- Pros and Cons of a Forced System
- Calculation of the heating system at home
- How to calculate the heating of a private house?
- Designing heating with forced circulation
- System calculation
- Installation of heating with circulation
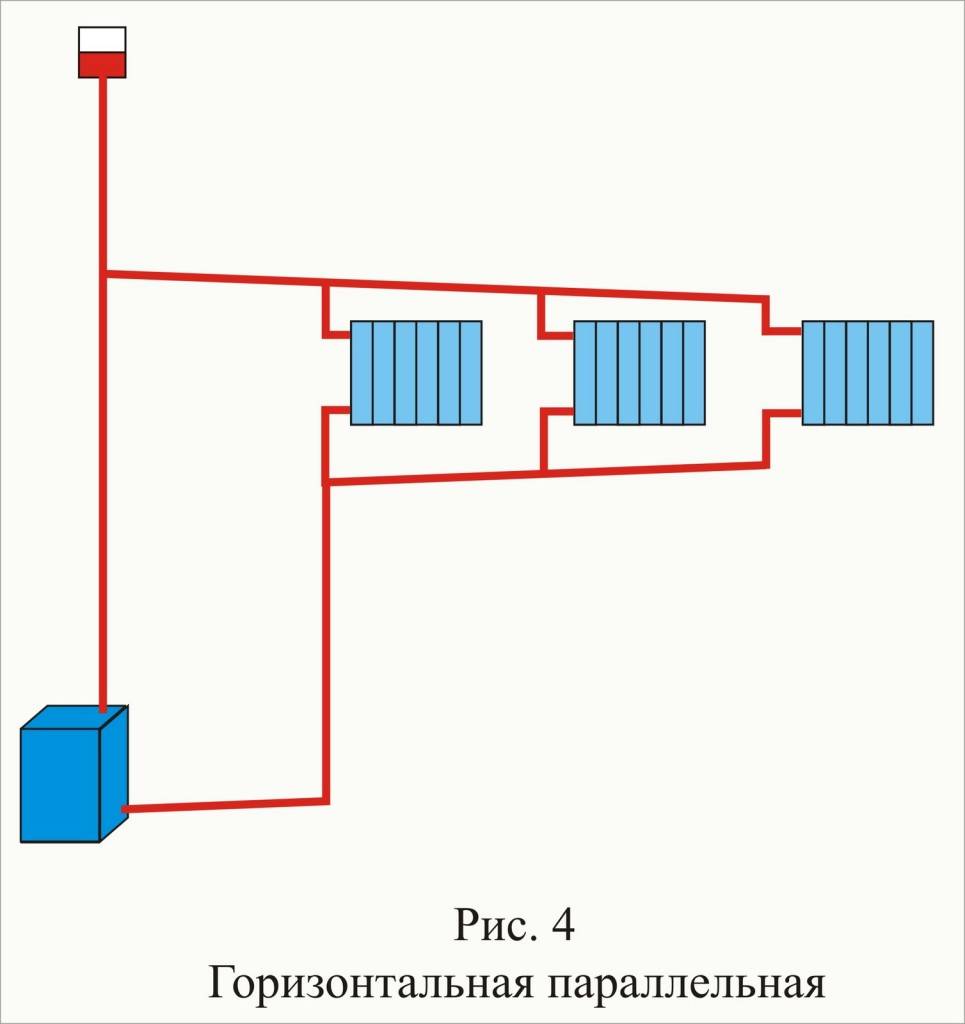
- Classification of water heating systems according to the principle of operation
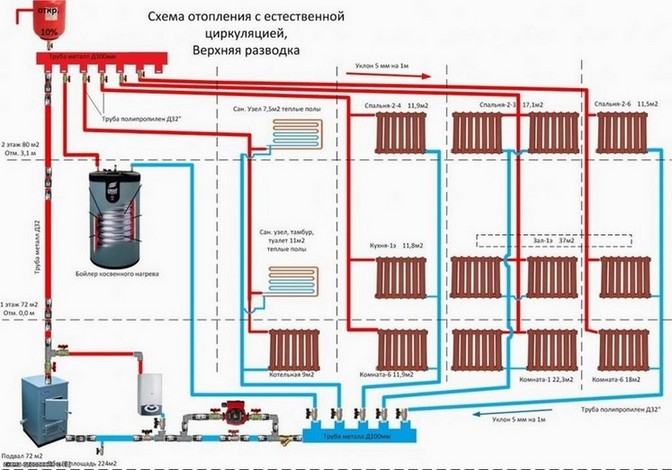
- with natural circulation
- Forced circulation scheme
- Mounting methods
- Collector heating
- Varieties of liquid autonomous heating systems
- Single-pipe system for the house: calculation of pipe diameter
- Pipes for heating
- Heating with metal pipes
- Heating a house with polypropylene pipes
- Heating with plastic pipes
- Centralized heating system
- bottom filling
- Top filling
- Temperature balance
- EC heating radiators
- How to choose the best heating system?
- 3 Rules for choosing components
Pros and Cons of a Forced System
The device of a thermal system with forced circulation helps to level the disadvantages of a gravity flow scheme, significantly expanding the efficiency of the system as a whole:
- The intensity of circulation of the working medium is determined by the pump, and is not directly dependent on the degree of heating.
- The uniform distribution of the coolant over all radiators allows the use of pipes of a smaller cross section during installation, saving in the construction process and winning in the aesthetic component.
- It becomes possible to adjust the mode and intensity of heating.
- The maximum allowed contour length is increased.
- Any arrangement of the pipeline is allowed - vertical, horizontal, combined.

The disadvantages of forced circulation options are not so critical, but they should definitely be mentioned:
- Power source dependent. All pumps require electricity to operate. If the house is regularly subjected to power outages, consider switching to an alternative power source. Otherwise, at strong negative temperatures, it is possible to defrost the heating system in a few hours and face the need for expensive repairs. The source of electricity can be an autonomous generator, or a more compact uninterruptible power supply unit equipped with a battery. Another option is to design the system in such a way that, if necessary, it functions as a gravity flow.
- Noise from the pump. Modern models of devices work almost silently, but outdated models sometimes make a lot of noise. To reduce discomfort, the device is placed in an isolated room.
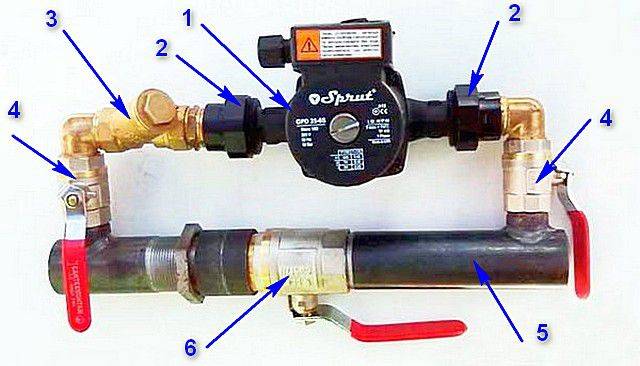
So that during the repair or replacement of the pump it is not necessary to drain all the liquid from the system, the device is included in the circuit with shutoff valves and bypasses.
Calculation of the heating system at home
| The calculation of heating systems for a private house is the very first thing that begins with the design of such a system.We will talk with you about the air heating system - these are the systems that our company designs and installs both in private homes and in commercial buildings and industrial premises. Air heating has many advantages over traditional water heating systems – you can read more about it here. |
System calculation - online calculator
Why is a preliminary calculation of heating in a private house necessary? This is required to select the correct power of the necessary heating equipment, which allows you to implement a heating system that provides heat in a balanced way to the corresponding rooms of a private house. A competent choice of equipment and the correct calculation of the power of the heating system of a private house will rationally compensate for heat loss from building envelopes and the flow of street air for ventilation needs. The formulas themselves for such a calculation are quite complex - therefore, we suggest you use the online calculation (above), or by filling out the questionnaire (below) - in this case, our chief engineer will calculate, and this service is completely free.
How to calculate the heating of a private house?
