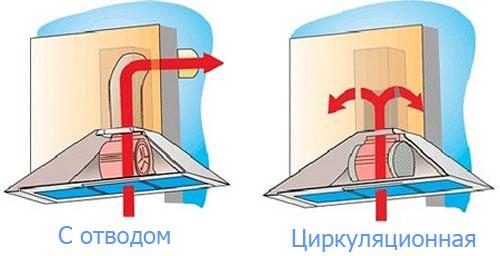
- Organization of air circulation in the apartment
- Device of ventilation ducts
- Brick ventilation ducts
- Lining with plastic pipes
- Main types of structures
- What scheme is better for a cottage?
- Other Solutions
- Recommendations for installation with a heat exchanger
- Features and schemes
- Conclusion
- Calculations
- Combined system type
- Ventilation system design stages
- Recommendations for individual rooms
- Ventilation system for a 2-room apartment (option 1)
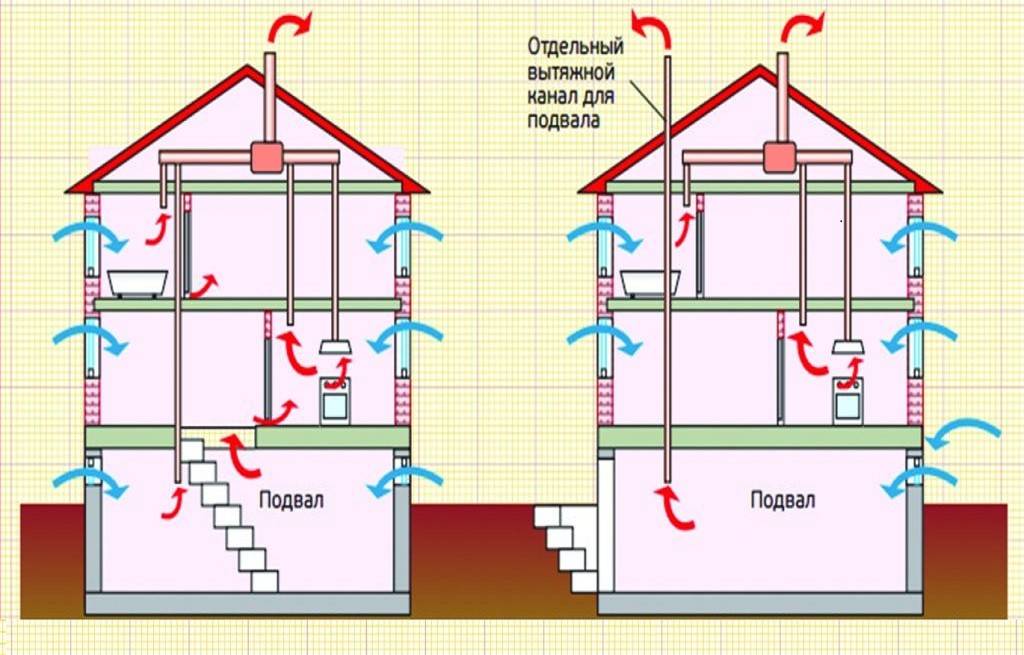
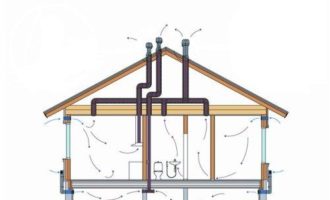
- Installation of ventilation ducts in the cottage: locations of supply and exhaust systems
- Ventilation systems on the second floor
- Units for local exhaust system
- Stages of ventilation design
- How to choose pipes?
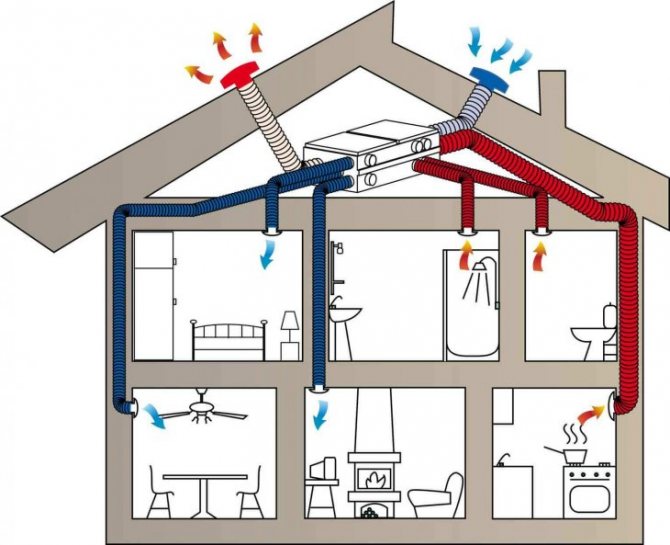
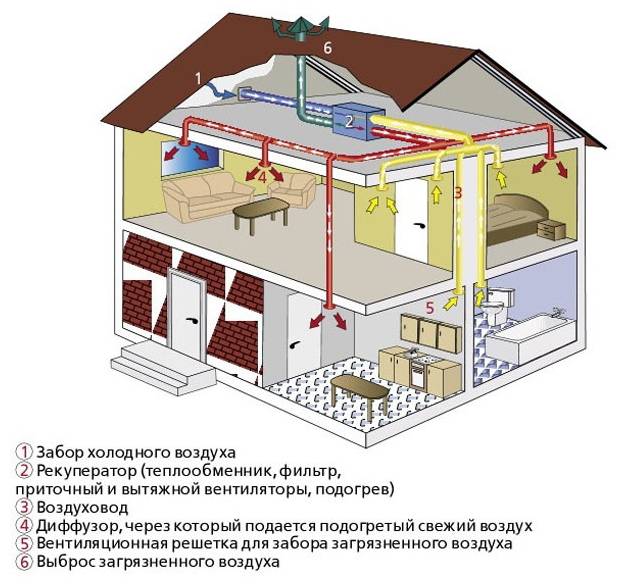
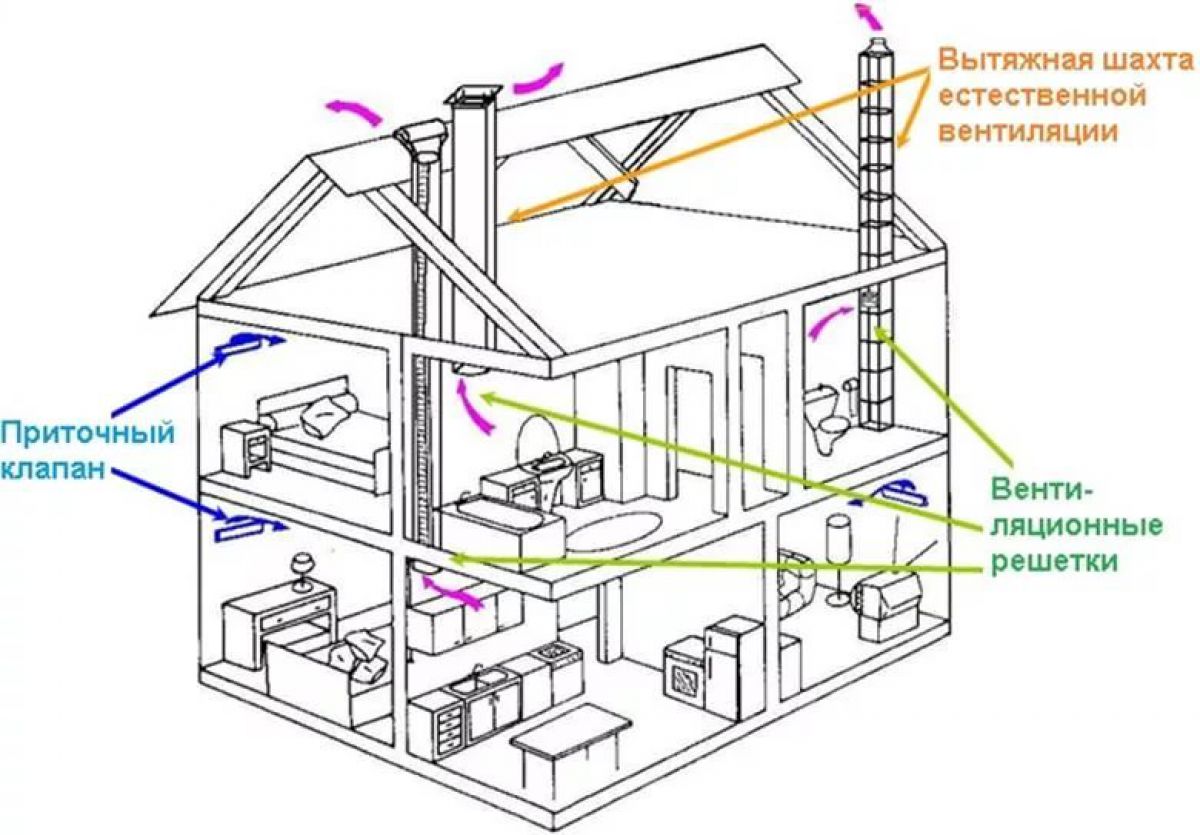
Organization of air circulation in the apartment
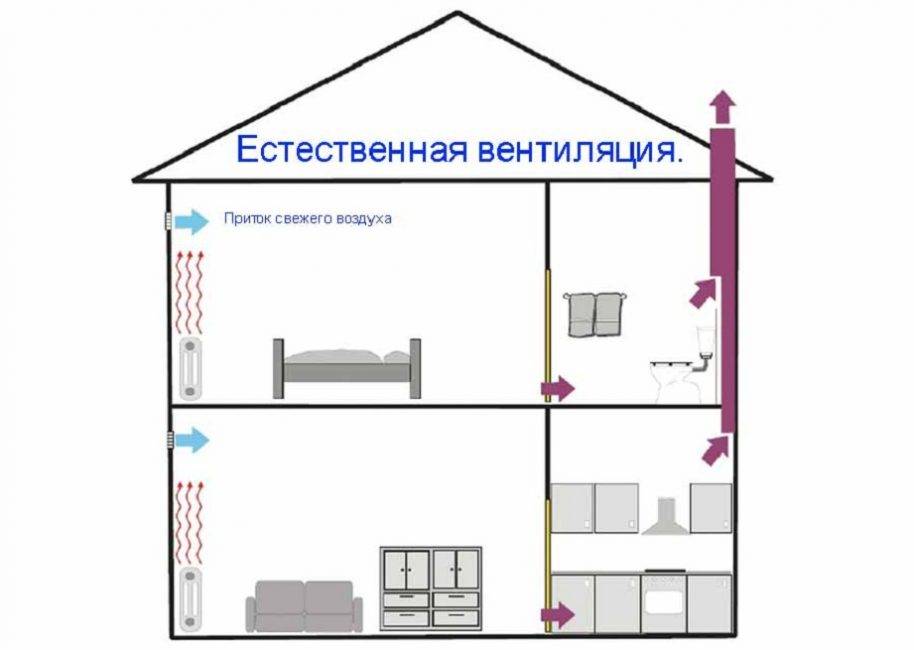
Consider how air circulates in a single apartment without installing additional air exchange devices.
As mentioned above, fresh air enters through all kinds of window slots and gaps, as well as through doorways - ajar doors and gaps under them.
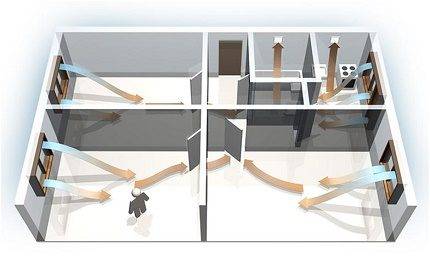
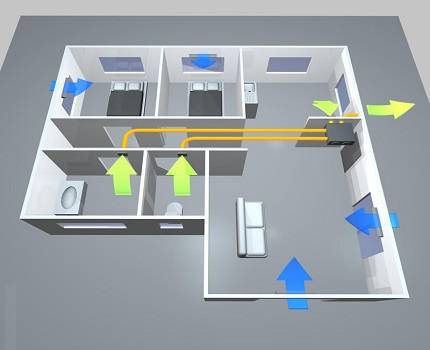
The diagram clearly shows the direction of air movement. It enters through the windows or doors of living quarters and travels towards the air vents.
Comfortable living in apartments is characterized by a number of factors, including the frequency of air exchange and the volume of regularly changing air.
There are rules governing the flow of air flows.
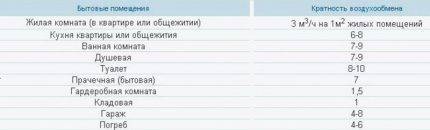 Table of air exchange rates suitable for an apartment building. The change of air should take place more actively where there is high humidity, that is, in the kitchen and in the bathrooms.
Table of air exchange rates suitable for an apartment building. The change of air should take place more actively where there is high humidity, that is, in the kitchen and in the bathrooms.
