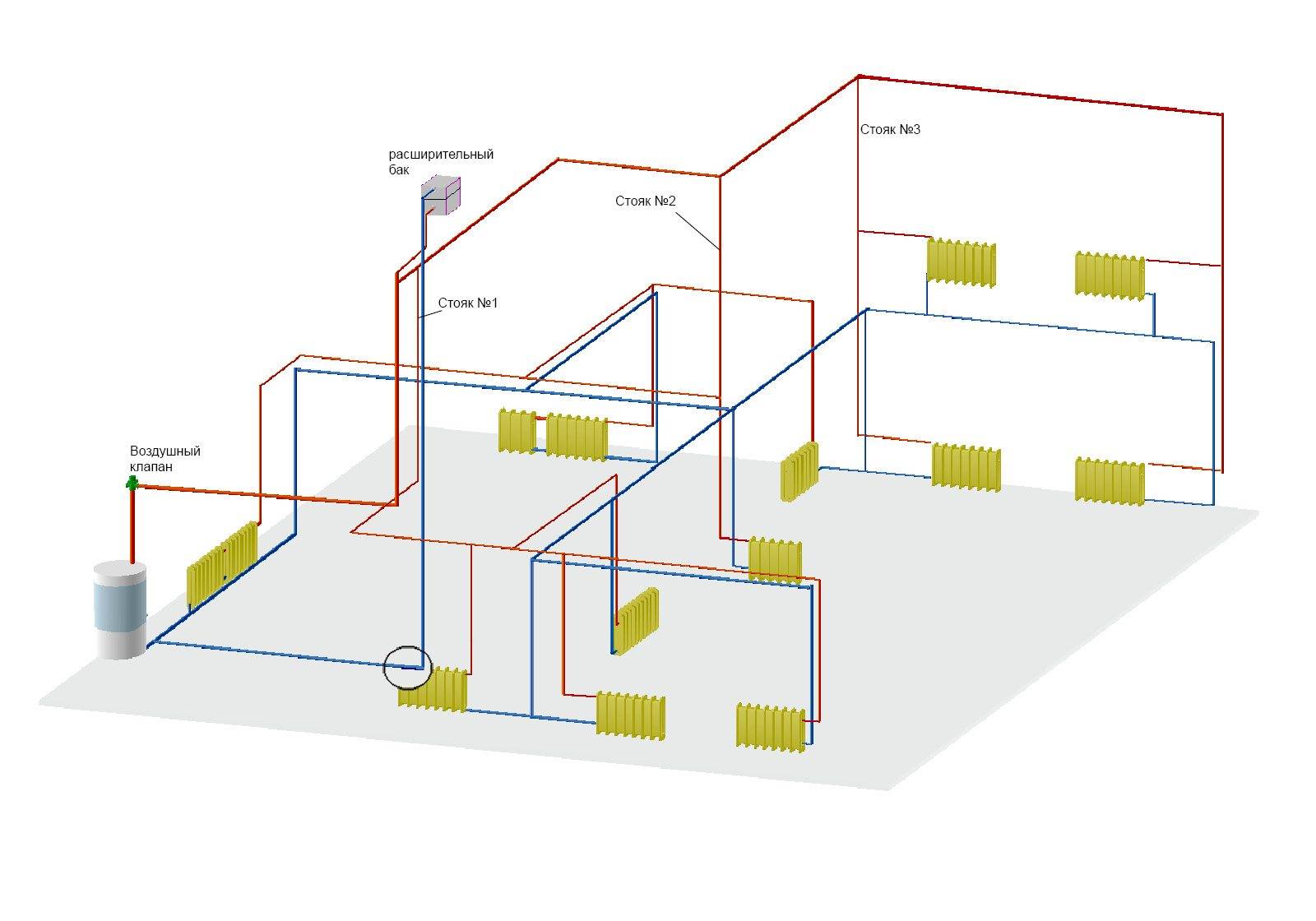
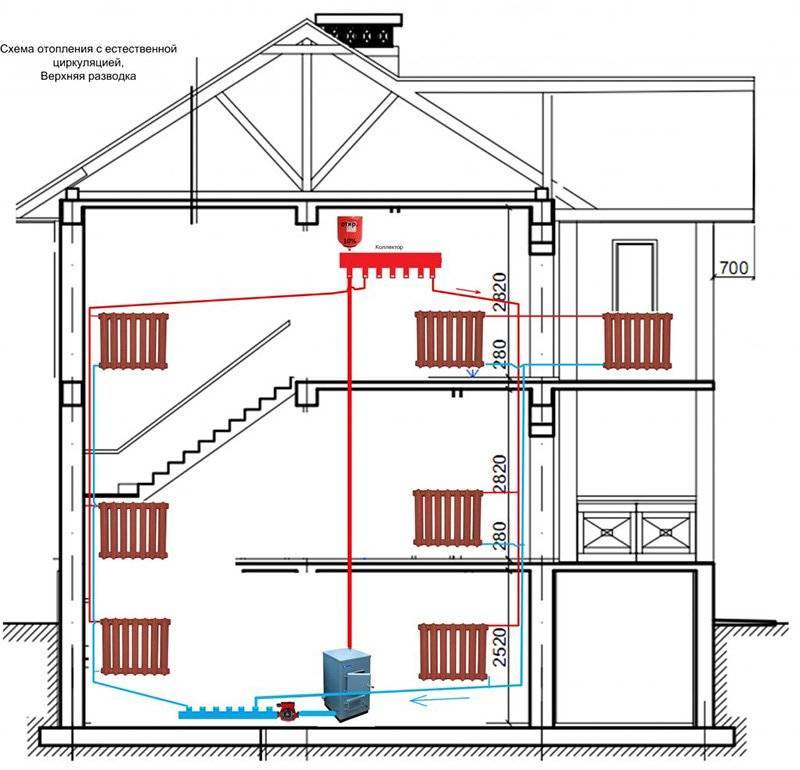
A simple scheme of coolant circulation in a private house with a natural circulation heating system.
Heating schemes with natural circulation of the coolant are distinguished by their simplicity. Here, the coolant moves through the pipes on its own, without the help of a circulation pump - under the influence of heat, it rises up, enters the pipes, is distributed over the radiators, cools down and enters the return pipe to go back to the boiler. That is, the coolant moves by gravity, obeying the laws of physics.
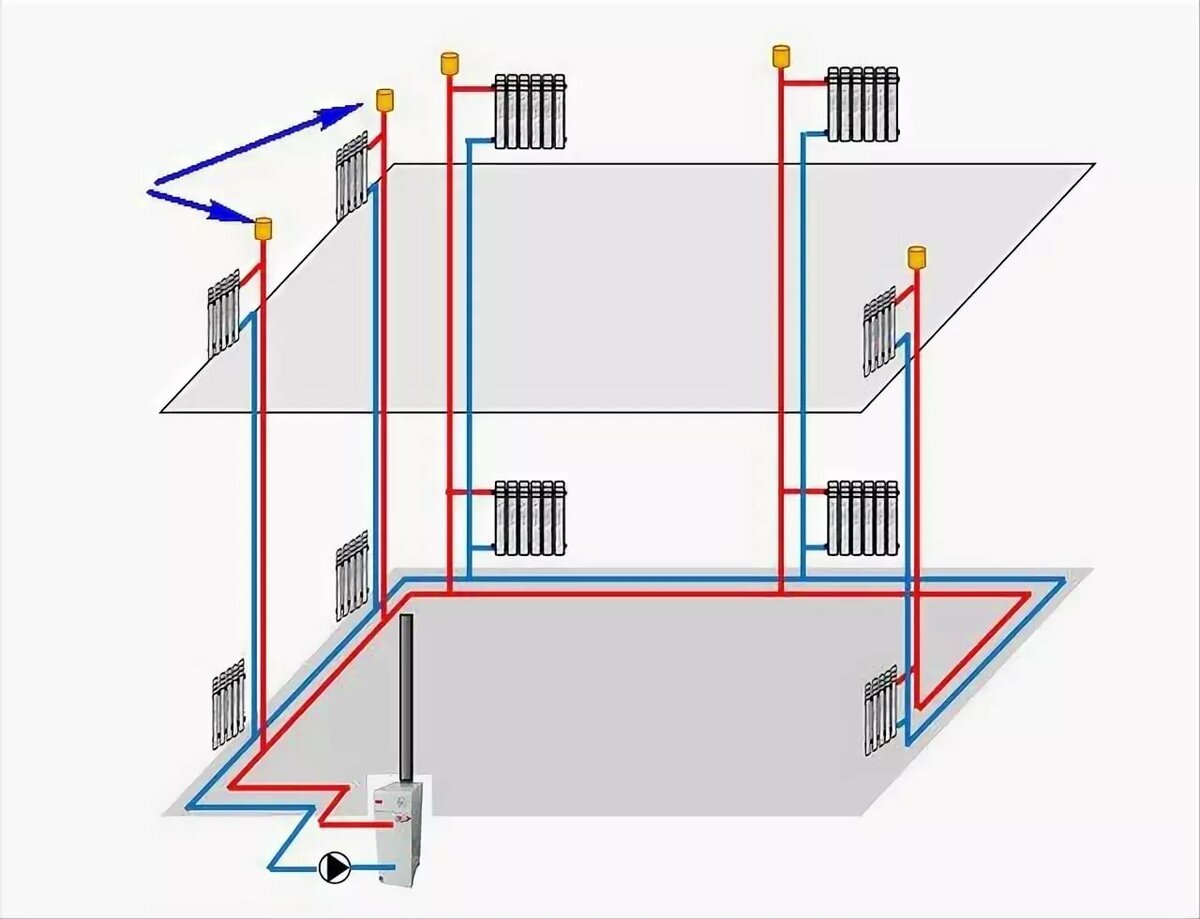
Scheme of a closed two-pipe heating system of a two-story house with forced circulation