Where does such a calculation begin? Firstly, it is required to determine the maximum heat loss of the object (in our case, this is a private country house) under the worst weather conditions (such a calculation is carried out taking into account the coldest five-day period for this region). It will not work to calculate the heating system of a private house on the knee - for this they use specialized calculation formulas and programs that allow you to build a calculation based on the initial data on the construction of the house (walls, windows, roofs, etc.).As a result of the data obtained, equipment is selected whose net power must be greater than or equal to the calculated value. During the calculation of the heating system, the desired model of the duct air heater is selected (usually it is a gas air heater, although we can use other types of heaters - water, electric). Then the maximum air performance of the heater is calculated - in other words, how much air is pumped by the fan of this equipment per unit of time. It should be remembered that the performance of the equipment differs depending on the intended mode of use: for example, when air conditioning, the performance is greater than when heating. Therefore, if in the future it is planned to use an air conditioner, then it is necessary to take the air flow in this mode as the initial value of the desired performance - if not, then only the value in the heating mode is sufficient.
At the next stage, the calculation of air heating systems for a private house is reduced to the correct determination of the configuration of the air distribution system and the calculation of the cross sections of the air ducts. For our systems, we use flangeless rectangular air ducts with a rectangular section - they are easy to assemble, reliable and conveniently located in the space between the structural elements of the house. Since air heating is a low-pressure system, certain requirements must be taken into account when building it, for example, to minimize the number of turns of the air duct - both the main and the terminal branches leading to the grates. The static resistance of the route should not exceed 100 Pa.Based on the performance of the equipment and the configuration of the air distribution system, the required section of the main air duct is calculated. The number of terminal branches is determined based on the number of feed grates required for each specific room of the house. In the air heating system of a house, standard supply grilles with a size of 250x100 mm with a fixed throughput are usually used - it is calculated taking into account the minimum air velocity at the outlet. Thanks to this speed, air movement is not felt in the premises of the house, there are no drafts and extraneous noise.
| The final cost of heating a private house is calculated after the end of the design stage based on the specification with a list of installed equipment and elements of the air distribution system, as well as additional control and automation devices. To make an initial calculation of the cost of heating, you can use the questionnaire for calculating the cost of the heating system below: |
online calculator
Designing heating with forced circulation