In old buildings, ventilation shafts do not always function 100%, and this can be checked in a simple way. It is necessary to take a sheet of paper and attach it to the technical ventilation hole. If the paper is not held by the traction force and falls, the natural ventilation is broken.
Instead of a sheet, you can use a burning candle or a match. By the movement of the flame tongue, it becomes clear whether there is a draft from the room to the outside.
We examined in more detail the rules for checking ventilation in an apartment and ways to find a problem in another article.
Ventilation problems negatively affect the well-being of people living in apartments. Lack of fresh air causes unhealthy drowsiness, fatigue, headaches.
People with diseases of the heart and respiratory system are especially sensitive to this. They constantly want to keep the vents and windows open, and this leads to a sharp cooling of the premises and, as a result, an increase in the number of colds.
We also recommend that you familiarize yourself with the information on how to restore ventilation and air duct performance.

You can increase the efficiency of the natural exhaust system using the simplest device - a fan installed in the ventilation outlet in the bathroom
If a regularly switched on hood is installed above the stove with air outlet to the ventilation shaft, this will also contribute to the rapid change of air masses in the kitchen and adjacent rooms.
If desired, residents can independently organize the flow of air. To do this, use both ordinary ventilation and special mechanical and technical devices, for example, a supply valve on the window.
Valves are installed not only on double-glazed windows, but also in walls, most often under windows, near heating appliances. Air from the street enters the room through a small hole with a diameter of 5 to 10 cm and is heated by the heat of a radiator or convector.
There are automatic models that are sensitive to changes in temperature and humidity: as soon as the parameters exceed the norm, airing occurs.