- More uniform heating of the entire household;
- Significantly longer horizontal sections (depending on the power of the pump used, it can reach several hundred meters);
- Possibility of more efficient connection of radiators (for example, diagonally);
- Possibility of mounting additional fittings and bends without the risk of pressure drop below the minimum limit.
Thus, in modern two-story houses, it is best to use heating systems with forced circulation. It is also possible to install a bypass, which will help you choose between forced or natural circulation in order to select the most optimal option. We make a choice towards coercive systems, as more effective.
Forced circulation has a couple of disadvantages - this is the need to purchase a circulation pump and the increased noise level associated with its operation.
What is two-pipe wiring
Heating of a two-story private house is best mounted on the principle of a two-pipe system. It allows you to regulate the temperature in the rooms more efficiently and is better suited for private homes. This principle lies in the fact that a pipe with a heated coolant is supplied to each radiator and a cold pipe.
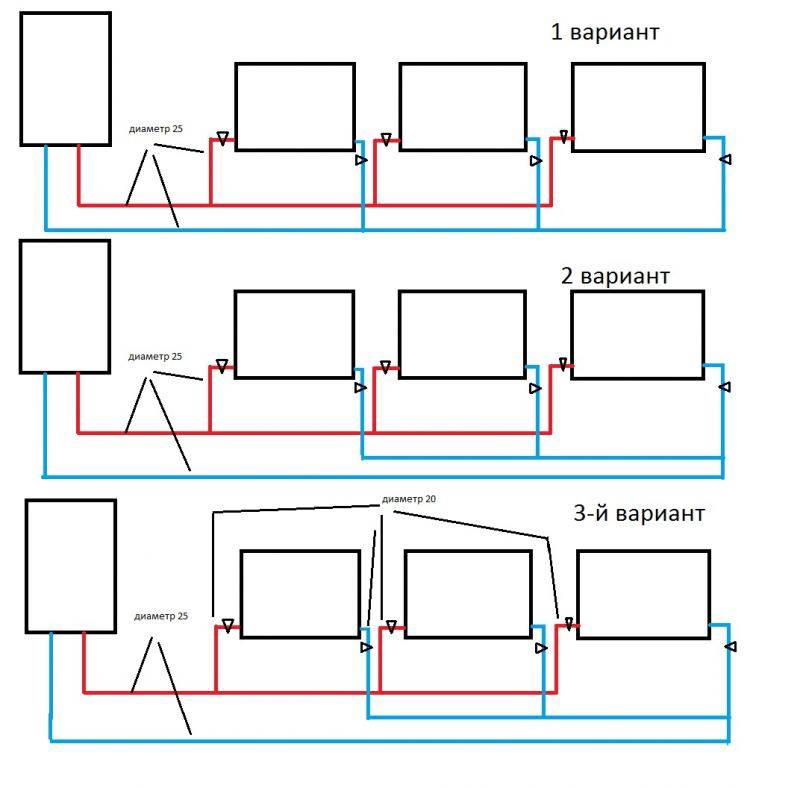
There are several ways of piping in a two-pipe system:

- Star-shaped: a pipe with a hot coolant is connected to the radiator, and it leaves with a cold one. The temperature of all batteries is the same.