The primary task for self-installation of water heating with a circulation pump is to draw up the correct scheme. To do this, you need a plan of the house, on which the location of pipes, radiators, valves and safety groups is applied.
System calculation
At the stage of drawing up the schemes, it is necessary to correctly calculate the parameters of the pump for the forced heating system of a private house. To do this, you can use special programs or do the calculations yourself. There are a number of simple formulas that will help make the calculation:
Pн=(p*Q*H)/367*efficiency
Where Rn is the rated power of the pump, kW, p is the density of the coolant, for water this indicator is 0.998 g / cm³, Q is the flow rate of the coolant, l, N is the required pressure, m.
To calculate the pressure indicator in the forced heating system of a house, it is necessary to know the total resistance of the pipeline and heat supply as a whole. Alas, it is almost impossible to do it yourself. To do this, you should use special software systems.
Having calculated the resistance of the pipeline in a water heating system with circulation, it is possible to calculate the required pressure indicator using the following formula:
H=R*L*ZF/10000
Where H is the calculated head, m, R is the resistance of the pipeline, L is the length of the largest straight section of the pipeline, m, ZF is a coefficient, which is usually equal to 2.2.
Based on the results obtained, the optimal model of the circulation pump is selected.
Installation of heating with circulation

Based on the calculated data, pipes of the required diameter are selected, and shut-off valves are selected for them. However, on The diagram does not show how to install. highways. Pipelines can be installed in a hidden or open way. The first is recommended to be used only with full confidence in the reliability of the entire heating system of a private cottage with forced circulation.
It must be remembered that the quality of the components of the system will depend on its performance and performance. In particular, this applies to the material for the manufacture of pipes and valves. In addition, for a two-pipe scheme of a forced circulation heating system, it is recommended to heed the advice of professionals:
- Installation of an emergency power supply for the circulation pump in the event of a power outage;
- When using antifreeze as a coolant, check its compatibility with the materials for the manufacture of pipes, radiators and the boiler;
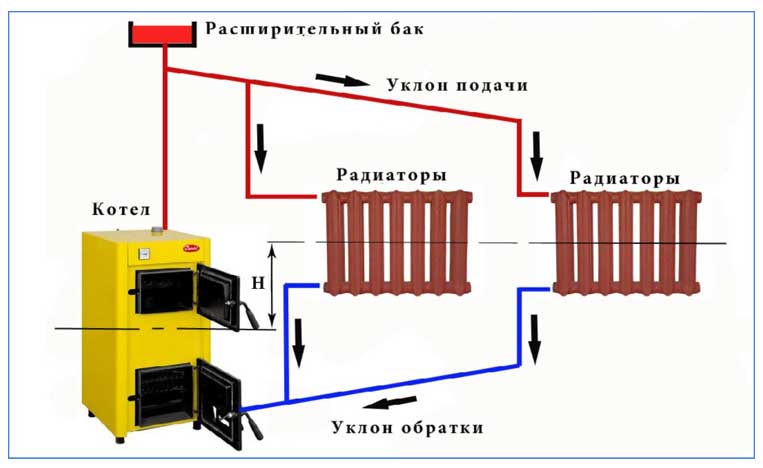
- According to the house heating scheme with forced circulation, the boiler should be located at the lowest point of the system;
- In addition to the pump power, it is necessary to calculate the expansion tank.
Analysis of the parameters of heating systems with forced circulation will help to form an objective opinion about it:
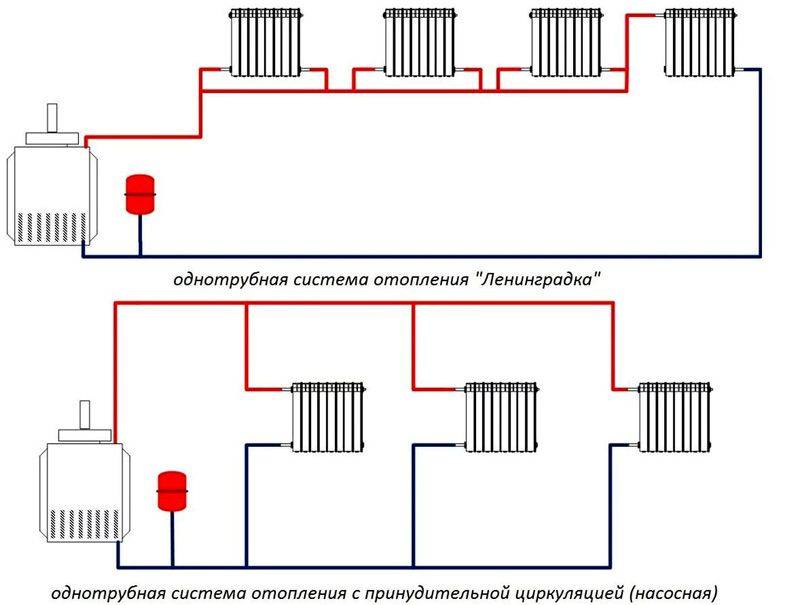
Classification of water heating systems according to the principle of operation
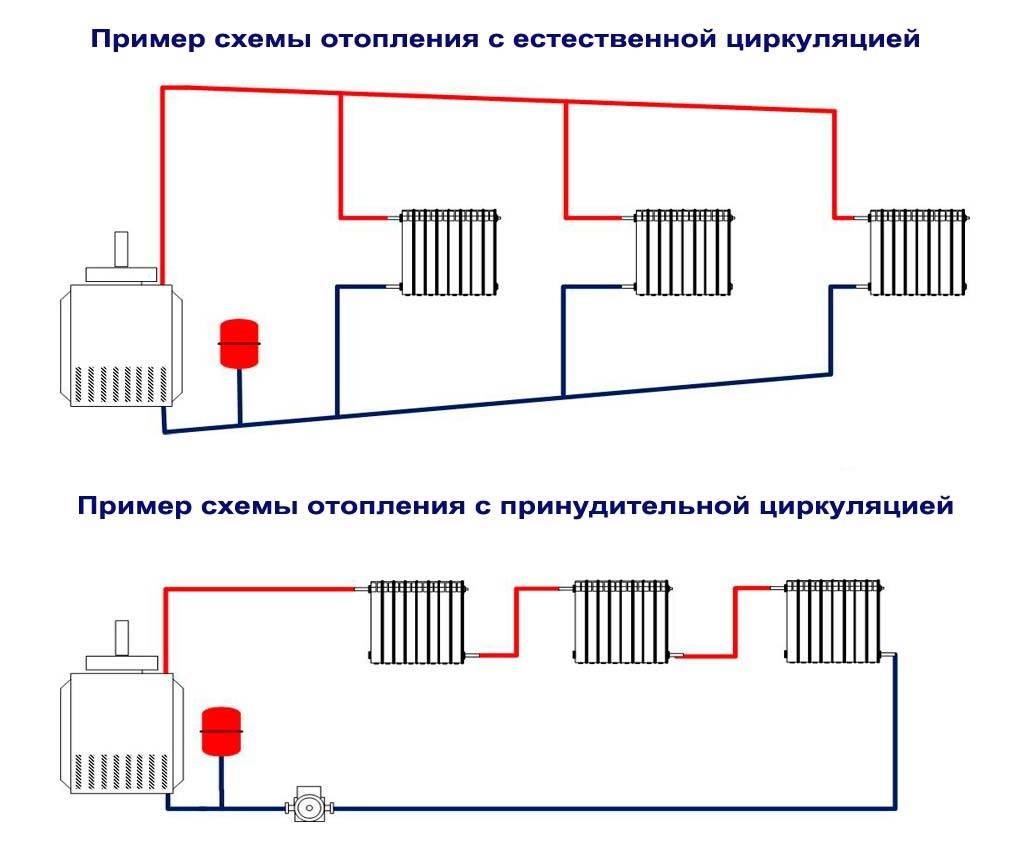
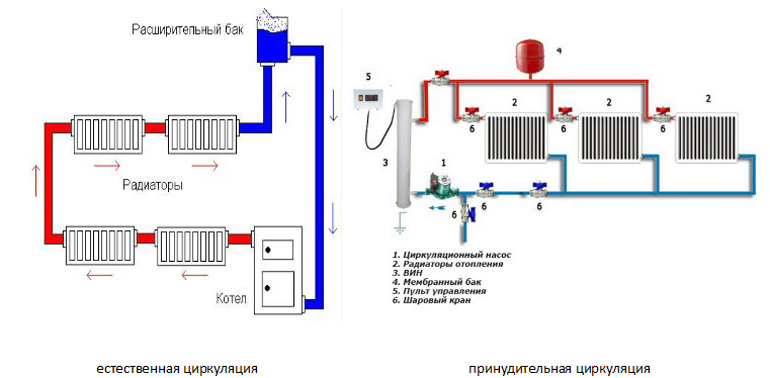
According to the principle of operation, heating has natural and forced circulation of the coolant.
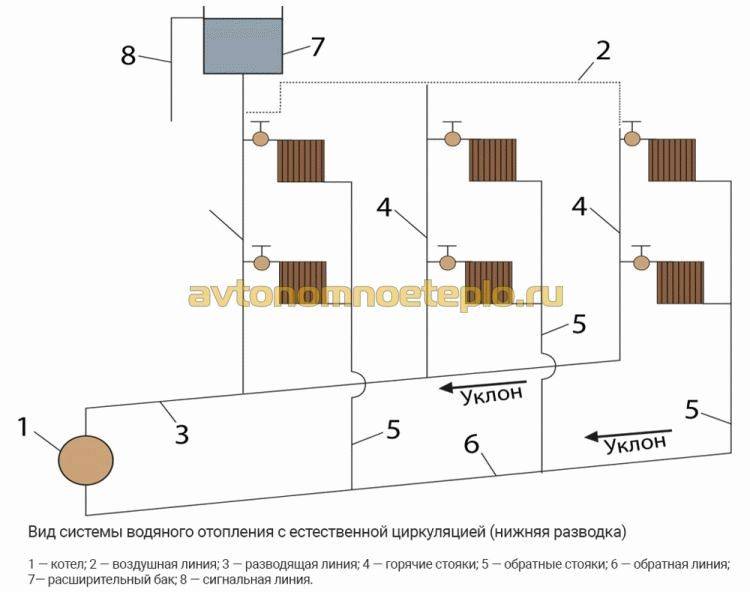
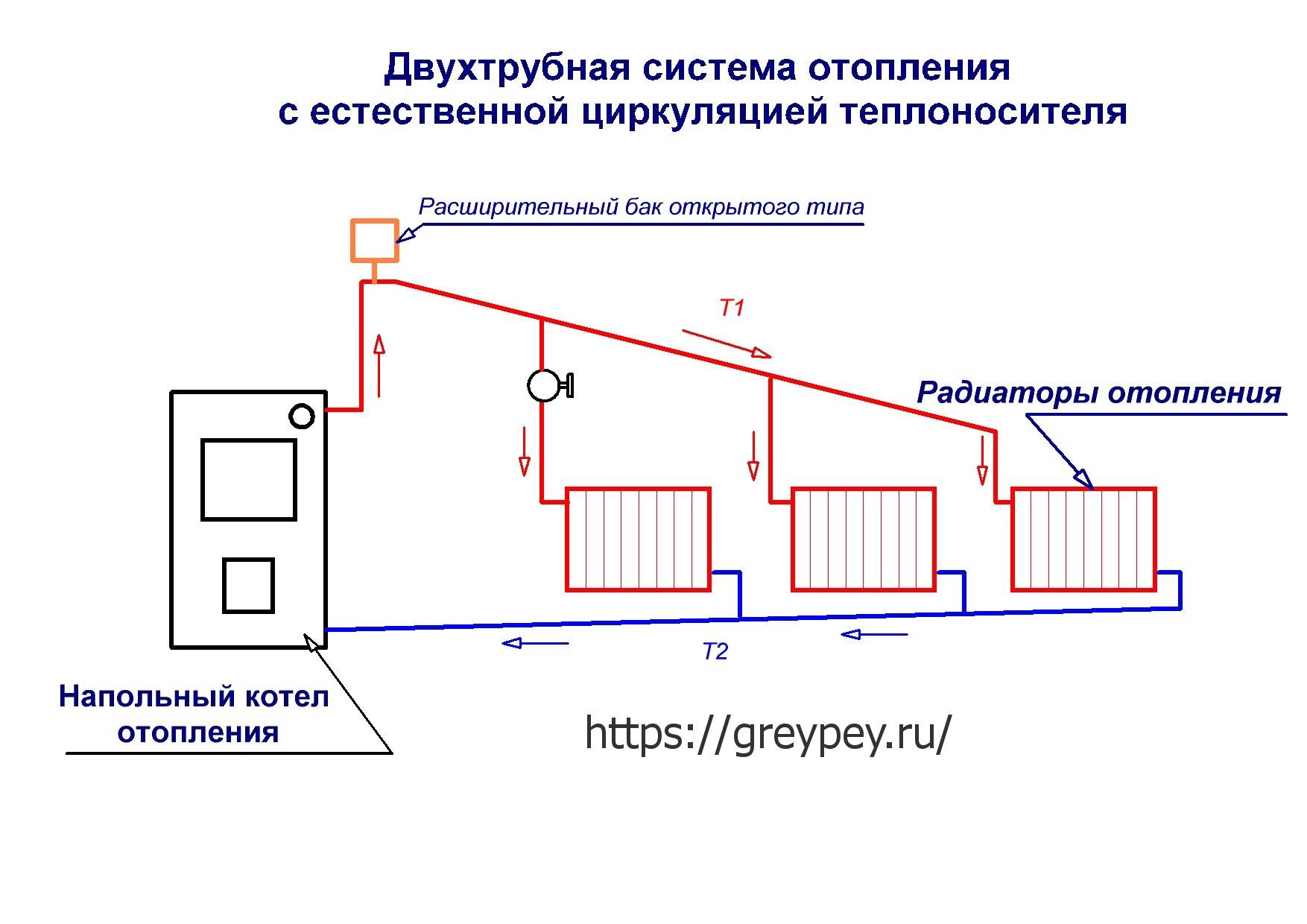
with natural circulation
Used to heat a small house. The coolant moves through the pipes due to natural convection.