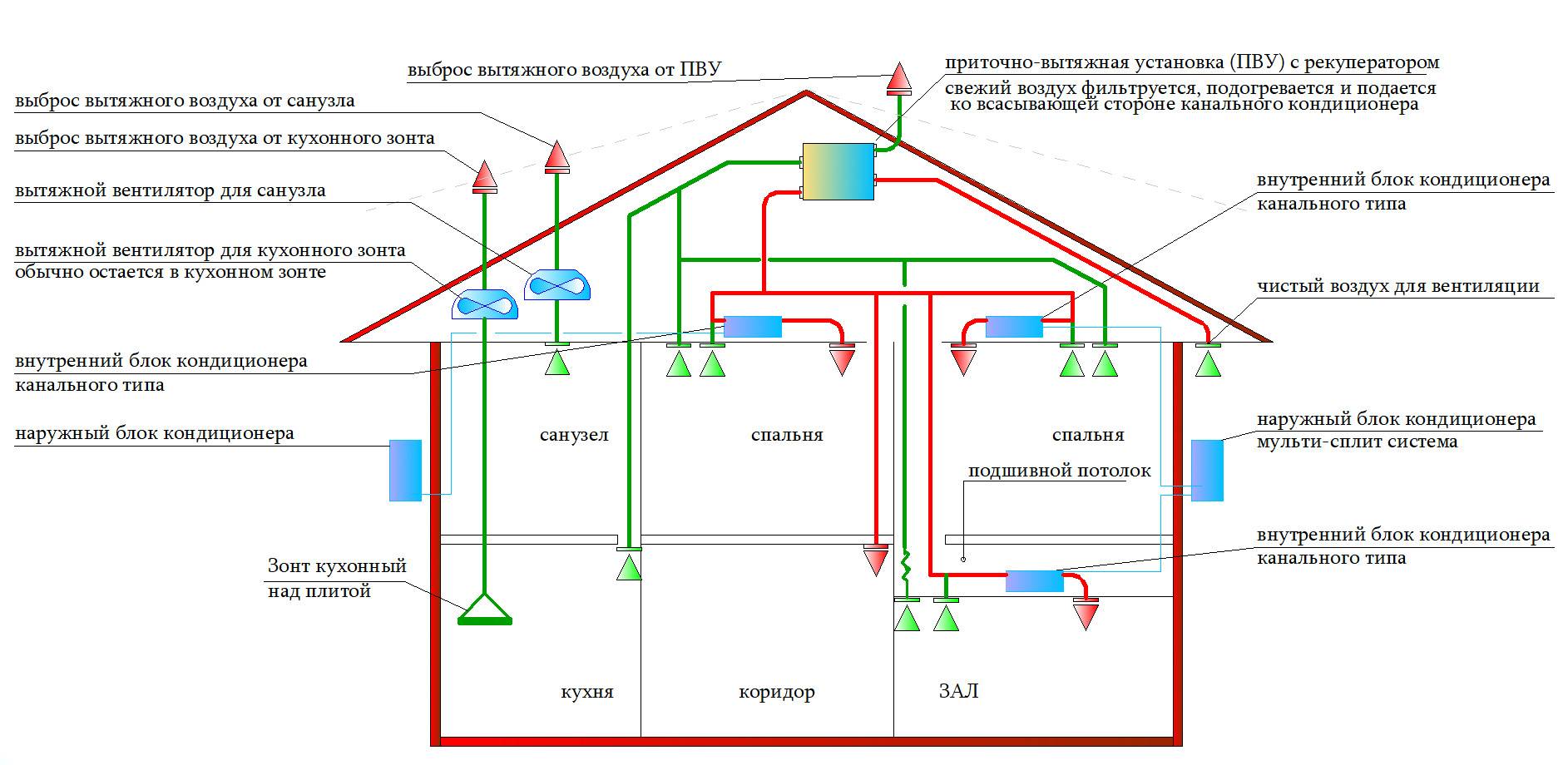
But the centralized supply system of the channel type is recognized as more perfect. You can install it yourself only in a private house, because in high-rise buildings special services are involved in systems of this magnitude.
Air ducts and air supply / heating devices are located above the premises, in the ceilings, pass through the walls, so they are installed during the construction process.

Supply duct ventilation is equipped in new buildings of the so-called elite class. One of the installation conditions is high ceilings, which allow installation without damage to the interior.
As you can see, the lack of a well-established natural ventilation system can be partially compensated by installing additional appliances. There is only one minus - additional one-time expenses for the purchase of devices and regular ones - for paying for electricity.
Device of ventilation ducts
When deciding how to make ventilation in a house made of aerated concrete, special attention should be paid to the installation of ventilation ducts.Considering the fragility of the material, its ability to absorb moisture and instability to high temperatures
Ventilation ducts in aerated concrete houses are built in one of the following ways:
- Laying a channel out of bricks;
- Lining with asbestos or plastic pipes;
- Installation of a galvanized steel box lined with small-sized aerated concrete blocks.
 Galvanized steel air ducts
Galvanized steel air ducts
The latter method is rarely used because of its complexity and high cost. In addition, condensate forms on the walls of metal structures, which is detrimental to aerated concrete, so such channels must be additionally insulated.
Brick ventilation ducts
If you decide to lay out the ventilation ducts of brick, the following instructions will come in handy:
The fewer such channels in the house, the better. Therefore, it is desirable to arrange them in the walls of adjacent rooms with high humidity (boiler room, laundry room, bathroom, kitchen). As a rule, they are located nearby, as they are united by a common water supply and sewerage system.
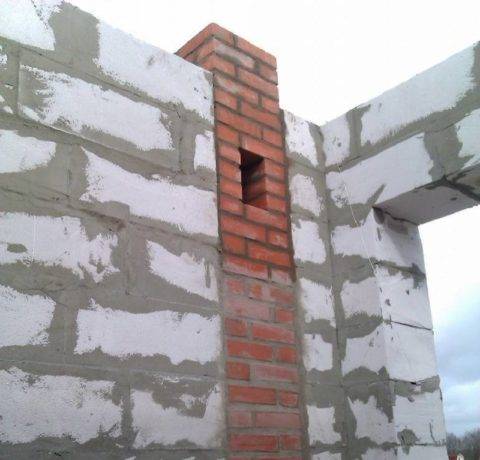 Brick air duct in the wall between the kitchen and the bathroom
Brick air duct in the wall between the kitchen and the bathroom
For masonry, you can use only solid brick or hollow, but with filling all the voids with mortar.
 The channels are made of solid ceramic bricks with careful sealing of the seams.
The channels are made of solid ceramic bricks with careful sealing of the seams.
It is very important to carefully apply the solution, preventing the mixture from falling into the canal. The seams should be filled completely and rubbed every 2-3 rows of masonry so that the exhaust air does not penetrate into adjacent channels and rooms
 Brick ventilation ducts are laid out with special care and accuracy
Brick ventilation ducts are laid out with special care and accuracy
The walls of the channels inside should be as smooth as possible so that the protrusions do not interfere with the free circulation of air.Therefore, the excess mortar from the joints must be constantly removed and the surface smoothed with a trowel. Or the brick channel during the masonry process is lined with a metal duct.
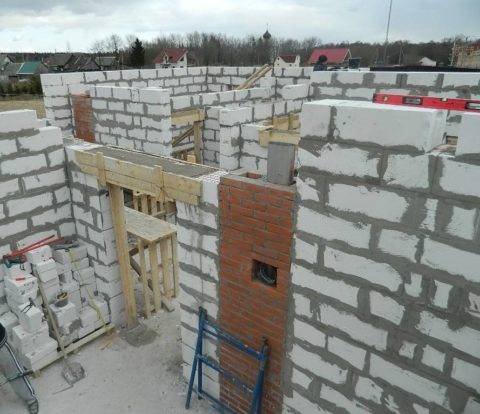 Galvanized air duct in masonry
Galvanized air duct in masonry
Lining with plastic pipes
For a forced ventilation device, this method is considered the most effective, since there is practically no condensation on the plastic.
 Rectangular plastic air ducts
Rectangular plastic air ducts
As a rule, round pipes with a diameter of 13 cm or rectangular pipes with a cross-sectional area of 150 cm2 are used for its installation. The cross section of channels for natural ventilation should be larger.
 Standard forced ventilation diameter - 13 cm
Standard forced ventilation diameter - 13 cm
But this is approximate data. To accurately calculate the size of the air ducts, you need to know the volume of air output, the number of people living in the house, take into account climatic conditions and other parameters. This is a task for specialists.
The ventilation device in the house of aerated concrete is carried out in parallel with the construction of walls.
In a block located at the level of the vent, a branch is fixed and connected to a plastic pipe.
 Laying plastic channels from sewer pipes
Laying plastic channels from sewer pipes
To bypass the air ducts in the blocks, during further laying, holes are cut out that are several millimeters larger than the dimensions of the pipes. Aerated concrete is very easily sawn with a regular hacksaw.
 Drilled hole in block
Drilled hole in block
The space between the walls of the blocks and the air ducts is filled with mortar. Pipes, as the height of the masonry grows, are joined to each other, building up.
 At this stage, the following element is attached to the pipe immured in the wall
At this stage, the following element is attached to the pipe immured in the wall
In places where pipes pass through the attic and the roof, they must be insulated.