- The “loop” method: the batteries are located one after the other, with one pipe to each, hot water is sequentially supplied and cold water is similarly discharged. This method is worse than the previous one, since the radiators closest to the boiler heat up more than the far ones.
- Collector (beam) wiring: in this case, a collector cabinet is installed near the free wall (if possible, in an integrated way), and in it there are two collectors: for hot and cold pipes. Pipes are laid to the batteries under the screed. This allows you to hide the wiring, and in addition, make the floor warm.The advantage of the collector system is the ability to easily adjust the temperature: each outlet on the collector is equipped with a shut-off valve. If necessary, you can completely turn off any radiator.
Only a specialist familiar with the laws of thermodynamics and the basics of heat engineering can correctly calculate and make a project for a heating system for a house. However, the information will be useful to the customer in order to make the right choice and be able to manage the system.
A video will help you better get acquainted with the device of various heating systems.
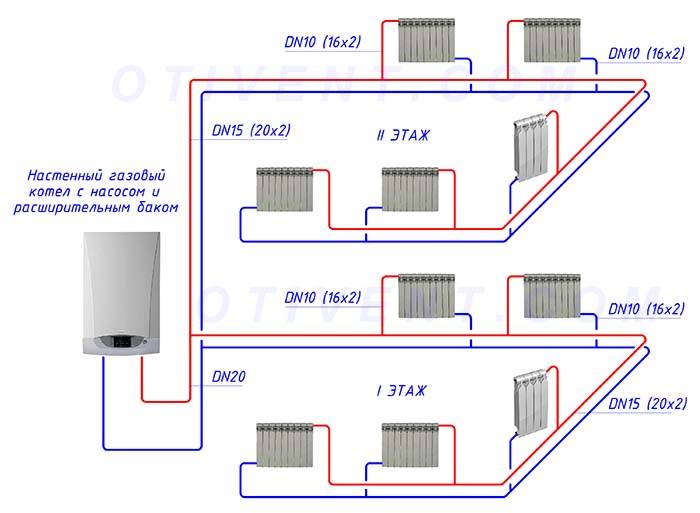
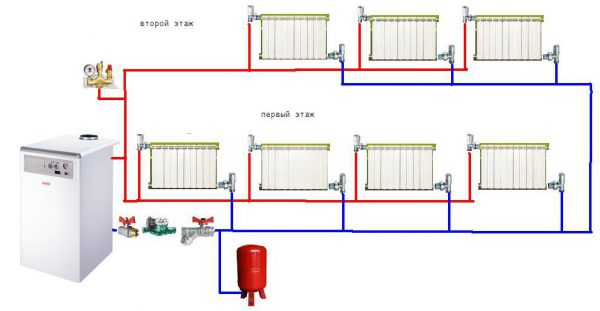
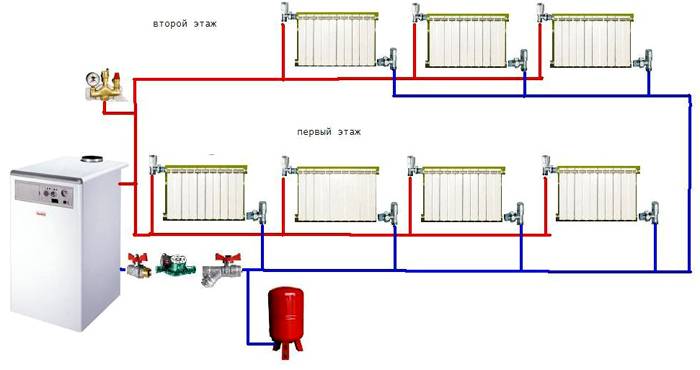
Two-pipe system with bottom wiring
Next, we will consider two-pipe systems, which are distinguished by the fact that they provide an even distribution of heat even in the largest households with many rooms. It is the two-pipe system that is used to heat multi-storey buildings, in which there are a lot of apartments and non-residential premises - here such a scheme works great. We will consider schemes for private houses.
Two-pipe heating system with bottom wiring.