Photo 1. Scheme of a water heating system with natural circulation. Pipes must be installed at a slight slope.
According to the laws of physics, a warm liquid rises. Water, heated in the boiler, rises, after which it descends through pipes to the last radiator in the system. Cooling down, the water enters the return pipe and returns to the boiler.
The use of systems operating with the help of natural circulation requires the creation of a slope - this simplifies the movement of the coolant. The length of the horizontal pipe cannot exceed 30 meters - the distance from the outermost radiator in the system to the boiler.
Such systems attract with their low cost, no additional equipment is required, they practically do not make noise when they work.The downside is that the pipes need a large diameter and should be laid as evenly as possible (there is almost no coolant pressure in them). It is impossible to heat a large building.
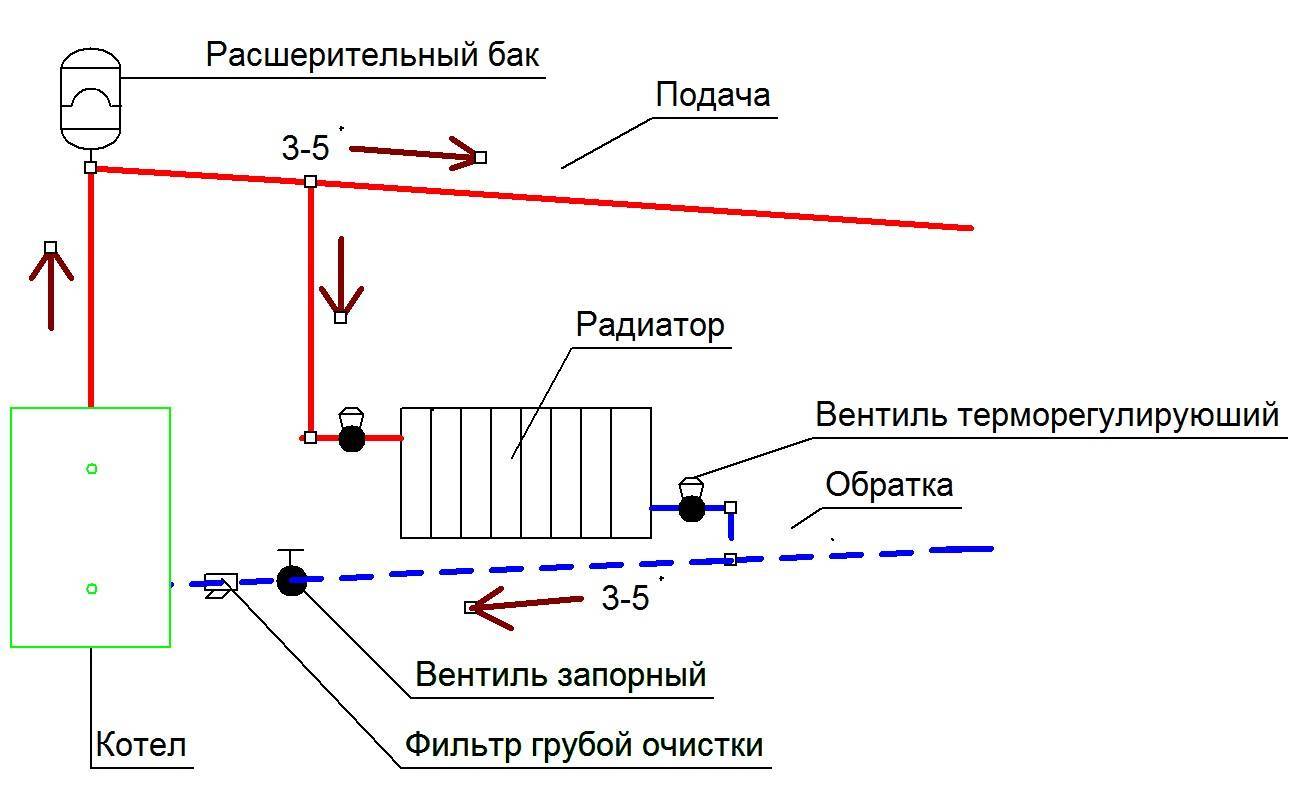
Forced circulation scheme
The scheme using the pump is more complicated. Here, in addition to heating batteries, a circulation pump is installed that moves the coolant through the heating system. It has higher pressure, so:
- It is possible to lay pipes with bends.
- It is easier to heat large buildings (even several floors).
- Suitable for small pipes.
Photo 2. Scheme of a heating system with forced circulation. A pump is used to move the coolant through the pipes.
Often these systems are made closed, which eliminates the ingress of air into the heaters and coolant - the presence of oxygen leads to metal corrosion. In such a system, closed expansion tanks are required, which are supplemented with safety valves and air vent devices. They will heat a house of any size and are more reliable in operation.
Mounting methods
For a small house consisting of 2-3 rooms, a single-pipe system is used. The coolant moves sequentially through all the batteries, reaches the last point and returns through the return pipe back to the boiler. Batteries connect from below. The downside is that the distant rooms warm up worse, as they receive a slightly cooled coolant.
Two-pipe systems are more perfect - a pipe is laid to the far radiator, and taps are made from it to the rest of the radiators. The coolant at the outlet of the radiators enters the return pipe and moves to the boiler.This scheme evenly heats all rooms and allows you to turn off unnecessary radiators, but the main disadvantage is the complexity of installation.
Collector heating
The main disadvantage of a one- and two-pipe system is the rapid cooling of the coolant; the collector connection system does not have this drawback.
Photo 3. Water collector heating system. A special distribution unit is used.
The main element and basis of collector heating is a special distribution unit, popularly called a comb. Special plumbing fittings necessary for the distribution of the coolant through separate lines and independent rings, a circulation pump, safety devices and an expansion tank.
The manifold assembly for a two-pipe heating system consists of 2 parts:
- Input - it is connected to a heating device, where it receives and distributes hot coolant along the circuits.
- Outlet - connected to the return pipes of the circuits, it is necessary to collect the cooled coolant and supply it to the boiler.
The main difference between the collector system is that any battery in the house is connected independently, which allows you to adjust the temperature of each or turn it off. Sometimes mixed wiring is used: several circuits are connected independently to the collector, but inside the circuit the batteries are connected in series.
The coolant delivers heat to the batteries with minimal losses, the efficiency of this system increases, which makes it possible to use a boiler of lower power and consume less fuel.
But the collector heating system is not without drawbacks, these include:
- Pipe consumption. You will need to spend 2-3 times more pipe than when connecting batteries in series.
- The need to install circulation pumps. Requires high pressure in the system.
- Energy dependence. Do not use where there may be power outages.
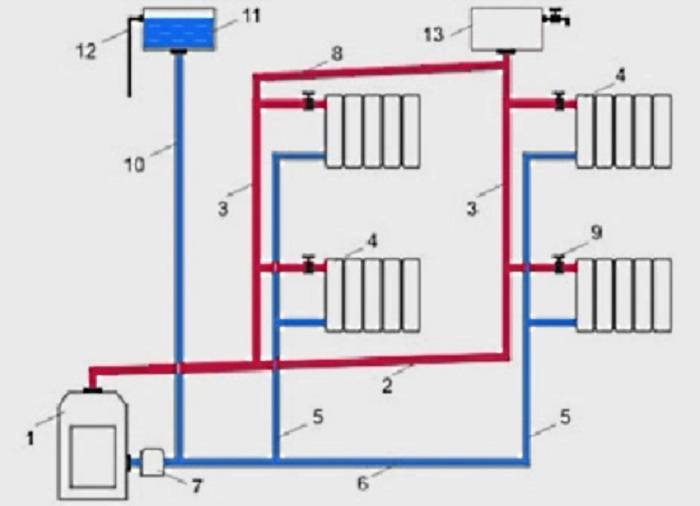
Varieties of liquid autonomous heating systems
Heating systems for heating an individual house using water and non-freezing liquids (antifreeze) as a coolant differ in a number of ways, the main differences are:
By type of fuel used. The most popular types of energy for heating heat carriers are electricity, gas, liquid combustible hydrocarbon mixtures (diesel fuel, fuel oil, oil, kerosene), a large number of solid combustible materials - firewood, coal, peat briquettes and pellets of various compositions. Electricity can be generated both from energy companies and independently using solar panels, wind or hydraulic generators.