 Insulated ventilation duct on the roof
Insulated ventilation duct on the roof
At the attic level, individual air ducts are combined into one channel and led out through the roof to the street or connected to a duct fan or heat exchanger. All openings with channel outlets in the walls are sealed and sealed.
Main types of structures
Experts focus on the fact that there are several types of ventilation systems with heat recovery:
- lamellar;
- with separate heat carriers;
- rotary;
- tubular.
Varieties of air recuperators
Plate type - includes a structure based on aluminum sheets. Such a heat exchanger installation is considered the most balanced in terms of the cost of materials and the value of thermal conductivity (efficiency varies from 40 to 70%). The unit is distinguished by its simplicity of execution, affordability, and the absence of moving elements. Installation does not require specialized training. Installation without any difficulties is carried out at home, with your own hands.
plate type
Rotary - quite popular solutions among consumers. Their design provides for a rotation shaft powered by the mains, as well as 2 channels for air exchange with counterflows. How does such a mechanism work? - One of the sections of the rotor is heated by air, after which it turns and the heat is redirected to the cold masses concentrated in the adjacent channel.
rotary type
Despite the high efficiency, the installations have a number of significant drawbacks:
- impressive weight and size indicators;
- exactingness to regular maintenance, repair;
- it is problematic to reproduce the recuperator with your own hands, to restore its performance;
- mixing of air masses;
- dependence on electrical energy.
You can watch the video below about the types of recuperators (starting from 8-30 minutes)
Note! A ventilation unit with tubular devices, as well as separate heat carriers, is practically not reproduced at home, even if all the necessary drawings and diagrams are at hand. Making a heater for your home with your own hands
Making a heater for your home with your own hands
What scheme is better for a cottage?
To decide which and how best to equip a private house with ventilation, you need to take into account a lot of factors. The characteristics of all engineering systems and building heating devices are important here.
When choosing the right type of ventilation system, consider:
- climatic features of the area;
- the presence of sources of unpleasant and harmful impurities in the air near the house;
- appointment of different premises;
- individual features of the architecture of the building;
- the presence of gas stoves or boilers, as well as fireplaces or stoves on wood / coal;
- the number of permanent residents in the cottage and much more.
It is recommended to independently design and mount only natural ventilation. For its calculation, simplified methods with averaged indicators are used. Understanding them is not difficult.
For living rooms, the air exchange rate is set at 30 m3 / h, for bathrooms and toilets within 25–30 m3 / h, and for the kitchen - 70–100 m3 / h. Based on these data and the cubic capacity of the rooms, you only need to calculate the width of the ventilation ducts, and then arrange them in the building.
Moreover, it is best to do this at the design stage of the cottage.Often the best option is a ventilation shaft in the middle of the building with its output above the roof ridge.
To correctly calculate mechanical ventilation, you need to have the proper competence. Mistakes in calculations can lead to constant breakdowns of ventilation equipment and inflated installation costs.
If a private house is being built on two or three floors and a forced air exchange system is chosen for it, then it is better to entrust its design to a professional. Installation can then be done by hand.
However, if there is no experience in this matter and you do not want to face problems in the future, then the installation of all ventilation equipment should also be entrusted to a specialist.
Compared to mechanical ventilation, natural ventilation is cheaper, less noisy and does not depend on the availability of power. However, it is more difficult to regulate. Plus, the thrust in it is highly dependent on external atmospheric factors.
But the absence of electric fans is the absence of problems with breakdowns and the need for their maintenance.
The forced ventilation system in a private house in a combined or only exhaust or supply version is more difficult to install and operate. However, it allows you to save on heating and more accurately control the microclimate in the cottage.
Other Solutions
The market does not stand still, and new solutions are being offered today. For example, there are recuperator systems that immediately, through one hole in the wall, remove the exhaust air and supply fresh air. This is an ideal solution if ventilation is taken care of after renovation or if it is necessary to solve the problem only in some rooms. The main thing is that these rooms have at least one wall facing the street.
There is a device that removes exhaust air through one hole, takes fresh air. It also heats up/cools it down.
The disadvantage of this method of organizing ventilation in a house or apartment is one - the price of such equipment. The cost of one such device is more than $400.
Recommendations for installation with a heat exchanger
Installation recommendations mainly refer to the rooms in which the heat exchanger should be installed. First of all, boiler rooms are used for this (if we are talking about private households). Also, recuperators are mounted in basements, attics and other technical rooms.
If this does not differ from the requirements of the technical documentation, then the unit can be installed in any unheated room, while the wiring of ventilation ducts, if possible, should be installed in rooms with heating.
Ventilation ducts passing through unheated premises (as well as outdoors) should be made insulated. Also, thermal insulation is necessary in places where exhaust ducts pass through the outer walls.
Considering the noise that the equipment can produce during operation, it is best to place it away from bedrooms and other living areas.
As for the placement of the heat exchanger in the apartment: the best place for it would be a balcony or some technical room.
In the absence of such an opportunity, free space in the dressing room can be allocated for the installation of the heat exchanger.
Be that as it may, the location of the installation largely depends on the design features of the ventilation system, on the location of the ventilation wiring and on the dimensions of the device.
The main mistakes in the installation of ventilation systems in the following video:
Features and schemes
Each type has its own characteristics that affect its choice for operation. There are several main points:
most of the frame houses have a pre-installed air exchange system;
Pipes for air exchange are mounted according to the project during the construction of the house
- each house uses its own scheme and layout of ventilation ducts;
- automation ensures full-fledged functioning only if there are good and serviceable sensors;
- the ventilation scheme and plan should be drawn up even when planning the house, but if this did not happen, then the plan is carried out before the arrangement of all premises;
- most often, metal pipes are not used in the ventilation system due to their heat loss and too high sound conductivity;
- for permanent residence, mechanical ventilation is used, which can fully provide a good microclimate and air exchange in the premises at any time of the year and at any temperature.
For the arrangement of frame houses of a certain type, a ventilation system has already been thought out, which facilitates planning. This approach provides a complete ventilation system based on all the characteristics of the premises and the building as a whole.
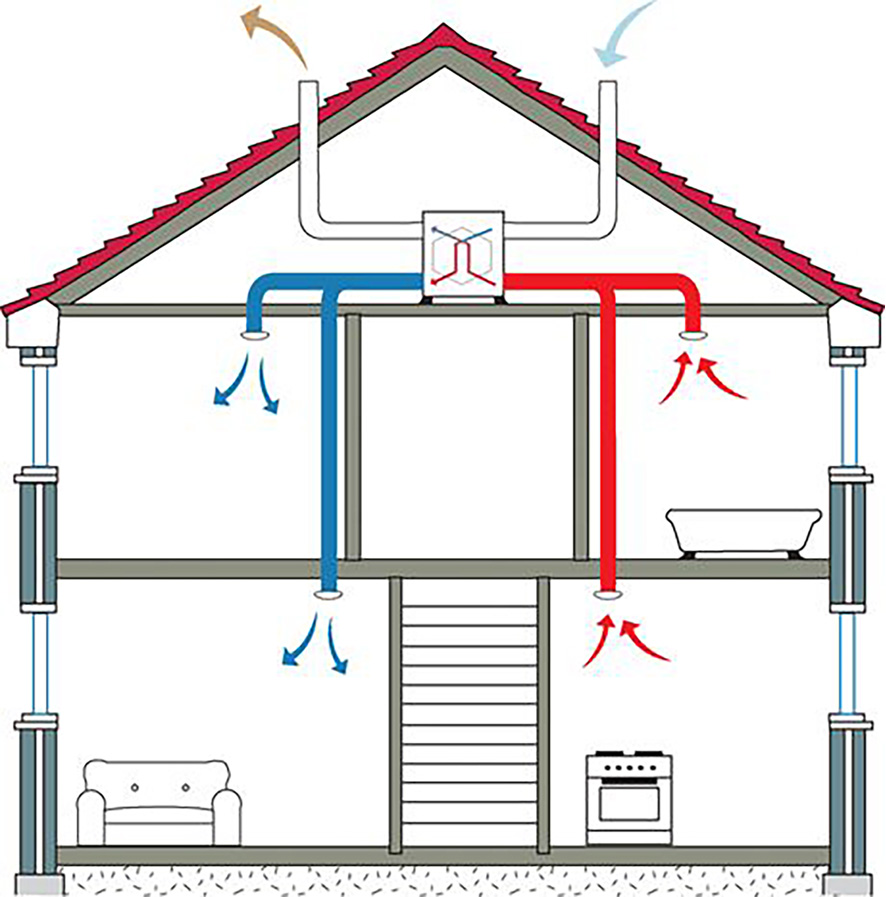
The scheme also depends on the type of building. For example, for a two-story house, you can use a mixed type, which will be different on two floors.