A two-pipe heating system consists of a supply and return pipes. Radiators are installed between them - the radiator inlet is connected to the supply pipe, and the outlet to the return pipe. What does it give?
- Uniform distribution of heat throughout the premises.
- Possibility to regulate the temperature in the rooms by completely or partially blocking individual radiators.
- Possibility of heating multi-storey private houses.
There are two main types of two-pipe systems - with lower and upper wiring. To begin with, we will consider a two-pipe system with a bottom wiring.
Lower wiring is used in many private homes, as it allows you to make heating less visible.The supply and return pipes pass here next to each other, under the radiators or even in the floors. Air is removed through special Mayevsky taps. Heating schemes in a private house made of polypropylene most often provide for just such a wiring.
Advantages and disadvantages of a two-pipe system with bottom wiring
When installing heating with a lower wiring, we can hide the pipes in the floor.
Let's see what positive features two-pipe systems with bottom wiring have.
- The possibility of masking pipes.
- The possibility of using radiators with a bottom connection - this somewhat simplifies installation.
- Heat losses are minimized.
The ability to at least partially make heating less visible attracts many people. In the case of the bottom wiring, we get two parallel pipes running flush with the floor. If desired, they can be brought under the floors, providing for this possibility even at the design stage of the heating system and the development of a project for the construction of a private house.
If you use radiators with a bottom connection, it becomes possible to almost completely hide all the pipes in the floors - the radiators are connected here using special nodes.
As for the disadvantages, they are the need for regular manual removal of air and the need to use a circulation pump.
Features of mounting a two-pipe system with bottom wiring
Plastic fasteners for heating pipes of different diameters.
In order to mount the heating system according to this scheme, it is necessary to lay the supply and return pipes around the house. For these purposes, there are special plastic fasteners on sale.If radiators with side connection are used, we make a tap from the supply pipe to the upper side hole, and take the coolant through the lower side hole, directing it to the return pipe. We put air vents next to each radiator. The boiler in this scheme is installed at the lowest point.
It uses a diagonal connection of radiators, which increases their heat transfer. Lower connection of radiators reduces heat output.
Such a scheme is most often made closed, using a sealed expansion tank. The pressure in the system is created using a circulation pump. If you need to heat a two-story private house, we lay pipes on the upper and lower floors, after which we create a parallel connection of both floors to the heating boiler.
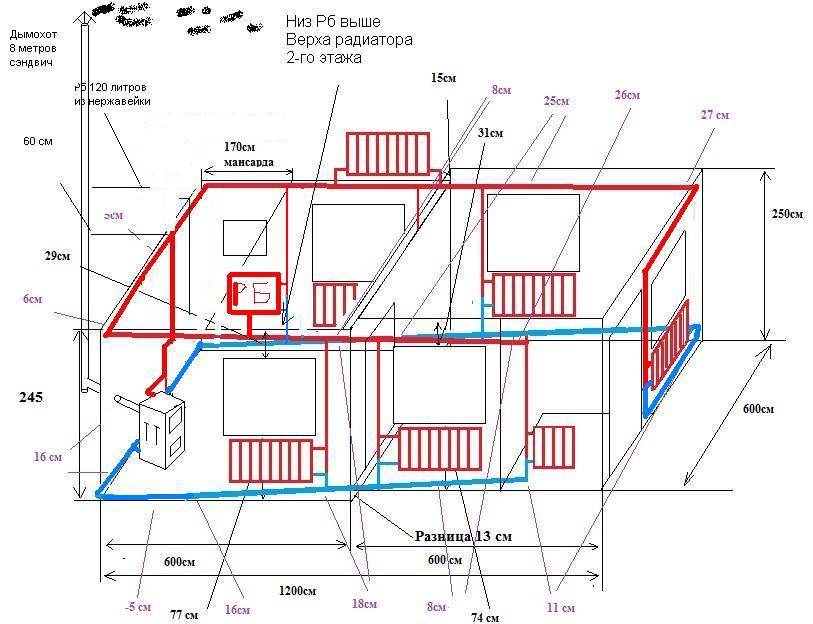
Types of water heating of a private two-story house with their own hands with diagrams
The most popular and suitable options for heating systems using water are those with forced and natural circulation. The second option does not require a permanent connection to the network, it is practical, since power outages do not affect us in any way. When installing such a system, it is necessary to use pipes with an impressive diameter and install them at an angle.