By type of heat generators. In modern heating systems, heating boilers are used to transfer energy to the coolant, which have design features and differences between analogues for each type of fuel. With a lack of funds, many craftsmen assemble independent heating with their own hands, using instead of factory boilers self-assembled structures mainly on solid fuels, a typical example is a metal stove in a residential area with an expansion tank in the attic and a steel piping system with radiators.
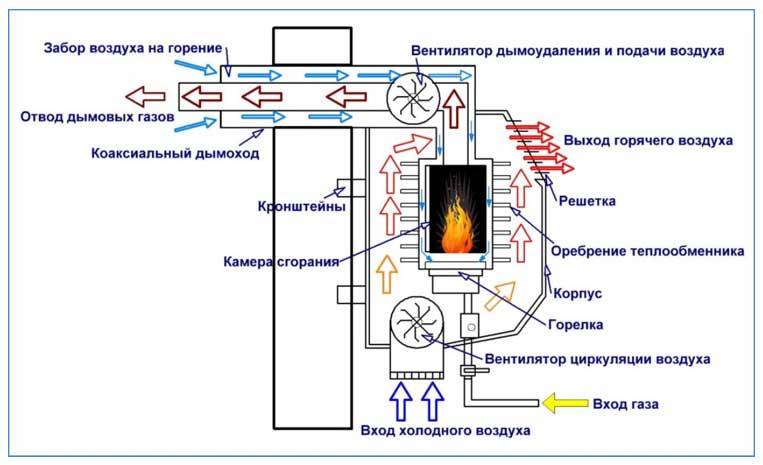
Rice. 7 The principle of operation and the main components of the gas convector
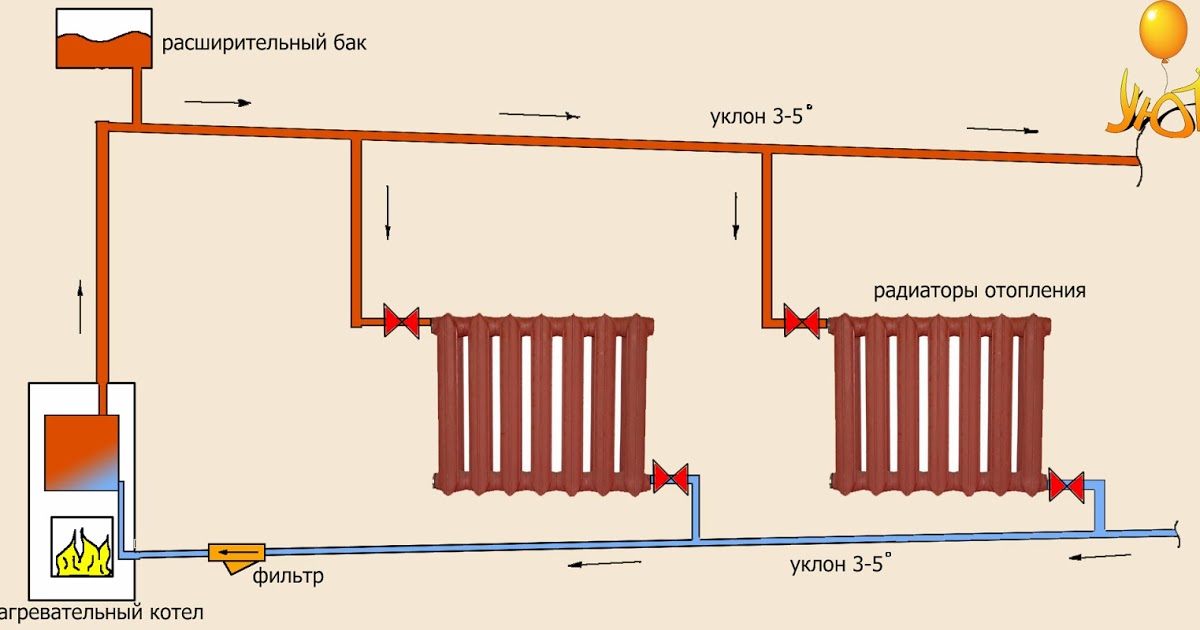
According to the material of the pipeline.Polymeric pipes made of PP polypropylene, cross-linked polyethylene and PEX metal-plastic are gradually replacing metal products; at old buildings, external steel pipelines are still used to supply water to radiators. Some homeowners, with significant financial resources, make the coolant supply through copper pipelines completely or in separate sections. Modern advanced systems are mounted from special thin-walled steel pipes using a crimping technology for connecting elements of sanitary fittings using fittings.
According to the method of supplying the coolant to the heat exchangers. There are 2 main ways to supply heated liquid to the pipes of heating radiators - one-pipe and two-pipe, sometimes a combined connection is used. To connect the underfloor heating pipeline, collector wiring is used, which allows several circuits to be connected to one distribution unit, systems from a large number of radiators are connected through hydraulic arrows or radiator manifolds. When connecting heat exchange radiators, various piping layouts are used - radial, dead-end, associated, special horizontal (Leningrad).
There are also various ways to connect the inlet and outlet pipes of heat exchange radiators to the heat main - vertical, horizontal, diagonal, bottom.