Scheme of air inflow and outflow in a two-story house
Previously, the scheme should be drawn up depending on the wishes of the residents. Having forced ventilation in a seasonal home does not make sense. It is also worth considering that frame houses can be made of various materials, which facilitates the integration of ventilation of one type or another.
All schemes are drawn up according to the parameters of the premises and the design of the house. In addition, all channel outlets must have gratings, as well as bolts. From the side of the interior, special dampers are installed, which are necessary not only to regulate the flow, but also for the full conservation of the house during the absence of residents.
What is ventilation and how does it work in this video:
Conclusion
Ventilation in a frame house necessary. For different options for buildings for use and residence, you can select your own ventilation systems. Each system has its own characteristics and characteristics that must be taken into account when arranging. Part of the frame houses during production already has a layout of ventilation ducts and everything for their installation.
Calculations
Competent calculation of supply and exhaust ventilation implies the determination of its following parameters:
- total air flow;
- normal pressure in the system;
- heating power;
- cross-sectional area;
- the size of the inlet and outlet holes;
- electrical energy consumption (for mechanical systems).
Productivity is calculated based on data on the height and area of the premises, on the use of each site and on its workload. When choosing the frequency of air passage through ventilation, one must not deviate from the values prescribed by SNiP. If necessary, only corrections are made for heating characteristics and for the number of people present. For most residential apartments, it is required to ensure the supply of 100-500 cubic meters. m of air in 60 minutes. And if the area of the apartment is large (or you need to ventilate a private house), this figure will already be 1-2 thousand cubic meters. m.
For an overview of the design of ventilation systems, see the following video.
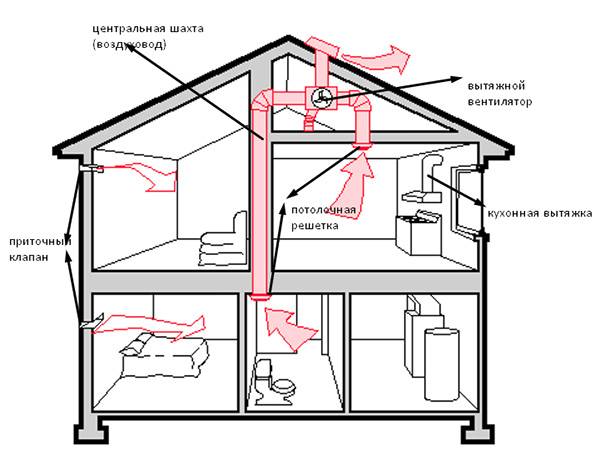
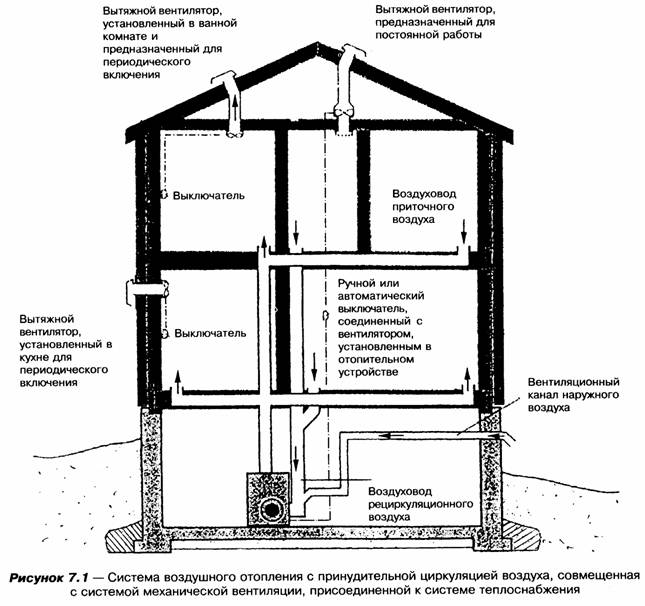
Combined system type
Combined ventilation is implemented mainly in the form of a scheme with natural inflow and mechanical, that is, forced, exhaust of waste masses.
Fresh air enters the rooms through the valves due to the rarefaction created by the exhaust fans. In this case, the preliminary heating of the supply air masses is not performed. But this is not a problem if you install a correctly selected heating element under the valve - an open radiator.
Mechanical exhaust in a private house is performed by fans, usually ducted. There may be several, but sometimes one is enough.
To ensure efficient circulation of air currents, exhaust fans must operate without interruption. In order to save energy resources, speed controllers with automatic / manual control are connected to the system.
The flow of air flows into the house is organized in a natural way. To do this, use wall or special window inlet valves. The design of such devices does not provide for the presence of moving parts.
Experts characterize combined ventilation as functional, relatively inexpensive and easy to operate. For the location of related equipment does not require a lot of space. In addition, all functional elements require minimal maintenance.
Among the disadvantages of the combined type of system, it is worth noting the lack of filtration and heating of the supply air, as well as the minimum air exchange rates.
Ventilation system design stages
The scope and content of the project will vary depending on its complexity, but the main components will be approximately the same. So, at the preliminary stage, a technical project is drawn up, which, in fact, is a feasibility study (feasibility study). At this stage, specialists go to the site to record the initial information, including the purpose and functions of the building or premises, its area, and the number of residents/employees.
The initial stage ends with the selection of equipment, consideration of the main characteristics and properties. Optimization decisions are made on interaction with other engineering systems. And the calculation of the air exchange of each specific room is carried out in accordance with the technical conditions, construction and sanitary standards.
Next, a scheme is developed for calculating the diameter and area of air ducts and the noise level is determined. The drawings are sent for approval. The project designer or direct customer can make changes.
At the next stage, after agreement, a package of documents on plumbing, construction work and electrical power is prepared.
Only after completion of all the above stages, ventilation is installed and launched.
 Ceiling height plays an important role in the design of the ventilation system. The low-lying ceiling significantly complicates the task, as a rule, this is found in the living room, bedroom and kitchen, if the corridor is completely adjacent to the wall of the living room
Ceiling height plays an important role in the design of the ventilation system. The low-lying ceiling significantly complicates the task, as a rule, this is found in the living room, bedroom and kitchen, if the corridor is completely adjacent to the wall of the living room
Of no small importance in the design is also the rational distribution of funds intended for the purchase of equipment and materials.On the modern market there is a huge range of equipment and devices from various manufacturers of different price categories.
For the purchase of equipment, special calculations will be required:
- With the help of the area and purpose of the premises indicated in the floor plan of the structure, the required performance is determined. The indicator is calculated in m3 / h.
- Taking into account the performance, the value of the air temperature at the outlet of the ventilation system and the minimum ambient temperature determine the power of the air heater. The duct heater is used exclusively in the cold season as a building heater.
- The characteristics of the fan depend on the length and complexity of the route. To calculate the required power, the type and diameter of the duct, diameter transitions, and the number of bends are used.
- Calculation of air flow velocity in air ducts.
- The air speed affects the noise level.
The project budget is calculated after the completion of all calculations, drawing on the building plan of the proposed ventilation ducts. The prepared TOR must be approved by the customer and departmental structures.
 In a private house, a project for a ventilation system should be in hand even before the foundation is laid. All details must be thought out in advance to the smallest detail, which will ensure an effective air exchange system.
In a private house, a project for a ventilation system should be in hand even before the foundation is laid. All details must be thought out in advance to the smallest detail, which will ensure an effective air exchange system.