A variant of the heating scheme for a private house with natural circulation
The scheme with the natural supply of heat carrier is more acceptable for one floor; in two-story buildings, the method of forced water supply is used. For it, a boiler, an expansion tank, a collector, a heating device and a pipe system should be installed. Circulation occurs due to the operation of the pump, and a variety of fuels are used for heating.It can also be powered by electricity to heat the house.
Possible scheme
Let us analyze why the preference is given to the forced system.
Natural variant of heat carrier supply
The scheme for two floors is not much different from the option with one floor. It is quite common and justifies its popularity.
It is not at all necessary to mount the expansion tank in the attic, however, leave it on top, on the second floor. In this way, the flow of the heat carrier will be ensured. Entering the batteries from above, the heat will be distributed evenly over the area of the entire house. The slope of the pipes should be 3-5 degrees for a constant flow of fluid.
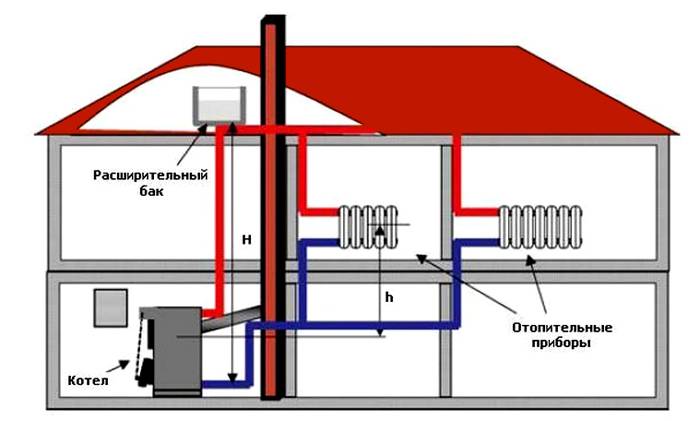
The expansion tank is located on the second floor
Supply pipes can be located under the ceiling or window sills. Such a building heating system has a number of advantages:
- there is no need for a permanent connection to the network;
- works without interruption;
- ease of use;
- no noise during operation.

How to hide large pipes
There are much more disadvantages in this option, so the owners of two-story houses prefer a heating scheme with forced circulation of a two-story house. Disadvantages of natural water supply in a circle:
- complex and lengthy installation;
- it is not possible to heat an area over 130 sq. m;
- low productivity;
- due to the large temperature difference between the supply and return, the boiler is damaged;
- internal corrosion due to oxygen;
- the constant need to monitor the condition of the pipes and the inability to use antifreeze;
- installation cost.
Self-installation of such a heating system is very difficult, so the owners of buildings prefer a forced system that can be installed independently without much effort.
Related article:
Requirements for a room with two boilers
In the event that the same type of heating sources are selected, the requirements for the furnace are applied, which apply to a certain type of fuel used: gas, coal, pallets or electric heating.
The boiler room in the house must be treated with due attention
If units are selected that operate on different types of energy carriers, the premises must comply with both, while choosing a larger indicator.
Requirements for units using solid fuel:
- The floor area of the furnace room is selected according to the total thermal power of the devices: up to 32 kW, 7.50 m2 is needed, up to 62 kW - 13.50 m2, up to 200 kW - 15.0 m2.
- A unit of more than 30 kW is installed in the center of the furnace to ensure reliable circulation of air masses.
- The surface elements of the furnace: the floor, walls, ceiling and partitions are made of fire-resistant building materials, with the use of waterproofing protection.
- The boiler is installed on a reliable foundation made of fire-resistant building materials.
- For units up to 30 kW, the requirements for fire resistance of the floor are lower, it is enough to cover it with a steel sheet.
- The stock of solid fuel is stored in a separate dry room, and the daily stock can be located in the boiler room at a distance of at least 1 m from the boiler.
- In the furnace, a door and windows must be installed that can provide reliable threefold air circulation based on the existing volume of the room.
Requirements for furnaces with gas-fired boilers:
- Gas boilers with a total power of up to 30 kW can be installed in non-residential premises of the house, where there are windows and doors that can provide 3-fold air circulation.
- With a gas source power of more than 30 kW, a separate furnace is required with a ceiling height of at least 2.5 m and a total area of more than 7.5 m2.
- If this equipment will be installed in a kitchen in which a gas stove operates, then the room must be at least 15 m2.