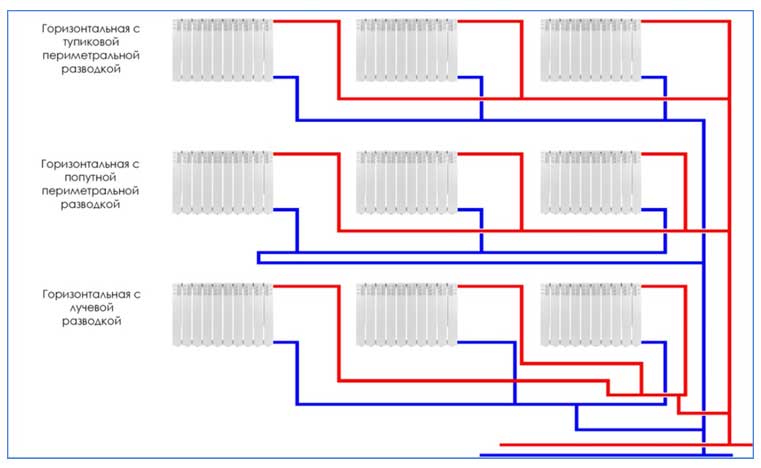
Rice. 8 Piping diagrams
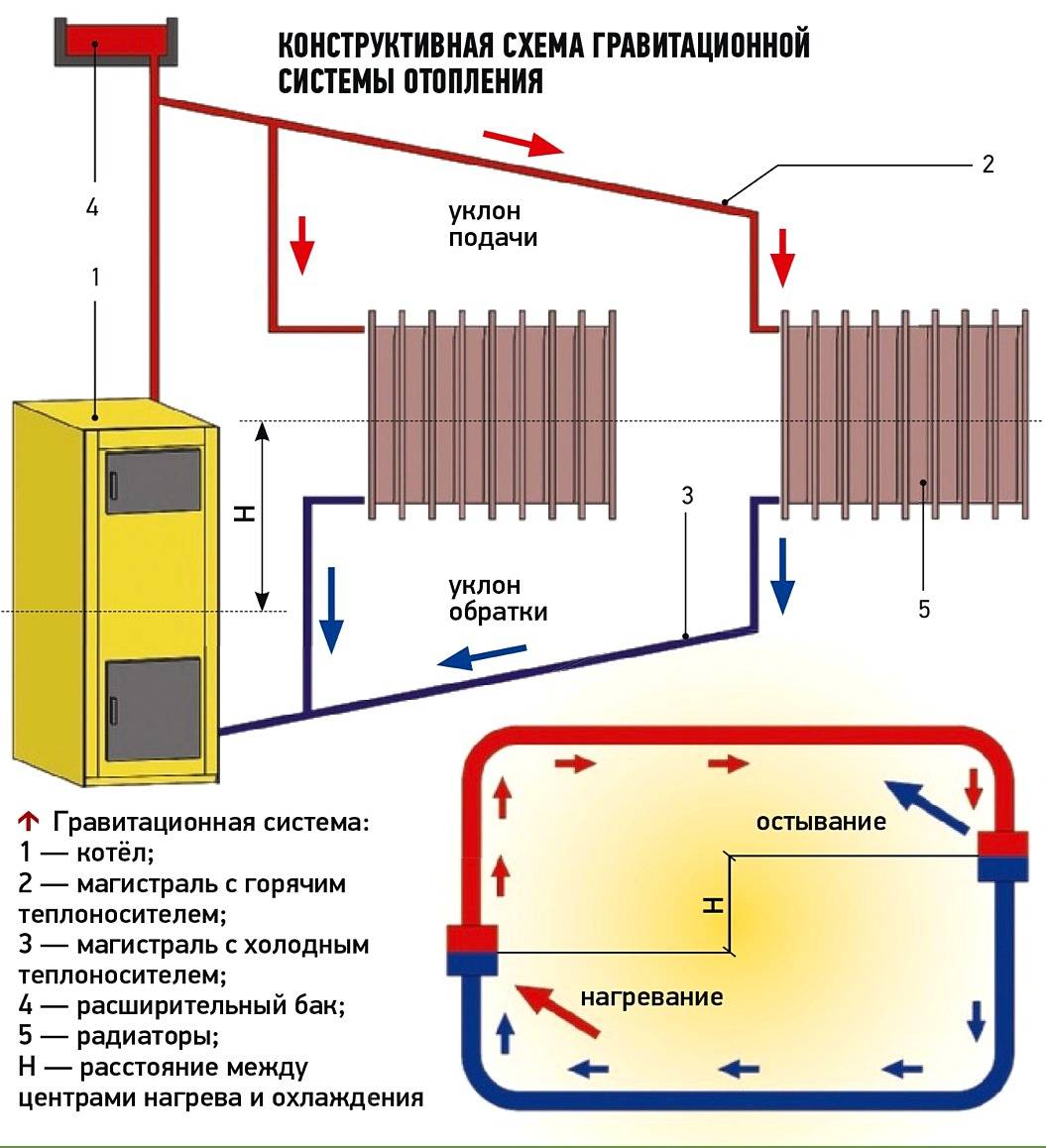
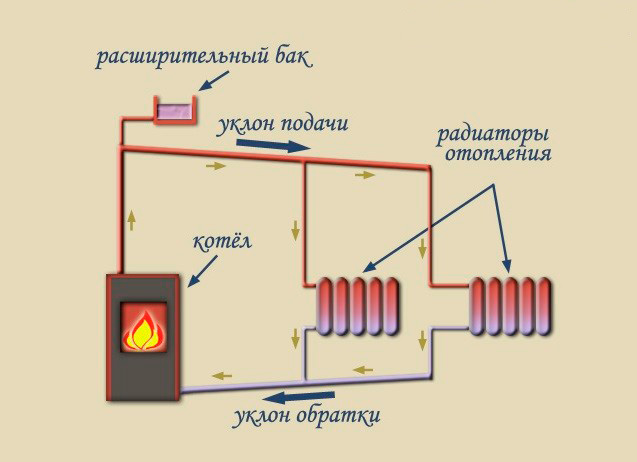
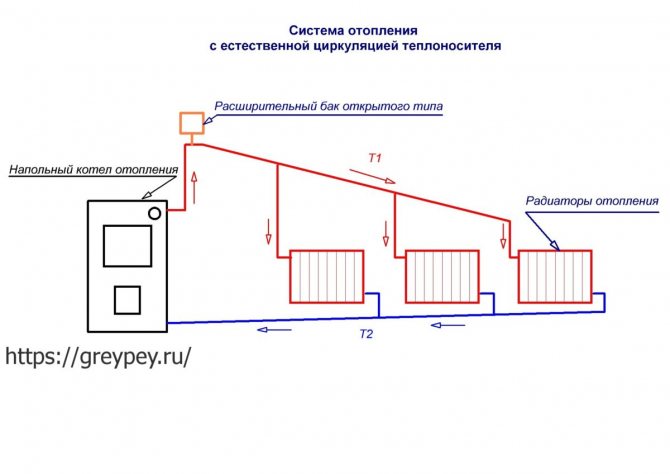
According to the location of the storage tank.The expansion tank, which is an important element of any heating system, can be factory-made sealed (red accumulator) and mounted in the circuit in any convenient place - such systems are called closed, since there is no direct access to the coolant. The movement of liquid through the pipeline in systems of this type is carried out using a circulating electric pump installed at the bottom near the boiler next to the hydraulic accumulator.
In another type of heating systems, called gravity, the storage tank is installed at the top in the attic, the pipelines have a slight slope when approaching the radiators, at their exit a small angle of inclination is maintained towards the boiler. The circulation of liquid in the system occurs by gravity due to the fact that heated water or antifreeze have a lower density and therefore are pushed upward by denser cold layers.