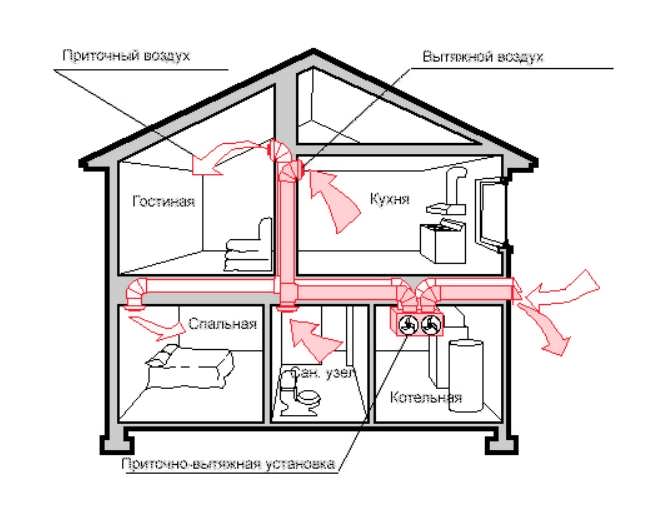
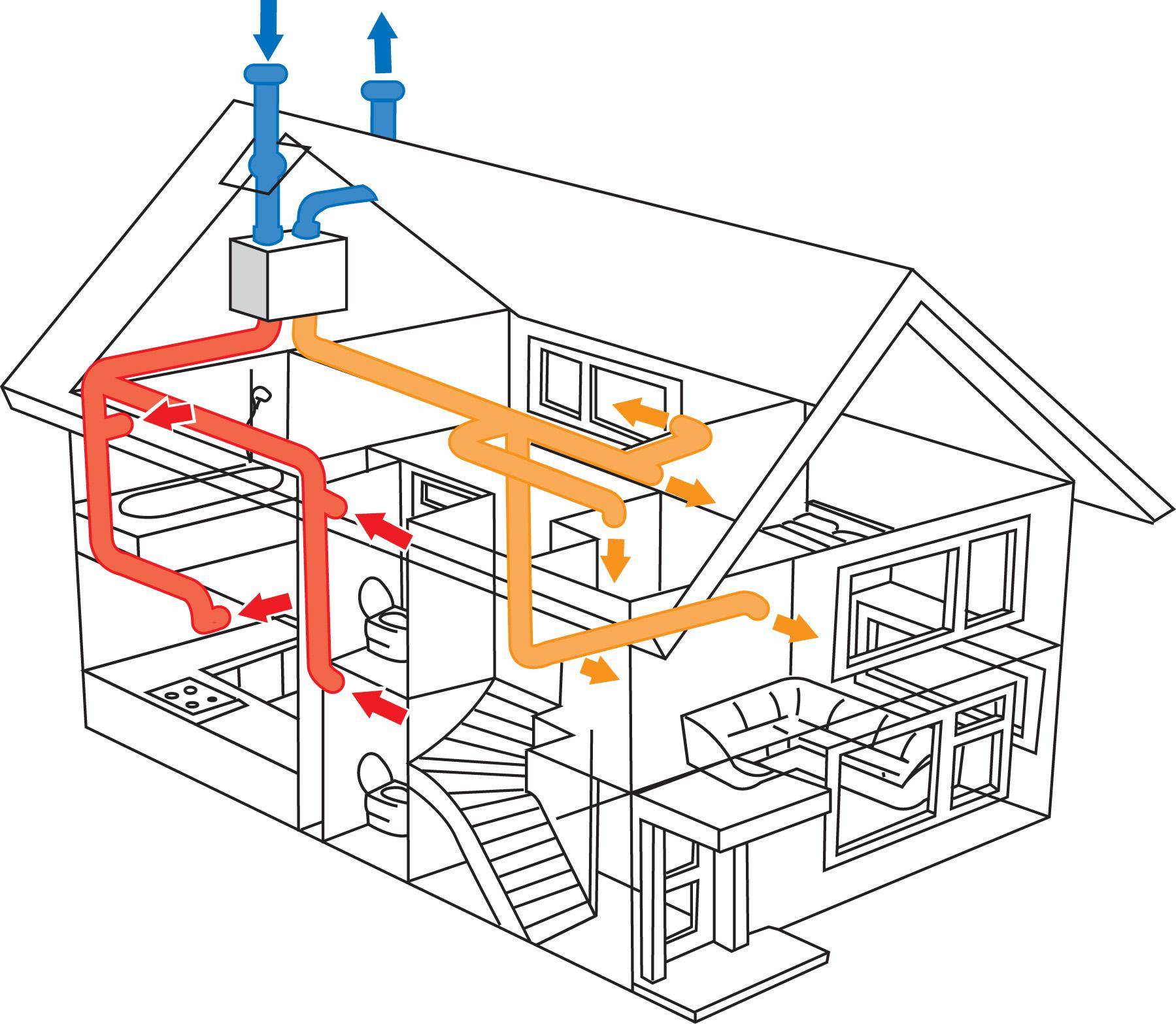
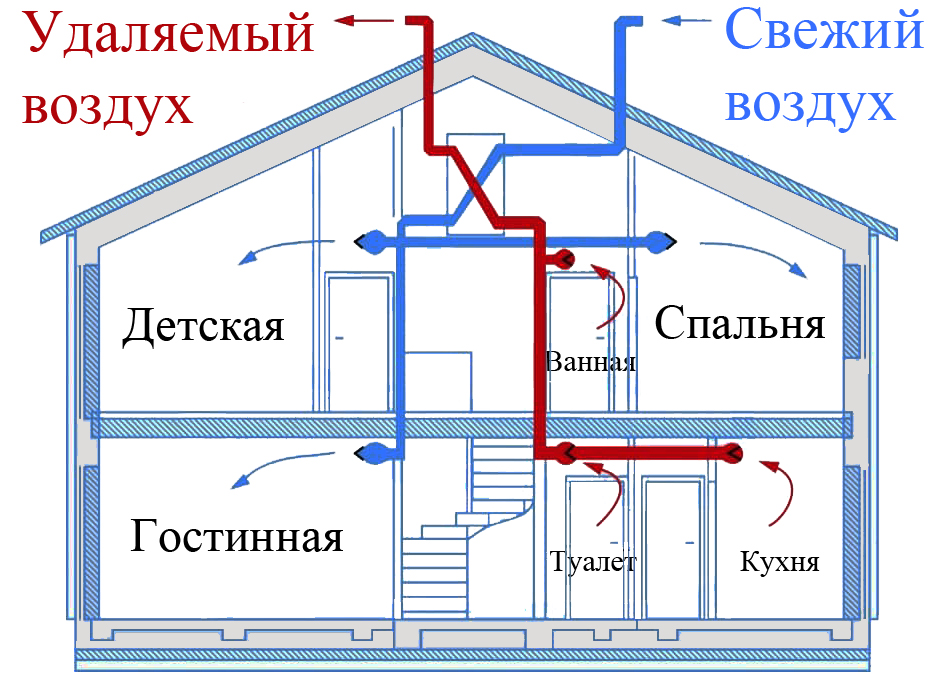
Recommendations for individual rooms
When arranging any ventilation in a private house, air flows are arranged in such a way that clean outdoor air first enters the living room, bedrooms, office and library.
And then, along the corridors, he should go to the kitchen, to the bathroom and to the pantry with access to the exhaust ventilation shaft.
To ensure unhindered natural air flow through the cottage, all interior doors must have a gap of 2–3 cm between the door leaf and the threshold.
If the cottage is wooden, then an additional hood should also be provided in the bathroom. The humidity in this room is high, it will be difficult to do without an exhaust fan
In the kitchen, in addition to the ventilation hole, it is recommended to additionally install an extractor fan above the stove in the ventilation duct. It will allow you to quickly remove the smells of cooking, preventing them from spreading to the rest of the rooms in the house.