Rice. 9 Open heating system
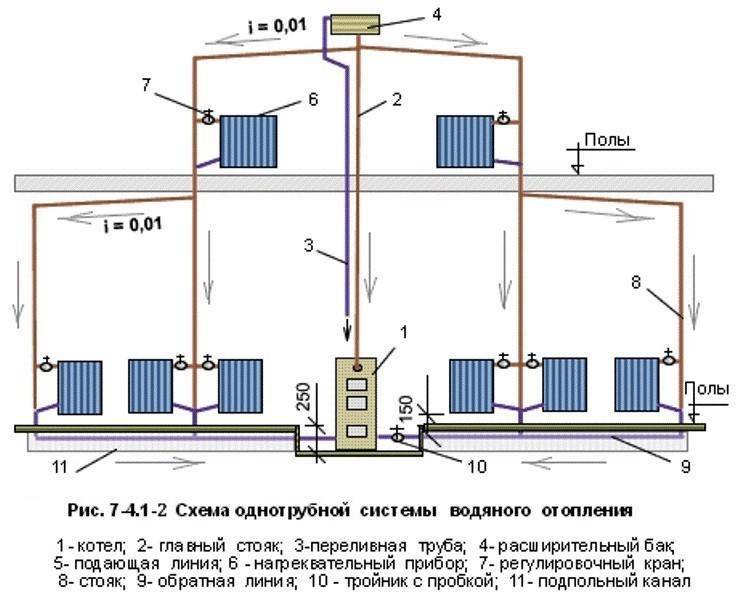
Single-pipe system for the house: calculation of pipe diameter
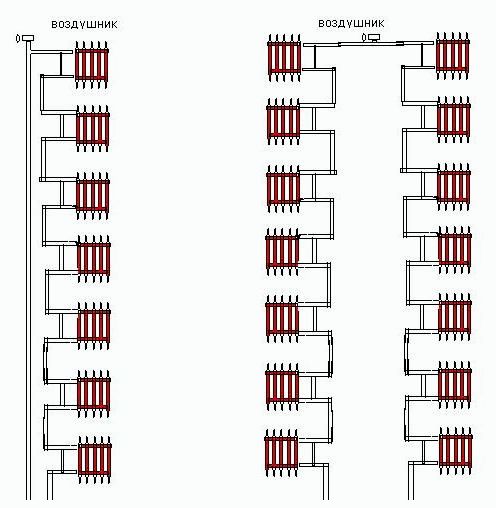
One-pipe heating system is popular because it is very simple
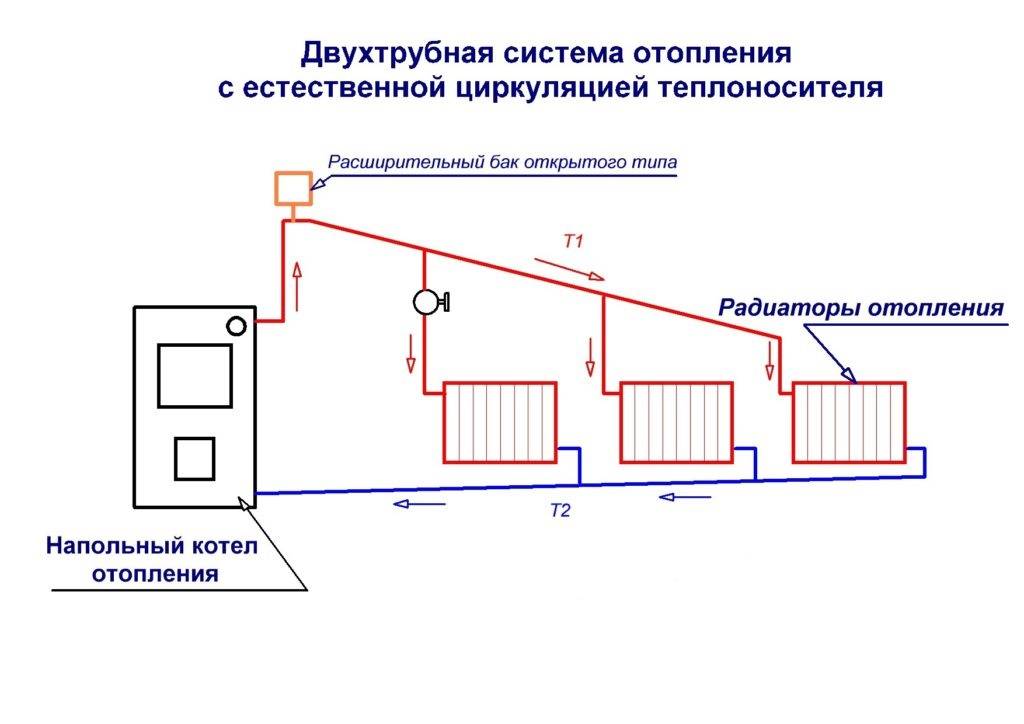
The distinctive features that a single-pipe heating system with natural circulation has include:
- Absence of a return line: the cooled return line flows back to the heating element through the same pipe.
- Radiators of the lower floors warm up worse, because. the water coming down has already been cooled in the radiators located above. Therefore, the farther the battery is from the boiler, the more sections it must have in order to ensure uniform heating of all rooms.
- Water circulates through pipes driven by temperature differences.A tap can be installed on each radiator, which will vary the amount of incoming water, sending the rest to other radiators and regulating the heating of the room.
- If water flows sequentially from one radiator to another, cooling along the way, you should not place shut-off valves on the radiators, because. this can lead to a slowdown in the movement of the coolant through the pipes.
Heating systems with natural circulation with series connection of radiators are mounted using top wiring. Accordingly, a single-circuit scheme can only be used in a house with an attic, where the supply line will be located. Despite this, such a heating scheme with natural circulation is popular, because. it is easy to mount it, and less pipes are required than for a two-pipe one.
Pipes for heating
Separately, one should consider the issue of the types of pipes used for heating private houses. Each material definitely has its positive and negative sides. Let's see which option is the best.
Heating with metal pipes
Metal pipes include steel and copper pipes.
Wiring water heating at home from steel will cost you relatively inexpensively (and this is the main plus of this material). This metal is quite versatile, suitable for both steam and water heating. Withstands great pressure. The main disadvantage of steel pipes is that they quickly corrode. This is reflected not so much in the quality of heating as in the appearance of your home - rusty pipes are not the best interior decoration.
Copper pipes have more advantages: they are extremely durable, keep the temperature well, and do not corrode. Another advantage of copper pipes is the smoothness of their inner surface, which ensures a high speed of fluid movement through the heating system. The main disadvantage of copper is its high price.
It is worth noting that both steel and copper pipes are only suitable for open heating systems and cannot be mounted in walls or floors. Therefore, as we see, their universality has a limit.
Heating a house with polypropylene pipes

The main advantage of polypropylene pipes is their resistance to external environmental factors: corrosion, decay processes, bacteria and chemical compounds.
Also one of the big advantages of this material is its lightness. Other advantages follow from this: such pipes are easier to install, they are suitable for use both on the supporting and on the interior wall.
Heating from polypropylene saves fuel consumption (gas or electricity) used to heat the boiler due to the low coefficient of friction, since the coolant easily passes through the heating system. But the difference is insignificant.
In addition, polypropylene pipes are quite plastic, have various modifications with many joints, and are also supplemented with a huge selection of various components, which allows the installation of complex heating systems.
And, finally, heating with polypropylene pipes can be done both in open and closed systems, when all pipes are hidden in the floor or walls.
With all the visible pluses, these pipes also have minuses.Firstly, with a fairly high resistance to chemical attack, such pipes are easily amenable to mechanical action (you can cut it with an ordinary kitchen knife). Secondly, polypropylene is not suitable for all types of heating systems. It absolutely cannot be used in combination with a steam generator, but they are great for the water heating we are considering. Also, water heating with polypropylene implies the presence of a large number of joints, which greatly affects the reliability of the system.
Heating with plastic pipes

If we talk about the advantages of metal-plastic pipes, then we can highlight the same advantages as those of polypropylene counterparts. But separately it is worth highlighting the fact that they are able to hold a higher temperature. And also, and this is their main distinguishing feature, metal-plastic bends perfectly. In this case, you can not be afraid for its damage. And this fact makes this type of pipe an ideal option for the "warm floor" system.
Among the disadvantages is a higher price compared to polypropylene counterparts.
Centralized heating system
No one will argue with the fact that the centralized system of heat supply to apartment buildings, in the form in which it currently exists, to put it mildly, is obsolete.
It is no secret that losses during transportation can reach up to 30% and we have to pay for all this. Refusing central heating in an apartment building is a complicated and troublesome procedure, but first, let's figure out how it works.
Heating a multi-storey building is a complex engineering structure.There is a whole set of drains, distributors, flanges that are tied to the central unit, the so-called elevator unit, through which the heating is regulated in an apartment building.
Two-pipe heating scheme.
It makes no sense now to talk in detail about the intricacies of the operation of this system, since professionals are engaged in this and a simple layman simply does not need this, because nothing depends on him here. For clarity, it is better to consider the scheme for supplying heat to an apartment.
bottom filling
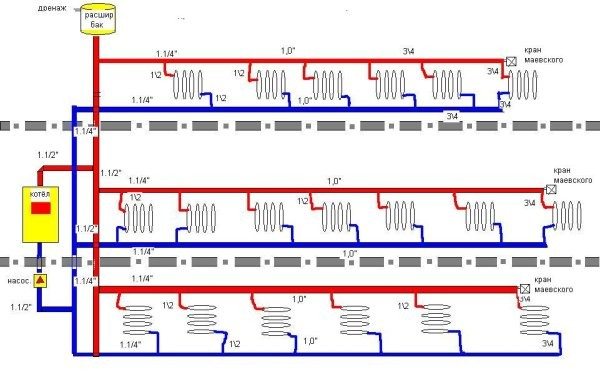
As the name implies, the distribution scheme with bottom filling provides for the supply of coolant from the bottom up. Classical heating of a 5-storey building, mounted exactly according to this principle.
As a rule, the supply and return are installed along the perimeter of the building and run in the basement. The supply and return risers, in this case, are a jumper between the highways. This is a closed system that rises to the last floor and descends again to the basement.
Two types of bottling in comparison.
Despite the fact that this scheme is considered the simplest, putting it into operation is troublesome for locksmiths. The fact is that at the top of each riser, a device for bleeding air, the so-called Mayevsky crane, is installed. Before each start, you need to release air, otherwise the air lock will block the system and the riser will not be heated.
Important: some residents of the extreme floors are trying to move the air release valve to the attic so as not to encounter housing and communal services workers every season. This modification can be costly.Attic - the room is cold and if you stop heating for an hour in winter, the pipes in the attic will freeze and burst
The attic is a cold room, and if heating is stopped for an hour in winter, the pipes in the attic will freeze and burst.
A serious disadvantage here is that on one side of the five-story building, where the input passes, the batteries are hot, and on the opposite side they are cool. This is especially felt on the lower floors.
Radiator connection option.
Top filling
The heating device in the nine-story building is made on a completely different principle. The supply line, bypassing the apartments, is immediately taken out to the upper technical floor. An expansion tank, an air release valve and a system of valves that allow you to cut off the entire riser if necessary are based here.
In this case, the heat is more evenly distributed over all the radiators of the apartment, regardless of their location. But another problem comes up here, the heating of the first floor in the nine-story building leaves much to be desired. After all, having passed through all the floors, the coolant comes down already barely warm, you can only deal with this by increasing the number of sections in the radiator.
Important: the problem with freezing water on the technical floor, in this case, is not so acute. After all, the cross section of the supply line is about 50 mm, plus in the event of an accident, it is possible to completely drain the water from the entire riser in a few seconds, just open the air vent in the attic and the valve in the basement
Temperature balance
Of course, everyone knows that central heating in an apartment building has its own clearly regulated standards.So during the heating season, the temperature in the rooms should not fall below +20 ºС, in the bathroom or in the combined bathroom +25 ºС.
Modern heating of new buildings.
In view of the fact that the kitchen in old houses does not have a large quadrature, plus it is naturally heated due to the periodic operation of the stove, the permissible minimum temperature in it is +18 ºС.
Important: all the above data are valid for apartments located in the central part of the building. For side apartments, where most of the walls are external, the instruction prescribes an increase in temperature above the norm by 2 - 5 ºС
Heating regulations by region.
EC heating radiators
For gravity systems, the main thing is the minimum resistance to water flow. Therefore, the wider the radiator clearance, the better the coolant will flow through it. Cast iron radiators are practically ideal from this point of view - they have the smallest hydraulic resistance. Aluminum and bimetal are good to use, but you need to make sure that their inner diameter is at least 3/4”. You can use steel tubular batteries, steel panel or any other with a small cross section and high hydraulic resistance is definitely not recommended - water will either not flow through them or it will be very weak, which, for example, with a single-pipe system can lead to no circulation at all.
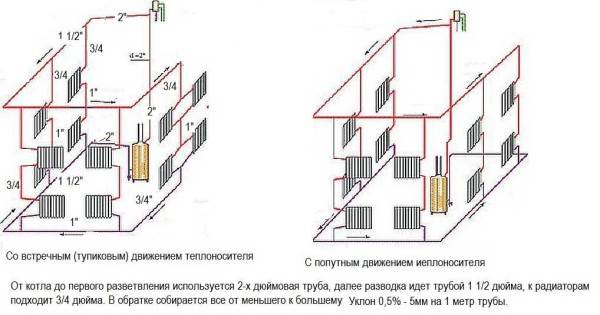
Natural circulation systems (click on image to enlarge)
There are subtleties in connecting radiators. The method of installation is especially important in a one-pipe system: only with the help of different types of connection can better work of the heating elements be achieved.
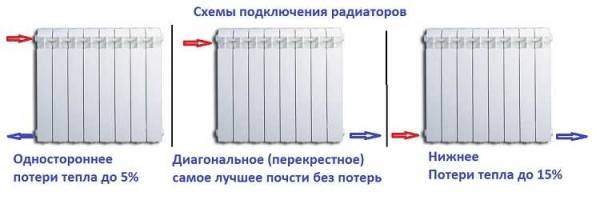
Radiator connection diagrams
The figure below shows the connection diagrams for radiators. The first is an unregulated serial connection. With this method, all the disadvantages of the "Leningrad" will appear: different heat transfer from radiators without the possibility of compensation (regulation). The situation is a little better if you put an ordinary jumper from the pipe. With this scheme, the possibility of regulation is also absent, but when the radiator is aired, the system functions, since the coolant passes through the bypass (jumper). By installing additionally two ball valves behind the jumper (not shown in the figure), we get the opportunity to remove / turn off the radiator when the flow is blocked without stopping the system.
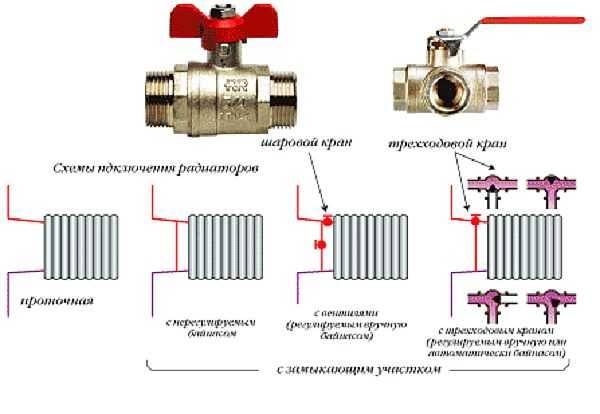
Features of connecting radiators in single-pipe systems
The last two mounting methods allow you to control the flow of coolant through the radiator and bypass - they have devices for adjusting the temperature of the radiator. With this inclusion, the circuit can already be compensated (heat transfer is set on each heater).
No less important is the type of connection: side, diagonal or bottom. By operating with these connections it is possible to facilitate/improve the compensation of the system.
How to choose the best heating system?
There are many heating systems. All of them have attractive sides and significant disadvantages. It is quite difficult for an unprepared person to navigate them and make the right choice.
In order not to be mistaken, you need to know exactly what points you should pay attention to.
First, it is the availability of fuel and its cost. You can consider this as a key point.As much as you like the system, but if the fuel for it is difficult to obtain, is supplied intermittently to the region, or is too expensive, you should consider another option. Otherwise, heating the house will cost a pretty penny and turn out to be inefficient.
According to statistics, most owners of private houses choose heating systems with a liquid coolant. This is a practical, reliable and quite economical option.
The second point is the possibility of combining heating systems. In some cases it can be very practical to use a primary and secondary system. This gives confidence that in case of possible interruptions in the supply of energy, the house will not be left without heat.
In addition, there is an opportunity to save money, since you can use the most economical heating method at the moment.
And finally, the financial side of the issue. It is necessary to determine how much the consumer will be able to allocate for the purchase of equipment, its competent installation and subsequent regular maintenance.
3 Rules for choosing components
Due to the fact that the highest temperature of the coolant passes in the collector (riser), the pipe itself must be installed metal. In addition, if a stove is used, and not a boiler, as a heat source, then steam can pass inside, which can adversely affect the operation of the system.
It should also be taken into account that with gravity-type heating, the diameter of the pipes of the water circuit should be slightly larger than in the scheme with a pump. As practice shows, for heating a house of 160 square meters, two-inch pipes are enough at the outlet (riser) and at the inlet to the heat exchanger.This is necessary because the water velocity is slower in the natural pattern, which can lead to the following problems:
- at low pressure, water will not be able to break through blockages and air pockets;
- several times less heat is received by the room from the boiler during the period of water passage from the start to the end point.
If the scheme provides for the supply of water from below the radiator batteries, then an important task remains to arrange the removal of air from the system. It cannot be completely removed through the expansion tank, since water enters through a line that is lower in level than the consumer appliances themselves (radiators)
If a forced circuit is used, then the pressure is sufficient for oxygen to escape through the air collectors installed at the top of the device. With the help of Mayevsky cranes, heat transfer can be regulated. Such taps in the gravity circuit are just used to vent air from a system in which water is supplied through a pipe located below the batteries.