Separate moment - boiler room and kitchen with gas equipment. They must be equipped with a separate channel for air flow directly from the street. Plus, don't forget the chimney.
This way, oxygen for combustion will enter the furnace in the right amount, and carbon monoxide will immediately leave the room.
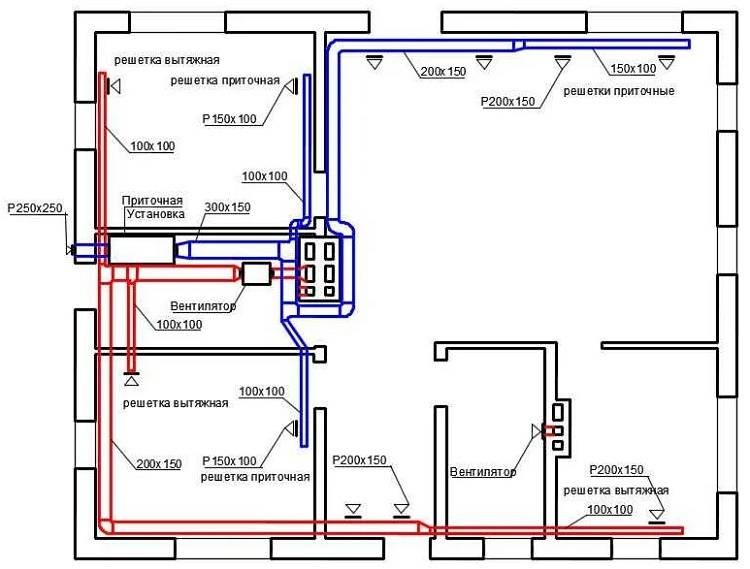
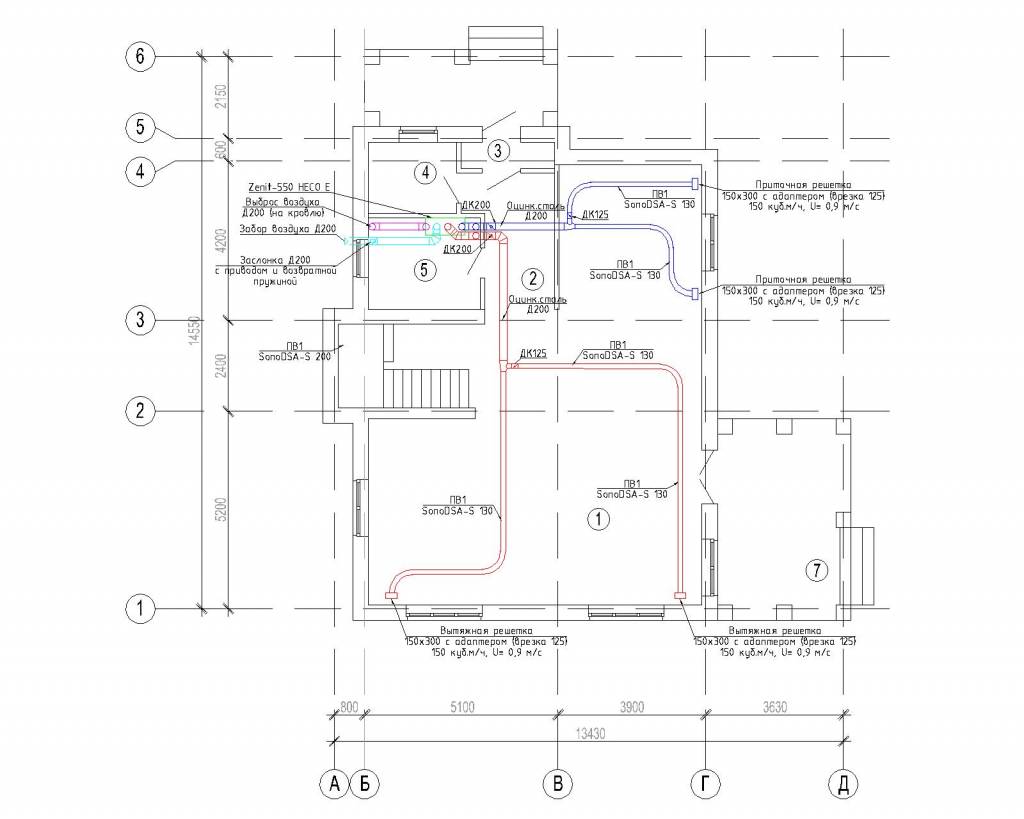
Ventilation system for a 2-room apartment (option 1)

Ventilation project in a 2-room apartment (option 1)
Common parameters:
- Apartment area: 51.4 m².
- Ventilation capacity: 240 m³/h.
| equipment identification | Marking | Qty | Price, rub | Cost, rub |
| Equipment | ||||
| PU with electric heater and automation | Breezart 350 Lite* | 1 | 70000 | 70000 |
| Duct silencer | CSA 160/900 | 1 | 3080 | 3080 |
| Air distribution network and materials | ||||
| Valve with manual drive (optional - electric drive) | KVK-160M | 1 | 1100 | 1100 |
| Galvanized steel air duct, m | D160 | 3 | 450 | 1350 |
| Flexible air duct noise-thermoisolated, unitary enterprise. | Sonoduct D125 | 1 | 4201 | 4201 |
| Branch-90, pcs. | 125 | 1 | 319 | 319 |
| Branch-90, pcs. | 160 | 3 | 392 | 1176 |
| Tee-90, pcs. | 160/125 | 1 | 410 | 410 |
| Transition, pcs. | 160/125 | 1 | 301 | 301 |
| Plug, pcs. | 125 | 1 | 196 | 196 |
| Ventilation grille, pcs. | AMN-300×150 | 2 | 554 | 1108 |
| Adapter type 7, pcs. | 300x150 | 1 | 698 | 698 |
| Adapter type 1, pcs. | 300x150 | 1 | 752 | 752 |
| Outer grille, pcs. | ННР(С) 200х200 | 1 | 1719 | 1719 |
| Throttle valve, pcs. | DK-125 | 2 | 709 | 1418 |
| Thermal insulation, m2 | Penofol 30 mm | 6 | 492 | 2952 |
| Consumables and fixing material, set | 1 | 6142 | 6142 | |
| Works | ||||
| Installation and commissioning at the facility within the Moscow Ring Road | 1 | 21000 | 21000 | |
| Add. payment when the object is located outside the Moscow Ring Road, rub/km | 42 | needs clarification | ||
| TOTAL | 117 922 |
* It is possible to use other models of air handling units.
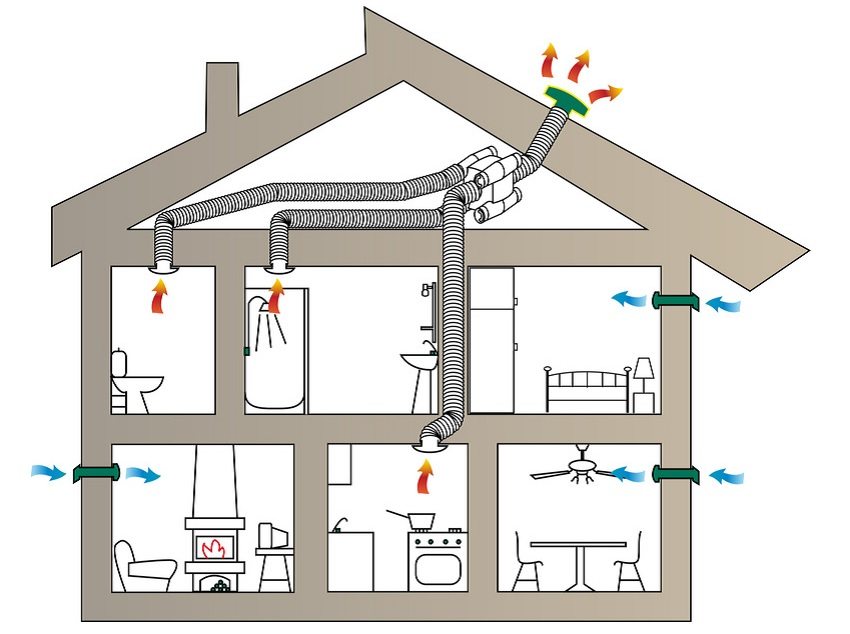
Installation of ventilation ducts in the cottage: locations of supply and exhaust systems

External ventilation grilles of forced inlet valves
Condition one. Fresh air must be supplied to all living rooms:
- to the nursery;
- to the hall (to the living room);
- to the bedroom;
- to the office;
- to the dining room.
Condition two. Air extraction must be present:
- from the restroom;
- from the shower;
- from the bathroom;
- from the bath (sauna);
- from the combined bathroom;
- from the kitchen;
- from home laundry;
- from the room where clothes are dried;
- from a home workshop, if it contains dust, smoke, harmful fumes, unpleasant odors;
- from pantries, dressing rooms, if these areas are separated from the living room by a door (if these areas have an entrance to the sanitary zone, then they must have a supply valve).
Condition three. Some rooms require both supply and exhaust ventilation. First of all, it is:
- room connected to the kitchen;
- any of the rooms, if the air flow passing through it has to overcome more than 2 doors to the hood;
- a room in which devices using gas are installed (boiler room, kitchen).
Ventilation systems on the second floor
The rooms on the second floor have their own characteristics. As warm air tends to rise, the ventilation systems in this area are under increased load.
If the entire second floor is separated from the first floor by a completely door structure (taking into account the landing), and the door opens and immediately closes, then the general principles of the ventilation system are preserved.
When the second floor is not fenced in any way from the first, then both supply and exhaust channels are constructed. For this, any room is selected, its operational purpose does not play a role.
Units for local exhaust system
Existing shelters, which are equipped with exhaust ventilation systems, are divided into several specialized categories:
- units installed at the source of pollution;
- solutions that block the source of pollution;
- reblowing products.
In practice, units with the help of which the source of the spread of hazardous substances is localized in a certain area are very popular. However, such solutions are not always convenient and appropriate to apply. They were replaced by more modern hoods with a vent to the ventilation:
- metal and polycarbonate umbrellas with hood function;
- local suction units;
- powerful fume hoods;
- encapsulated solutions;
- removal of secretions from the body of machine tools and working units;
- showcase, shaped and board solutions.
Local ventilation systems are very common in places where it is necessary to ensure the required standards for air exchange in a specific, local area.
Exhaust hoods are the most popular and common suction designs. They equip small working areas (tables for soldering, cooking).Dangerous impurities are quickly collected and redirected upwards, after which they are discharged. Ventilation for the hood functions both through natural draft and forced draft.
Specialized suction - draw out unwanted and potentially dangerous substances with a minimum consumption of oxygen. Industrial exhaust ventilation is often represented by several local units. Their main feature is that they do not interfere with work.
Fume hoods are one of the most effective solutions for the forced removal of harmful fumes, substances, while forming a minimum level of air exchange. There are several types of such cabinets on sale:
- with an upper outlet device, through which hot and humid air is removed;
- with the removal of contaminated streams of the side structure - we are talking about some analogue of a "snail", for collecting residual products;
- with diverting solutions of the combined type located at the bottom of the unit.
Local hoods: a - fume hood; b - display case; c - shelter-casing for a grinding machine; g - exhaust hood; e - umbrella-visor over the open opening of the furnace; e - exhaust funnel when welding large-sized products; g - lower suction; h - lateral suction; and - inclined exhaust panel; j - double-sided suction from the galvanic bath; l - single-side suction with blowing; m - annular suction for a manual welding gun
The fan, located in the air exchange system, creates a swirl in the flow so that the dust is localized in a small area, and does not spread throughout the room. An example of such an installation is a welding post, where forced exhaust ventilation is represented by a small cabinet.The suction in them is located at the top of the structure.
If we are talking about the removal of non-hazardous substances, then the speed of movement is allowed within the following limits:
- 0.5 – 0.7 m/s;
- 1.1 - 1.6 m / s - for those cases when toxic impurities, metal fumes are removed from the room.
Fume hoods are installed in chemical laboratories
As for the suction panels, they are used in cases where the air in a confined space is saturated with toxic gases, dust and heat. The panel is positioned so that the toxic compounds are at the maximum distance from the worker. Exhaust pipes for ventilation complement the built-in motor and quickly remove dangerous suspensions. The installations under consideration are used at welding posts, when processing large products. From welding, they are located at a distance of up to 3.5 m, equipped with fans with one or two motors.
The speed of movement of air masses must meet the following criteria:
- from 3.5 to 5 m / s, when it comes to the release of hot dust;
- from 2 to 3.5 m / s, if toxic or non-dusty suspensions are released during operation.
Experts focus on one important point - the installation of exhaust ventilation is carried out on the condition that 1 m2 of the panel removes 3.3 thousand m3 of air hourly
Onboard suctions are relevant for cases when the source of pollution is held in a vertical position using special lifts. Such installations are widely used in the shops where the galvanic processing of metals is carried out, in which hazardous substances are poured into a special container and then sucked in through a small hole.
From a constructive point of view, the exhaust ventilation of industrial premises consists of several air ducts, the inlets of which have a narrow shape (up to 10 cm), they are located at the edges of the bath.
Stages of ventilation design
There are 2 main stages, completely equivalent in terms of the amount of work. The first stage (50%) is the collection of initial data for design and the coordination of the main fundamental decisions. The second stage (50%) is the development of a ventilation project.
Collecting initial data After contacting our team, we have to go through the following path:
① Select type of ventilation system There are 3 options for ventilation systems. Natural ventilation - shafts in the bathrooms of any building. Hybrid ventilation - supply valves and mini-supply units in each room. Supply and exhaust ventilation - just that requires detailed design. In detail - the pros and cons of each ventilation system.
② Select the complete set and brand of ventilation equipment If you have chosen a forced ventilation system, we will have to determine the brand and additional equipment of the equipment. Mechanical ventilation can combine the functions of filtration, heating, cooling, humidification and even air ionization. The standard unit includes a filter, an air heater and a silencer section.
③ Select air distribution methods and grille type In short, you can make grilles from the wall or from the ceiling, and in some cases from the floor. You can connect ventilation to the air conditioning system and supply air through the gratings of channel blocks. You can lay air ducts under the ceiling, and even in the floor screed. You can buy simple and cheap gratings, or you can buy vortex, nozzle or slotted gratings.Instead of a full-fledged expensive ventilation system, you can make ducted air conditioners with the function of adding fresh air from the street, but everywhere there are pitfalls.
④ Select the type of air ducts, equipment location, intake and exhaust openings, heating system for heating air in winter. We have to agree on the Terms of Reference and the draft design so that we do not have to adjust the finished projects several times.
⑤ Additional questions before starting ventilation design: “Do you have architectural plans in digital version, in AutoCAD (or ArchiCAD)?”
PDF or even JPEG layouts are fine for us, but converting drawings to the AutoCAD standard will take time. We need layouts in AutoCAD for accurate calculation of the amount of materials and the correct selection of equipment.
Development of the ventilation project After collecting all the initial data, agreeing on the Terms of Reference and the Draft Design, we begin the development of project documentation. We carry out the necessary calculations according to the sketches already agreed with you. In this case, we do not have to correct the finished projects and recalculate the network. We will discuss all issues in advance.
How to choose pipes?
Mostly plastic or polyethylene is used, as well as polypropylene.
You will also need 45 and 90 degree bends, tee connections and couplings. It is best to use polyethylene products, since attics are not always heated. Aggressive environment - frost and sun - can break the tightness.
Polyethylene is very elastic and perfectly reacts to changes in weather conditions.In each case, the amount of material must be calculated separately, we can only say that at least one compensator must be present in any project, and instead of bends of 90 degrees, it is better to use 45.
As for the tool, each employee chooses it for himself. To fix or cut the pipe, you need a puncher or screwdriver (it all depends on the walls of the building), a grinder with adjustable speed or a hacksaw.